Atoms, Elements, and Compounds
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
The building block of matter. It is the smallest unit of a pure substance that still has the properties of the substance.
atom
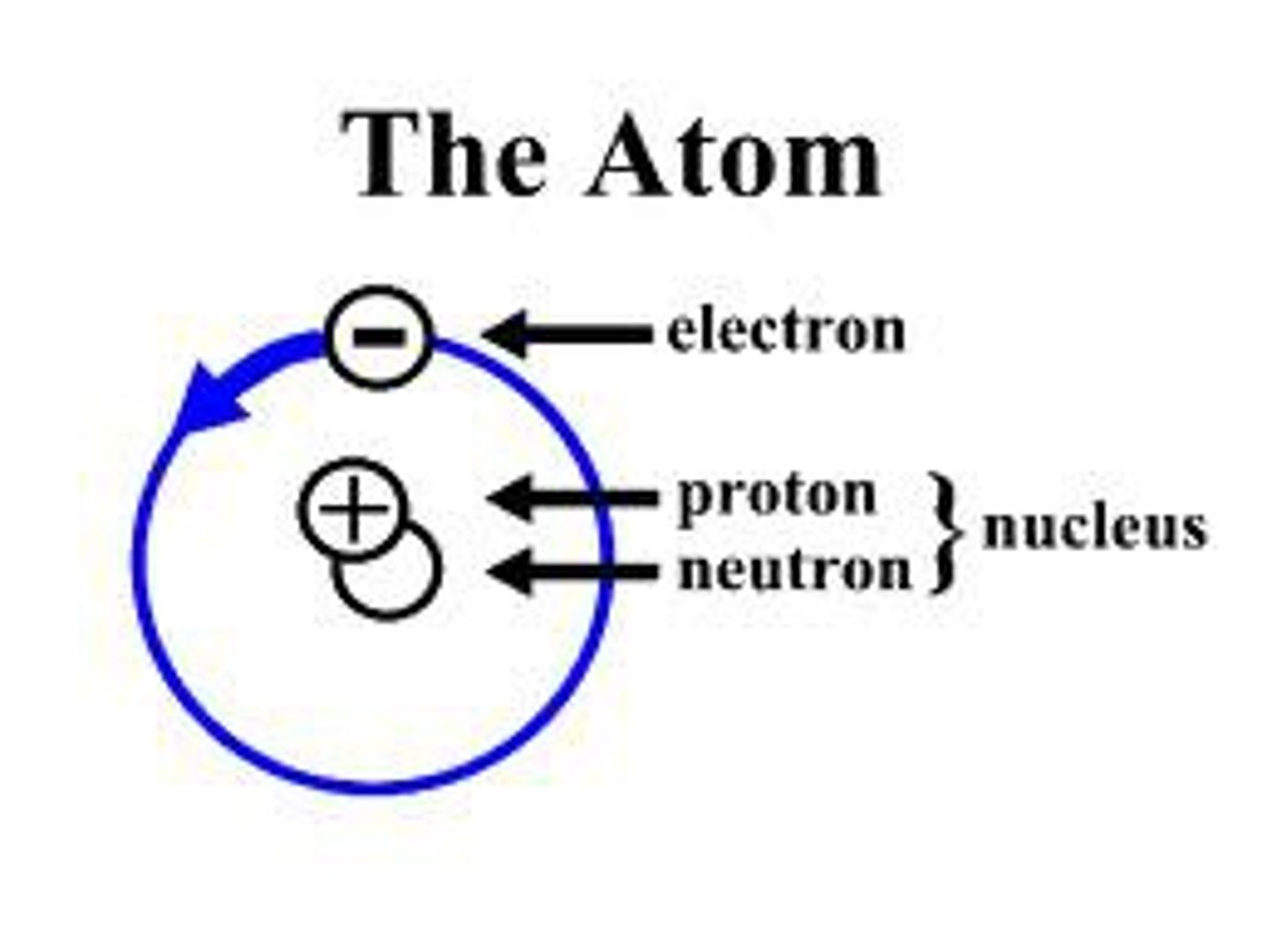
The center of an atom; contains neutrons and protons.
nucleus
The positively charged particles in an atom's nucleus.
proton

A particle without a charge in an atom's nucleus.
neutron
A negatively charged particle that occupies space around an atom's nucleus.
electron

A pure substance composed of only one type of atom; cannot be broken down into another substance by physical or chemical means.
element
Atoms that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons.
isotope
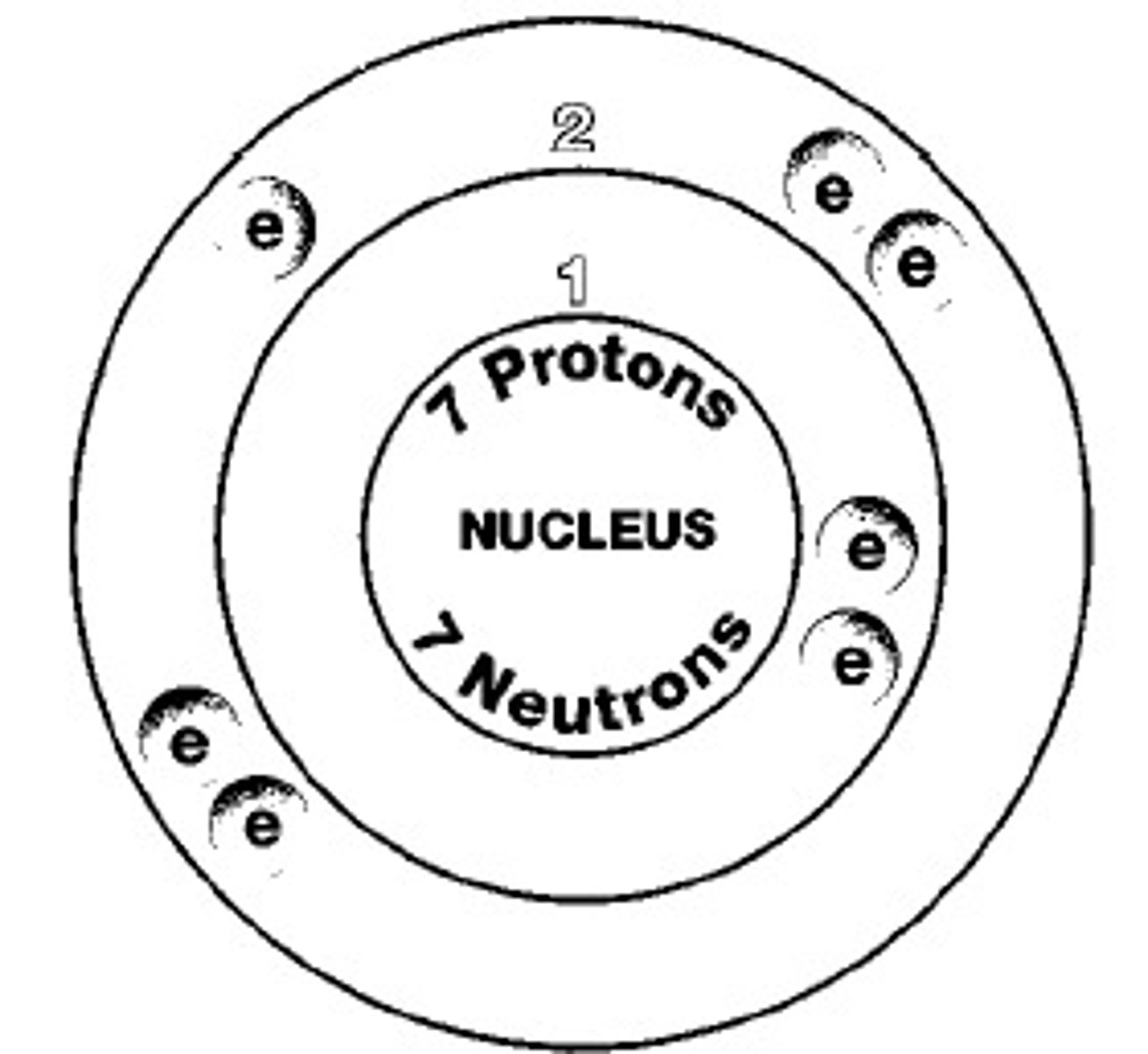
A pure substance with unique properties; formed when two or more different elements combine.
compound
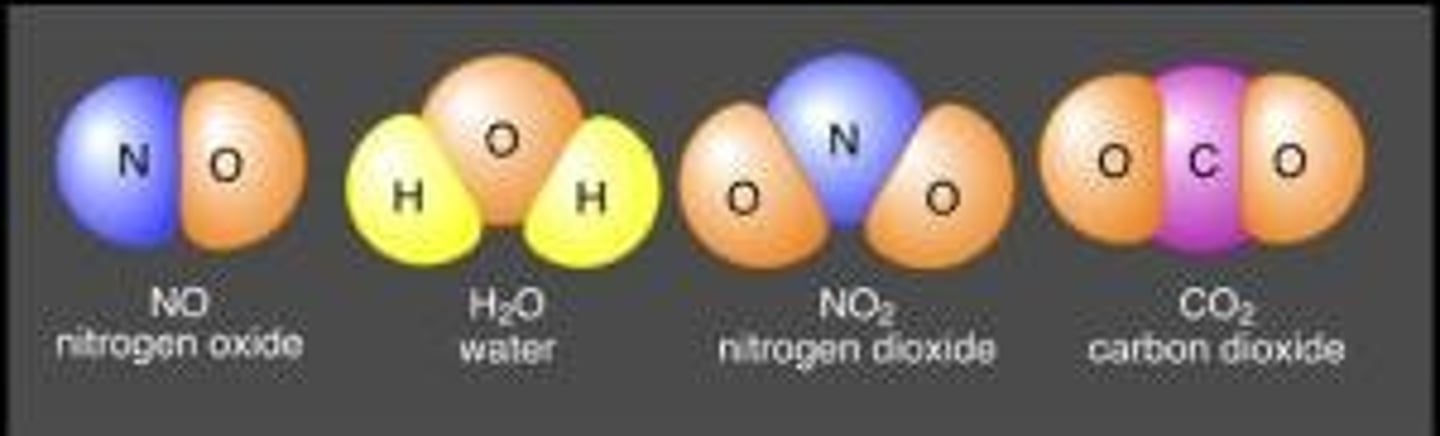
Two or more atoms that are held together by bonds.
molecule

