cycs 200 week 12 - physical, infrastructure, and human resources security
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
logical security
protects computer-based data from software-based and communication-based threats
physical security
also infrastructure security
protects the information systems that contain data and the people who use, operate, and maintain the system
must prevent any type of physical access or intrusion that can compromise logical security
premises security
also known as corporate or facilities security
protects the people and property within an entire area, facility, or building(s), and is usually required by laws, regulations, and fiduciary obligations
provides perimeter security, access control, smoke and fire detection, fire suppression, some environment protection, and usually surveillance systems, alarms, and guards
physical security (in depth)
involves two complementary requirements:
prevent damage to physical infrastructure
concerns include information system hardware, physical facility, support facilities, and personnel
prevent physical infrastructure misuse that leads to the misuse or damage of protected information
vandalism, theft of equipment, theft by copying, theft of services, and unauthorized entry
physical security threats
environmental threats
technical threats
human-caused threats
characteristics of natural disasters
tornado
advance warning of potential; not site specific
remain at site
brief but intense
hurricane
significant advance warning
may require evacuation
hours to a few ddays
earthquake
no warning
may be unable to evacuate
brief duration; threat of continued aftershocks
ice storm/blizzard
several days warning generally expected
may be unable to evacuate
may last several days
lightning
sensors may provide minutes of warning
may require evacuation
brief but may recur
flood
several days warning generally expected
may be unable to evactuate
sit may be isolated for extended period
temp thresholds for damage to computing resources
disks, tapes, optical media, hard disk media, computer equipment, insulation, paper products can be damaged due to heat. starting at 38 degrees celcius to 177 degrees
water damage
primary danger is an electrical short
a pipe may burst from a fault in the line or from freezing
sprinkler systems set off accidentally
floodwater leaving a muddy residue and suspended material in the water
due diligence should be performed to ensure that water from as far as two floors above will not create a hazard
chemical, radiological, and biological hazards
pose a threat from intentional attack and from accidental discharge
discharges can be introduced through the ventilation system or open windows, and in the case of radiation, through perimeter walls
flooding can also introduce biological or chemical contaminants
technical threats
electrical power is essential to run equipment
power utility problems:
under-voltage
dips/brownouts/outages, interrupts service
over-voltage
surges/faults/lightening, can destroy chips
noise
on power lines, may interfere with device operation
electromagnetic interference (EMI)
noise along a power supply line, motors, fans, heavy equipment, other computers, cell phones, microwave relay antennas, nearby radio stations
noise can be transmitted through space as well as through power lines
can cause intermittent problems with computers
human-caused threats
less predictable, designed to overcome prevention measures, harder to deal with
unauthorized physical access
information assets are located in restricted areas
can lead to other threats such as theft, vandalism, or misuse
theft of equipment/data
eavesdropping and wiretapping
insider or outsider who has gained unauthorized access
vandalism of equipment
misuse of resources
physical security prevention and mitigation measures
use of cloud computing
inappropriate temp and humidity
environmental control equipment, power supply
fire and smoke
alarms, preventative measures, fire mitigatioin
smoke detectors, no smoking
water
manage lines, equipment location, cutoff sensors
other threats
appropriate technical counter-measures, limit dust entry, pest control
mitigation measures human-caused physical threats
physical access control
restrict building access
controlled areas patrolled or guarded
locks or screening measures at entry points
equip movable resources with a tracking device
power switch controlled by a security device
surveillance systems that provide recording and real-time remote viewing
recovery from physical security breaches
most essential element of recovery is redundancy
provides for recovery from loss of data
ideally all important data should be available off-site and updated as often as feasible
can use bath encrypted remote backup
for critical situations a remote hot-site that os ready to take over operation instantly can be created
physical equipment damage recovery
depends on nature of damage and cleanup
may need disaster recovery specialists
physical and logical security integration
numerous detection and prevention devices
more effective if there is a central control
integrate automated physical and logical security functions
use a single ID card
single-step card enrolment and termination
central ID-management system
unified event monitoring and correlation
benefits to organizations (security awareness, training, and education programs)
improving employee behaviour
increasing employee accountability
mitigating liability for employee behaviour
complying with regulations and contractual obligations
human factors
employee behaviour is a critical concern in ensuring the security of computer systems and information assets
principal problems associated with employee behaviour are:
erros and omissions
fraud
actions by disgruntled employees
awareness
seeks to inform and focus an employee’s attention on security issues within the organization
aware of their responsibilities for maintaining security and the restrictions on their actions
users understand the importance of security for the well-being of the organization
promote enthusiasm and management buy-in
program must be tailored to the needs of the organization and target audience
must continually promote the security message to employees in a variety of ways
should provide a security awareness policy document to all employees
training
designed to teach people the skills to perform their IT-related tasks more securely
what people do and how they should do it
general users
focus is good computer security practices
programmers, developers, system maintainers
develop a security mindset in the developer
management-level
how to make tradeoffs involving security risks, costs, benefits
executive-level
risk management goals, measurement, leadership
education
most in depth program
targeted at security professionals whose jobs require expertise in security
fits into employee career development category
often provided by outside sources
college courses
specialized training programs
employment practices and policies
managing personnel with potential access is an essential part of information security
employee involvement:
unwittingly aid in the commission of a violation by failing to follow proper procedures
forgetting security considerations
not realizing that they are creating a vulnerability
knowingly violate controls or procedures
security in the hiring process
to ensure that employees, contractors and third party users understand their responsibilities, and are suitable for the roles they are considered for, and to reduce the risk of theft, fraud or misuse of facilities.
