Glencoe Biology - 6.4 Macromolecules
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
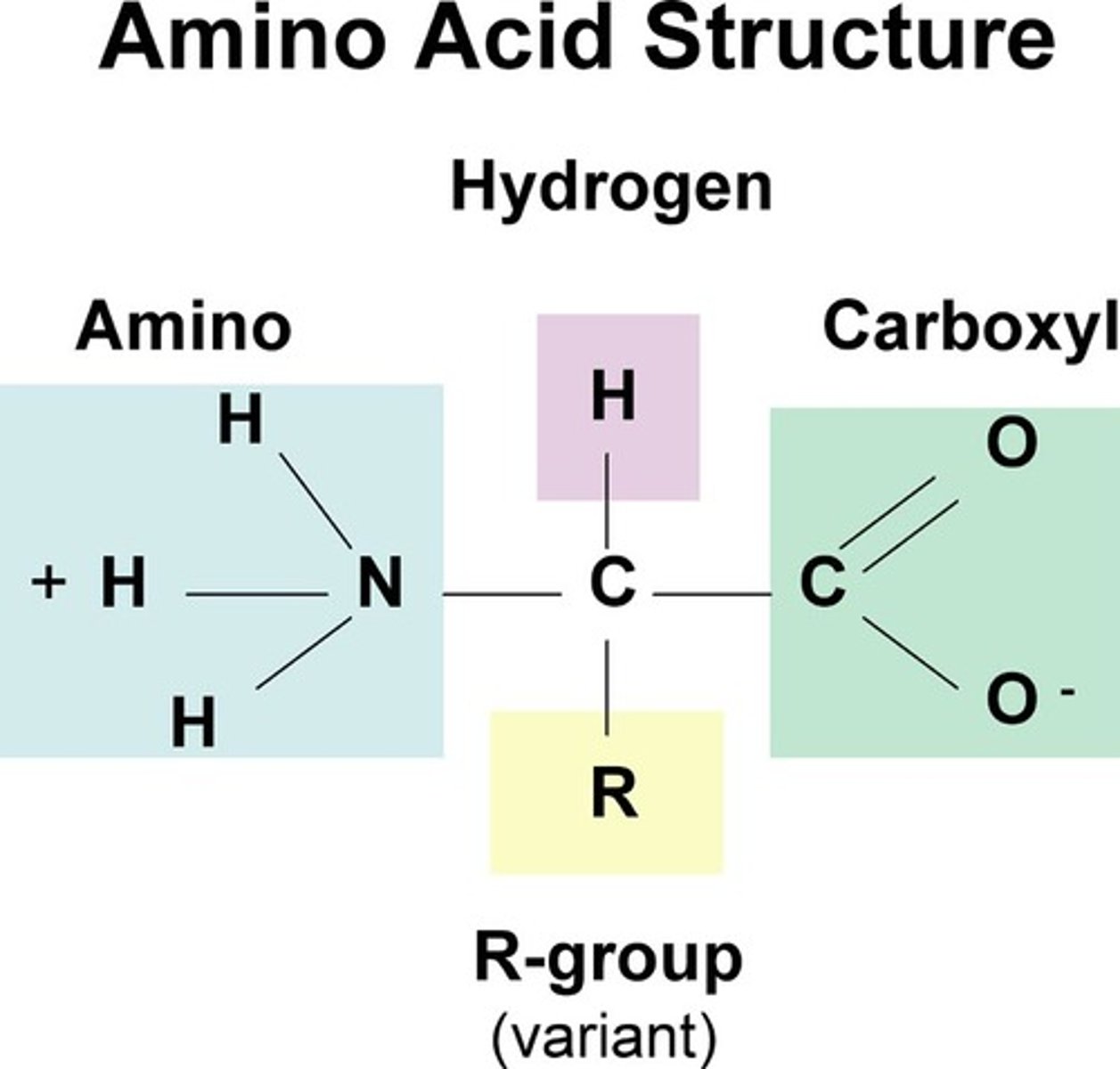
Amino acid
Small carbon compound joined by peptide bonds; monomers (building block) of proteins. "R" group makes each of the 20 amino acids unique.
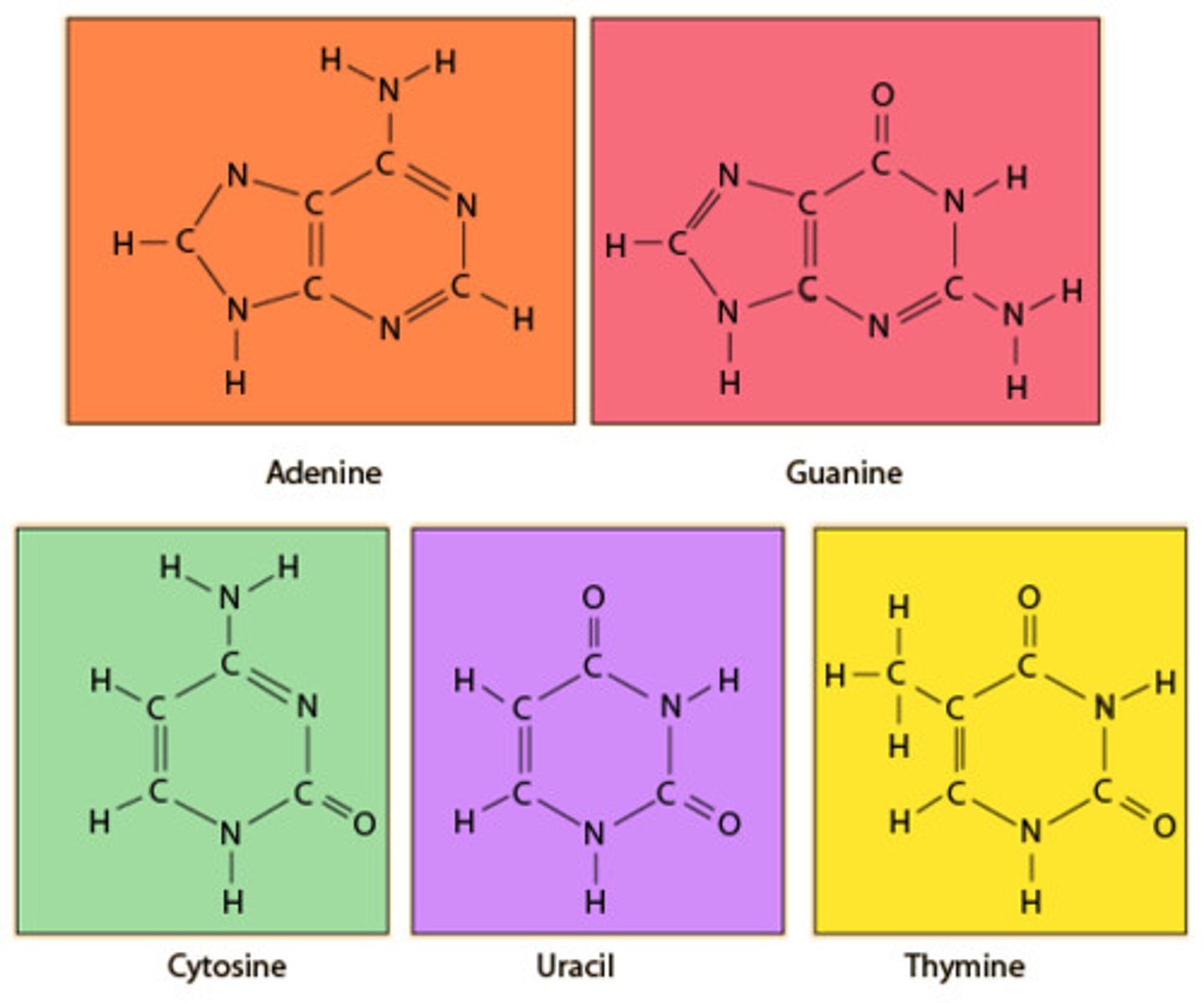
(Nitrogenous) Base
part of a nucleotide which make up Nucleic acids. It is the part that gives each nucleotide its identity. A,T,G,C or U
