Nature of Metals and Alloys
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
what kind of bonds to metals have
metallic bonds
in metallic bonds, atoms are bonded by ____________ interactions between the ______ and the _________ ________
electrostatic; ions and the electron could
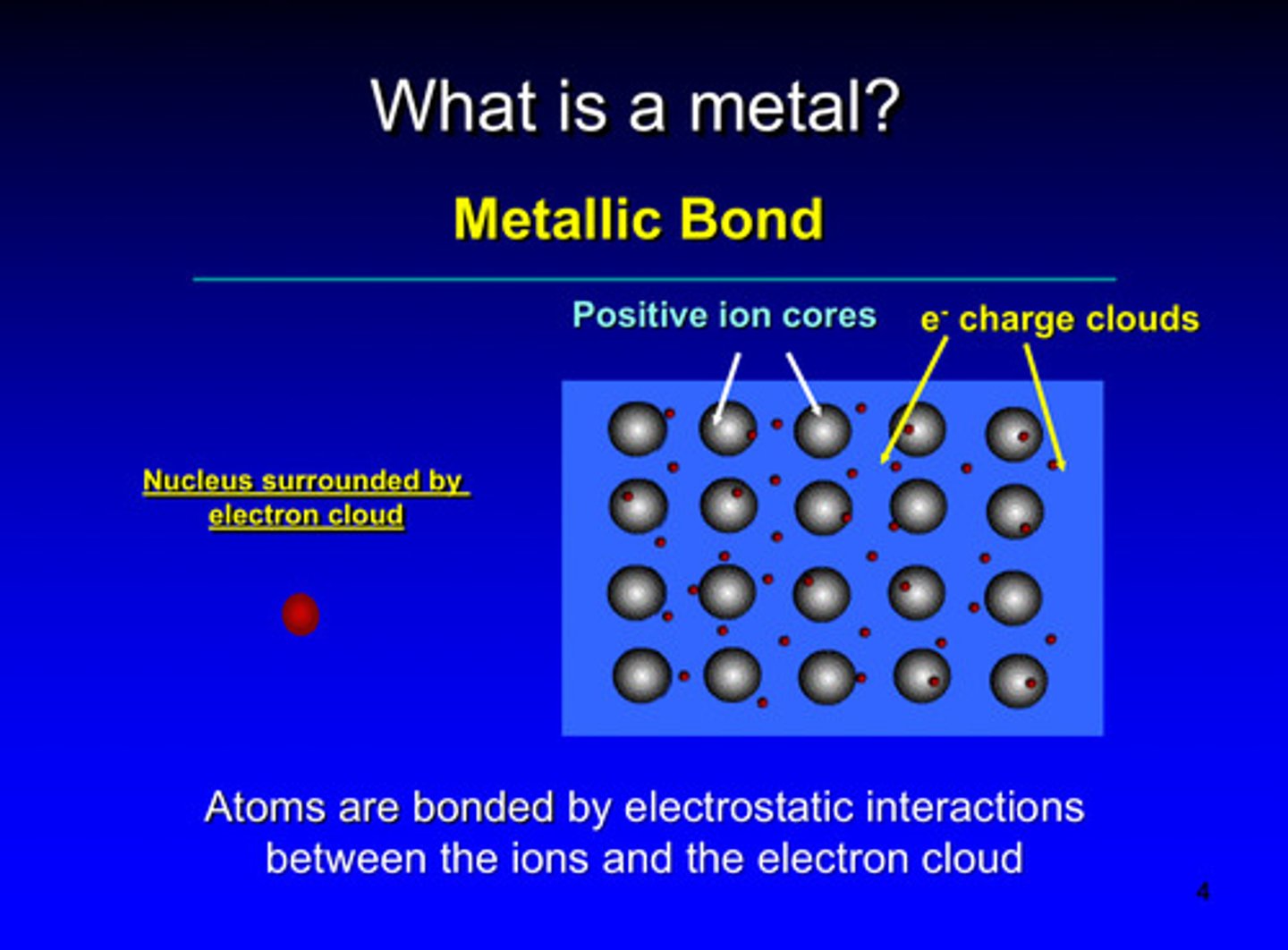
the nucleus in metals are surrounded by the
electron cloud
metals form what kind of ions and bonds with non-metals if alloys are placed into a suitable solution