An atom that is negatively or positively charged because it has lost or gained one or more electrons.
ion

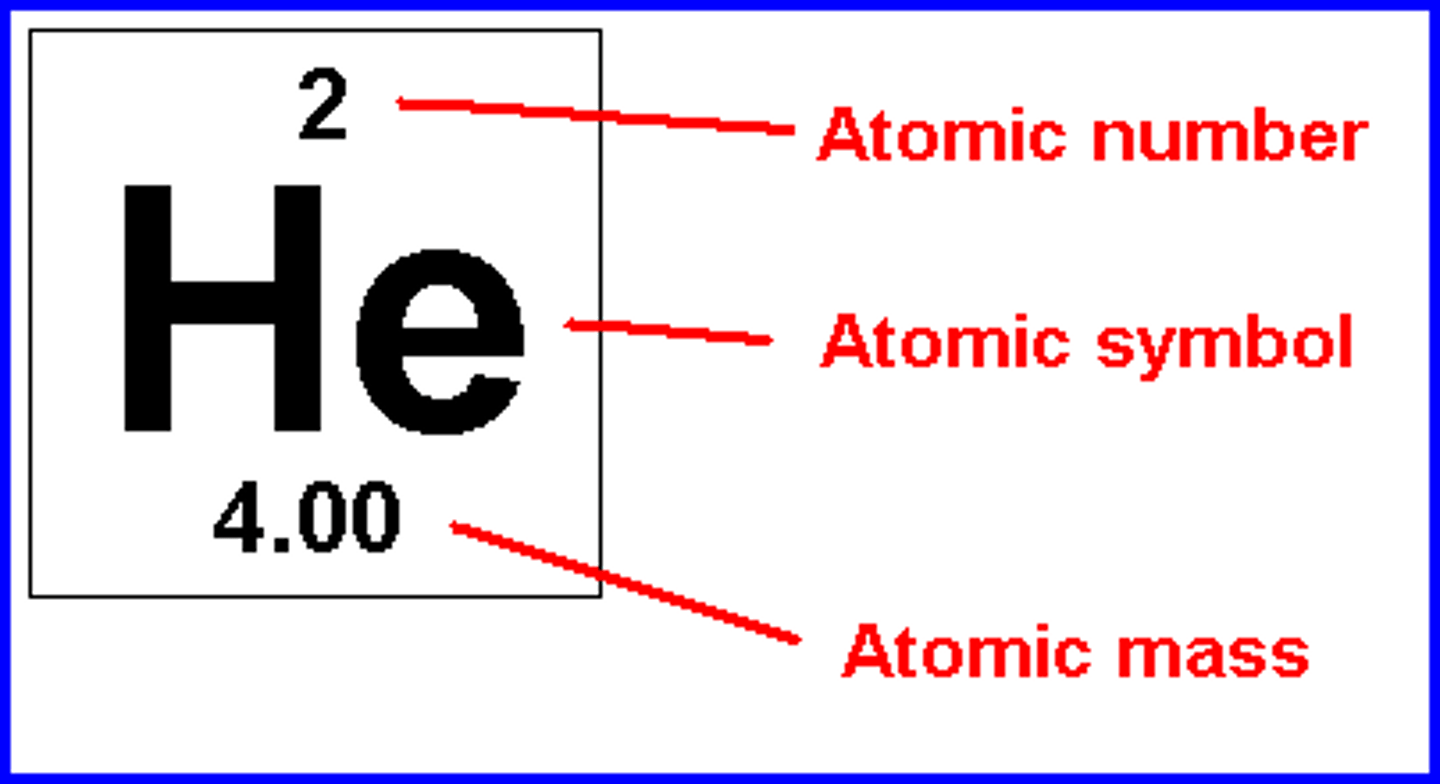
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
atomic number

What scientists measure the mass of an atom in.
atomic mass units or amu
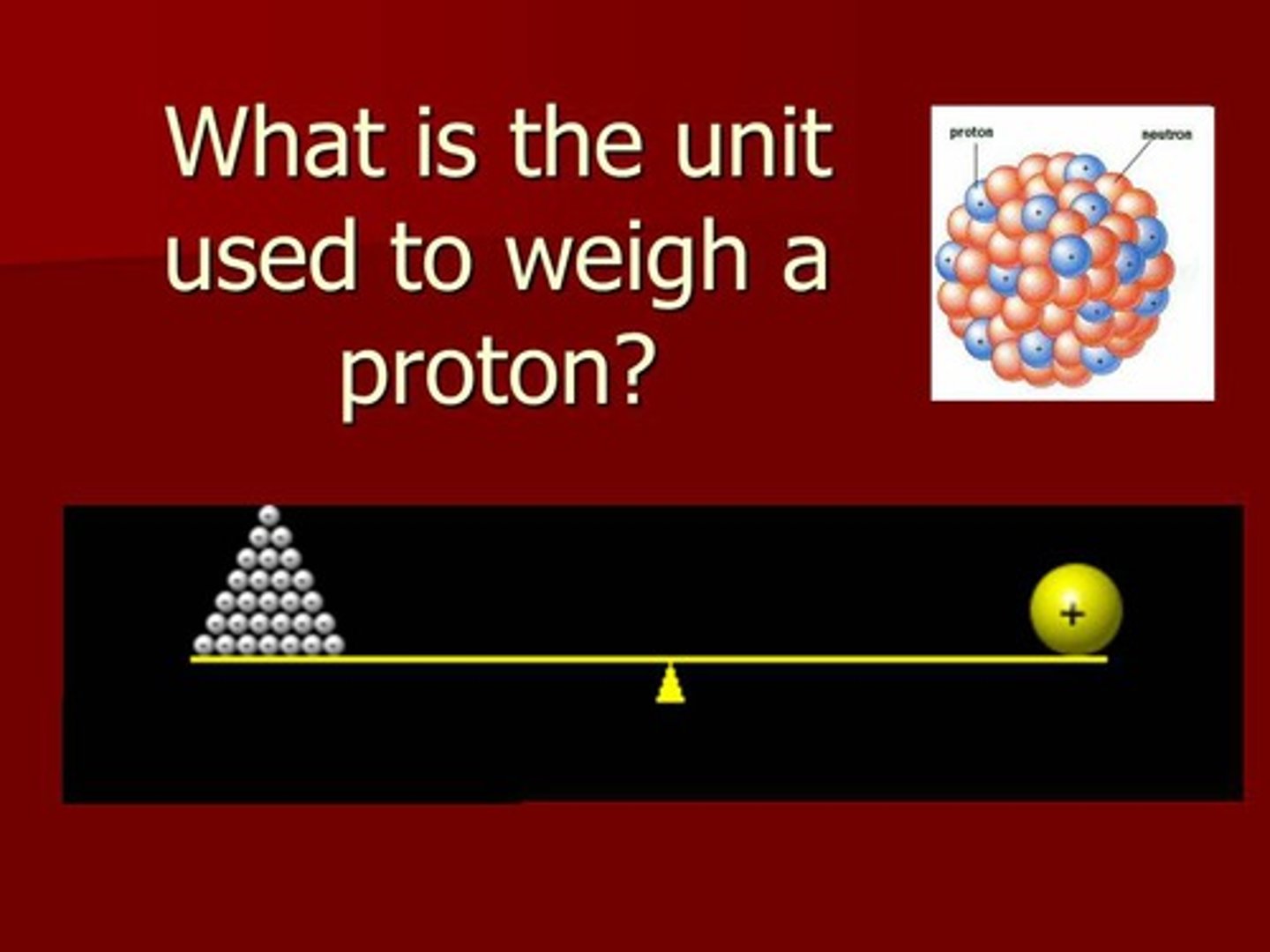
The average number of protons and neutrons in all of the isotopes of a substance.
atomic mass
An element that conducts heat and electricity well and are malleable. Most are solid at room temperature.
metal
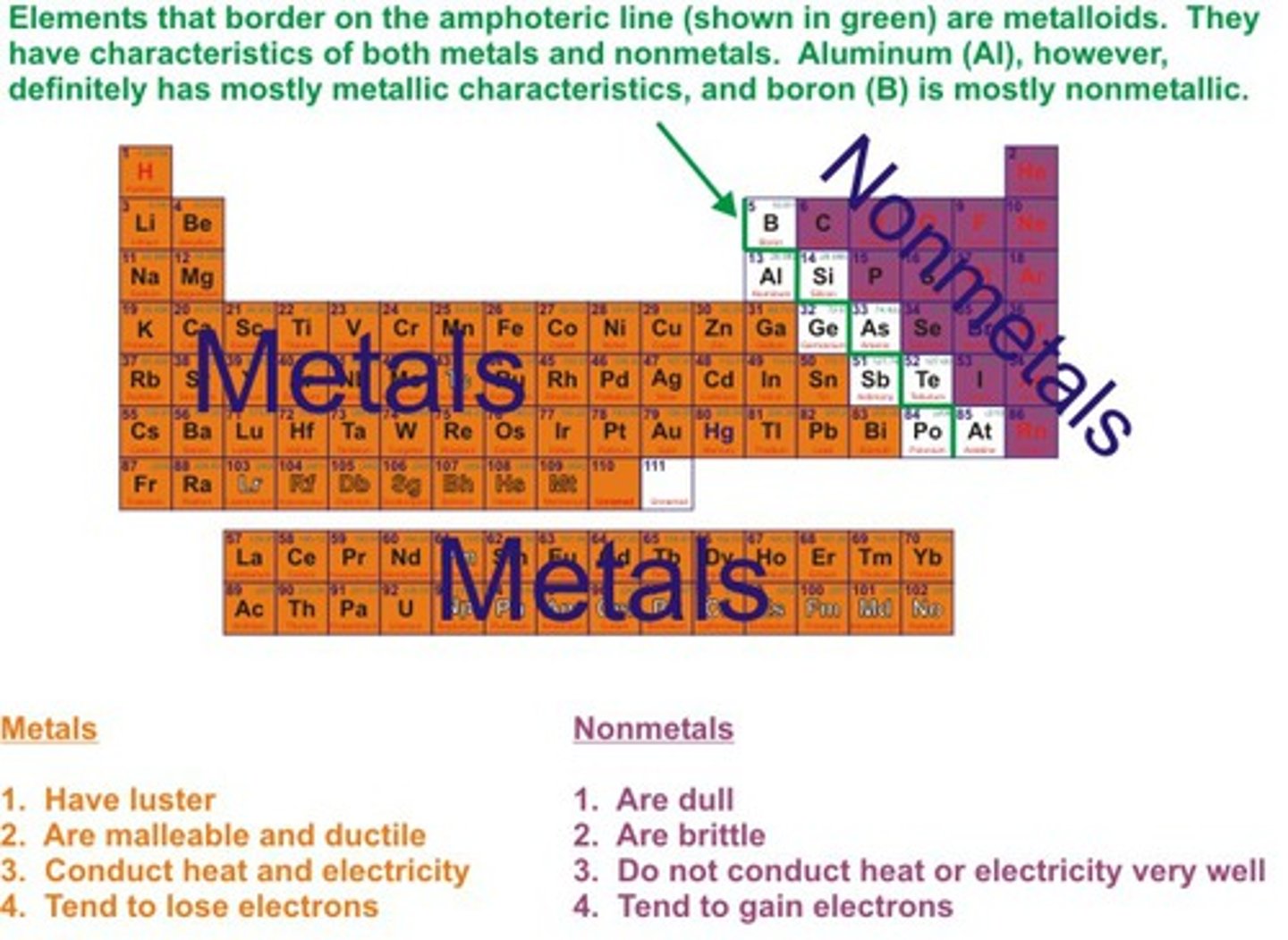
The only metal that is not solid at room temperature.
Mercury

