Function and Structure of the Brain
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
- location structure of brain + brain imaging techniques
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
b
What is localisation of functions?
Broad principle that specific regions of the brain are responsible for specific functions
What are the different structures of the brain?
3 main parts
Hindbrain
Midbrain
Forebrain

Where is the hindbrain and what does it do?
located: lower back part of the brain
Coordinates sensory and motor messages entering and leaving the spinal cord and is responsible for balance and coordination
Where is the midbrain and what does it do?
located: top portion of the brain stem
Receives sensory messages from all the senses,, except smell.
Sends information to the forebrain
Also has reticular formation:
the network of nuclei located within the length of the brain stem hat helps maintain wakefulness and alertness
Where is the forebrain and what does it do?
located: the ‘upper’ part of the brain. Largest part of the brain
Plays key role in cognition, emotion, behaviour, and processing sensory information.
Has the cerebrum inside
What are the structures of the Hindbrain?
Medulla
Cerebellum
What is the medulla?
lowest part of the brain stem that relays information between spinal cord and brain and regulates the respiratory and cardiovascular systems
What is the cerebellum?
Structure in the lower back of the brain
Involved in balance judging distance and coordination of fine motor movement
What is the cerebrum?
Largest part of the brain, consisting of white matter on the insidide and the cerebral cortex on the outside,
Thalamus and hypothalamus inside.
What is the thalamus?
double lodged structure located just above the brain stem that receives sensory information, except smell, and transmits information to the cerebral cortex
What is the hypothalamus?
structure sitting below the thalamus that regulates sleep, eating, body temp and sex.
Structure of brain
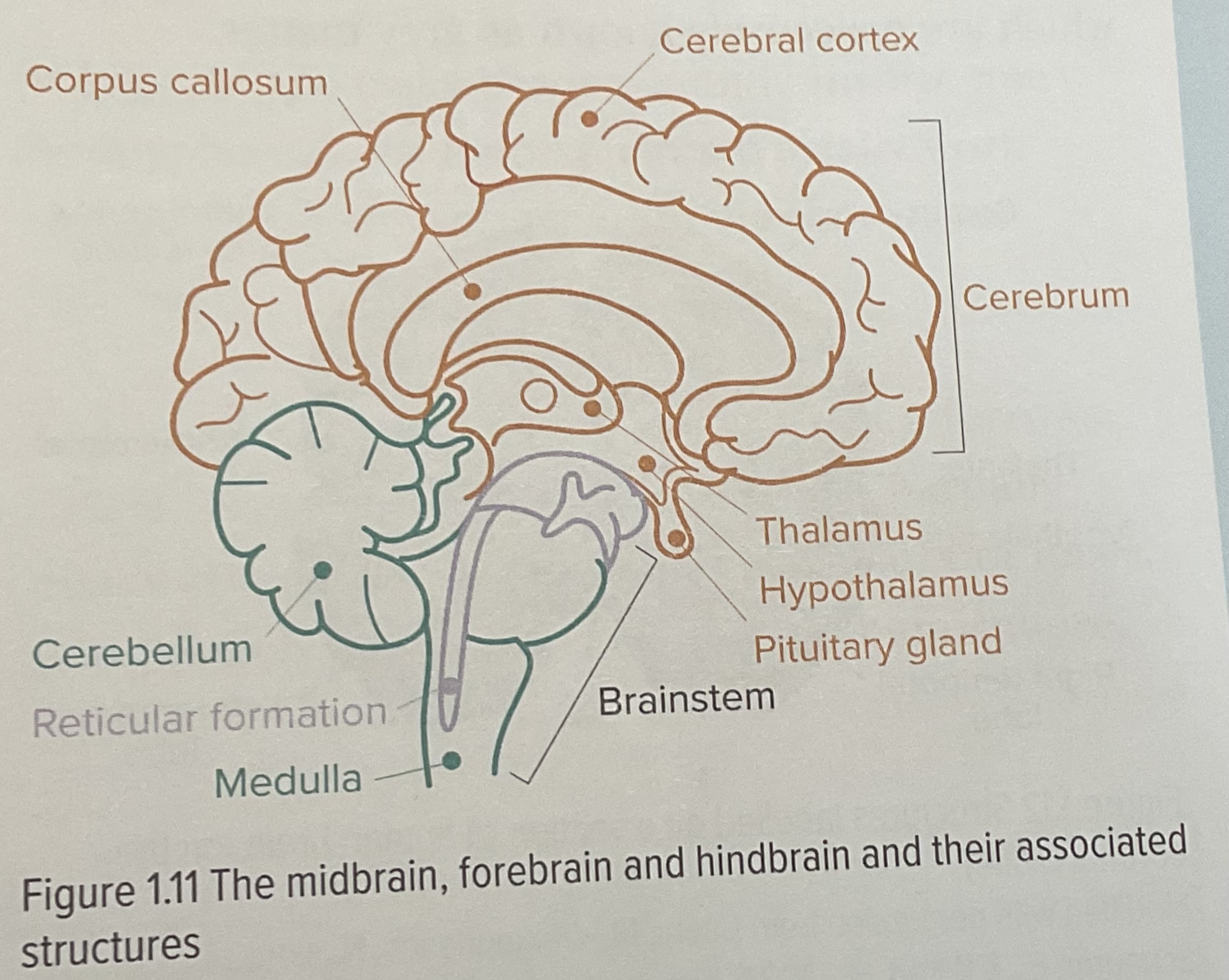
What is the cerebral cortex?