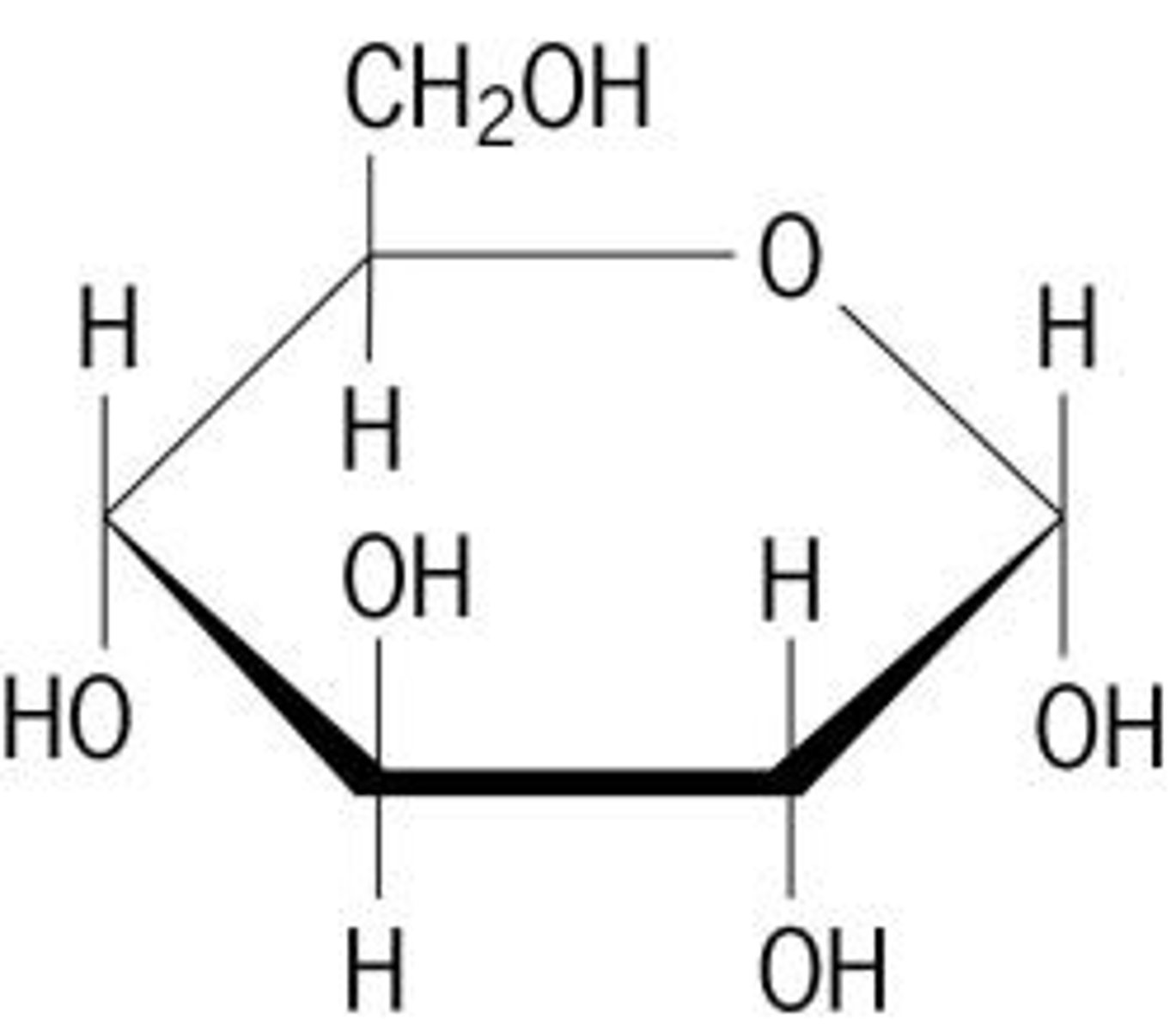
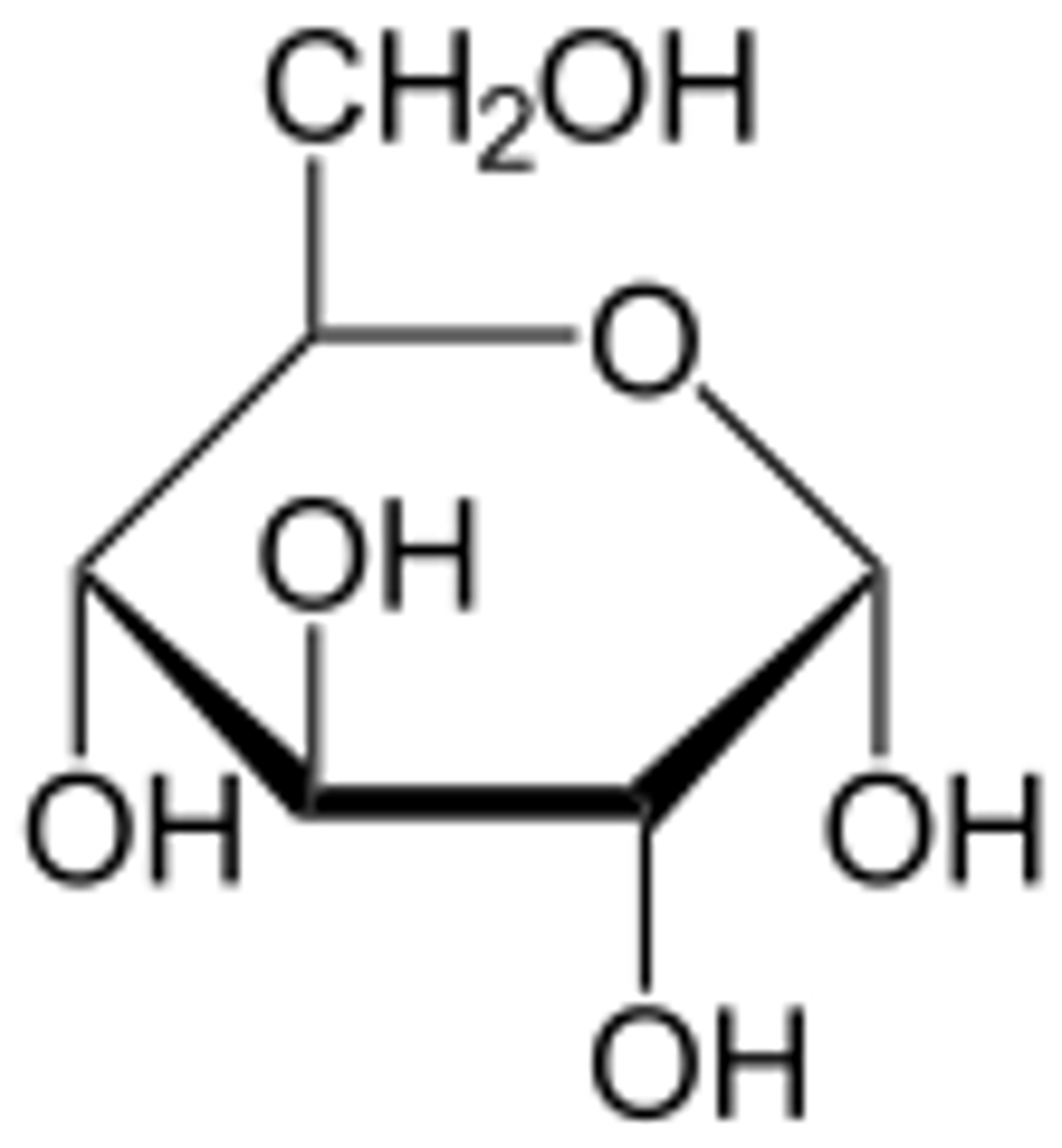
Carbohydrate
CHO 1:2:1 ratio of one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms for each carbon atom. CH2O. Used for quick energy and structure in plants.
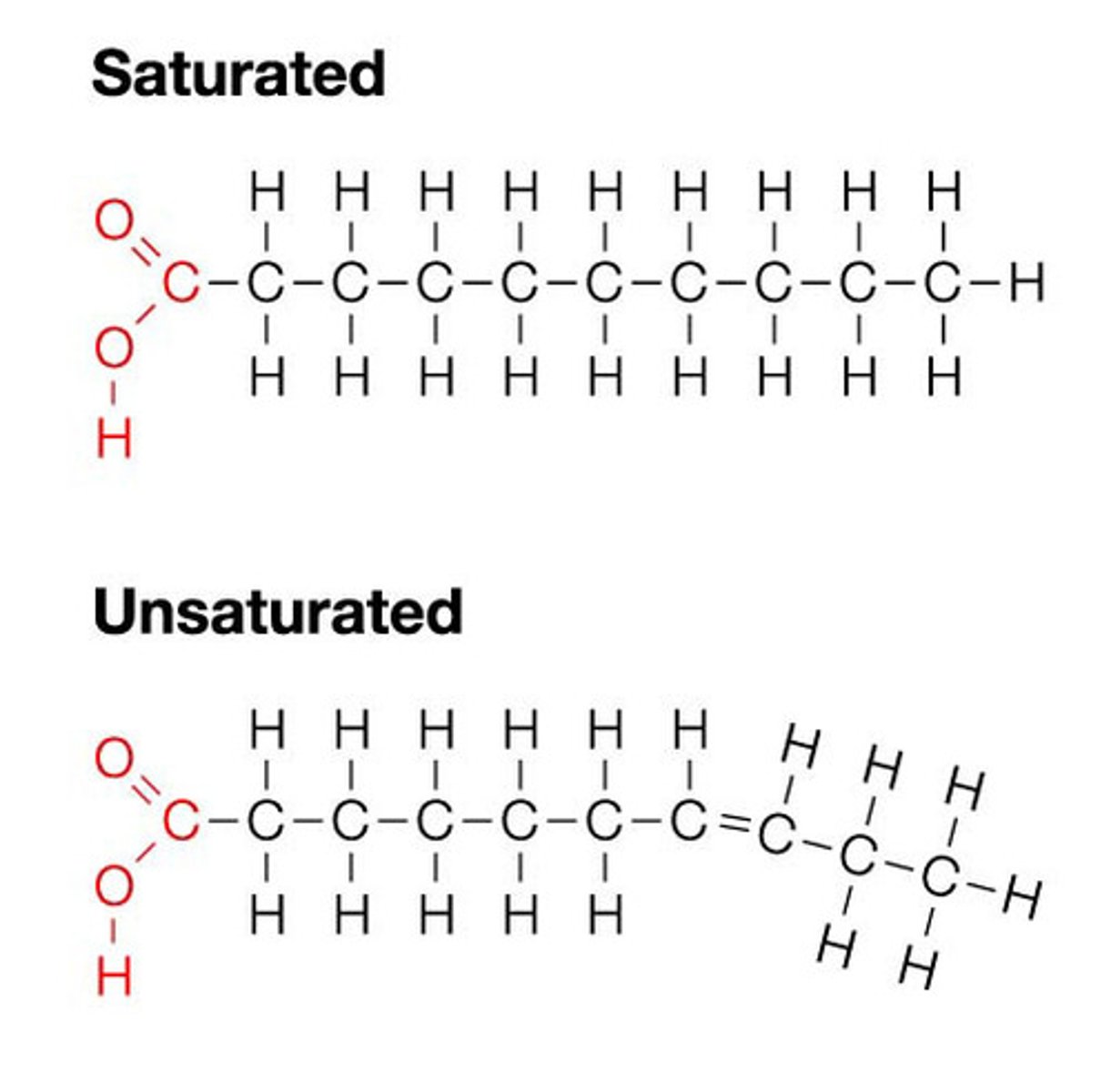
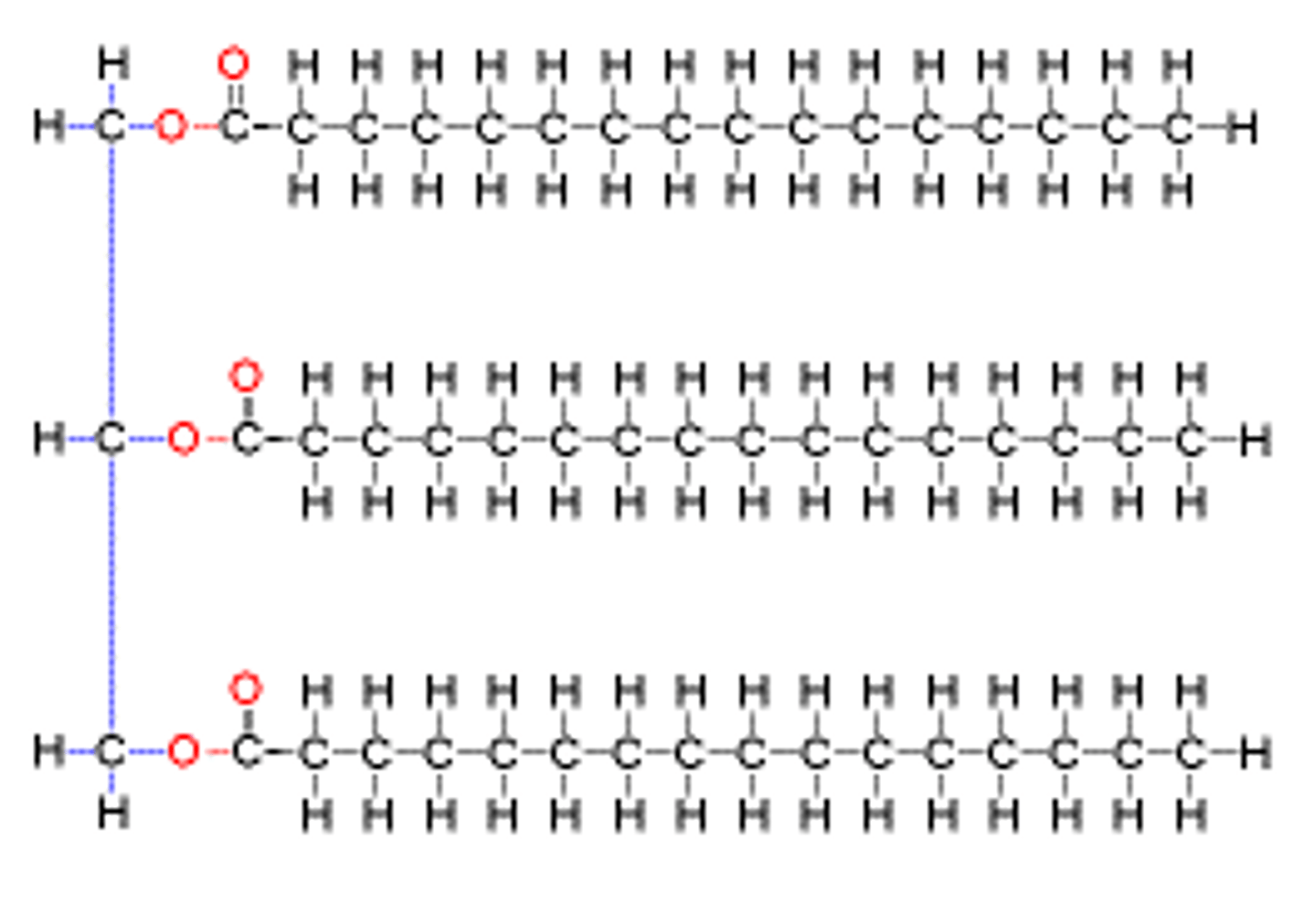
Lipid
CHO -biological molecule composed mostly of carbon and hydrogen; fats, oils, and waxes are lipids. Lots of CH bonds to break creates lots of energy.
