DiStefano Biology Test #1: First & Second Notes Packets, Main Topics, Vocabulary, Darwin, etc.
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
First step of the scientific method
observation
qualitative data
Information describing color, odor, shape, or some other physical characteristic
quantitative data
numerical data
Inference
A conclusion reached on the basis of evidence and reasoning
experiment
A research method in which an investigator manipulates one or more factors to observe the effect on some behavior or mental process
hypothesis
A testable prediction, often implied by a theory
independent variable
The experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied.
dependent variable
The outcome factor; the variable that may change in response to manipulations of the independent variable.
controlled experiment
An experiment in which only one variable is manipulated at a time.
controlled variables
held constant, used for reference, In any experiment there are 10-12 of these
control group
not being manipulated, baseline group
experiment group
exposed to manipulation of independent variable
Repitiion
something done multiple times during an experiment or running the same experiment more than one time to increase accuracy
replication
to replicate things exactly in a different experiment, done by a different group
theory
well-tested explanation that unifies a broad range of observations
properties of life
order, reproduction, growth and development, metabolism, regulation, response to the environment, evolutionary adaptation
are all properties of life necessary for something to be alive?
no
What did Darwin study that made him grossed out?
medicine
What did Darwin learn from a freed slave?
taxidermy
What was Darwin's profession when he was approached to join the HMS beagle?
Clergyman
HMS Beagle
5 yr trip to map the coast of S. America, Darwin studied a wide variety of plants and amimals