What percentage of elements are metal?
75 percent

The ability to be bent and rolled into sheets.
malleability

Elements that do not conduct heat or electricity well and are not shiny or malleable.
nonmetals
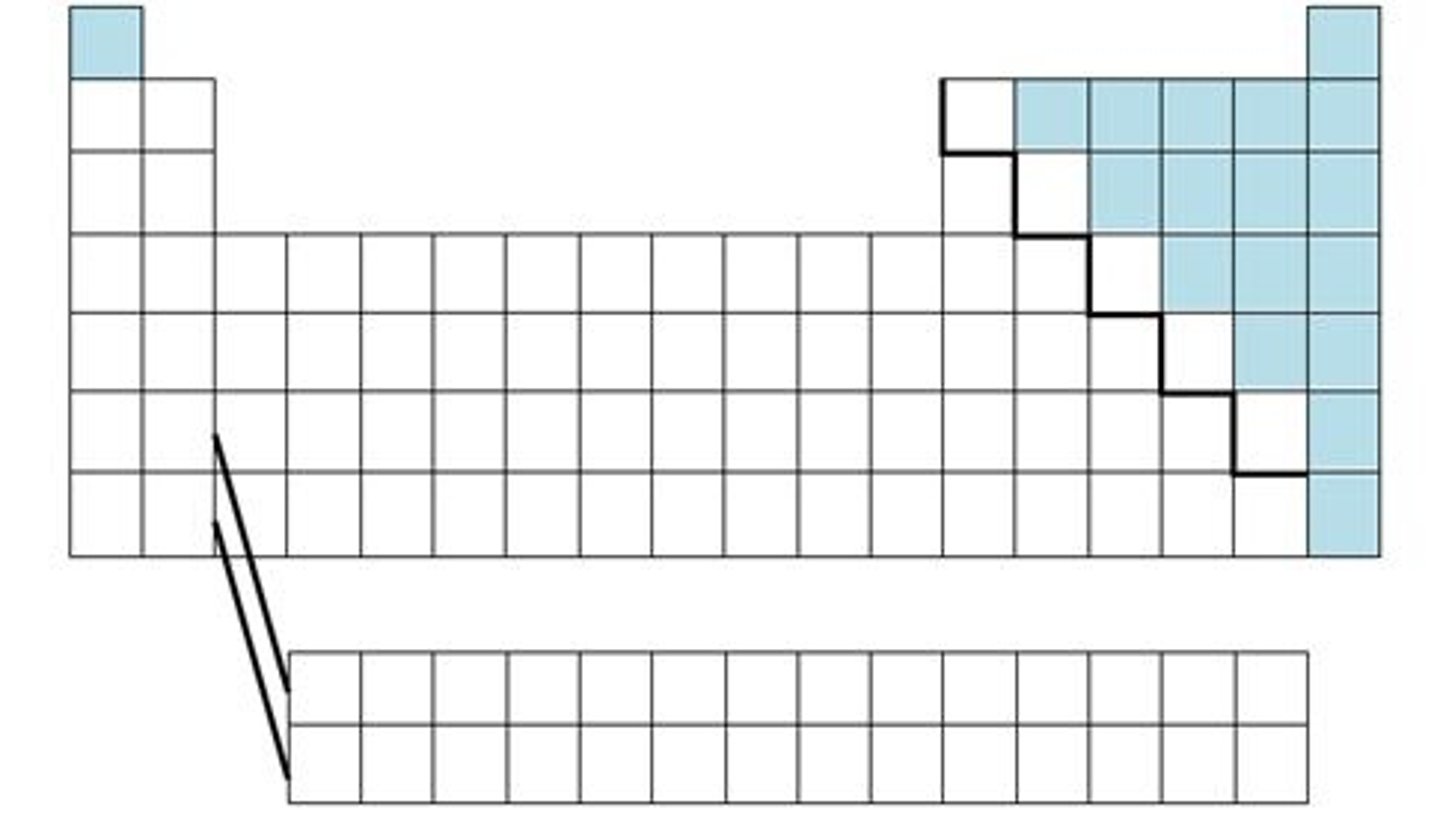
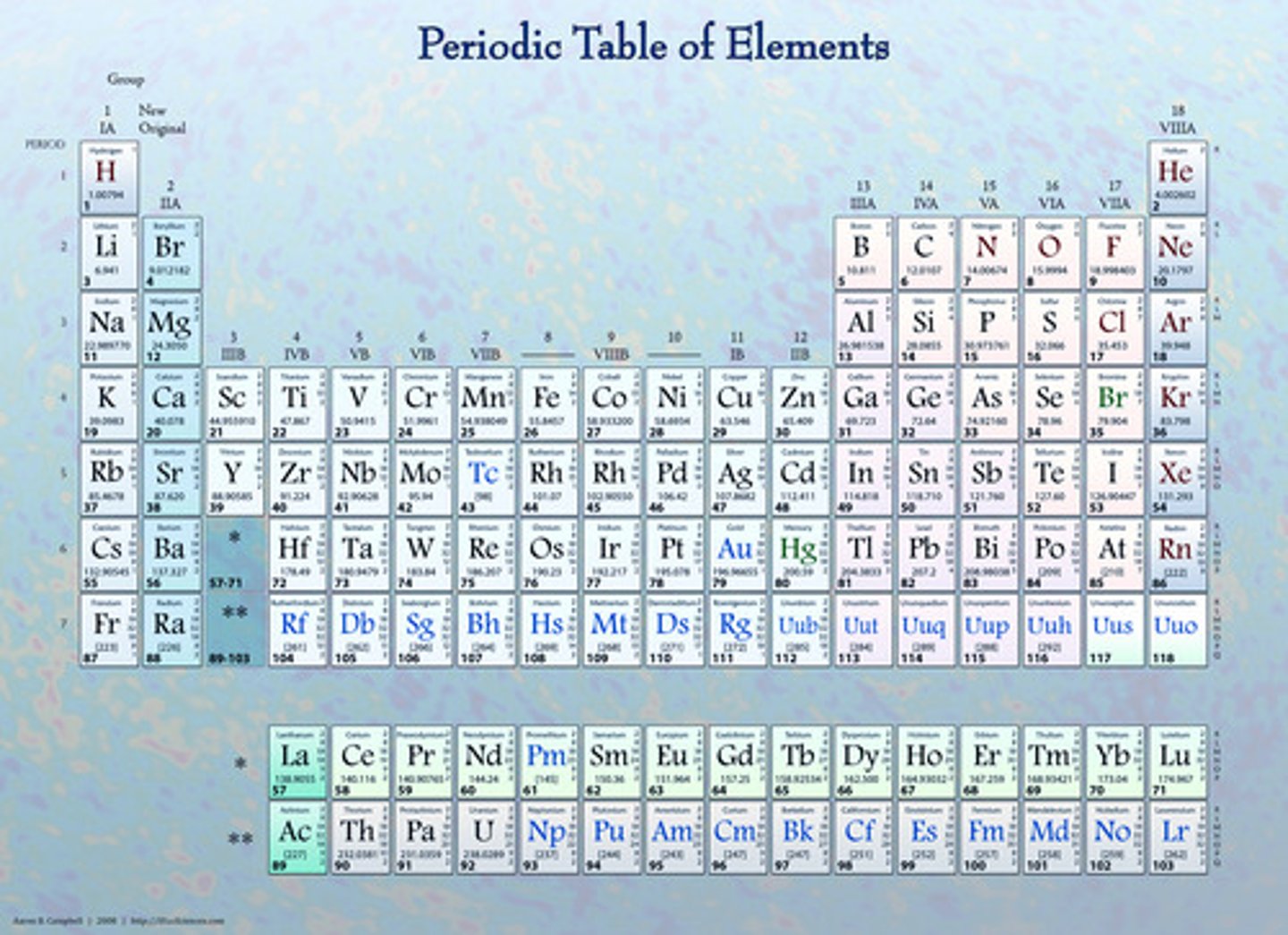
The first person to organize the elements into a table based on their atomic masses.
Dmitri Mendeleev

