Hypothesis Testing, t-Tests, and ANOVA for Social Science
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What is the purpose of hypothesis testing?
To determine whether there is enough evidence in a sample to infer that a certain condition is true for the entire population.
What are the two types of hypotheses in hypothesis testing?
Null hypothesis (H0) which expects no difference or effect, and alternative hypothesis (H1) which expects some difference or effect.
What does H0 represent in hypothesis testing?
H0 represents the assumption that there is no difference or effect, such as the salary of men and women not differing.
What is a directional hypothesis?
A hypothesis that specifies the direction of the expected difference, often using terms like 'more than' or 'less than'.
What is a non-directional hypothesis?
A hypothesis that states there is a difference without specifying the direction, often using phrases like 'there is a difference between'.
What is the first step in hypothesis testing?
Formulate the hypothesis, which includes defining both the null and alternative hypotheses.
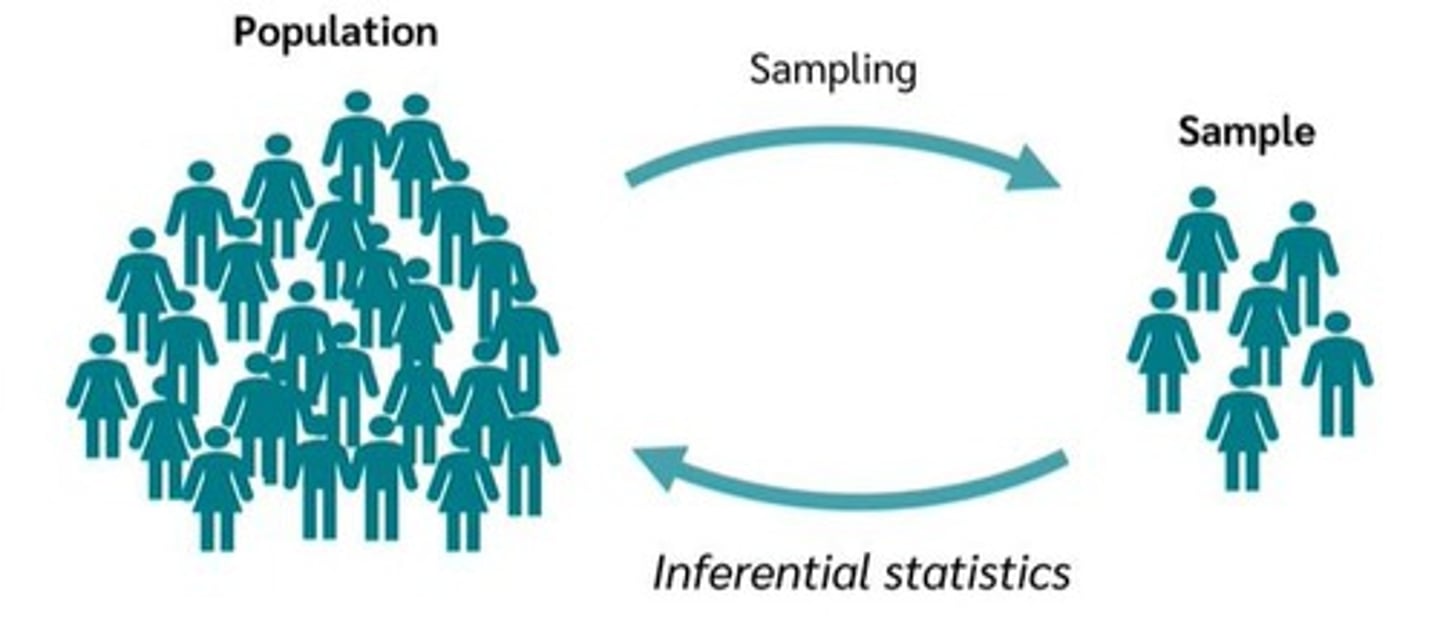
What is the role of a sample in hypothesis testing?