Macromolecule
Large molecule formed by joining smaller organic molecules (subunits, monomers) together.
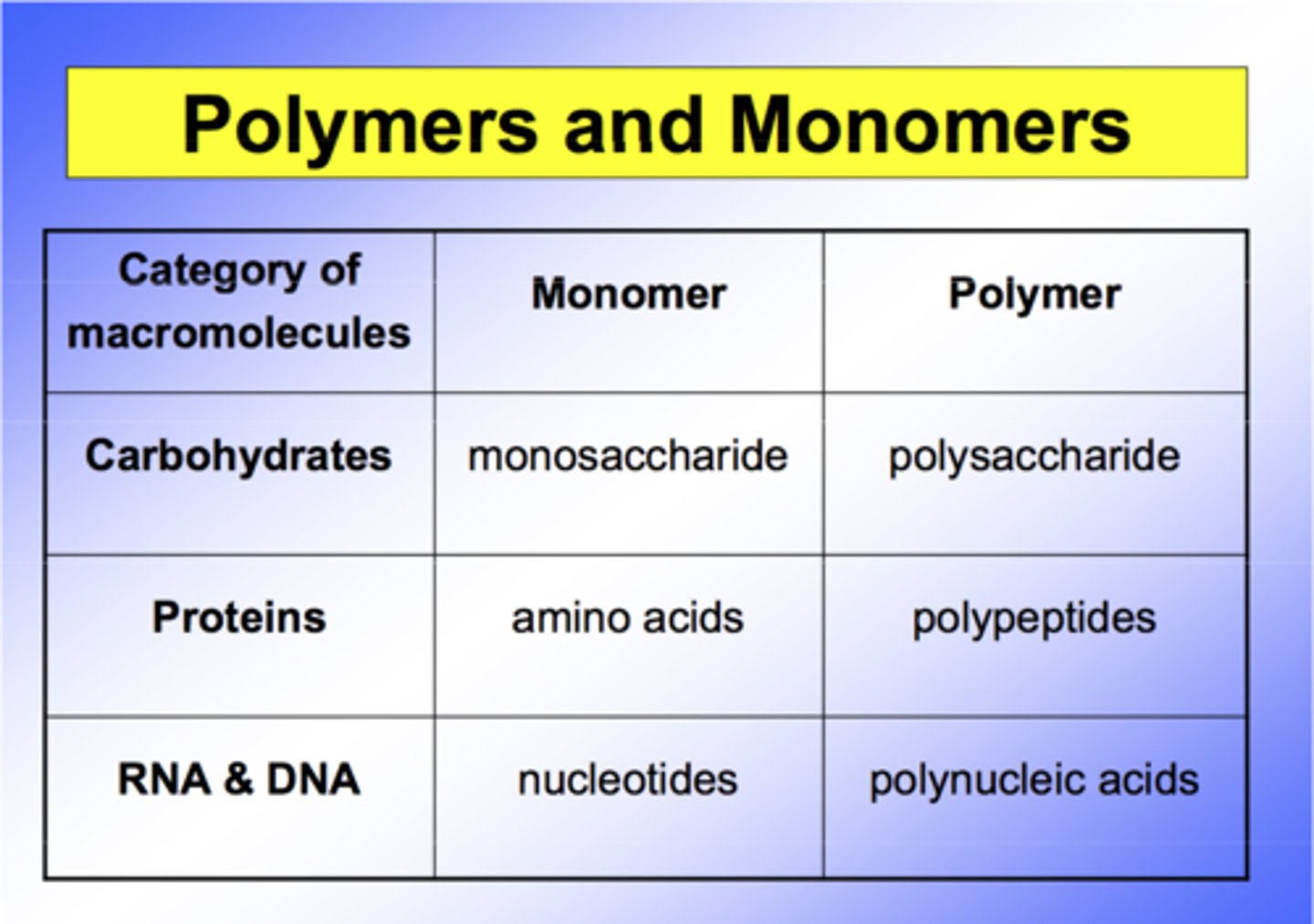
Nucleic acid
CHONP -Complex macromolecule that stores and communicates genetic information. monomer is a nucleotide. DNA or RNA
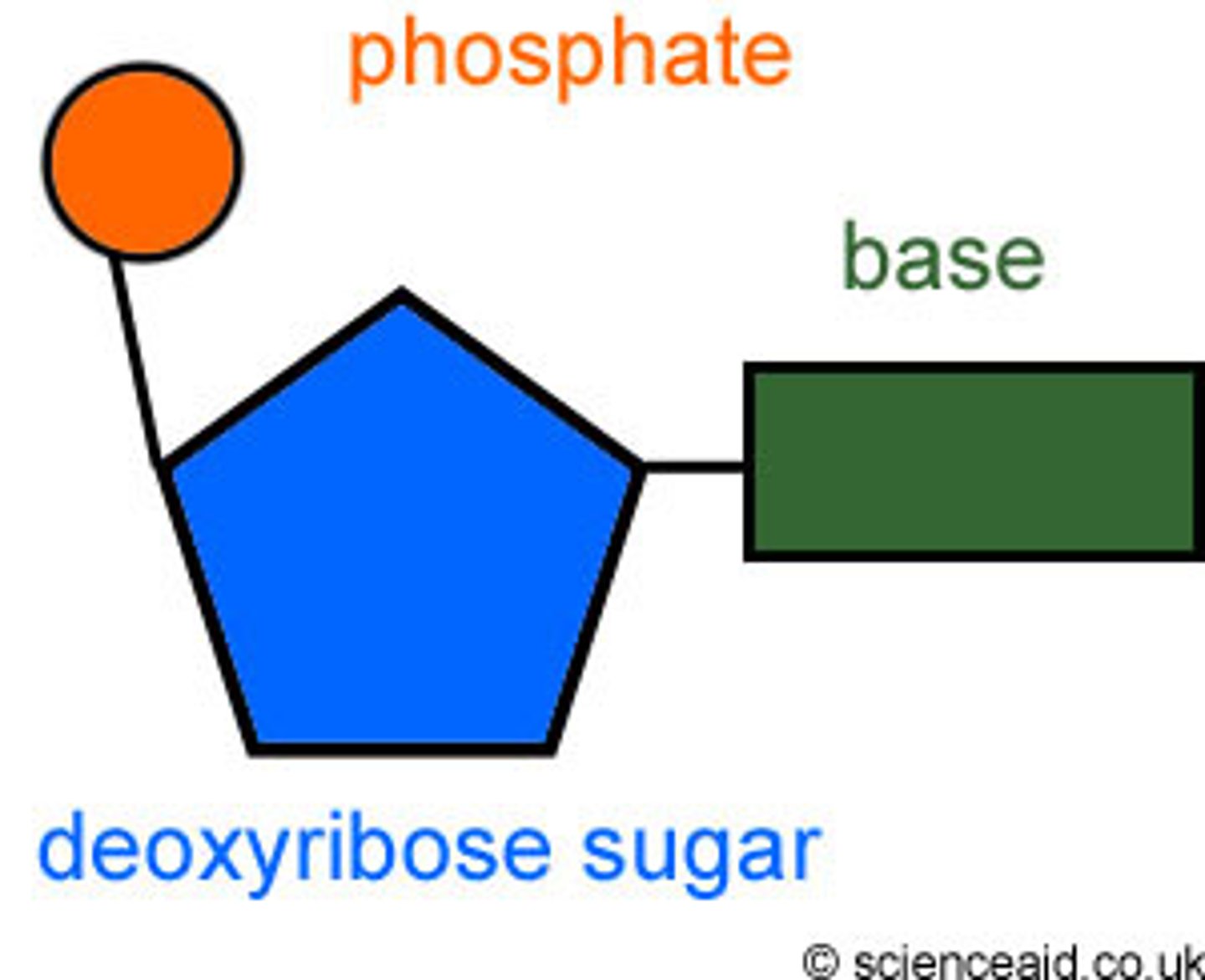
Nucleotide
A subunit of nucleic acid formed from a simple sugar, ribose(RNA) or deoxyribose(DNA), a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base.
