Ionic and Metallic Bonding Study Guide
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Ion
An ion is an atom, radical, or molecule that has gained or lost one or more electrons and has a negative or positive charge.
Cation
A positive ion formed when an atom loses one or more electrons.
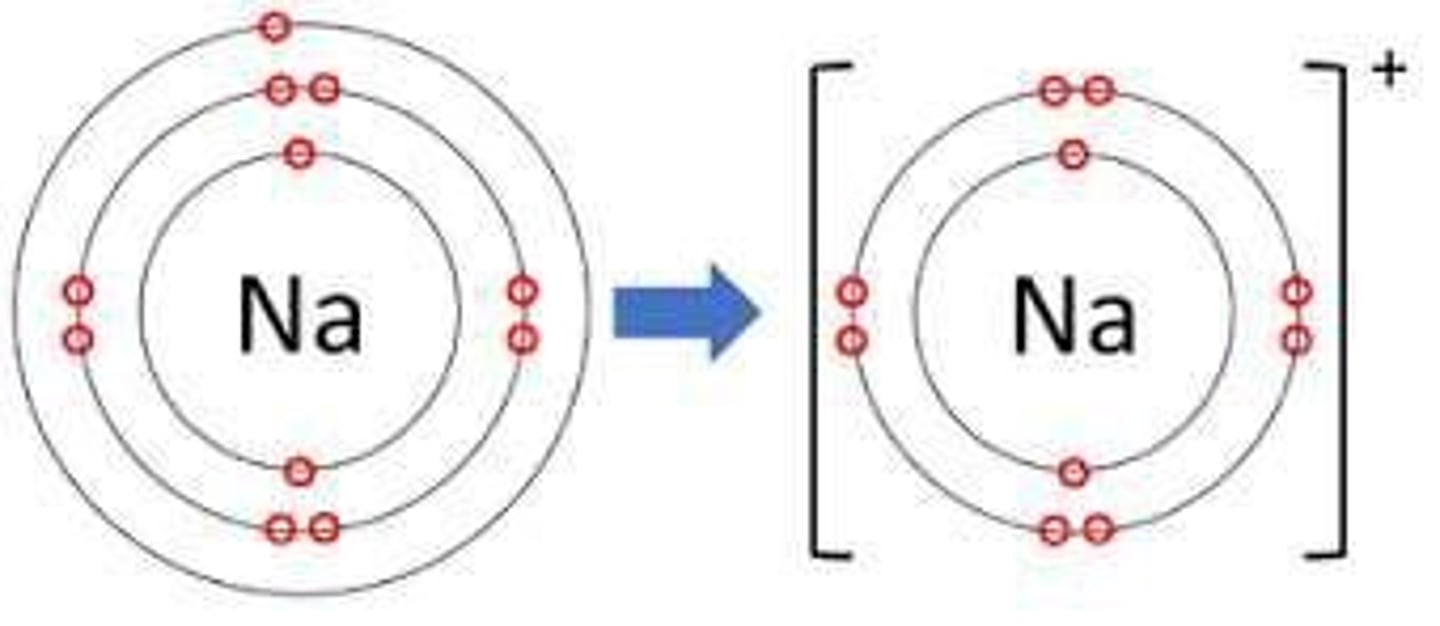
Anion
A negative ion formed when an atom gains one or more electrons.
Octet Rule
The principle that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration with 8 electrons in their outermost shell.
Electron Configuration (EC)
The distribution of electrons in an atom's electron shells and subshells, which determines its chemical properties.
Stable Noble Gas Electron Configuration
An electron configuration that resembles that of a noble gas, typically with 8 electrons in the outermost shell.
Transition Metals
Elements that can form stable cations with different charges and often do not achieve complete octets.
