dna replication
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
how did Watson, Crick and Franklin’s discovery of DNA’s molecular structure serve to explain how DNA replicates?
the complementary bases allow for DNA strands to be predicted as complementary pairs of bases are always the same
describe semi conservative replication:
DNA helix unwinds
each strand acts as a template for synthesis of a new complementary strand
results in 2 DNA molecules w/ 1 original and 1 new strand each
name the enzymes involved in semi conservative DNA replication:
DNA helicase
DNA polymerase
DNA ligase
what is the function of DNA helicase?
unzips DNA helix by breaking H bonds
DNA unwinds and separates into 2 strands
what is the function of DNA polymerase?
free nucleotides that have been activated are attracted to their complementary bases and joined together
this forms a phosphodiester bond
what is the function of DNA ligase?
joins 2 fragments on the lagging strand
compare the synthesis occurring in the leading strand to the synthesis occurring in the lagging strand:
leading strand - catalysed by DNA polymerase and is constantly synthesising
lagging strand - must synthesise DNA in short sections
which end of a polynucleotide chain is the 3’ end?
the end having a free hydroxyl group at the 3rd C of the deoxyribose sugar
which end of a polynucleotide chain is the 3’ end?
the end containing the free Pi group attached to the 5th C of the deoxyribose sugar
why does DNA polymerase only work in the 5’ - 3’ direction?
DNA strands antiparallel
DNA polymerase active site is specific and only complementary to 5’ endshape of 5’ end different to shape of 3’ end
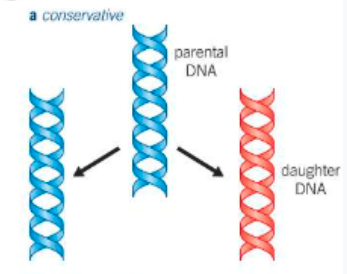
describe the (incorrect) conservative model of DNA replication:
original DNA molecule remains intact
separate daughter DNA copy built up from new molecules of deoxyribose, phosphate and organic bases
→ one molecule made up of entirely new material, another entirely original
describe and explain an experiment that shows evidence for semi-conservative replication:
grew bacteria on a medium containing 14N for multiple generations before transferring bacteria to a medium containing 15N for a single generation
extracted and centrifuged DNA
if conservative: original DNA would only contain 15N and settle at bottom of tube, new DNA would only contain 14N and settle at top of tube
if semi-conservative: all DNA would contain both 15N and 14N and so all would settle in middle of tube
one band formed in middle of tube → each DNA molecule contained a mixture of the heavier and lighter N isotopes
(if left to continue, ratio of 15N:14N would go from 1:1 to 3:1 to 7:1 etc.)
who conducted the experiment which provided evidence for semi-conservative replication?
Meselsohn and Stahl