A table of the elements arranged according to their atomic number.
periodic table
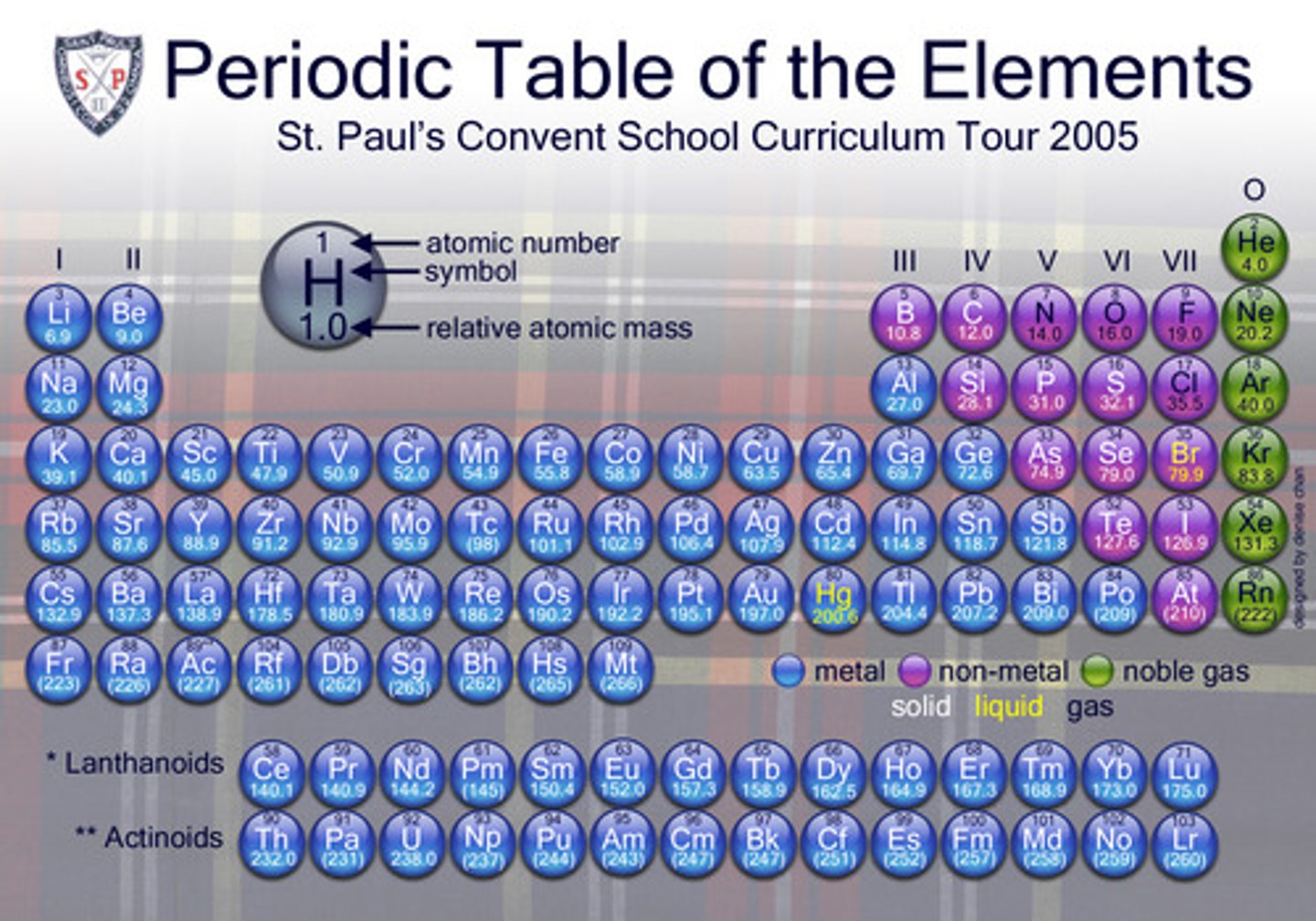
Each column of the periodic table.
group or family

Each row in the periodic table.
period

Which column or family of elements are the most reactive?
column or family one, Alkali Metals
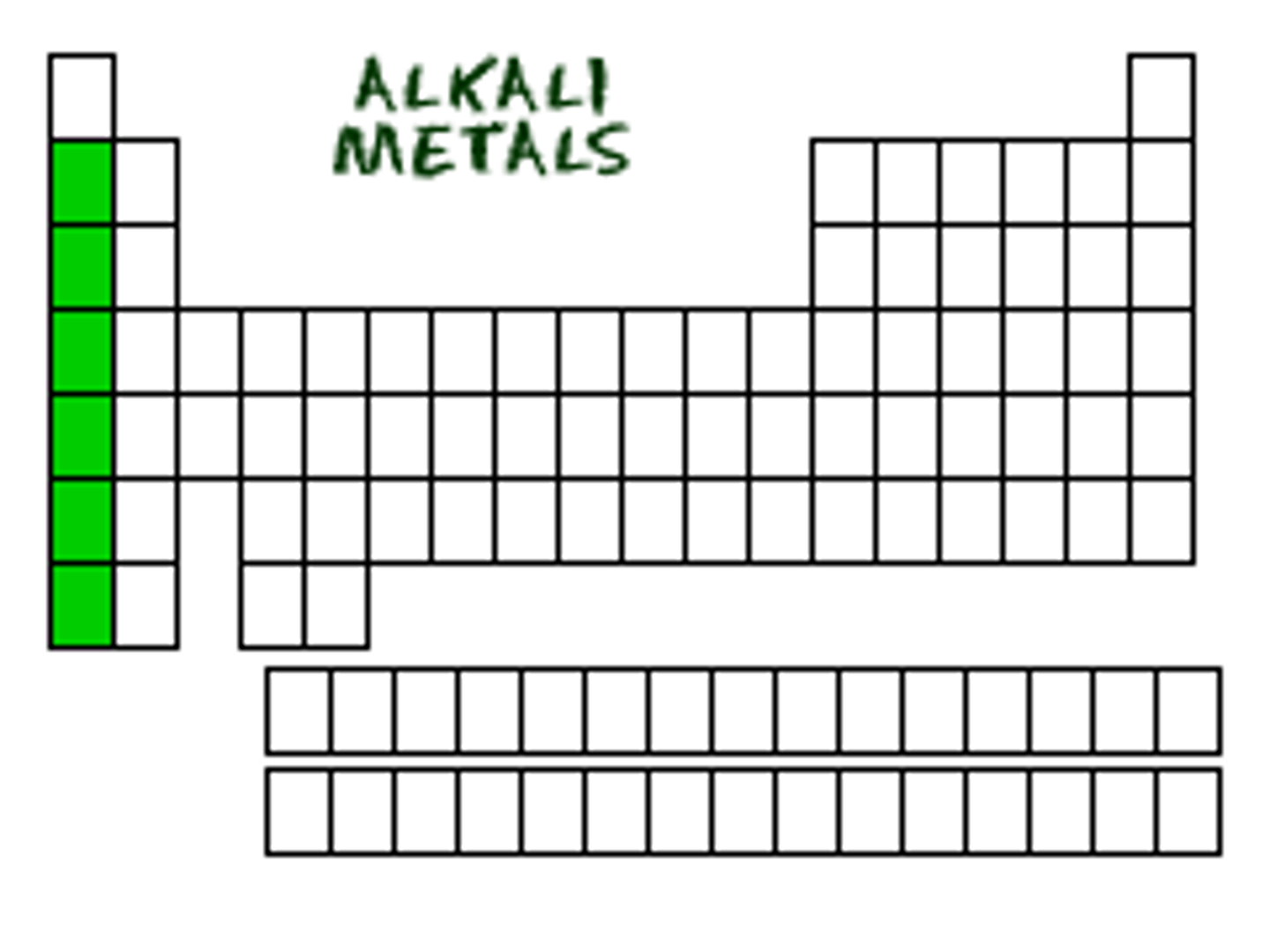
Which family found in the last column is the least reactive elements?
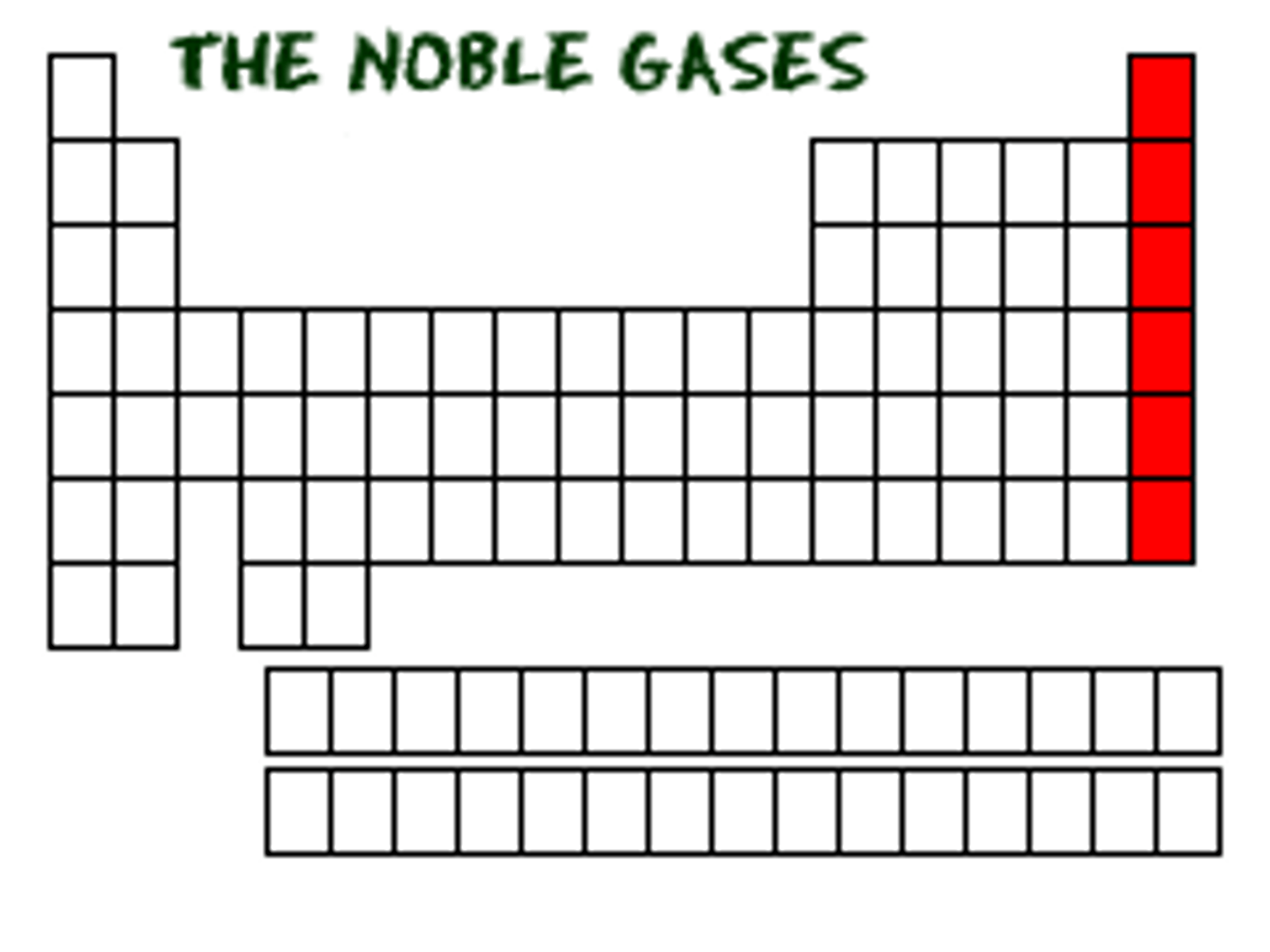
the noble gases
A substance that has a definite shape and volume. Its particles vibrate in place.
solid