form positive ions (cations) and ionic bonds with non metals
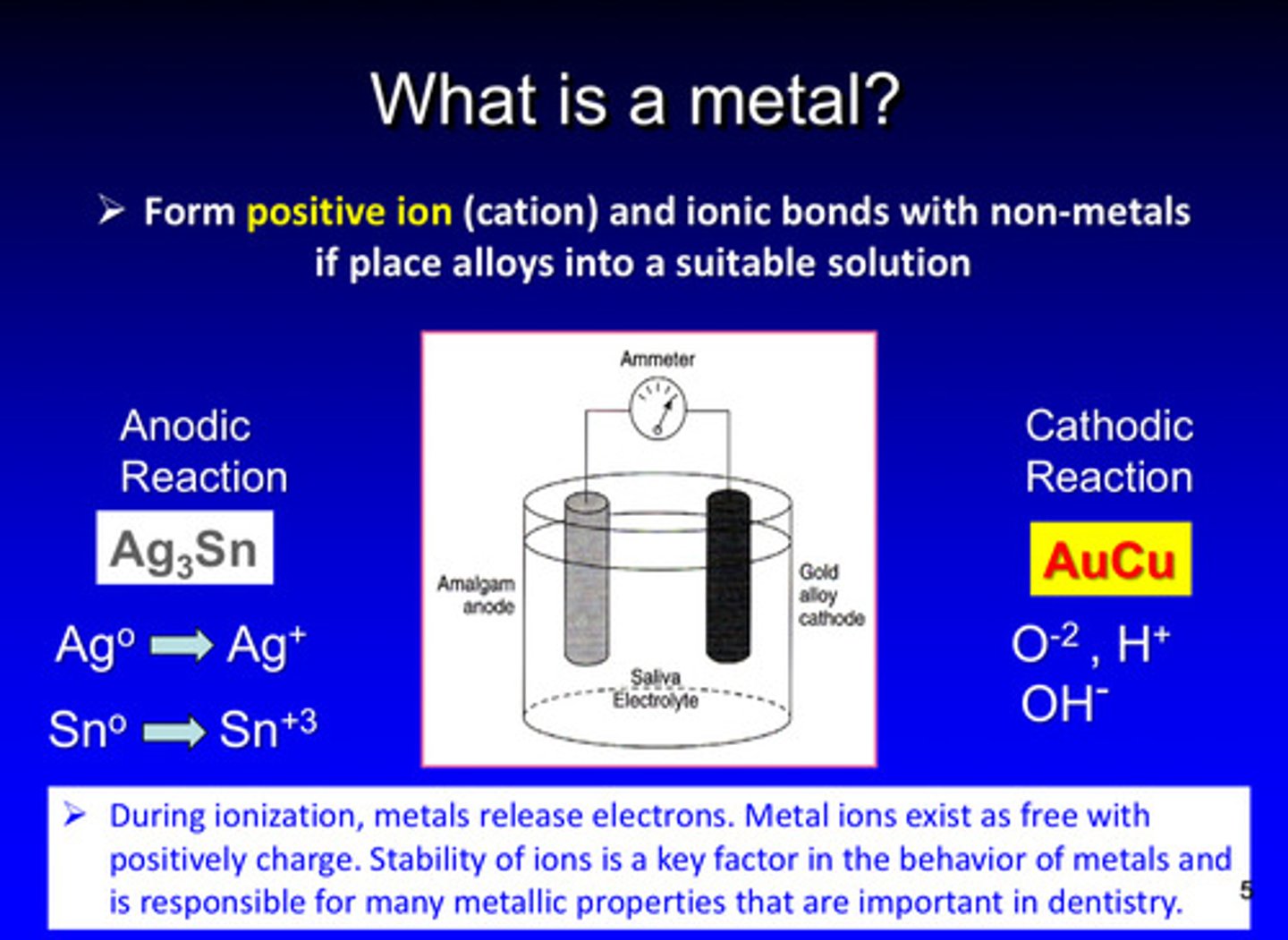
during ionization, metals release what
release electrons
metal ions exist as free with ________ charges
positive
what is a key factor in the behavior of metals and is responsible for many metallic properties that are important in dentistry
stability of ions
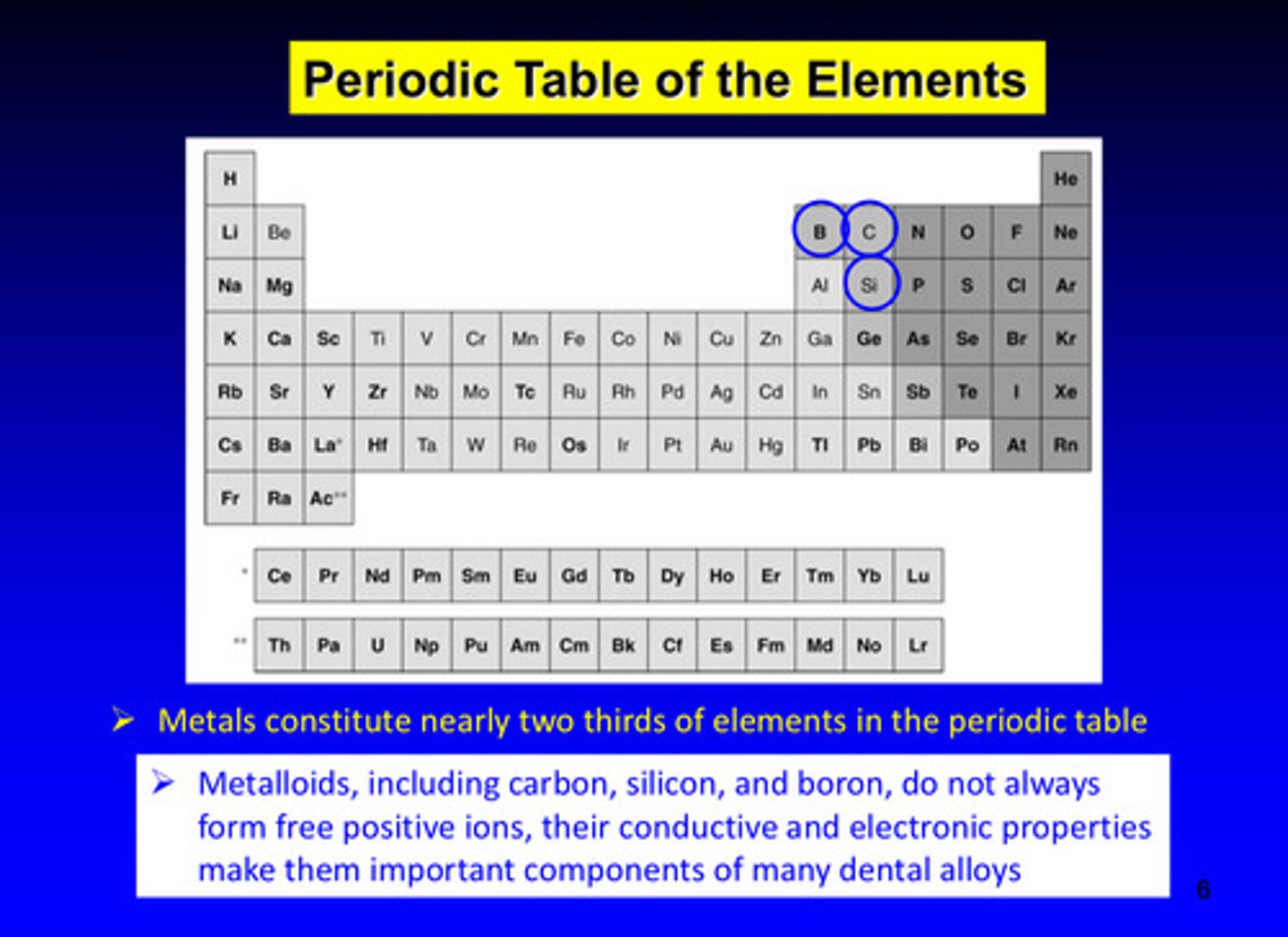
metals constitute nearly _____ of elements in the periodic table
2/3
