Enamel and Dentin Bonding
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Buonocore
"Father of operative dentistry", inspired by industries use of 85% phosphoric acid as adhesive of paints/resins to metal, he envisioned the use of acids to etch enamel for sealing pits & fissures
Gwinnet and Mitsui
identified the use of resin micro-tags on etched enamel adhesion
Fusayama
created total-etch technique to etch enamel and dentin at the same time (remove smear layer and open dentinal tubules)
Nakabayashi
He describes resin infiltration of dentin collagen to form "hybrid layer"
Kanca and Gwinnett
identified the wet bonding relationship that increases resin-dentin bond retention with slightly wetted tooth
Watanabe
created self-etch adhesives
Enamel
homogeneous structure, predictable bonding, and excellent long term bonding durability (96% mineral and 4% organic/water)
Dentin
heterogenous structure, tubular structure, and fair long term bonding durability (45% mineral, 33% organic, and 22% water)
Smear layer
thin layer of debris on newly prepared tooth that obstructs entrances of dentinal tubules and decreases dentin permeability
Etch-and-rinse (total-etch)
uses strong acid (phosphoric acid) to completely etch enamel/dentin and wash excess with water followed by adhesive application. It can come in 3-step or 2-step forms
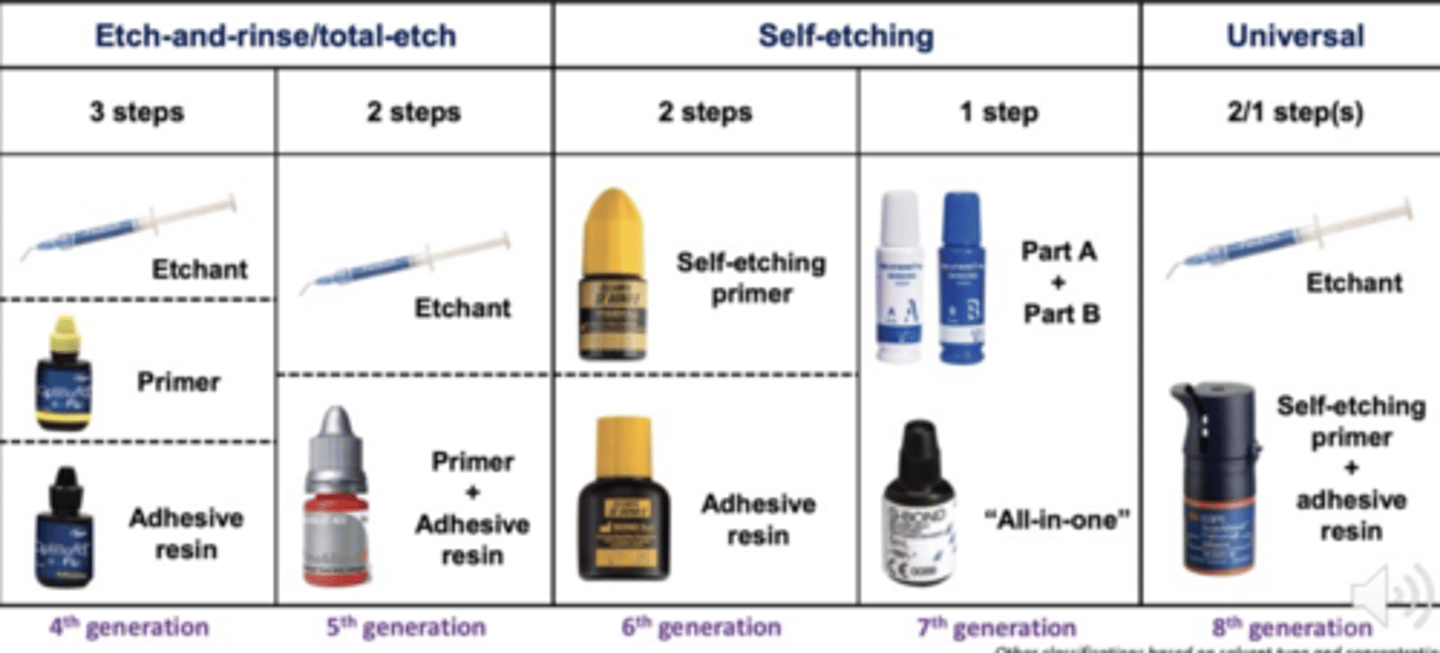
Etch-and-dry (self-etch)
uses nourishing solutions of acidic monomers to dissolve smear layer (increase permeability but not removed) and demineralize dentin/enamel. It can come in 2-step or 1-step forms
Universal etch
can be used as self-etch, etch-and-rinse, or selective-etch. It can come in 2-step or 1-step forms
Etch-and-rinse 3-step
etchant: phosphoric acid gel
primer: solvent and bifunctional/amphiphilic monomers
adhesive: hydrophobic non-solvated film forming monomers
Etch-and-rinse 2-step
etchant: phosphoric acid gel
primer and adhesive: solvent and bifunctional/amphiphilic monomers (hydrophobic film forming monomers)
Self-etch 2-step
primer: acidic monomer, solvents, and bifunctional/amphiphilic monomers
adhesive: hydrophobic non-solvated film forming monomers
Self-etch 1-step
All in one: acidic monomers, solvents, bifunctional/amphiphilic monomers, hydrophobic film forming monomers
Enamel etching Type I
removes prism core
Enamel etching Type II
removes prism periphery
Enamel etching Type III
combination and not prism structure evident
hybrid layer
a resin/dentin layer formed by intermixing of the dentin bonding agent with collagen fibrils exposed by acid etching. It serves as an excellent resin rich layer onto which the restorative material, such as composite resin, can be bonded
Selective etching
technique where enamel is etched first with phosphoric acid prior to the application of self-etch acidic primers that lack sufficient acidity to produce a good etch of the enamel
