Intro to Community Health pt. 3
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
unique opportunities of communicable diseases (single pathogen)
prevention
eradication
unique challenges of communicable diseases
unpredictable
transmissibility
potential for explosive global impact
eradication not always possible
antibiotic resistance
why is eradication not always possible in communicable diseases?
non-human host, asymptomatic carrier, rapid mutations
why are antibiotics becoming less effective? (antibiotic resistance)
people are overusing them → people use it when they dont reallyyyyyyyyyyyyy need it
eradicated or nearly eradicated communicable diseases
smallpox + polio
re-emerging or emerging communicable diseases
measles
tuberculosis
whooping cough (pertussis)
dengue fever
malaria
cholera
ebola
avian flu
what percent of emerging communicable diseases are zoonotic? (can be transmitted between animals and humans)
75%
why is there an increase in mosquito-borne illnesses?
climate change → increase in mosquitos
epidemiologic triangle
describes what impacts the risk of and response to infection
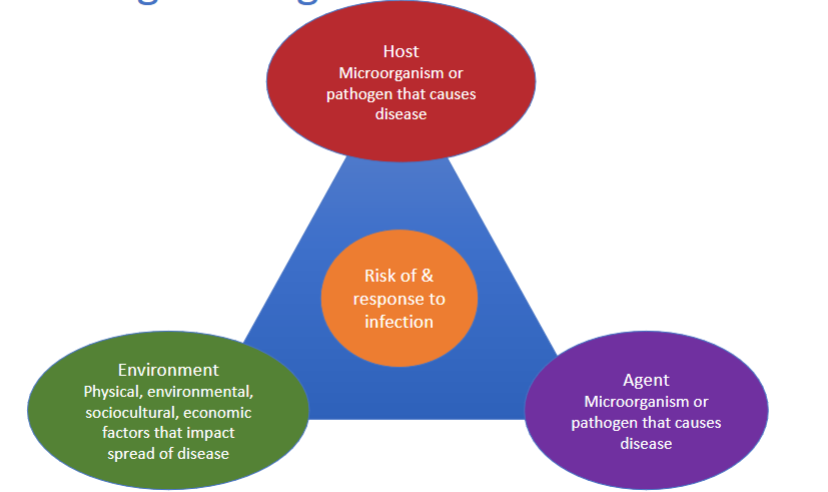
what are the three pillars of the epidemiologic triangle?
host
environment
agent
host → epidemiologic triangle
organism (usually a human or animal) that the agent can infect
agent → epidemiologic triangle
the cause of the disease → typically a microbe such as a virus, bacterium, parasite, or fungus
environment → epidemiologic triangle
physica, environmental, sociocultural, economic factors that impact spread of disease
host microorganism
humans or animals that have been exposed to or harbor an agent
herd immunity
resistance to the spread of an infectious disease within a population that is based on pre-existing immunity as a result of previous infection or vaccination
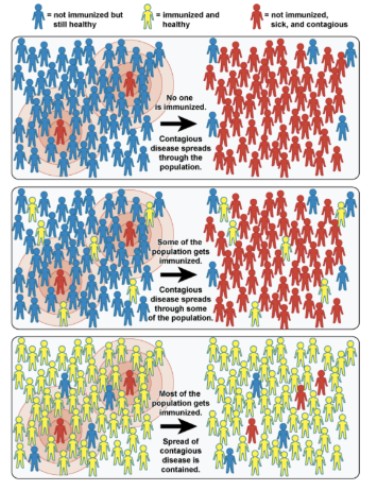
T or F: the level required for herd immunity differs per disease
T → depends on how transmissible it is
ex → measles = 95%, covid = 70%
epidemiologic curve
number of cases spike up and then decrease when it becomes under control (think covid) → considerd the pattern of disease
in contrast, sporadic is NOT widespread, and endemic is SUPERRRRRR widespread and always high num cases
social determinants of communicable diseases
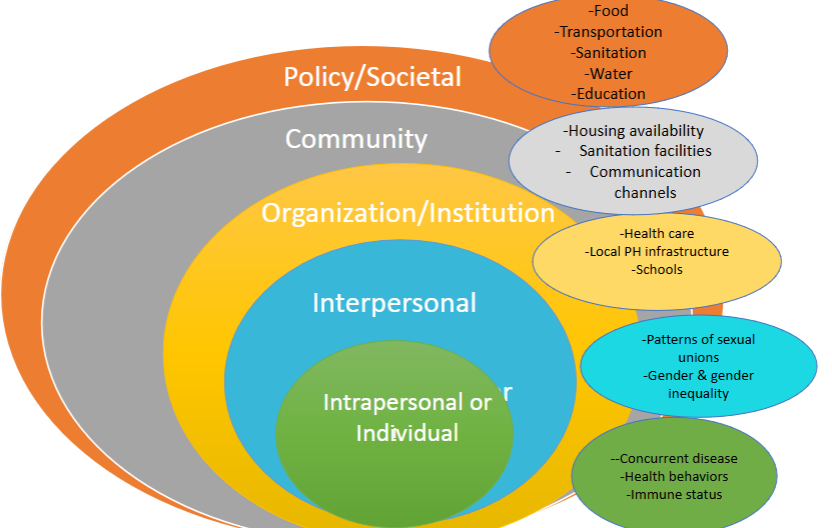
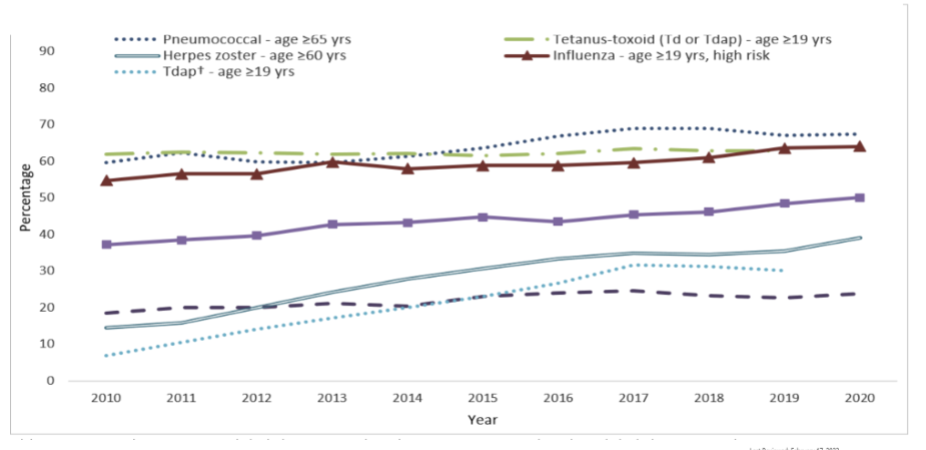
trends in child vaccination
in general, most vaccines remain steady
MMR has the greatest controversy
children are vaccinated with hep a the least (46% of children)