metalloids, including carbon, silicon, and boron, do not always form ______ _______ ions, but their _________ and __________ properties make them important components of many dental alloys
free positive ions; conductive and electronic properties
what are the 4 general properties of metallic elements
1) crystalline solid in normal environment
2) at >/= 1800 degrees C, many would be liquid or gas
3) dense, luster, malleable, ductile, and strong
4) good thermal and electrical conductivities

periodic table of the elements image
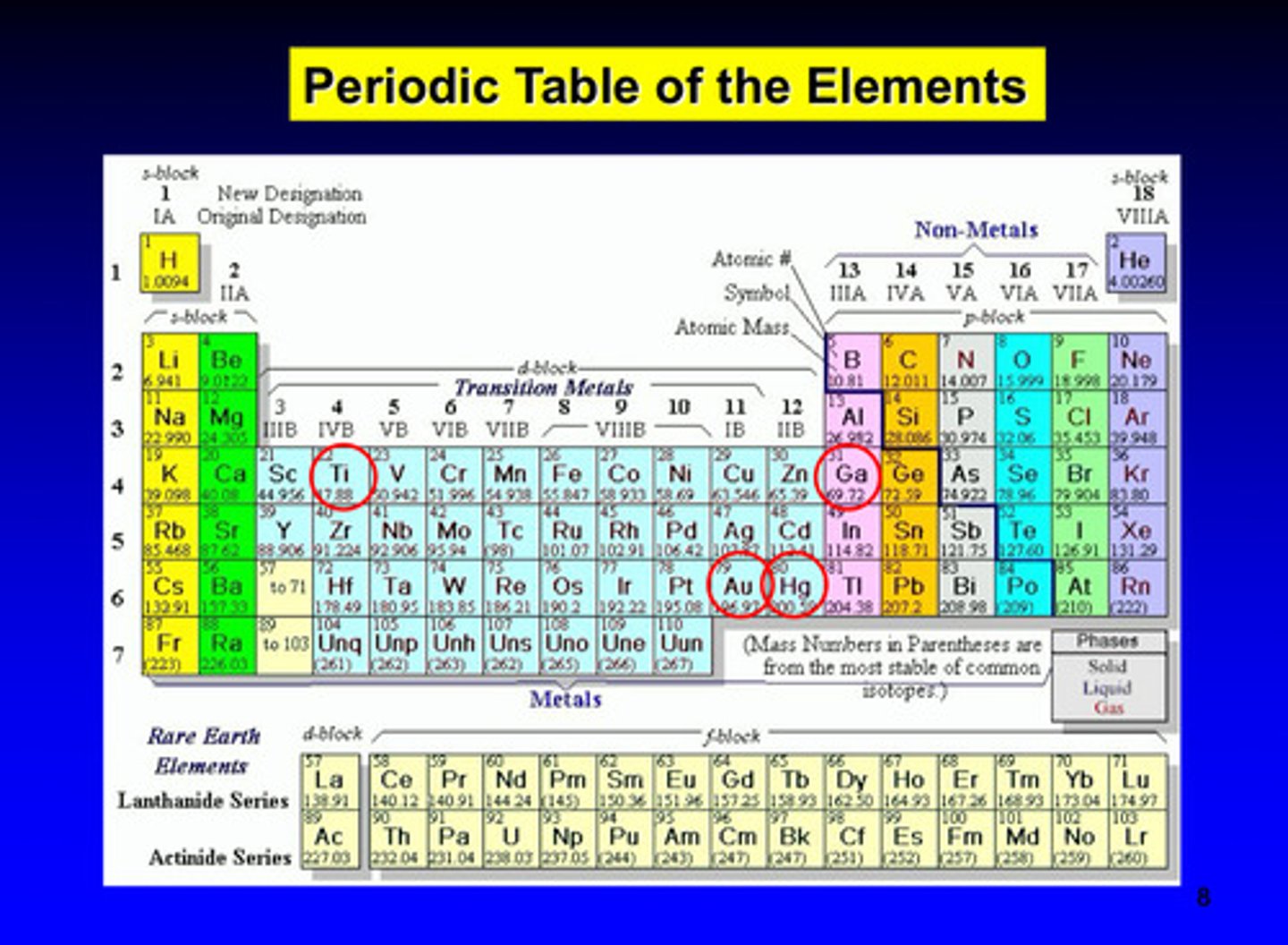
