Tissue Types w/ Function & Location
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
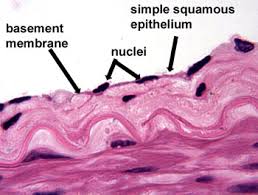
Function w/ name
Simple Squamous - allows for easy diffusion and filtration
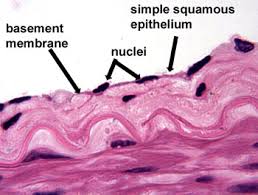
Location w/ name
Simple Squamous - Air sacks of lungs, walls of blood capillaries/blood vessels
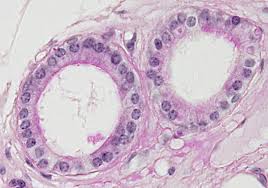
Function w/ name
Simple Cuboidal - Absorption, secretion, and protection
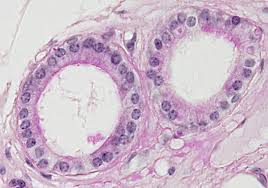
Location w/ name
Simple Cuboidal - Surface of ovaries, kidney tubules, ducts, and tubes
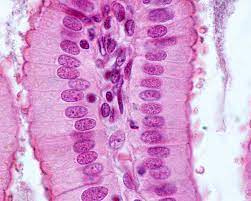
Function w/ name
Simple Columnar - Absorption and secretion of substances in kidneys, secretion of mucus
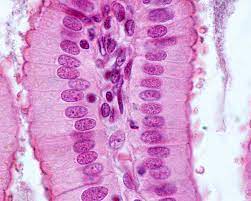
Location w/ name
Simple Columnar - Lining of uterus, stomach, and intestines
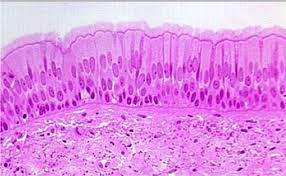
Function w/ name
Pseudostratifed Columnar - Protects foreign particles from entering respiratory airways and the secretion of mucus
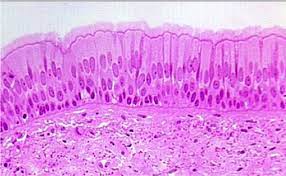
Location w/ name
Pseudostratified Columnar - Lining of respiratory passageways
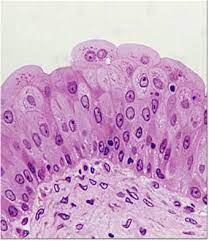
Function w/ name
Transitional - Allows tissue to expand and contract
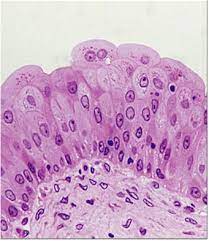
Location w/ name
Transitional - Inner lining of bladder, ureters, and urethra
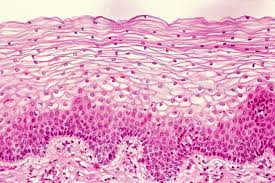
Function w/ name
Stratified Squamous - Protects against microorganisms from invading underlying tissue; abrasion resistance
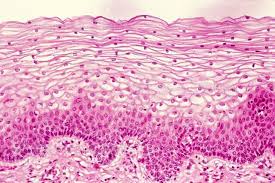
Location w/ name
Stratified Squamous - Outer layer of skin, lining of oral cavity, and the throat
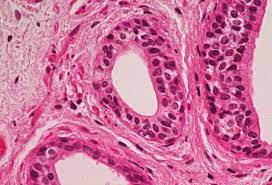
Function w/ name
Stratified Cuboidal - Protection, secretion, and excretion
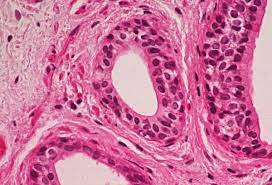
Location w/ name
Stratified Cuboidal - Lining of larger ducts in mammary, sweat, and salivary glands; also in pancreas
Function w/ name
Stratified Columnar - Protection of underlying tissues
Location w/ name
Stratified Columnar - Vas deferens, parts of the male urethra, and parts of the pharynx
Function w/ name
Merocrine Gland - secretes watery, protein-rich fluid
Location w/ name
Merocrince Gland - Sweat, salivary, pancreatic glands (all over the body)
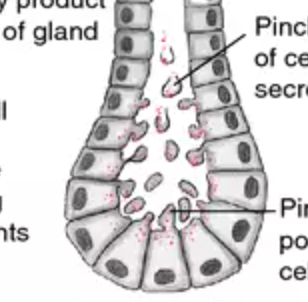
Function w/ name
Apocrine Gland - Procuced pheromones (body odor) and secretes portions of cells
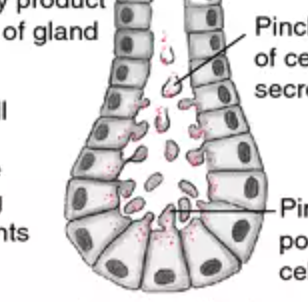
Location w/ name
Apocrine Gland - Face, breasts, scalp, axilla, and perineum
Function w/ name
Holocrine Gland - Secretes secretory products and whole cells
Location w/ name
Holocrine Gland - Breasts and some sweat glands
Function w/ name
Loose Connective - Binds organs together and holds tissue fluids in place
Location w/ name
Loose Connective - Beneath the skin, between muscles, beneath epithelial