Patterns of Diversity
Why habitats had animals (isolation)
Fossils
Preserved remains of once-living organisms, Darwin wondered why they died out
Galapagos Islands
Chain of islands near South America where Darwin developed his theory of natural selection by studying the unique life there. Finches and Tortoises, different species depending on island.
Adaptive Radiation
Rapid speciation of many species to fill many ecological niches
Lonesome George
The last of it species, extinct in 2012 on Pint Island
Hutton
Father of Geology, believed earth was very old and it was shown in rocks
Lyell
principles of geology, believed that the present earth was the key to the past
Malthus
economist who was focused on population growth, birthrate and deathrate, and when we would run out of surplus as it relates to evolution
Lamark
inheritance of acquired characteristics, use and disuse, his theories were disproved by Darwin later
Alfred Wallace
Came up with the idea of natural selection to explain evolution, joint published with Darwin, survival of the fittest
Homologous structures
Structures in different species that are similar because of common ancestry. Similar form but different function
vestigial organs
organ that serves no useful function in an organism, left over from ancestors
Analogous structures
environmentally related due to environmental pressure, not related closely species wise
Co-evolution
Process by which two species evolve in response to changes in each other.
developmental homology
A similarity in embryonic form, or in the fate of embryonic tissues, that is due to inheritance from a common ancestor.
genetic homology
animals and plants in different groups that share common ancestor with similar genes (house cats and lions)
Geographic distribution
the natural arrangements of animals and plants in particular regions of the world based on land connections and migration over time
Induviduals do not evolve, _________________ evolve.
