MMDST (Metro Manila Developmental Screening Test)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
MMDST
an early detection model that applies to the detection of developmental disabilities in children 6 ½ years old and younger
MMDST
• Simple & clinically useful tool
• A screening instrument to determine if child’s development is within normal.
• To determine early serious developmental delays
• Developed for health professionals
• (MDs, RNs, etc)
MMDST
• To evaluate the four aspects of a child’s development
• To provide referrals to attending physician regarding essential evaluation or patient outcomes of MMDST
4 aspects of child development
personal-social
fine motor-adaptive
language
gross motor development
personal social
ability to take care of himself and get along w/ people
fine motor-adaptive
ability to see and use his hands to pick up objects and to draw
Language
ability to hear, follow directions and to speak
gross motor behavior
ability to sit, walk and jump
MATERIALS NEEDED
Bright red yarn pom-pom
A rattle with a narrow handle
Eight 1 inch colored wooden blocks (red, blue, green, yellow)
A small clear glass/bottle with 5/8 inch opening
A small bell with 2 ½ inch diameter mouth A rubber ball 12 ½ inch in circumference
Cheese Curls
A pencil & bond Pape
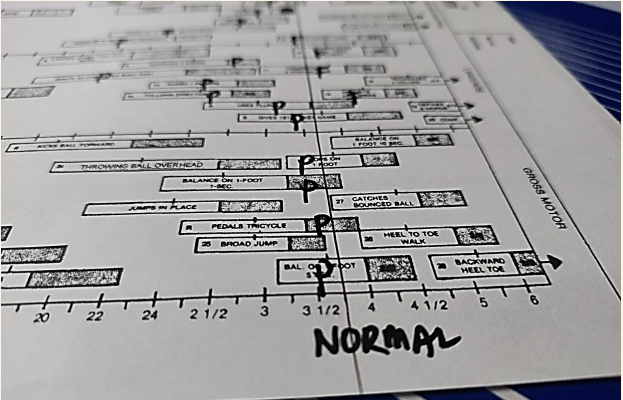
PREPARE THE FORM
Date, Name, Address
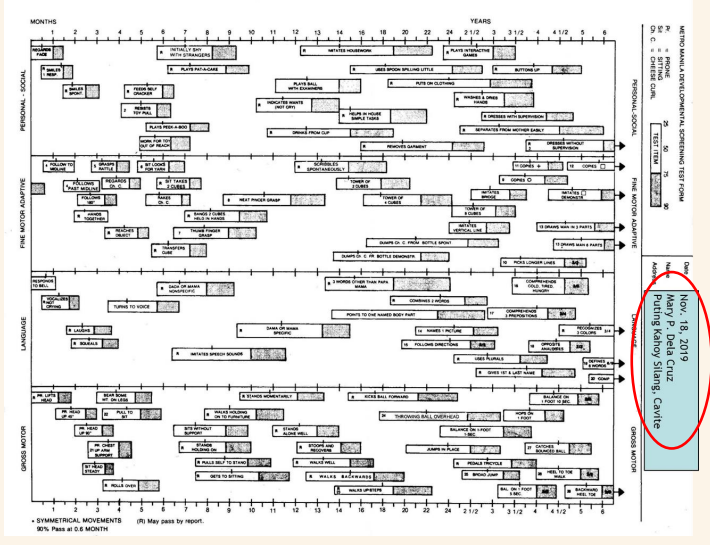
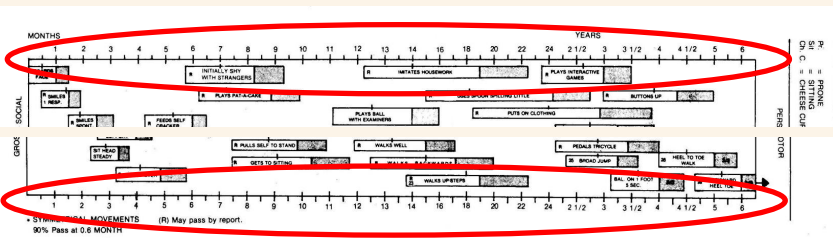
THE AGE LINE
months… years…
space between age marks represents:
2 weeks until 24 months
3 months from 24 months to 5 years
6 months from 5 years to 6 years