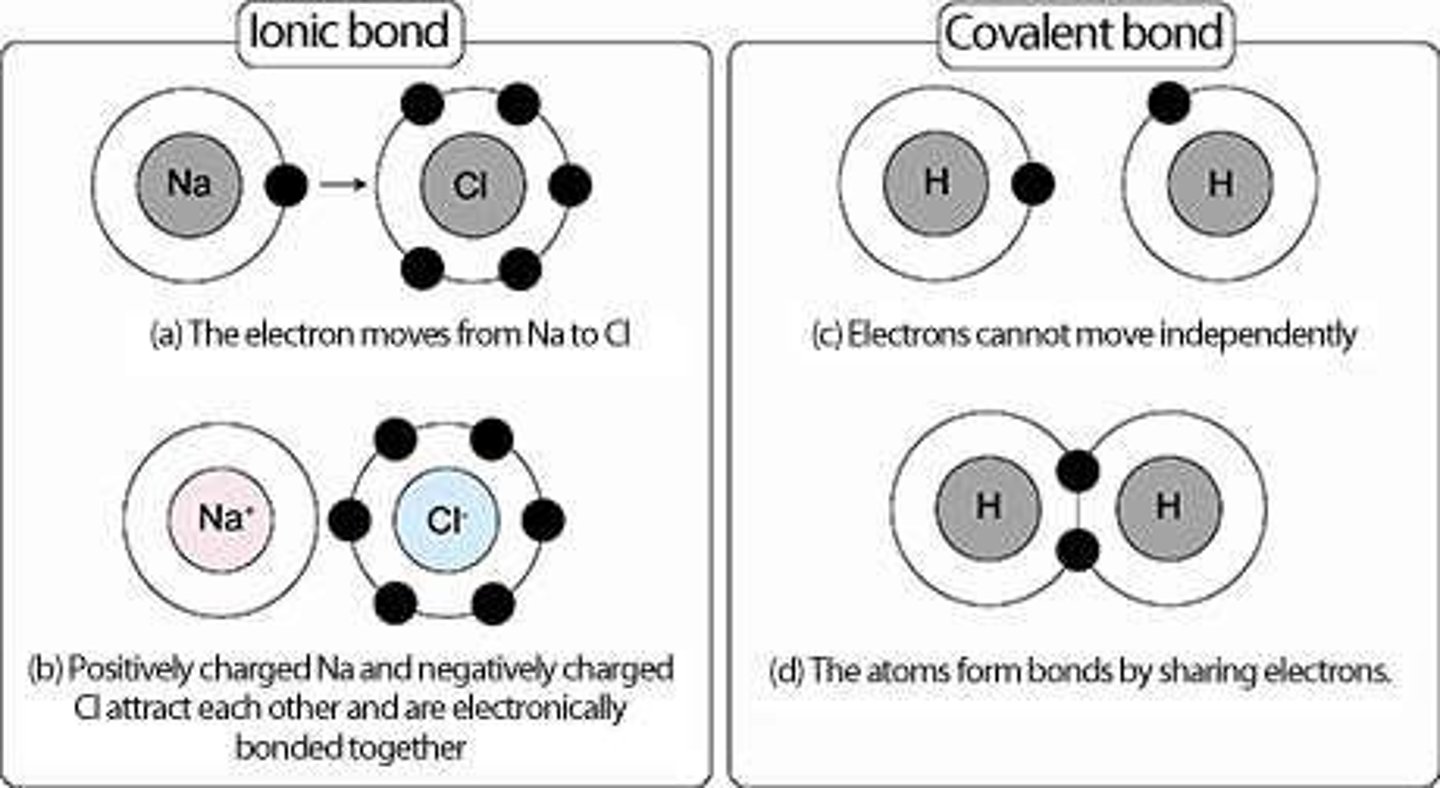
Ionic Bond
A chemical bond formed through the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions.
Metallic Bond
A bond formed by the attraction between positively charged metal ions and the electrons in a metal lattice.