what is an alloy
a blend of two or more metals in all their possible combinations considered as a whole
in order to form an alloy, the two metals are __________ to a liquid state
heated
when a combination of two metals is completely ________ in the liquid state, the 2 metals can form an alloy
miscible
a binary alloy results from what
two metals and all different possible combinations are considered
what is the goal of alloys and alloy systems
1) to optimize practical properties
2) to form metallic materials with adequate strength, ductility, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility for application in the oral environment
states of matter image
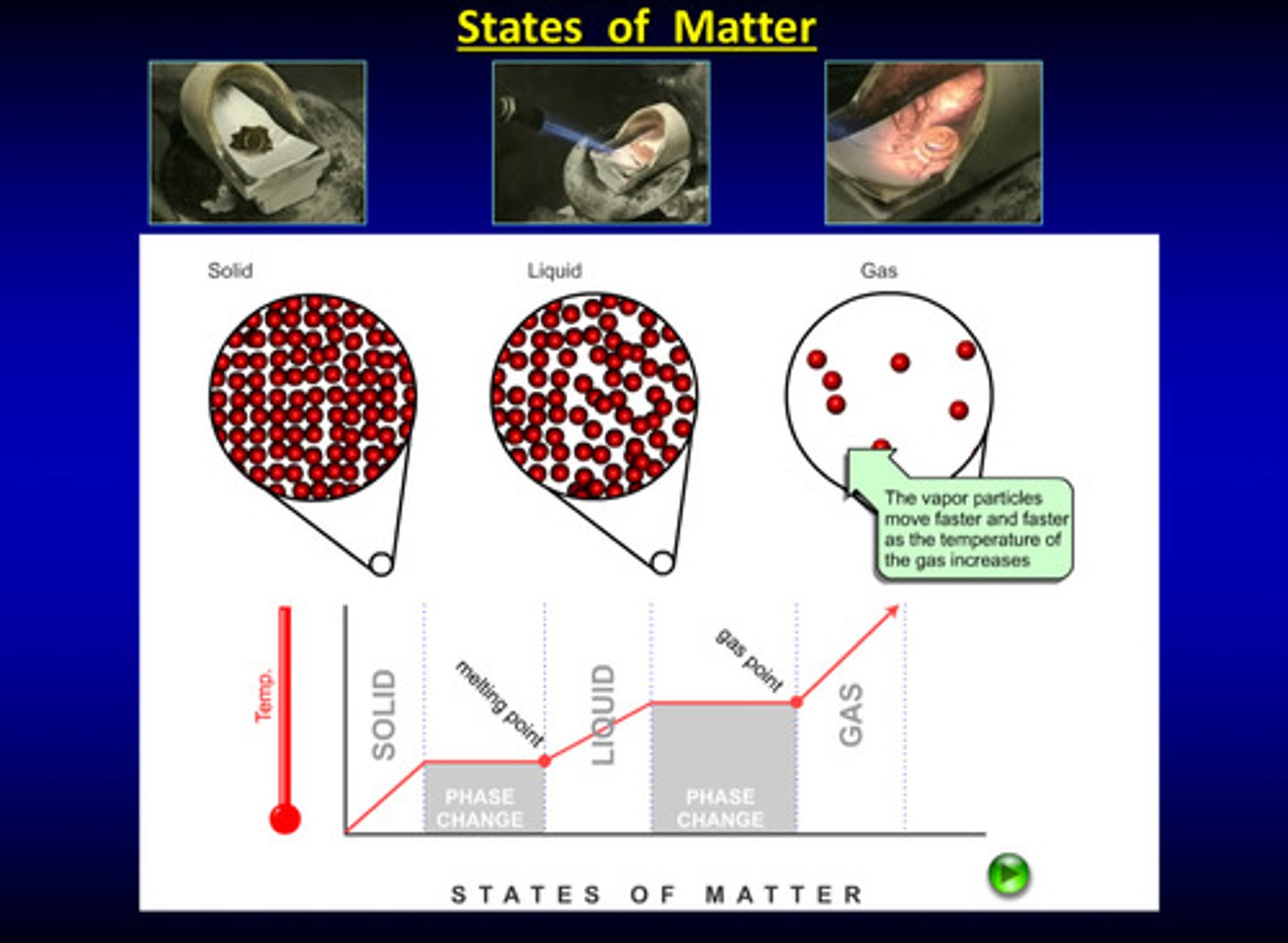
phase changes are _______ changes
physical
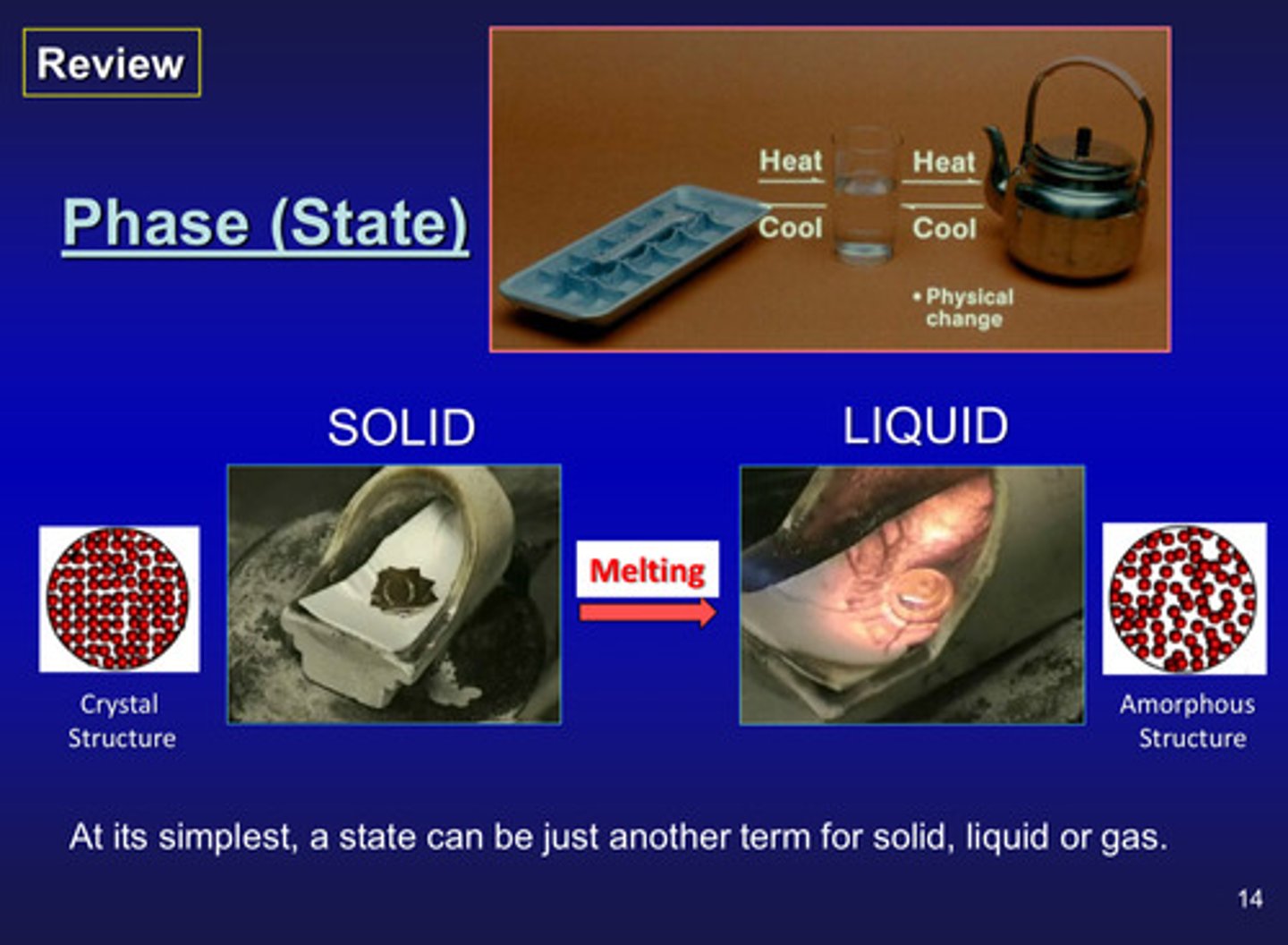
what is melting
solid to liquid
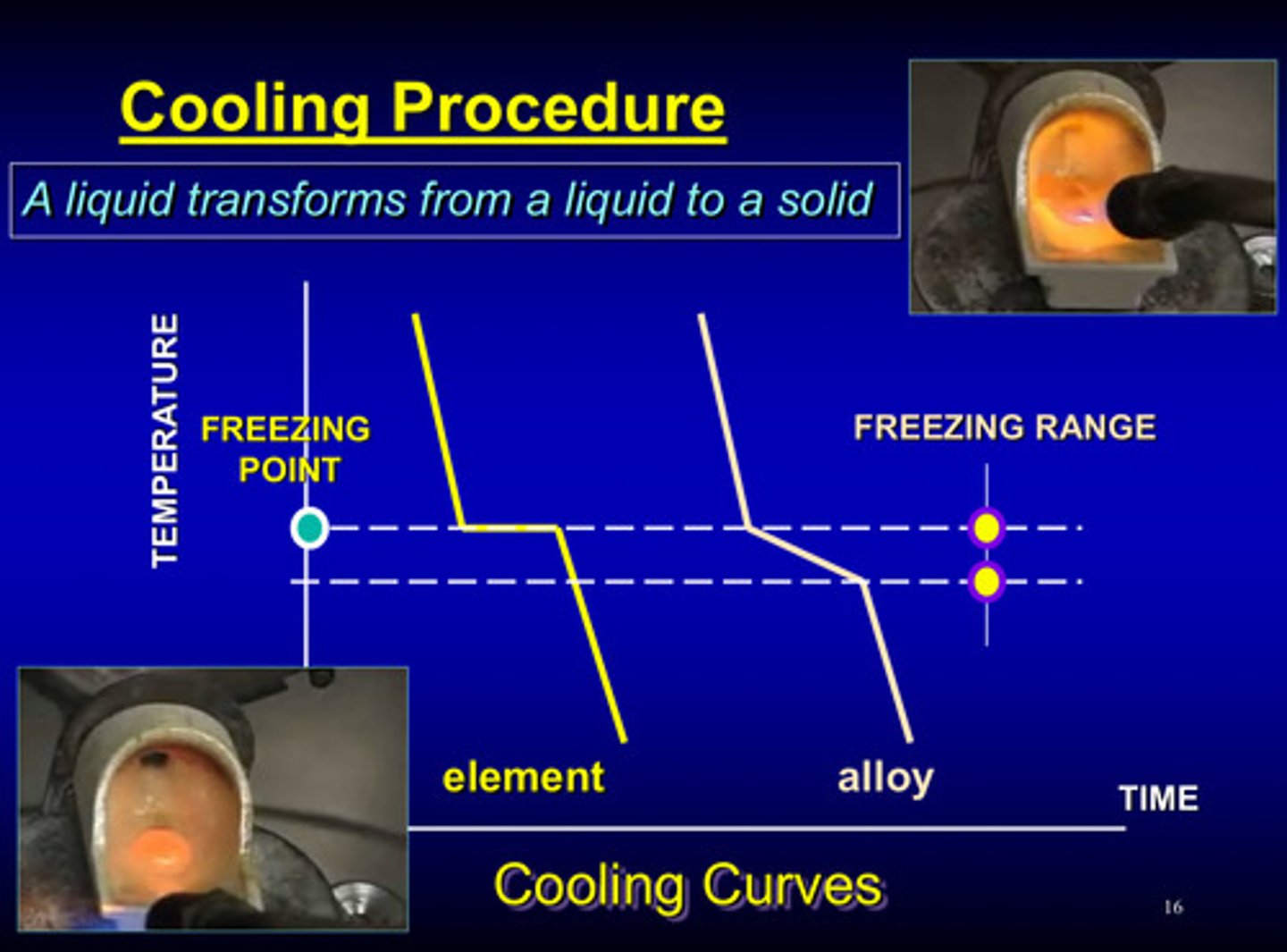
what is cooling
liquid to solid
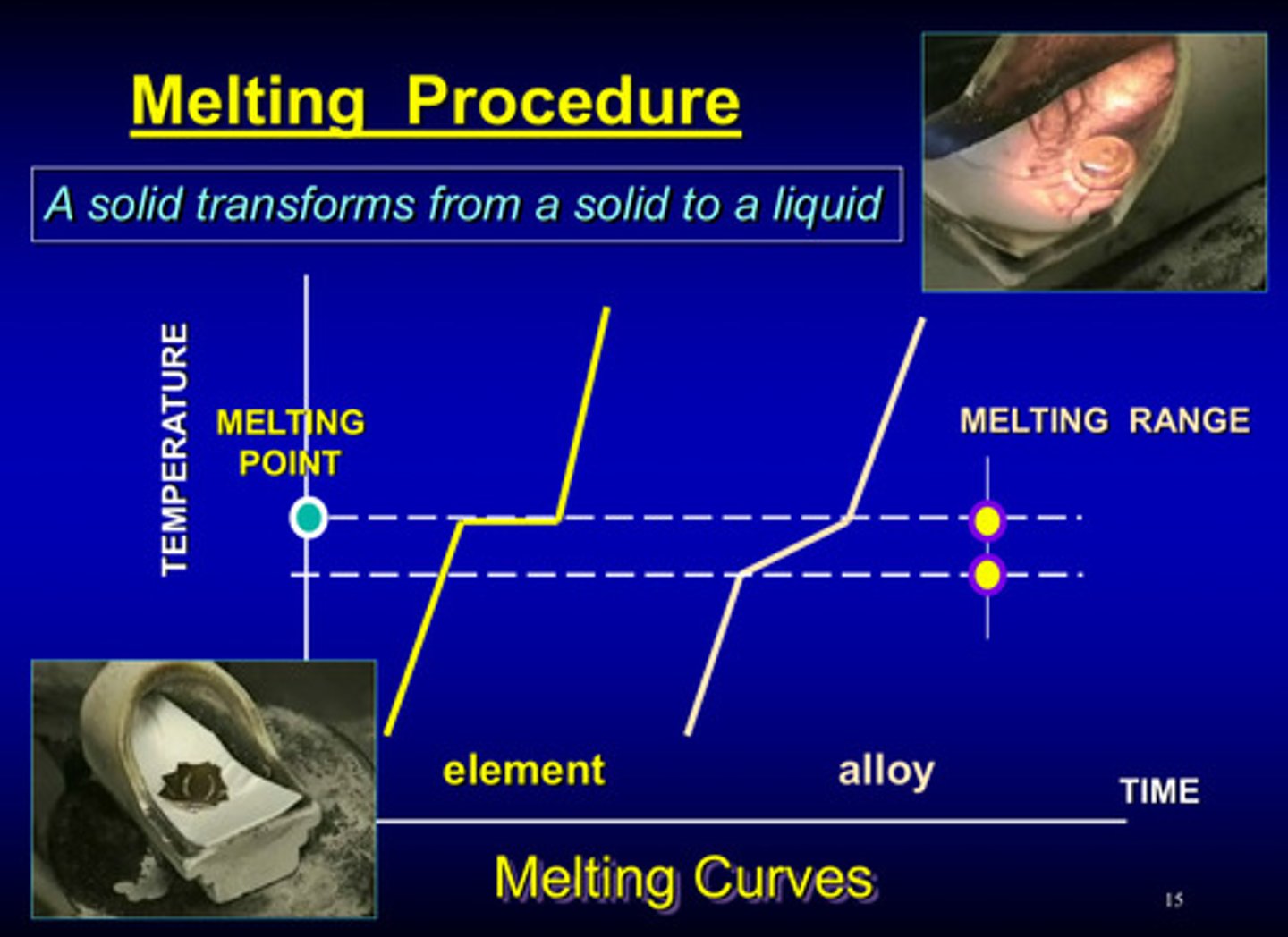
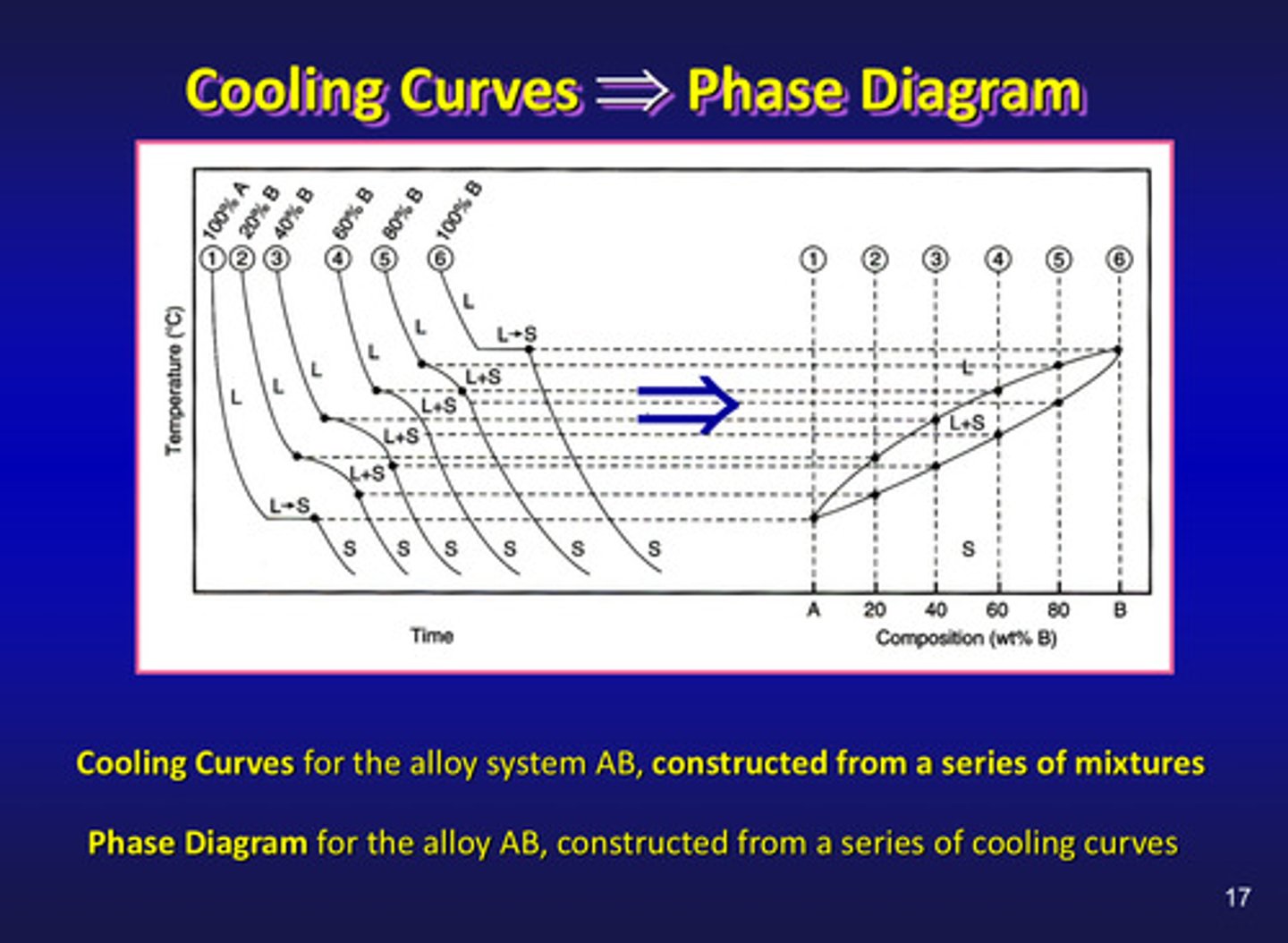