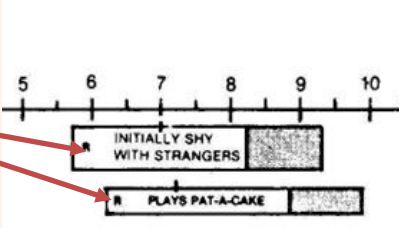
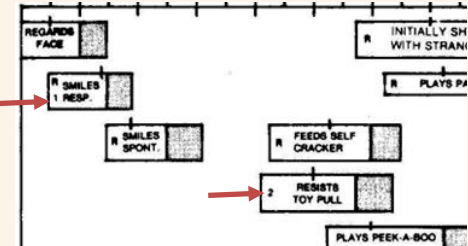
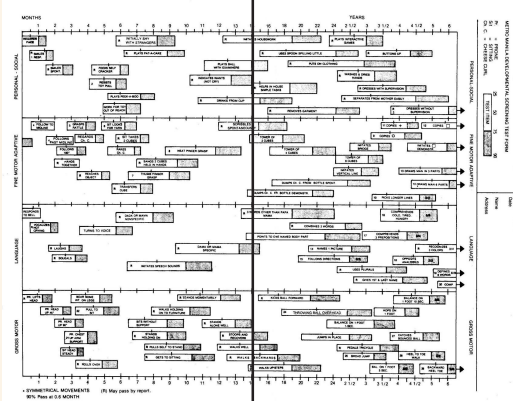
THE LETTER “R”
letter “R” in the bar indicates “Passed by Report” of the parent
-whenever possible, observe what the child can do rather than ask for a report from the parent
FOOTNOTES
numbers located at the left end of the bar
indicates corresponding instruction for administering item
found at the back of the test form

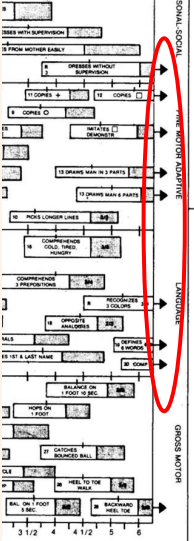
ARROW ITEMS
9 items have arrows (→) at the right end of these bars
indicates that normal children may pass these items even beyond 6 ½ years of age
arrow items types
backwards heel-toe 6.8y
recognizes 3 colors 8.1y
defines 6 words 8.8y
composition of… 8.4y
copies 8.0y
imitates square, demonstrated 6.8y
draws man, 3 parts 6.6y
draws man, 6 parts 8.1y
dresses without supervision 7.6y
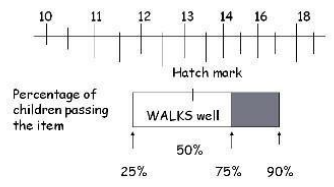
HATCH MARKS
each test item is represented by a bar
the bar is placed along the age scale to show when 25%, 50%, 75%, and 90% of children pass the item (indicated by a hatch mark)
CALCULATING THE AGE OF THE CHILD
determines the basis for drawing the age line later
determines the test item to be administered
AGE CALCULATION
ask the child’s birthday and calculate the exact age using the formula:
DATE OF TEST - BIRTHDAY = age of child
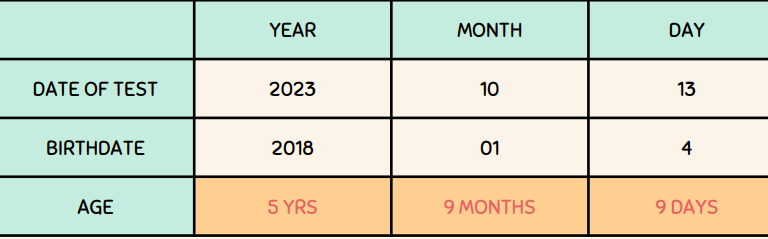
AGE CALCULATION example
test is administered on october 13, 2023. the child’s birthday is on jan 4, 2018
5 years, 9 months, 9 days
FOR KIDS BORN PRETERM (LESS THAN 37 WEEKS AOG)