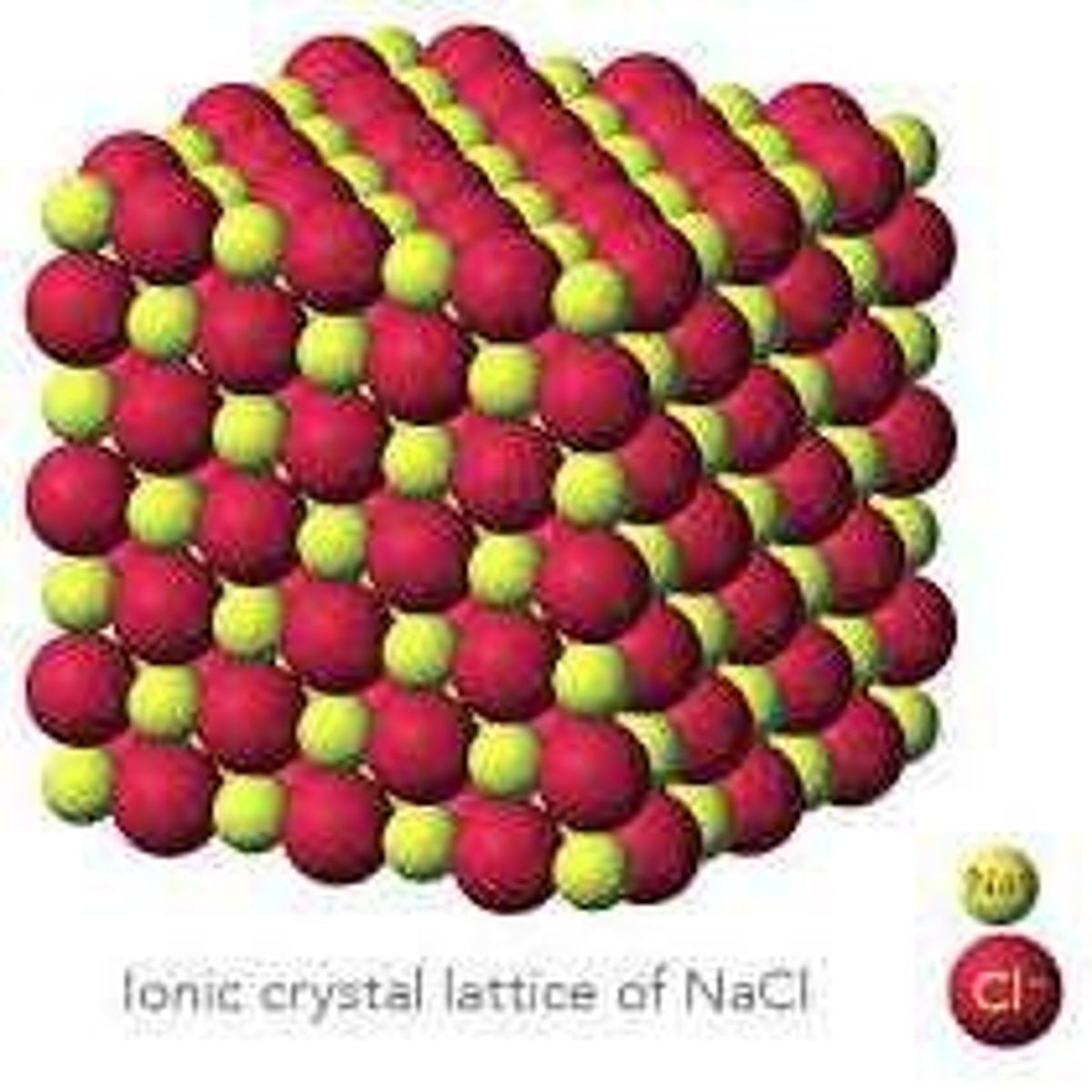
Salt
A typical ionic compound that is electrically neutral and consists of cations and anions held together by ionic bonds.

Crystalline Lattice Structure
The orderly, repeating arrangement of ions in a solid ionic compound, resulting in a tightly packed structure.

