Principles of biochemistry exam 1 review
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
CH 2
What is the ratio of [A-]:[HA] in solution at pH 5 that contains a weak acid with pKa = 5?
a 1:10
b 1:2
c. 1:1
d. 2:1
e. 10:1
C. 1:1
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
[A-] = conjugate base concentration
[HA] = weak acid concentration
![<p><strong>C. 1:1</strong></p><p></p><p>Henderson-Hasselbalch equation</p><ul><li><p>[A-] = conjugate base concentration</p></li><li><p>[HA] = weak acid concentration</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e07ac644-cdd1-49f8-97f1-94b48bd93e9e.png)
Buffers work to maintain pH balance because….
they obey LeChatlier’s principle
Buffering capacity refers to…
The extent to which a buffer solution can counteract the effect of added acid or base
What is the pH of the solution that has a 1:4 ratio of acetate ion and and acetic acid (pK acetic acid 4.75)?
4.1
pH = 4.75 + log ([1]/[4])
![<p><strong>4.1</strong></p><p></p><p>pH = 4.75 + log ([1]/[4])</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ad038761-6bde-47a6-9d3d-dae3688ce876.png)
Which has the greater pKa, a weak acid or a strong acid?
a weak acid
has a stronger pKa, while a strongacid has a smaller
(or even negative ) pKa
CH 3
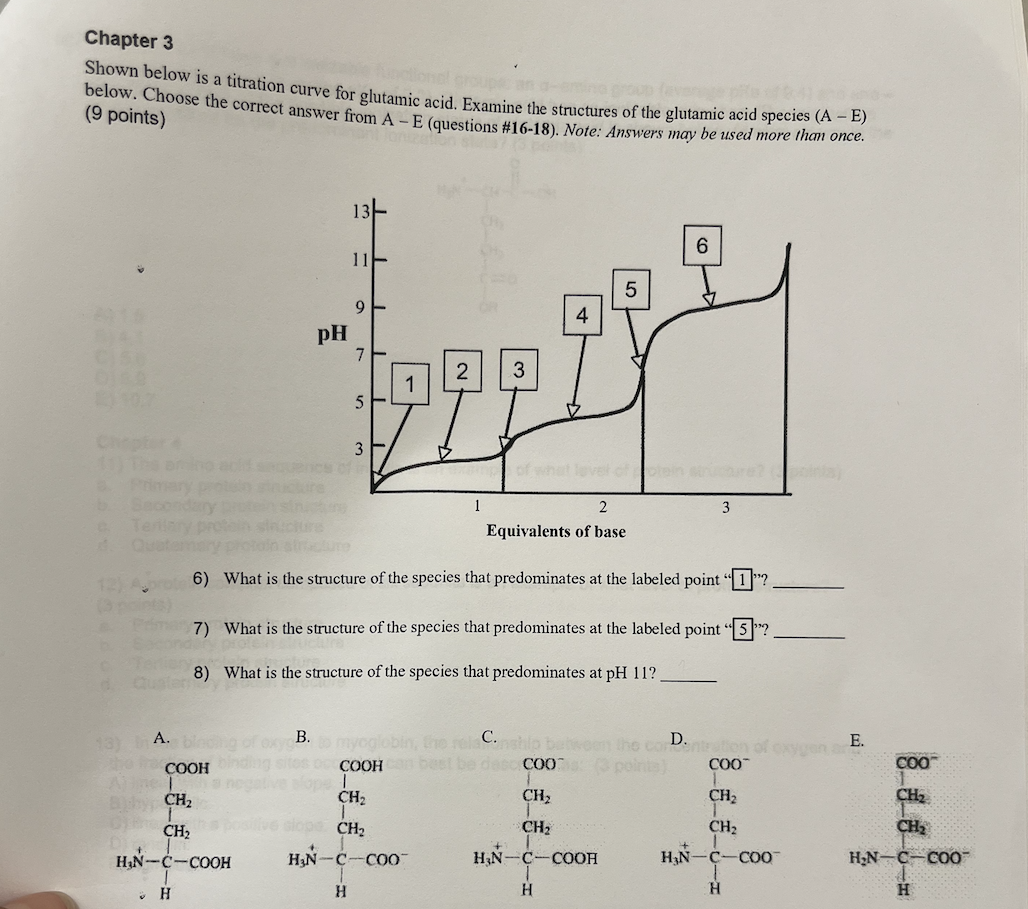
Shown below is a titration curve for glutamic acid. Examine the structures of the glutamic acid species (A-E). Choose the correct answer from (A-E)
6. What is the structure of the species that predominates at the labeled point “1”?
7. What is the structure of the species that predominates at the labeled point “5”?
8. What is the structure of the species that predominates at pH 11?
A
D
E
Which one of the following amino acids contains an aromatic group?
a. Arginine
b. Phenylalanine
c. Leucine
d. Methionine
e. Glycine
B. Phenylalanine
Arginine → basic, positively charged side chain (guanidinium), not aromatic.
