Chemistry Vocab: Polar vs Non-Polar Molecules and IMFs
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
molecule
a group of two or more atoms bonded together, representing the smallest fundamental unit of a chemical compound
polar molecule
a molecule with an uneven distribution of charge, resulting in a positive and a negative end (dipole)
non-polar molecule
a molecule with an even distribution of charge, lacking distinct positive or negative ends
hydrophillic
a term describing substances that mix well with water, typically polar molecules
hydrophobic
a term describing substances that do not mix well with water, typically non-polar molecules
intermolecular forces
the attractions between molecules that influence their physical properties, such as boiling and melting points
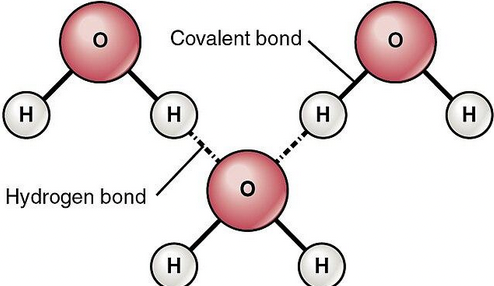
hydrogen bond
a strong type of dipole-dipole interaction that occurs when hydrogen is bonded to highly electronegative atoms like oxygen, nitrogen, and fluorine
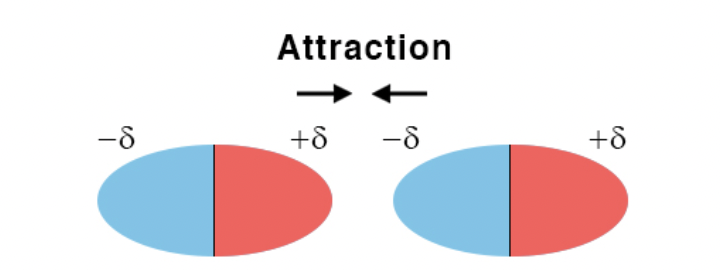
dipole-dipole interaction
an attractive force between the positive end of one polar molecule and the negative end of another polar molecule
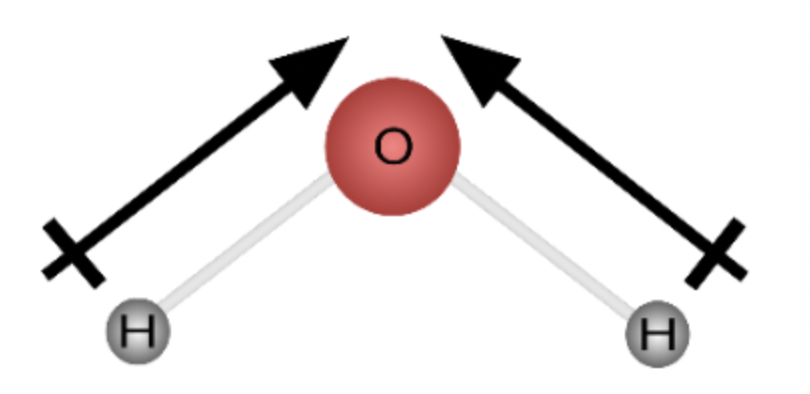
dipole moment
an occurrence in a molecule where one end is slightly positive and the other is slightly negative due to the unequal sharing of electrons
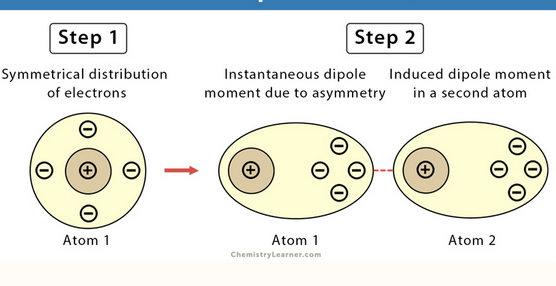
London dispersion forces
the weakest type of intermolecular force present in all molecules, resulting from temporary shifts in electron density, particularly significant in non-polar molecules
solubility
the ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent, often influenced by the polarity of the molecules involved
biochemistry
the branch of science that explores the chemical processes within and related to living organisms
pharmacology
the study of drugs and their effects on living systems, including how molecular interactions influence drug formulation and efficiency
environmental science
the study of the interactions between the physical, chemical, and biological components of the environment, including the impact of substances like pollutants