Muscles Region 1-9
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
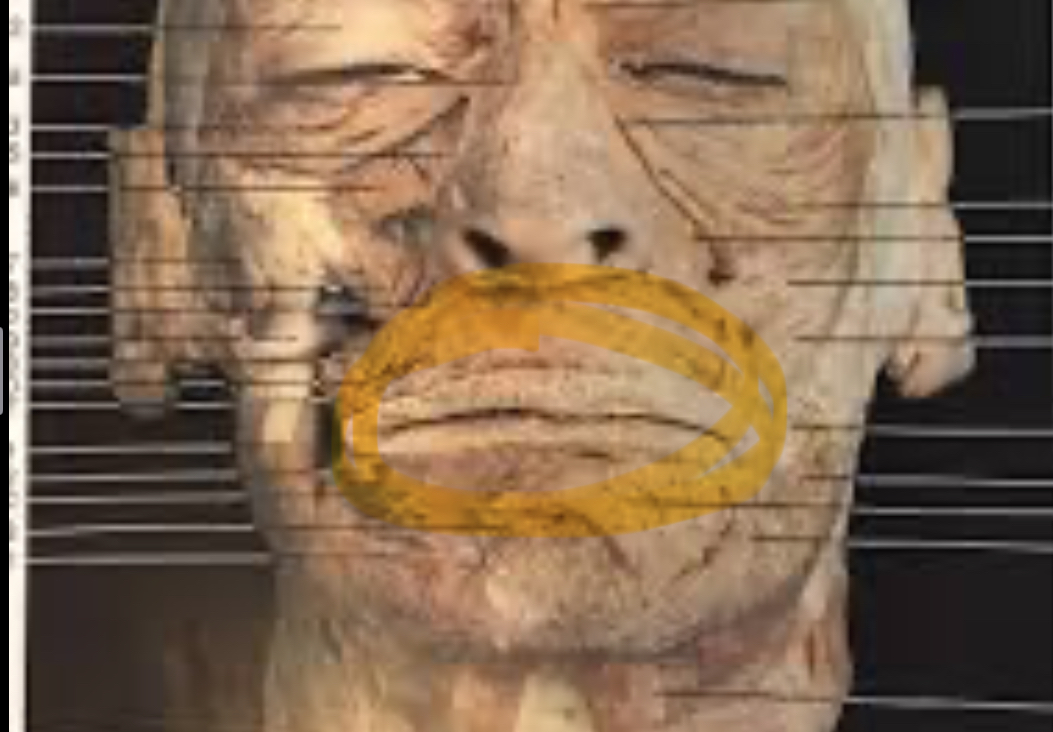
Orbicularis oris
Closes, protrude lips “kiss muscle “
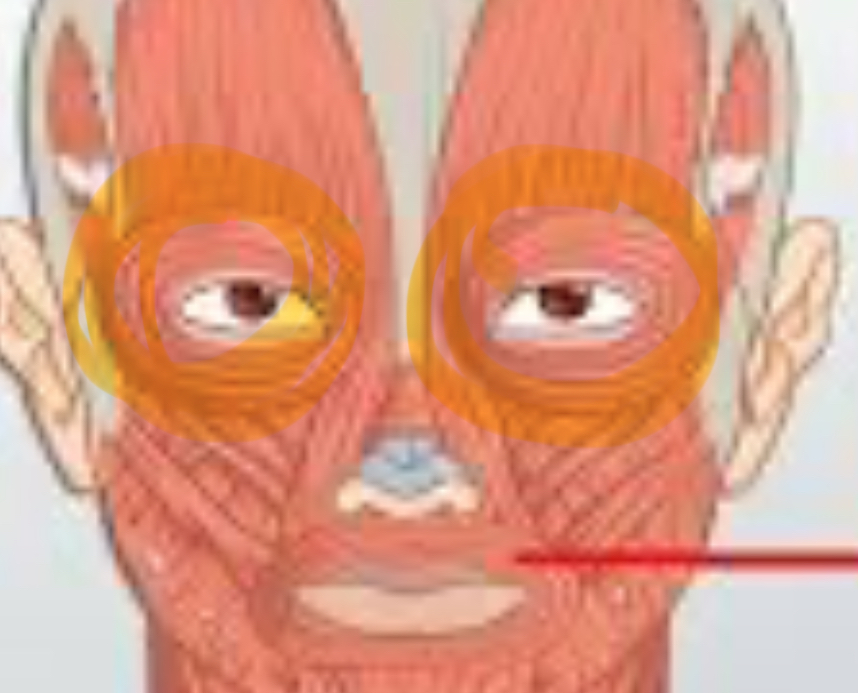
Orbicularis oculi
Action: closes eyes (squint, blink)
Temporalis
Actions: elevate, retract mandible
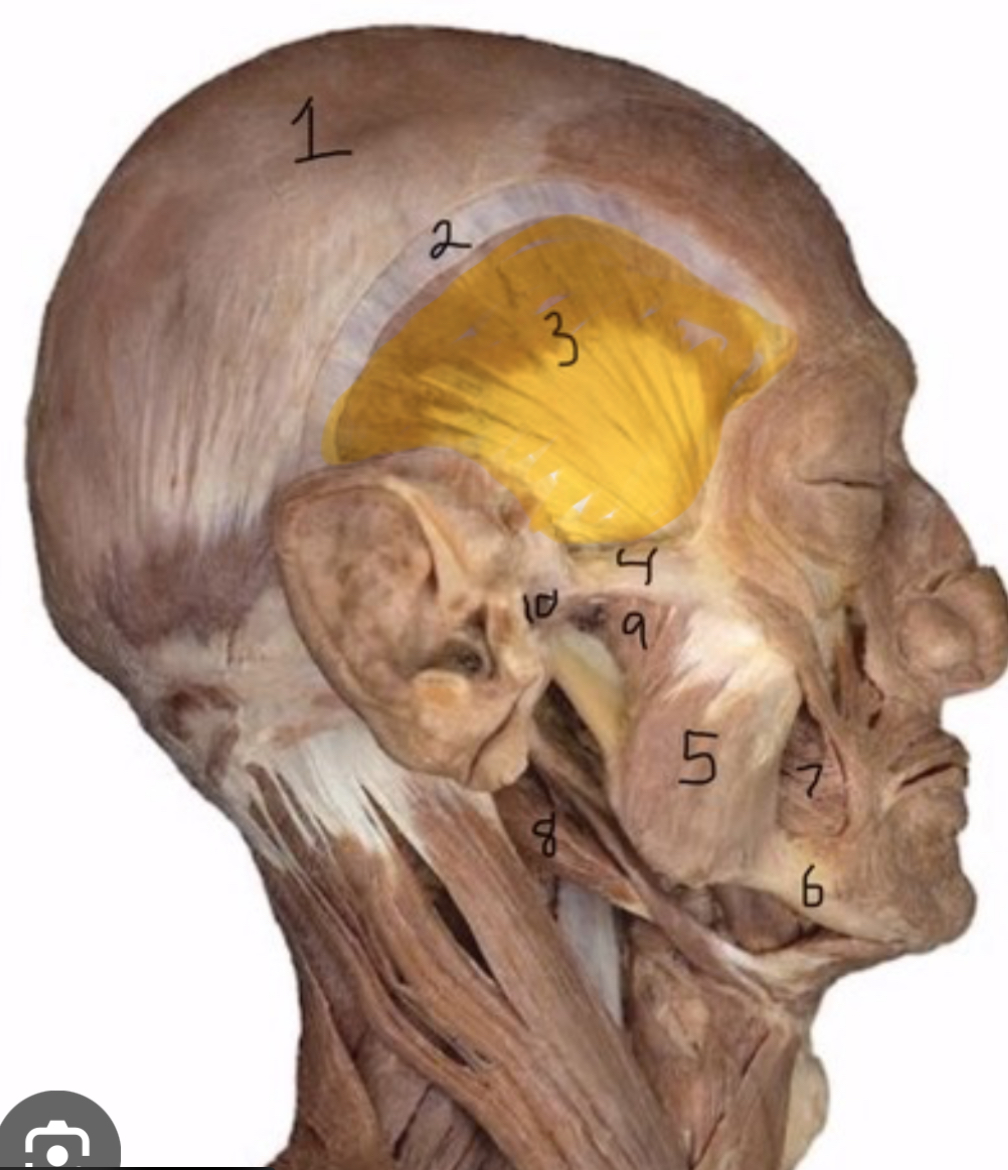
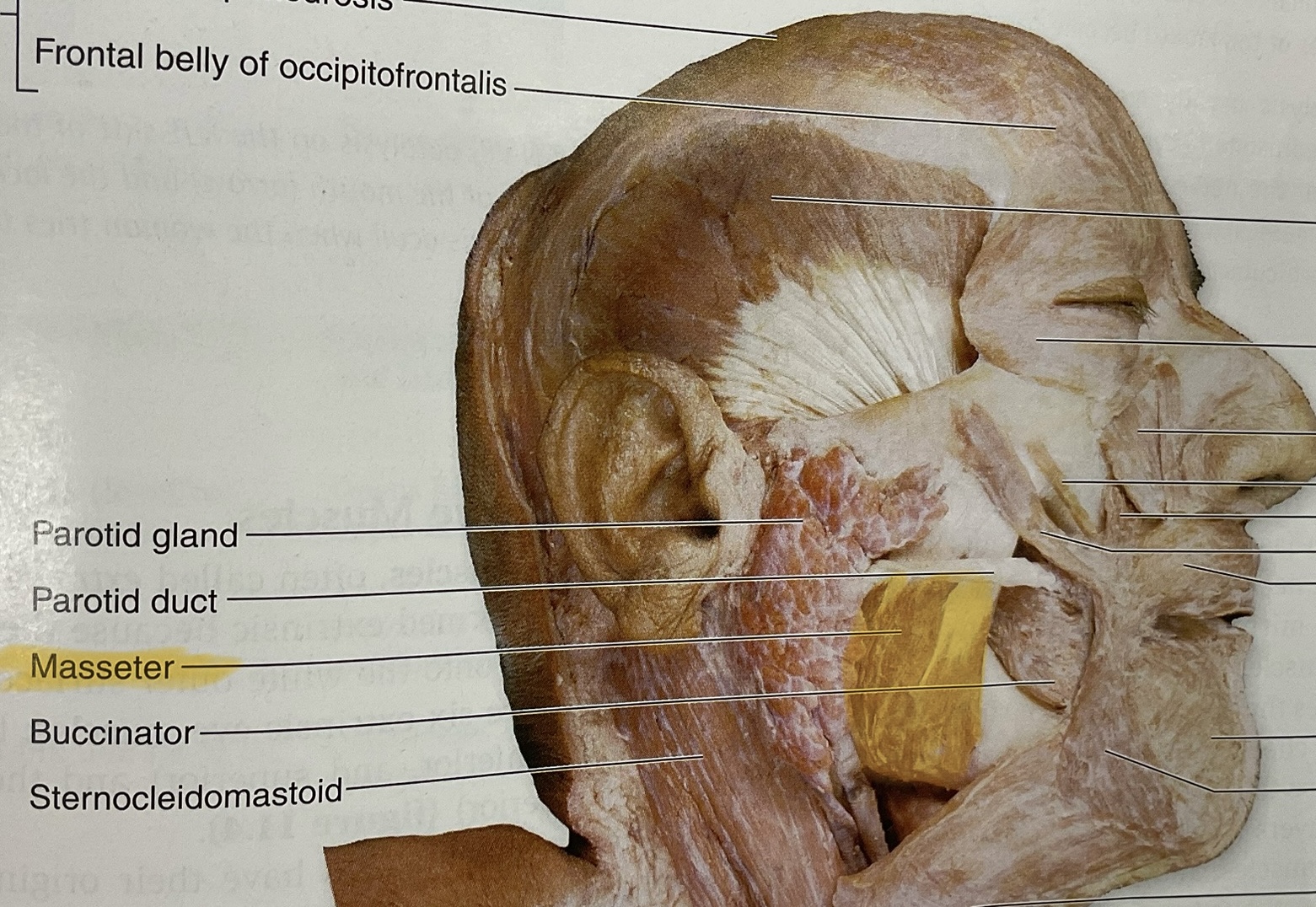
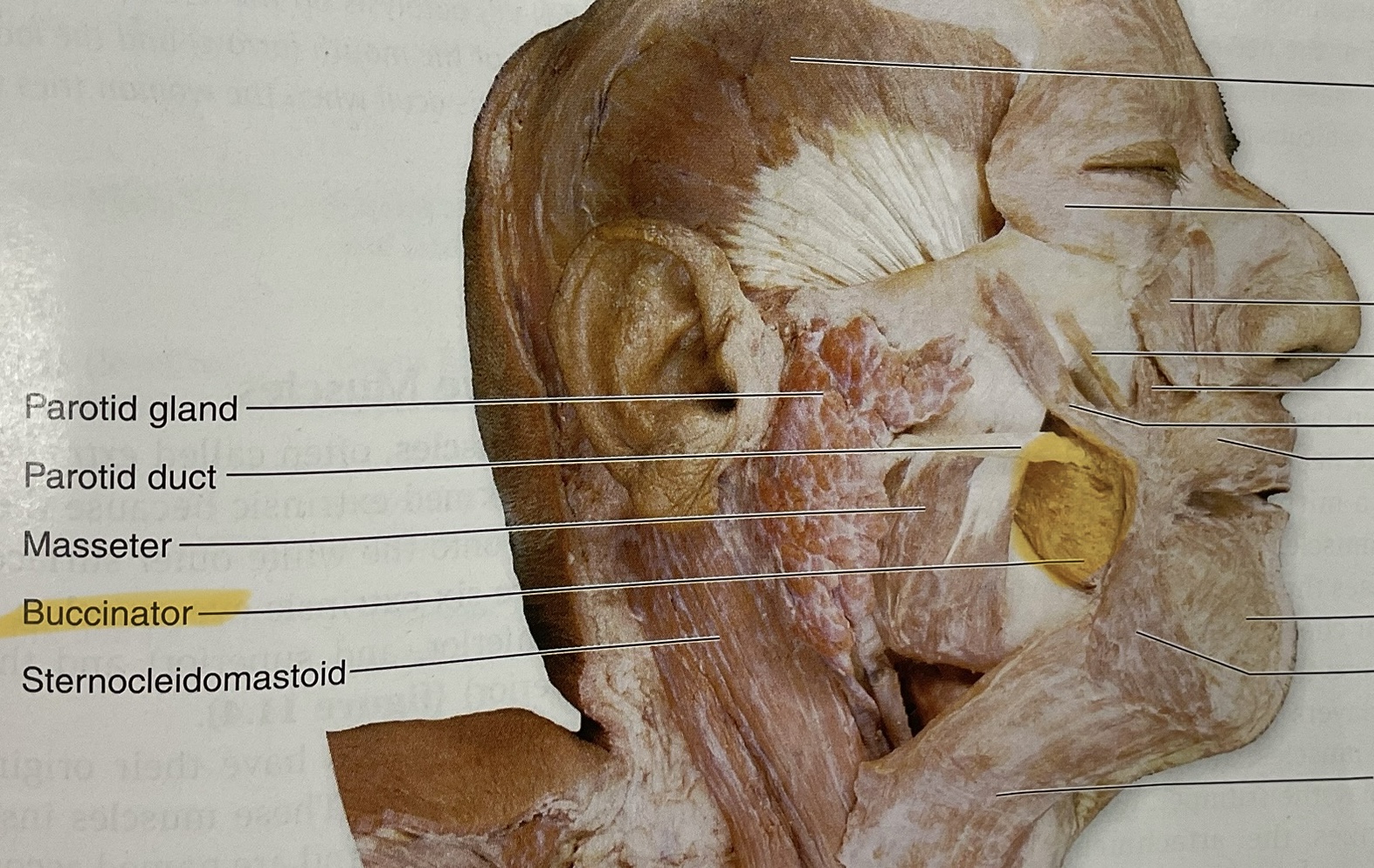
Masseter
Elevate, protract mandible
Frontalis
Action: Elevates eyebrows
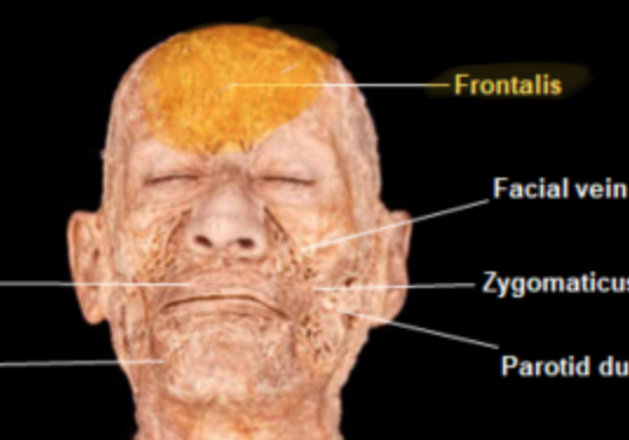
Buccinator
Action: compress cheeks, assist in mastication(keep food between teeth)
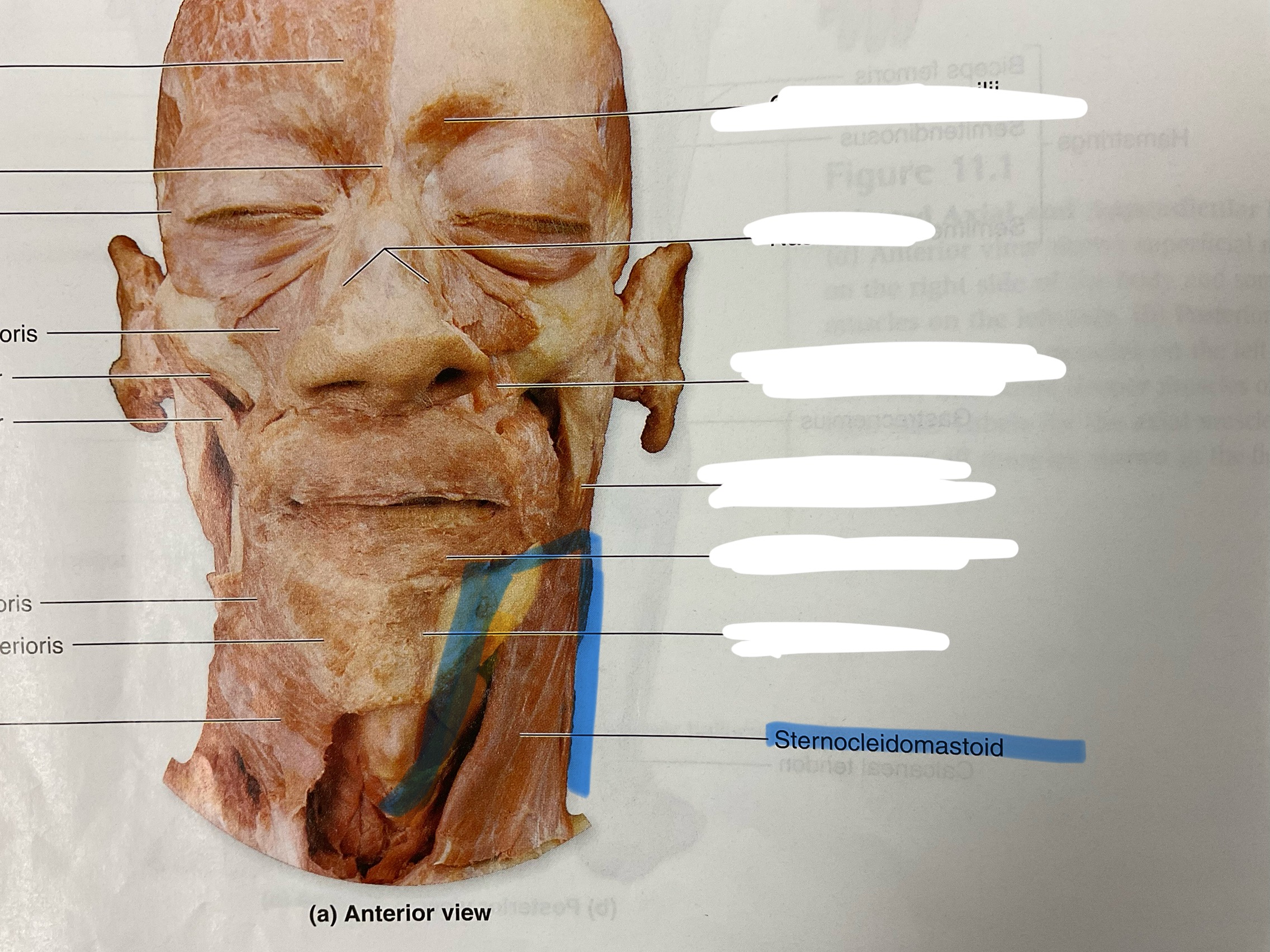
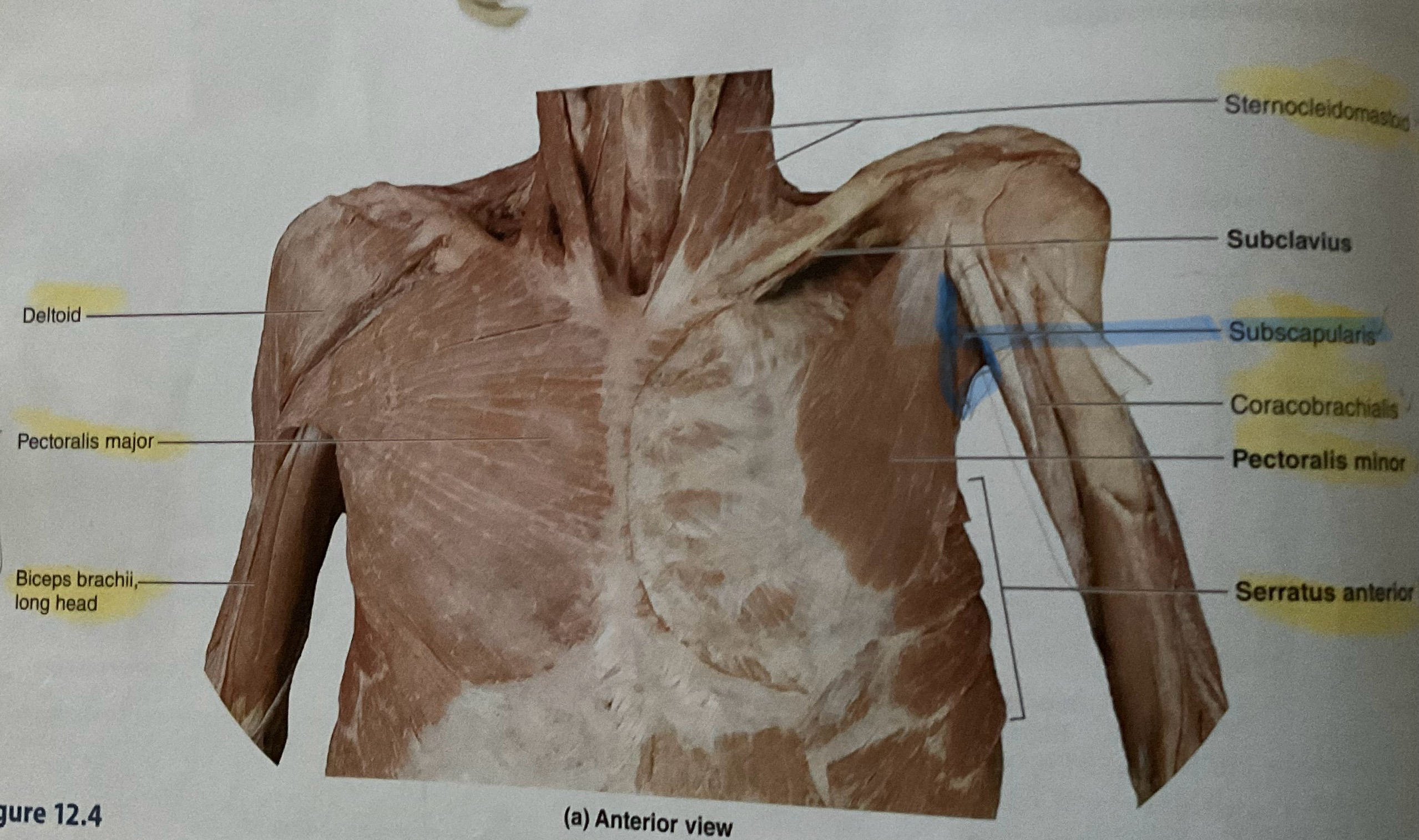
Sternocleidomastoid
Origin: manibrium and sternal end of clavicle
Insertion: Mastoid process
Action: flex neck: rotate head to opposite side
Trapezius
Action: elevates, adduct, stabilizes scapula; extend neck
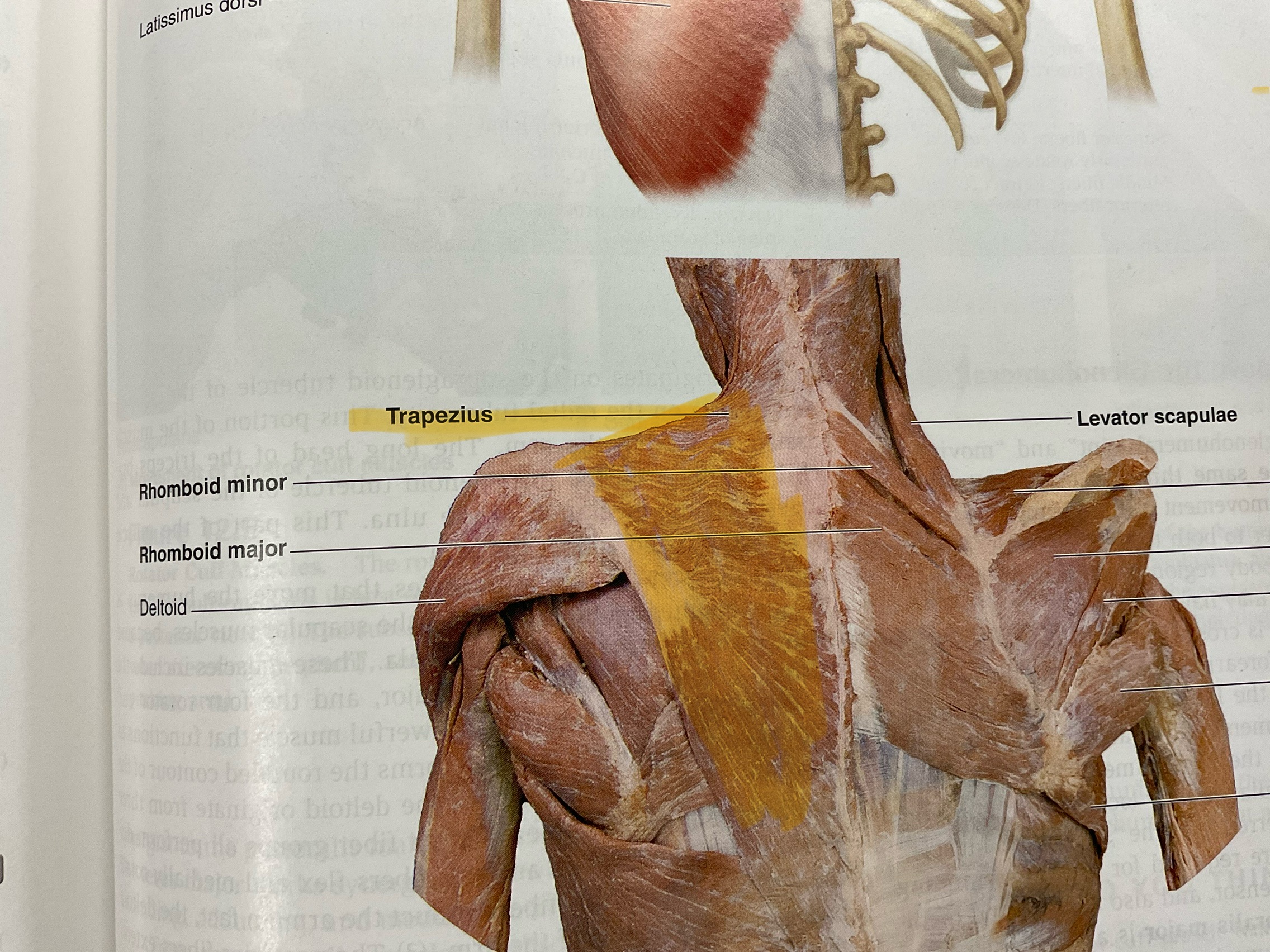
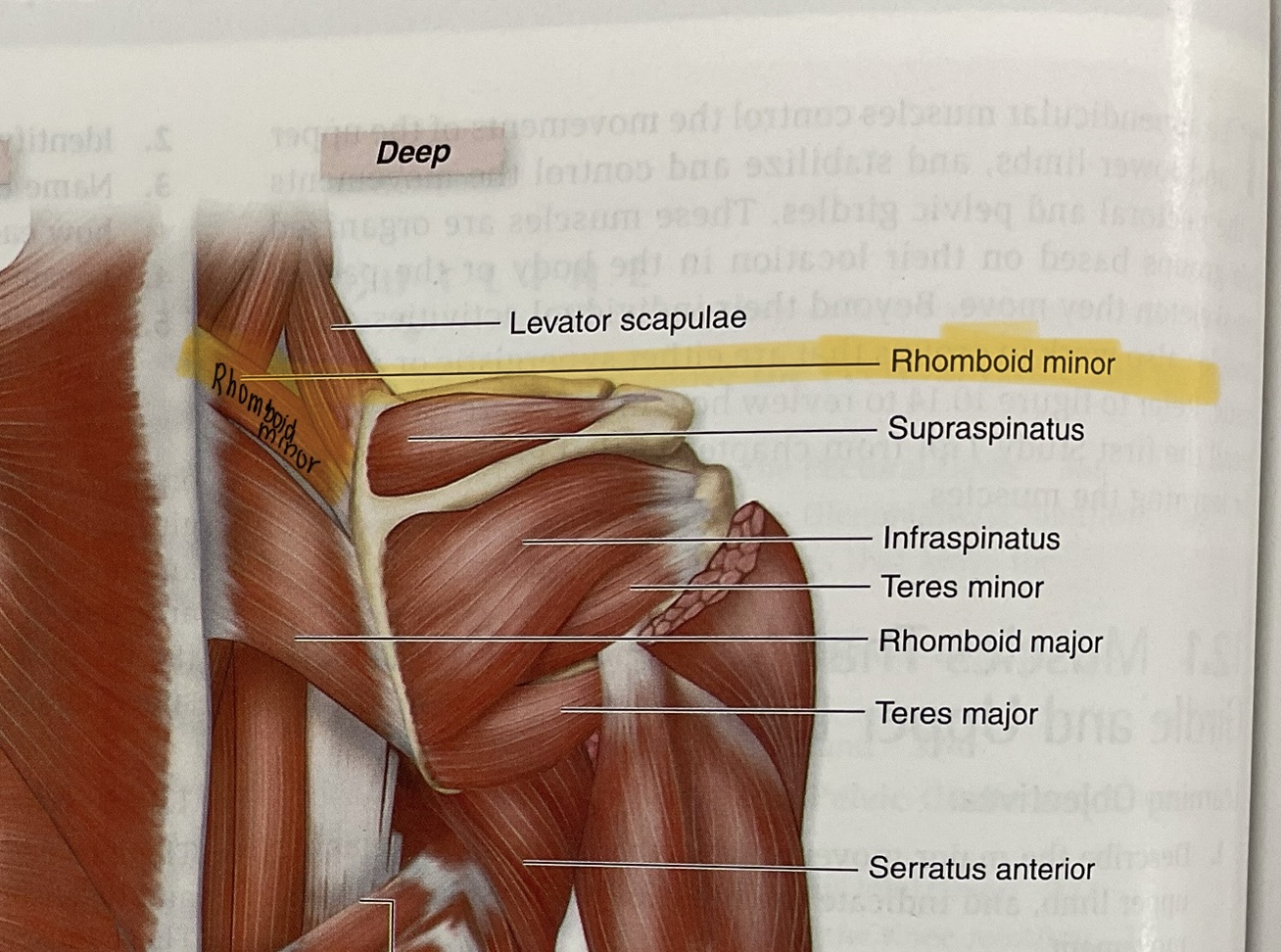
Levator scapulae
Action: elevate scapula
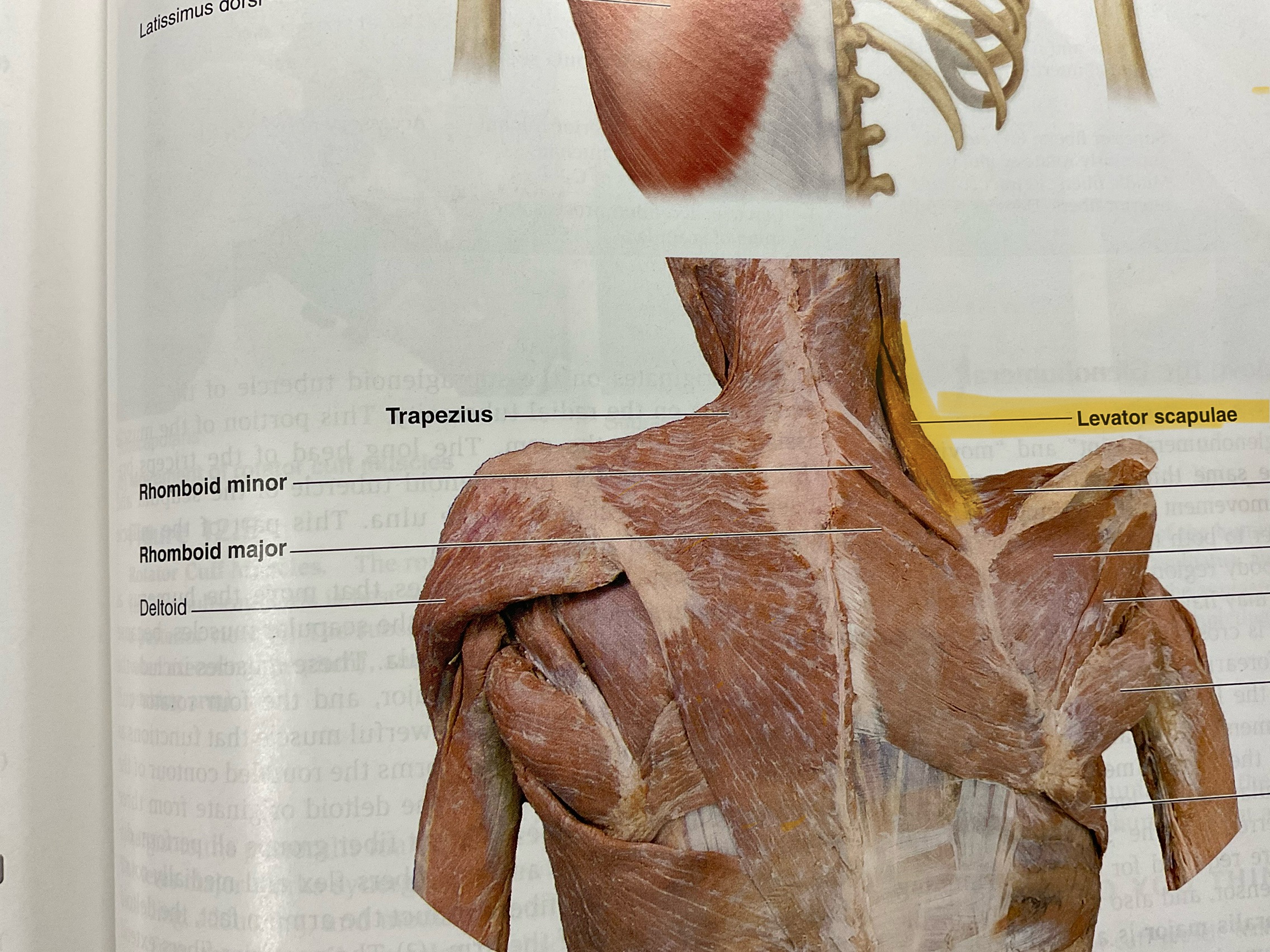
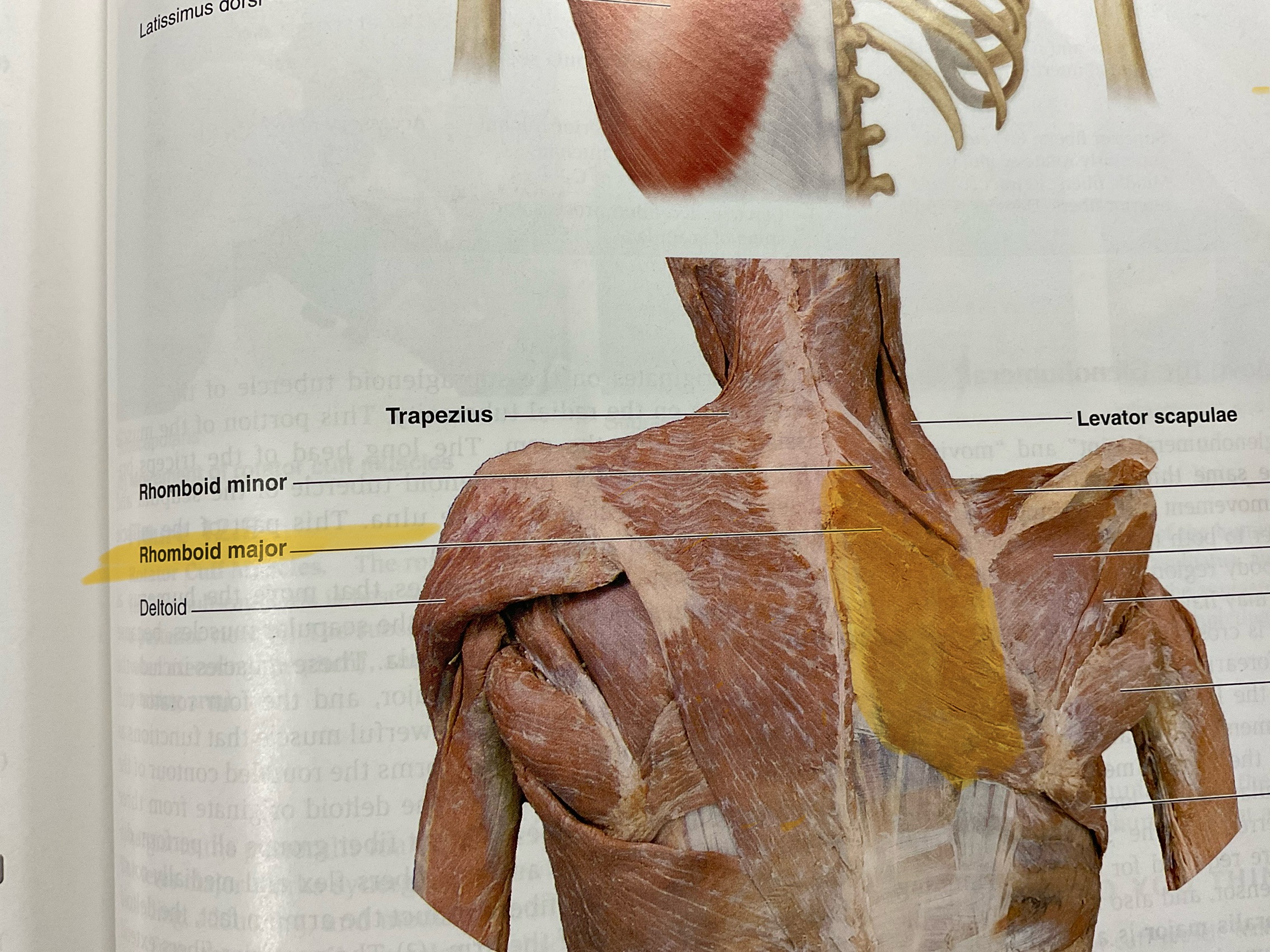
Rhomboid major
Actions: retract, adduct scapula
Rhomboid minor
Actions: retract,adduct scapula
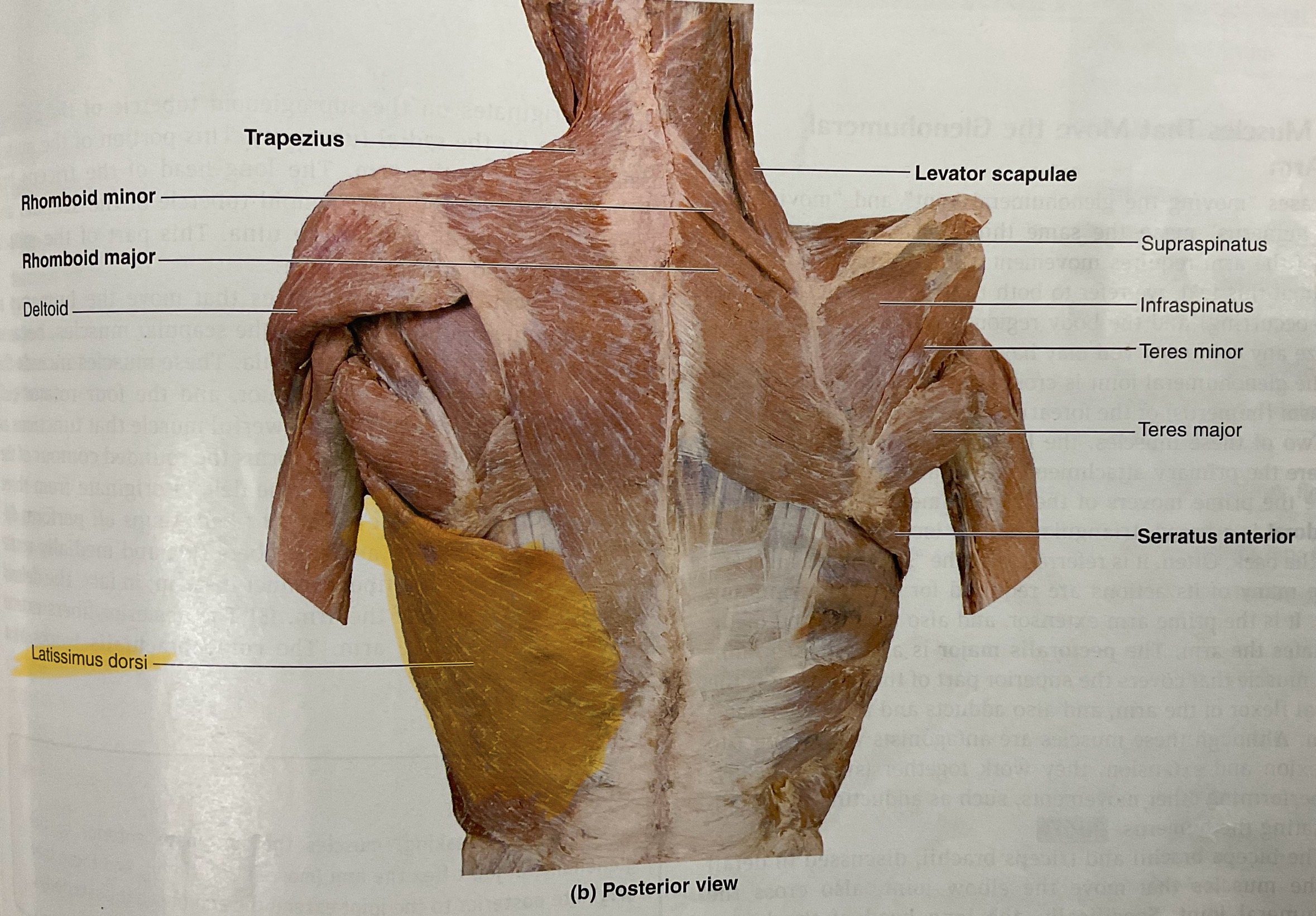
Latissimus Doris (lats)
Action: extend, adduct, medially rotate glenohumeral joint