A sample is drawn from the population to make inferences about the entire population since it's often impractical to sample the whole population.
What is the p-value in hypothesis testing?
The p-value indicates the probability that a sample deviates at least as much as observed, assuming the null hypothesis (H0) is true.
What does it mean if the p-value is less than .05?
It indicates that the result is statistically significant, allowing for the rejection of the null hypothesis (H0).
What is a Type I Error?
Occurs when the null hypothesis (H0) is rejected when it is actually true, indicating a false positive.
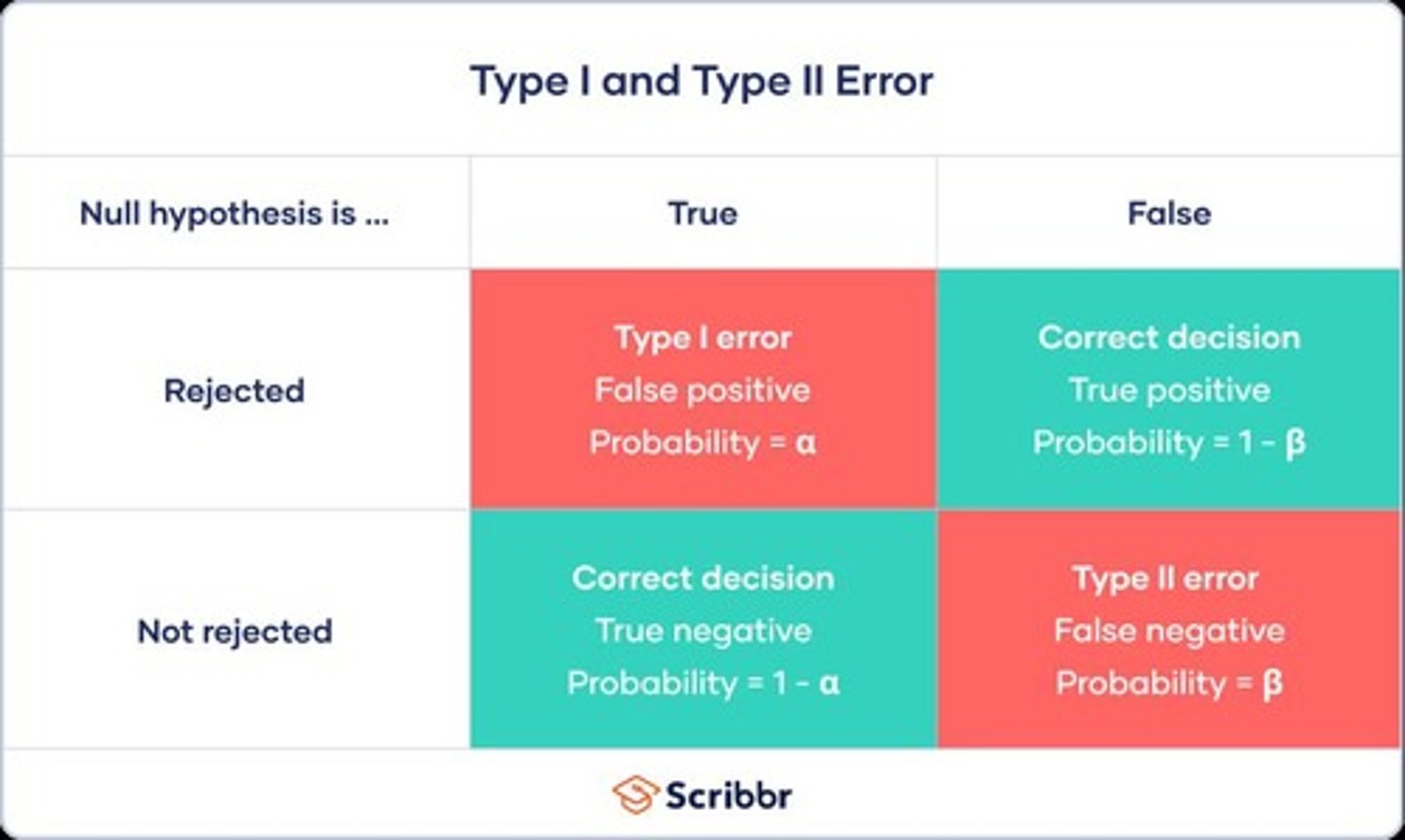
What is a Type II Error?