populations
Acquired traits __________ be passed on to offspring
can not
Mutations, gene shuffling, and sexual reproduction can all be:
sources of variation
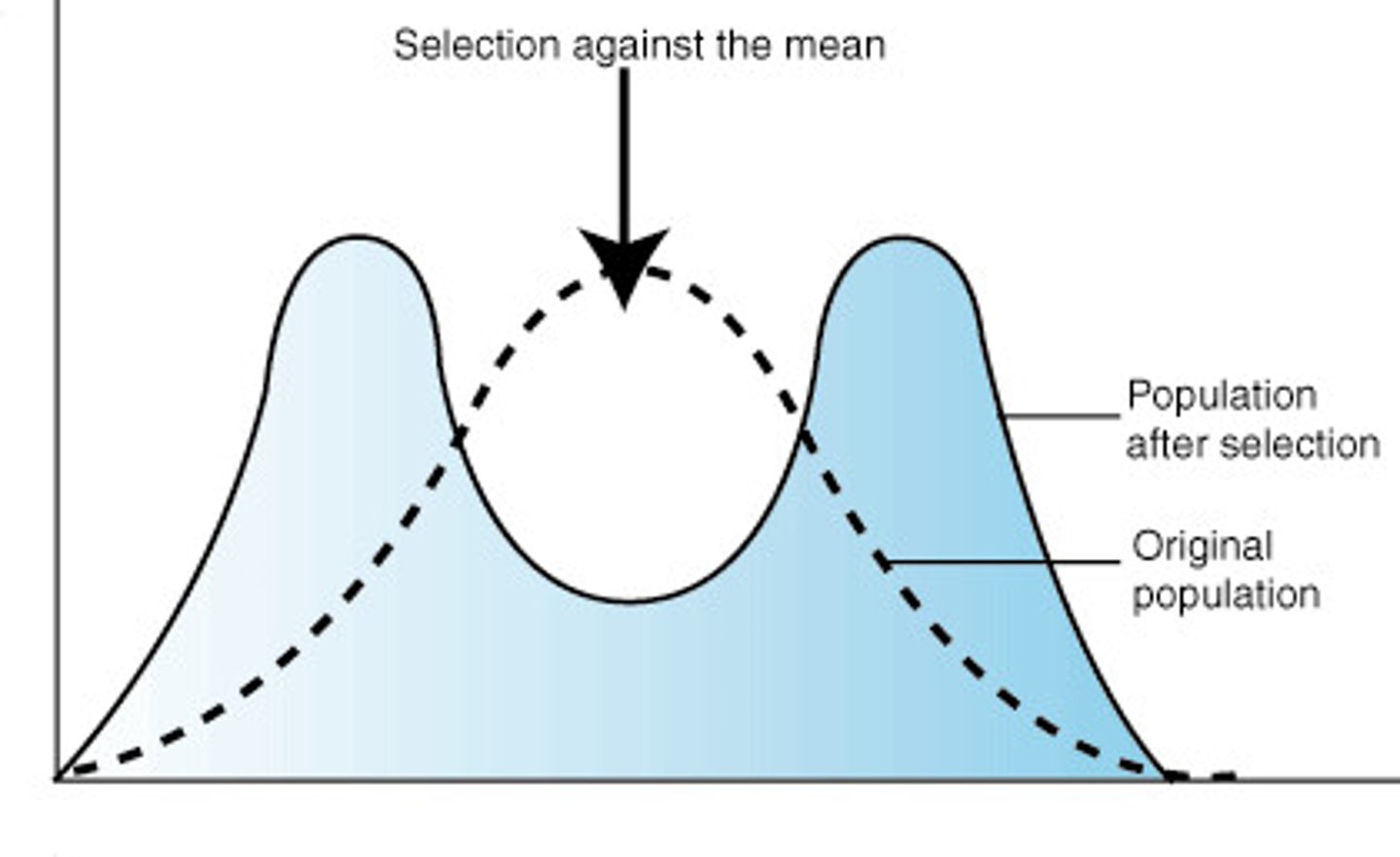
disruptive selection
form of natural selection in which a single curve splits into two; occurs when individuals at the upper and lower ends of a distribution curve have higher fitness than individuals near the middle
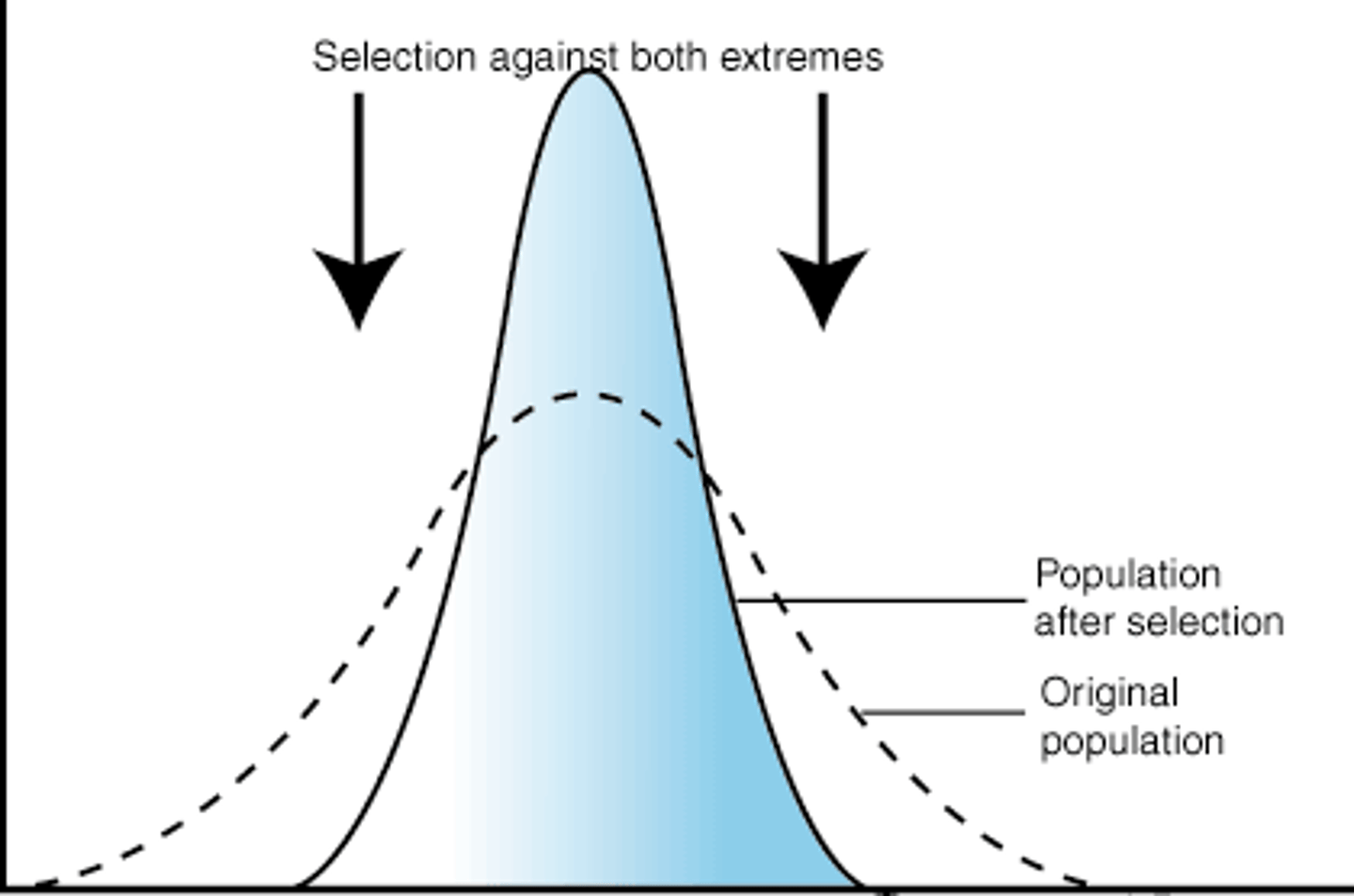
stabilizing selection
Natural selection that favors intermediate variants by acting against extreme phenotypes
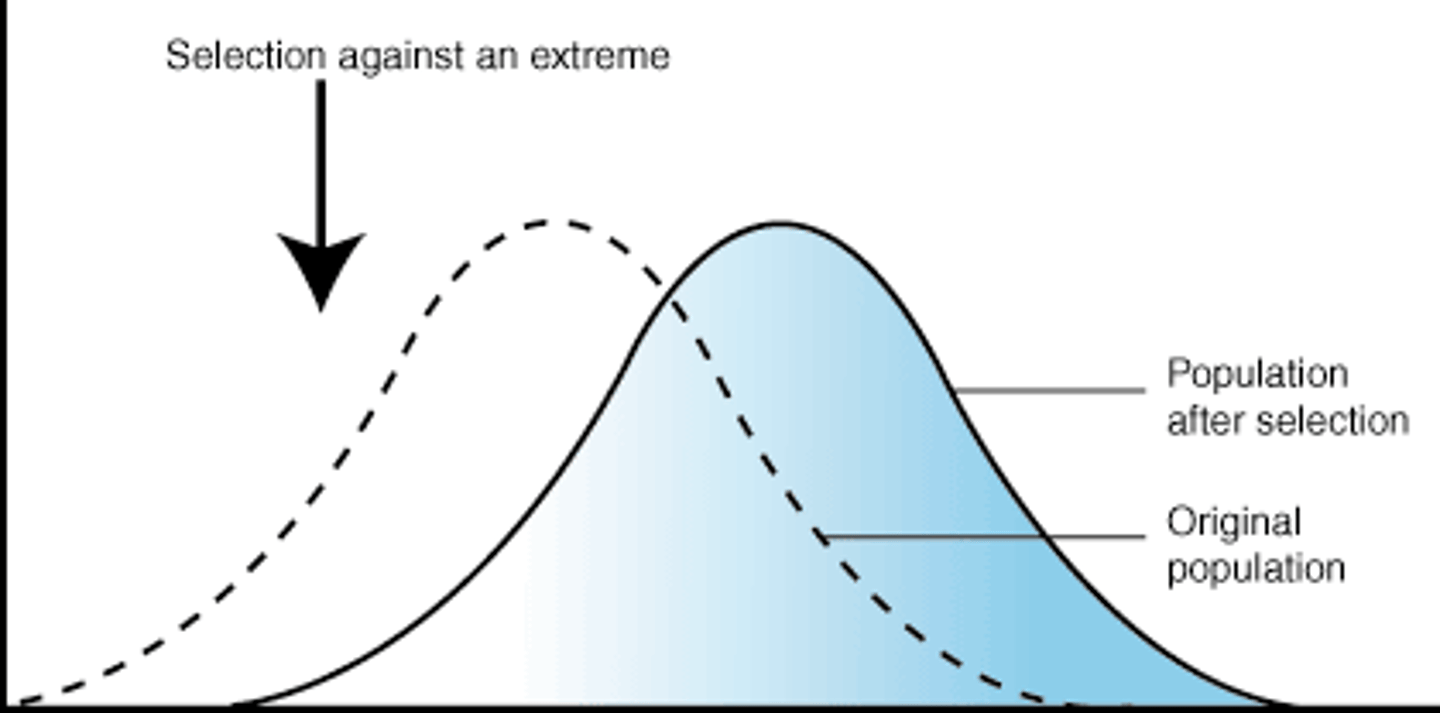
directional selection
Form of natural selection in which the entire curve moves; occurs when individuals at one end of a distribution curve have higher fitness than individuals in the middle or at the other end of the curve
artificial selection
Breeding organisms with specific traits in order to produce offspring with identical traits. (farming plants and breeding them)
sexual selection
A form of natural selection in which individuals with certain inherited characteristics are more likely than other individuals to obtain mates.
what is a sneaky salmon?
a male who looks like a female to sneak their sperm onto the eggs without other males noticing
Changes in gene frequency due to chance that has a bigger impact on smaller populations
genetic drift
allopatric speciation
The formation of new species in populations that are geographically isolated from one another. (often caused by human intervention)
sympatric speciation
when a new species arises within the same geographic area as its parent species
3 domains of life
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
Archaea
domain of single cell organisms, can live in extreme conditions
Eucarya
have a more complex internal structure than Archaea or Bacteria AND have a membrane around the DNA. Resistant to anti-bacterials and anti-biotics.