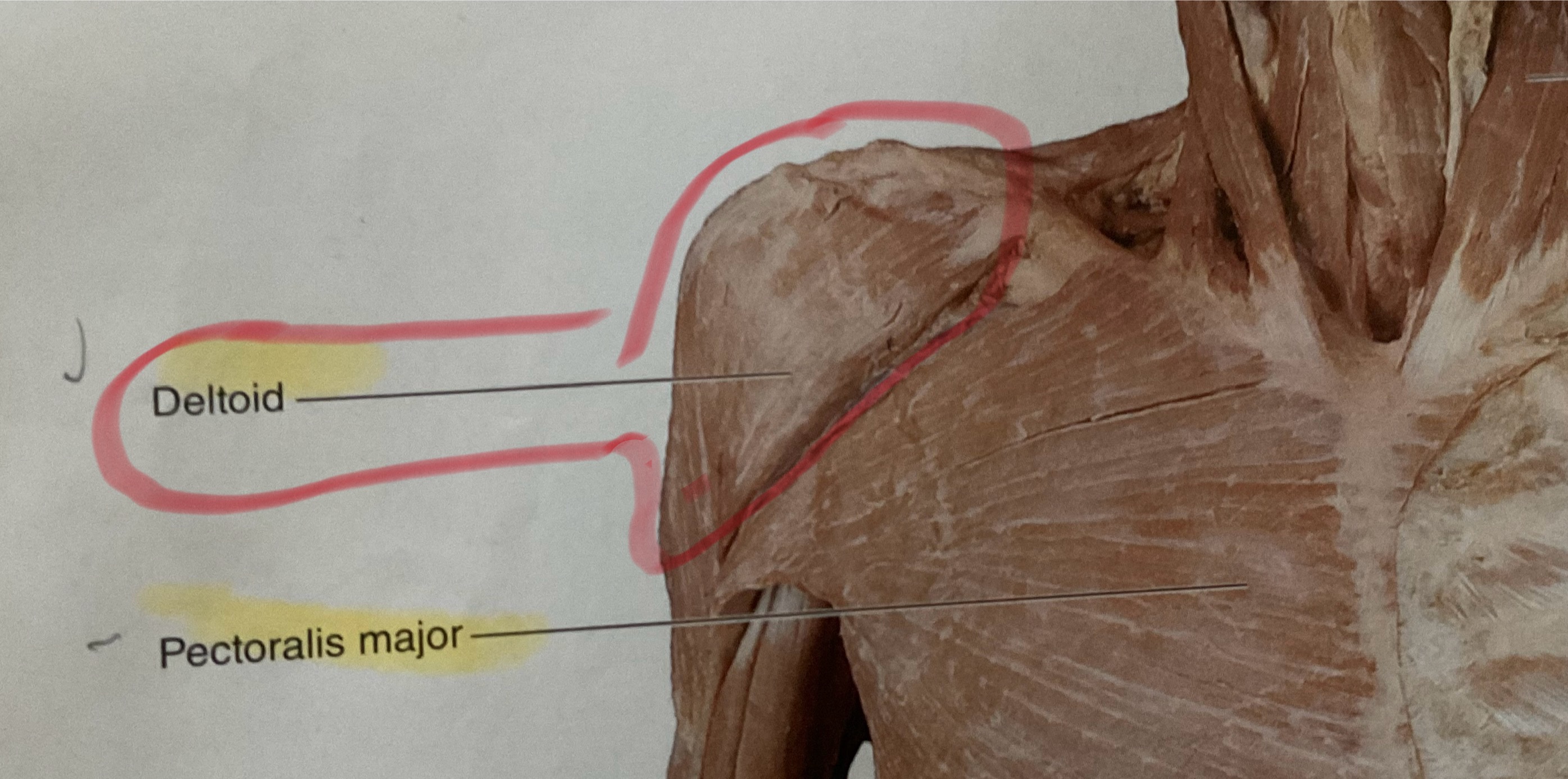
Deltoid
Origin: Clavicle, acromion process and spine of scapula
Insertion: Deltoid tuberosity
Action: Abduct glenohumeral joint
Supraspinatus
Origin: supraspinous fossa
Insertion: superior part of greater tubercle
Action: Abduct glenohumeral joint
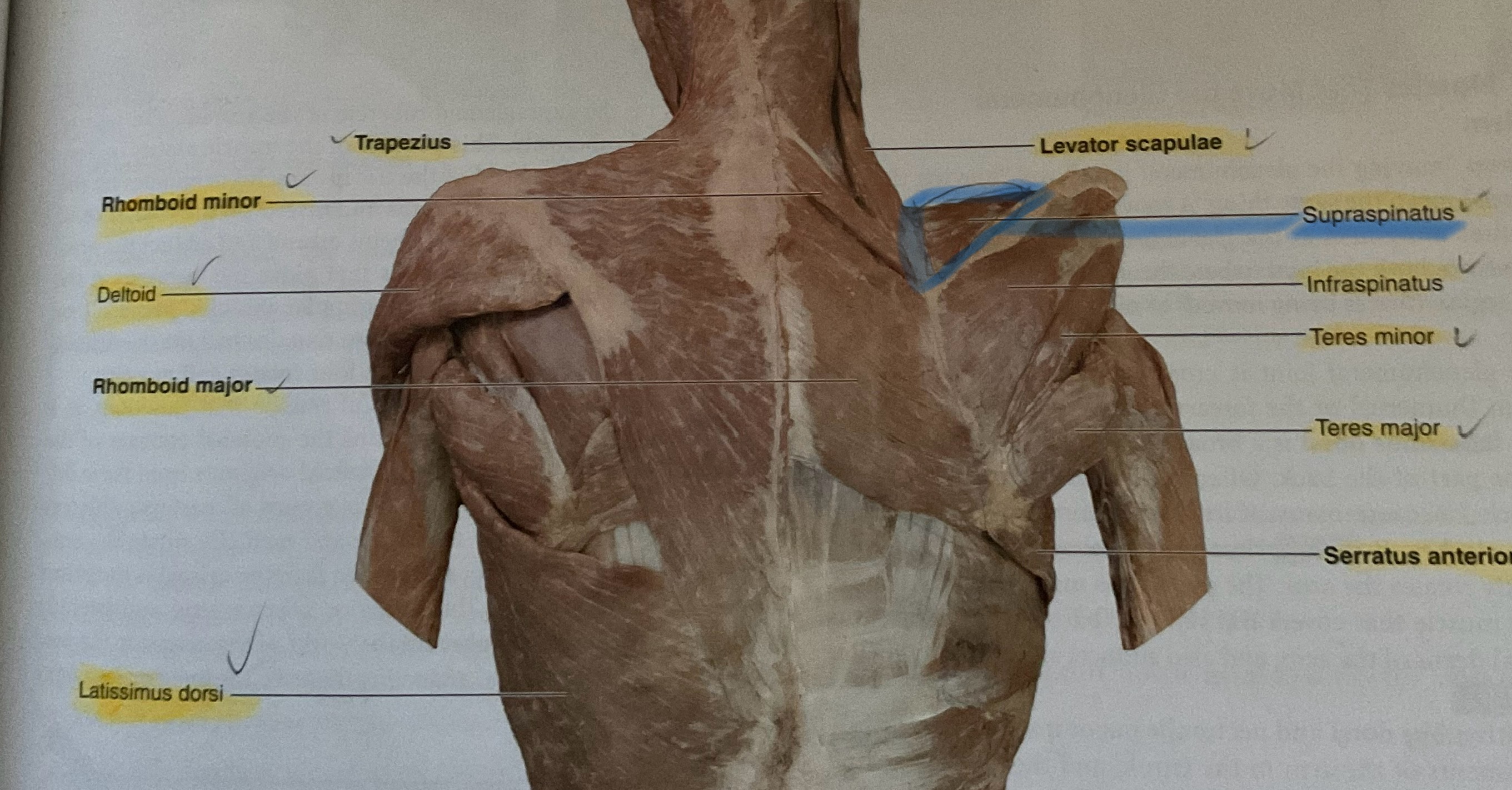
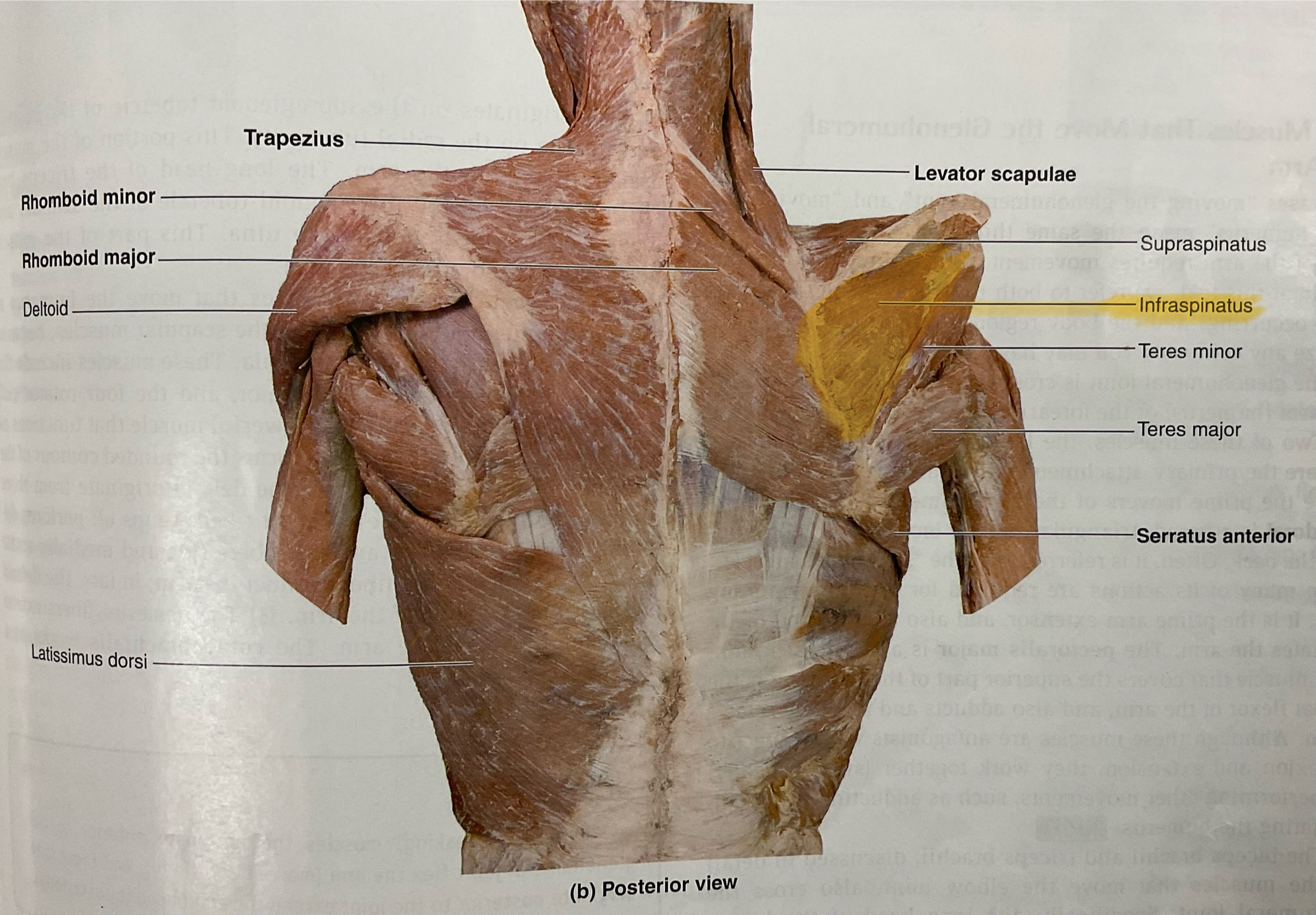
Infraspinatus
Origin: Infraspiousfossa of scapula
Insertion: Middle part of greater tubercle of humerus
Action: Laterally rotates glenohumeral joint
Subscapularis
Origin: Subscapular fossa of scapula
Insertion: Lesser tubercle of humerus
Action: Medially rotates glenohumeral joint
Teres Minor
Origin: Lateral border of scapula
Insertion: Inferior part of greater tubercle of humerus
Action: Laterally rotates glenohumeral joint
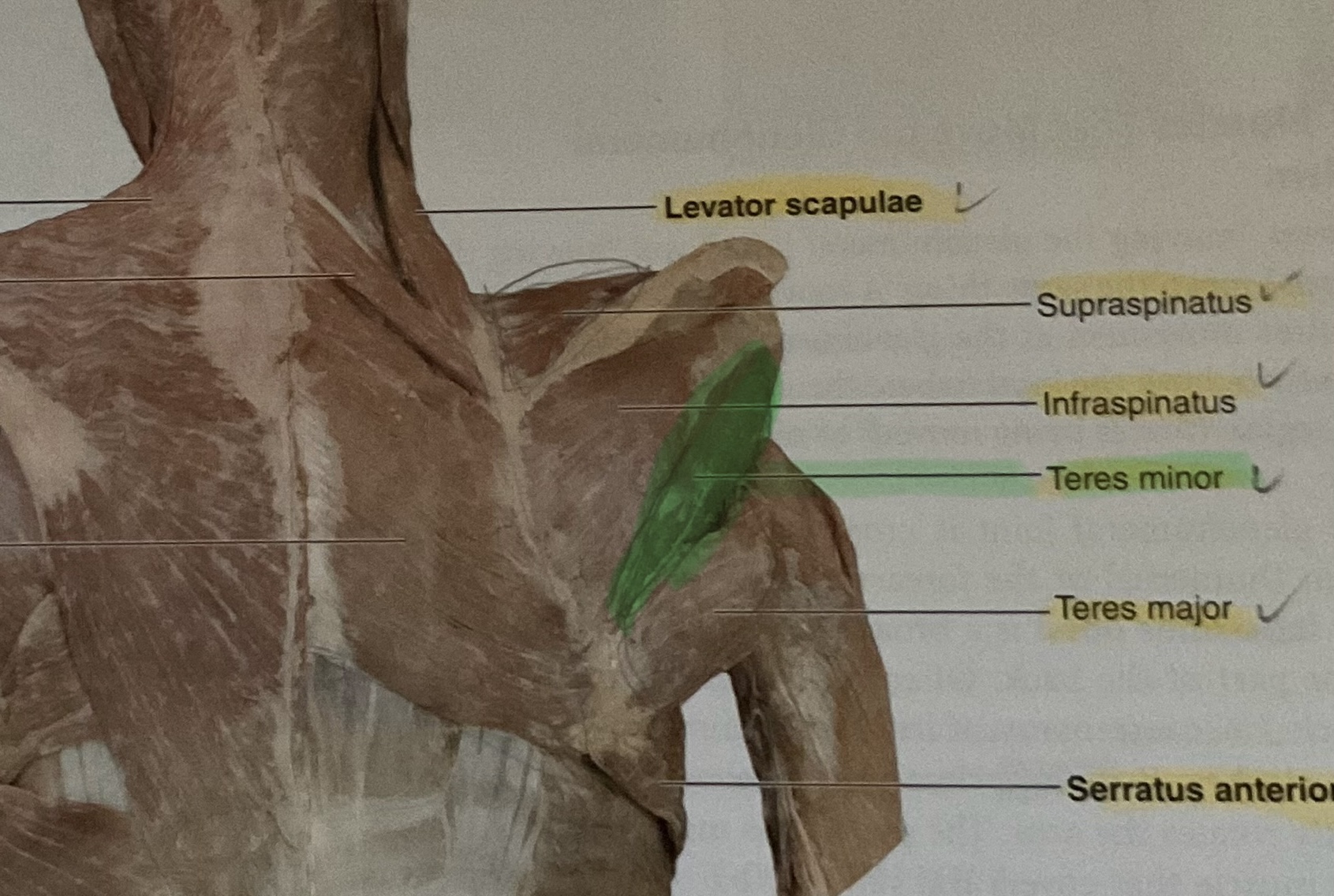
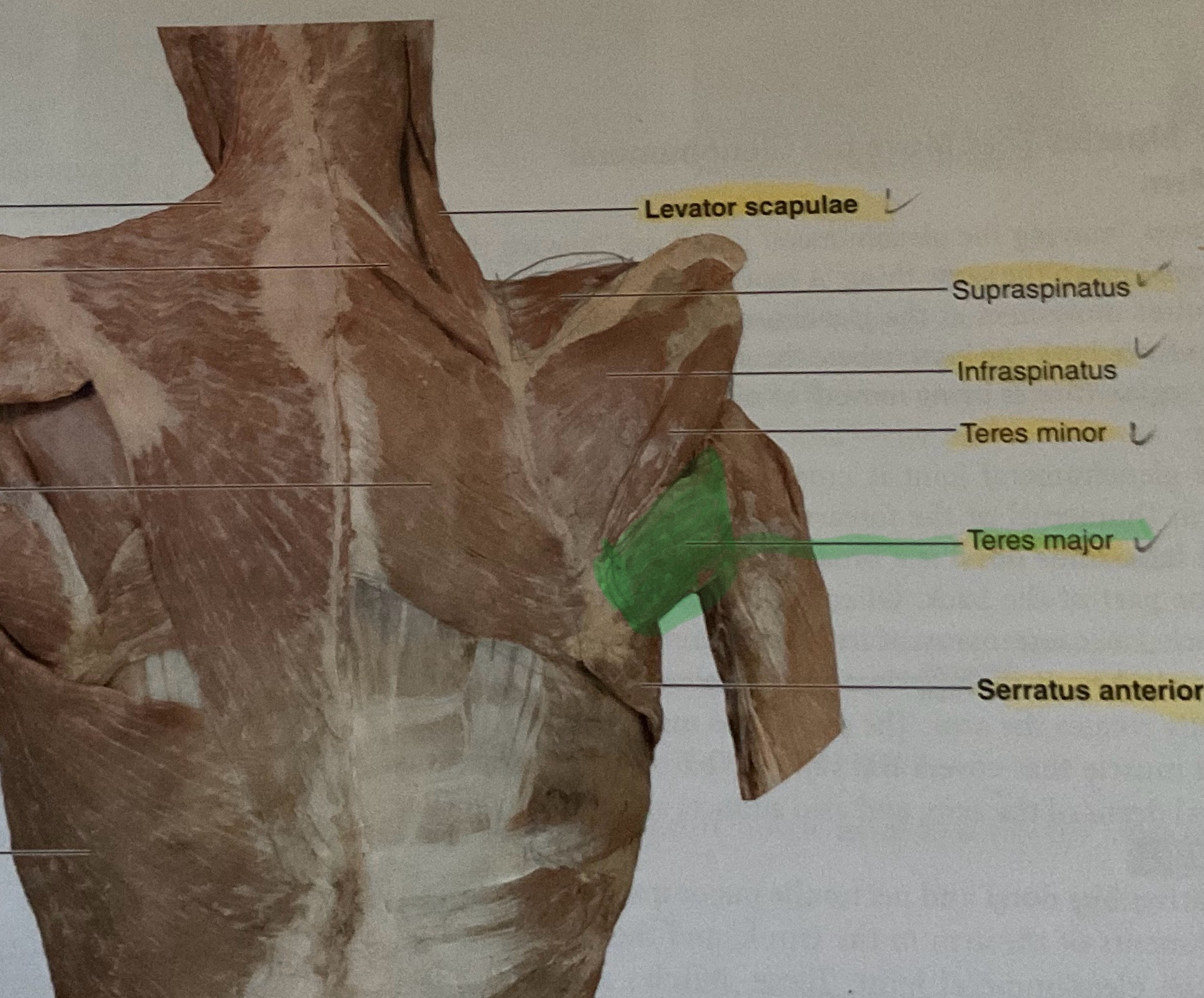
Teres Major
Origin: Inferior angle of scapula
Insertion: distal of lesser tubercle of humerus
Action: Extend, adduct, medially rotates glenohumeral joint
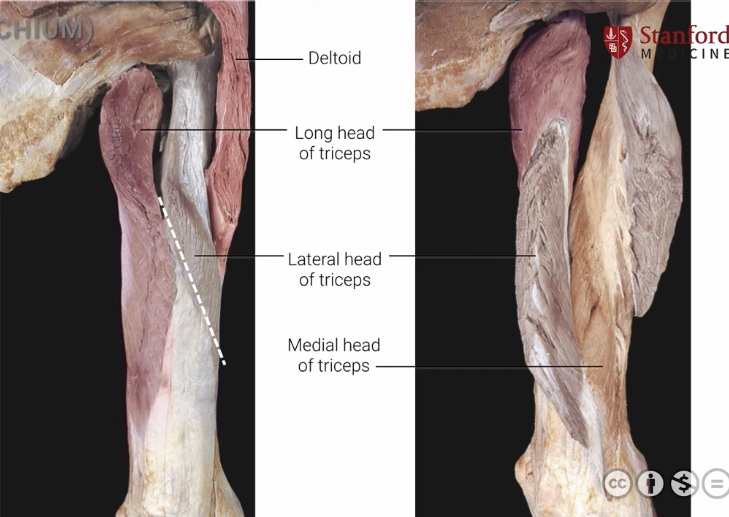
Triceps Brachii( Long head, lateral, medial)
Origin: Infraglenoid tubercle (long head), Lateral and posterior diaphysis of humerus(Lateral head) posterior diaphysis of humerous (medial head)
Insertion: Olecranon process of ulna
Action: Extends elbow and shoulder, assists in adduction.