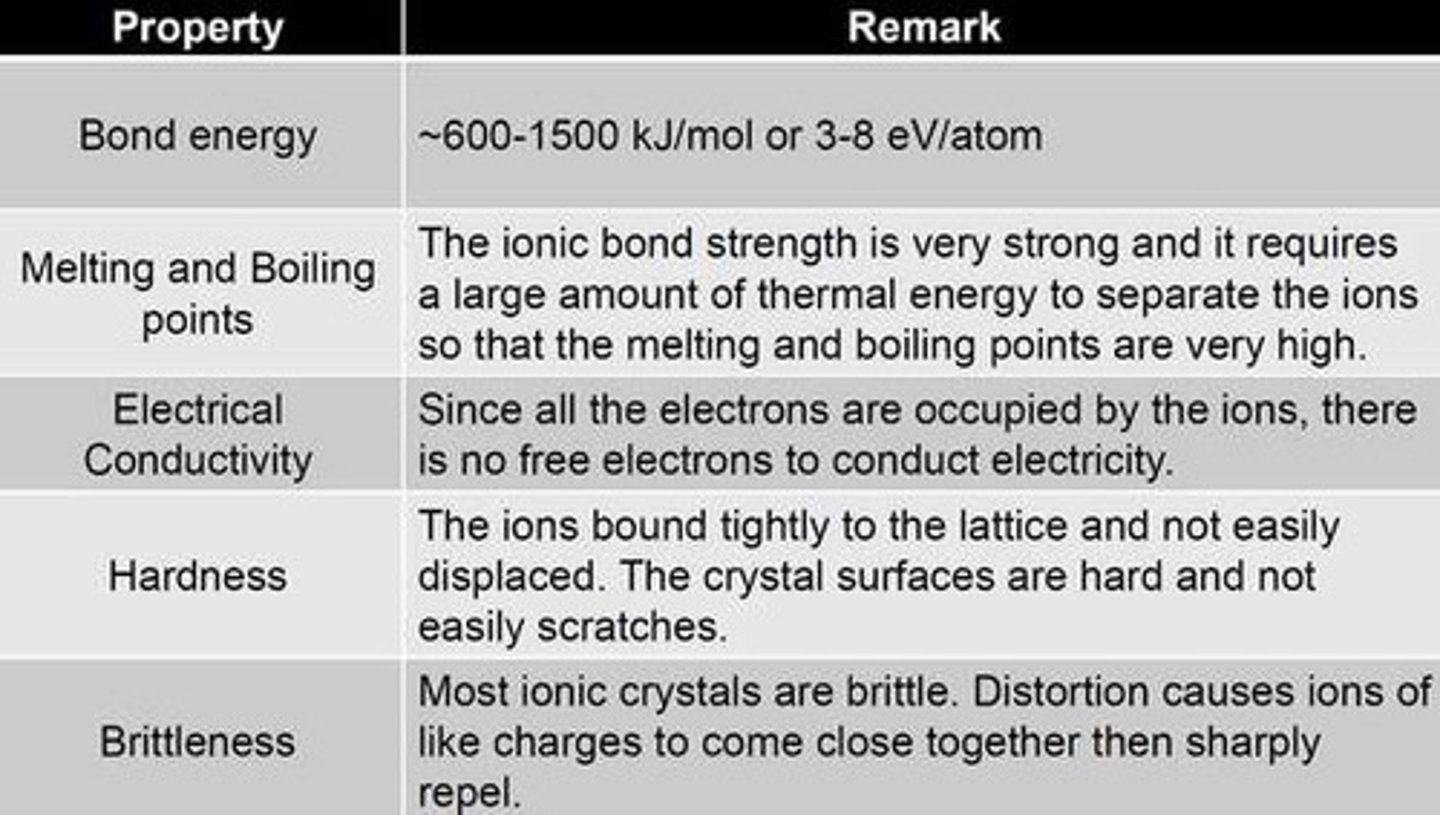
Properties of Ionic Compounds
The characteristics of ionic compounds that depend on the nature of ionic bonds, such as high melting points and electrical conductivity when dissolved in water.
Electrostatic Attraction
The force that attracts oppositely charged ions to each other, forming ionic bonds.
Neutral Sodium and Chlorine Atoms
Atoms that have not gained or lost electrons and thus have no net charge.
Formation of Ionic Compounds
Occurs when one atom transfers electrons to another atom, resulting in the formation of cations and anions.
Different Chemical Properties
The distinct behaviors and reactions of an atom and its ion due to differences in electron configuration.