A substance that has a definite volume but takes the shape of its container.
liquid

A substance with no definite shape or volume. Its particles move the fastest in all directions.
gas
The temperature at which a substance changes from a solid to a liquid.
melting point
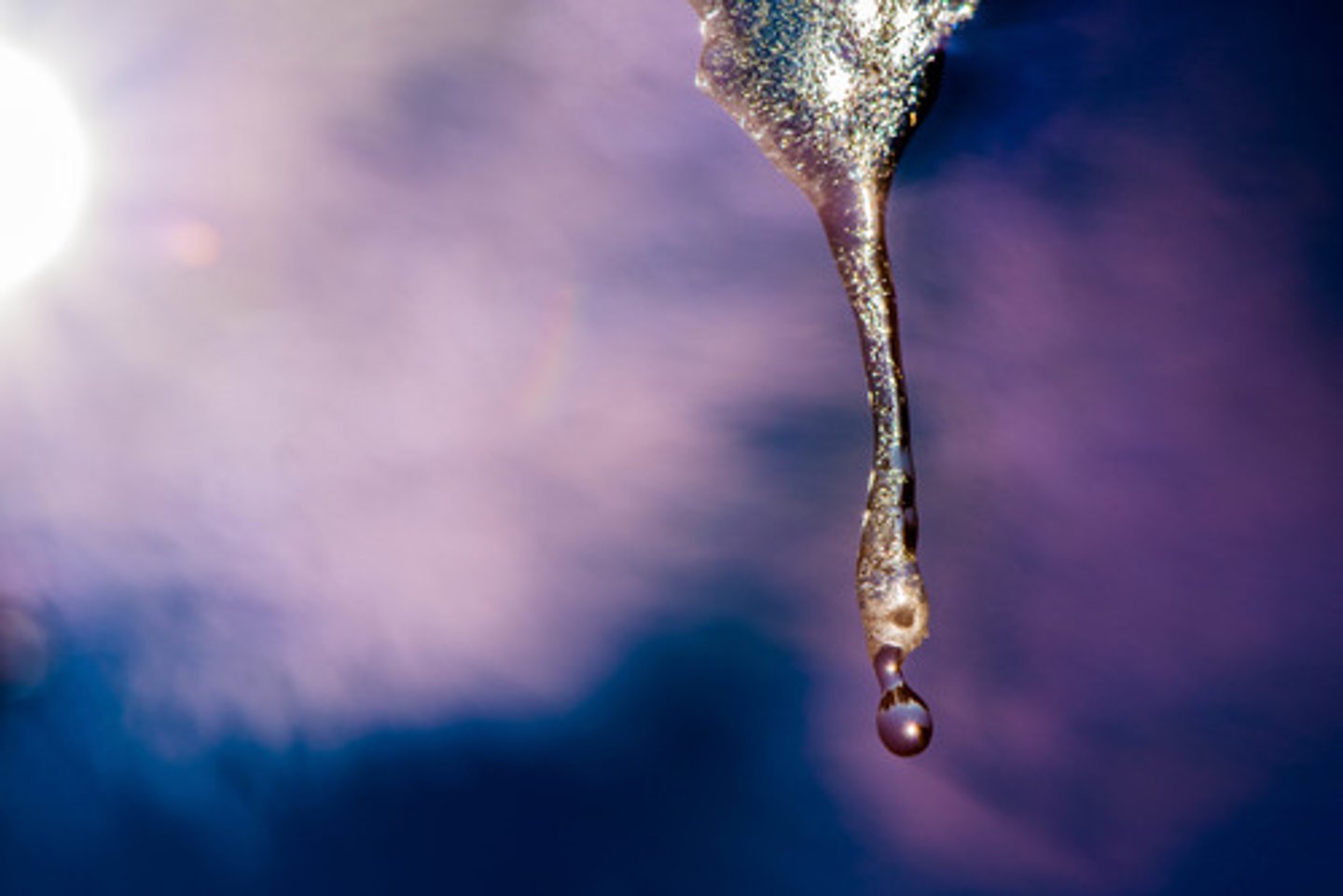

The temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a solid.
freezing point
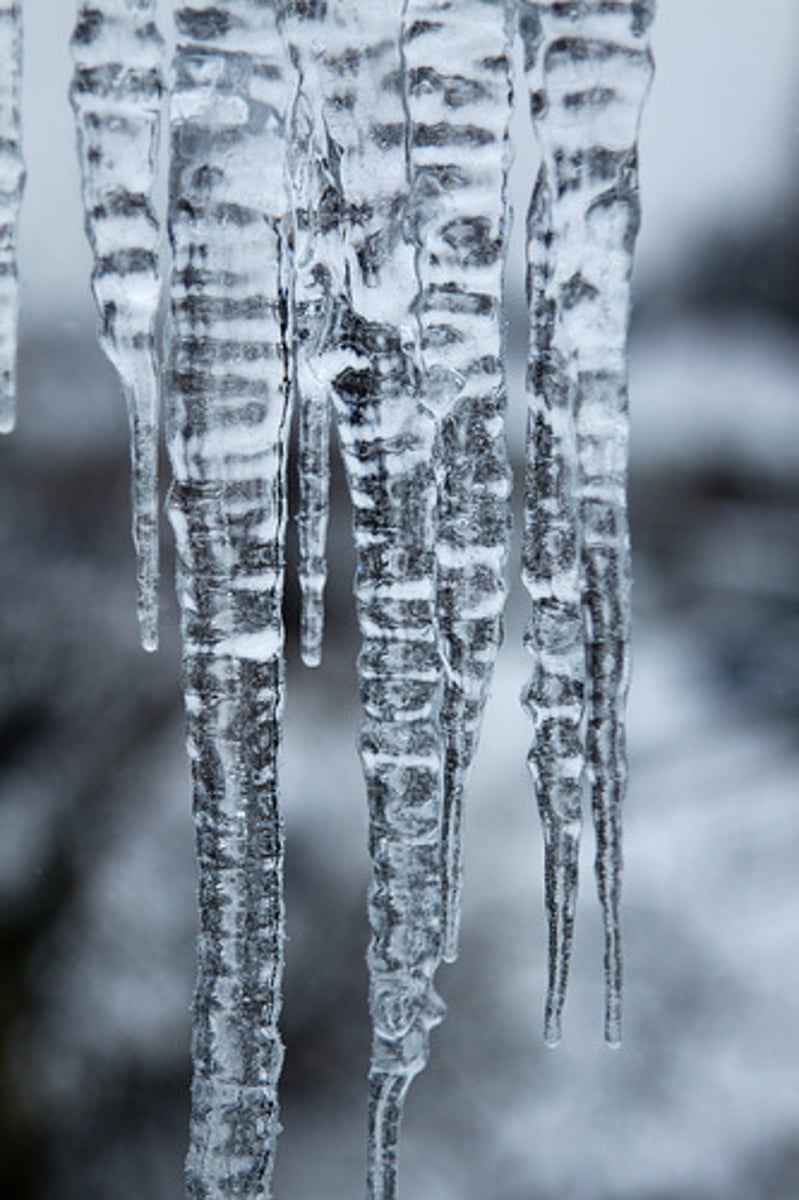