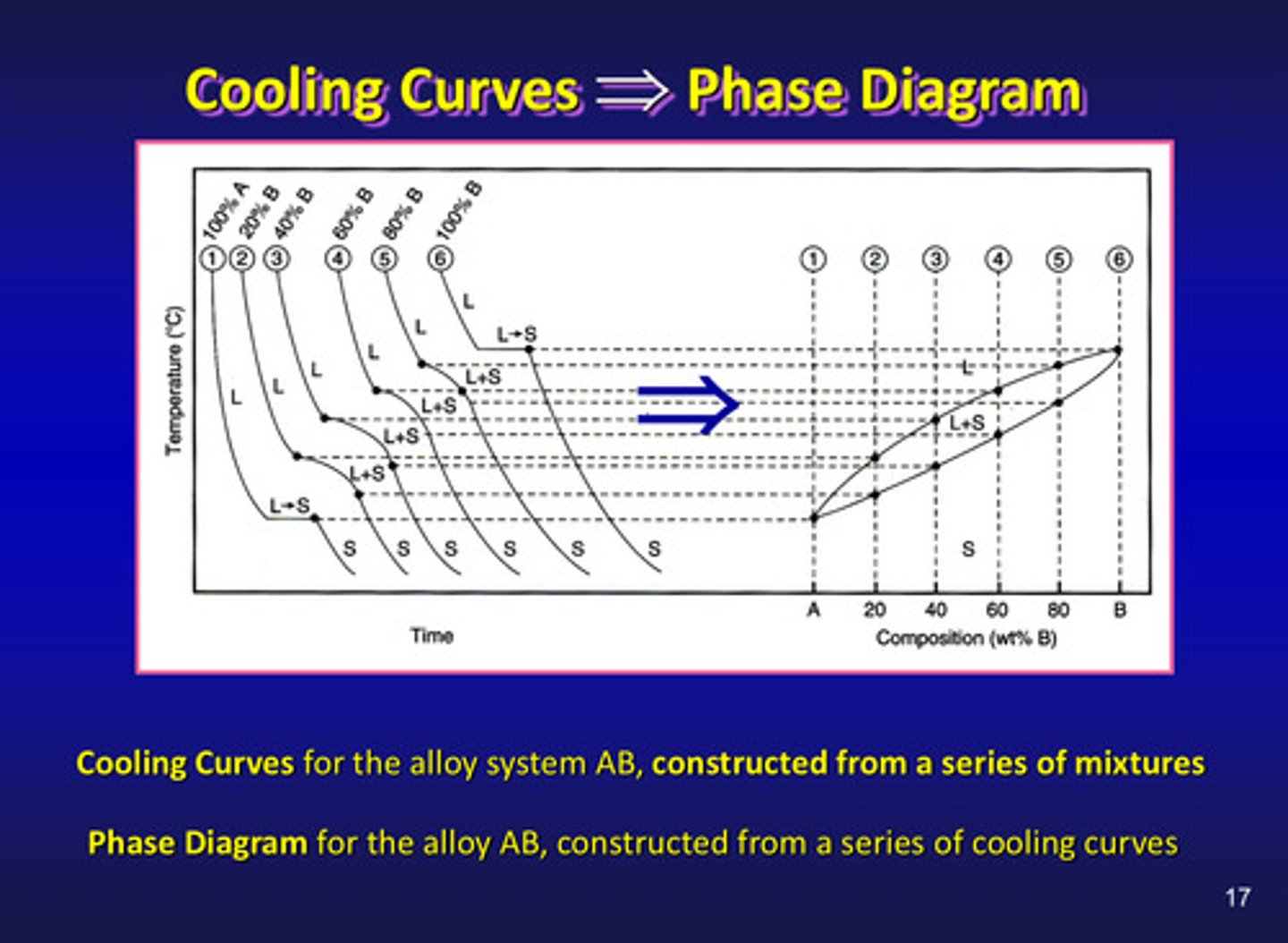
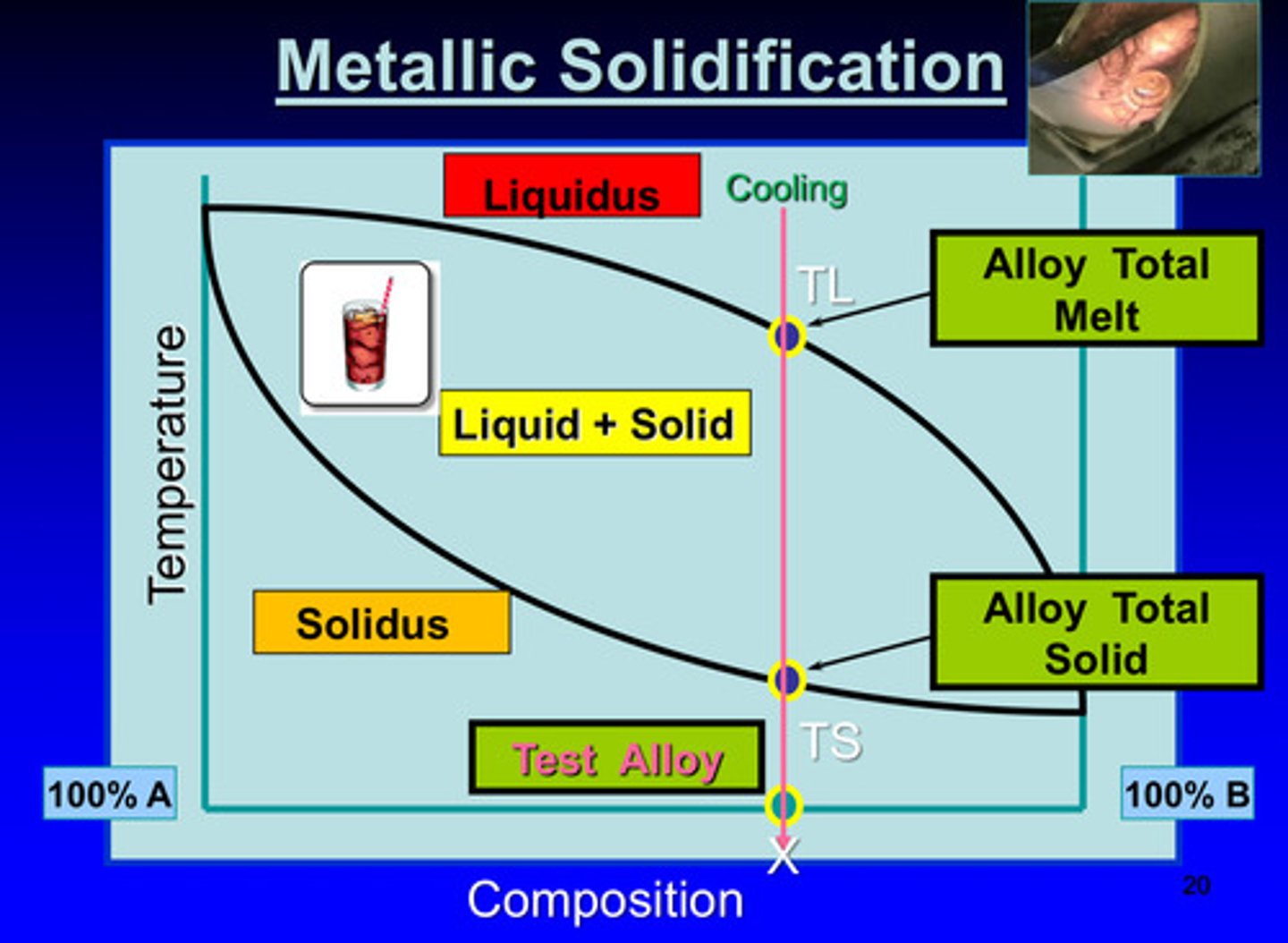
cooling curves for the alloy system AB are constructed from a ?
series of mixtures (left side)
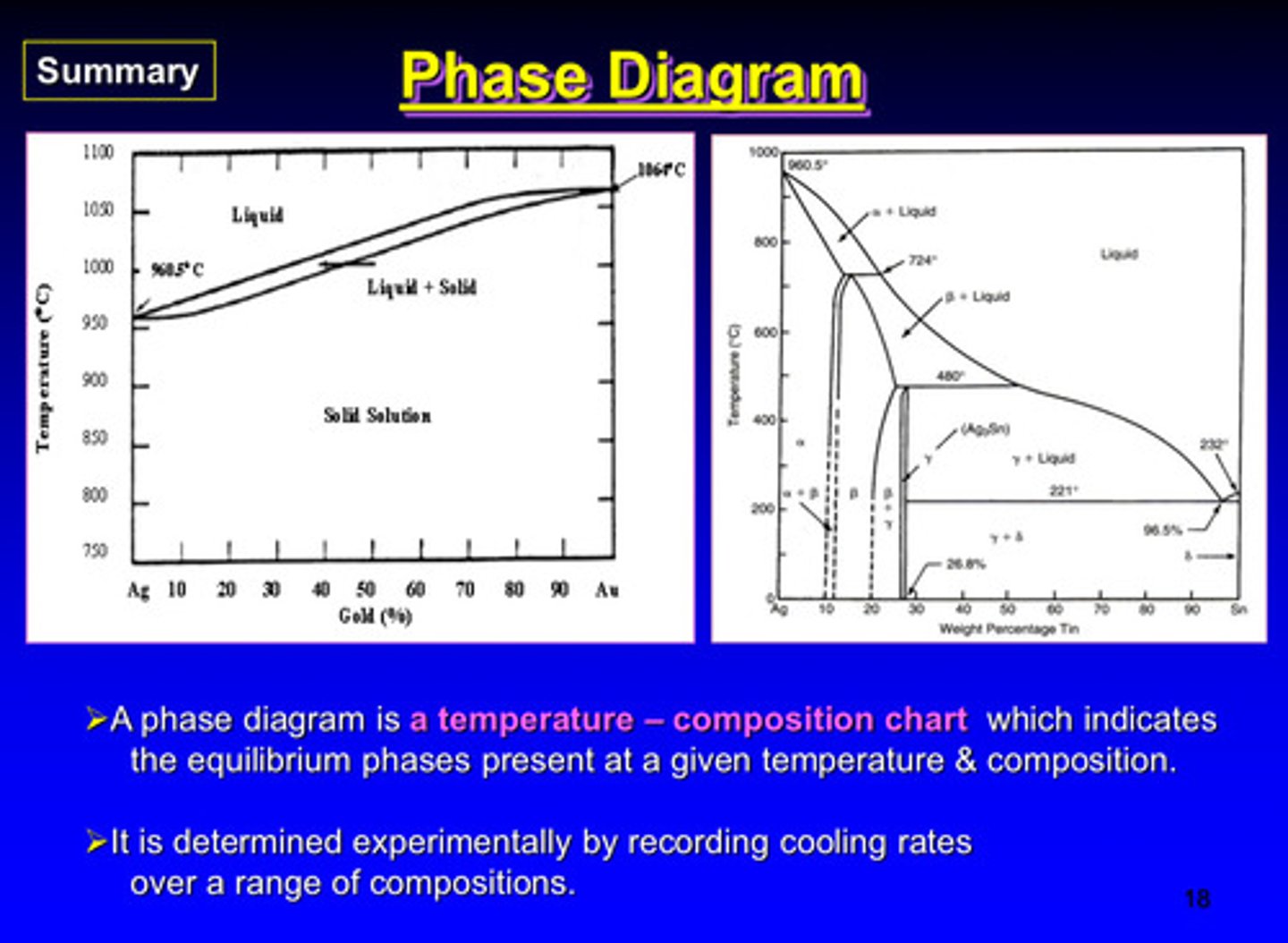
phase diagrams are determined experimentally by recording what
cooling rates over a range of compositions
what is a phase diagram
a temperature - composition chart which indicates the equilibrium phases present at a given temperature and composition
phase diagrams for the alloy AB are constructed from a ?