Key differences between self-etch and total-etch (4)
1)self-etch occurs simultaneously and primes dental substrates while total-etch is separated out
2)Self-etch is less technique sensitive and does not require rinses
3)Self-etch has reduced steps
4)Self-etch has worse binding to intact enamel (does not etch it as well)
Challenges of enamel bonding with self-etching adhesives (4)
1)dentin and enamel are two different substances
2)Self-etching adhesive (pH 2) is not as acidic as phosphoric acid (pH 0.5)
3)Dentin bonding with self-etch adhesives is reliable but not with enamel (needs more etching)
4)Separate phosphoric etching of enamel enhances bonding (can damage dentin)
Selective enamel etch-technique (6)
1)Phosphoric acid etching of enamel only (15-30s)
2)Water rinse (30s)
3)Remove cotton pellet and air dry vigorously
4)Apply acidic primer (20s)
5)Gentle solvent evaporation (shiny surface)
6)Apply adhesive resin (20s)
Gold standard etches (2)
1)Optibond FL (3-step)
2)Clearfil SE Bond w/selective enamel etching (2-step)
Adhesion
An attraction between molecules of different substances
Cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance
Ideal conditions for bonding
high substrate surface energy and low adhesive surface tension so that adhesives spread and bind well
Sclerotic dentin
A form of reparative dentin formed in response to trauma that requires increased etching time
Three main components of dental adhesins
etchant, primer, and bonding resin
Solvents
increase penetration and evaporation of water
Four classification methods for adhesives
1)generation
2)solvent type
3)mechanism of smear removal (etch-and-rinse or etch-and-dry)
4)number of clinical steps (3, 2, and 1 step)
Sound dentin etching
should not be etched for more than 15 seconds to avoid decreasing bond strength
Sclerotic dentin etching
should be etched for 30 seconds to increase bonding strength
Wet bonding technique
increase resin-dentin bind retention by having tooth slightly wetted (shiny/hydrated surface)
Viscosity
a liquid's resistance to flow
OptiBond FL application steps (6)
1)Apply phosphoric acid to dentin (15 sec) or enamel (30 sec) followed by 15 seconds of rinsing (leave surface moist)
2)Apply primer to moist surface with microbrush (30 sec)
3)Initially let primer air dry and then apply air pressure to evaporate solvents (shiny surface)
4)Apply adhesive in thin even layer with microbrush
5)Light cure long enough to apply 18 Joules of radiant energy
6)Apply resin composite and light cure long enough for 8 Joules of radiant energy
Why do you want the tooth surface to be wet before applying primer?
increases penetration of primer and hydration of dentin, which helps with adhesion
Why do you want the tooth surface to be shiny after primer application?
indicates that primer has been applied properly, and it is ready for adhesive/bonding