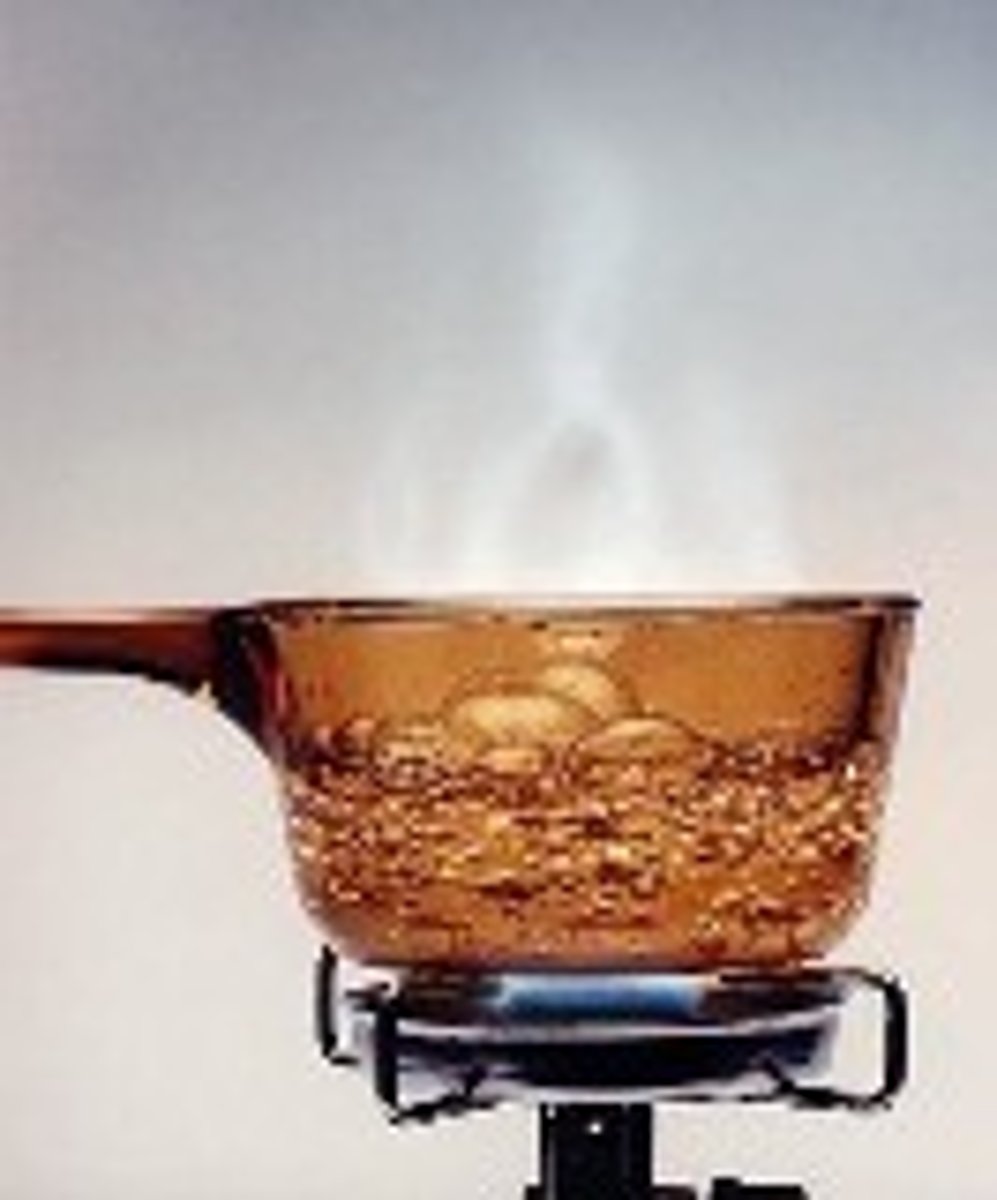
The temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a gas. This is the same temperature at which a gas condenses into a liquid.
boiling point

When a substance changes states directly from a solid to a gas without first becoming a liquid.
sublimation

A gas in which some of the electrons have been removed from the atoms or molecules and can readily conduct electricity.
plasma

The chemical symbols of a compound showing the elements and how many atoms of each,
chemical formula
A compound that reacts easily with other substances and turns blue litmus paper red. They have a sour taste and a pH of less than 7.
acid
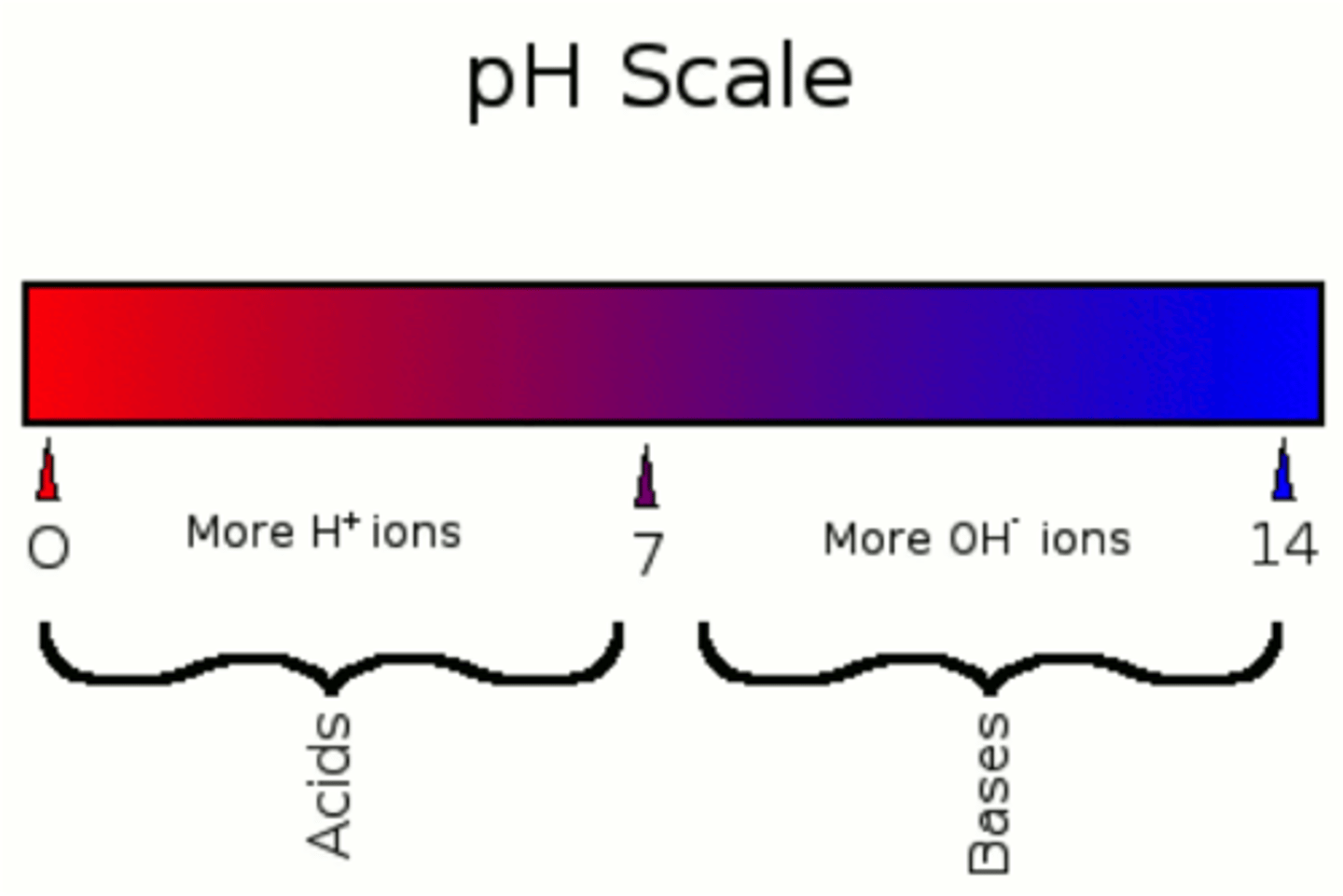
A compound that reacts easily with other substances and turns red litmus paper blue. These have a bitter taste, slippery feel, and a pH of more than 7
base