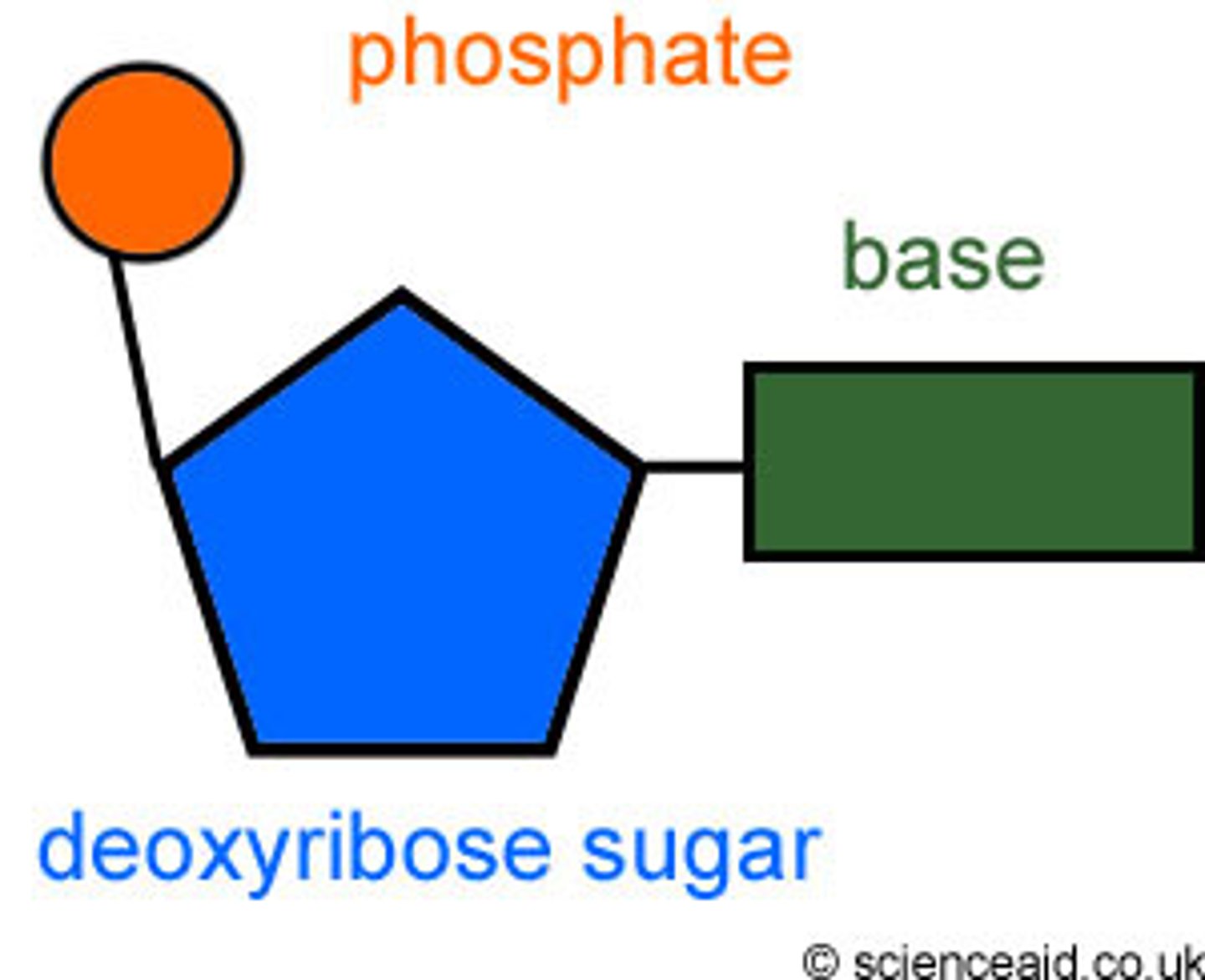
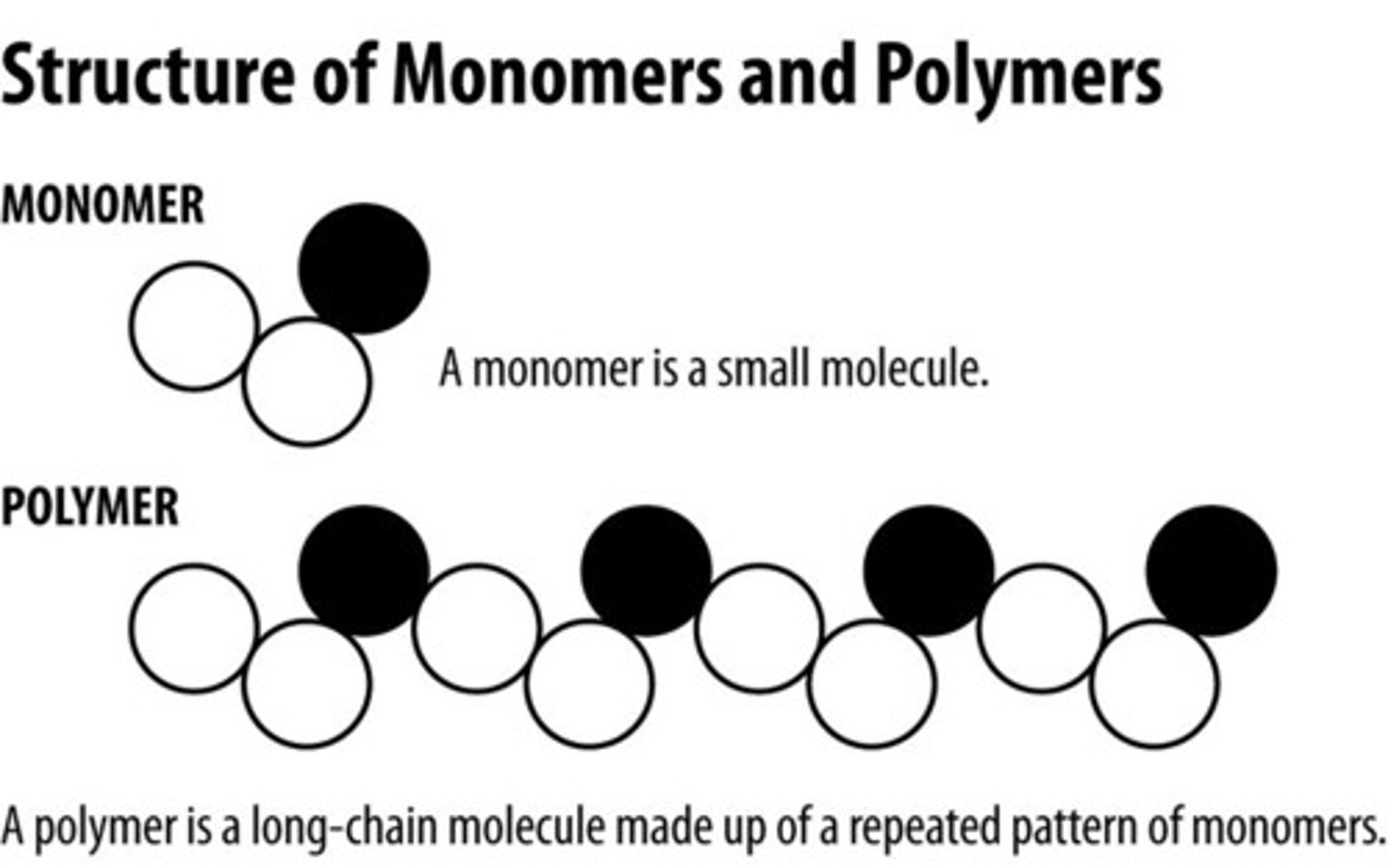
Polymer
Large molecule formed from smaller repeating units of identical, or nearly identical, compounds linked by covalent bonds. poly=many
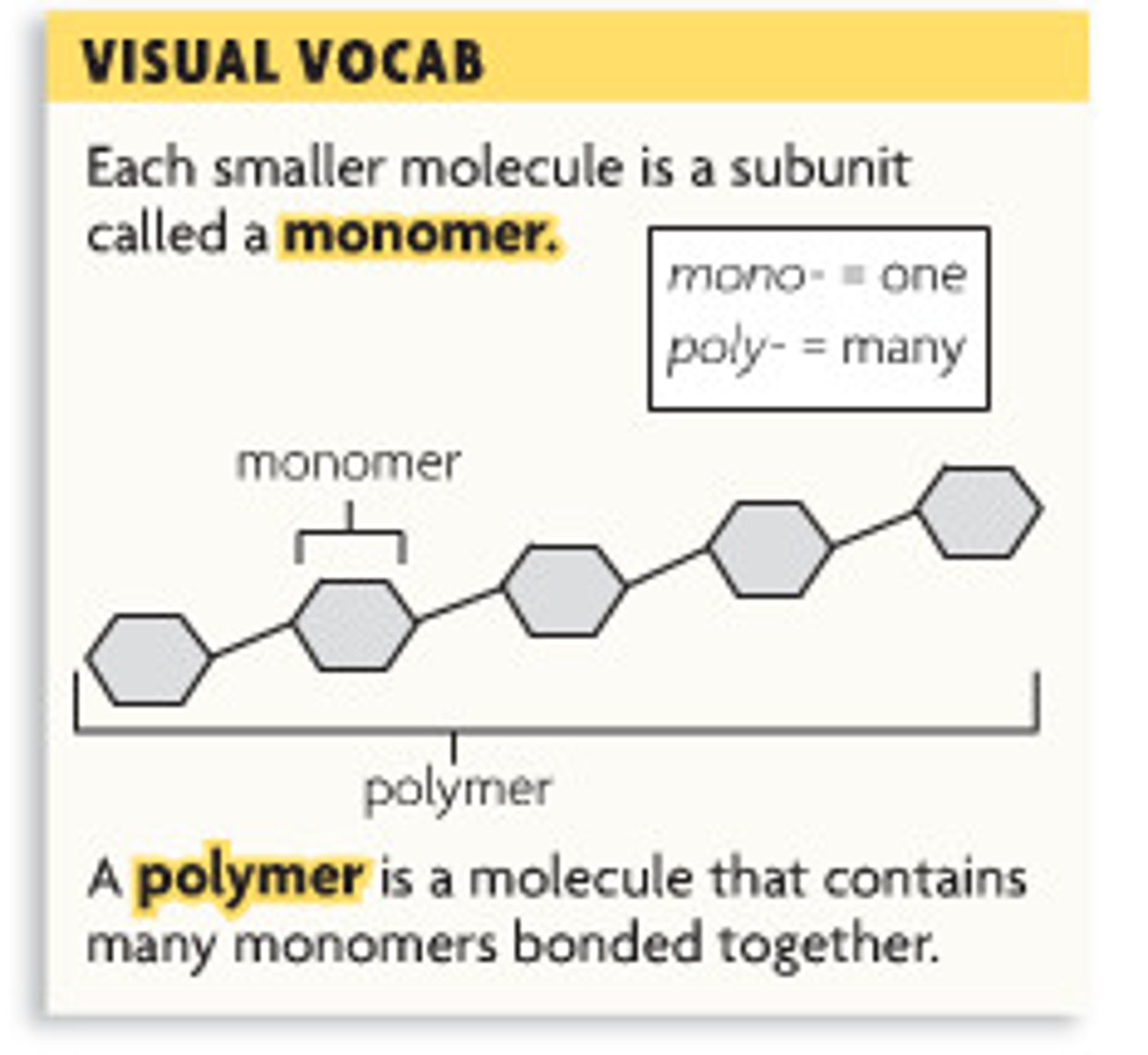
Protein
CHON Organic compound made of amino acids joined by peptide bonds; primary building block of organisms. Used mainly for structure, enzymes, hormones
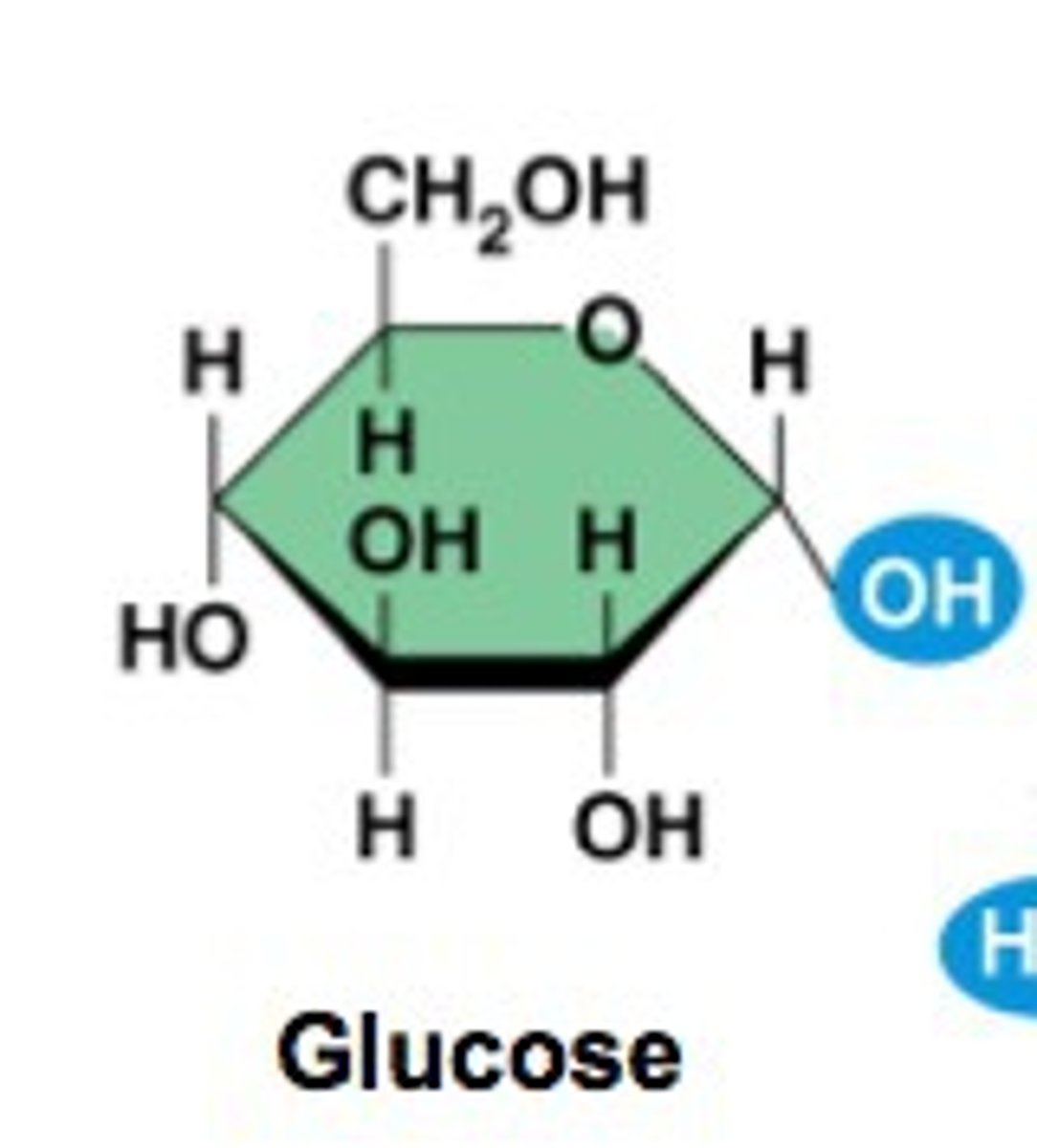
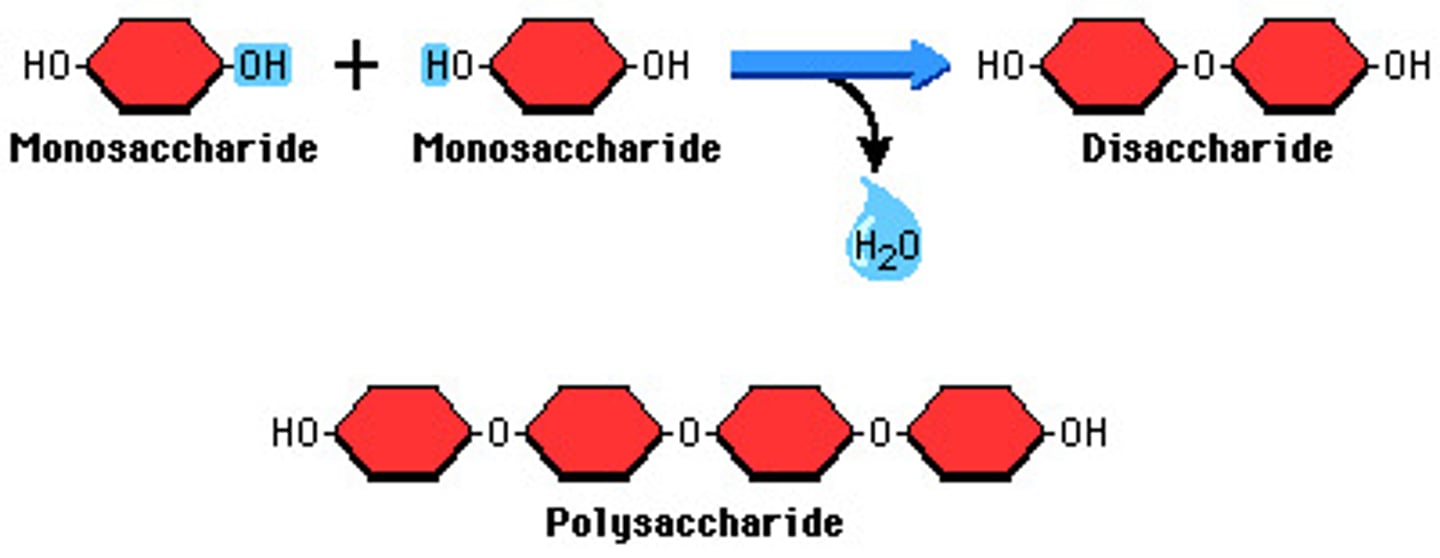
Monosaccharides