subtract the number of weeks premature from the age of the child and draw the line at this adjusted age (no adjustments should be made for children born later than expected)
write under the date the number of weeks adjusted (after two years of age, it is no longer necessary to compensate for prematurity
practice problem for less than 37 weeks AOG
computed age: 1 yr, 2 mos & 13 days (52 weeks + 8 weeks + 1 week)
AOG at birth: 33 weeks (4 weeks premature)
ADJUSTED AGE: 57 WEEKS (14 ¼ months)
DRAW THE AGE LINE
example: 1 year, 2 months, 13 days (14 months)
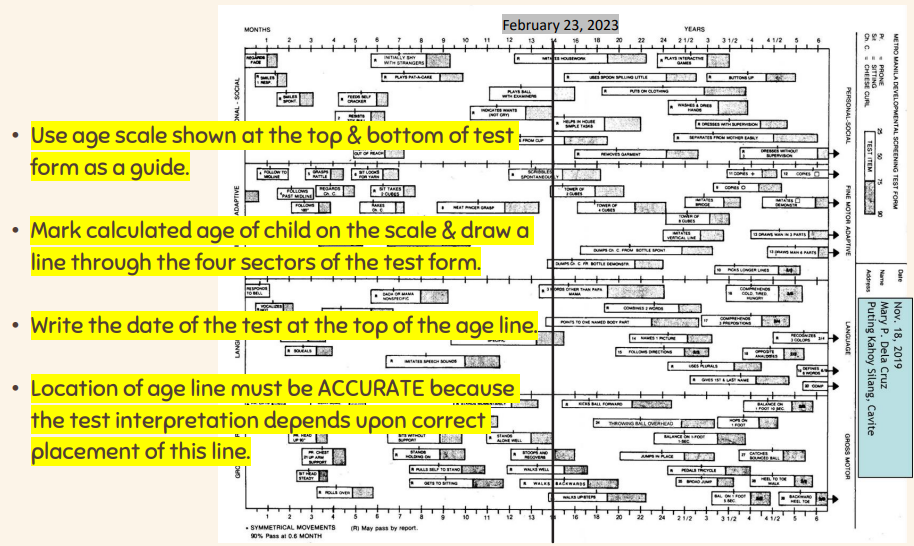
DRAW THE AGE LINE instructions
use age scale shown at the top and bottom of test form as a guide
make calculated age of child on the scale and draw a line through the four sectors of the test form
write the date of the test at the top of the age line
location of age line must be ACCURATE because the test interpretation depends upon correct placement of this line
DRAW THE AGE LINE example
if actual age of the child is 14 months and the child was born 6 weeks prematurely or 1 ½ months earlier than the due date
therefore the age line is drawn 6 weeks earlier than the actual age (12 ½ months—not 14 months)
SELECT ITEMS TO BE ADMINISTERED
administer first those items on w/c child’s chronological age line passes
if a failure occurs in any of these items, proceed to administer items to the left of the age line until you obtain three passes, then stop
in items passed, continue testing to the right where the items become progressively more difficult until the child fails three times in that sector.
