History of the periodic table / electron configuration / atom
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
atom
is a basic unit of matter and the smallest unit of an element that retains the elements chemical properties.
Solid sphere / billiard ball model
By John Dalton
STRENGTH: Recognised that atoms of a particular element differ from other elements.
WEAKNESS: atoms are not indivisible - they’re composed from subatomic particles.
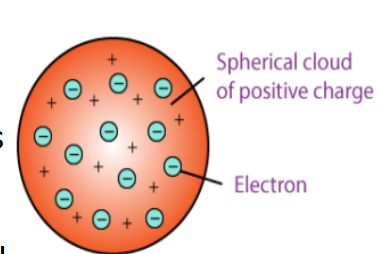
Plum pudding model
by JJ Thompson
STRENGTH: recognised electrons as components of atoms
WEAKNESS: No nucleus, and did not explain later experimental observations.
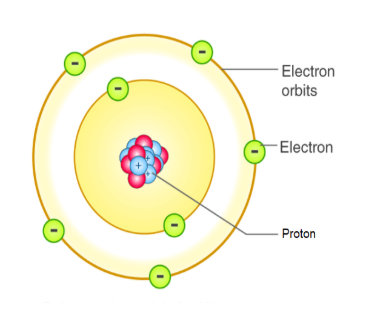
Nuclear Model
by Ernest Rutherford
STRENGTH: Realised that positive charge was located in the nucleus of an atom.
WEAKNESS: Did not explain why electrons remain in orbit around the nucleus
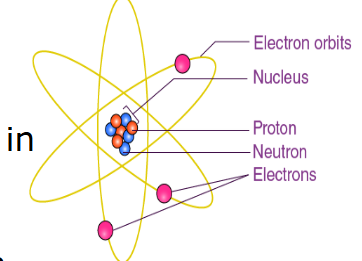
Planetary Model
by Bohr
STRENGTH: proposed stable electron orbits ; explained the emission spectra of some elements.
WEAKNESS: Moving electrons should emit energy and collapse into the nucleus ; model did not work well for heavier atoms.
Electron Cloud Model / Quantum Model
By schrodinger
STRENGTH: shows that electrons dont move around the nucleus in orbits, but in clouds where their position is uncertain.
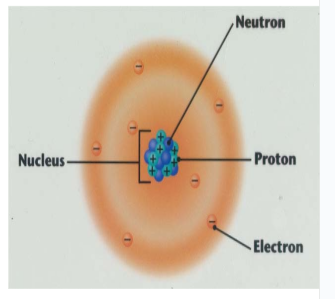
Protons
positively charged particles located in the nucleus
Neutrons
Neutral particles (no charge) located in the nucleus.
Electrons
Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus
Aristotle
300 BC
a greek philosopher who proposed that everything on earth was made up of Earth, Water, Fire and Air.

Hennig Brand
1669
an Alchemist searching for the Philosopher’s stone
He was the first to discover a new element: Phosphorus

Antoine de Lavoisier
1789
He published the Traite Elementaire de Chimie (Elementary Treatise of Chemistry)
He classified the elements based on their properties

Johann Wolfgang Dobereiner
1817
He noticed that some elements could be grouped into triads w/ similar properties and atomic weights
Elemental triad
Alexandre - Emilie Béguyer de Chancourtois
1862
proposed a spiral arrangement of the elements, where similar elements appeared at a regular intervals.
first attempt to arrange in increasing periodicity of the elements.
telluric helix

John Newlands
1864
He arranged the elements by atomic weight
created the Law of Octaves
classified the elements according to physical properties and noticed that there is difference of multiples of eights in the atomic weight.

Dmitri Mendeleev
1869
Organized the known elements by atomic weight and chemical properties.
He published the first periodic table
He arranged them in increasing atomic weight leaving spaces for undiscovered elements.

William Ramsey
1890
He included the noble gases : Argon, Helium, Neon, Krypton and Xenon

Henry Moseley
1913
he rearranged the elements according to increasing atomic number

Glenn Seaborg
1940 - 1950
Transuranium elements
Introduced the actinide series