Occurs when the null hypothesis (H0) is not rejected when it is false, indicating a false negative.
What are parametric tests?
Statistical tests that assume the data follows a certain distribution, typically normal distribution.
What are non-parametric tests?
Statistical tests that do not assume a specific distribution and are used when data is not metric or the sample size is small.
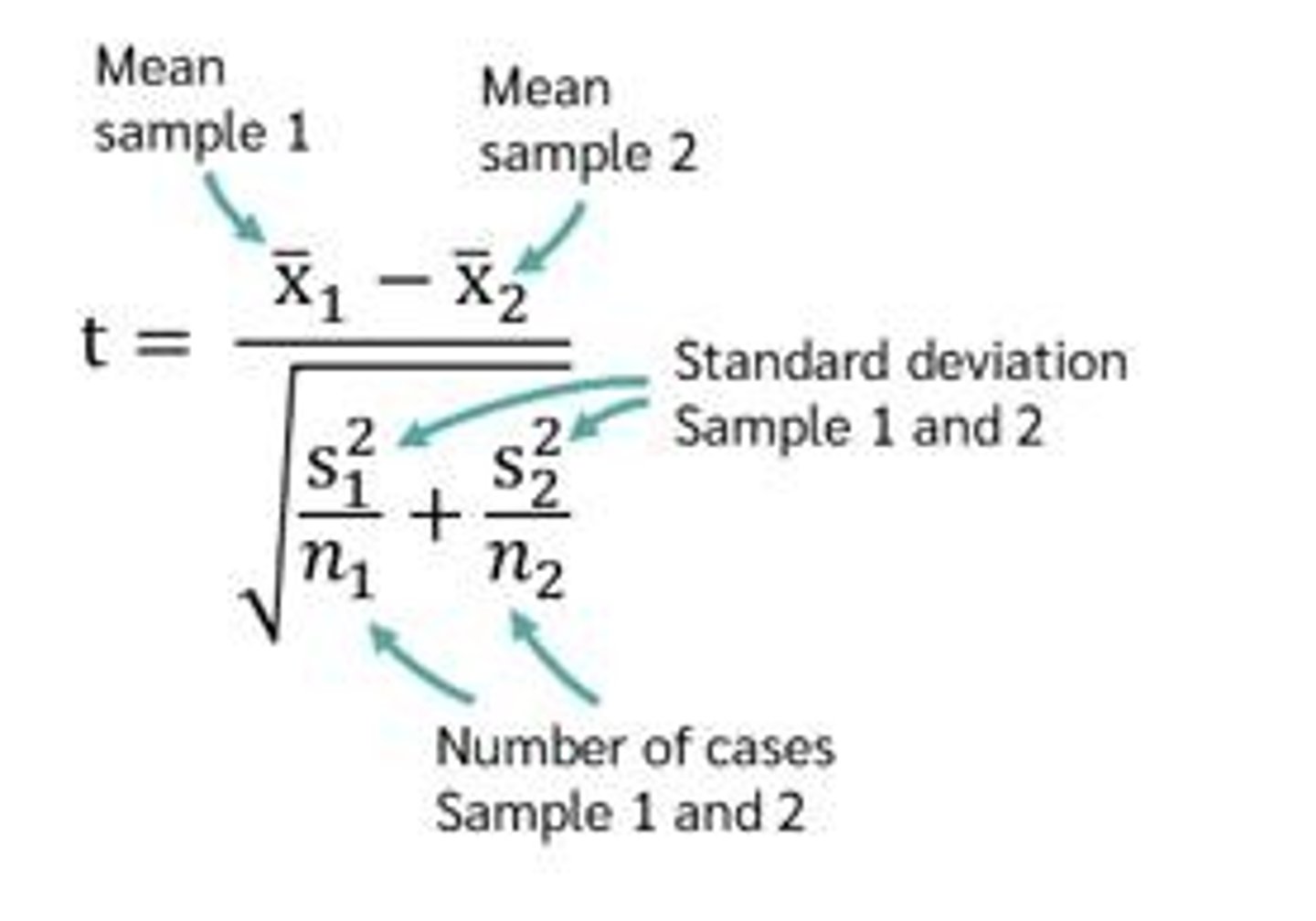
What is the difference between a sample t-test and a t-test for independent samples?