trends in adult vaccination
adults have never been great in getting all their vaccines → remain super steady, but not super high → most vaccines are only about 60%
T or F: there is a broad range of kindergartener vaccination rate for MMR (some states super vaxed, some super not) for 2021-2022
T → also caused by differing opinions towards COVID vaccines
T or F: epidemics occur in “pockets”
F → epidemics are wide-spread
T or F: There has been a resurgence of vaccine-preventable disease
T
the continuum of vaccine acceptance
refuse all → refuse but unsure → delay/refuse some → accept but unsure → accept all
T or F: all vaccines have benefits and potential harms
T
examples of harms caused by vaccines
DTP vaccine → linked to seizures and brain damage
Rotavirus vaccine → linked to intussusception (inversion of the bowels)
Oral poliovirus vaccine → linked to paralytic polio
vaccine adverse event reporting system (VAERS)
national “early warning” system co-managed by the CDC and FDA
post-vaccination adverse events, regardless of whether the cause is vaccine-related
“passive reporting system” - accepts reports from anyone
includes minor to major vents
number of reports alone cannot be interpreted as evidence of a casual relationship
around a million reports following COVID-19 vaccination as of December 2024
history of inoculation
2000 BC in china→15th century smallpox → 1721 smallpox → 1796 jenner’s smallpox vaccine → 1885 rabies pasteur → 1940s to 1950s polio vaccine
history of vaccine hesitancy
has been around since the history of vaccines
ex → anti-vacc society in 1902
has gotten worse
what has caused the increase towards vaccine hesitancy?
parents these days havent seen the harmful effects of these diseases since they havent been around for a while → makes it hard for people to understand the importance
T or F: the number of recommended vaccines has increased
T
rising prevalence of autism spectrum disorders
however, more kids are being tested so more kids are being diagnosed
disregards other causes such as dietary choices
people link autism to vaccines because the first signs of autism often occur around the same time as vaccination
myths of covid vaccine
the covid vaccine can affect women’s fertility
researchers rushed the development of the COVID-19 vaccine, so its effectiveness and safety cannot be trusted
getting the COVID vaccine actually gives you COVID
breakthough cases prove that even if i get the vaccine, i might still get COVID, so why bother?