Pectoralis Major
Action: Flex, adduct, medially rotate glenohumeral joint
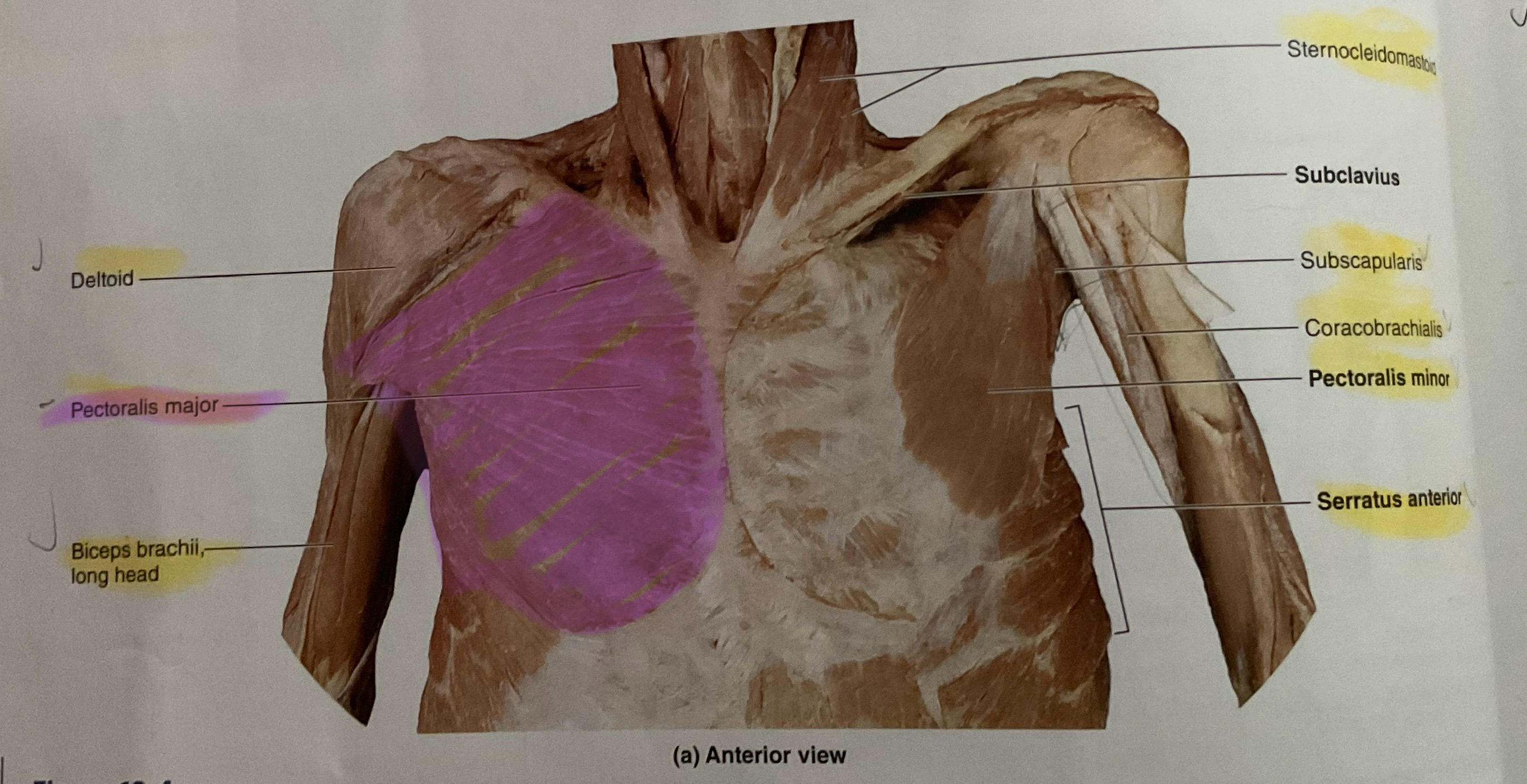
Pectoralis Minor
Action: Depress scapula
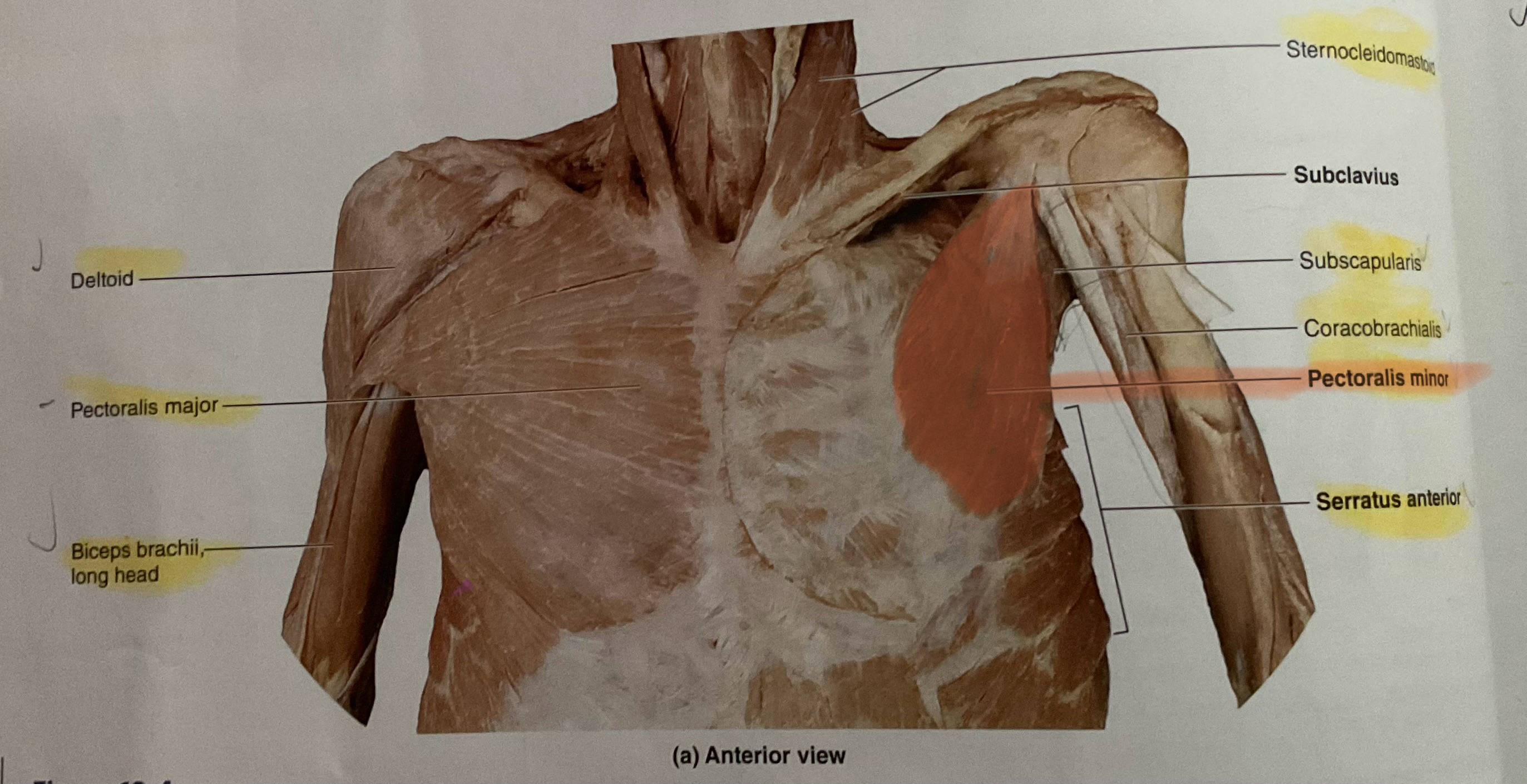
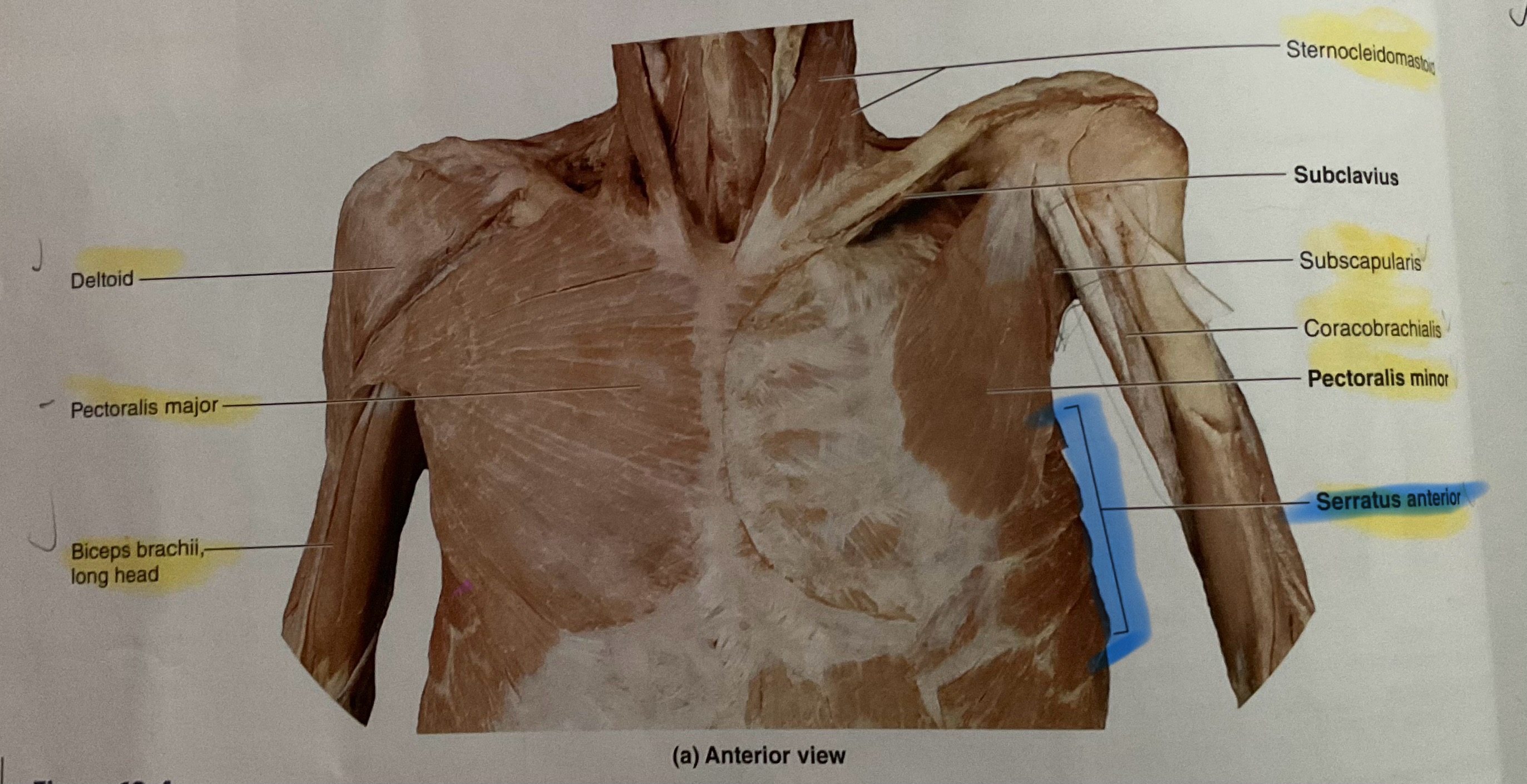
Serratus Anterior
Action: Abduct, protract scapula
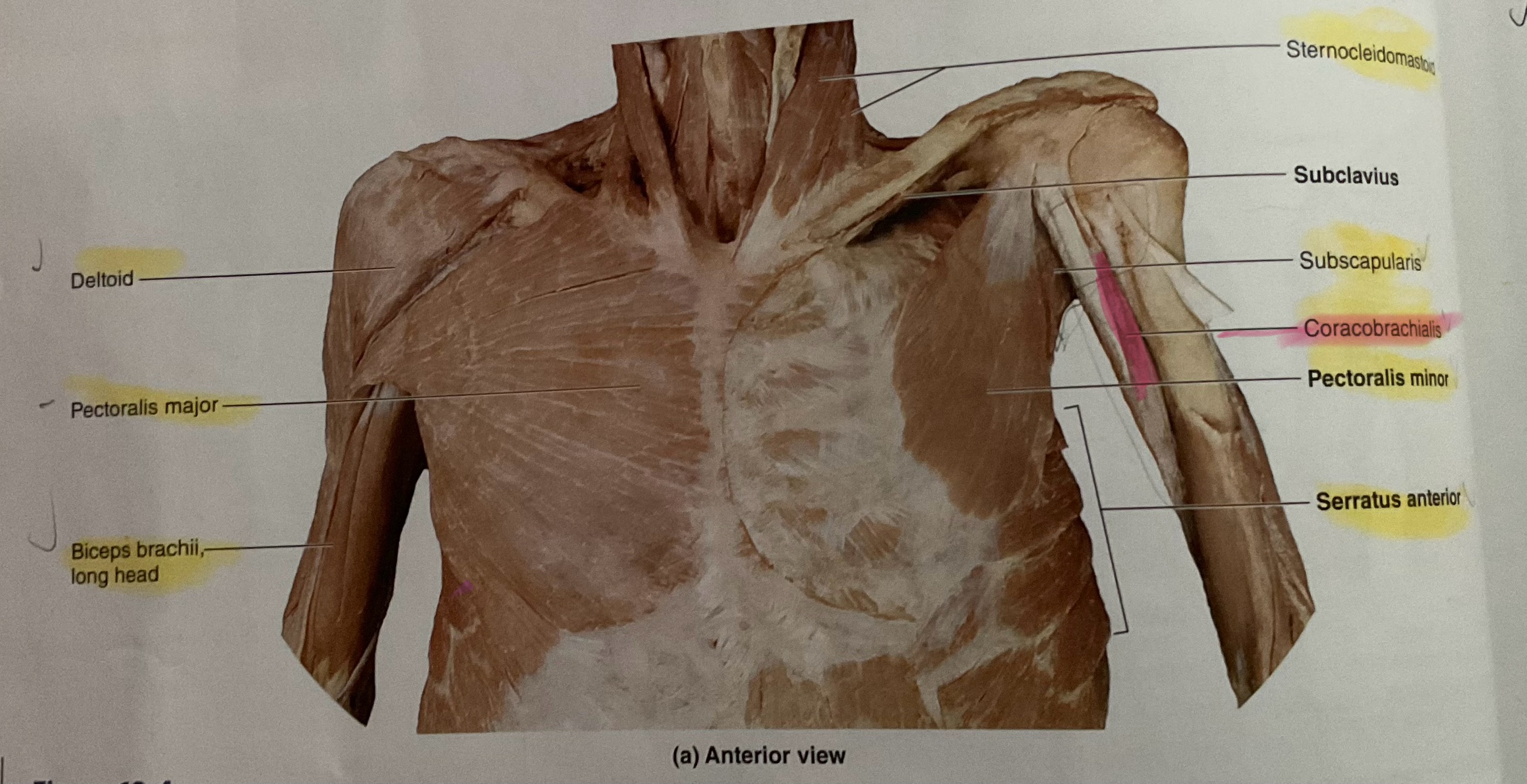
Coracobrachialis
Origin Coracoid process
Instertion: Medial diaphysis of humerus
Action: Flex, adduct glenohumeral joint
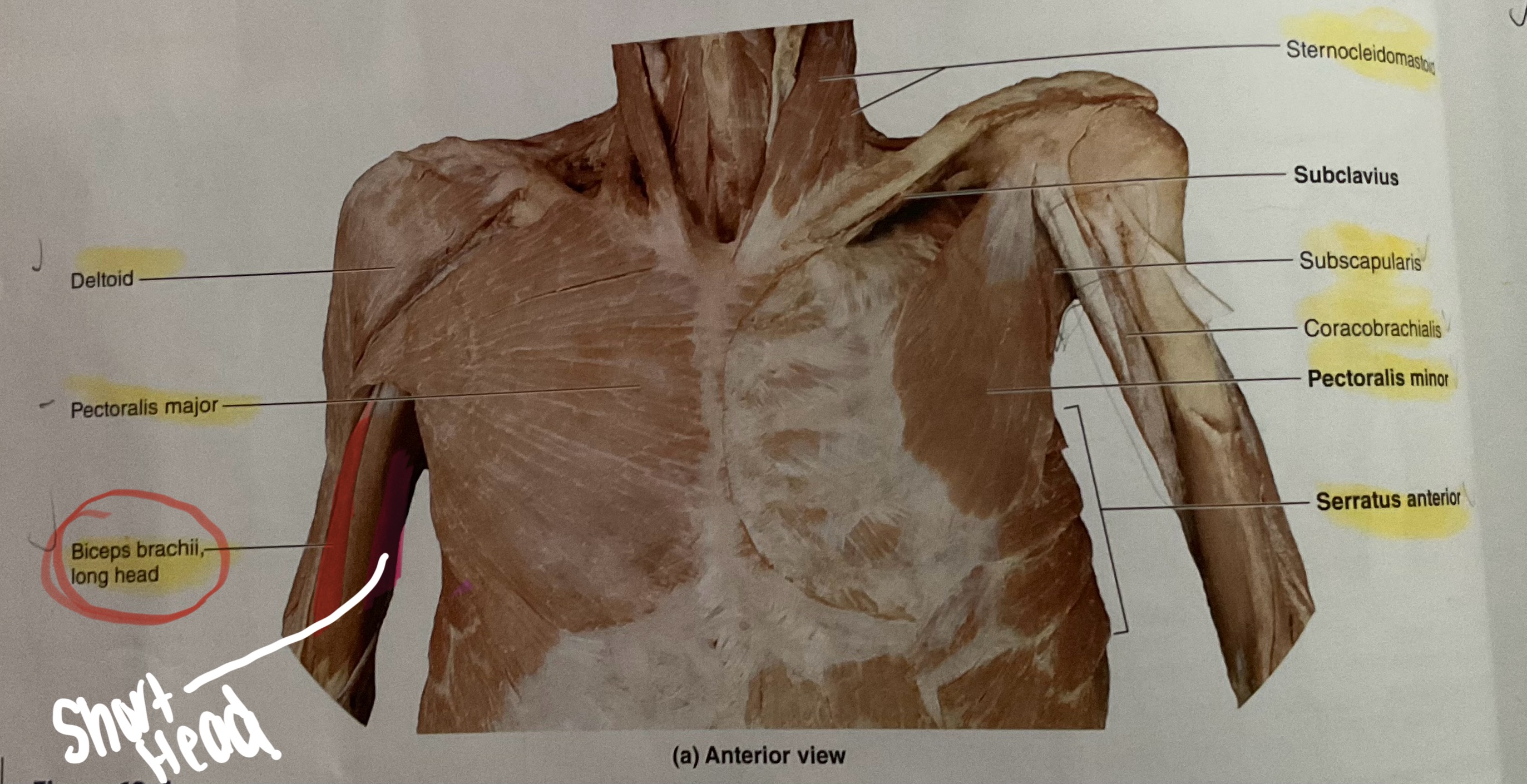
Biceps Brachii
Origin: Long head- supraglenoid tubercle; Short head- Coracoid process
Insertion: Radial tuberosity
Action Flex elbow; supinate radius
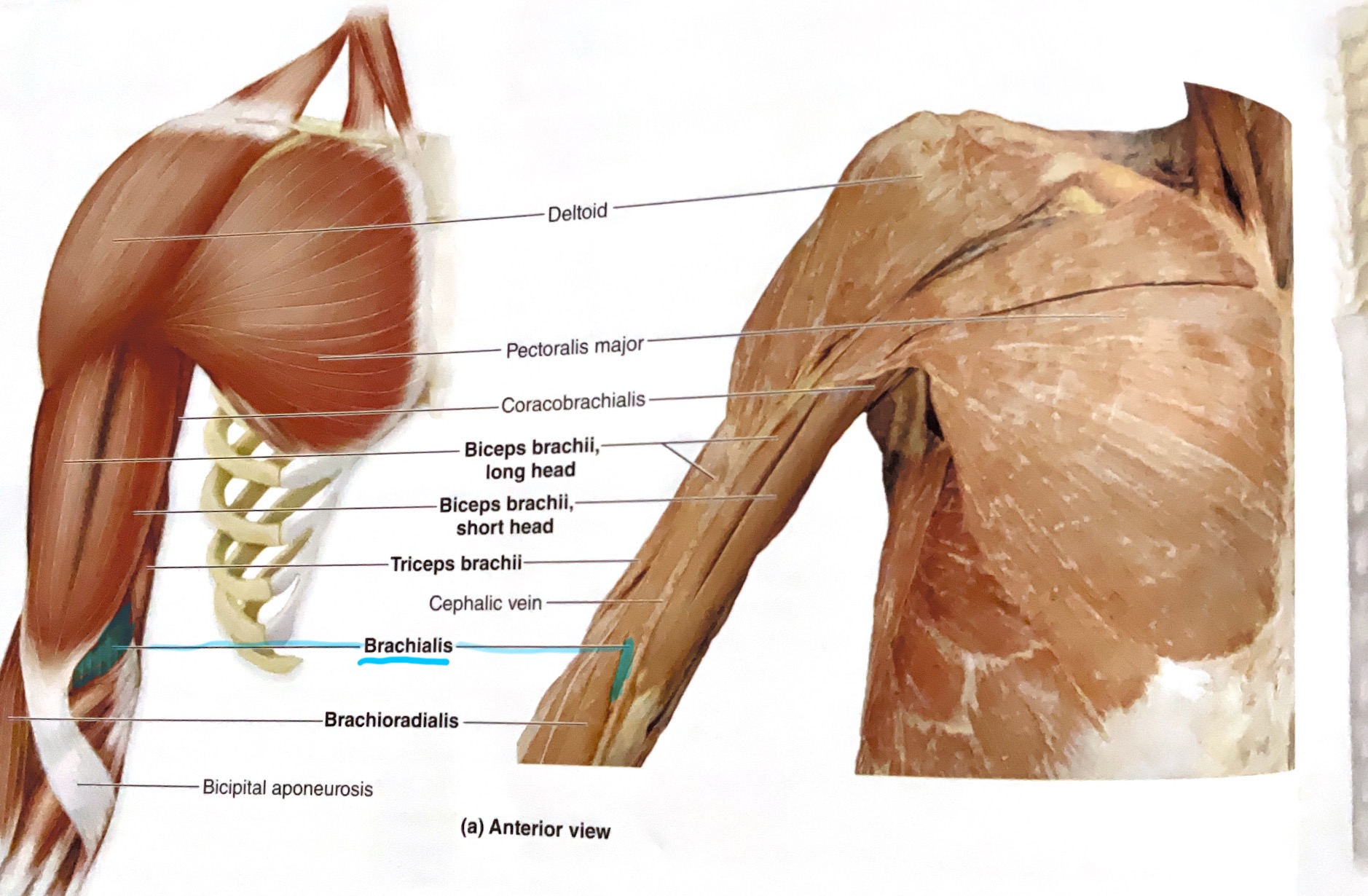
Brachialis
Origin: Anterior diaphysis of humerus
Insertion: Ulnar tuberosity and coronoid process of ulna
Action: Flex elbow
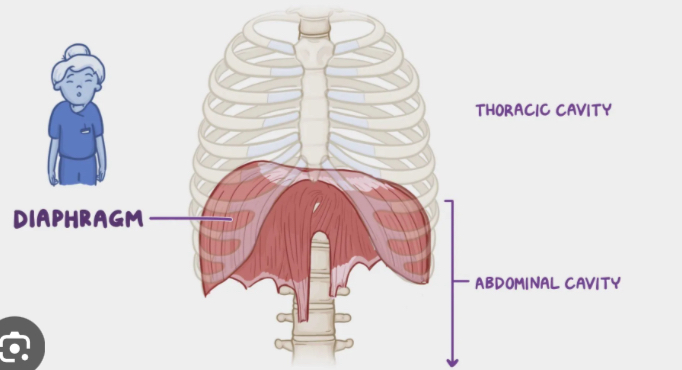
Diaphragm
Action:inhalation
Dome-shaped, broad muscle: separates thoracic & abdominalpelvic cavities
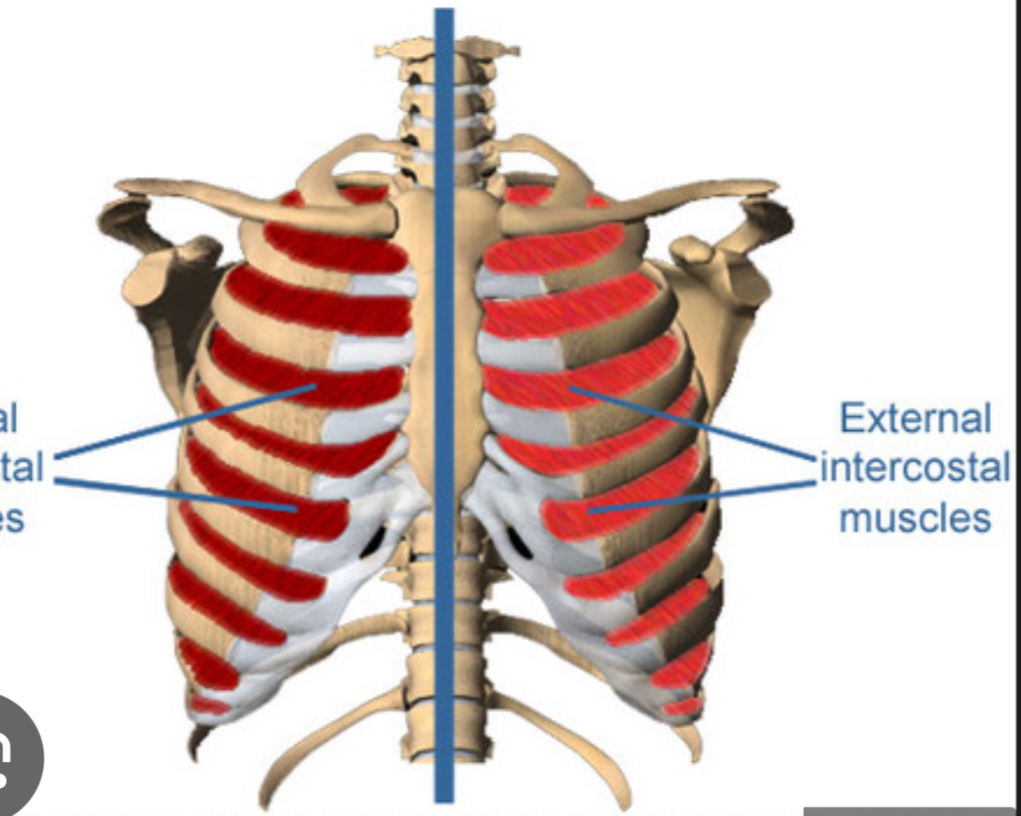
External Intercostals (hint : pockets down)
Elevate ribs during inhalation
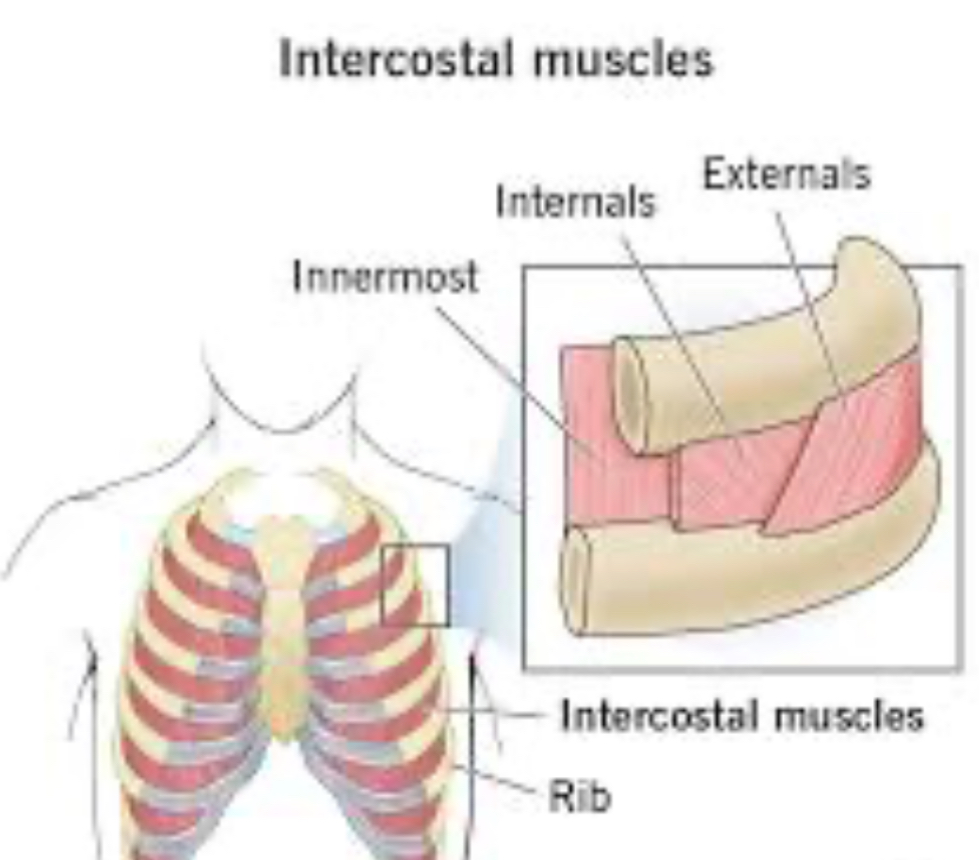
Internal Intercostals(up)