simplest form of sugar. water-soluble. often have a sweet taste. glucose. building blocks(monomers) of all carbohydrates
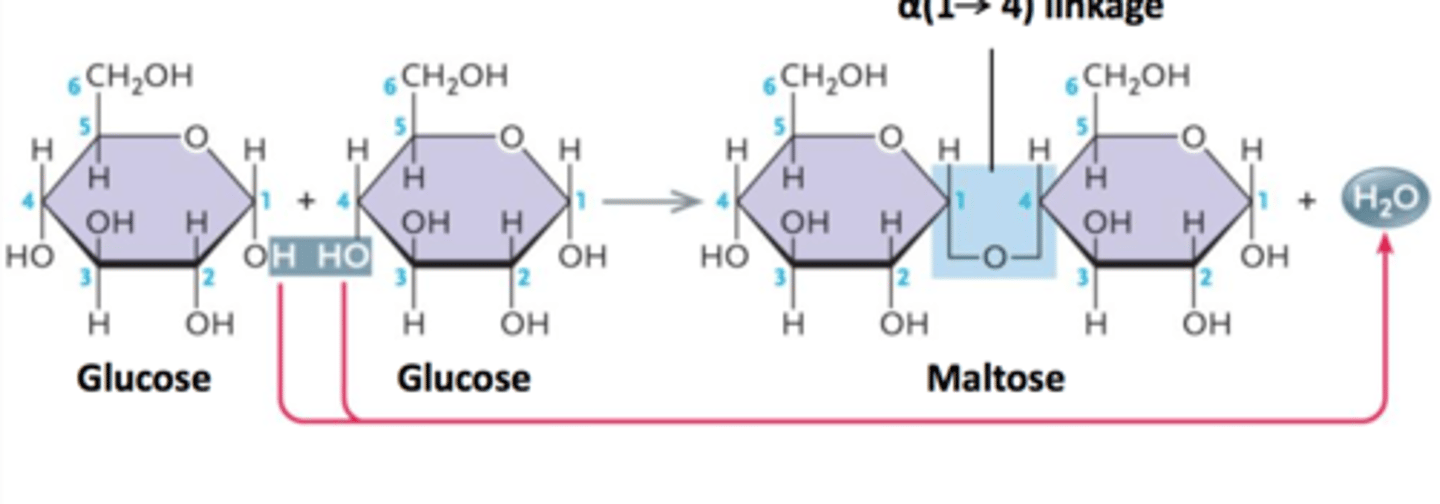
Disaccharides
A double sugar, consisting of two monosaccharides joined by dehydration synthesis.
Polysaccharide
A polymer of many simple sugars formed by dehydration synthesis.
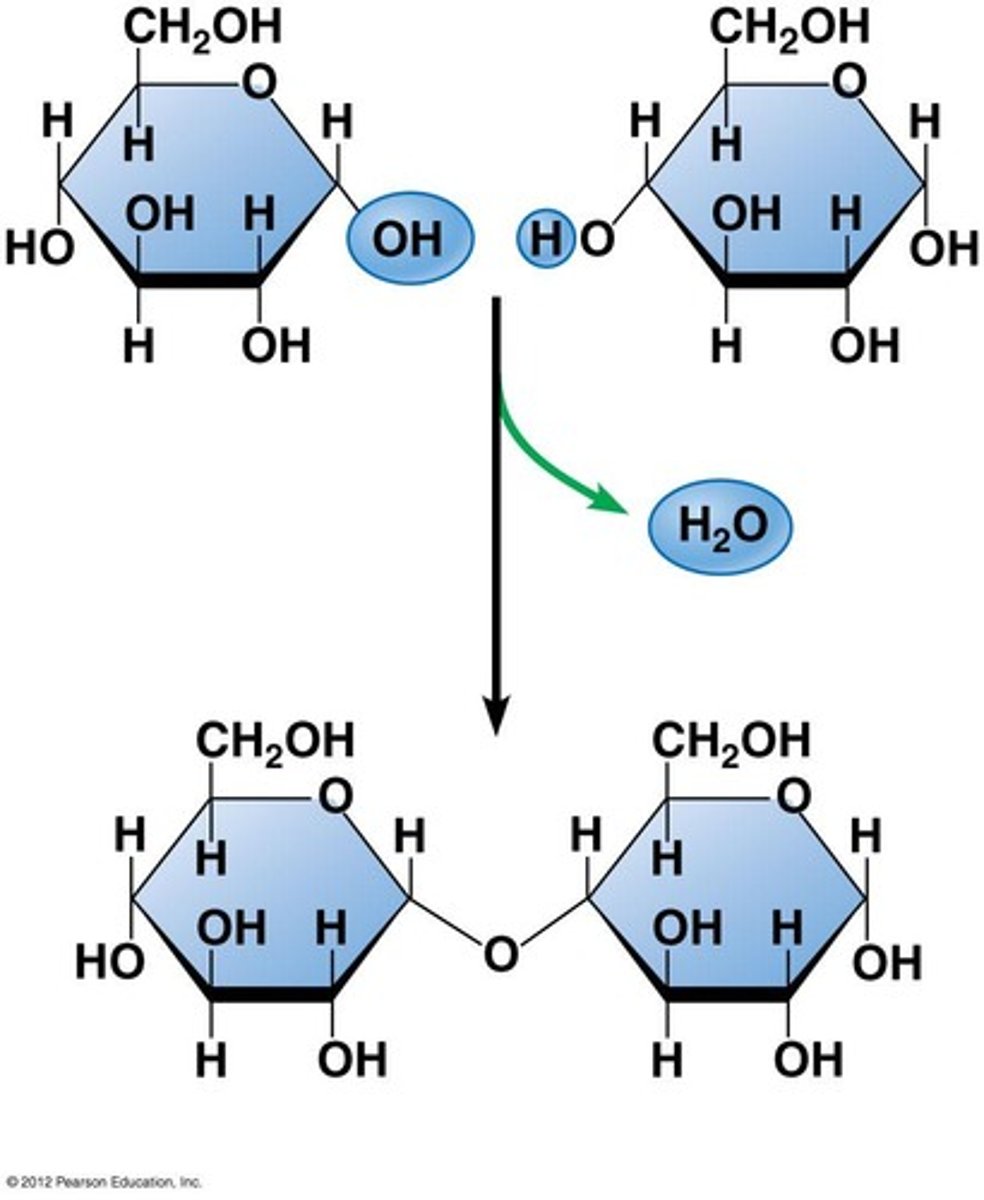
Dehydration Synthesis
A chemical reaction in which two molecules covalently bond to each other with the removal of a water molecule. Occurs when larger molecules are created.
