CompSci - Organisation & Architecture
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
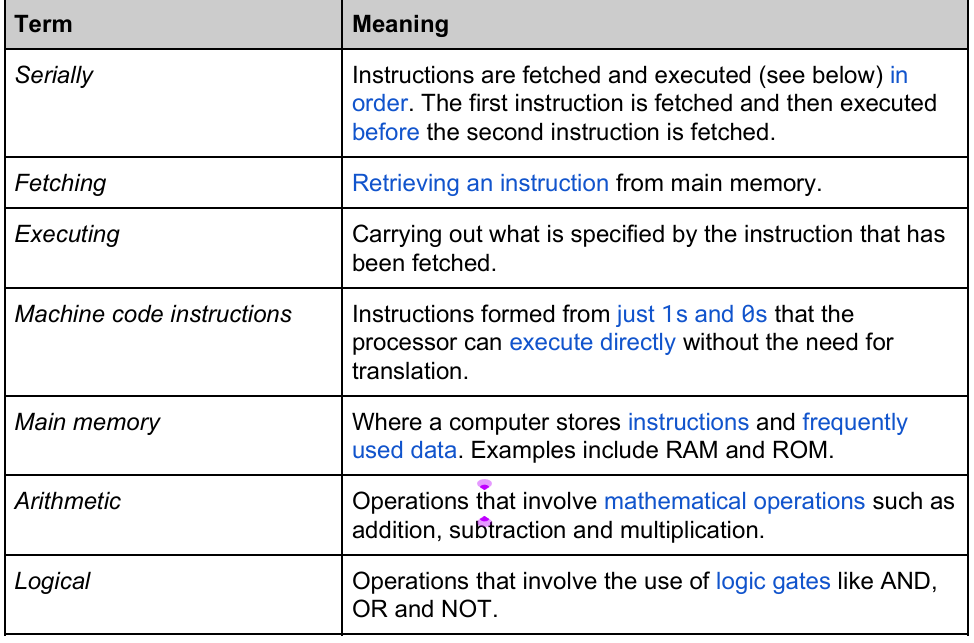
Define Processor.
Executes instructions.
Define main memory.
Contains RAM and ROM
→ Store instructions and frequently used data.
→ Faster than secondary storage ; ROM and RAM enables fast processor.
Buses?
Series of parallel wires that connect internal components.
Number of parallel wires = WIDTH
Width has direct relationship to number of bits that can be transferred simultaneously.
A____ Bus?
Address Bus
Transports memory addresses.
Increase bus width → Increases range of addresses (Addressable memory increases too)
Add single wire → Doubles number of addressable memory locations.
Addressable memory location - Portion of memory that can be accessed by address.
IF not enough locations, some memory can be unused.
Define data bus.
Sends data and instructions
Increases volume of data that can be transferred over the bus at any one time.
C____ Bus
Control Bus
carries control signals and clock signals
I/O Controllers?
Hardware that controls communication of data between processor and xternal hardware.
WHat are the two types of architecture?
Harvard and Von Neumann
Both ways of setting up processor access to main memory.
Explain H____ Architecture?
Harvard
Two separate main memory locations → Instructions + Data
Each piece of main memory has different characteristics. (E.g. memory used for instructions could be read-only)
Used in embedded systems such as digital signal processing.
V__ N______ Architecture?
Von Neumann
Instructions and data stored in same memory
Performs worse + Buses shared.
Used for general-purpose systems like laptops and smartphones.
What is the Stored Program Concept?
serially fetching and executing machine code instructions stored in main memory by a processor that performs arithmetic and logical operations
Early computers were made to run one specific program
But with this concept, it allows for instructions to be switched out with another, enabling modern computing of the present day to run different applications simultaneously.
What do processors contain? Explain each.
ALU Arithmetic Logic Unit
→ Performs arithmetic and logic operationsCU Control Unit
→ Controls components of processor (FDE as well)Registers
→ Small storage for temporary data, high read write speeds.
General Purpose Vs. Special purpose R______? Examples?
General Purpose Registers store any data for instruction to be executed.
Special Purpose Registers are assigned to store specific information.
What does the processor have to synchornise its components?
System Clock
Timing signal set at frequency to synchronise communication between processor components.