a microchip, with the backing of Bill Gates, is being implanted with the vaccine
results of vaccine conspiracy beliefs and covid 19 vaccine study
43% of parents endorsed at least one conspiracy belief
parents who were hesitant about vaccines were less likely to vaccinate their own kids
Why is vaccine hesitancy increasing?
trust in science down
trust in government and public authorities down (73% complete trust in 1958 to 19% trust in 2015)
“vaccine altruism” → grounded in social responsibility and the concept of herd immunity → belief that everyone should be vaccinated to protect those with a weaker immune system
trust in each other down (mistrust in neighbors has gone up)
“infodemic” → lots of info out there
WHO Top threat to global health
vaccine hesitancy sits in the top 10 (#8)
misinformation
no intent to deceive, just inaccurate
ex → click baiting, satire/parody, newspaper hoax
disinformation
specific intent to deceive
ex → manipulated (deepfakes, falsified photos, counterfeit websites), taken out of context, purey fictional (biased claims)
why do we believe things that aren’t true? → why does mis/disinformation circulate so easily?
affect heuristic → relying on emotions, rather than concrete information (heart over brain) (shortcut)
bandwagon effect → adopting certain behaviors or beliefs because many other people do the same
confirmation bias → tendency to notice, focus on, and give greater credence to evidence that fits with our existing beliefs
commitment bias → tendency to remain committed to our past behaviors, particularly those exhibited publicly, even if they do not have desirable outcomes
framing effect → equivalent info can be more or less attractive depending on what features are highligthed (20% fat vs 80% fat-free)
interventions to combat mis/disinformation
innoculation (prebunking) → pre-emptively warn people to look for potential for being misled and train them to identify the techniques used to mislead or misinform
debunking → lead with the facts (make them simple and sticky using expert sources)
fact checking → improve media literacy-encourage verification of info + provide authoritive context alongside search results or online posts about dubious claims
accuracy nudges → think critically about message before sharing it
tagging/warnings → ex, “this page has repeatedly shared false info”
interventions to combat misinfo that are not effective
shaming or mocking → can deepen mistrust and entrench beliefs
censorship alone → may limit spread but can fuel conspiracy theories about suppression →overloading w facts
excessive detail → cognitive overload can lead to confusion or disengagement
impact of interventions for vaccination (biggest impact to smallest impact)
policy changes → clinical interventions → individual/health education
what types of interventions are generally considered to be most effective in increasing vaccination?
policy
epidemiologic transition
the shift in disease patterns and causes of death within a population over time, typically moving from a focus on infectious and parasitic diseases to a focus on chronic, non-communicable diseases
endemic
a disease that is regularly occurring within an area or community
epidemic
the rapid sprread of disease to a large number of hosts in a given population within a short period of time
pandemic
an epidemic that occurs worldwide or over a very wide area, crossing international boundaries and usually affecting a large number of people
T or F: exemptions permitted for state childcare and school immunization requirements differ per state
T → ex, only medical exemptions are permitted, medical and religious, medical and personal belief, medical and religiousand personal belief
Why is vaccination so important for population health?
they protect individuals and communities, reduce healthcare costs, and contribute to herd immunity
what are the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
A set of UN goals to end proverty, protect the planet, and promote prosperity by 2030
replaced the MDGS that were in place form 2000-2015
main goal = “universal and equitable access to safe and affordable drinking water”
what is safely managed water?
drinking water from an improved water source which is located on premises, available when needed and free from fecal and priority contamination
safe water is water that is safe to drink in the users’ cup
NOT JUST HEALTH, safety, dignitiy
under-five mortality worldwide
the under-five mortality rate has fallen by more than half since 1990
12.6 mil in 1990, 5.6 mil in 2016
causes of death for children less than five, ranked most prevalent to least
neonatal causes, pneumonia, other/misc, diarrheal diseases, congenital/birth, injuries, malaria, menigitis, AIDS, measles
why do children die of diarrhea
youngest children → immature immune system, less physiologic reserve (skinny babies have no protection when they lose weight from diarrhea)
multiple physiologic insults → malnutrition, frequent infections
feces contaminated environment → water, food, environment
limited access to effective clinical care
organisms that cause diarrhea
bacteria → chlorine inactivates, ~1 micron (filterable), cholera, typhoid
protozoa → (Oo)Cyst chlorine resistant, 3-10 microns (filterable), cryptosporidiosis, giardiasis
viruses → chlorine inactivates, <1 micron (not filterable), rotavirus, norovirus
The incidence of ______ fell steeply during the early part of the 20th century after the introduction of filtration (1906) and chlorination (1913)
typhoid fever
advantages of WASH infastructure
provision of reliable, quality water
disease reduction
increase quality - better hygeine
what does a WASH infastructure require?