A sample t-test compares the mean of a single group to a known value, while a t-test for independent samples compares the means of two different groups.

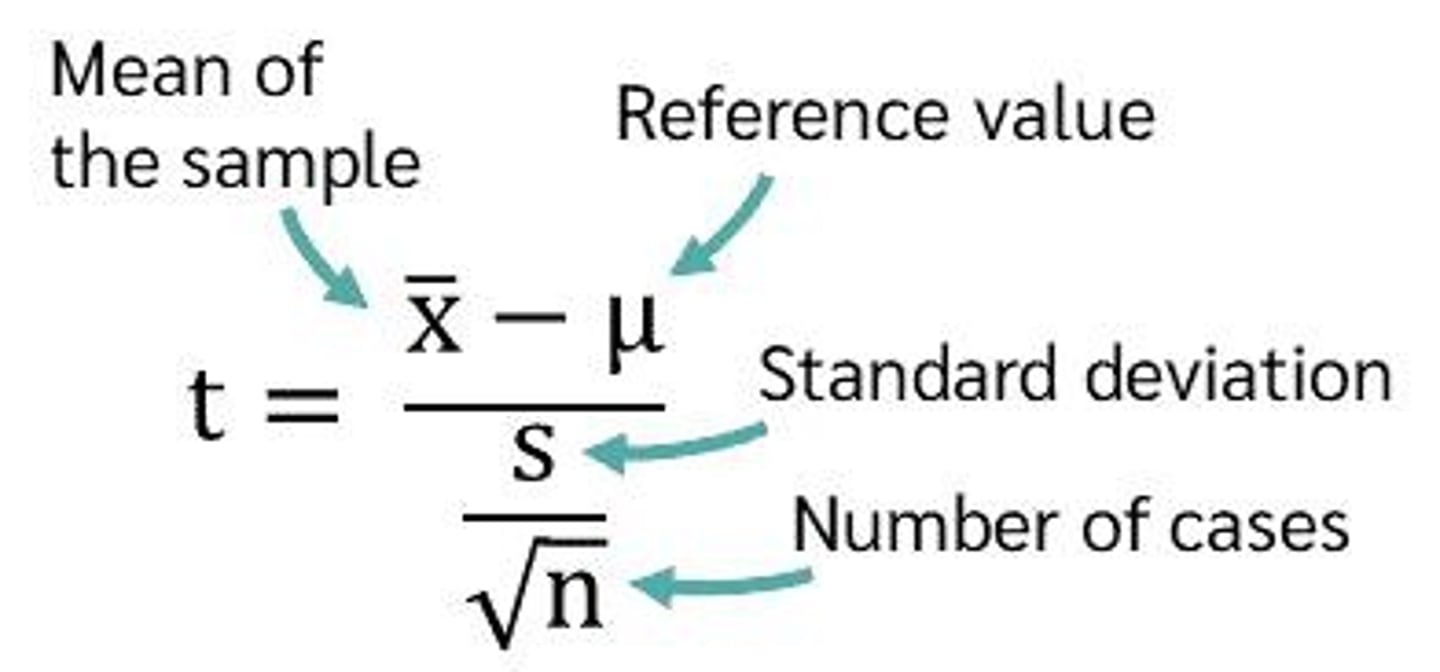
What is the formula for calculating t-values in a sample t-test?