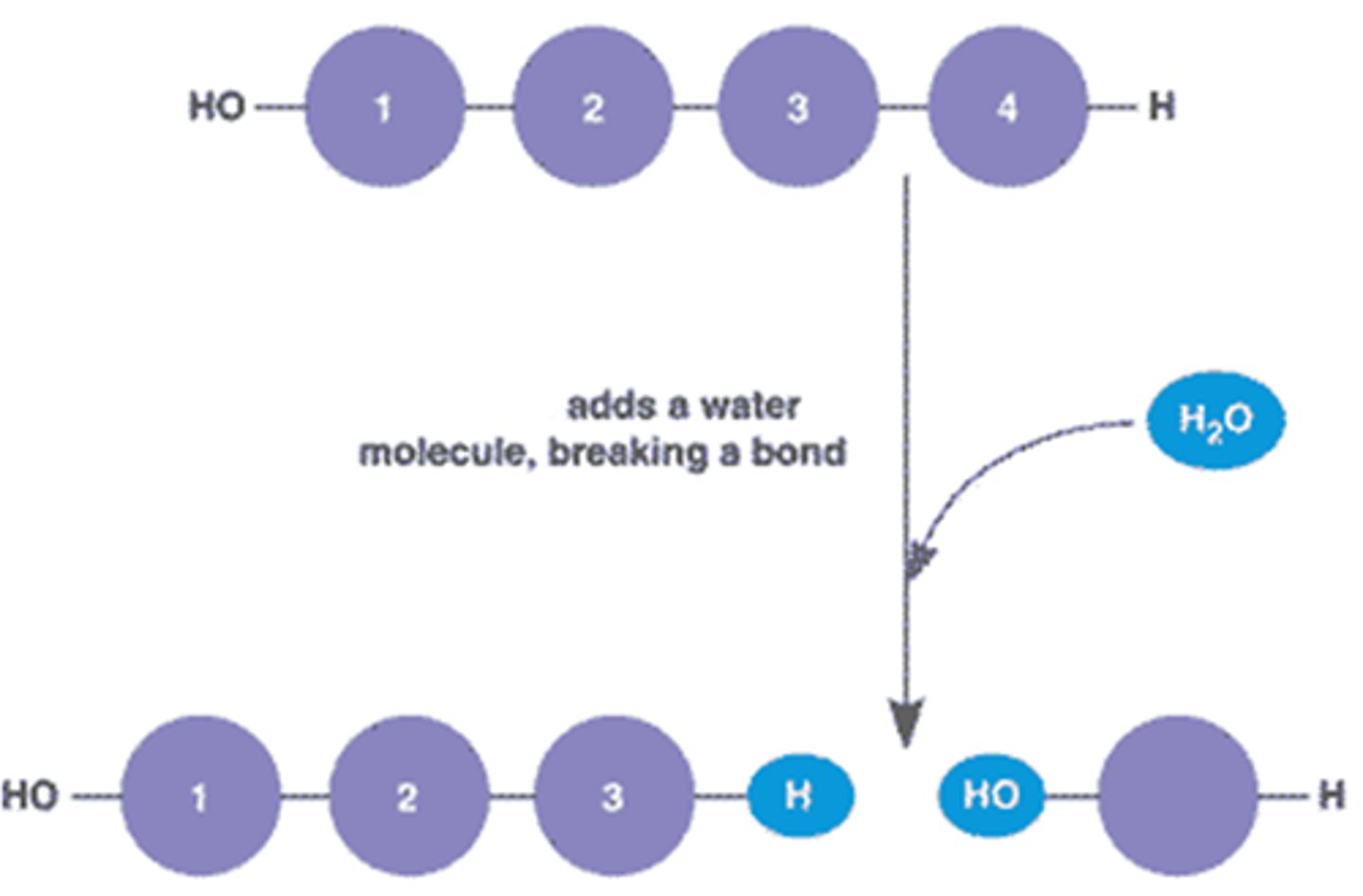
Hydrolysis
Breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water
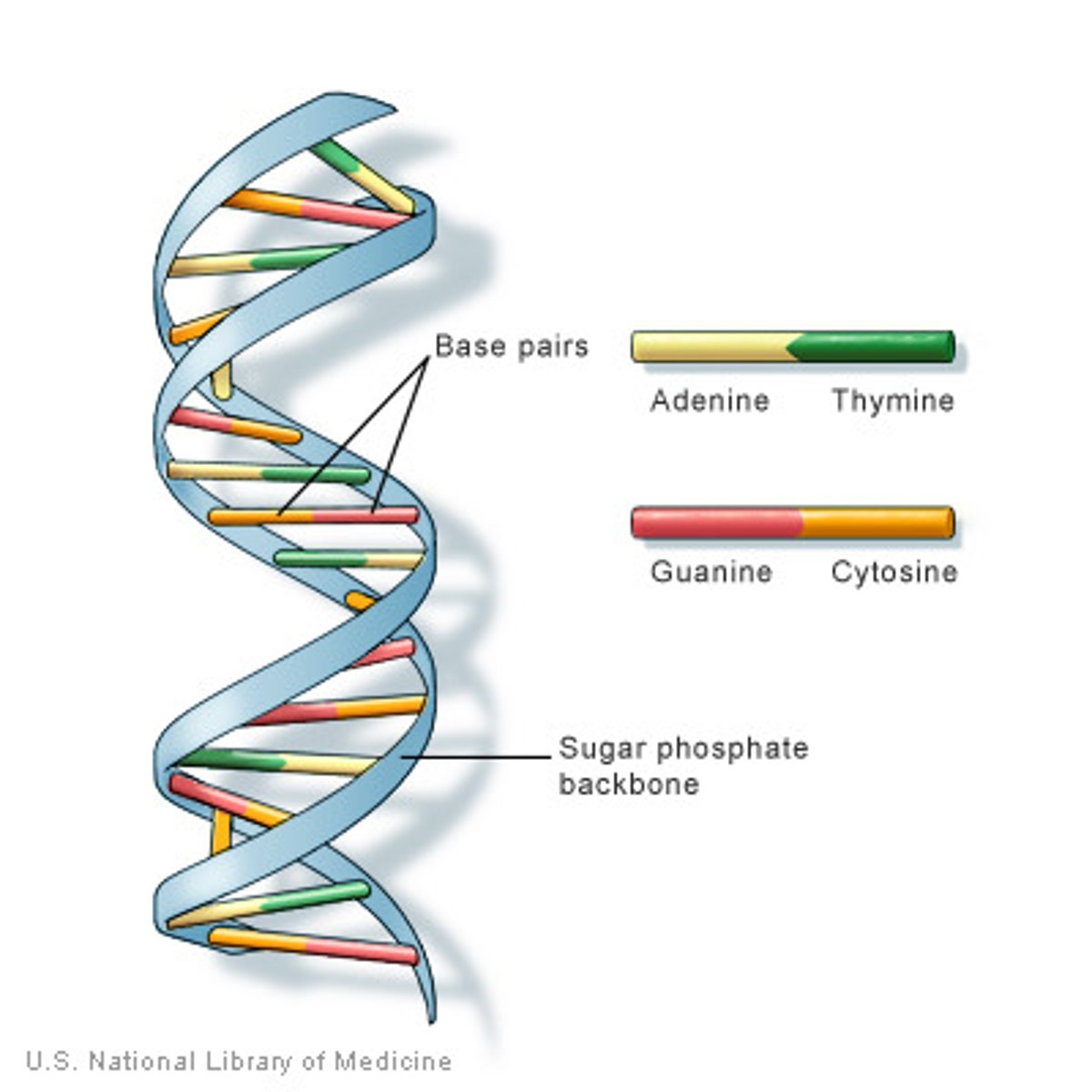
DNA
A double-stranded, helical nucleic acid molecule which caries the information for heredity. It determines the structure of proteins.
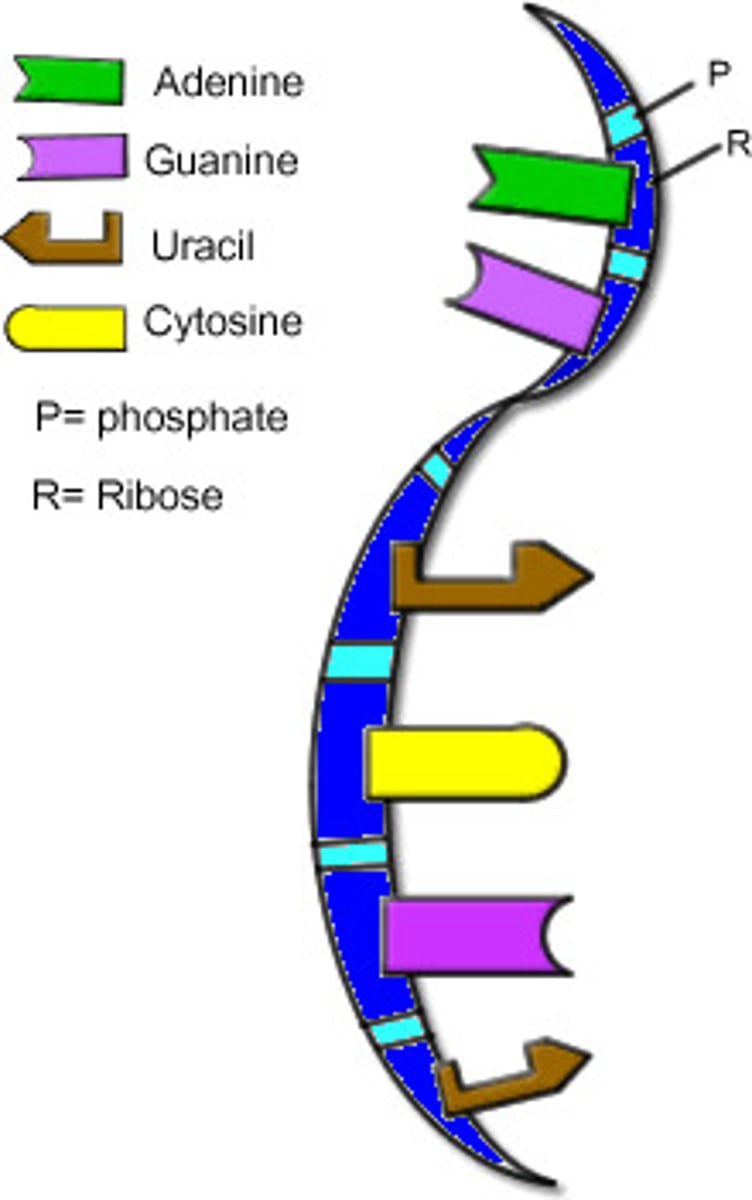
RNA
A single-stranded nucleic acid that passes along genetic messages to DNA
Glycerol