Bacteria
single-celled organisms that lack a nucleus; can cause diosease but moslty can help organisms (eg. human digestion)
What does a T. rex taste like?
chicken
The best adapted individuals survive and reproduce
natural selection
What percentage of salmon eggs survive to spawn?
less than 0.1%
Different stages of a salmons life include:
eggs, alevin, fry, parr, smolts, returning adults, adults spawning
are all salmon smolts absolutley identical?
no
Adaptation
any characteristic that improves the survival or reproductive success of an organism, often the result of natural selection, organisms match closely with their enviornment.
Darwinian fitness
the contribution an individual makes to the gene pool of the next generation relative to the contributions of other individuals
fitness value of 1
assigned to phenotype with the highest reprodcution
how is fitness value calculated
reproductive success divided by the dominant type's reproductive success
Do you have to be the strongest to be fit?
no
experimental design
planning a set of procedures to investigate a relationship between variables
Ethics
the principles of right and wrong that guide an individual in making decisions
4 tenets of ethics
autonomy, beneficence, non-maleficence, and justice
autonomy
independence
Beneficence
Doing good or causing good to be done; kindly action
Non-maleficence
do no harm
Justice
fairness
Cladogram
Diagram that shows the evolutionary relationships among a group of organisms
How to read a cladogram
start at the bottom and work your way up
the organisms above a trait has that trait
Fitness
Ability of an organism to survive and reproduce in its environment
convergent evolution
Process by which unrelated organisms independently evolve similarities when adapting to similar environments
selective pressure
when the environment pushes an individual or population to adapt or evolve
what is the selective pressure of elephants?
poaching