Number of Valence Electrons
The number of electrons in the outermost shell of an atom, which determines its reactivity and ion formation.
Electrically Neutral
A condition where the total positive charge equals the total negative charge in a compound.
S- and D-Orbitals
Types of atomic orbitals that transition metals can use to form cations.
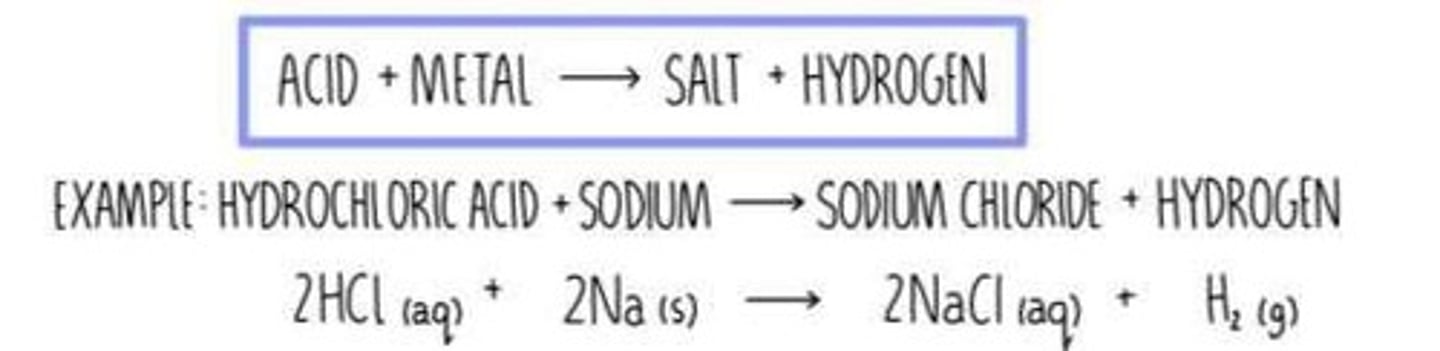
Ionic Compounds and Acids
Ionic compounds can also be formed by immersing a metal into an acid, such as HCl.
Chemical Reactivity
The tendency of an atom to undergo chemical reactions, influenced by its electron configuration.
Properties of Ions
The characteristics of ions that differ from their parent atoms due to changes in electron configuration.
Ionization energy
The energy that it takes to remove the outermost electron from an atom.
Lattice energy
The energy released when ionic bonds are formed as the separated ions bond.
Endothermic process
A process that requires energy to occur.
Exothermic process
A process that releases energy.
Neutral ionic compound
An ionic compound that has no overall charge.
Ionic compounds
Compounds formed by metals and nonmetals that do not consist of molecules but compound units.
Naming ionic compounds
Ionic compounds get the first part of their name from the metal and the second part from the anion with an ending -de.
Examples of ionic compounds
NaCl is sodium chloride, Mg3N2 is magnesium nitride, K2O is potassium oxide.
Transition metal naming
When a transition metal forms two or more ions, the name includes roman numerals to indicate the charge.
Examples of transition metal compounds
CuCl2 is copper (II) chloride, ZnS is zinc (II) sulfide.
Writing ionic formulas
Ionic compounds have a balance of positive and negative charges.
Charge balance in NaCl
In NaCl both ions have a charge of 1.
Charge balance in ZnS
In ZnS both ions have a charge of 2.
Electroneutrality in Mg3N2
Three Mg2+ cations are needed for every two N3− anions for electroneutrality.