series of cooling curves (right side)
in a phase diagram, the upper curve is called what line
liquidus line since the alloys in this system are entirely liquid for temperatures and compositions above this line
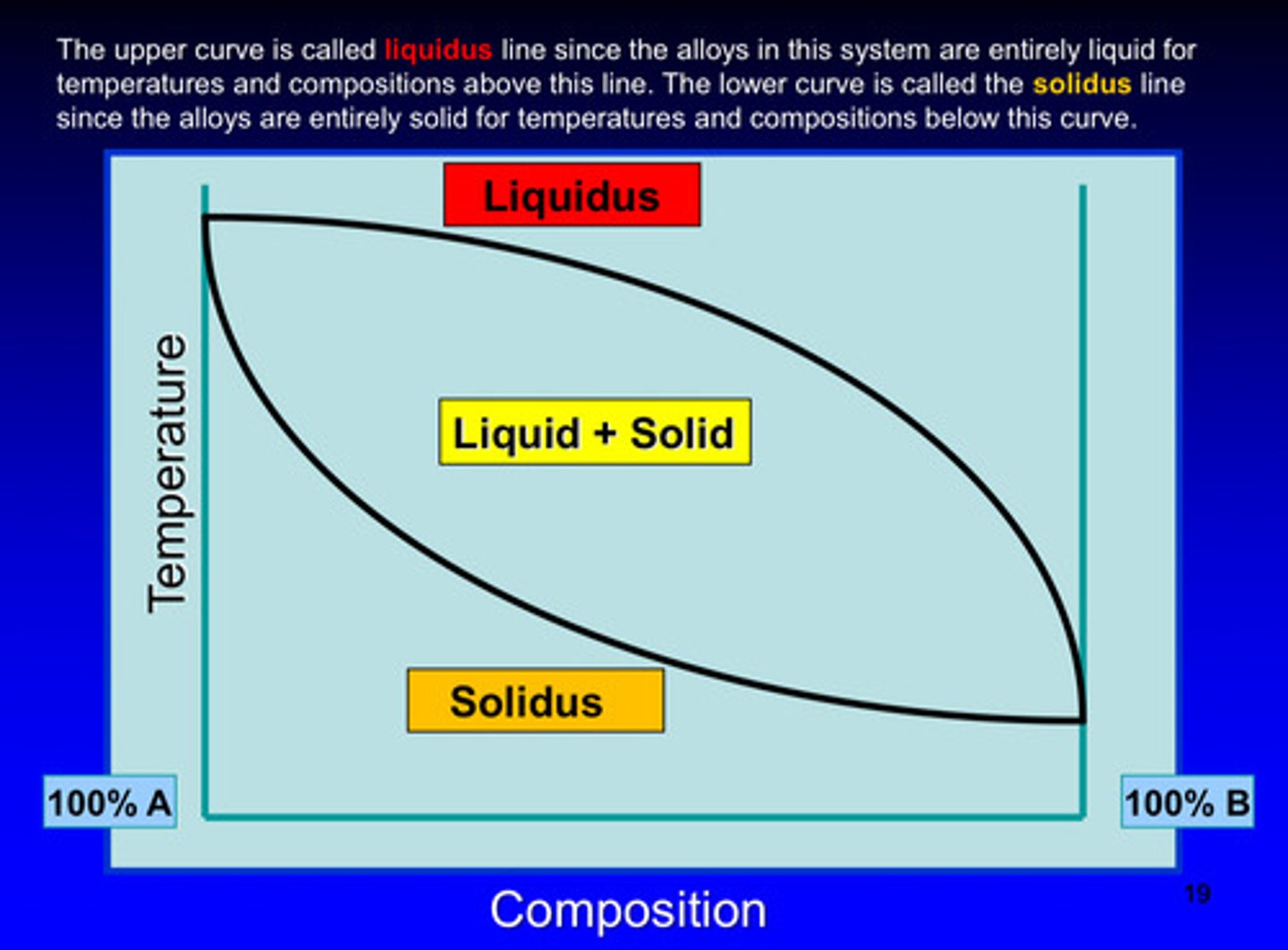
in a phase diagram, the lower curve is called what line
solidus line since the alloys in this system are entirely solid for temperatures and compositions below this curve
metallic solidification image
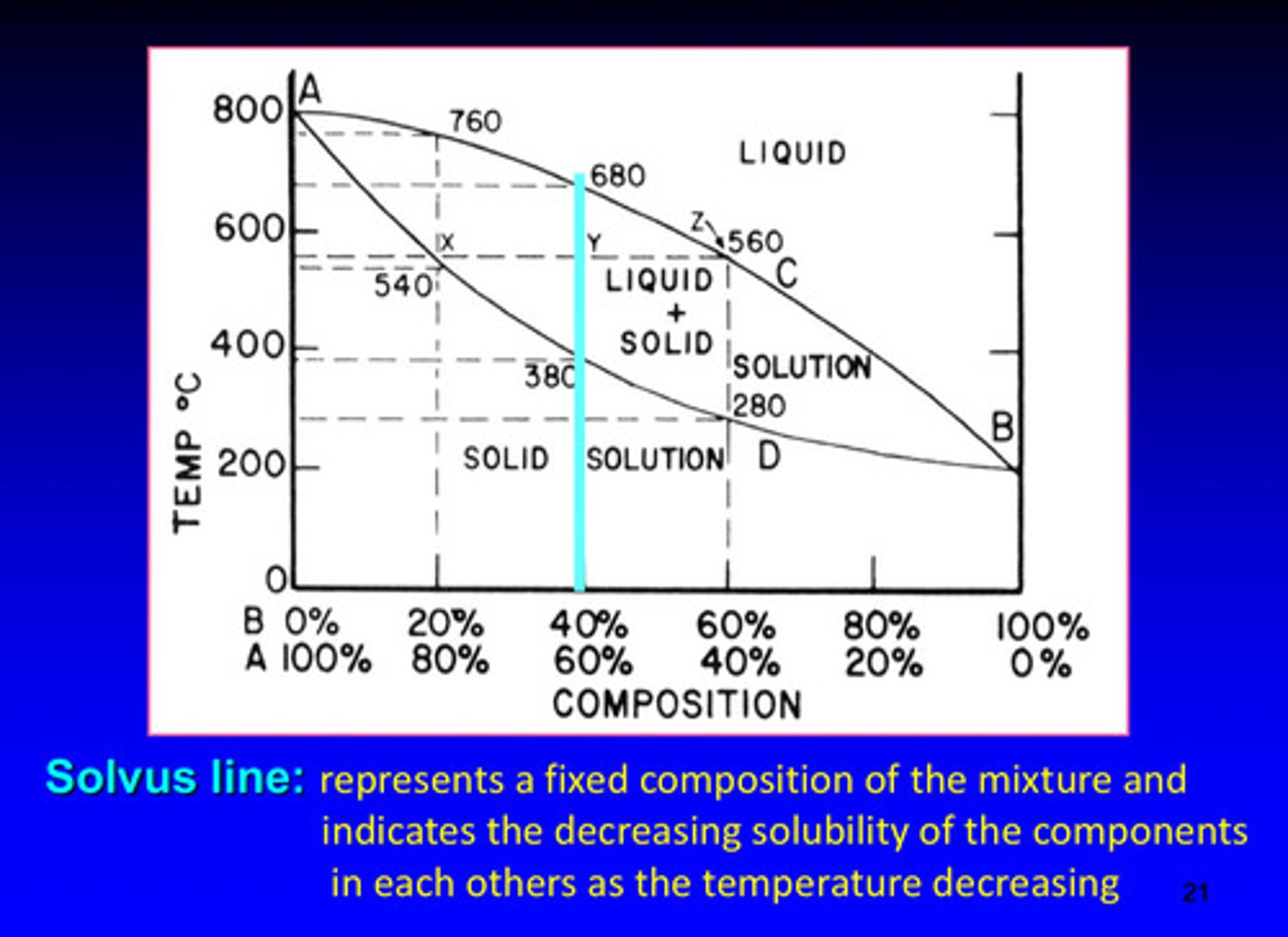
what is the solvus line in a phase diagram