depress ribs during forced inhalation
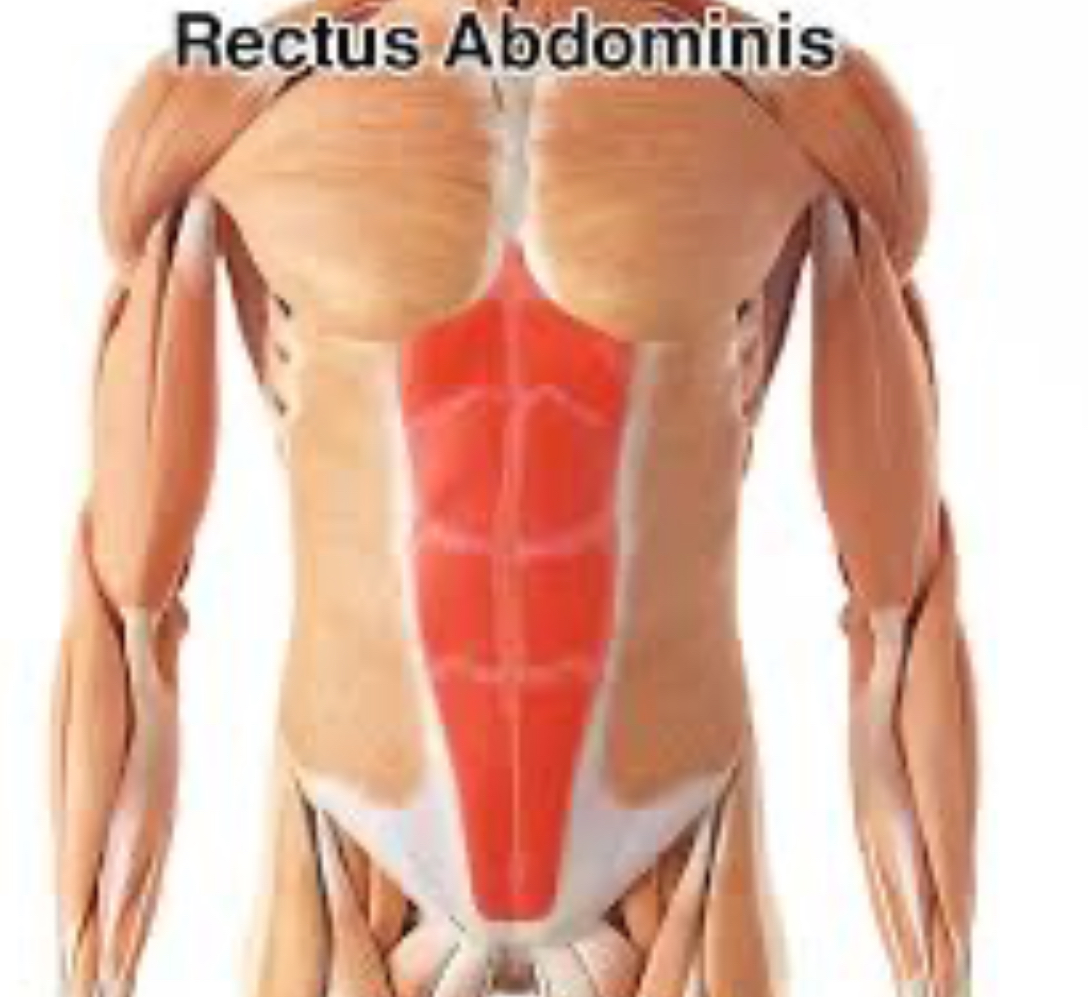
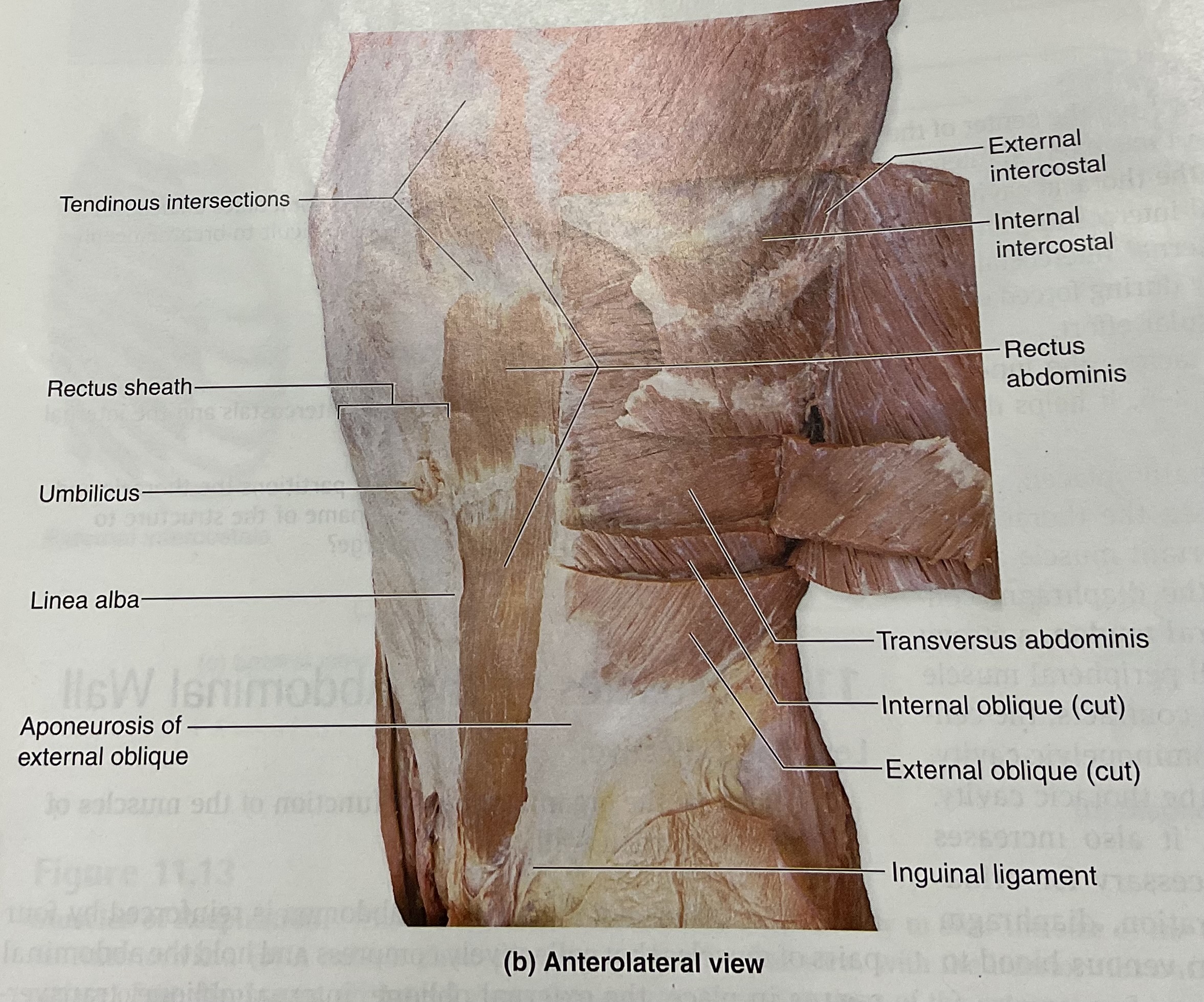
Rectus Abdominis
flex vertebral column; compress abdomen
External obliques
flex, laterally flex, rotate vertebral column; compress abdomen
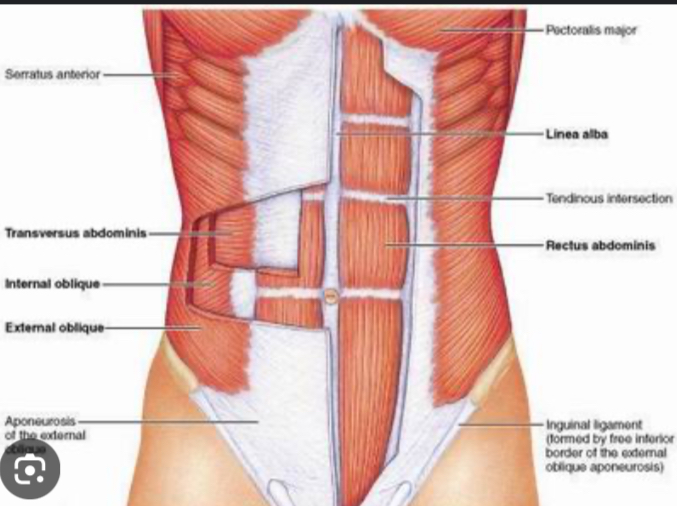
Internal obliques(same action as external obliques)
Action: flex, laterally flex, rotate vertebral column; compress abdomen
Deep to external obliques and superficial to transverse abdominis
Transverse Abdominis
Action:Compress abdomen Deep
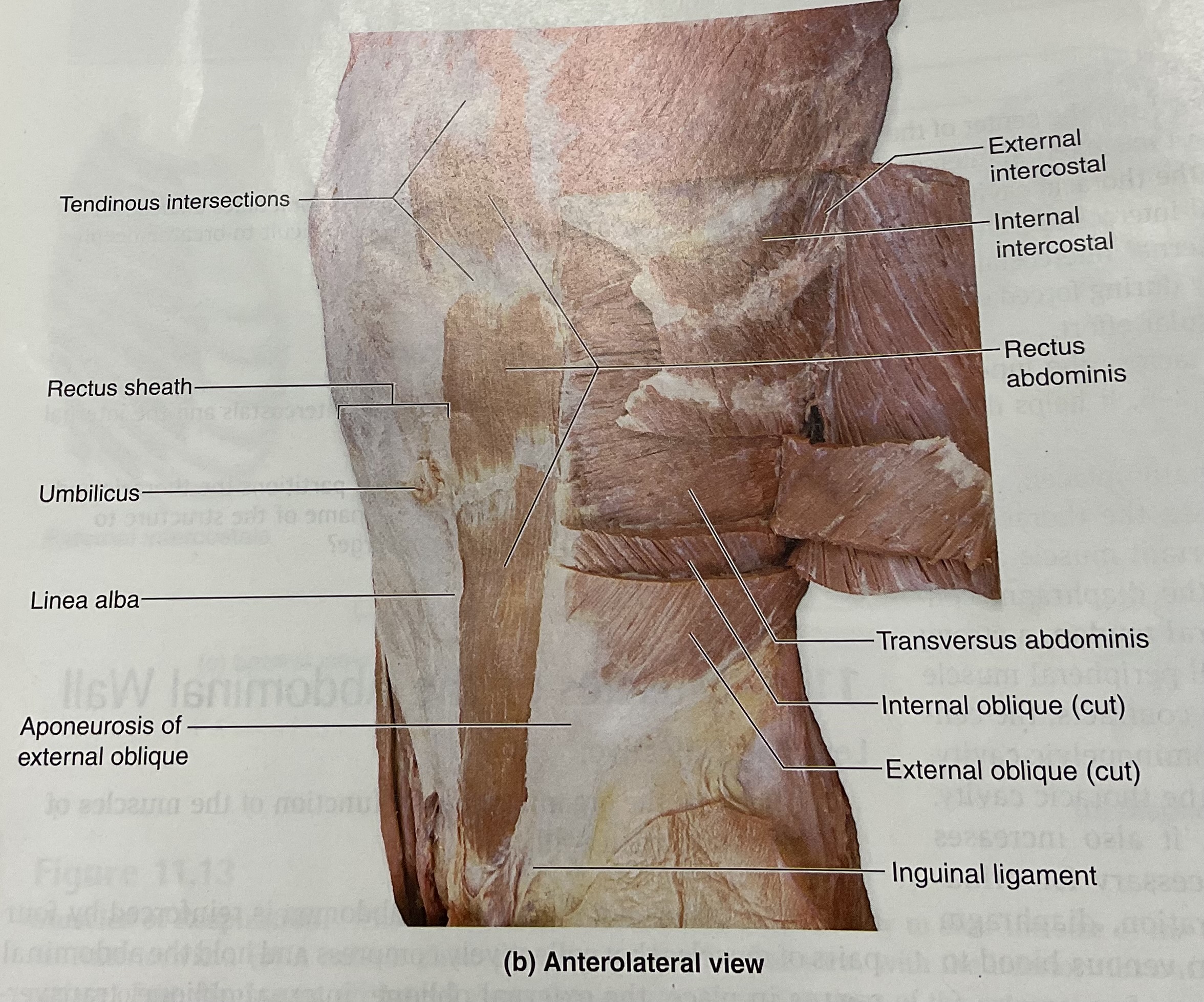
Inguinal ligament
set of two narrow bands in the inguinal area of the body(the groin) connects the oblique muscles in abdomen to the pelvis
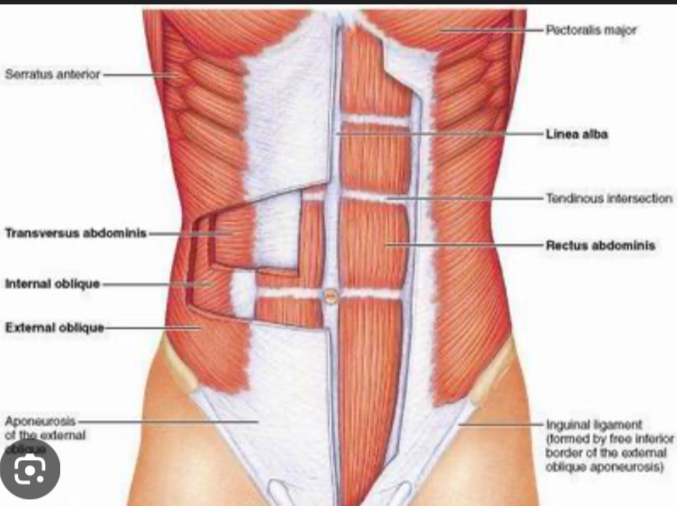
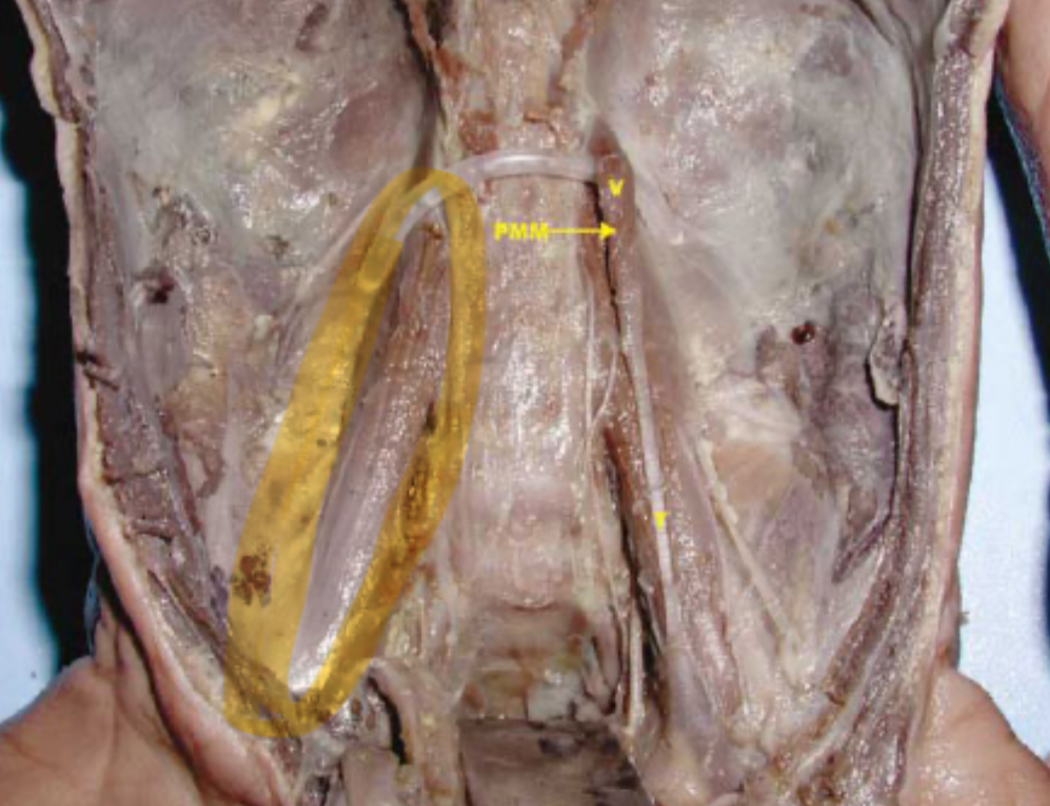
Psoas Major
Action: flex vertebral column; flex hip
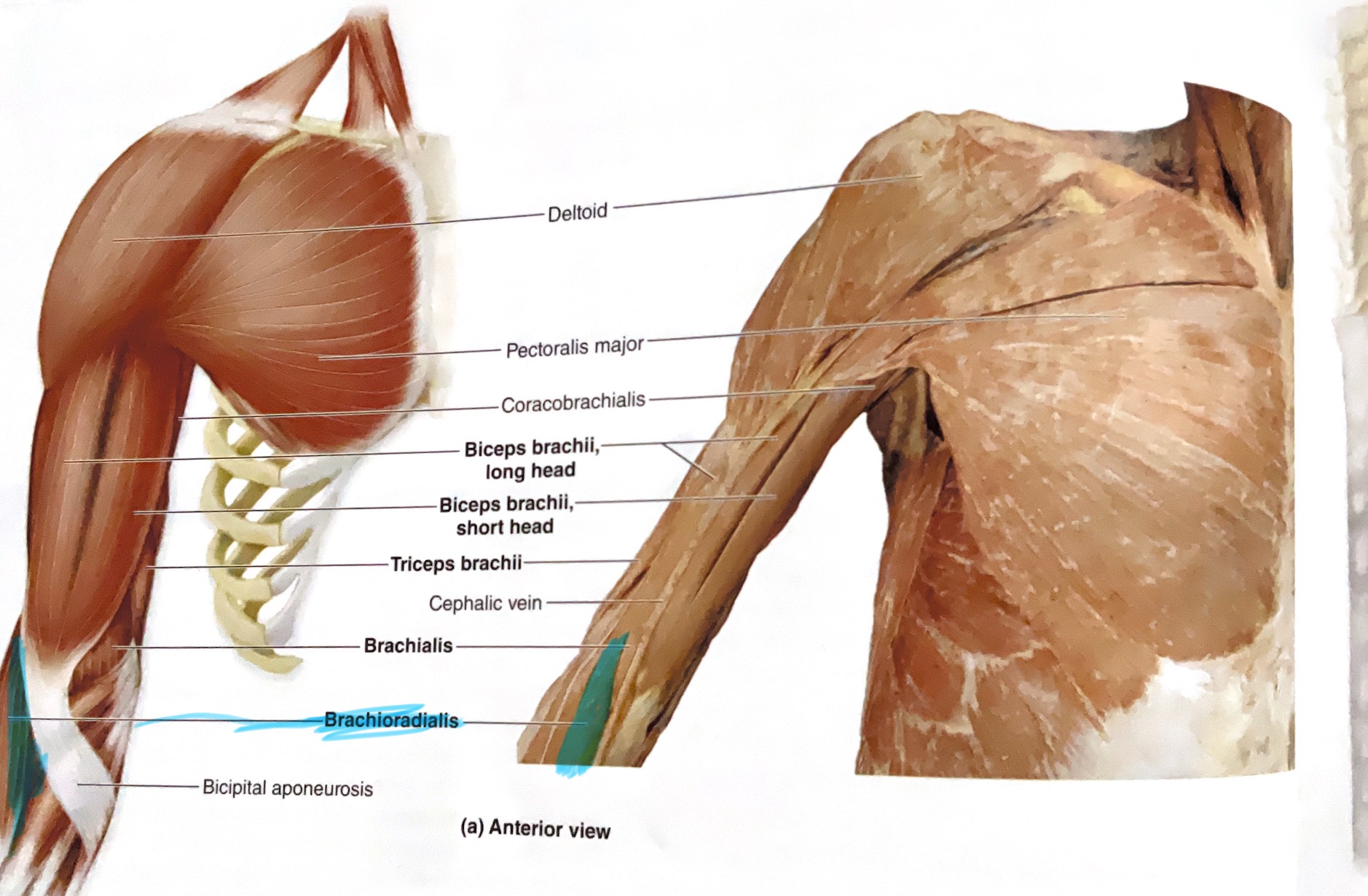
Brachioradialis
Action: Flex forearm; supinate(outward rotation), pronate(rotation of a body part inward or toward the midline of the body) radio-ulnar joints(return to relaxed postion)
Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus
Action:Extend, abduct wrist
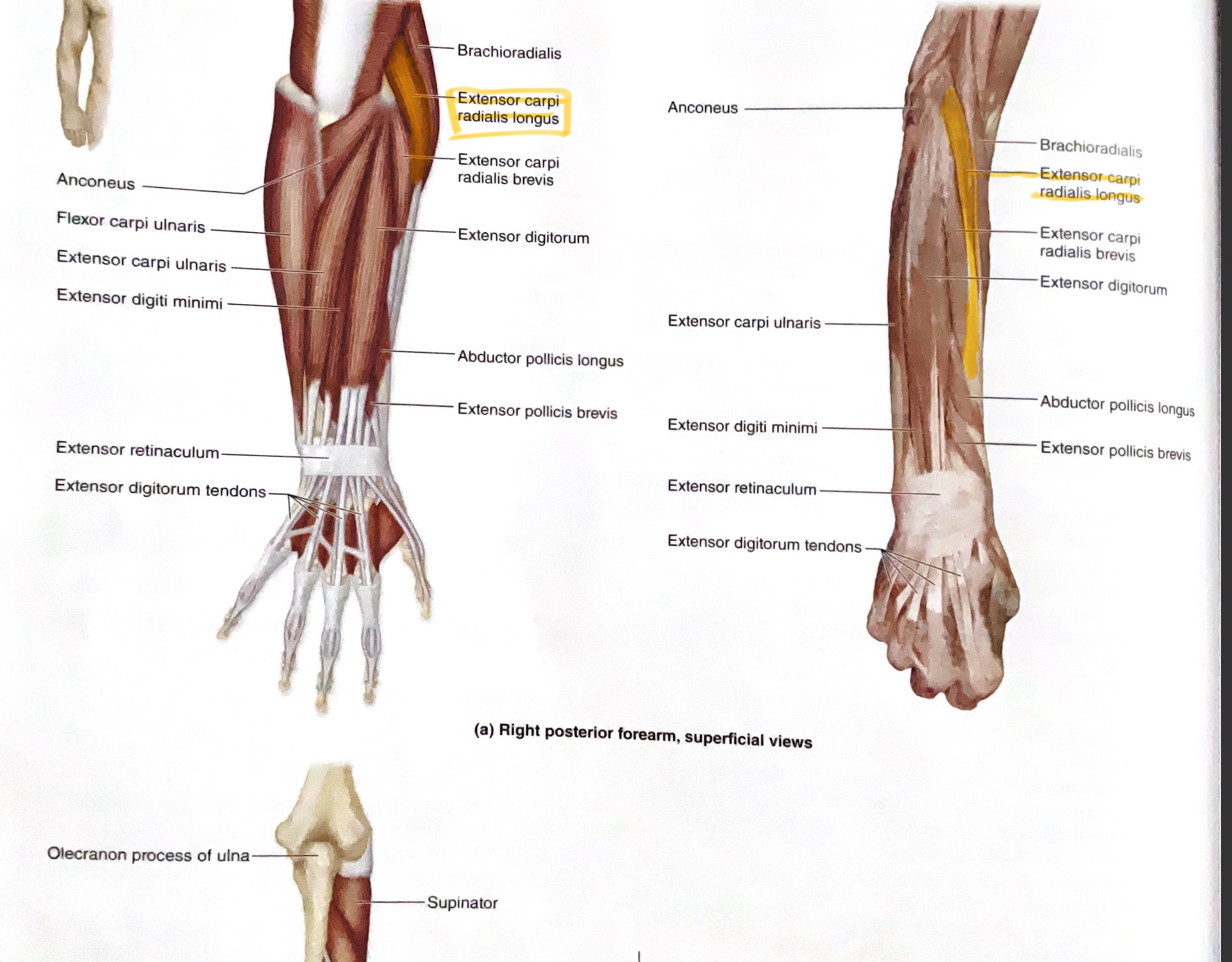
Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis
Action: Extend, abduct wrist
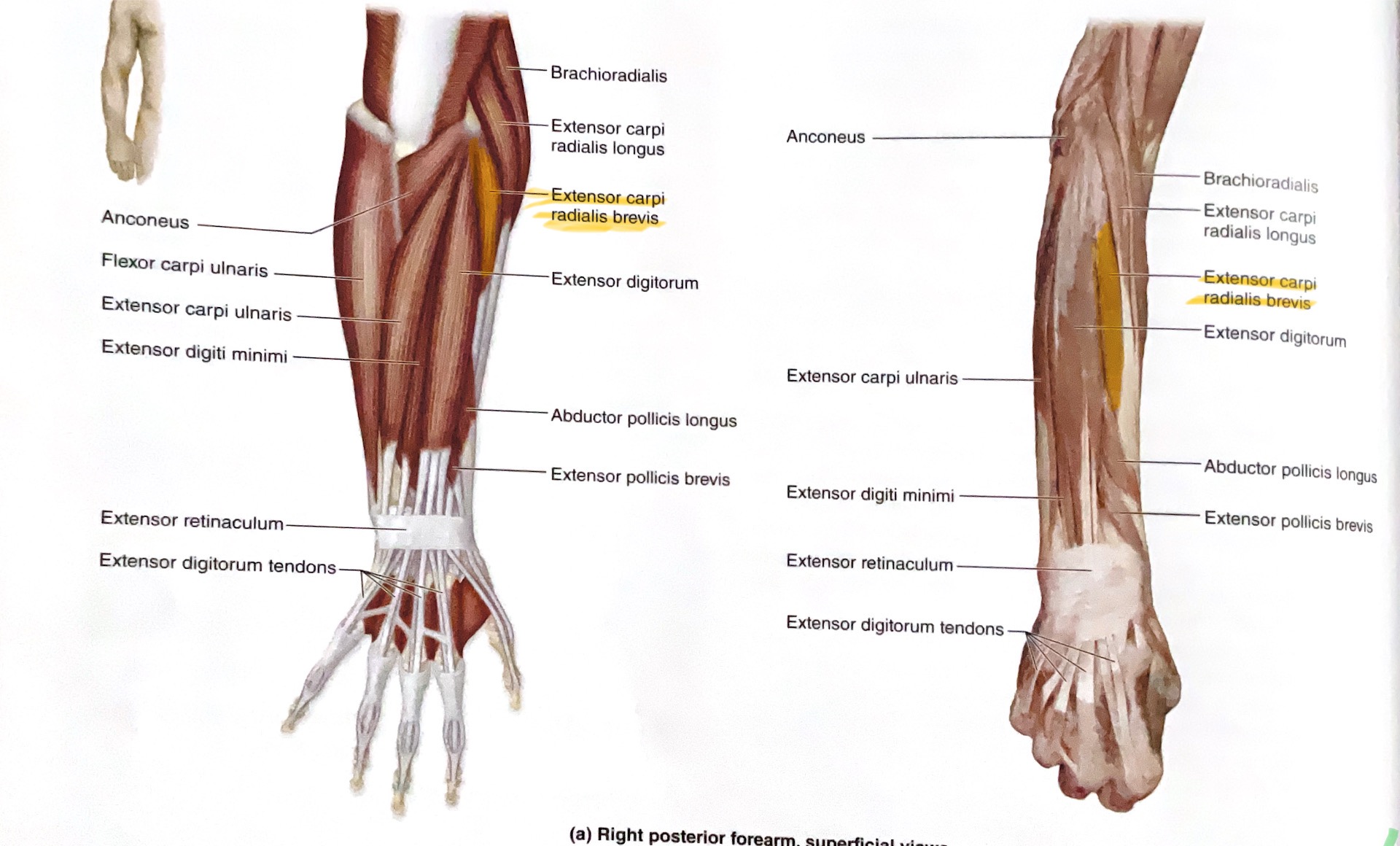
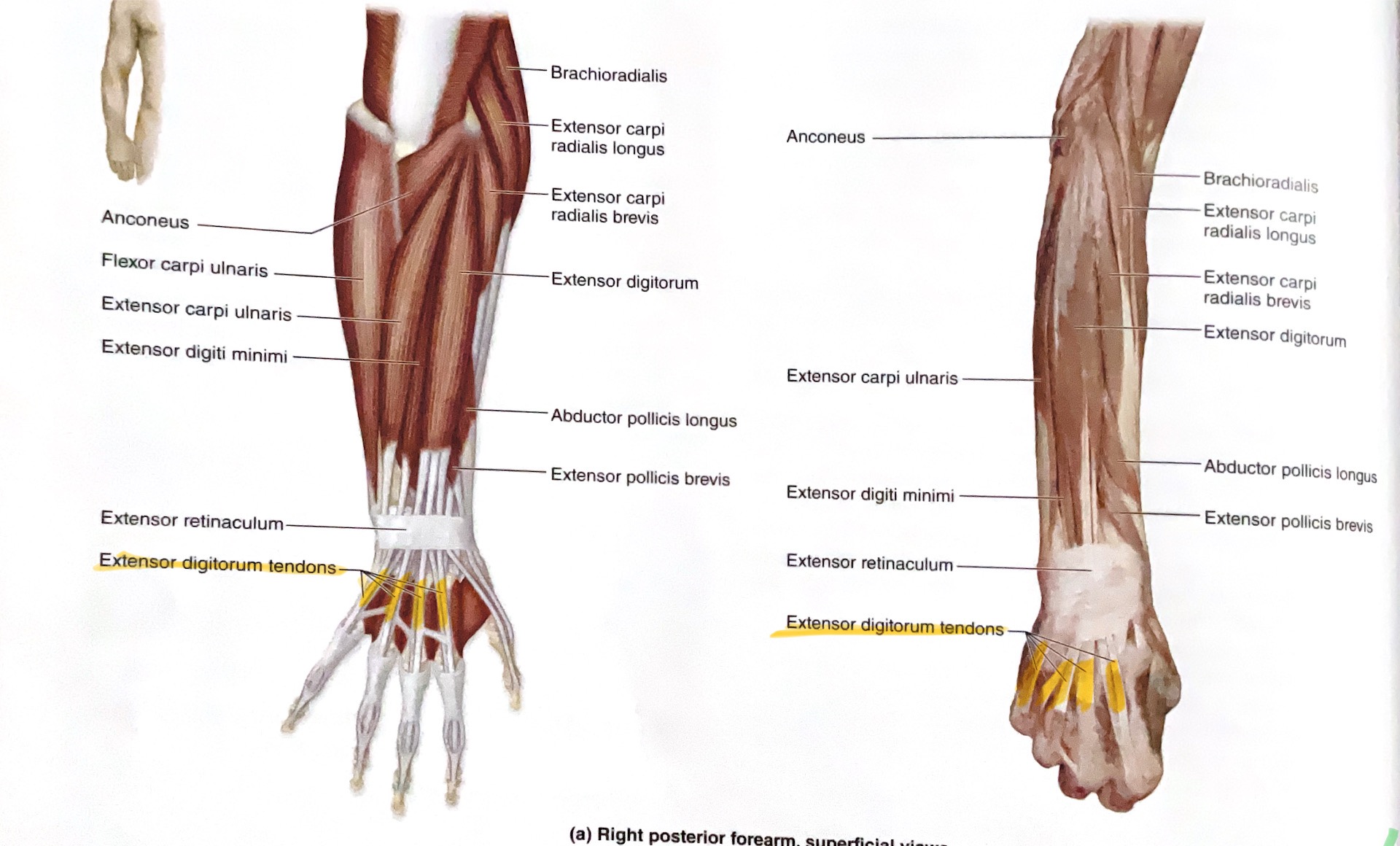
Extensor Digitorum
Action: Extend fingers
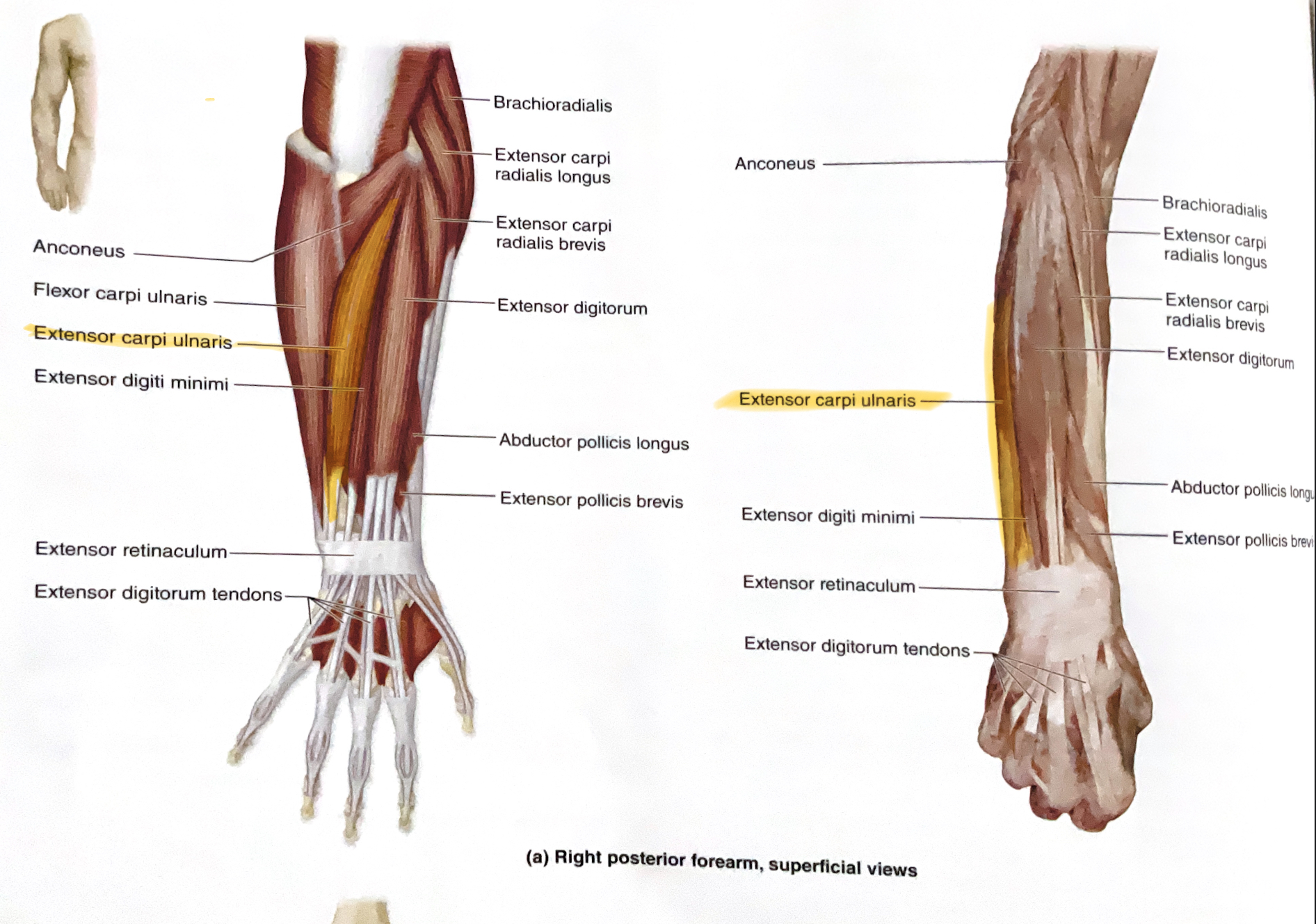
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris
Action: Extend, adduct wrist ( towards body midline, ulnaris= pinky side)
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
Action: Flex, adduct wrist
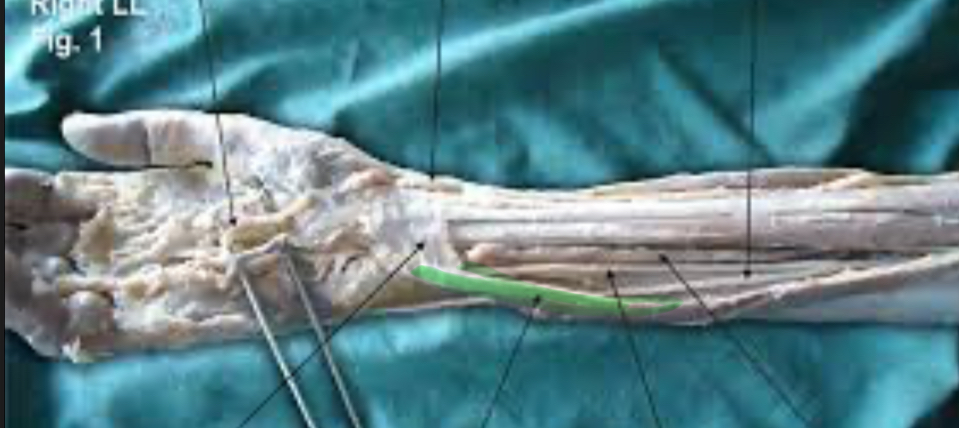
Palmaris Longus
Action: Flex wrist
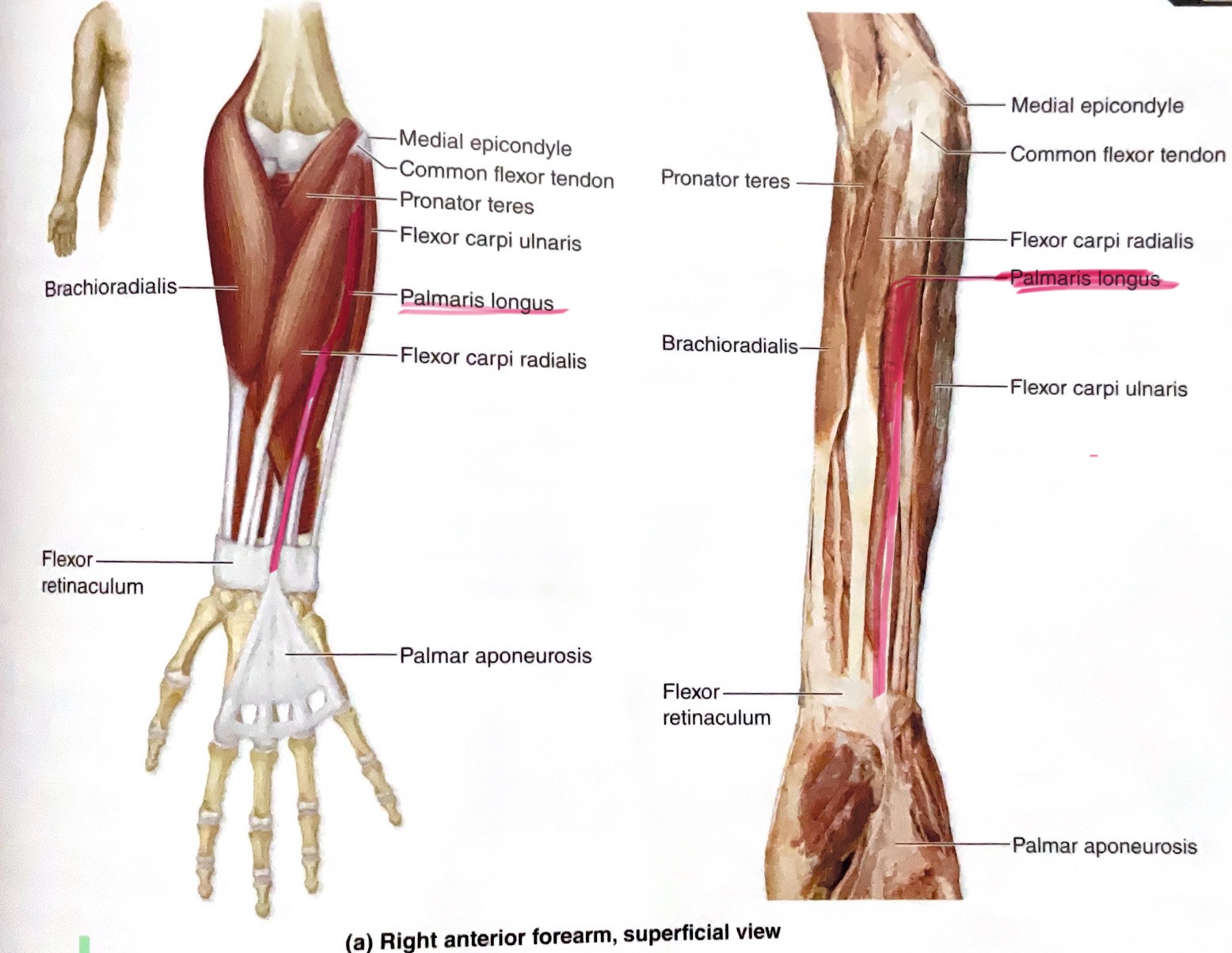
Flexor Carpi Radialis
Action: Flex, abduct wrist
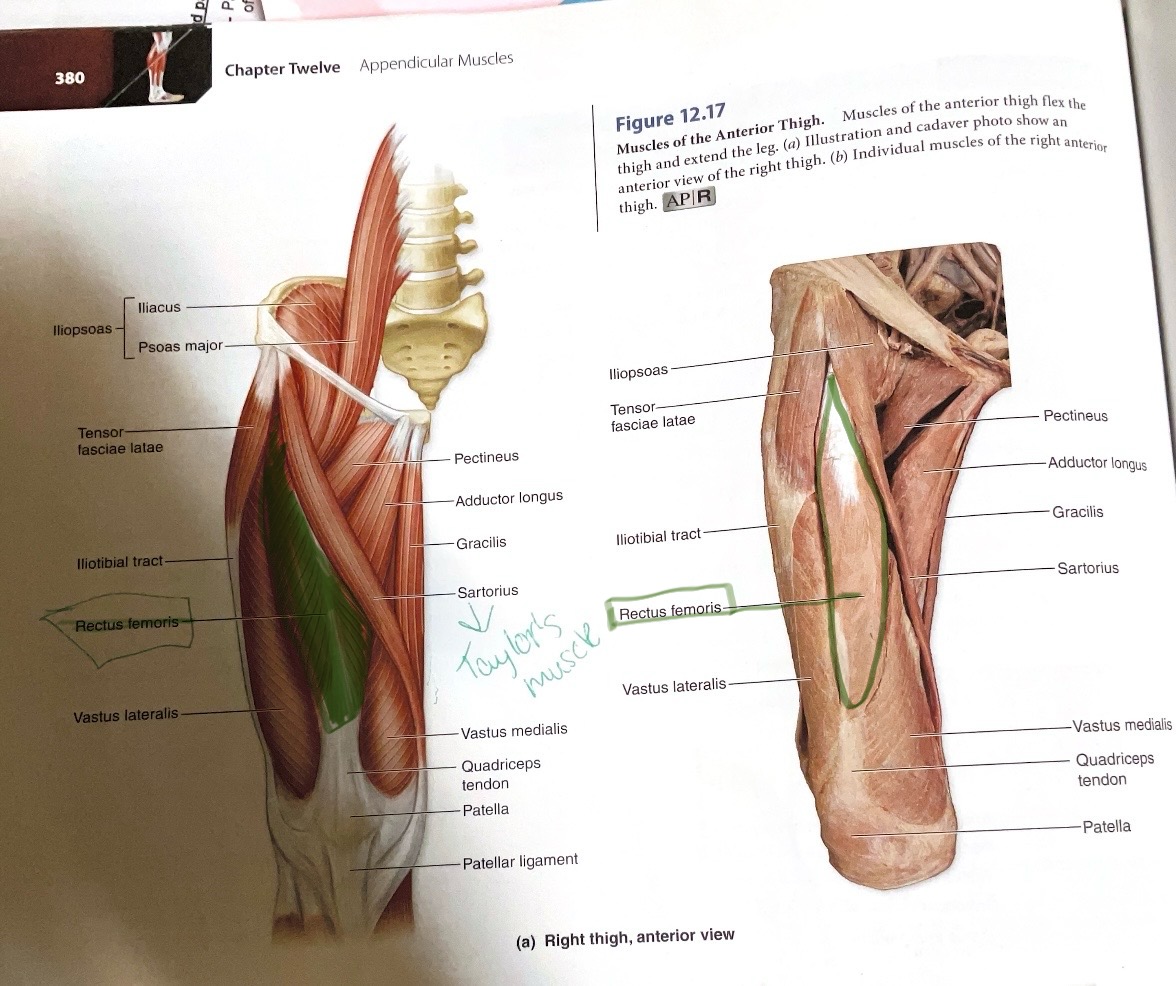
Rectus Femoris
Origin:Anterior inferior iliac spine
Insertion:Tibial Tuberosity
Action:Flex hip; extend knee
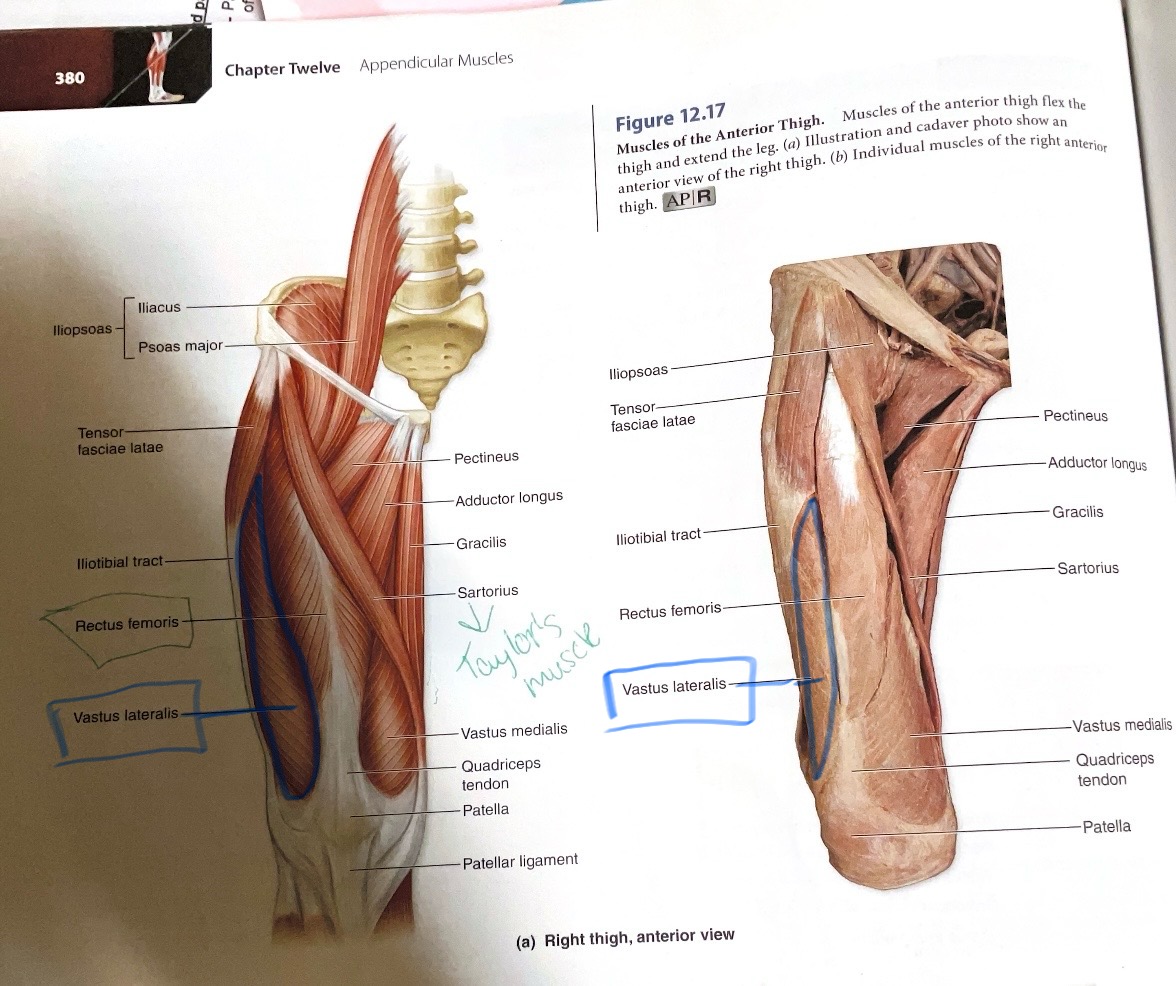
Vastus Lateralis
Origin:Greater trochanter and linea aspera
Insertion: Tibial tuberosity
Action: Extend knee
Vastus Medialis
Origin: Linea aspera
Insertion:Tibial Tuberosity
Action:Extend knee
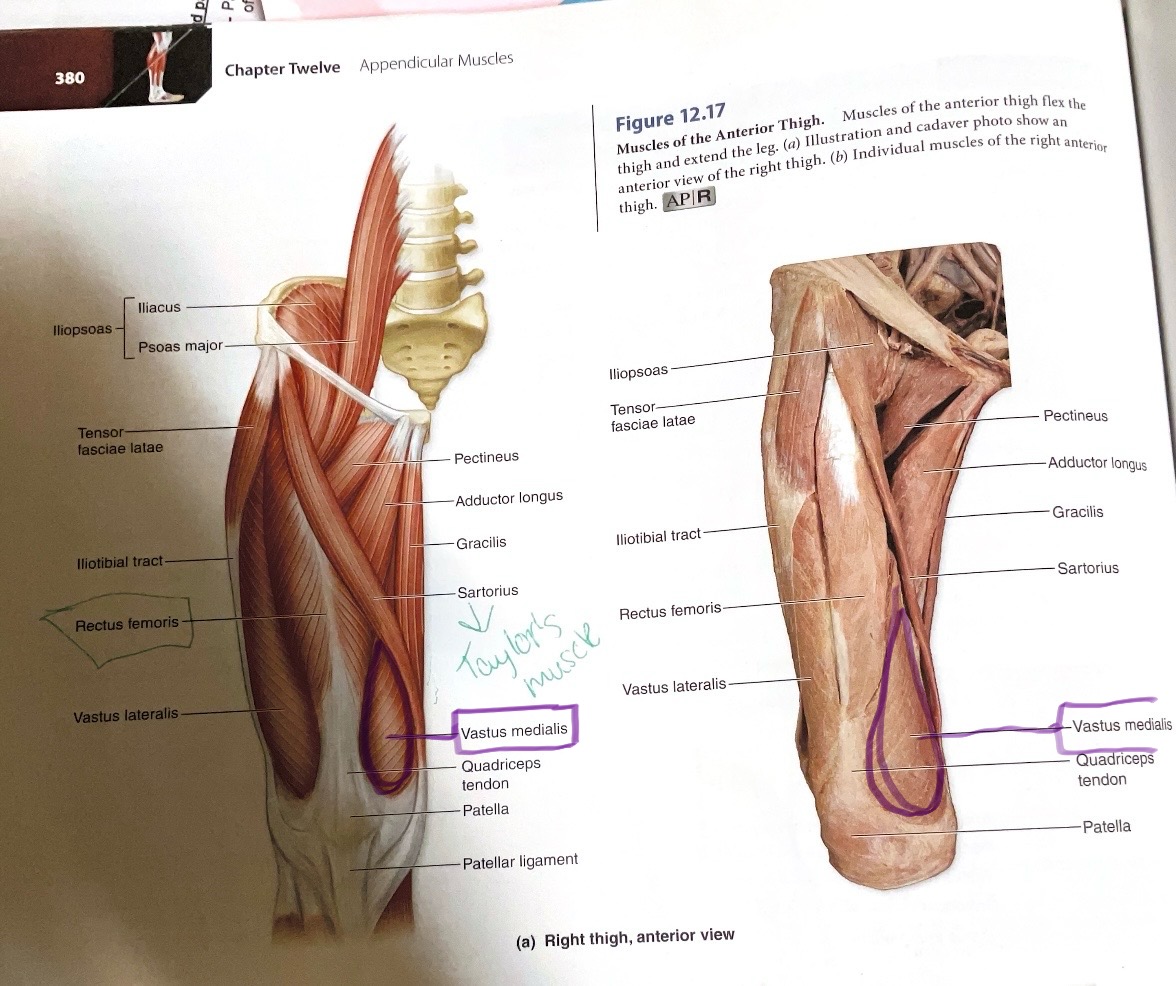