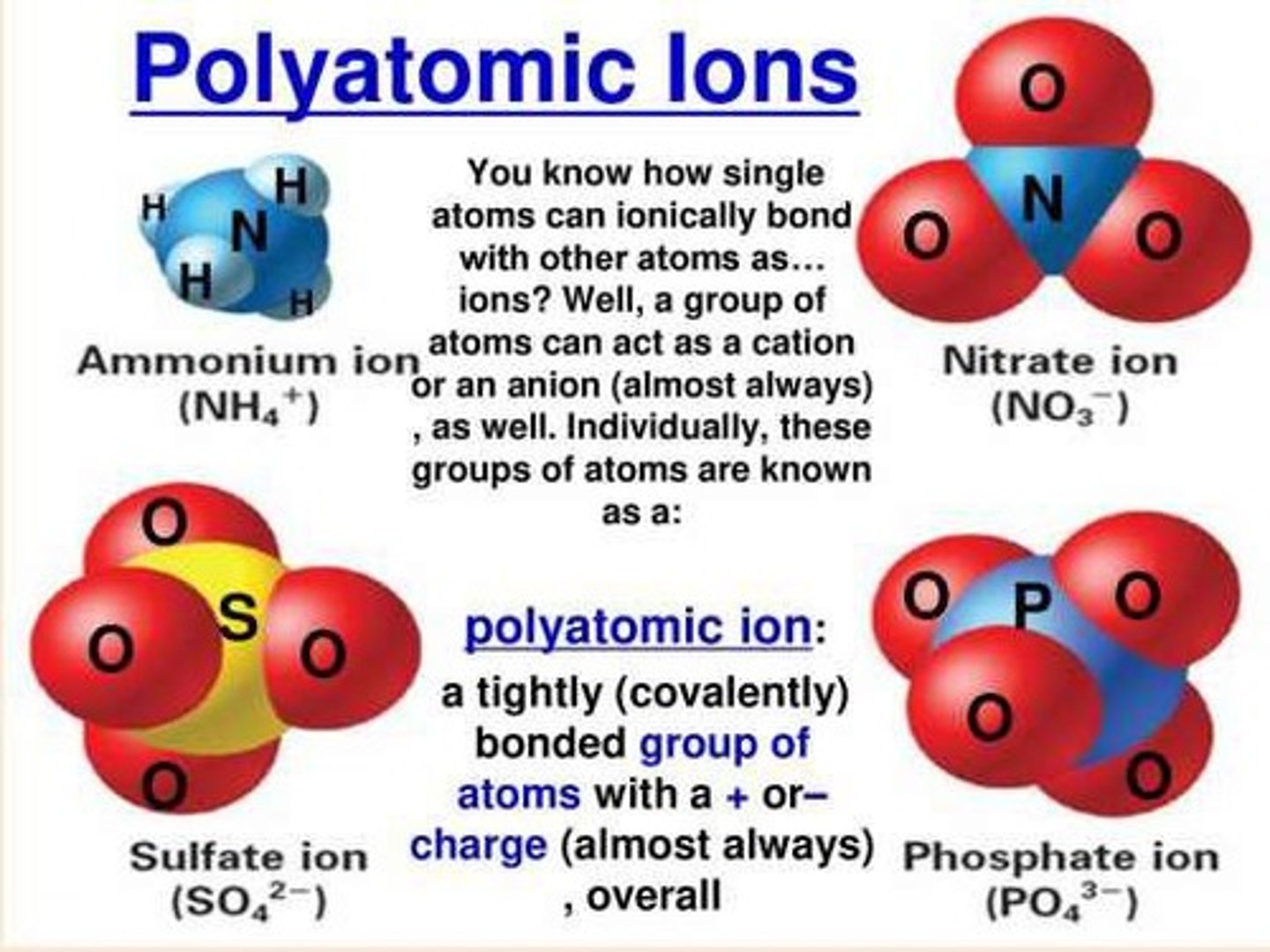
Polyatomic ion
A charged group of two or more bonded atoms that can be considered a single ion.
Example of a polyatomic ion
The nitrate anion, NO3-, is a polyatomic ion.
Crystal structure formation
The energy released when the crystal structure of a salt is formed as the separated ions bond.
Overall process spontaneity
Without lattice energy, there would not be enough energy to make the overall process spontaneous.
Metallic bond
A type of bond that is not described in detail in the notes but is mentioned.
High melting points of ionic bonds
Ionic bonds have high melting points, but metals have even higher melting points.
Ratio of cations to anions
The ratio of cations to anions in ionic compounds is always such that the compound is neutral.