outermost layer of the brain. Made up of nerve cell tissue that is responsible for higher order thinking.
What are the cerebral hemispheres?
two halves of the cerebrum
Connected by corpus callosum
Left & Right hemispheres
What is the corpus callosum?
Thick band of nerve fires connecting the cerebral hemispheres of the brain and. Allowing the transfer of information between them.
What is hemispheric specialisation?
Concept that each hemisphere has greater control over certain functions
What is contra lateral control?
arrangement whereby each hemisphere of the brain controls the opposite side of the body.
Left hemisphere controls right
Right hemisphere controls left
What is the left hemisphere responsible for?
controlling movement of the right side of the body
Producing speech
Language comprehension
Writing
Reading
Analytical thinking
Sequential processing
Reasoning (problem solving, decision-making, logical thinking etc..)
Mathematic processes
What is the right hemisphere responsible for?
controlling movement of the left side of the body
Spatial reasoning
Visualisation
Creativity
Creative drawing
Art and music appreciation
Recognising global patterns
Facial recognition
Expressing emotion
Recognising the emotion of others
What are the main Structures of the limbic system?
forebrain but 2 main structures:
Amygdala
Hippocampus
What is the amygdala responsible for?
controles fear and agression
What is the hippocampus responsible for?
Memory formation
What are the four lobes of the brain?
Frontal lobe
Temporal lobe
Occipital lobes
Parietal Lobes
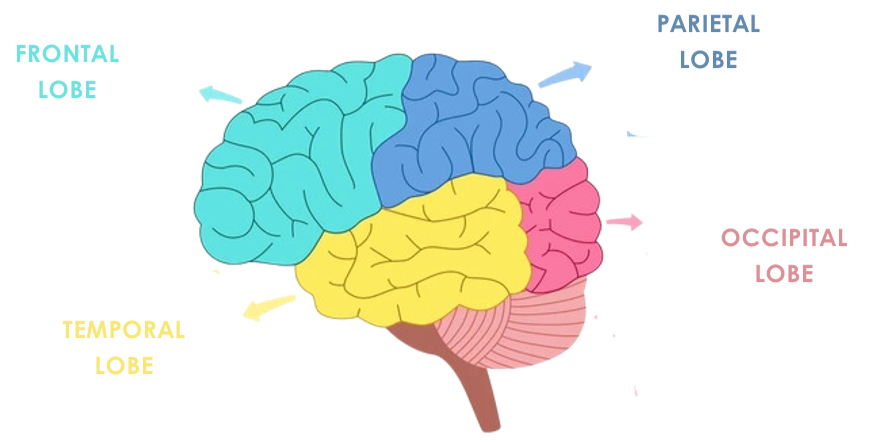
What is the frontal lobe responsible for?
voluntary movement
Planning and decision making
Problem solving
Organise information
Recognition of emotions
Speech production
Impulse control
What is the temporal lobe responsible for
understanding speech
Interprets auditory information
Processing sense of smell
Facial recognition
Partial responsibility for recognition of emotions
Involved in long-term memory formation
What are the occipital lobes responsible for
visual perception and processing
Interpreting visual information
Involved in facial recognition
Depth perception
What is the parietal lobe responsible for?
processing sensory information
Spatial awareness
Proprioception
Integrating sensory information
What is localisation of functions?
