Business Cycles
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
What are business cycles?
Periodic but regular up and down movements in GDP, fluctuating around potential GDP
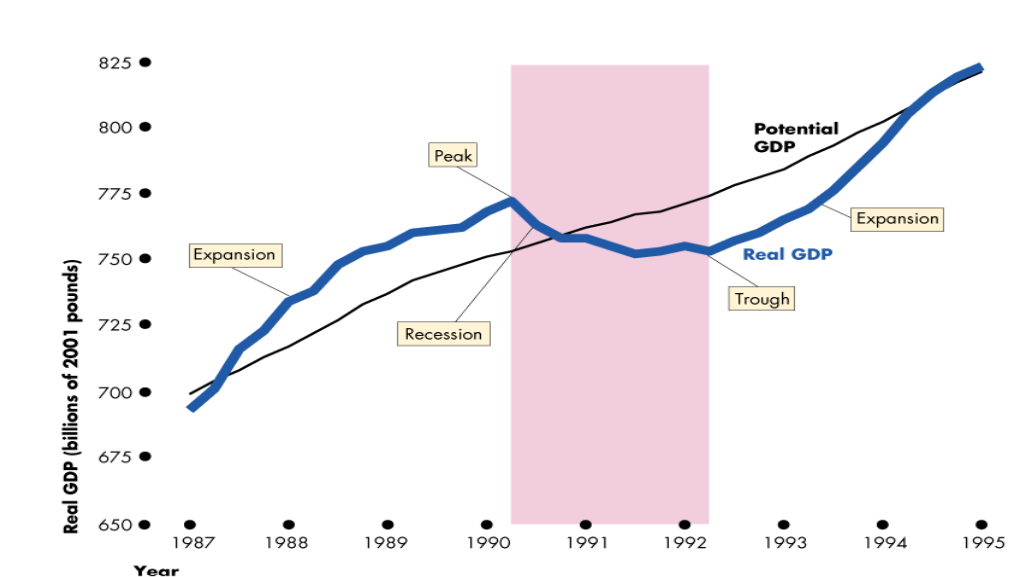
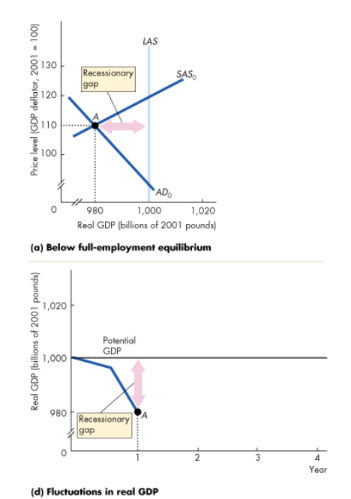
What is a recessionary phase of a business cycle, and when does it occur?
A below full employment equilibrium
Actual GDP < Potential GDP
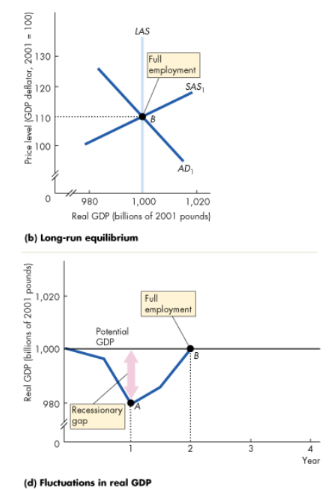
When is a business cycle at full employment?
When Potential GDP = Actual GDP
What is an expansionary phase, and when does it occur?