The three carbon backbone molecule of the triglycerides
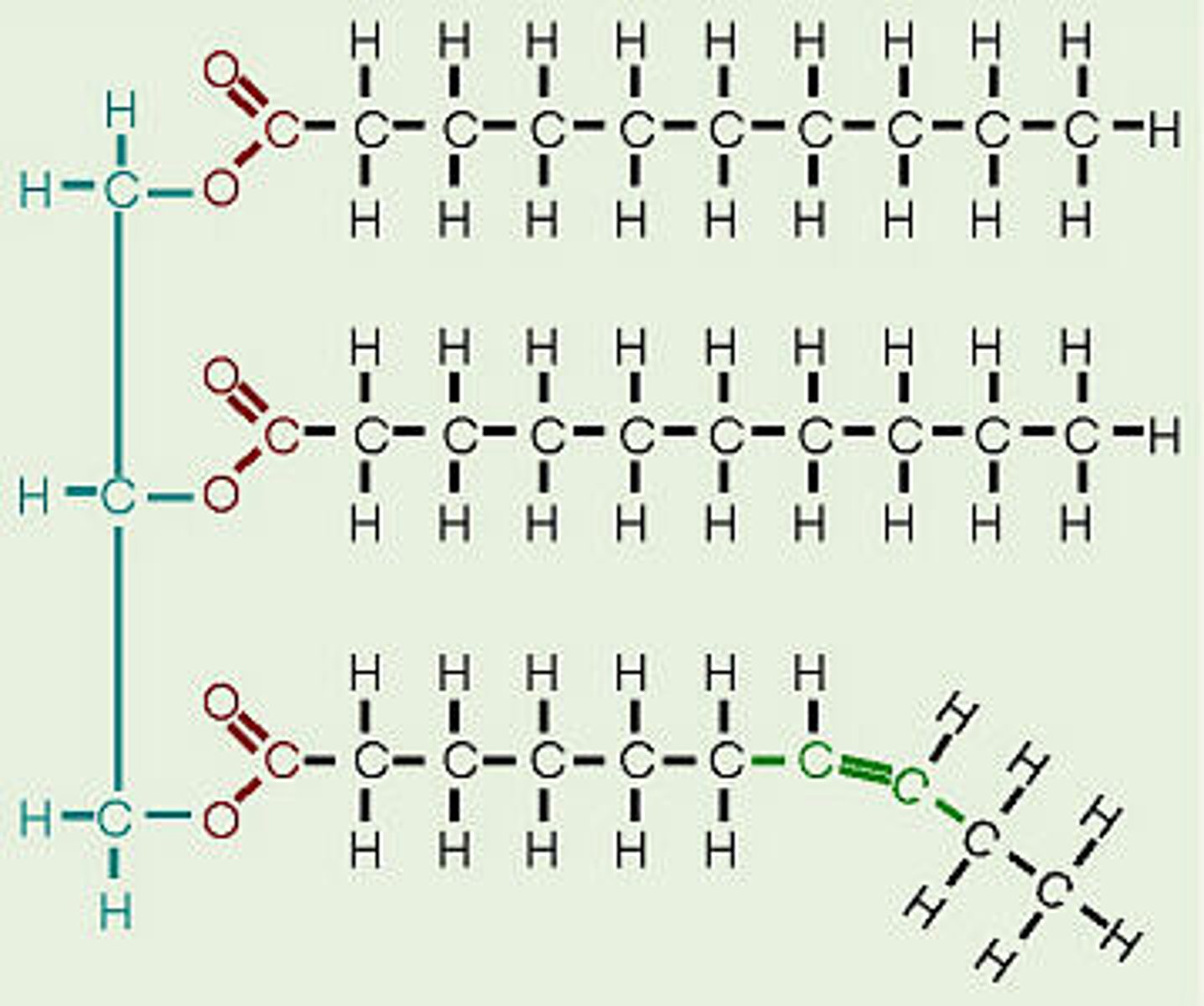
Fatty Acid
chains of carbon atoms bonded to hydrogen atoms
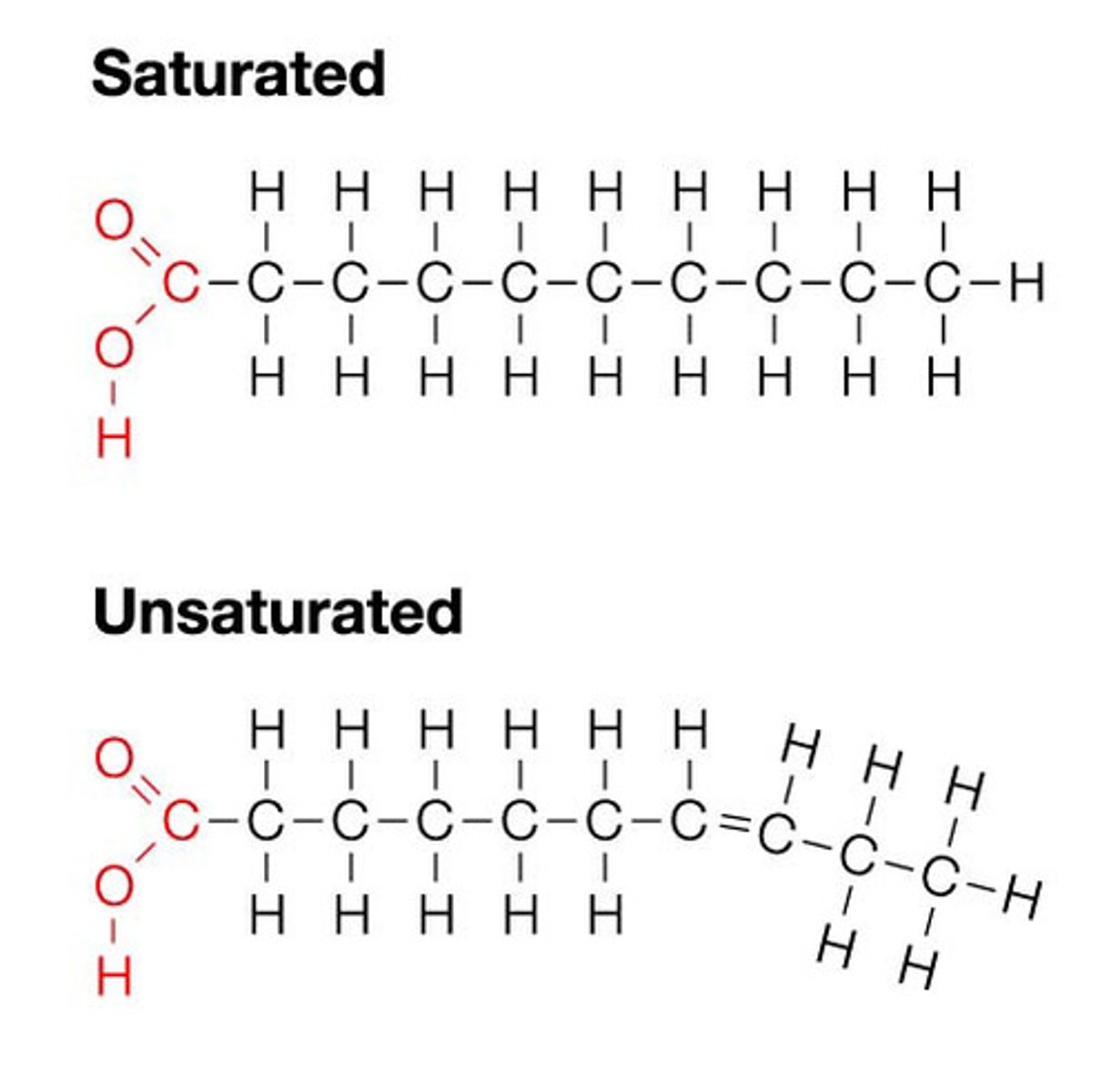
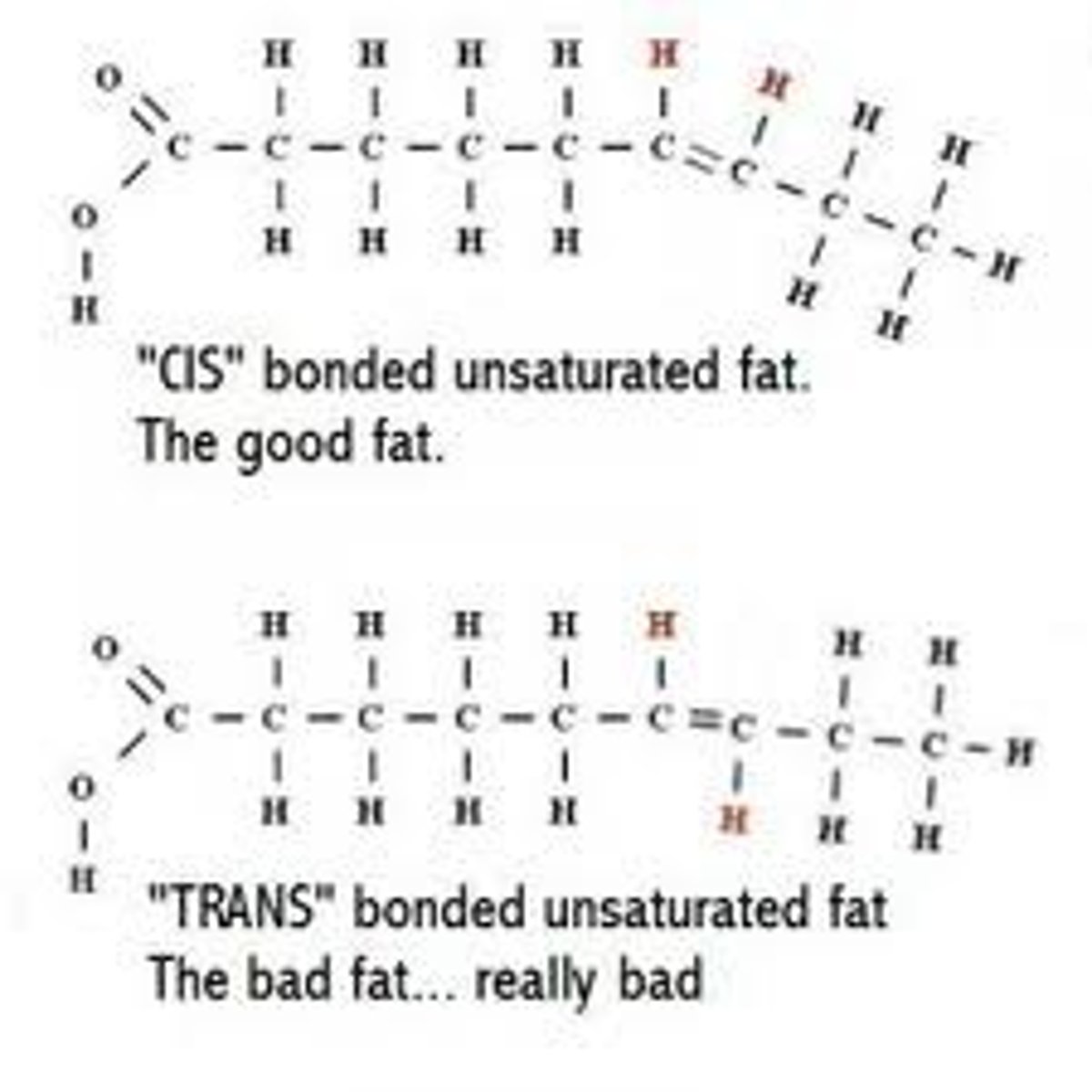
hydrogenated fats (trans-fats)
Unhealthy. Created by the partial hydrogenation of unsaturated fats. Found in many processed foods and margarines. Lowers good cholesterol, raises bad.