The formula is t = (X̄ - μ) / (s / √n), where X̄ is the sample mean, μ is the population mean, s is the sample standard deviation, and n is the sample size.
What is the formula for a paired samples t-test?
The formula is t = (D̄) / (sD / √n), where D̄ is the mean of the differences, sD is the standard deviation of the differences, and n is the number of pairs.
What is the significance of the level of significance (α)?
It is the threshold for determining whether to reject the null hypothesis, commonly set at 0.05.
What does it mean to reject the null hypothesis?
It means that the evidence suggests that there is a statistically significant effect or difference present.
What is the relationship between sample size and hypothesis testing?
Larger sample sizes generally provide more reliable results and reduce the risk of Type I and Type II errors.
What is the role of statistical significance in hypothesis testing?
Statistical significance indicates that the observed results are unlikely to have occurred by chance alone.
What is an example of a difference hypothesis?
An example is 'men earn more than women' where one variable is categorical (gender) and the other is ordinal (salary).
What is an example of a correlation hypothesis?
An example is 'the taller the person, the more they spend at a restaurant', involving two ordinally scaled variables.
What is the formula for degrees of freedom in a one sample t-test?
df = n - 1
What is the formula for degrees of freedom in an independent samples t-test?
df = n1 + n2 - 2
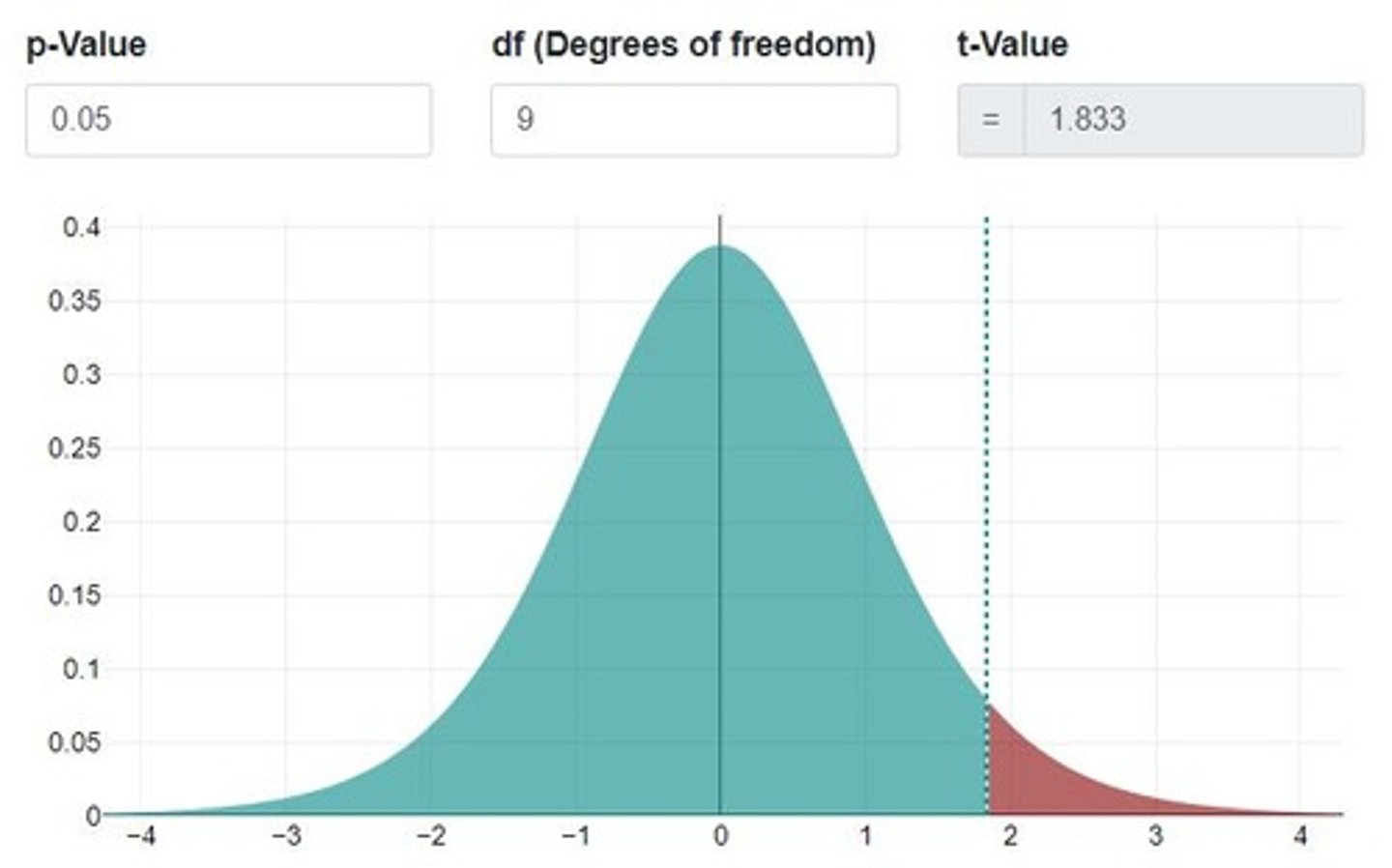
What critical t-value corresponds to a significance level of 5% and 9 degrees of freedom for a one-sided test?
1.833
What critical t-value corresponds to a significance level of 5% and 9 degrees of freedom for a two-sided test?
2.262
What is the decision rule regarding H0 when the calculated t-value is greater than the critical t-value?
Reject H0.
In the chocolate bar example, what was the sample mean weight?
48 grams
What was the null hypothesis (H0) in the chocolate bar example?
The sample mean is equal to 50g.
What was the calculated t-value in the chocolate bar example?
2.488
What was the critical t-value for the chocolate bar example with 29 degrees of freedom?
2.045
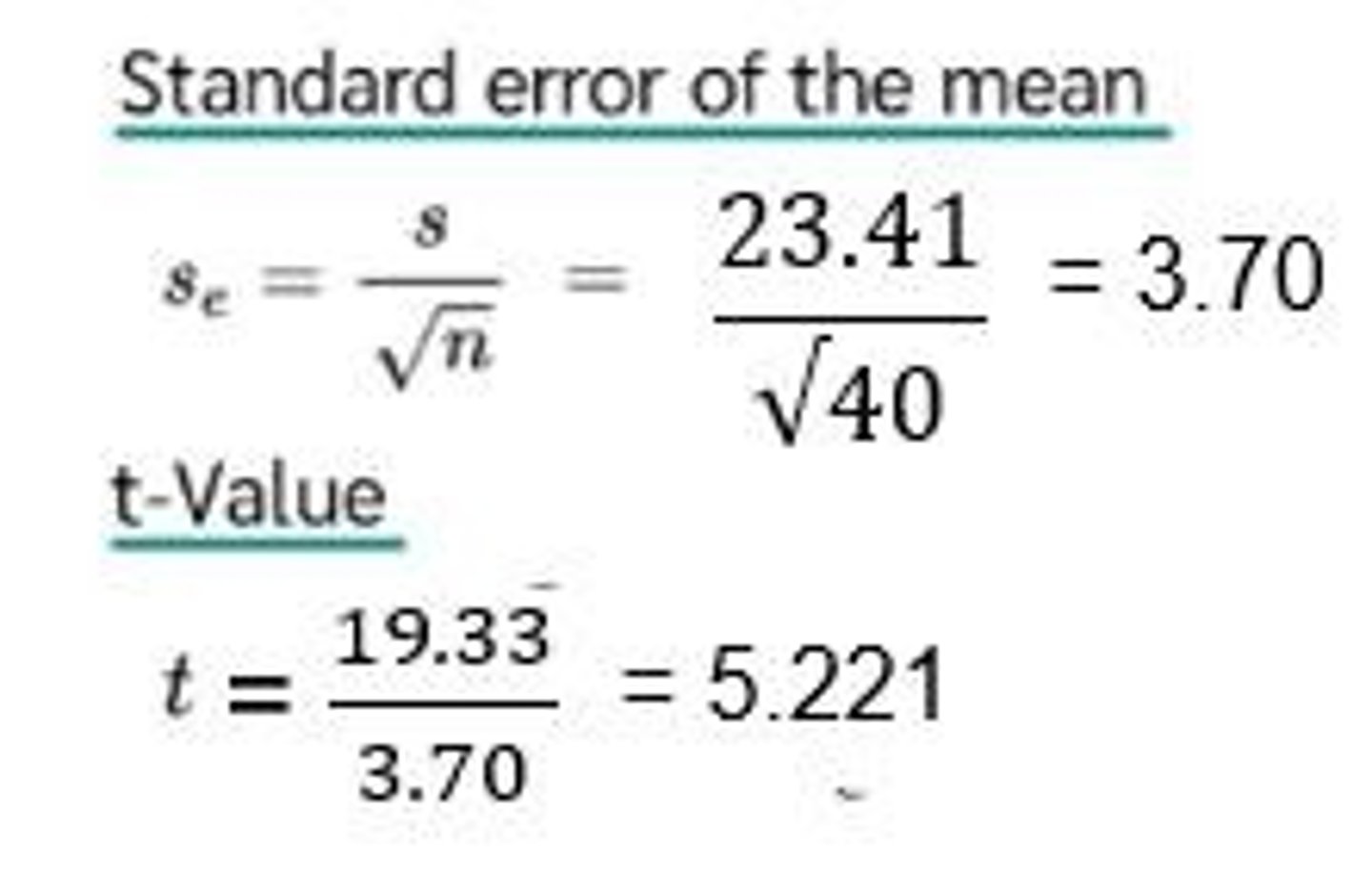
What does a calculated t-value of 5.221 indicate in the Lowe's coupon example?
H0 can be rejected; the promotion has an impact on consumer spending.
What is the purpose of ANOVA?
To test whether statistically significant differences exist between more than two samples.
What does one-way ANOVA investigate?
Whether one independent variable has an influence on a metric dependent variable.
What is the hypothesis for a one-way ANOVA comparing calorie consumption?
H0: There is no difference in calorie consumption between groups.
What is the hypothesis for a two-way ANOVA regarding social crowding and type of crowding?
H0: These two factors do not interact.
What are the assumptions required for a repeated measures ANOVA?
Dependent samples, normality, sphericity, homogeneity of variances, no significant outliers.
What is the null hypothesis for the weight loss program in a repeated measures ANOVA?
There is no difference over time.
What is the significance of Levene's test in ANOVA?
It tests for homogeneity of variances across groups.
What is the significance of Mauchly's test in repeated measures ANOVA?
It tests for sphericity of variances of the differences.
What is the SPSS command to perform a one sample t-test?
Analyze → Compare Means → One Sample T Test.
What is the SPSS command to perform a paired samples t-test?
Analyze → Compare Means → Paired Samples T Test.
What is the SPSS command to perform a two-way ANOVA?
Analyze → General Linear Model → Univariate.
What does a calculated t-value less than the critical t-value indicate?
H0 cannot be rejected.
What is the significance level typically set at for hypothesis testing?
5%.
What is the purpose of defining groups in an independent samples t-test in SPSS?
To compare means between different groups.