Refers to the idea that certain functions have certain localisation or areas within the brain
What are the 7 localised areas? (That we focus on)
Broca’s area
Wernicke’s area
Pre-frontal cortex
Primary motor cortex
Primary sensor cortex
Primary auditory cortex
Primary visual cortex
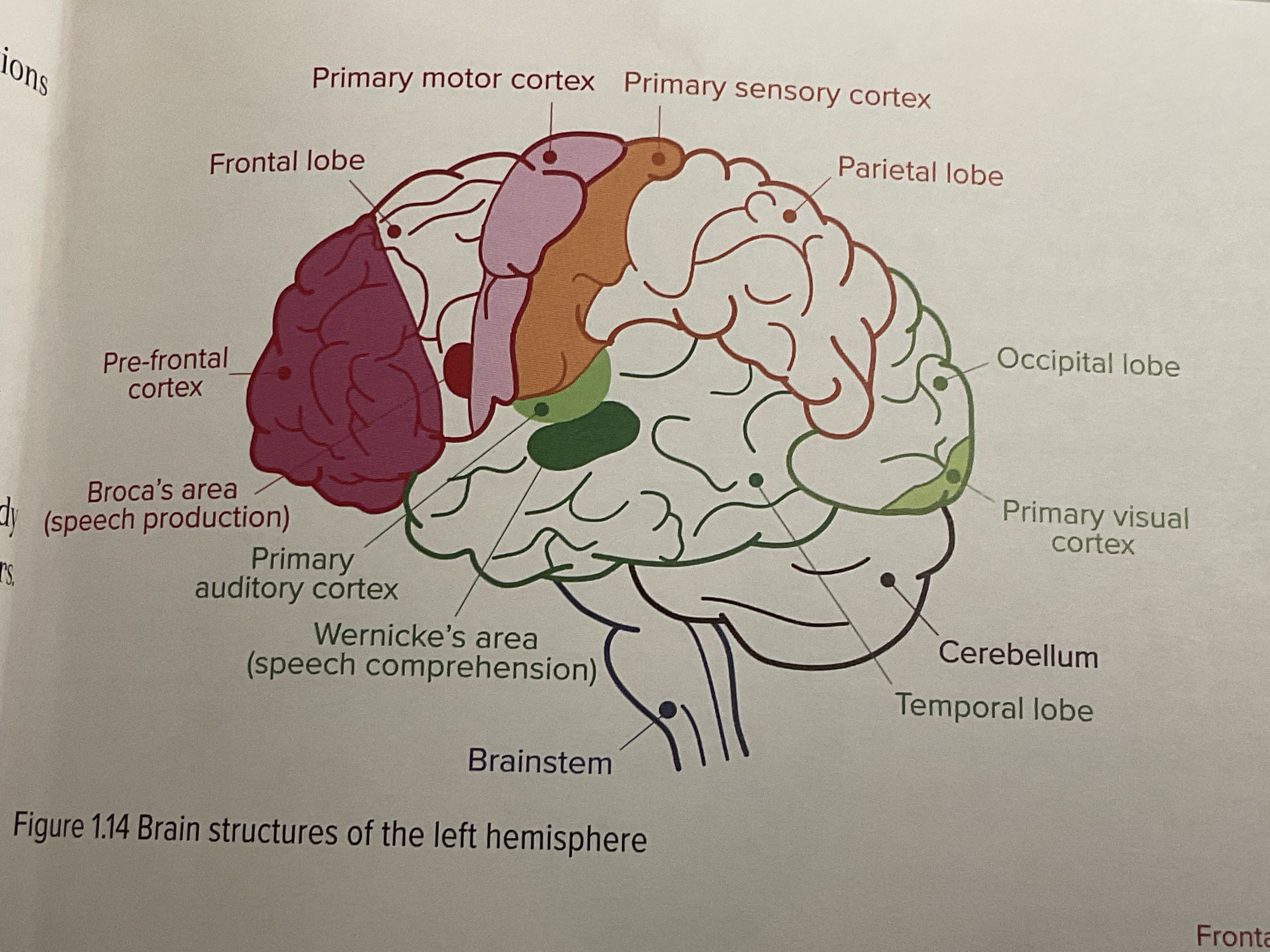
What is Broca’s area responsible for?
Location: adjacent to primary motor cortex in left frontal lobe
Function: controls the fine muscles responsible for clear, articulate speech
What is wernicke’s area responsible for?
location: adjacent to primary auditory cortex in left temporal lobe
Function: responsible for understanding of language and the production of meaningful speech
What is the pre-frontal cortex responsible for?
front layer of the frontal lobes that coordinates executive functions
What is the primary motor cortex responsible for?
strip of cerebral cortex running through the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movement of the body
What is the primary sensory cortex responsible for?
a strip of cerebral cortex running through the parietal lobes that perceives and processes sensory information
What is the primary auditory cortex responsible for?
an area within both temporal lobes that perceives and processes auditory information that is received from the ears
What is the visual cortex responsible for?
an area within both occipital lobes that perceives and processes visual information that is received from the eyes
What is broca’s aphasia?
the impairment in the ability to produce articulate speech due to damage of broca’s area
What is Wernicke’s aphasia?
The impairment in the ability to understand language and produce meaningful speech due ti damage of wernicke’s area