Occurs at above full employment equilibrium
When Actual GDP > Potential GDP
Amount by which Actual GDP exceeds Potential GDP known as an inflationary gap
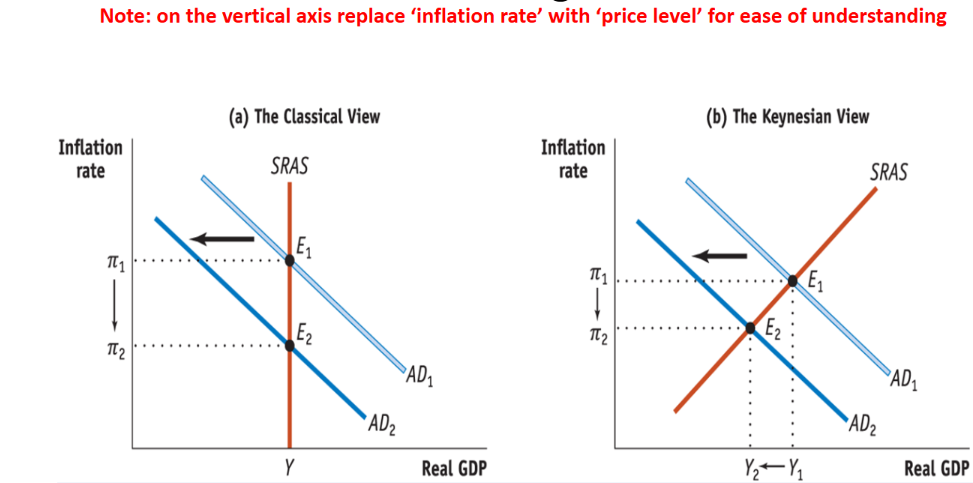
What are the main themes from the Classical School about business cycles?
Attributed cycles to various types of shock like good or bad harvests
Believes the SR is unimportant
Prices assumed to be flexible
AS curve is vertical even in SR
Shift in AD is almost exclusively due to a shift in the MS
An increase in MS leads to inflation and has no effect on aggregate output
What does Keynes suggest about business cycles?
Emphasised the SR effects of the business cycle, unlike Classicists would focussed purely on the LR
Any shift in AD caused by shifting business confidence.
E.g. an expected fall in profits can lead to decreased investment which can cause recession
His views led to MP and FP being used to smooth the business cycle
What are the monetarists’ views on the business cycle?
Argued that during Great Depression, MP ineffective as interest rates already close to zero
Argues for non-discretionary MP: GDP grows steadily if MS increases steadily on autopilot
Advocates to not change interest rates to stabilise the economy
MV = PY
How does the interactions of the multiplier and accelerator affect the business cycle?
Each firm plans investment for the period to start
It’ll have an optimum capital to output ratio
Effects a shock starts one period in a business cycle e.g. shock could be an increase in investment
Investment decisions depend on instincts or ‘animal spirits’
How do monetarists and the Keynesians differ in their beliefs about business cycles?
Monetarists attributed cycles chiefly to demand shocks caused by a change in the MS
Keynesians attribute shocks caused by any other factors
What is the new Keynesian view on business cycles?
Caused by demand shocks, perhaps ones resulting from a change in the money stock
Sticky wages mean that output may take a long time to return to its potential level after a shock, unless the govt intervenes
What are the new classicals view on business cycles?
Similar to new Keynesian, but argue that wage flexibility may quickly return output to its potential level after any shock
Accept output may stay away from its potential level if there are repeated demand shocks
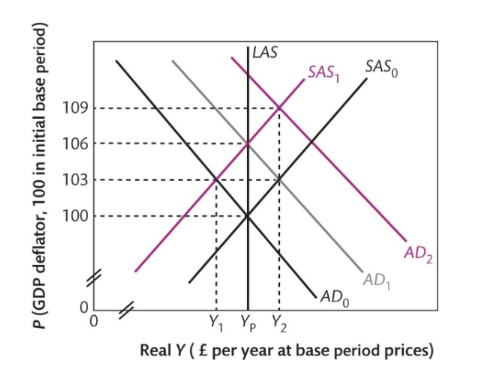
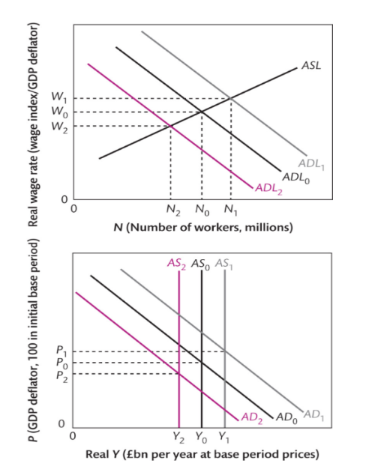
What are the main tenets of the Real Business Cycle Theory?
Business cycles caused by fluctuations in AS
AS fluctuates due to fluctuations in the demand for labour
Demand for labour fluctuates due to technology shocks that change labour productivity
Criticism is that it relies of AS to be elastic, which is potentially contentious