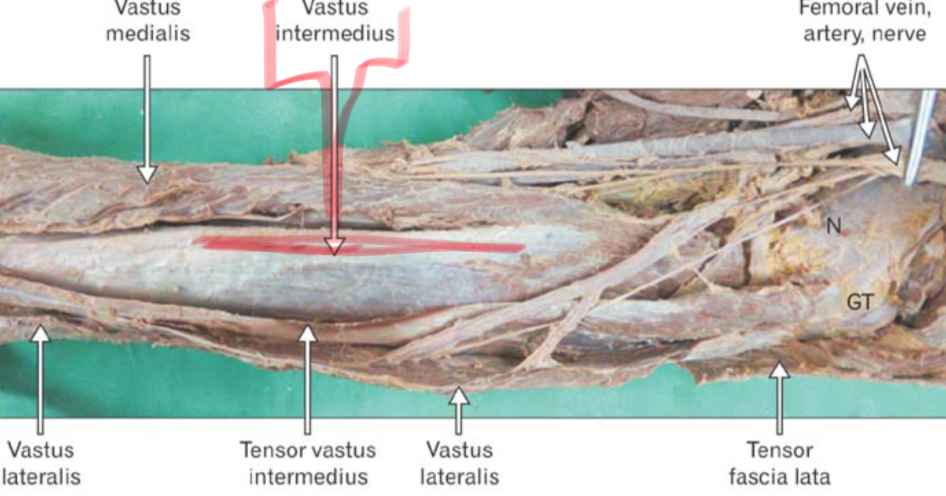
Vastus Intermedius
Origin: Anterior and Lateral diaphysis if femur
Insertion:Tibial tuberosity
Action: Extend knee
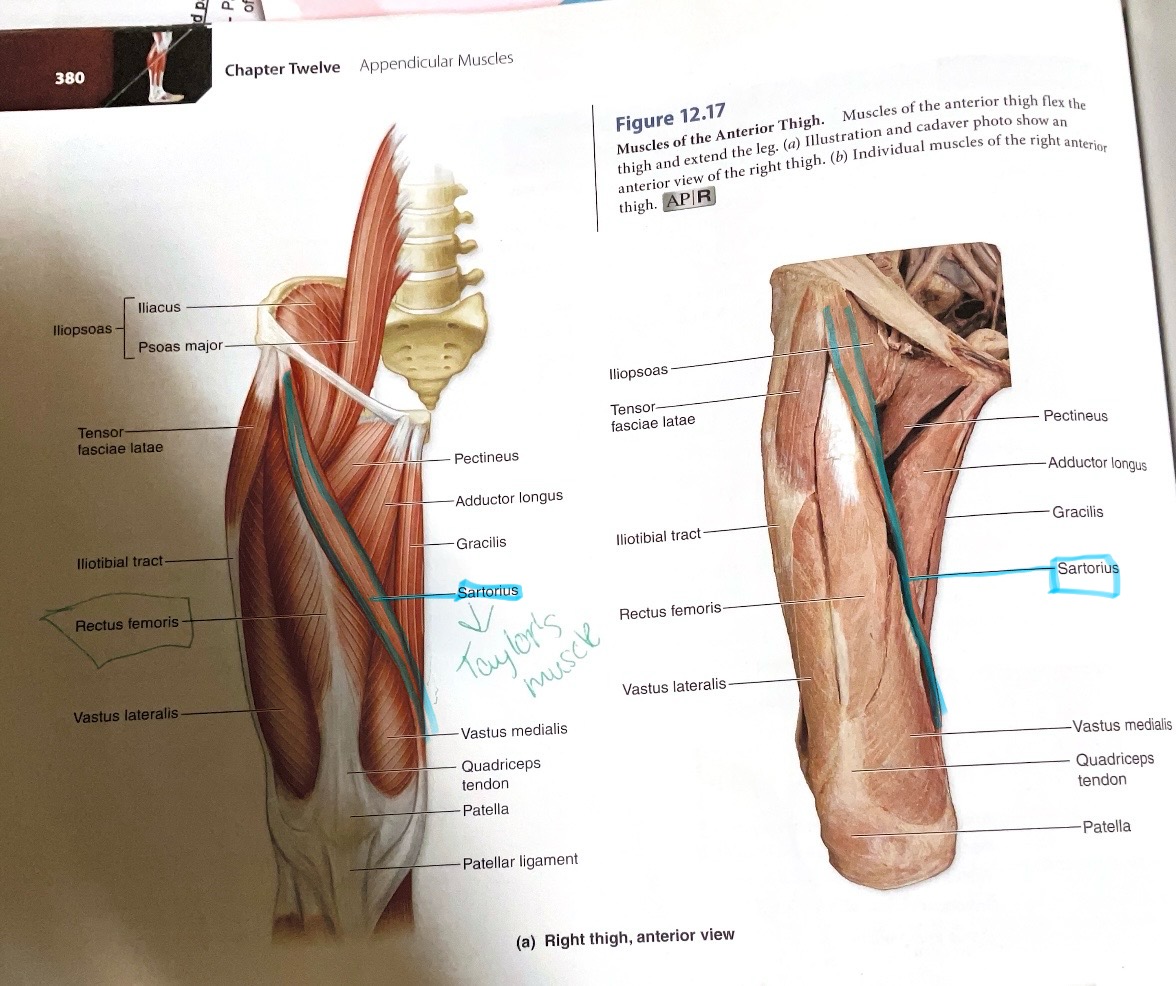
Sartorius
Action: Flex, laterally rotate hip; flex knee
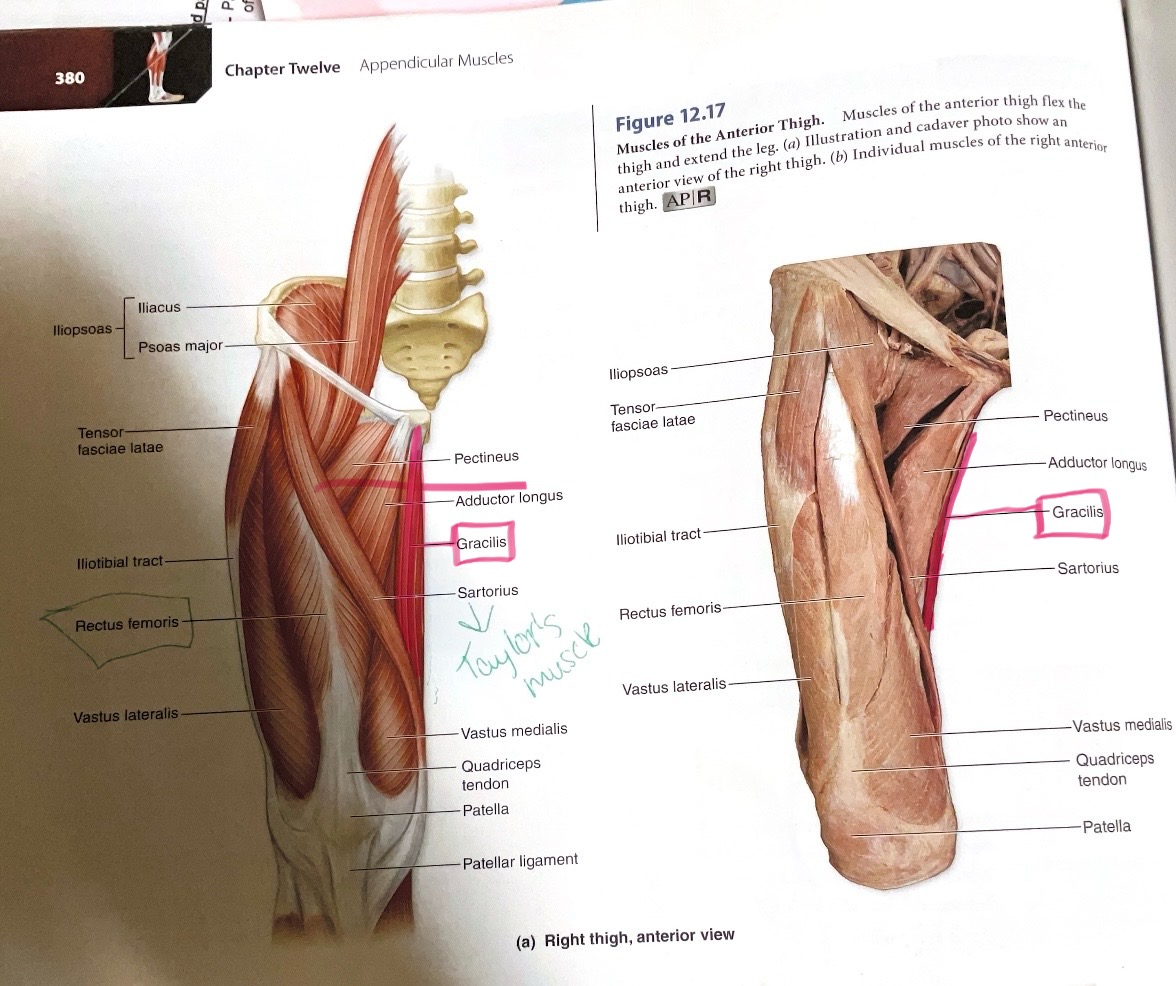
Gracilis
Action: Flex, adduct hip; flex knee
Pectineus
Action:Flex, adducts hip ( towards body midline)
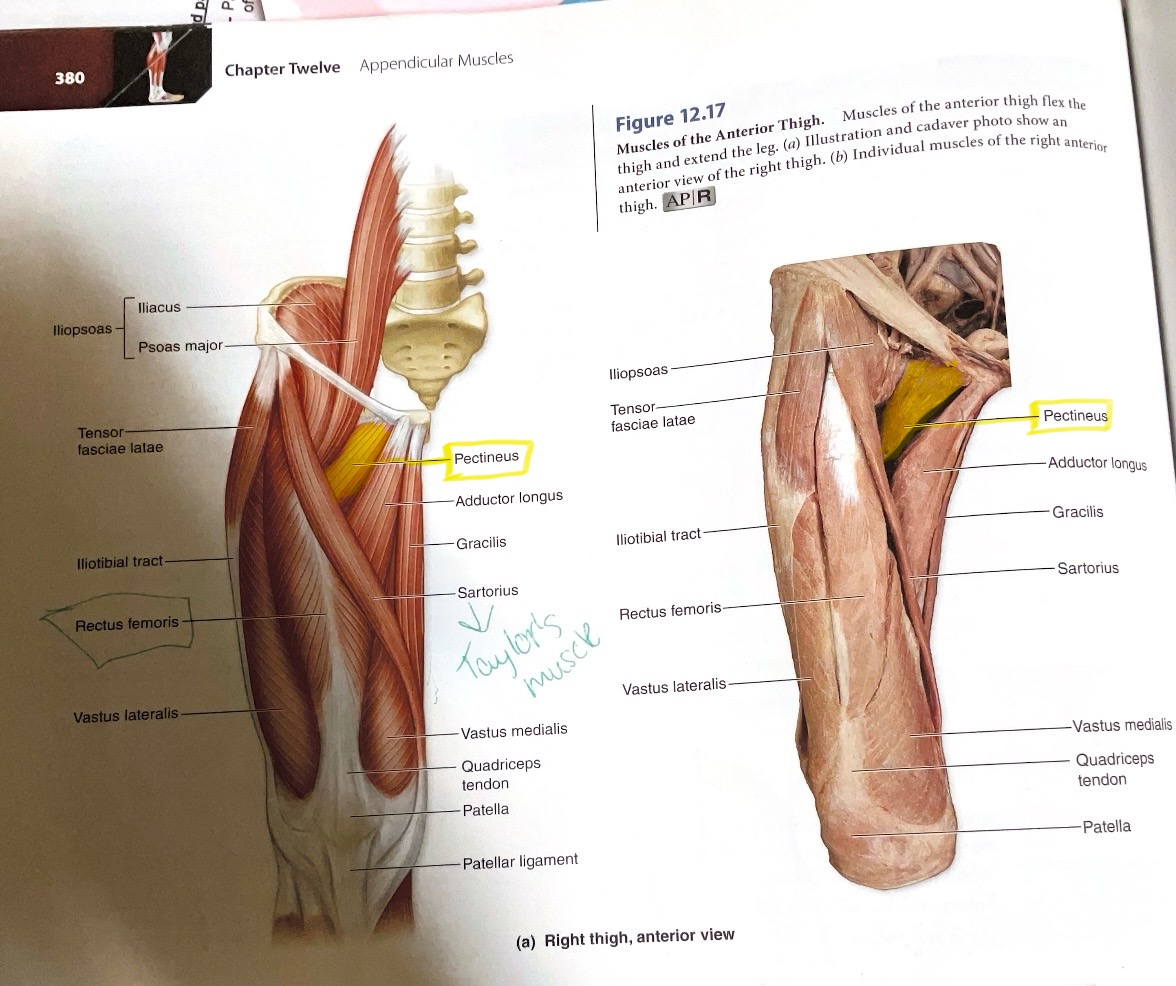
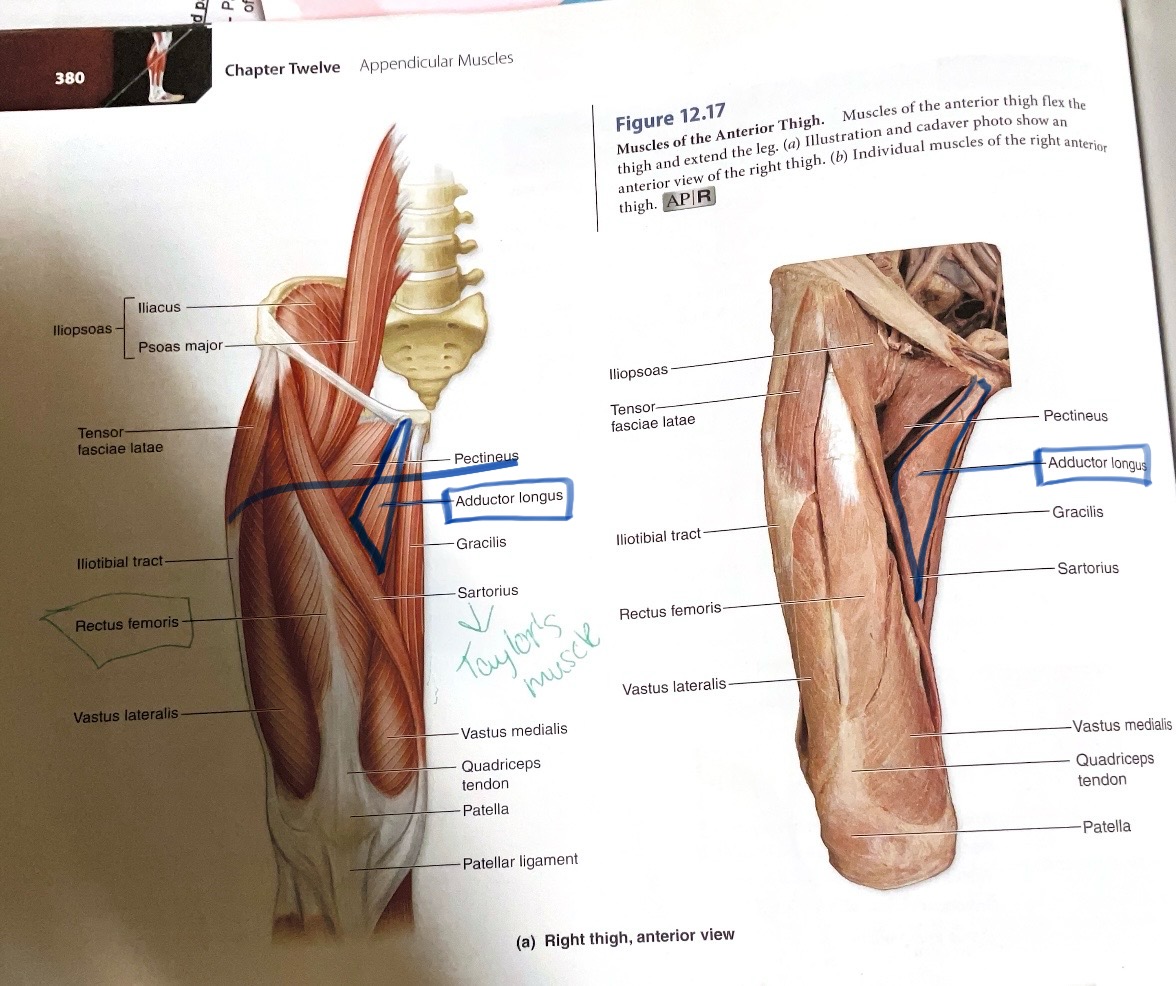
Adductor Longus
Origin: Anterior body of pubis
Insertion: Linea aspera
Action:Adduct hip
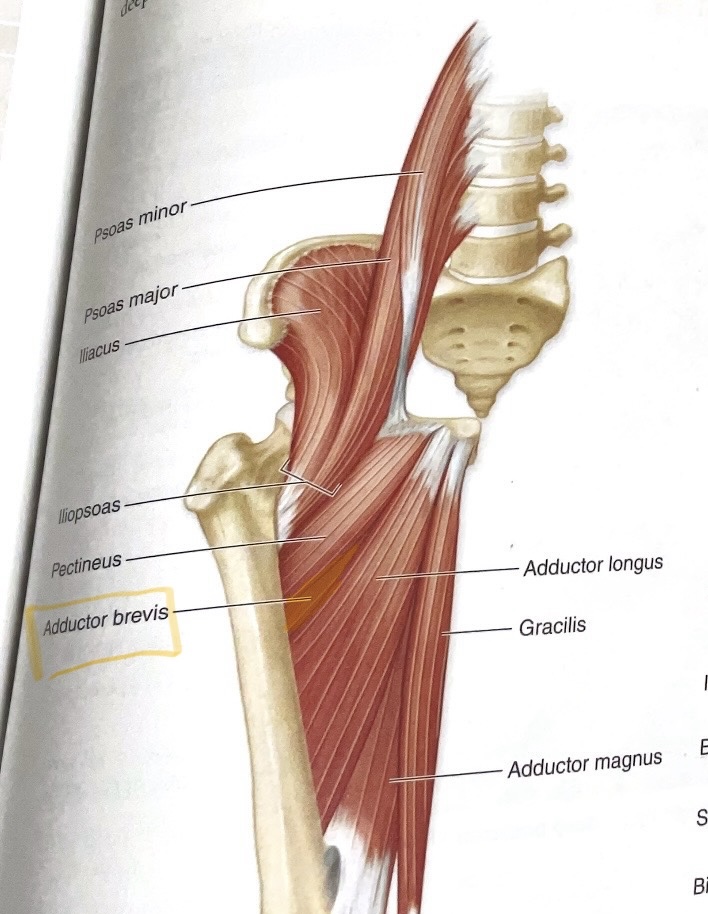
Adductor Brevis
Origin: Inferior pubic ramus
Insertion: Linea aspera
Action:Adduct hip
Adduct Magnus
Origin: Inferior pubic ramus, ischial ramus, and ischial tuberosity
Insertion: Linea aspera(roughened ridge on the posterior (back) surface of the femur)
Action:Adduct, flex hip
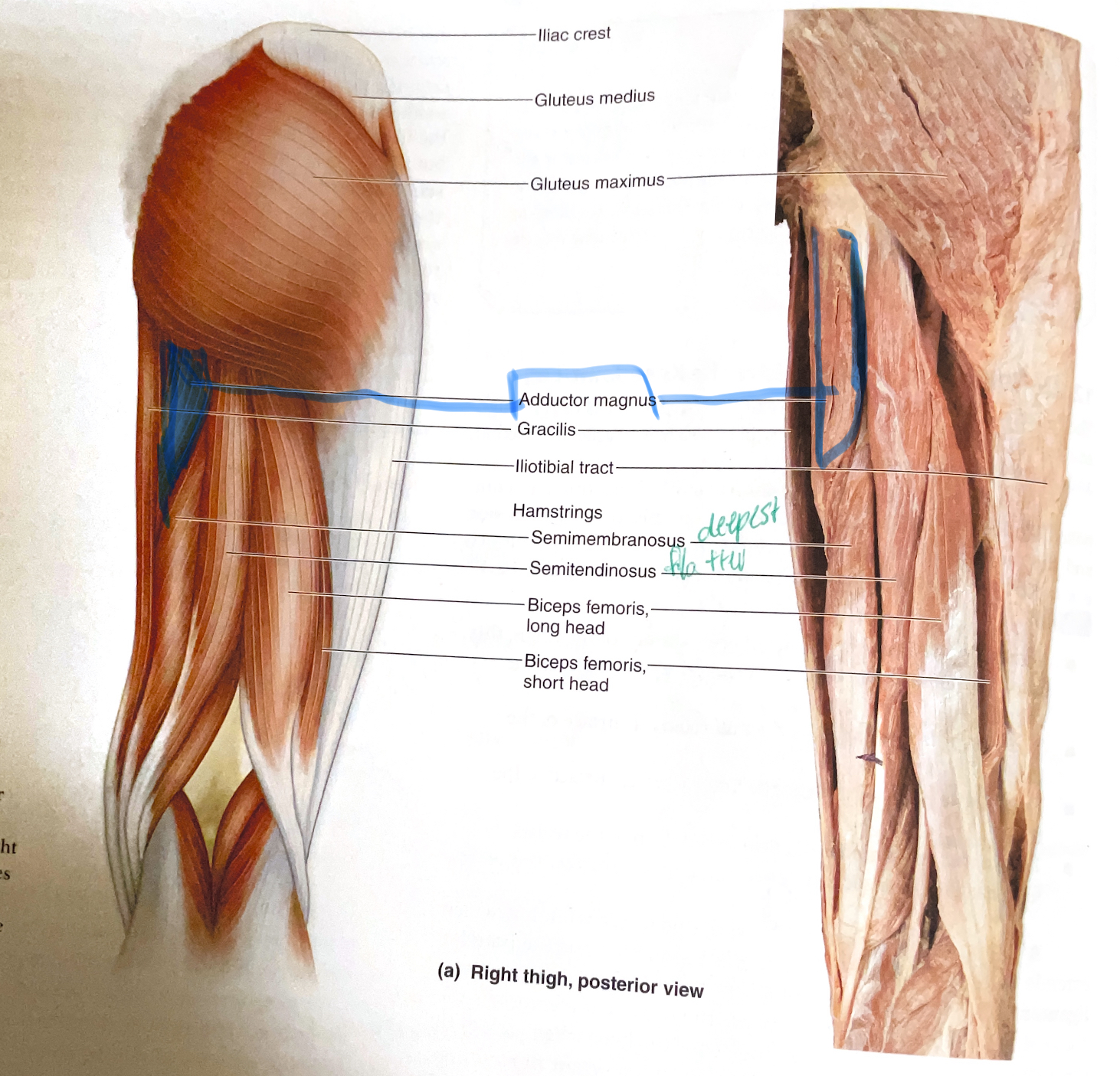
Gluteus Maximus
Action:Extend, laterally rotates hip
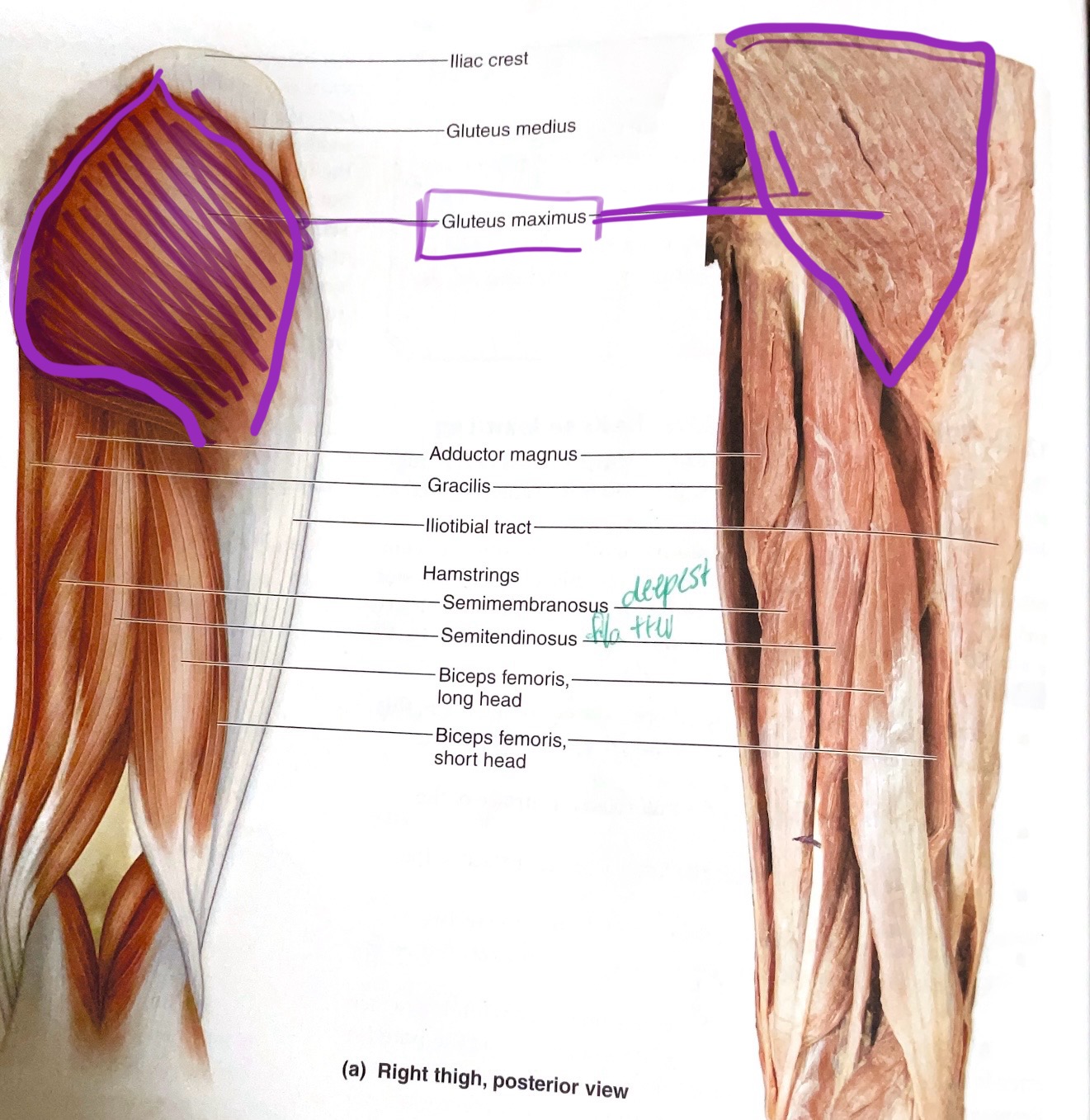
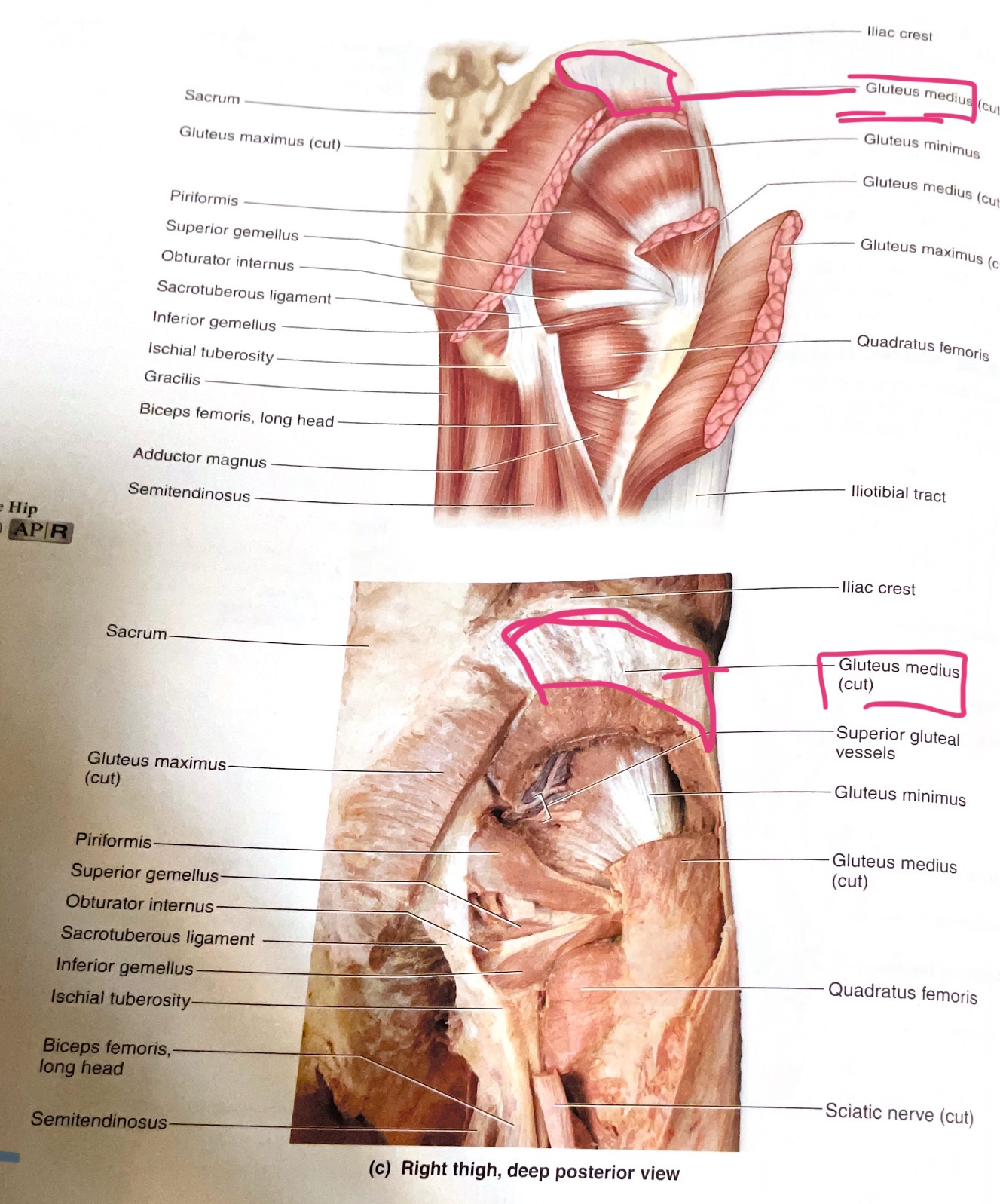
Gluteus Medius
Action: Abduct hip(move away from body midline )