Chemicals that help you determine whether a compound is an acid or a base.
indicators

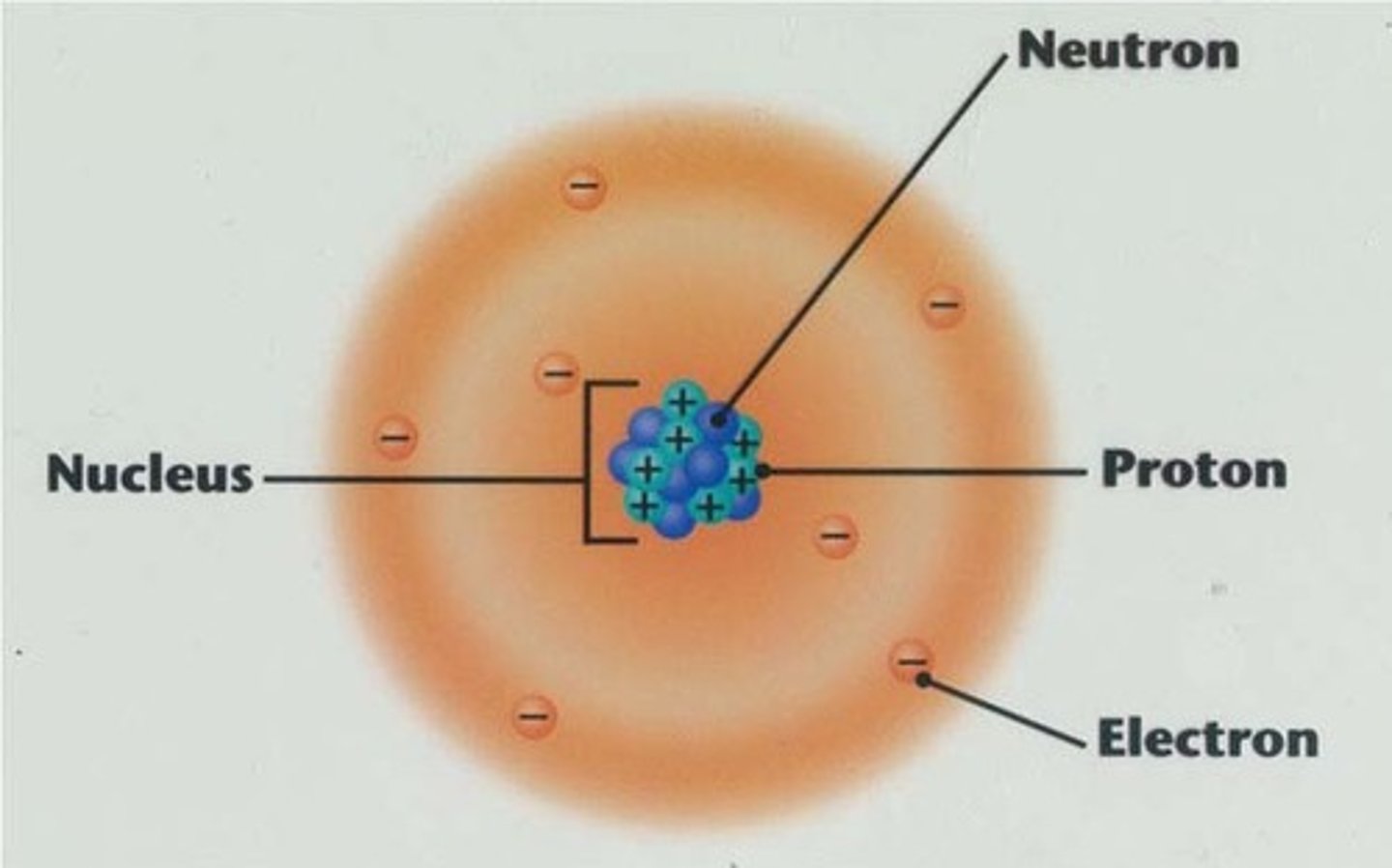
What makes up most of an atom?
empty space