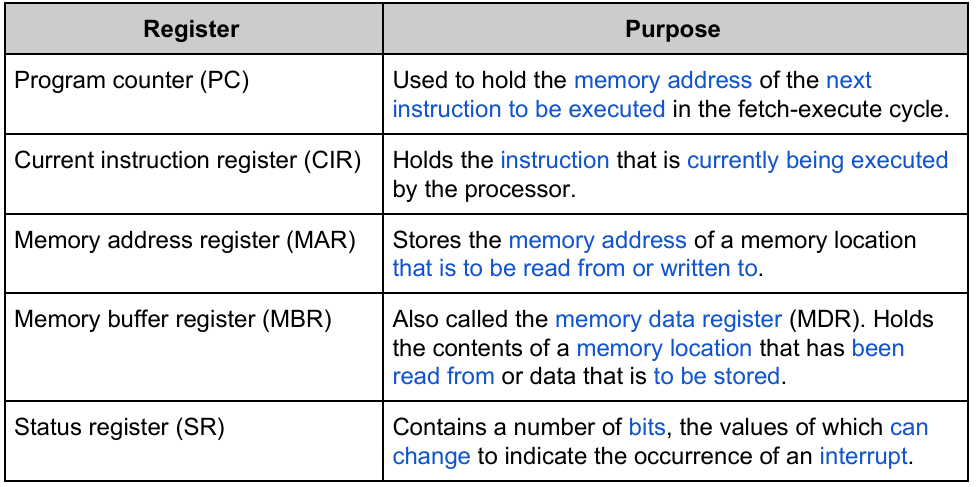
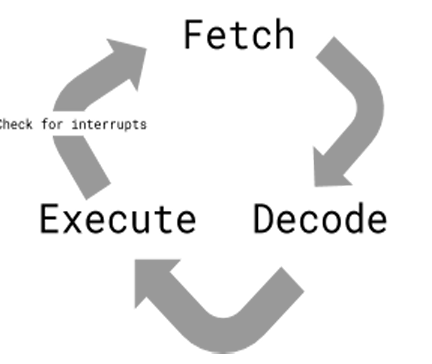
Explain Fetch Execute Cycle.
Fetch:
Contents of PC copied to MAR
MAR → Main memory
Main Memory → MBR (Via bus)
PC +1
MBR → CIR
Decode:
Content of CIR decoded by Control unit
Split into opcode and operand
Execute:
Any remaining data fetched
Instruction executed
Calculations stored in main memory or general purpose registers.
Checks for interrupts in Status register.
What is an instruction set
Group of instructions for processor.
May not be compatible with other processors.
What is machine code stored as?
Opcode or Operands.
Opcode: Operation to be carried out
Operand: Data on which operation is performed.
What is a bit usually assigned to? Explain.
Usually assigned to addressing modes.
2 types:
Immediate (Actual value)
Direct (Memory Address)
What is an interrupt?
signal that requests attention of processor.
Detected as change in status register.
True or False: Software can also send interrupts.
True; Division by zero or stack overflow For example.
How are interrupts handled?
Using vectored interrupt method.
Stops executing program
Sends register contents onto system stack
referred to as saving the “volatile environment”
Loads appropriate interrupt service routine (Series of instructions specific for interrupt)
Restores volatile environment and continues with program.
What affects processor performance?
1 - Number of cores
Directly affects processor, each core can work independently.
2 - Cache Memory
Reduces time wasted fetching data from main memory
Caches stores frequently used data.
3 - Clock Speed
Frequency of pulses → Components can work faster in synchronisation with eachother.
4 - Word Length
Group of bits treated as single unit by processor
Represents both instructions and data.
Higher word length means more bit can be transferred and manipulated as a single unit.
5 - Address bus Width
More data can run simultaneously
Increases range of addresses
Adding single wire doubles number of addressable memory locations
6 - Data Bus width
Increases volume of data transferred at once
Reduces number of cycles required to fetch large volumes of data.
2D Vs. 1D Barcodes
2D → more information in same space as 1D BUT more processing
What do barcode readers contain?
Laser light source, lens, photodiodes, and mirror
1 - Mirror reflect light onto diode which turns it into electrical charge.
2 - Charge can be measured and processed to form digital signal.
what do the light portions of a barcode do?
Reflects the most light.
What can Barcode have?
Error detection and prevention methods such as parity bits or check digits.
if Barcode fails to scan it scans again until 100%
This occurs 1000s of time in a second so no delay for humans.
Describe Digitial cameras?
Contain lens that focuses light onto sensor.
Path of light is regulated by shutter.
Two Sensors: CMOS and CCD
Cells each represent a pixel
Their charges are each measured and converted into digital value.
Colour Cameras:
Multiple cells for each pixel
Each have filter to only allow specific wavelengths.
enables separate image for each colour before being combined.
What is a filter used in digital cameras?
Bayer Filter
Produces closer approximation of what human eye is seeing.
Explain Laser printer.
Prints whole pages at a time.
Contains Laser light source, mirror, drum, toner roller, fusers.
1 - When printed a paper, toner is positively charged.
2 - laser is directed at toner, where it hits becomes discharged. → Leaves impression of page.
3 - Toner roller dispenses negatively charged toner onto drum.
4 - Opposite charges attract and paper is heated by fusers, putting toner onto paper.
Applies same process with FOUR different colour (CYMK) → Cyan, Yellow, Magenta and Black.
Explain RFID
Transfers information wirelessly between tag and reader.
Contains chip that acts as antenna.
When tag is scanned → emits radio wave
Antenna reads wave and induces power to power chip.
Chip emits own radio wave., containing information held on chip
Wave is picked up by reader which decodes information.