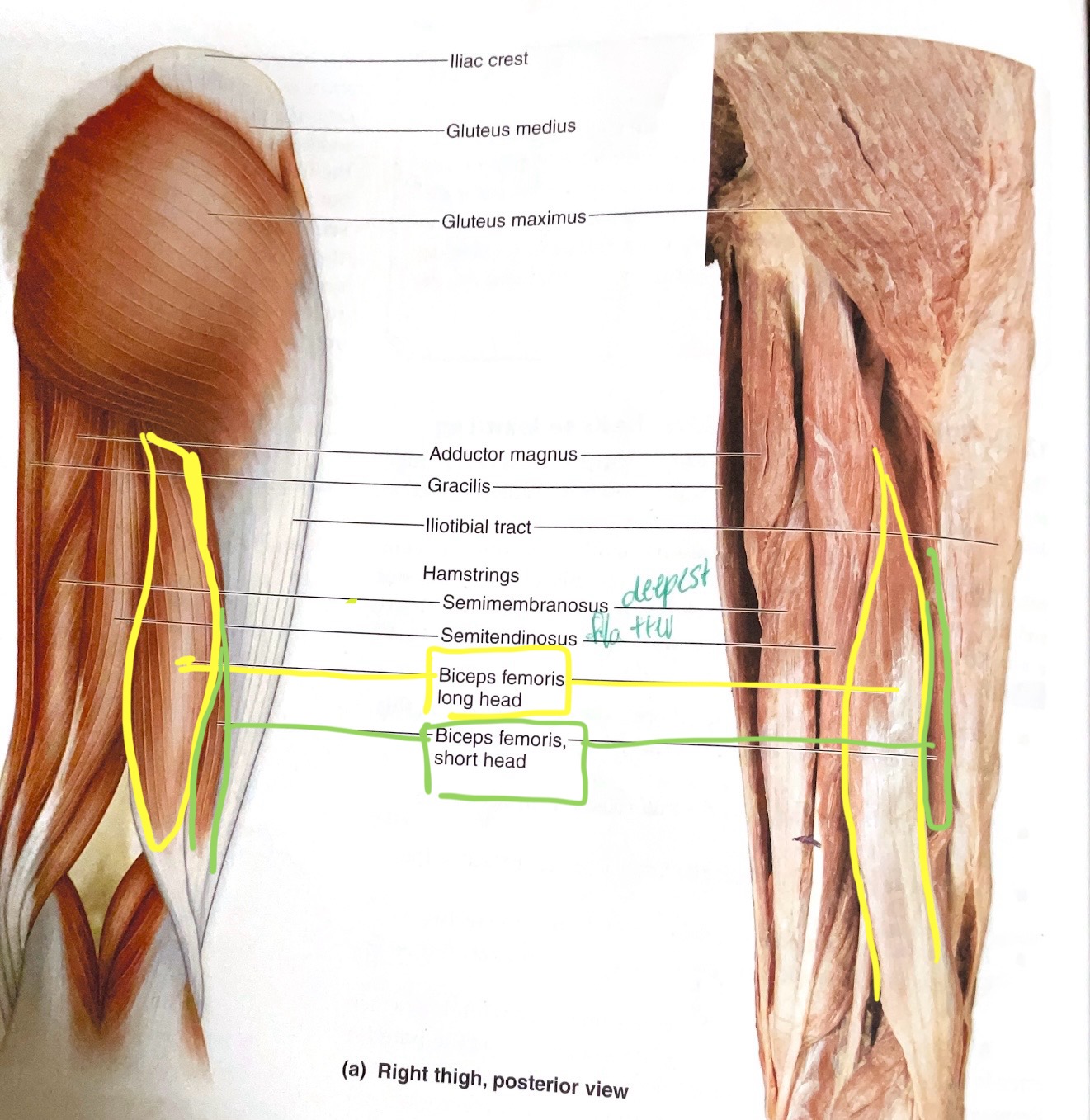
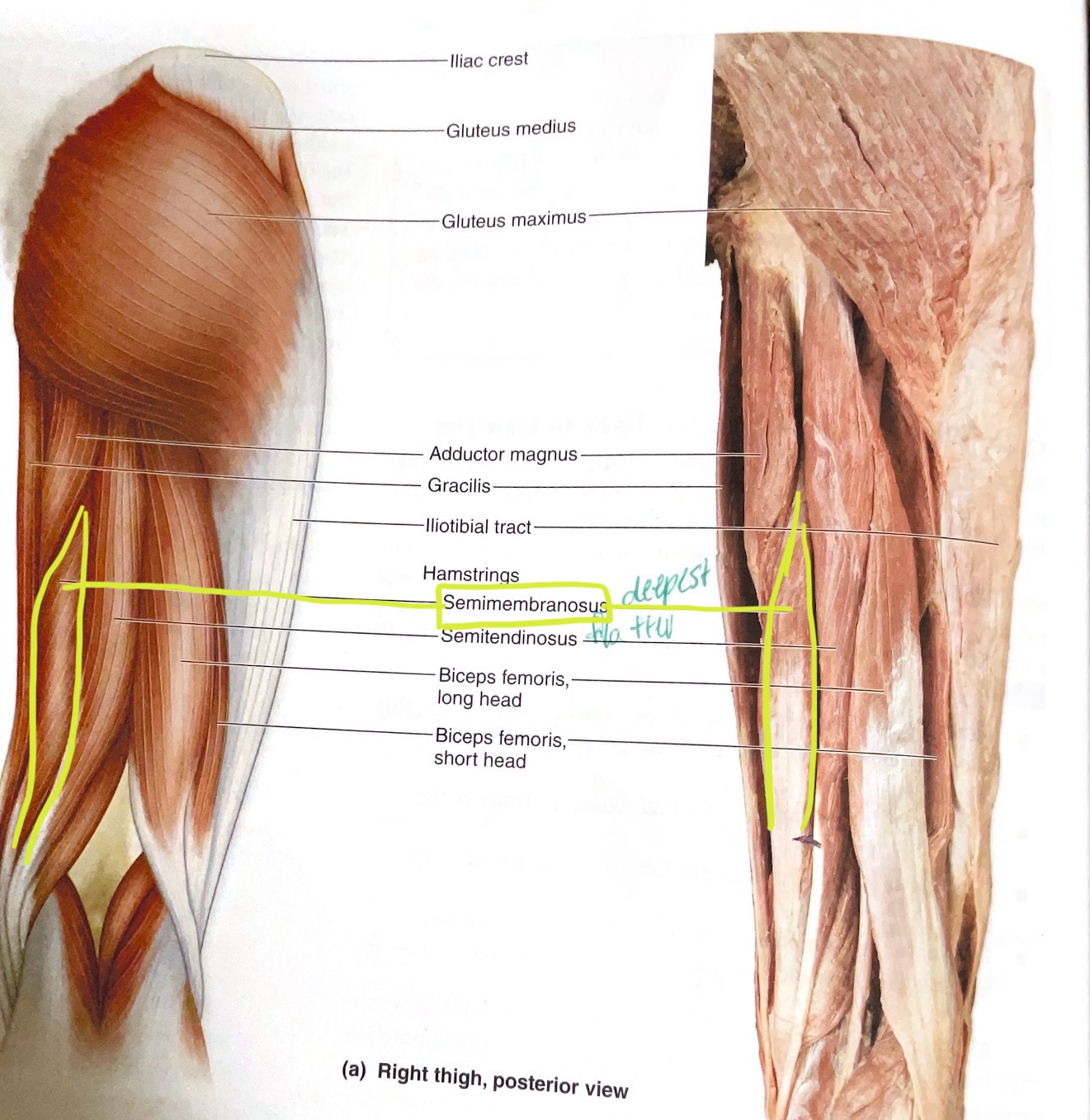
Biceps Femoris (2 heads)
Origin: Long head- ischial tuberosity; Short head- linea aspera. Insertion: head of fibula
Action:Long head- extend hip; flex hip
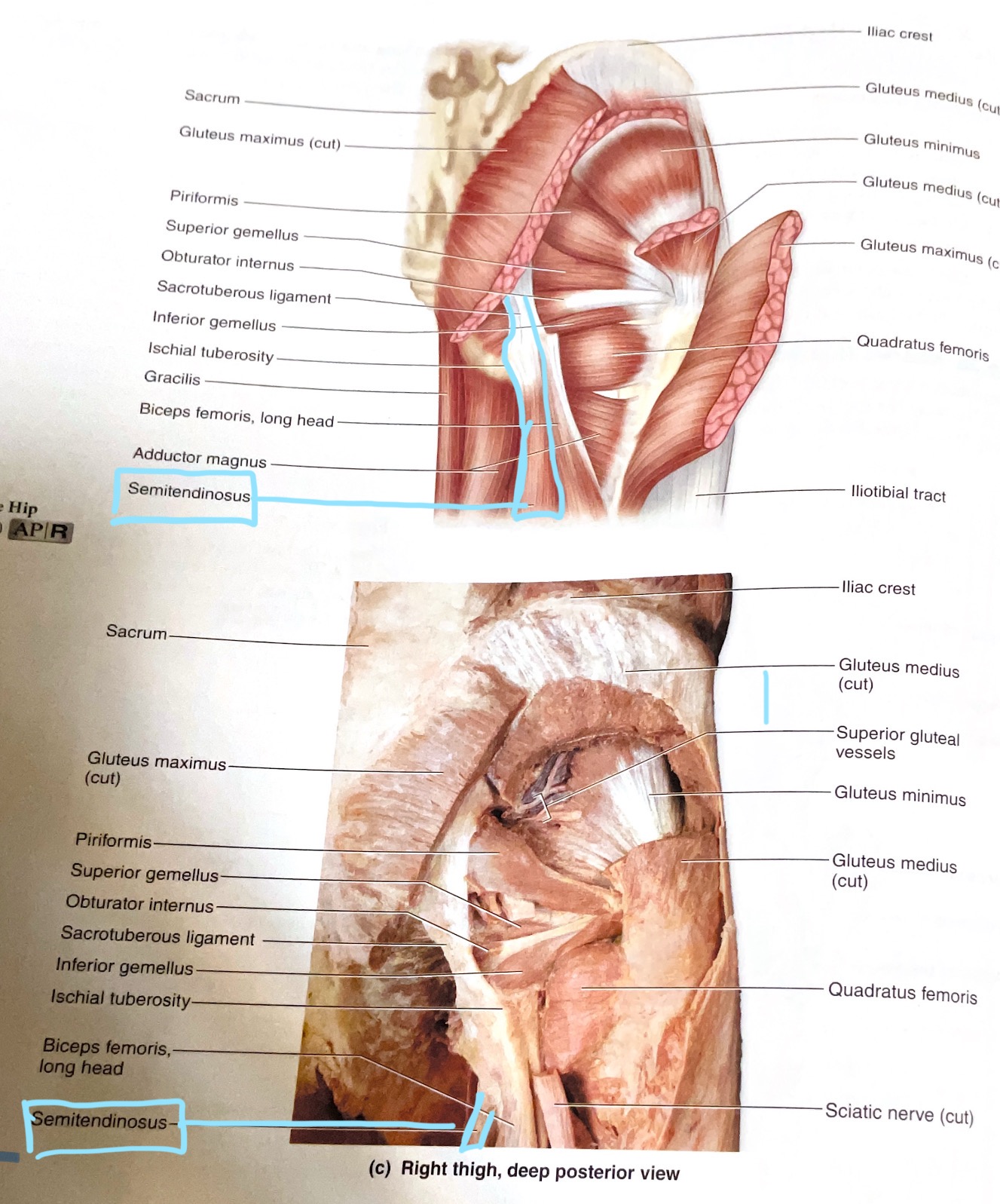
Semitendinosus
Origin:Ischial tuberosity
Insertion:Proximal medial diaphysis of tibia
Action:Extend hip; flex knee
Semimembranosus
Origin: Ischial Tuberosity
Insertion: Medial condyle of tibia
Action:Extend hip; flex knee
Plantaris
Action: Plantar flex ankle
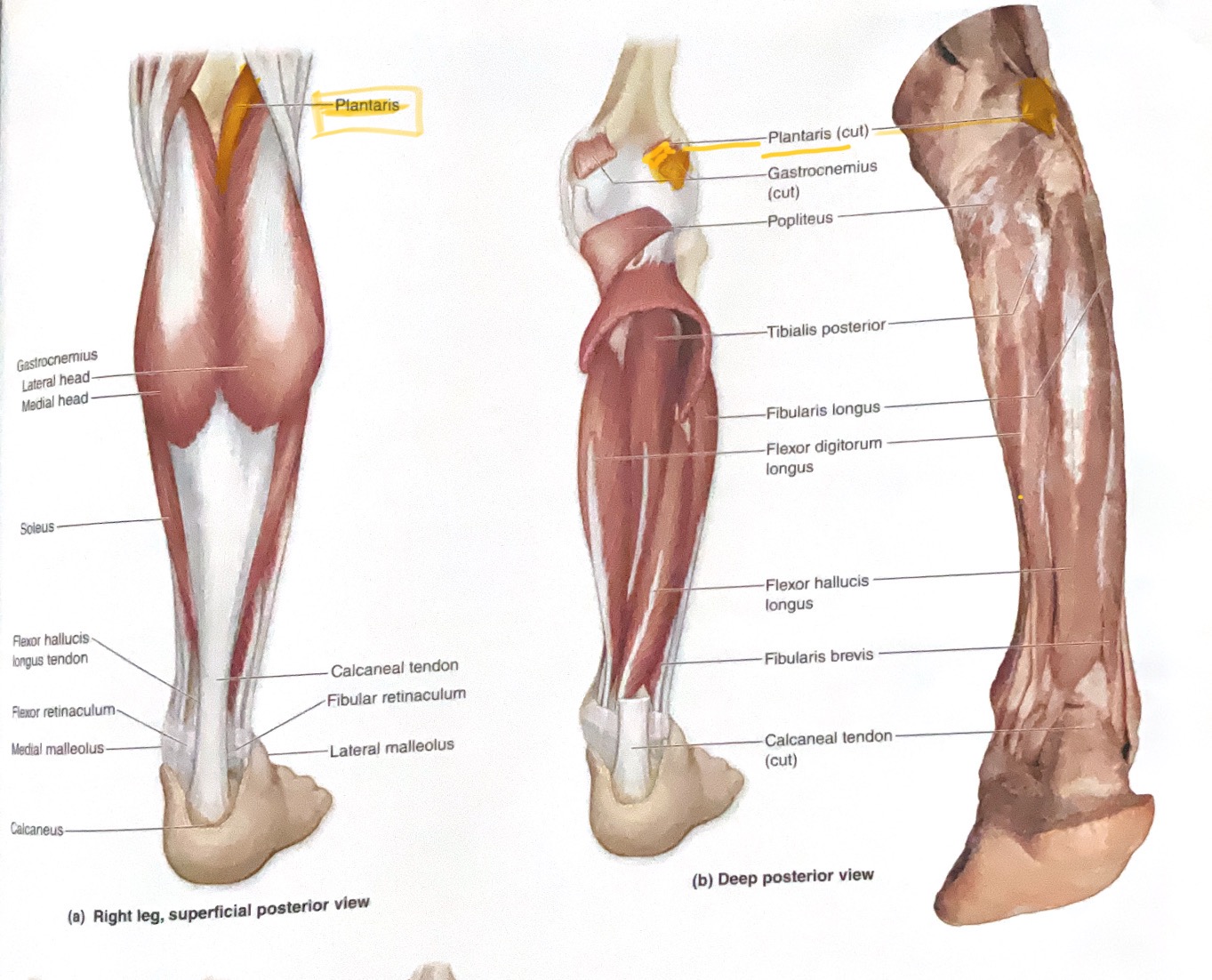
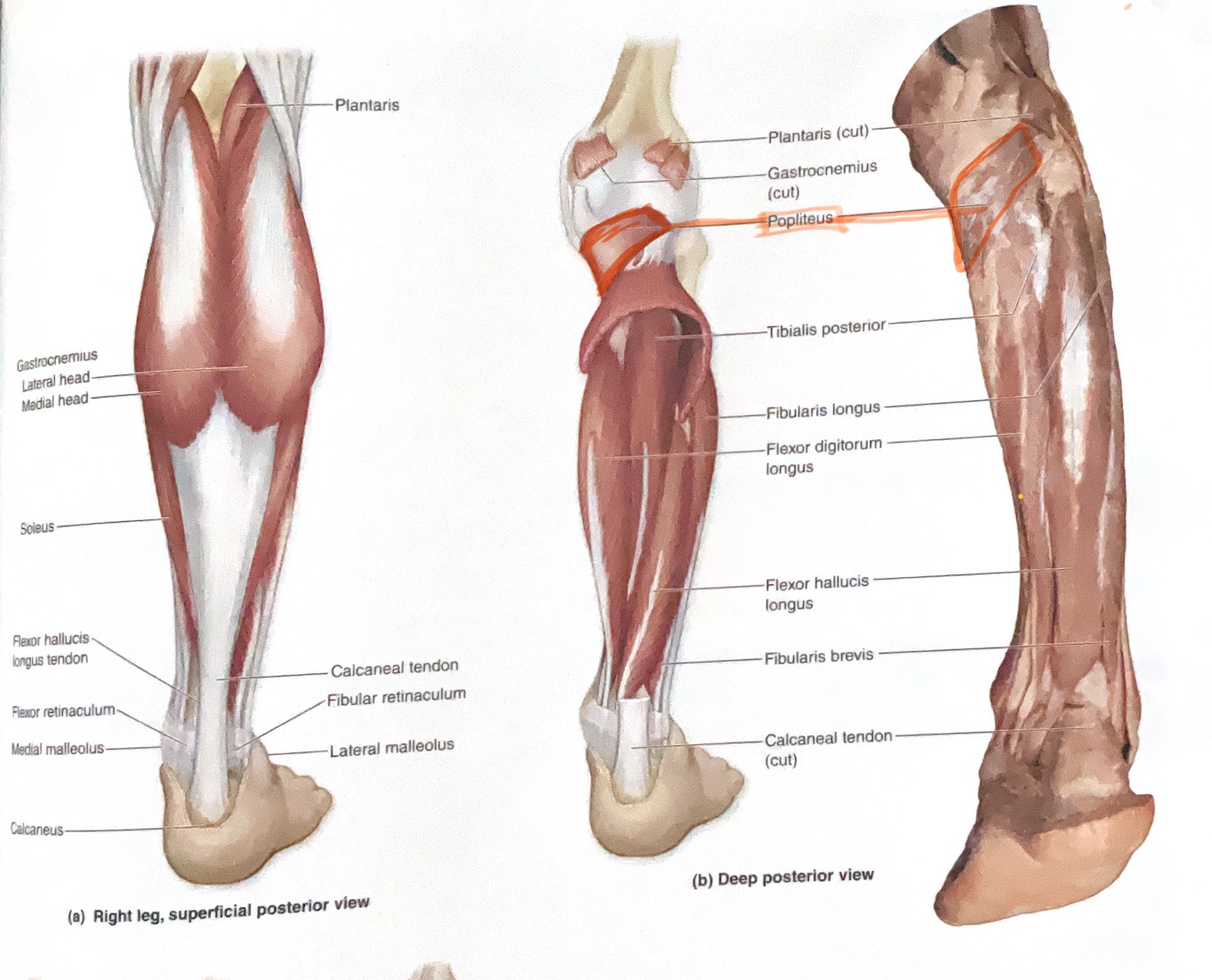
Popliteus
Action: Medially rotate tibia(unlock knee)
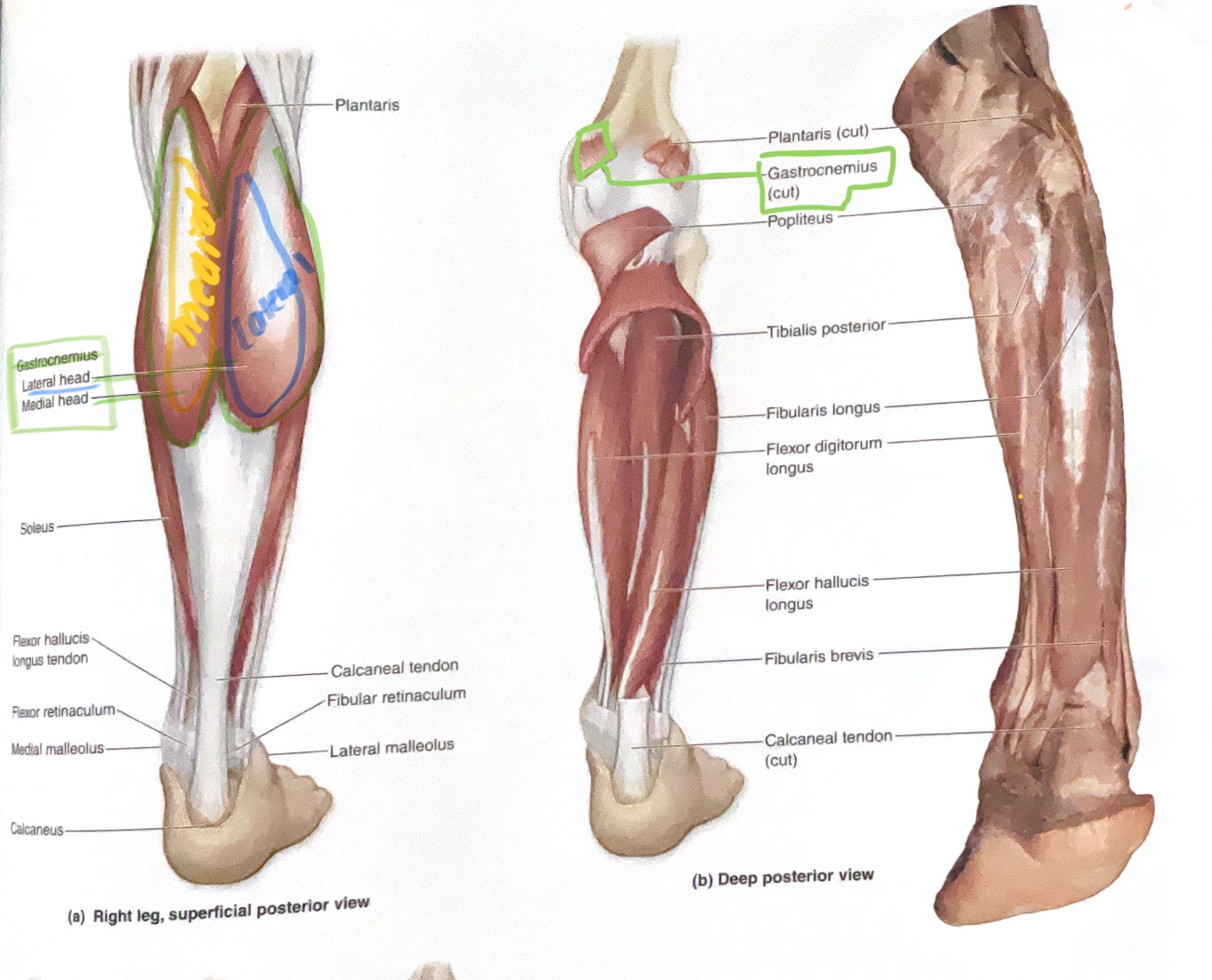
Gastrocnemius ( 2 heads)
Origin: Medial head- posterior side of medial condyle of femur
Lateral head- Posterior side of lateral condyle femur
Insertion: Calcaneus
Action: Flex knee; Plantar flex ankle
Soleus
Origin: Posterior fibula, and soleal line
Insertion: Calcaneus
Action:plantar flex ankle
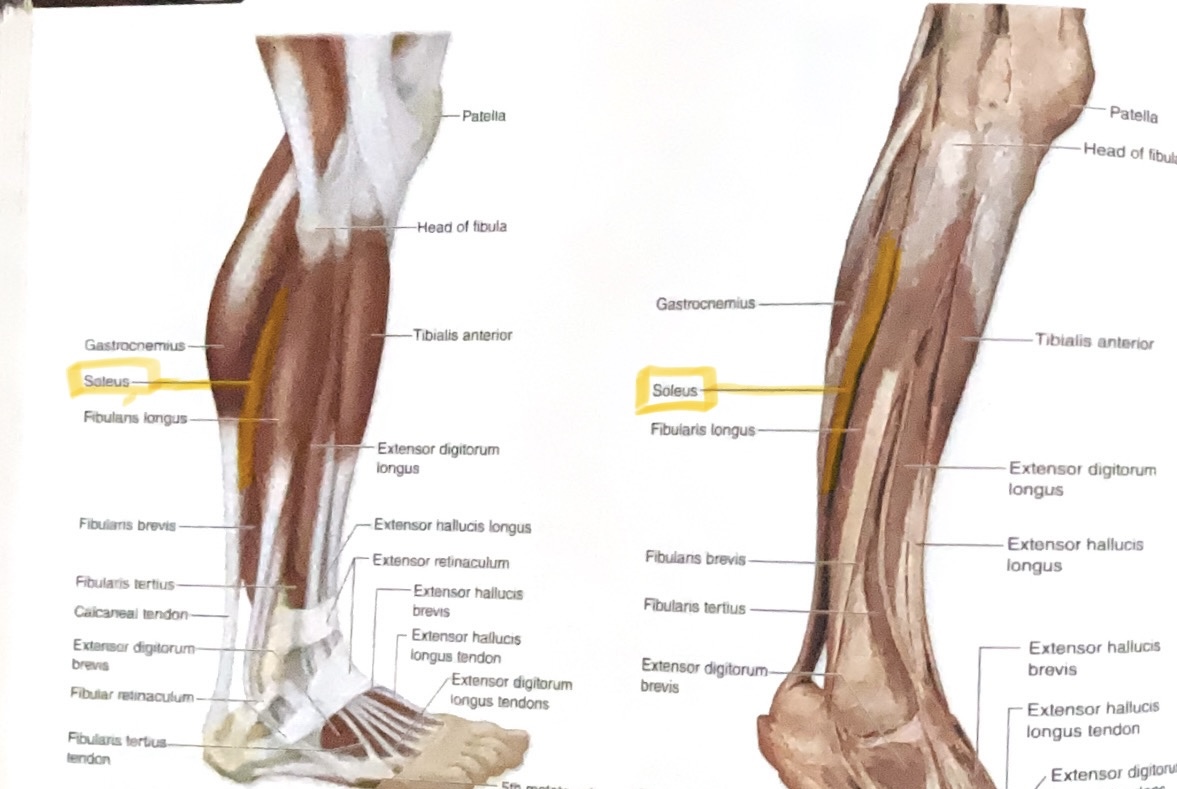
Tibialis Anterior
Origin: Lateral condyle and diaphysis of tibia