political stability
large investment of public dollars
terrain conducive
population density
population stability → slums, emergencies
land tenur → slums, emergencies
→ may be challenges in lower class countries
What are the benefits of WASH infastructure in low-resourced settings
Reliable, quality water
Reduction of infectious illnesses
improved hygiene
T or F: Humanitarian emergences are crises that threaten the health, safety, or well-being of large groups of people due to conflict, disaster, or disease
T
humanitarian emergencies
disasters caused by natural hazards → earthquales, eruptions, landslides, tsunamies, floods, drought. increasing unplanned settlements and climate change
outbreaks/epide,ics → disease → cholera, ebola, zika, COVID, mpox. increasing particularly animal → human spillover (zoonotic)
complex emergencies → conflict increasing
populations → refugees, IDPs, entrapped
each major categories of humanitarian emergencies are experiencing an increasing trend
T or F: IDs increase after flooding and displacement
T
syria water supply in conflict
pre-conflict syria = high access to safe drinking water and sanitation, not much of the population under extreme poverty. they achieved universal primary education
when conflict began in march 2011, 13.6 million needed assistance, 6.3 million internally displaced, 69% under the poverty line, 1.9 million needed shelter, 67% had no consistent water access
In southern syria in 2016+2017, what were the main sources of water?
trucked water (77% and 83%)
network (22% and 15%)
trucked water increasing, network water decreasing
where to intervene in low income countries → WASH
support private sector → get chlorine in trucks, cash to vulnerable populations
support infastructure → pay operators, rebuild/repair/maintain, get chlorine in system
household water treatment → tablets for when the above don’t work
risk management approach in low income countries → WASH
entry points, cash
WASH
safe drinking water, sanitation, hygiene
crucual to human health and well-being
environmental hygiene
aspects of the human health and disease that are determined by factors in the environment
also refers to the theory and practice of assessing and controlling factors in the environment that can potentially affect health
refugee
people who have fled war, violence, conflict, or persecution and have crossed an international border to find safety in another country
internally displaced people
persons or gorups of persons who have been forced or obliged to flee or leave their homes or places of habitual residence, in particular as a result of or in order to avoid the effects of armed conflict, situations of generalized violence, violations of human rights, or natural disasters
remain within the country’s borders
entrapped people
individuals who are unable to leave an area due to conflict, violence, natural disaster, or other crisis
spillover
when viruses move from one species to another
What is an examlpe of a success in terms of kenya’s sanitation?
the sanitation chain →
moving beyond latrines to collection → treatment → reuse
sanergy (in slums)
sanitation chain
waste is transported and removed from sanitation facilities
treated
and reused
hygiene kits
pre-packaged collections of items designed to promote and support hygiene practices, especially in emergency or disaster situations
a collection of items designed to prevent the spread of germs
chlorination tablets
solid forms of chlorine used to disinfect water in the process of water purification
they dissolve slowly, releasing chlorine that kills bacteria, algae, and other microorganisms
rapid response timing
the time taken from the initiation of a rapid response call to when a trained team arrives at the patient's bedside to assess and treat a deteriorating patient
What groups experience a disproportionate burden when there is inadequate WASH infastructure? Why are they particularly vulnerable?
marginalized inhabitants of border areas, such as the MEXICO-US border crossing, low income populations, communities of color, women, children, older adults, those with disabilities
They are particularly vulnerable due to limited access to resources, pre-existing health conditions, and social determinants
What are the four main categories of WASH interventions? What are the main interventions for water treatment? Sanitation? Hygiene?
water safety and supply, sanitation, hygiene, behavior change
water safety → source-based water treatment, household water treatment, improved water storage, improving water supply infastructure
sanitation → improved sanitation facilities, community-driven sanitation, solid waste management, wastewater management
hygiene → handwashing with soap, hygiene kit distribution, hygiene education
What are the main mechanisms by which WASH interventions operate to reduce disease?
improve water quality, provide sanitation facilities, promote handwashing → block fecal-oral transmission pathway, reduce environmental contamination, improve immune function, community empowerment
What are the challenges to doing “robust” research on WASH interventions in humanitarian responses and complex emergencies?