Phenylalanine → contains a benzyl aromatic ring (aromatic amino acid). ✅
Leucine → aliphatic side chain, not aromatic.
Methionine → sulfur-containing side chain, not aromatic.
Glycine → hydrogen side chain, not aromatic.
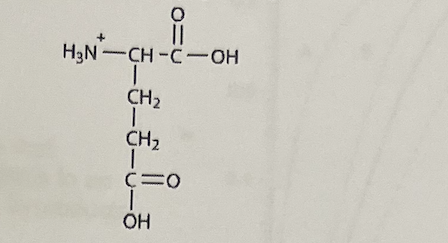
All amino acids have two ionizable functional groups: an a—amino group (average pKa of 9.4) anda — carboxylic acid group (average pKa of 2.2) Glutamic acid has ionizable side chain (Rn group) with a pKa of ~4.1. One of the possible ionization states of glutamic acid is shown below. At what pH would the above structure be the predominant ionization state?
1.5
CH 4
The amino acid sequence of insulin is an example of what level of protein structure?
primary protein structure
A protein complex composed of six subunits is an example of what level of protein structure?
quarternary protein structure
The binding of oxygen to myoglobin, the relationship between the concentration of oxygen and the fraction of binding sites occupied can best be described as:
hyperbolic
In hemoglobin, the transition from T state to R sate (low to high affinity) is triggered by:
oxygen binding
In the Bohr effect the binding of oxygen to hemoglobin
is increased by the presence of H+ and CO2
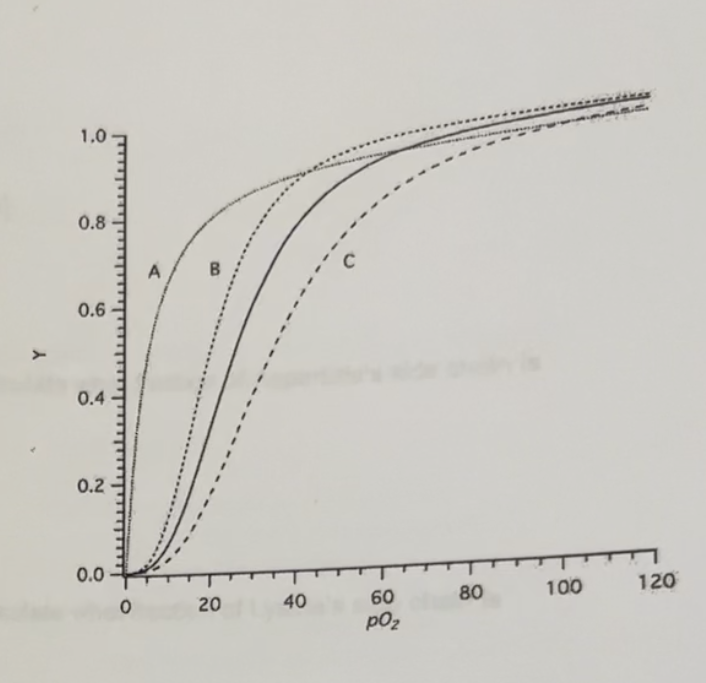
The graph below plots the oxygen saturation curves for hemoglovin under different conditions. The solid curve represents the curve under physiological conditions of pH, concentrations of CO2, and the metabolite 2,3-BPG
Which curve (A,B, or C) represents that predicted when metabolic activity leads to an increase in the production of acidic byproducts in the tissues?
Which curve (A,B, or C) represents that predicted when the B-subunits of hemoglobin are substituted when the y subunits found in fetal hemoglobin?
Hemoglobin differs from myoglobin because…
C
B
it is a tetramer, whereas myoglobin is a single polypeptide chain
When oxygen binds to a heme-containing protein, the two open coordination bonds of Fe2+ are occupied by:
one O2 molecule and one amino acid atom
CH 5
A separation of a mixture of cations of different charge requires
an anionic substance
The purity of an enzyme at various stages of purification is best measured by
specific activity of the enzyme
In affinity chromatography, a protein
which binds to the ligand will remain on the column
oxidoreductases