econs atar 11
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
factors affecting demand
price of related goods - complement and substitute goods
expectations of future prices
consumer income - inferior/normal goods
consumer preferences
factors affecting supply
cost of production
technology
price of other goods
number of suppliers
expectation of future prices
supply disruption - natural disaster
law of supply
as the price of a good rises, quantity supplied rises or as price falls, quantity supplied falls
due to profit motive
law of demand
as the price of a good rises, quantity demand decreases and vice versa
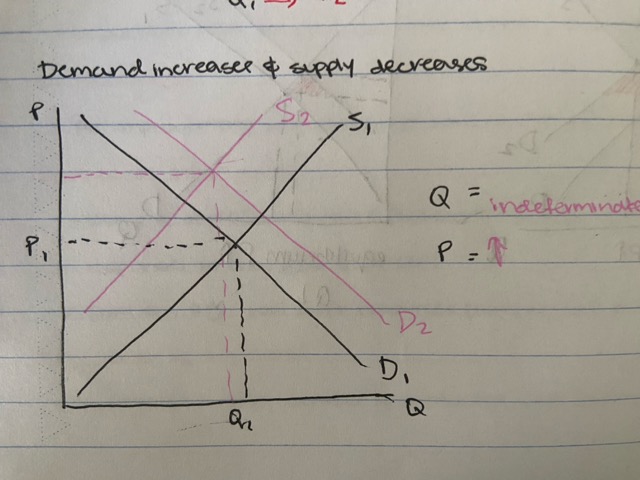
demand increases and supply decreases
banana market
- increase in health awareness and floods in queensland
price increases, quantity indeterminate
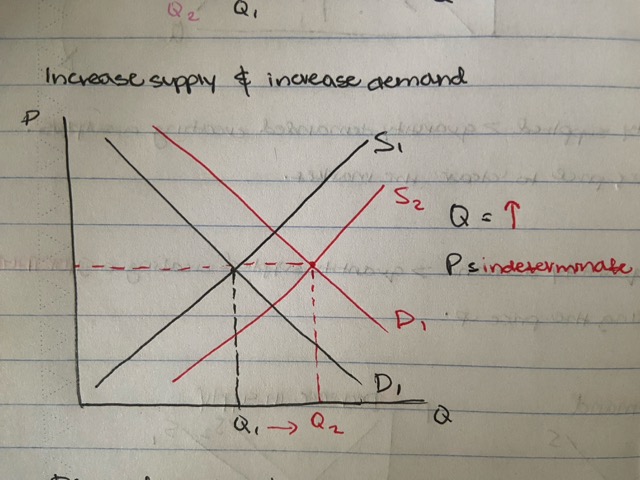
increase in supply and demand
car market
- increase in income and new car companies set up
quantity increases, price indeterminate
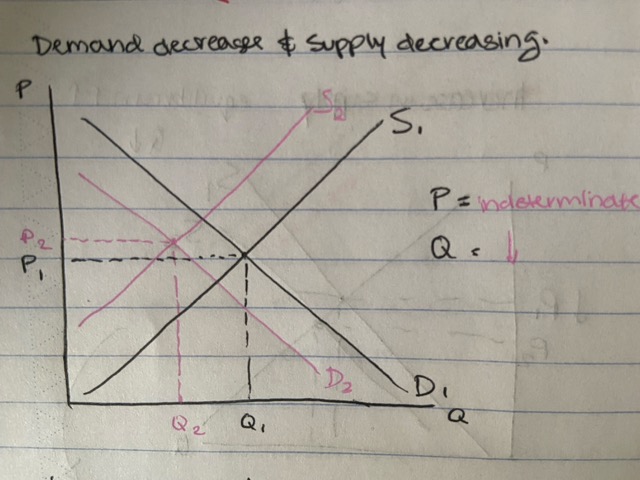
decrease in demand and supply
housing market
- interest rates rise and shortage in cement
quantity decreases, price indeterminate
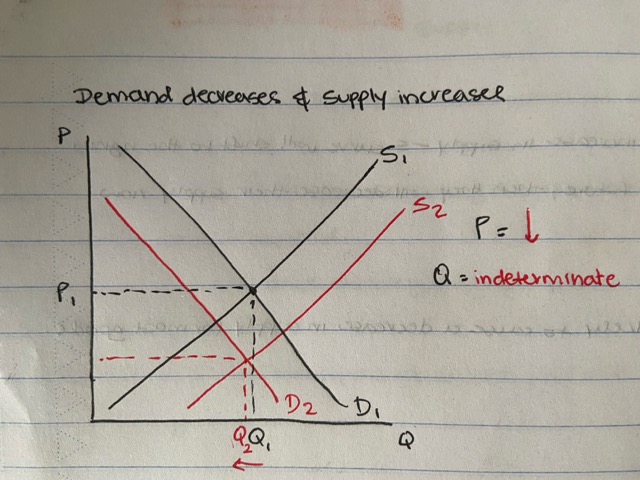
demand decreases and supply increases
airline market
- school holidays finish and new airline launched
price decreases, quantity indeterminate
changes in demand
increase in demand - line shifts right
decrease in demand - line shifts left
what are marginal benefits?
marginal benefits are the change in total benefits as the activity increases
what are marginal costs?
marginal costs are the change in total costs as the activity increases
what causes economic growth?
economic growth is caused by an increase in one of the factors of production
what is the economic problem?
the economic problem refers to how societies, individuals and businesses allocate resources when faced with unlimited wants and needs and limited resources to satisfy them
what is the difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics?
microeconomics attempts to understand how consumers and producers make decisions.
macroeconomics is concerned with the performance of the whole economy, it sees the economic problem from society’s point of view
what purpose does an economic model serve?
an economic model is a simplified representation of economic reality, showing the relationship between certain economic variables
explain the importance of the ceteris paribus assumption
it allows economists to isolate the effects of one variable on another by holding all other relevant factors constant
what is a positive economic statement?
a positive economic statement is one that can be tested objectively. e.g what effects would increasing taxes have?
what is a normative economic statement?
a normative economic statement is one that can only be tested subjectively. e.g should we increase taxes?
what does “there is no such thing as free lunch” mean?
“no free lunch” demonstrates opportunity cost. to get one thing that we want, we usually have to give up another thing that we want
how does ppf explain concepts of opportunity cost and economic growth?
to produce more of one good, more resources must be allocated for that good, so less resources can be used to produce the other good.
why does the ppf have a negative slope?
it has a negative slope due to scarcity of resources
what factors can cause the ppf curve to shift outwards?
if factors like labour or production of capital goods increase, then the economy is able to produce goods on any point along the frontier
what is a market economy?
a market economy is where the factors of production like labour, natural resources or capital goods are owned by the people
what are characteristics of a market economy?
individuals are allowed to profit from private ownership of business and property
market players are free to produce, sell and purchase as they please, subject to government regulations