31- Calculations & Glucose Handling
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
equation for RPF
RPF= (U PAH x V) / P PAH
equation for GFR
GFR = (U Inulin x V) / P inulin
FF equation
FF = GFR/ RPF
P Inulin Is used to calculate what
GFR
P PAH is used to calculate what
RPF (Renal Plasma Flow)
describe what the workload of kidneys entails
glomerular filtration
no energy consumed in filtering plasma
reabsorption and secretion of solutes and water
requires energy
what if reabsorption by the kidneys didnt occur?
massive loss of water and solutes
180 L filtered so loss of 180 L water, 25,200 mEq Na, 19,800 Cl , 4, 320 HCO3, 14, 400 glucose
the degree of reabsorption and secretion of filtered substances will determine what?
final excretion amounts in urine
describe reabsorption in the kidney
water and solutes REABSORBED from tubular fluid
Na
Cl
HCO3
glucose
AA
urea
Ca
Mg
Phosphage
lactate
citrate
describe renal secretion
organic acids and bases, K typically secreted into tubular fluid from peritubular capillaries
what is filtered load and whats the equation
amt of substrate in plasma
filtered load = GFR x [P]x
what is excretion rate and whats the equation
amt of substrate in urine
excretion rate = V x [U]x
reabsorption or secretion rate =
filtered load - excretion rate
if filtered load is GREATER THAN excretion rate….
net reabsorption of substance
if filtered load LESS THAN excretion rate…
net secretion of substance
where does glucose reabsorption occur?
in the proximal convoluted tubule
facilitated glucose transport across occurs
across peritubular membrane side using GLUT1 and GLUT2
why is there a transport maximum for glucose reabsorption?
due to limited # of glucose transporters
what does the glucose titration curve show
relationship bt plasma glucose concentration and glucose reabsorption
shows reabsorption rate of glucose as plasma concentration increases
freely filtered load
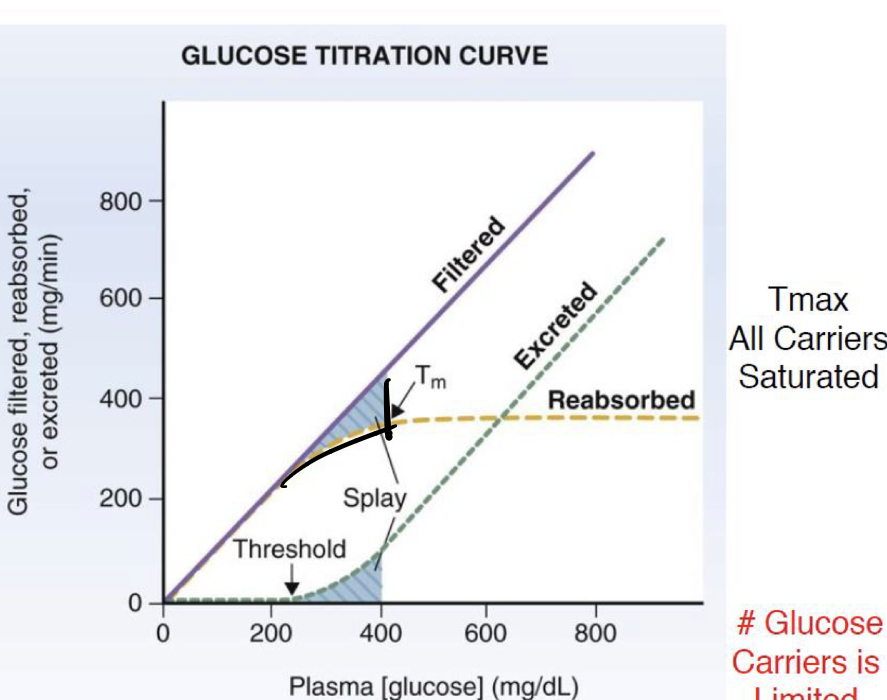
as plasma gluc increases, filtered load