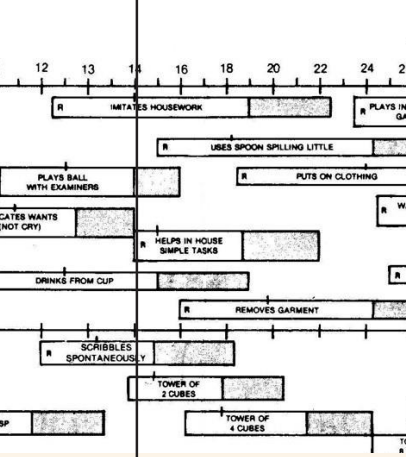
personal social
imitates housework
plays ball with examiner
helps in house simple tasks (R)
drinks from cup
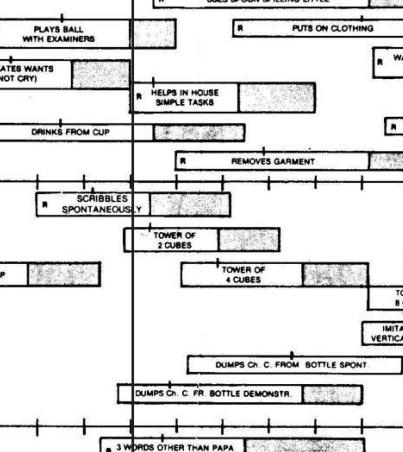
fine motor adaptive
scribbles spontaneously
tower of 2 cubes
dumps cheese curls from bottle (demonstration)
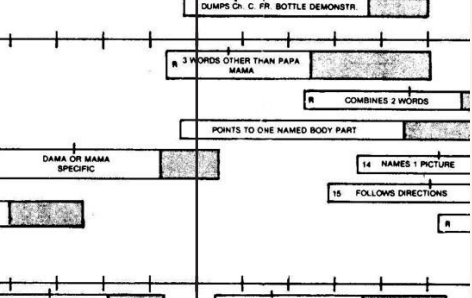
language
3 words other than mama and papa (R)
points to one named body part
Dada or Mama specific (R)
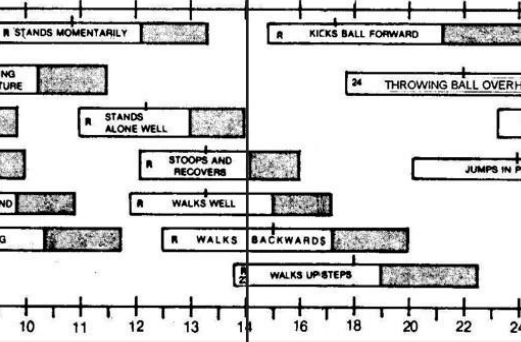
gross motor
stoops and recovers (R)
walks well (R)
walks backward (R)
walks upsteps (R) (23)
2. If a failure occurs in any of these items, proceed to administer items to the left of the age line until you obtain three passes, then stop.
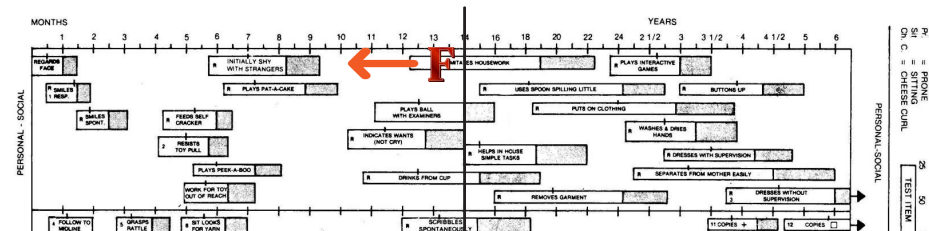
in items passed, continue testing to the right where the items become progressively more difficult until the child fails three times in that sector
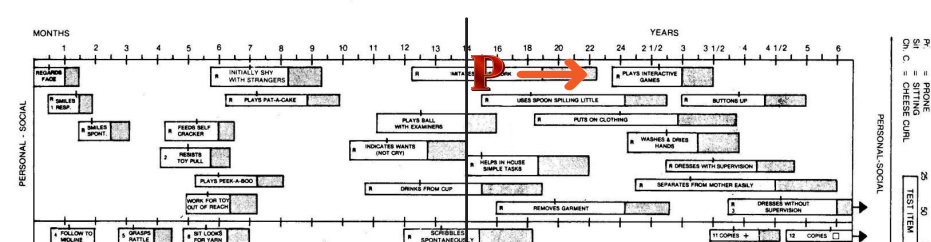
REMEMBER
the number of items to be administered will vary with age and abilities of the child
normally, a child is tested on only twenty simple tasks or items
the child may accomplish some of the tasks on his own w/o being asked
ESTABLISH RAPPORT AND ADMINISTER THE TEST
administering the test preparation
have everything you will need ready:
a quiet room
test form with the age line drawn
MMDST materials
ADMINISTERING THE TEST
start testing items
personal-social sector →
fine motor adaptive sector →
language sector →
gross-motor sector
ADMINISTERING THE TEST
sequence of items may vary but the manner (words and directions) in which each test item is administered may NOT change
begin testing items which you would expect the child can do easily
TELL the child what to do. Do not ask if he can or he will do the task
allow for 3 trials to perform each item before a failure is given
WHEN TO STOP THE TEST
… when items crossing the age line have already been administered
… when the child has a minimum of three passes to the left of any failure
… when each sector should have at least three passes and three failures
REMEMBER
-MMDST is designed to detect developmental delays in children 2 weeks to 6 ½ tears old
-avoid testing the child when he is ill, sleepy, tired, hungry or upset
INTERPRETING THE RESULT
a delay is any item failed which is completely to the left of the age line
-if the age line touches the right end of the bar, the item is not considered to be a delay
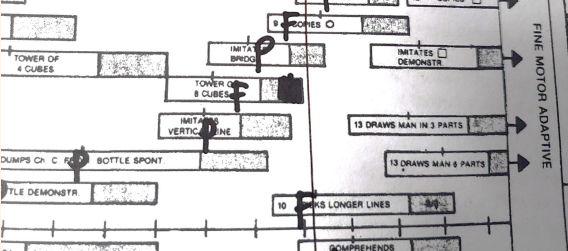
delay steps
mark each delay by heavily shading the right end of the bar
count the number of sectors that have 2 or more delays
count the number of sectors that have 1 delay with no passes intersecting the age line in the same sector

DELAY CRITERIA FOR INTERPRETATION
2 or more sectors with 2 or more delays → ABNORMAL
1 sector with 2 or more delays plus 1 or more sectors with 1 delay and in that same sector with no passes intersecting the age line → ABNORMAL