Function w/ name
Dense Regular Connective - Connects different organs and muscles and transmits stress or forces over long distances
Location w/ name
Dense Regular Connective - Tendons, ligaments, deeper skin layers
Function w/ name
Dense Irregular Connective - Makes the skin resistant to tearing caused by stretching pressure
Location w/ name
Dense Irregular Connective - Dermis (deep layers of skin)
Function w/ name
Adipose - Protects, insulates, and stores fat
Location w/ name
Adipose - Beneath the skin, around kidneys, behind eyeballs, the surface of the heart
Function w/ name
Hyaline - Supports, protects, provides framework
Location w/ name
Hyaline - Nose, ends of bones, and rings in the walls of respiratory passages
Function w/ name
Elastic - Supports, protects, and provides a flexible framework
Location w/ name
Elastic - Framework of external ear, parts of the larynx
Function w/ name
Fibrocartilage - Supports, protects, and absorbs shock
Location w/ name
Fibrocartilage - Between parts of the spinal column and parts of the flexible girdle
Function w/ name
Bone - Supports, protects, provides frameworks
Location w/ name
Bone - Skeleton
Function w/ name
Blood - Transports substances and helps maintain a stable internal environment
Location w/ name
Blood - everywhere
Function w/ name
Skeletal - voluntary movements
Location w/ name
Skeletal - Usually attached to bones
Function w/ name
Smooth - Involuntary movements
Location w/ name
Smooth - Walls of hollow internal organs, spindle-shaped appearance
Function w/ name
Cardiac - Heart movement
Location w/ name
Cardiac - Heart muscle, striated and inter-calculated disk
Function w/ name
Nervous - Sends and receives info to and from brain
Location w/ name
Nervous - Brain, spinal cord, and nerves
Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
The space between cells; it allows for cells to migrate to different places
Fibroblasts
Produces fiber for the matrix
Macrophages
Clears foreign objects from particles
Mast Cells
Thick strands of protein that lack elasticity and have great tensile strength
Elastic Fibers
Produces elastin and can stretch and resume shape
Reticular Fibers
Supports the early extracellular matrix during the formation of scar tissue, the healing of wounds, and the general development
4 Main Tissue Types
Connective, Epithelial, Muscle, Nervous
3 Main Components of Connective
Ground substance, fibers, cells
What makes up the ecm?
Ground substance and fibers
Greatest differentiate of everything vs. epithelial?
Epithelial is TIGHTLY PACKED
Basement Membrane
A sheet-like form of ecm that underlines the epithelia and endothelia and it surrounds muscle and fat
Is cartilage avascular or vascular?
Avascular
Is dense connective avascular or vascular?
Poorly Vascularized
Can muscle tissue contract?
Yes, it gets shorter