need appropriate background checks and screening
investigate accuracy of details
for highly sensitive positions:
have an investigation agency do a background check
criminal record and credit check
termination of employment
termination security objectives:
ensure employees, contractors, and third party users exit organization or change employment in an orderly manner
the return of all equipment and the removal of all access rights are completed
critical actions:
remove name from all authorized access lists
inform guards that ex-employee general access is not allowed
remove personal access codes, change physical locks and lock combinations, reprogram access card systems
recover all assets, including employee ID, portable USB storage devices, documents, and equipment
notify by memo or email appropriate departments
email and internet use policies
organizations are incorporating specific email and internet use policies into their security policy document
concerns for employers:
work time consumed in non-word-related activities
computer and communications resources may be consumed, compromising the mission that the IT resources are designed to support
risk of importing malware
possibility of harm, harassment, inappropriate online conduct
security incident response
response procedures to incidents are an essential control for most orgs.
procedures need to reflect possible consequences of an incident on the organization and allow for a suitable response
developing procedures in advance can help avoid panic
benefits of having incident response capability
systematic incident response
quicker recovery to minimize loss, theft, disruption of service
use information gained during incident handling to better prepare for future incidents
dealing properly with legal issues that may arise during incidents
triage function
goal!
ensure that all information destined for for the incident handling service is channeled through a single focal point
commonly achieved by advertising the triage function as the single point of contact for the whole incident handling service
responds to incoming information by:
requesting additional information in order to categorize the incident
notifying the various parts of the enterprise or constituency about the vulnerability and shares information about how to fix or mitigate the vulnerability
identifies the incident as either new or part of an ongoing incident and passes this information on to the incident handing response function
responding to incidents
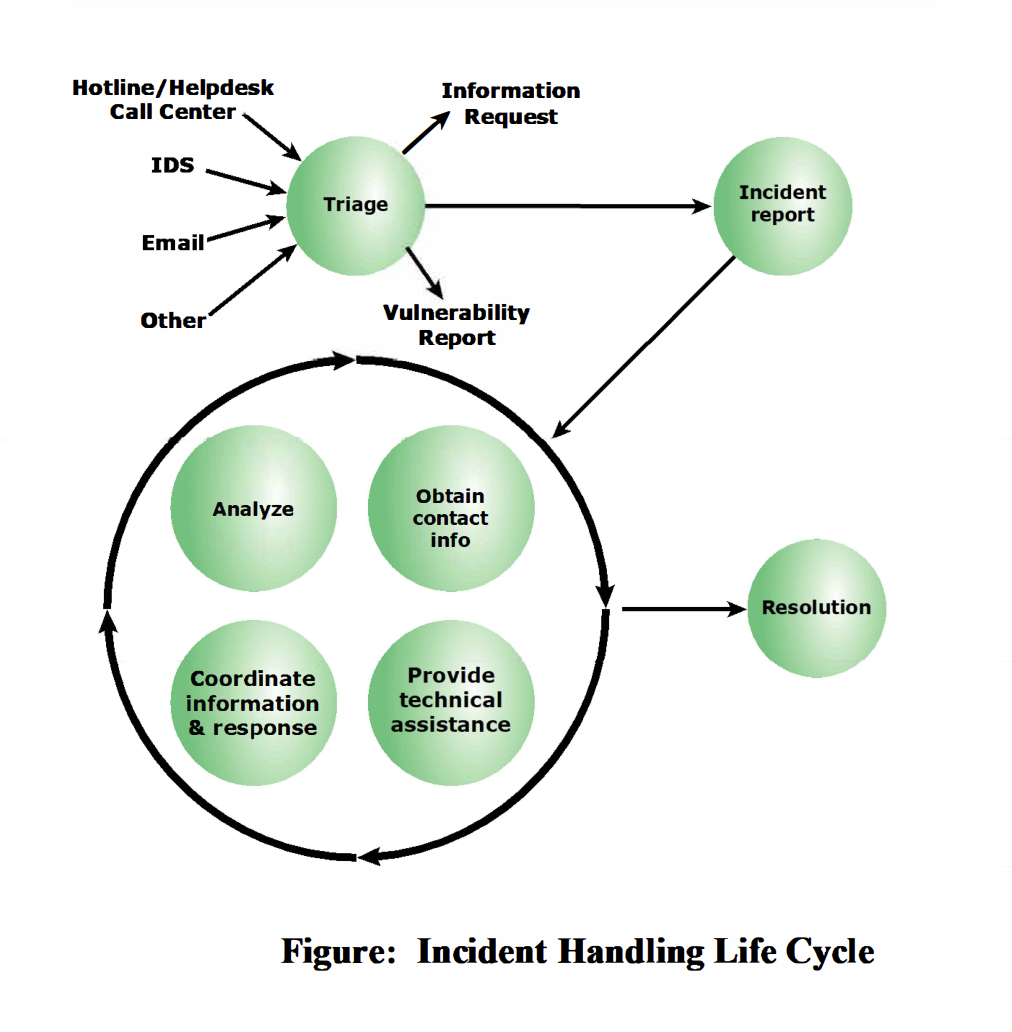
documenting incidents
should immediately follow a response to an incident
identify what vulnerability led to its occurence
how this might be addressed to prevent the incident in the future
details of the incident and the response taken
impact on the organization’s systems and their risk profile