Structure and Bonding Key terms CIE Checkpoint
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Subatomic
Particles smaller than an atom
Electron
A subatomic particle with a mass close to 0 and a charge of 1- that moves around the nucleus of the atom
Proton
A subatomic particle with a relative mass of 1 and a charge of 1+ that is in the nucleus of the atom
Neutron
A subatomic particle with a relative mass of 1 and a charge of 0 that is in the nucleus of the atom
Nucleus
The centre of an atom, containing protons and neutrons.
Electron Shell
The area around the nucleus where electrons are found.
Atom
The smallest part of an element that still has its properties
Element
A substance made of only one type of atom.
Molecule
Two or more atoms joined together by a covalent bond.
Chemical Property
A feature that describes how a substance reacts (e.g., flammability, reactivity). Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties.
Physical Property
A feature that can be observed or measured without changing the substance (e.g., melting point, colour).
Mass
The amount of matter in an object, measured in grams or kilograms (g or kg).
Volume
The amount of space an object or substance takes up, measured in millilitres (mL) or cubic centimetres (cm³)
Density
How much mass is in a given volume, measured in g/cm³ or Kg/cm³
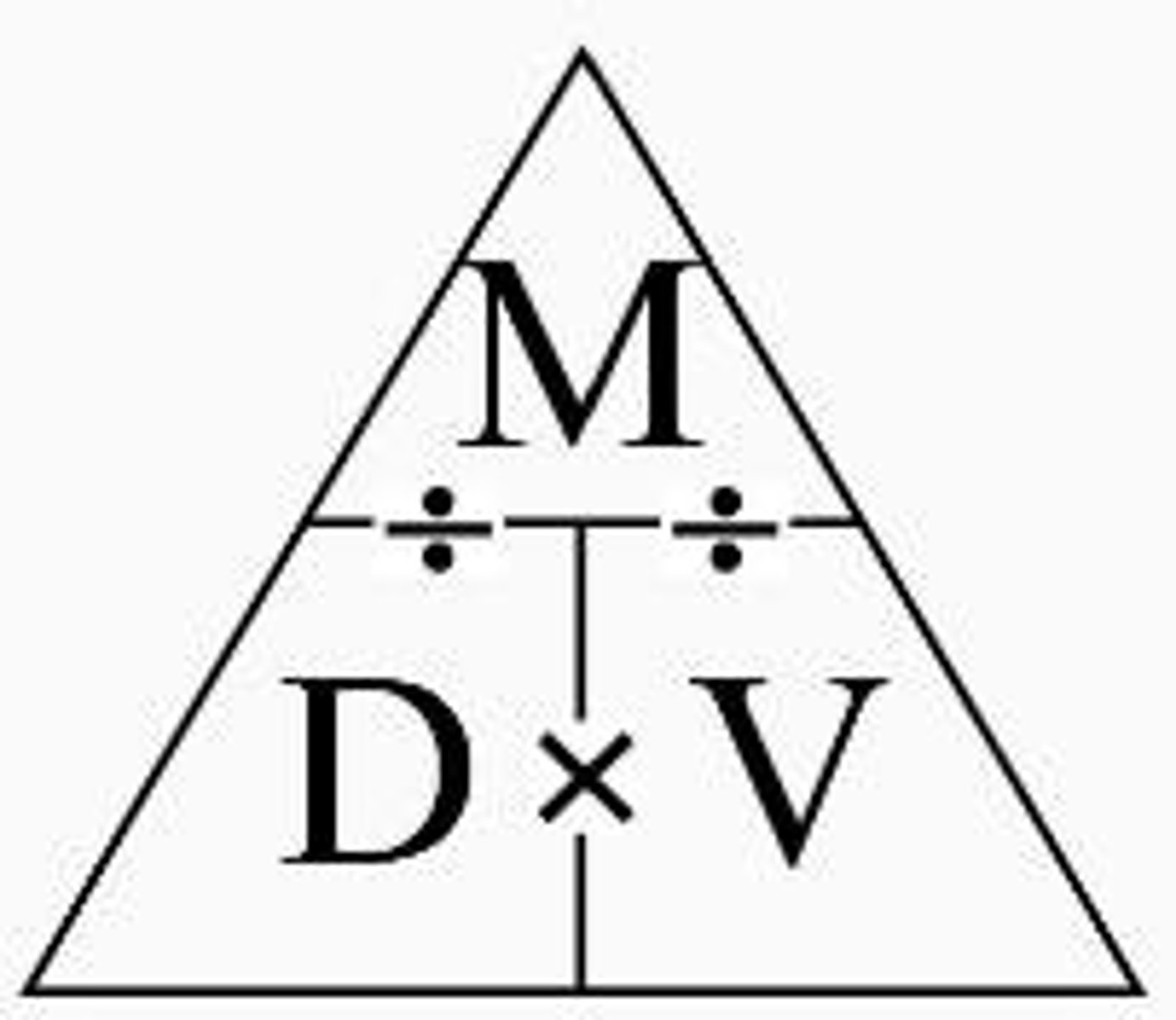
Density equation and triangle
Density = mass/volume
Float
When an object stays on the surface of a liquid because it is less dense than the liquid.
Sink
When an object falls to the bottom of a liquid because it is more dense than the liquid
Group (periodic table)
A column in the periodic table; elements in the same group have similar properties and the same number of valence electrons.
Period (periodic table)
A row in the periodic table; elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells.
Valence Electron
An electron in the outer shell of an atom that can be involved in forming bonds.
Valence Shell
The outermost electron shell of an atom.
Ion
An atom (or molecule) that has gained or lost electrons, giving it a negative or positive charge.
Anion
A negatively charged ion (formed when an atom gains electrons).
Cation
A positively charged ion (formed when an atom loses electrons).
Bond
A connection between atoms in a molecule or compound.
Covalent Bond
A type of bond where atoms share electrons.
Ionic bond
Forms when one atom gives away electrons to another atom. They become charged particles (called ions) The positive and negative ions bond together because of the electrostatic attraction.
Electrostatic Attraction
The force that pulls opposite charges together. For example: between a positive ion and a negative ion or between an electron and the nucleus.
Lattice
A regular, repeating arrangement of atoms or ions in a solid.
Diatomic
A molecule made of two atoms (e.g., O₂, H₂)
Simple Molecular Structure
A small number of atoms joined together by covalent bonds. Usually have low melting and boiling points. Often gases or liquids at room temperature that cannot conduct electricity.
Giant Structure
Lots of atoms or ions joined together in a huge network (lattice). Usually have high melting and boiling points and are solids at room temperature. Metal and Ionic Giant structures can conduct electricity.