Cardiovascular and Respiratory Systems
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/70
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
1
New cards
What does the cardiovascular system do?
transports food, hormones, metabolic wastes and gases to and from cells
2
New cards
What does blood do?
helps to maintain homeostasis
3
New cards
What does blood consist of?
red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma
4
New cards
What's another word for red blood cells?
erythrocytes
5
New cards
What's another word for white blood cells?
leukocytes
6
New cards
What's another word for platelets?
thrombocytes
7
New cards
What do erythrocytes do?
transport oxygen from the lungs to all of the living tissues of the body and carry away carbon dioxide
8
New cards
What do erythrocytes contain?
hemoglobin
9
New cards
where are erthrocytes produced?
bone marrow
10
New cards
What does hemoglobin do?
combines with oxygen and transports it from the lungs to body tissues
11
New cards
What do leukocytes do?
protect the body against invading organisms and remove dead cells and other waste from the body
12
New cards
What do leukocytes play a huge role in?
the immune system and the immune response
13
New cards
What are the types of leukocytes?
neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes
14
New cards
What do thrombocytes look like?
tiny colorless disk-shaped particles
15
New cards
How do thrombocytes prevent blood loss?
they form platelet plugs and promote the formation of clots
16
New cards
What is plasma?
liquid part of blood
17
New cards
What does plasma look like?
yellowish clear liquid
18
New cards
What does plasma do?
it serves as a transport medium for glucose, lipids, amino acids, hormones, metabolic end products, carbon dioxide (CO2) and oxygen (O2)
19
New cards
What are blood vessels?
hollow utensils for carrying blood
20
New cards
What are the types of blood vessels?
arteries, veins, capillaries
21
New cards
What do arteries do?
carry oxygen rich blood away from the heart
22
New cards
What do veins do?
carry low-oxygen blood back to the heart
23
New cards
What are the smallest blood vessels?
capillaries
24
New cards
What do capillaries do?
exchange oxygen, carbon dioxide and other molecules between blood and tissue
25
New cards
How are capillaries permeable?
various materials can easily be diffused into and out of them
26
New cards
What are the different layers of cardiac muscle?
endocardium, myocardium, and epicardium
27
New cards
What is the inner layer of the heart?
endocardium
28
New cards
What is the muscle layer of the heart?
myocardium
29
New cards
What is the outer surface of the heart?
epicardium
30
New cards
What is diastole?
relaxation of the heart
31
New cards
What is systole?
contraction of the heart
32
New cards
A bpm of less than 60 means what?
bradycardia
33
New cards
A bpm of more than 100 means what?
tachycardia
34
New cards
What is arteriosclerosis?
arterial walls gradually thicken and arterial fibers decline
35
New cards
What is atherosclerosis?
the build-up of plaque on the inner lining of the arteries causing them to narrow and be less flexible
36
New cards
What is coronary heart disease?
when the arteries which supply blood to the heart muscle (the coronary arteries) become hardened and narrowed
37
New cards
What is a stroke?
blood clot in the brain
38
New cards
What is hypertension?
high blood pressure
39
New cards
What are murmurs?
abnormal heart sounds
40
New cards
What is a heart attack?
blockage of coronary artery
41
New cards
What is the pathway of blood through the heart?
superior vena cava, right atrium, tricuspid valve, right ventricle, pulmonary valve, pulmonary artery, lungs for oxygenation, pulmonary veins, left atrium, mitral/bicuspid valve, left ventricle, aortic valve, aorta
42
New cards
What is the flow of air through the respiratory system?
nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs
43
New cards
Where is the pharynx located?
in the throat
44
New cards
What does the pharynx house?
tonsils
45
New cards
What are the 3 sections of the pharynx?
nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx
46
New cards
What does the nasopharynx connect?
nose and pharynx
47
New cards
What is the oropharynx located?
back of throat
48
New cards
What does the laryngopharynx connect?
esophagus and larynx
49
New cards
What is the larynx?
voice box
50
New cards
What is the larynx composed of?
epiglottis, hyoid bone, thyroid membrane, thyroid cartilage (Adam's apple), cricoid cartilage, and vocal cords
51
New cards
What does the trachea divide into?
right and left primary bronchi
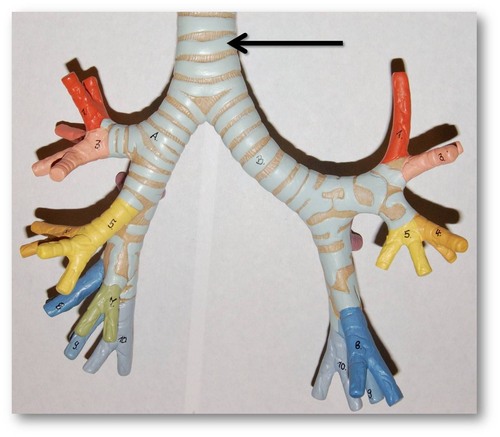
52
New cards
What is are bronchi?
large air tubes leading from the trachea to the lungs which convey air to and from the lungs
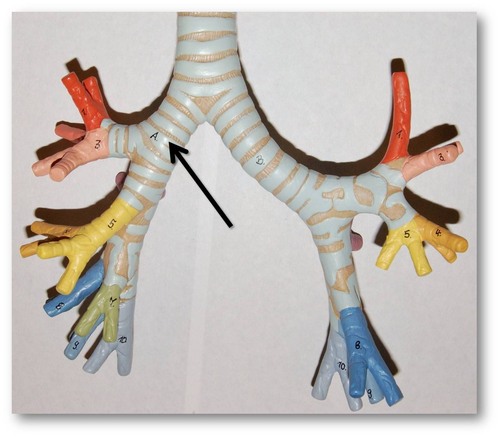
53
New cards
What are a pair of cone shaped organs in the thoracic cavity?
lungs
54
New cards
What does the pleural membrane do?
encloses and protects the lungs
55
New cards
What is the visceral pleural?
deep layer which covers the lungs
56
New cards
What does the alveoli do?
gas exchange
57
New cards
What is emphysema?
a long-term, progressive disease of the lung that primarily causes shortness of breath
58
New cards
What is the primary cause of emphysema?
cigarette smoking
59
New cards
What is asthma?
a chronic disease that affects your airways
60
New cards
What is influenza?
highly contagious viral infection of the upper respiratory system with sudden onset
61
New cards
What is lung cancer?
a disease where tissue in the lung grows out of control
62
New cards
What is the main cause for lung cancer?
exposure to carcinogens in tobacco through smoking or secondhand smoke
63
New cards
What is pneumonia?
inflammation of the alveoli in lungs which also filled w/ fluid
64
New cards
What is tuberculosis?
a common and deadly infectious disease that attacks the lungs and is caused by mycobacterium
65
New cards
What is another word for Carbon Dioxide Poisoning?
hypercapnia
66
New cards
What is Carbon Dioxide Posioning?
a condition where there is too much carbon dioxide (CO2) in the blood
67
New cards
What is Upper Respiratory Infection (URI) also called?
common cold
68
New cards
What is sleep apnea?
condition in which an individual stops breathing while asleep, causing a measurable decrease in oxygen levels
69
New cards
Does sleep apnea most commonly affect men or women?
men
70
New cards
What is laryngitis?
inflammation of the larynx
71
New cards
What is rhinitis?
inflammation of the nasal mucous membrane