increases linearly
describe glucose reabsorption
at plasma gluc < 200, all reabsorb = filtration
> 350 = transporters are saturated and levels off at Tmax
whats Splay indicate
reabsorption approaching saturation. gluc shows up in urine before tmax is reached
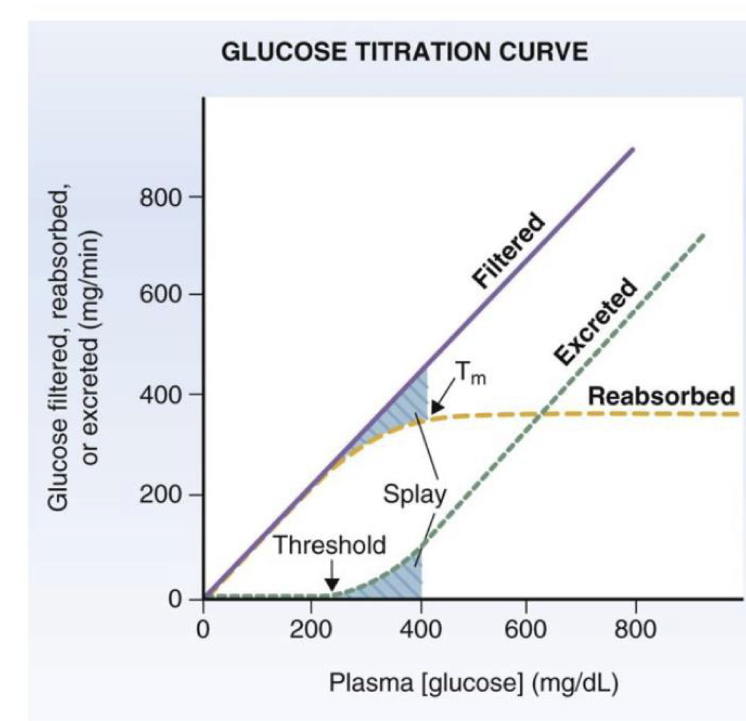
describe excretion values on the glucose titration curve
below 200 mg/dL all filtered glucose reabsorbed, none excreted
above 200 carriers near saturations, some glucose not reabsorbed
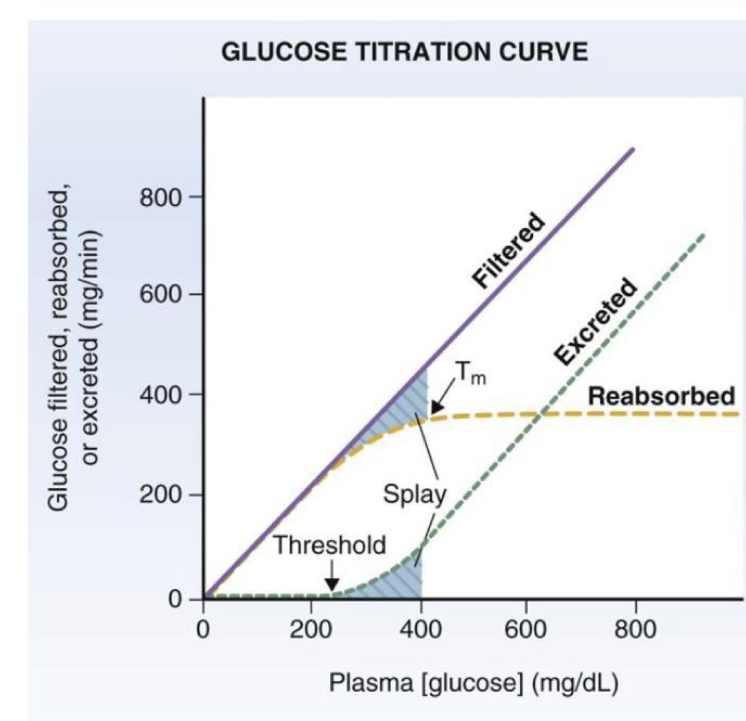
describe threshold on the glucose titration curve
plasma conc at which glc appears in urine
above 350, curve inc linearly
define glucosuria
excretion/spilling of glucose into urine
why can glucosuria occur in uncontrolled diabetes mellitus
due to high plasma glucose/hyperglycemia
filtered glucose load exceeds reabsorptive capacity (plasma glucose above Tmax)
why can glucosuria occur in preg
GFR inc which increases filtered glucose load
why can glucosuria occur due to abnormalities/defects
due to issues w Na/glucose co-transporter
can allow glucose to spill into urine at lower than normal plasma conc
whats the renal threshold for glucosuria in dogs and cats
dogs- 200mg/dL
cats- 280-300 mg/dL
when can cats get hyperglycemia
high stress times
what syndrome can occur even with normal glycemia
primary renal glucosuria
fanconi syndrome
can occur from disorder w proximal tubule, issues with gluc transport
describe fanconi syndrome
problems w absroping glucose, bicarb, phosphates, urea, potassium, certain AA and can spill into urine.
can be caused by exposure to certain drugs or exposure to heavy metals, vit d deficiency, kidney transport
what breed can have autosomal recessive fanconi syndrome since it is hereditary
basenji
describe acquired fanconi syndrome
caused by beef jerky treats imported from china
-affect small breeds more
-lethargy, v/d, pu/pd
-urine dipstick showed glucosuria, aminoaciduria, liver enzymes inc