Conducting robust research on WASH interventions in humanitarian responses and complex emergencies faces significant challenges, including limited funding, resource constraints, political obstacles, and the need for strong collaboration between stakeholders
What are the barriers to identifying and implementing effective evidence-based interventions during a humanitarian response?
time constraints, resource limitations, lack of relevance to humanitarian practice, and challenges in adapting evidence-based practices to specific contexts.
How do issues like political instability, terrain, population density, and funding impact the ability to build WASH infastructure?
Political instability can lead to corruption and diverted funding, while difficult terrain increases construction costs and logistics. High population density, particularly in informal settlements, strains resources and makes infrastructure expansion difficult. Insufficient funding hinders the planning, implementation, and maintenance of WASH projects
T or F: Residents still have not recieved their money after the Flint water crisis settlement
T
When did we first know lead was a problem?
200 BC → evidence of lead posioning from ceramics
1796 → ben franklin wrote abt it
1950s → herb needleman → associated with figuring out long-term negative effects
T or F: there is no safe level of lead
T
T or F: Lead is everywhere throughout the US in the water
T
impact of lead on health
young children - intellectual disability, underperforming at school, behavioral issues
in adults → ischaemic heart disease, stroke
pregnant women → affects the development of the fetus
short-term consequences of lead
immediate neurotoxic effects of lead poisioning → irritability, loss of appetite, weight loss, sluggishness and fatigue, pica, seizures
legionnaires disease
long-term consequences of lead
decreased intelligence (small change in mean IQ = shift in entire population’s IQ distribution)
behavioral issues
speech impairment
hearing loss
reduced sperm count and abnormal sperm
miscarriage, stillbirth or premature birth in pregnant women
hematologic, cardiovascular, etc
widespread lead exposure in Flint (2009-2016)
spike in blood levels of children in flint → represents an epidemologic curve
cost of lead poisioning in the US
economic cost in the US → 50.9 billion dollars
cost of detoxifying entire nation = 1 trillion
costs include → health care cost, lost productivity, special education
for $1 invested in lead paint hazard control results in net savings of $181-$269 billion
biggest lead producers in the US (prior to 1978)
paint manufacturers, petrolieum industry, batteries, plumbing and construction, mining and smeltering
When did the issue in Flint start?
Flint changes the water supply from the municipal water supply from Lake Huron to the Flint River → associated with corroded pipes
When did Flint change the water source back to Lake Huron?
October 2015 (despite initial switch and problems occuring in early 2014)
What happens when Flint switches its water source from Lake Huron to the Flint River?
2014 → legionnaires disease spikes
June = residents raise concerns
october = GM stops using water from flint
january 2015 = flint declares a state of emergency
feb = city announces high lead levels in water
october = flint switches back to the Detroit water system
jan 2016 = governor rick snyder declares a state of emergency, president obama declares a federal state of emergency
april = crimincal charges against government officials
june = the CDC rereport confirming a link between blood lead levels in children
june 2017 = michigan attorney general drops charges against several officials, stating a need for more thorough investigation
2018 = michigan neds the free bottled water program, stating that water quality has improved
2019 = former governor rick snyder and other officials face new charges, including willful neglect of duty
2020 = michigan attorney general announces a settlement with a $600 million fund for water crisis victims + the settlement is approved by a federal judge
2021 = charges against former governor rick snyder are dropped
2024 = payments not yet distributed
how to prevent lead posioning
elminiate exposure (banned in 1978)
#1 exposure in housing built before 1978
primary prevention → individual level → lead posioning
use a home testing kit
hire a risk assessor to check your home
wash your hands frequently
take a daily supplement of iron and calcium
mop and vacuum frequently
surveillance
research
recommendations
secondary prevention → individual level screening → lead posioning
blood test for elevated BLL (current)
X-ray fluorescence (cumulative)
blood film examination (changes in red blood cells)
tertiary prevention → individual level chelating therapy → lead posioning
chelation therapy (if BLL is >45 ug/dL) →
less value in chronic cases below this value
chelating agents actively bind to lead
oral or intravenous
administration
forms a non-toxic compound excreted in urine