Where are electrons found in an atom?
In a cloud surrounding the nucleus
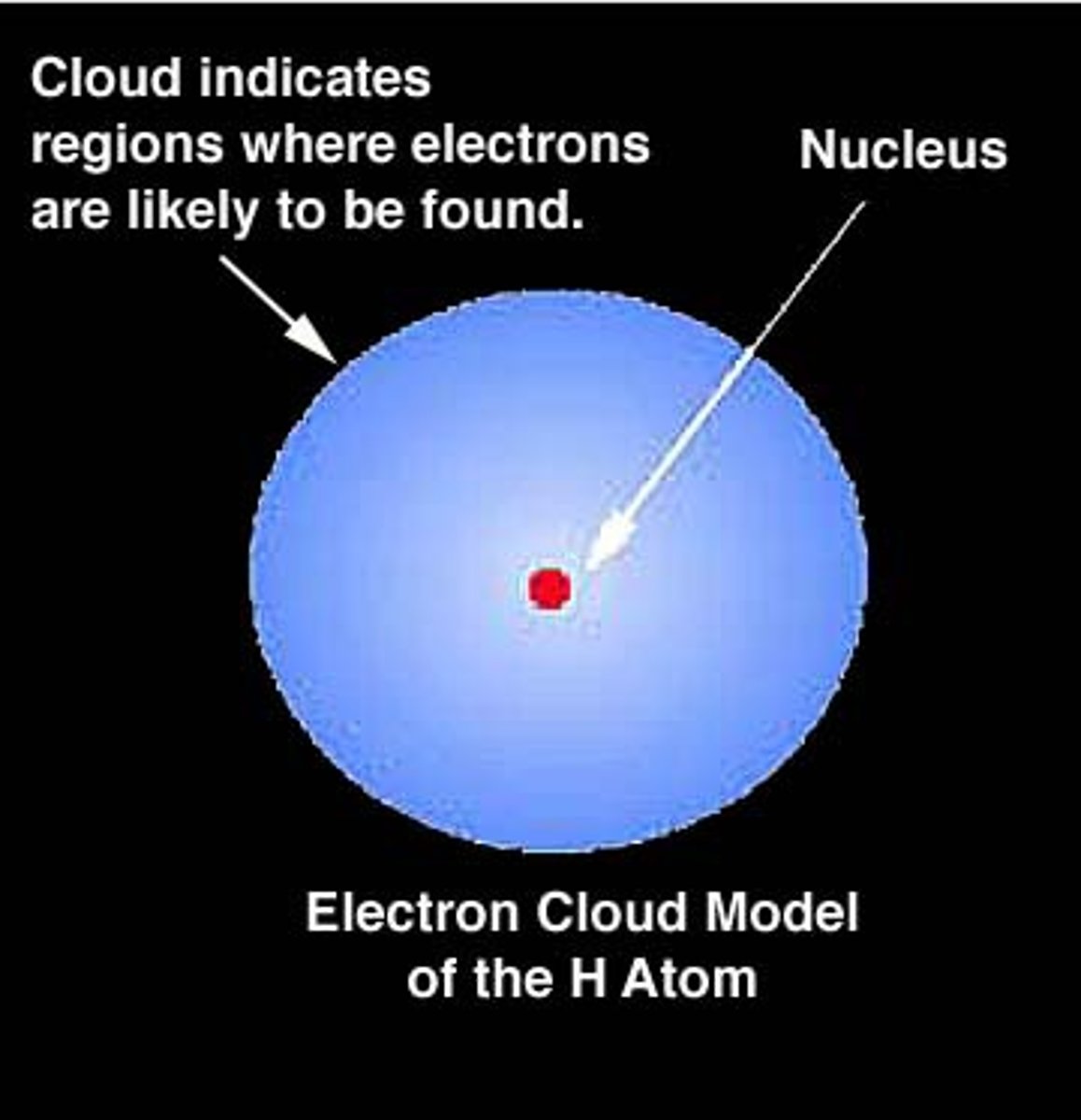
What is found in the nucleus of an atom?
protons and neutrons
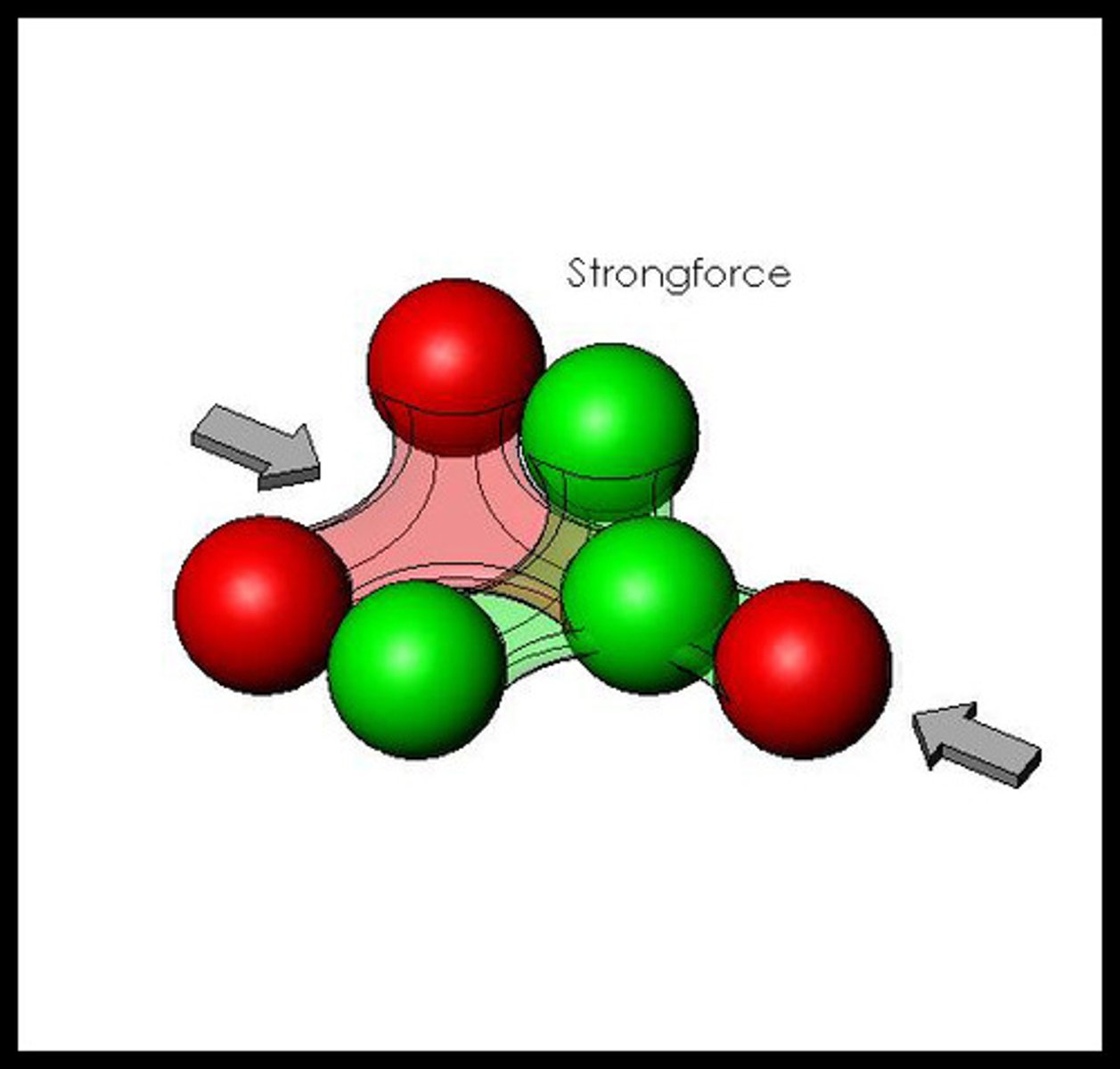
Where is most of an atom's mass found?
in the nucleus
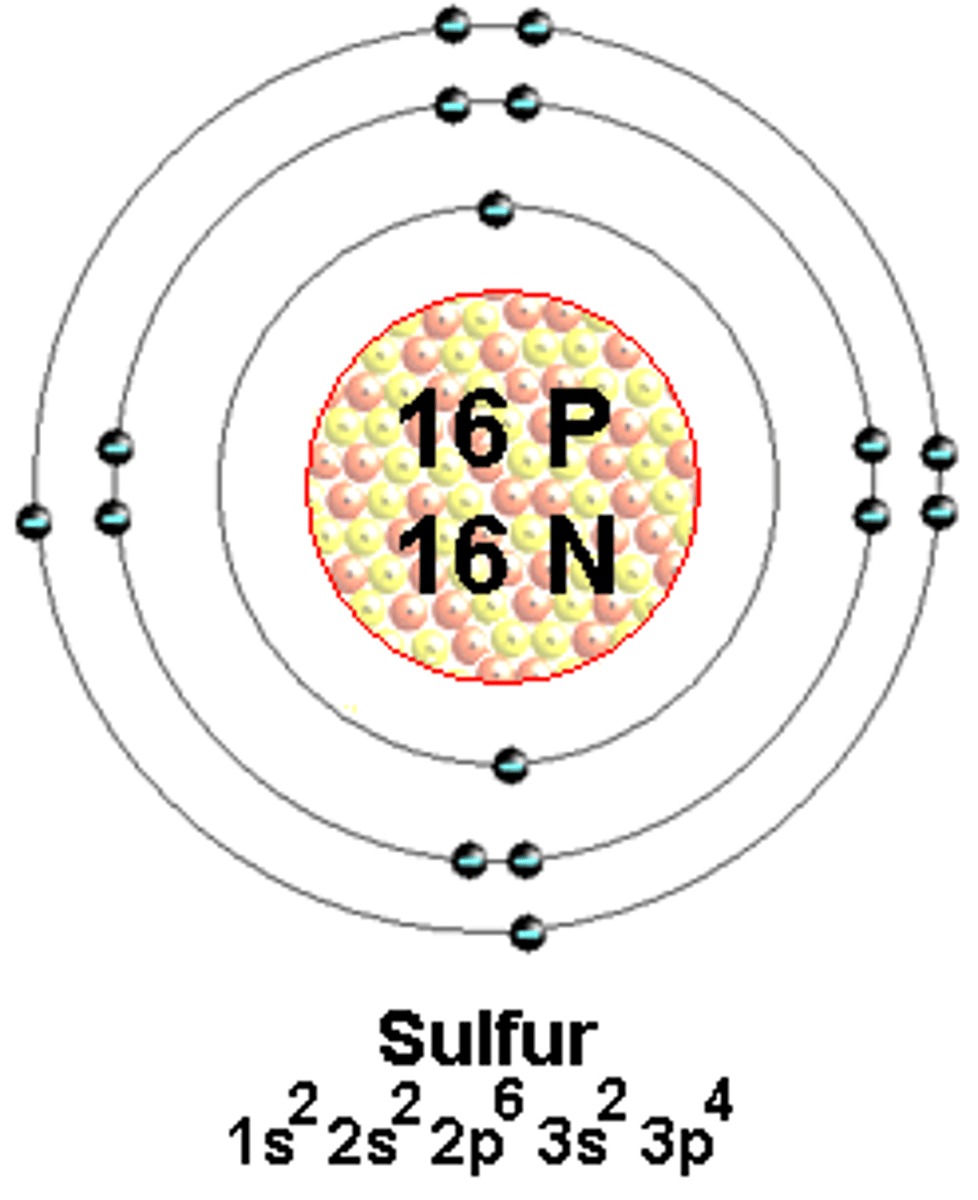
What is the same temperature as a substance's melting point?
Its freezing point

What is the same temperature at which a substance condenses?
the boiling point

The force that holds protons and neutrons together in the nucleus.
strong nuclear force
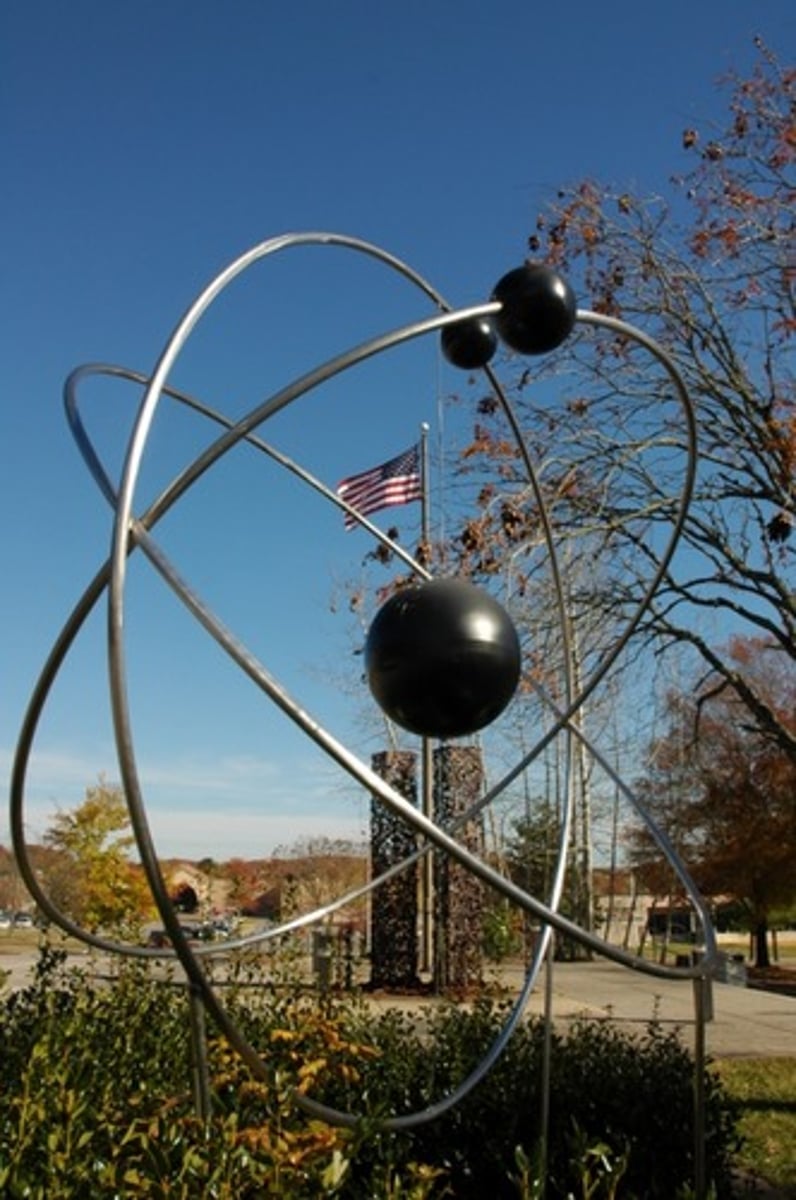

The theory that matter is made of atoms.
The atomic theory