"sacharride"
means sugar. mono, di, poly. All are carbohydrates of various lenghts
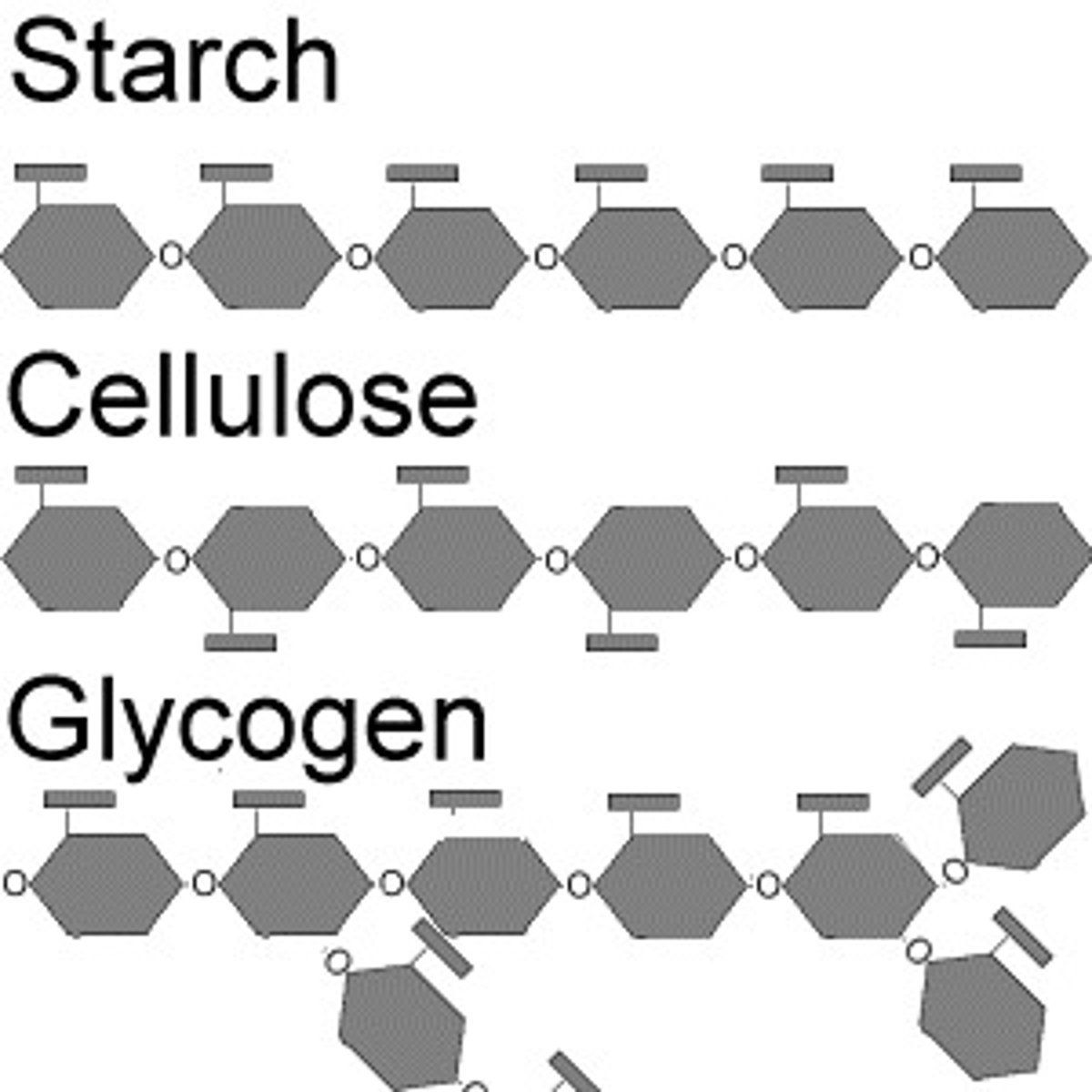
Glycogen
large glucose storage molecule or polysaccharide found in the liver and muscle of animals; the animal equivalent of starch in plants. Think energy reserves that are not fats
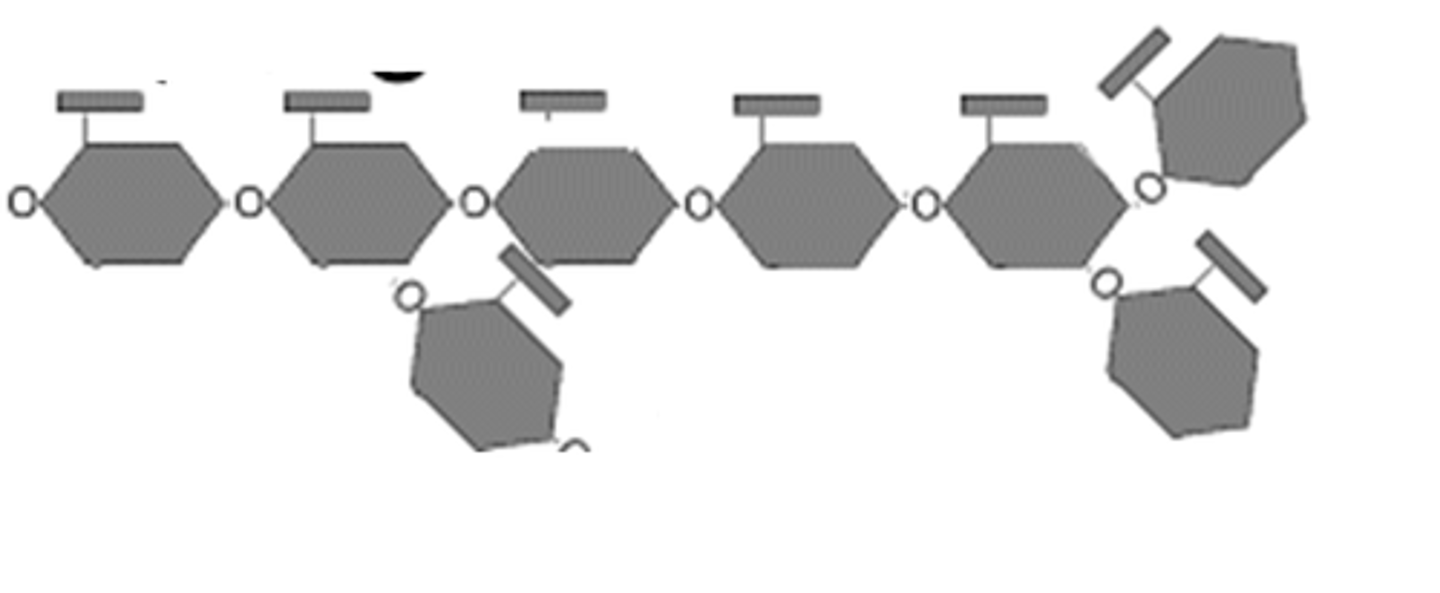
Starch
large sugar storage molecule in plants. Made soley of glucose. also foods pastas, potatoes
cellulose
(made of sugars) that is common in the cell walls of plants.. Structural - celery
end in "-ine"
most amino acids. i.e. leucine, valine, serine, glutamine...
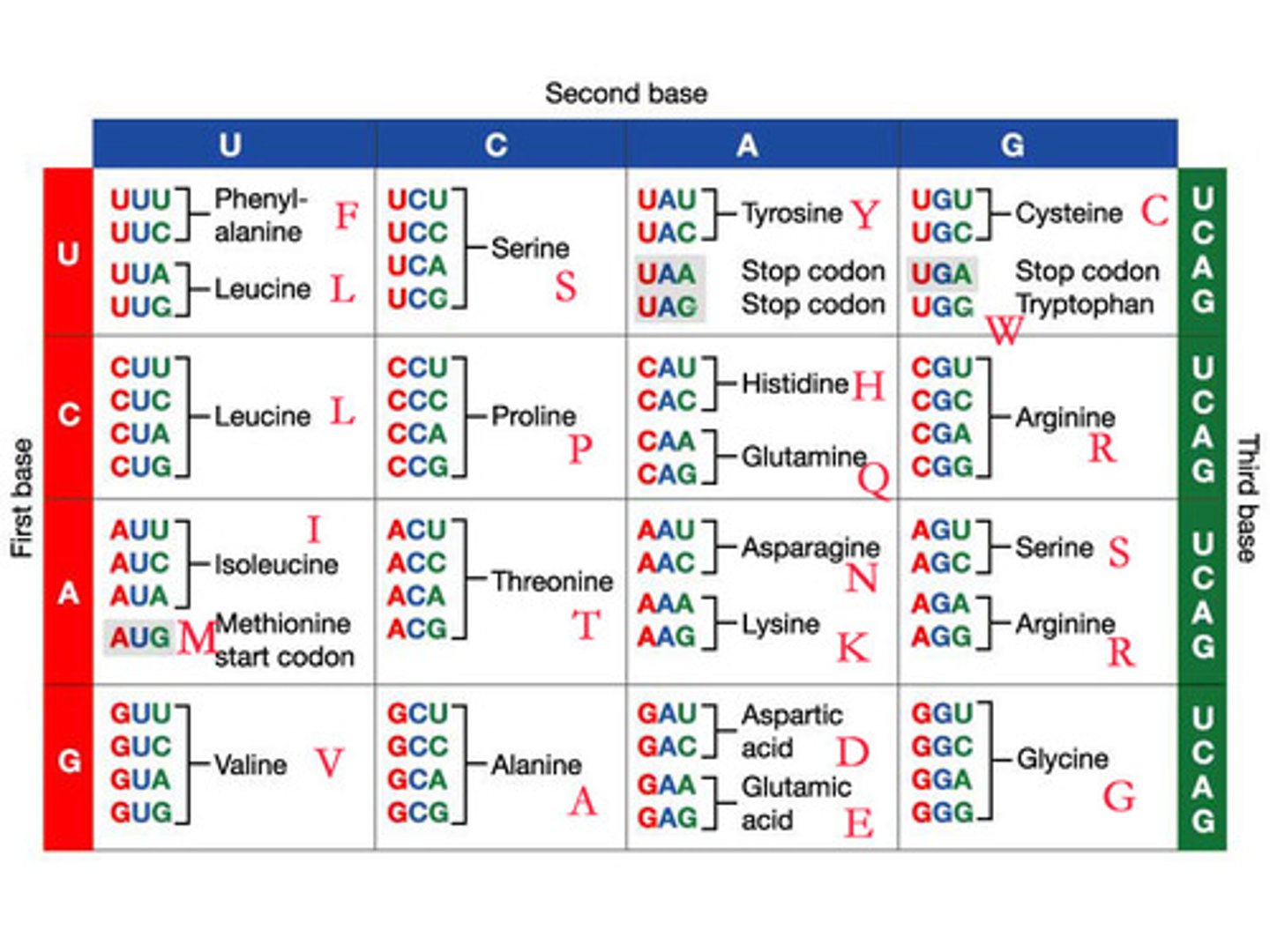
end in "-ose"
many of the sugars. glucose, fructose, lactose...
monomer
The subunit that serves as the building block of a polymer. ie amino acids, monosacharrides, nucleotides, fatty acid chains.
Organic compound
Compounds that contain carbon. Carbs, lipids, proteins, fats.
carb. molecule
lipid molecule
Nucleotide molecule
Steroids are
A lipid - hormones, cell membrane components