1 sector with two or more delays → QUESTIONABLE
1 or more sectors with 1 delay and in the same sector with no passes intersecting the age line → QUESTIONABLE
when REFUSALS occur in numbers large enough to cause the test result to be QUESTIONABLE or ABNORMAL if they were scored as failures → UNTESTABLE
any conditions not listed above → NORMAL
DISCUSSING THE TEST RESULTS
ask parent if the child’s performance of his ability and behavior at other times
avoid testing child if he is ill, sleepy, tired, hungry, or upset
overall interpretation of test results should be given to the parent, not the labels abnormal, questionable, or normal
praise the child for a job well done, and reassure the parent that the child is developing as he should be
if the child has a number of delays, remind the parent that this is a screening test and a retest is recommended withing approximately two weeks
RETESTING
use the same form
draw the new age line and score the new test with a different color of pencil
write the date of the new test at the top of that age line
refer a child with abnormal, questionable or untestable result to a pediatrician for further evaluation, if possible
after further assessment, teach parents regarding skills, in developmental stimulation of their children
perform continued surveillance and periodic retesting of the children identified to be at risk
HANDLING DIFFICULT SITUATIONS
the shy child
the uncooperative child
child with many siblings
hyperactive child
the interfering parent

the shy child
offer a toy or kit item to pllay with
give more time to become familiar with tester an test materials
ask the parent to adminster some items or to show how they are done
the uncooperative child
approaches for the sky child may also be used
ask parent to leave the room or to turn away but within seeing distance of the child
reverse psychology may work

child with many siblings
explain to the parent the need to test each child individually
ask the parent to send the siblings on errands

hyperactive child
bring out only the materials needed for each test item
do the test in a quiet room
call the child’s name or simply touch his arm to return his focus'
master the test items

the interfering parent
remind the parent that the child is not expected to perform everything asked of him
have the parent leave the room
discontinue the test and reset the re-screening within 2-3 weeks
MMDST IN THE CLINICAL SETTING
administer test only to:
infants and children whose age ranges from 2 weeks to 6 ½ weeks
newly admitted patients prior to blood extractions, IV insertions and any other invasive or non-invasive procedures
patients without IV lines
patients not in any form of distress or cardiopulmonary failure
patients awaiting surgery
post-operative patients without surgical complications