Insertion: first metatarsal and first cuneiform
Action: Dorsiflex, invert ankle

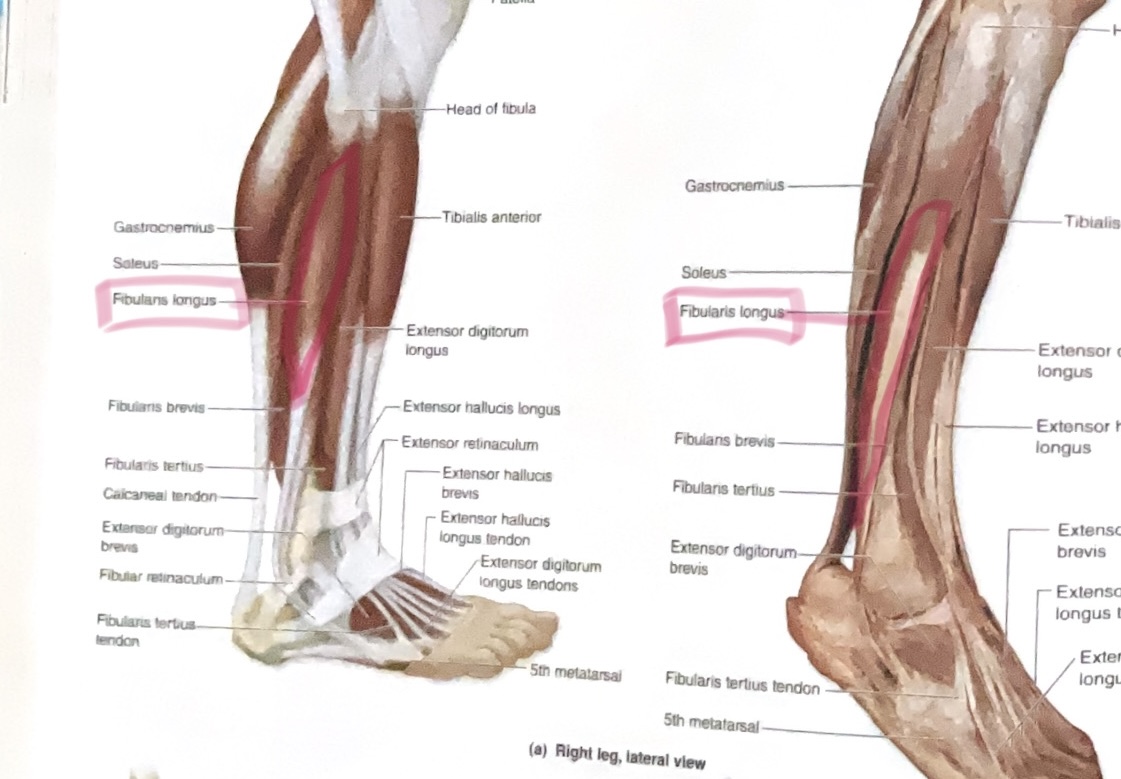
Peroneus (fibularis) Longus
Action: Plantar flex, evert ankle
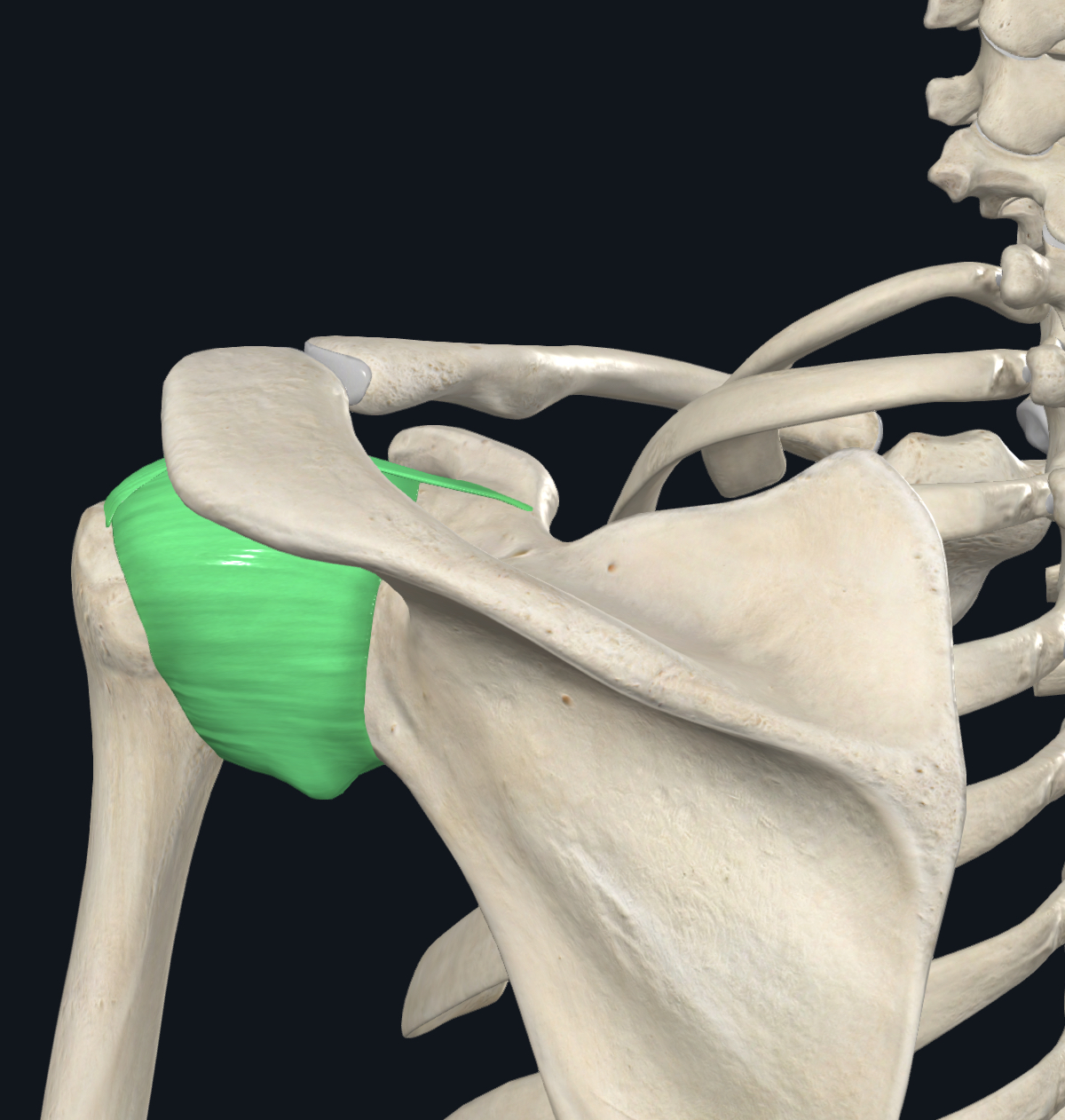
Glenoid humeral joint
type of Synovial joint( prevent friction),allows wide movement
Located between scapula
Lateral meniscus
Stabilizes laterally & shock absorber
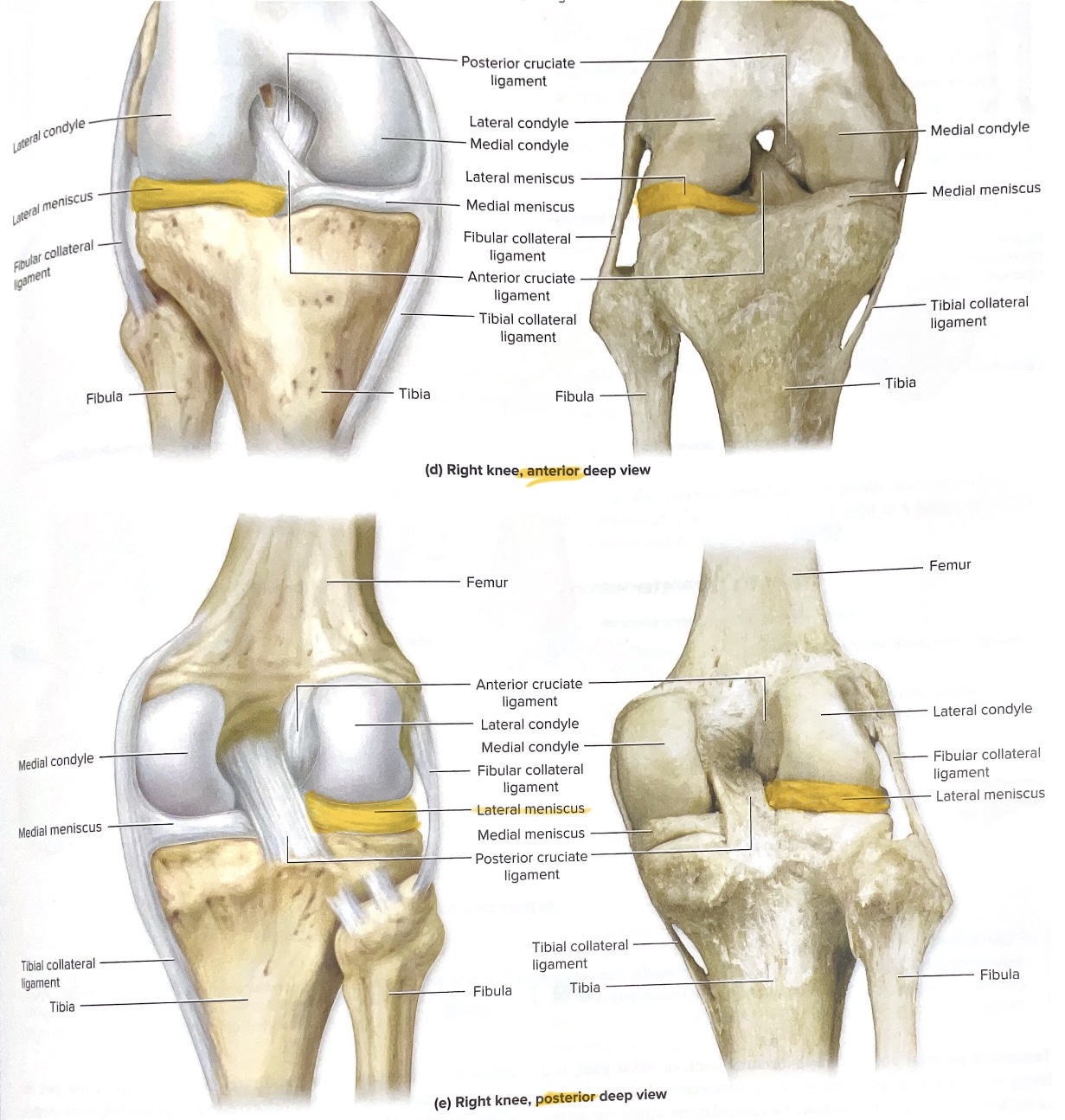
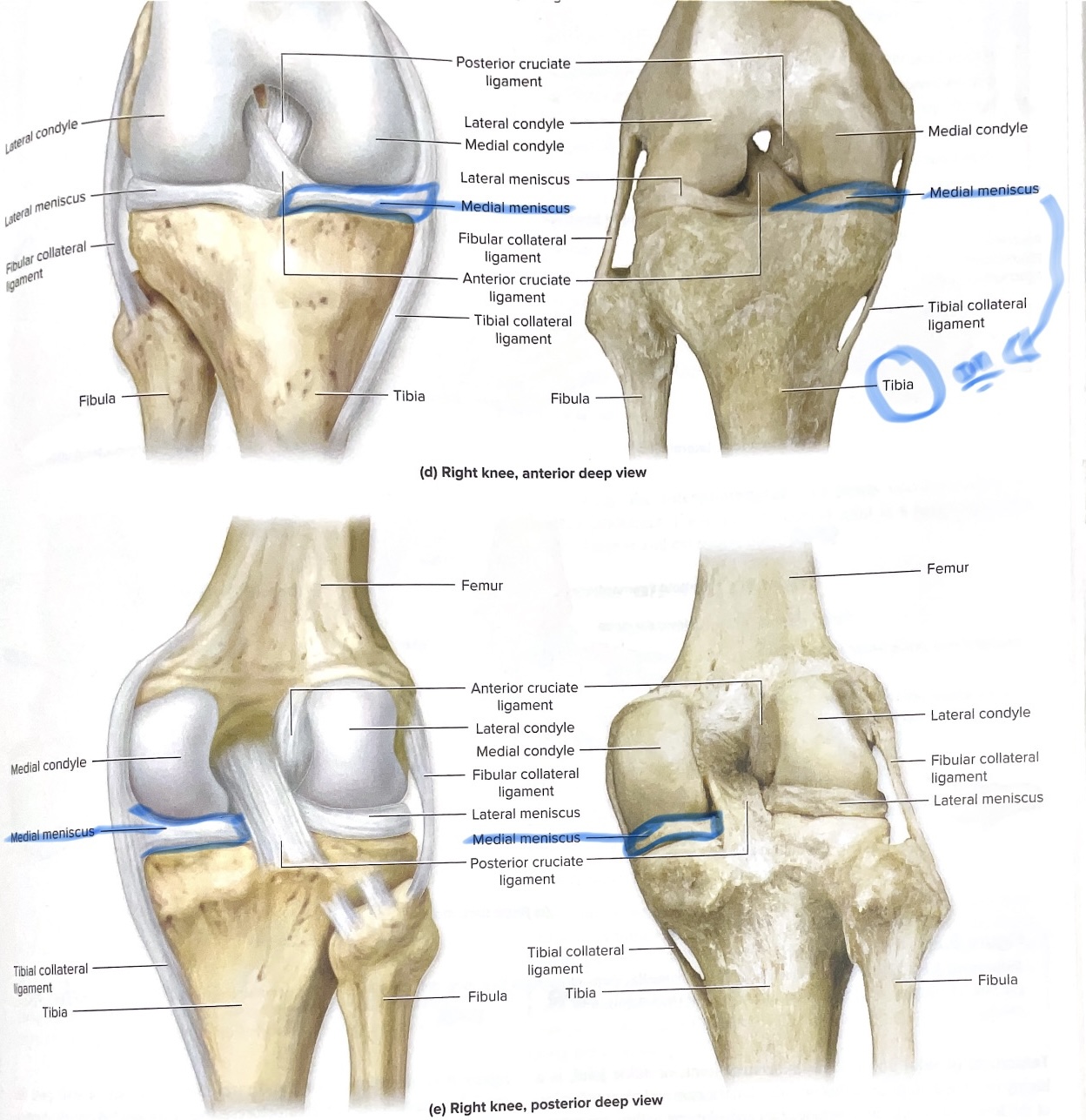
Medial meniscus
Stabilizes medically the knee & shock absorber
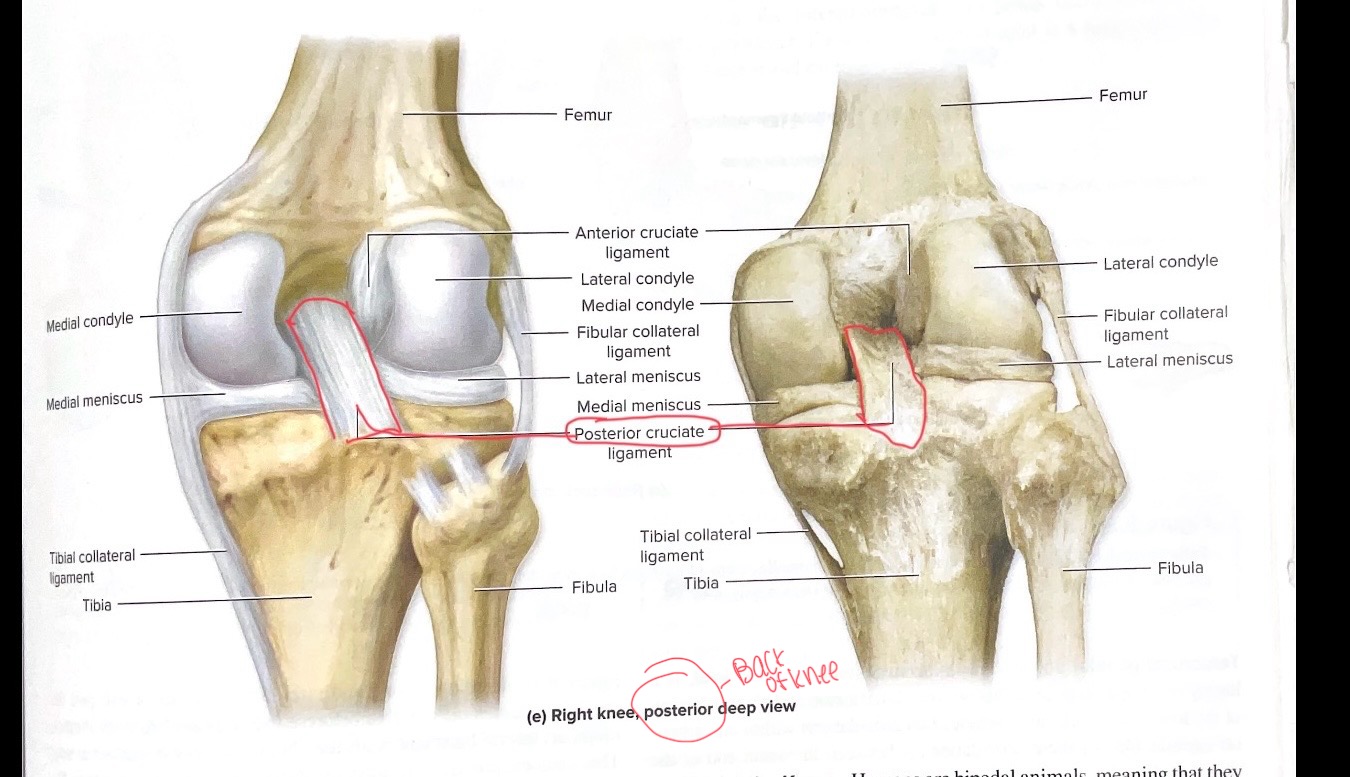
Posterior Cruciate ligament (PCI)
posterior knee
Limits posterior movement of knee
connects the thighbone (femur) to the shinbone (tibia), preventing the shinbone from sliding backward relative to the thighbone. The PCL is the strongest and largest ligament in the knee and is crucial for knee stability
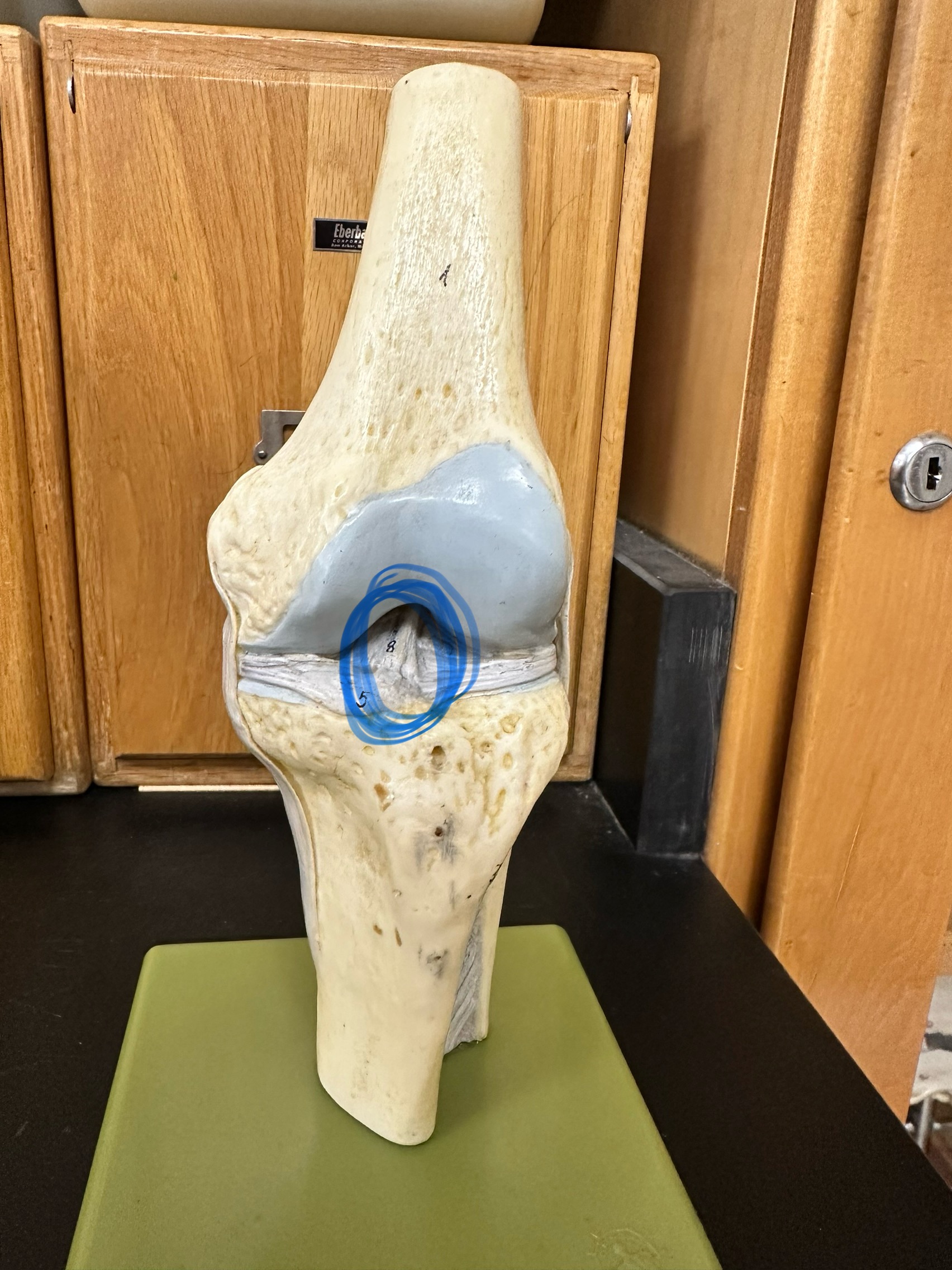
Anterior cruciate ligament

Fibular ( lateral) collate
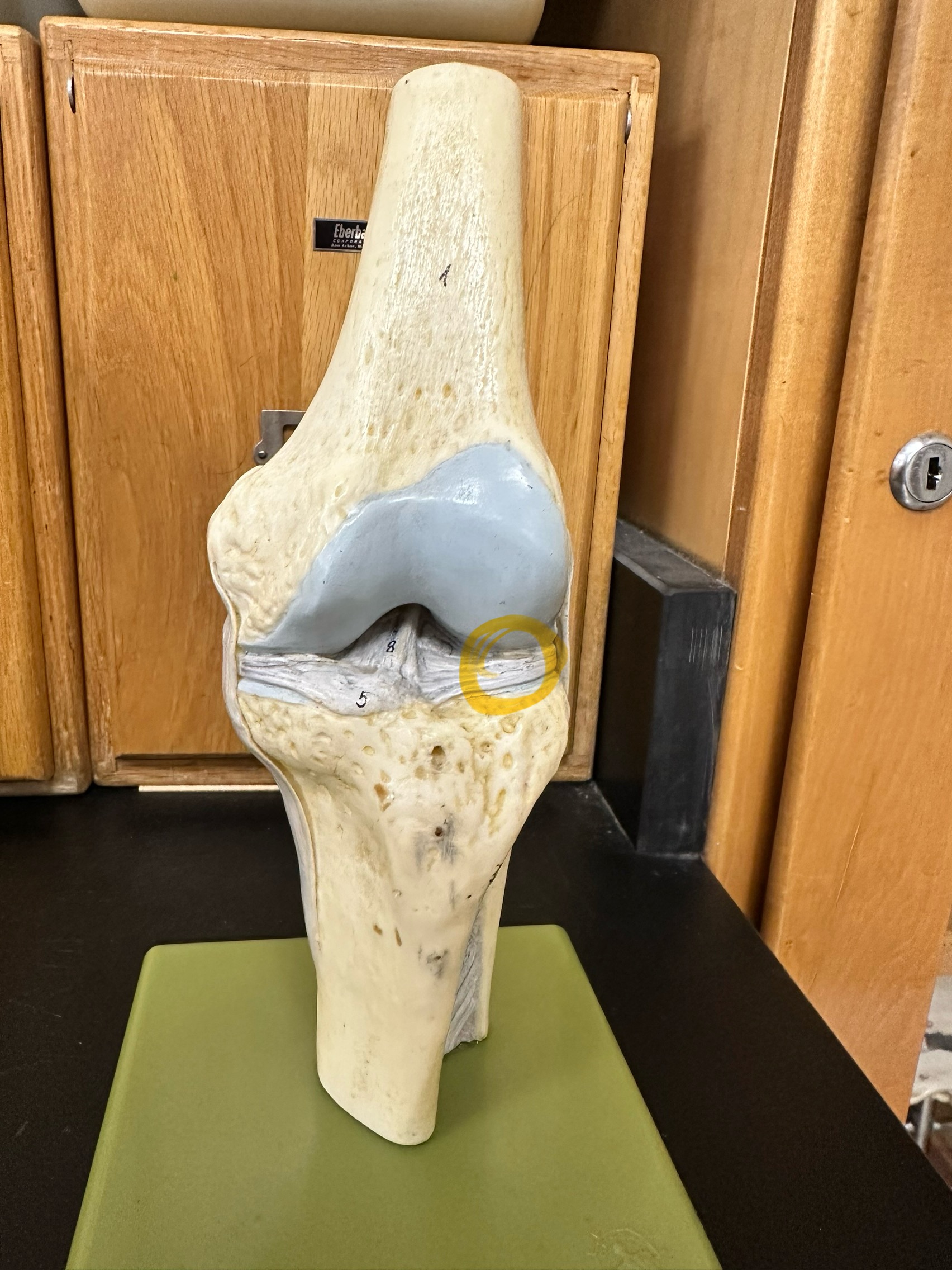
Tibial (medial) collateral ligament
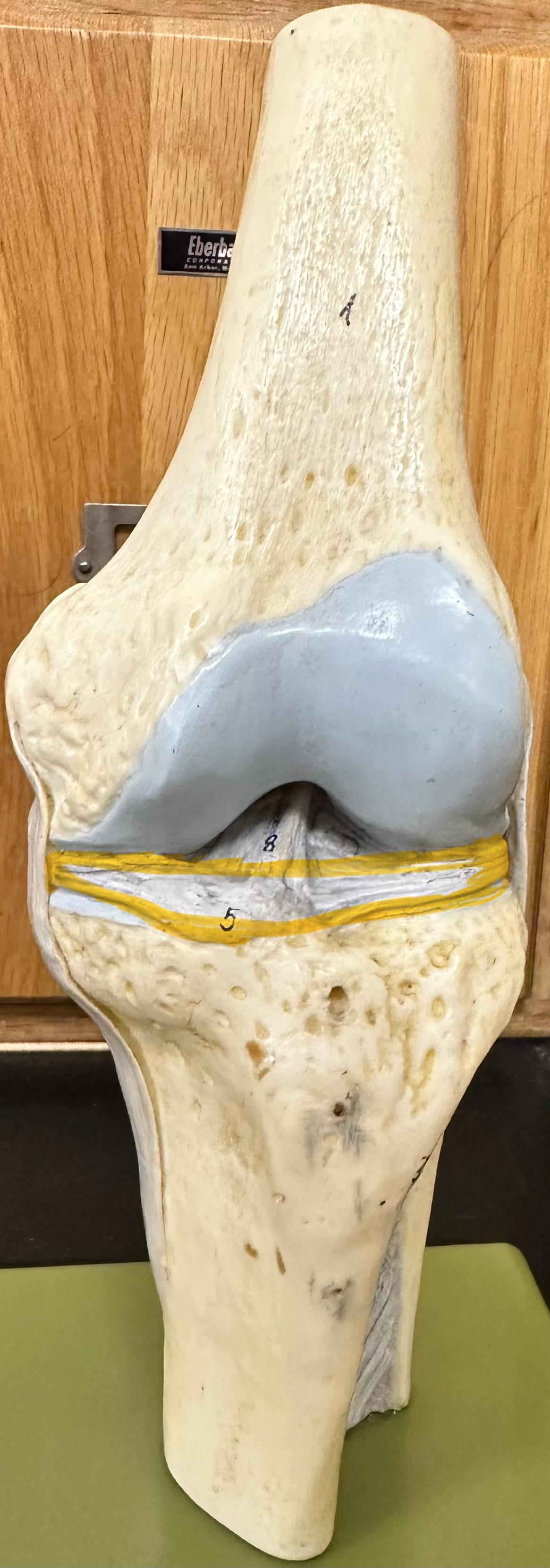
Transverse Ligament
Helps stabilize lateral and medial meniscus