represents a fixed composition of the mixture and indicates the decreasing solubility of the components in each other as the temperature decreases
what is the goal of the phase diagram
to understand and predict the alloy microstructure obtained at a given composition
the relative amounts of the two phases in the liquid-solid region can be determined at a given temperature by what rule
the inverse lever rule
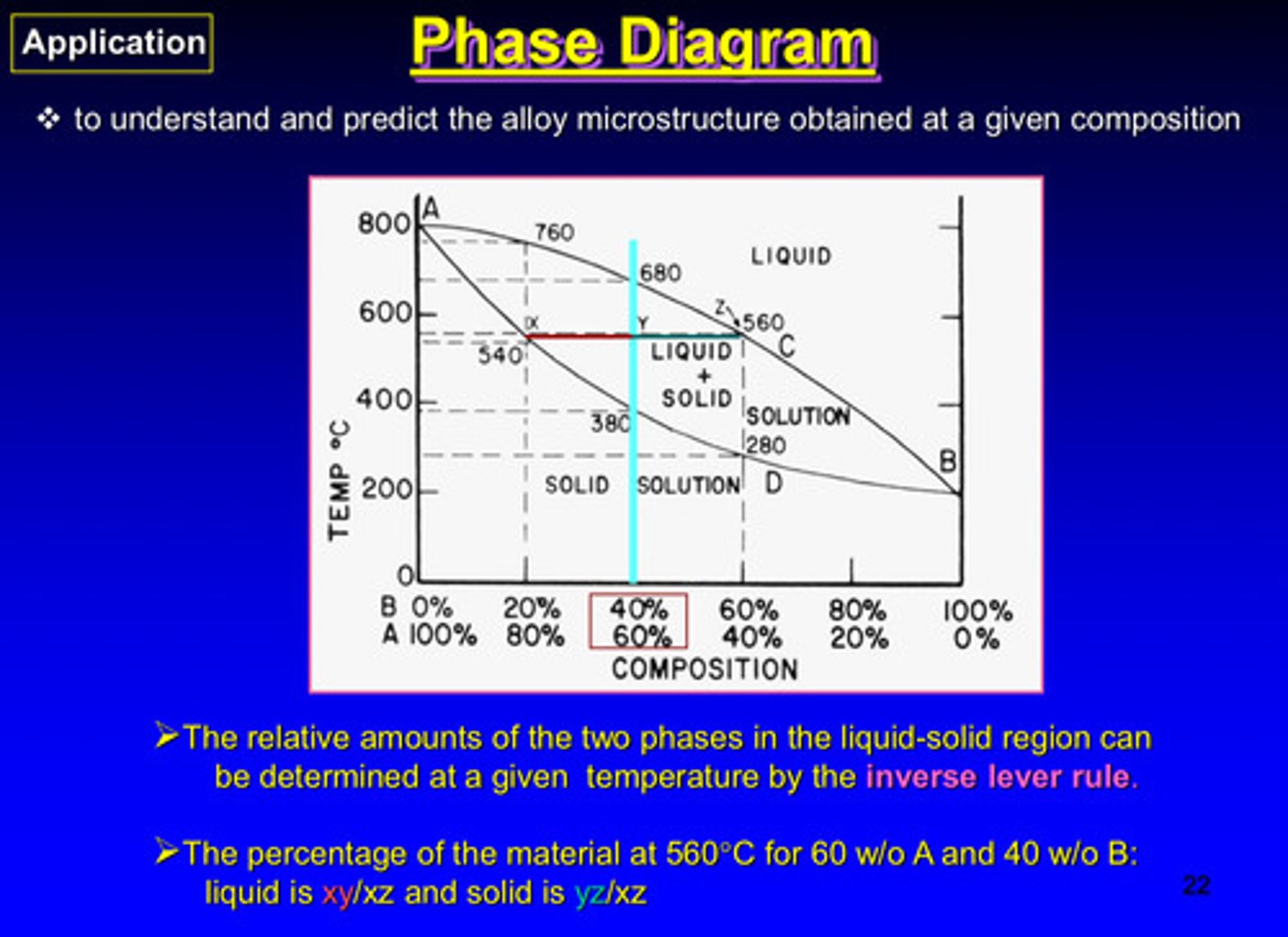
the percentage of the material at 560 C for 60% A and 40% B:
liquid is xy/xz and solid is yz/xz
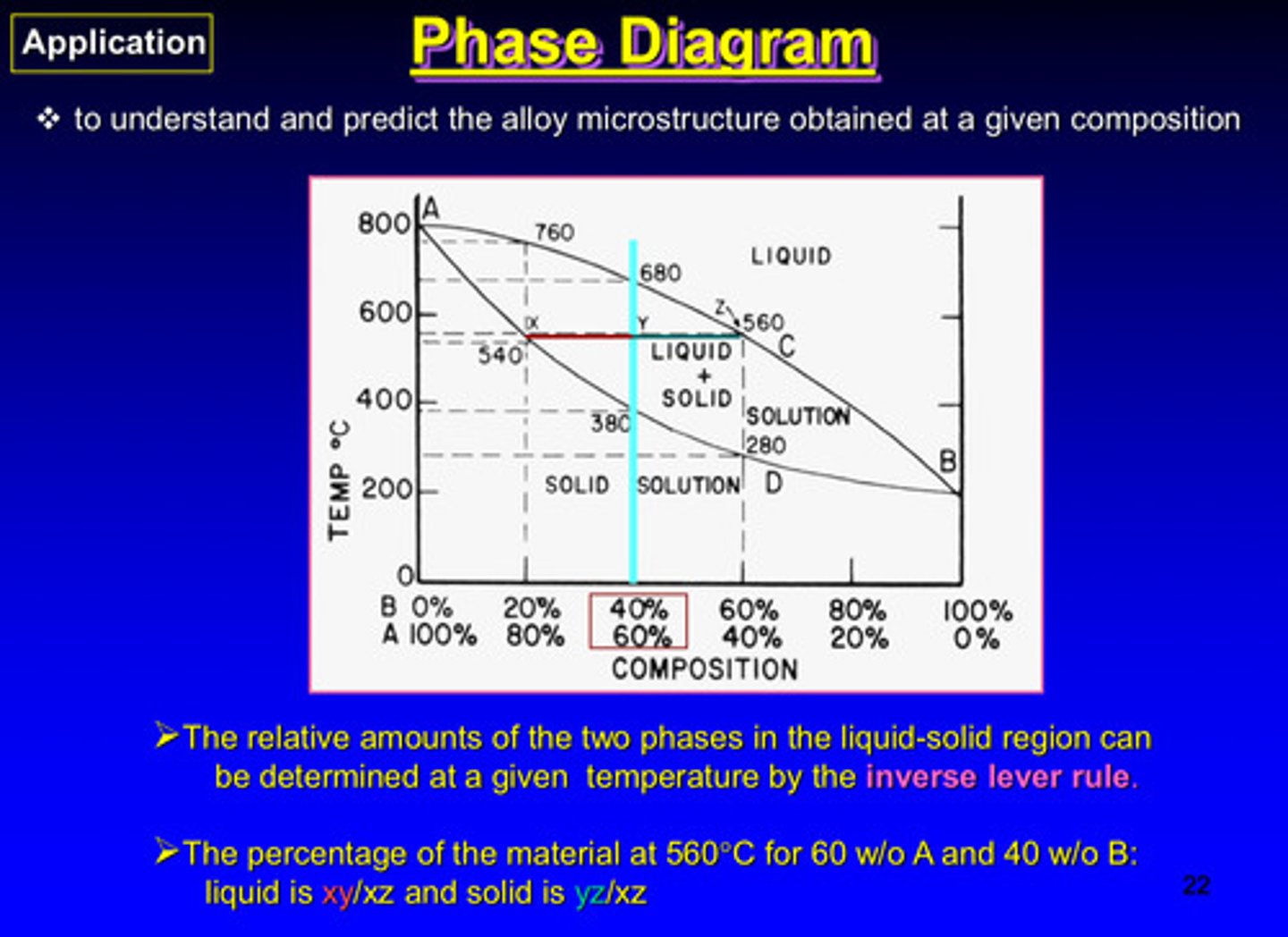
typical compositions (weight %) of noble dental casting alloys
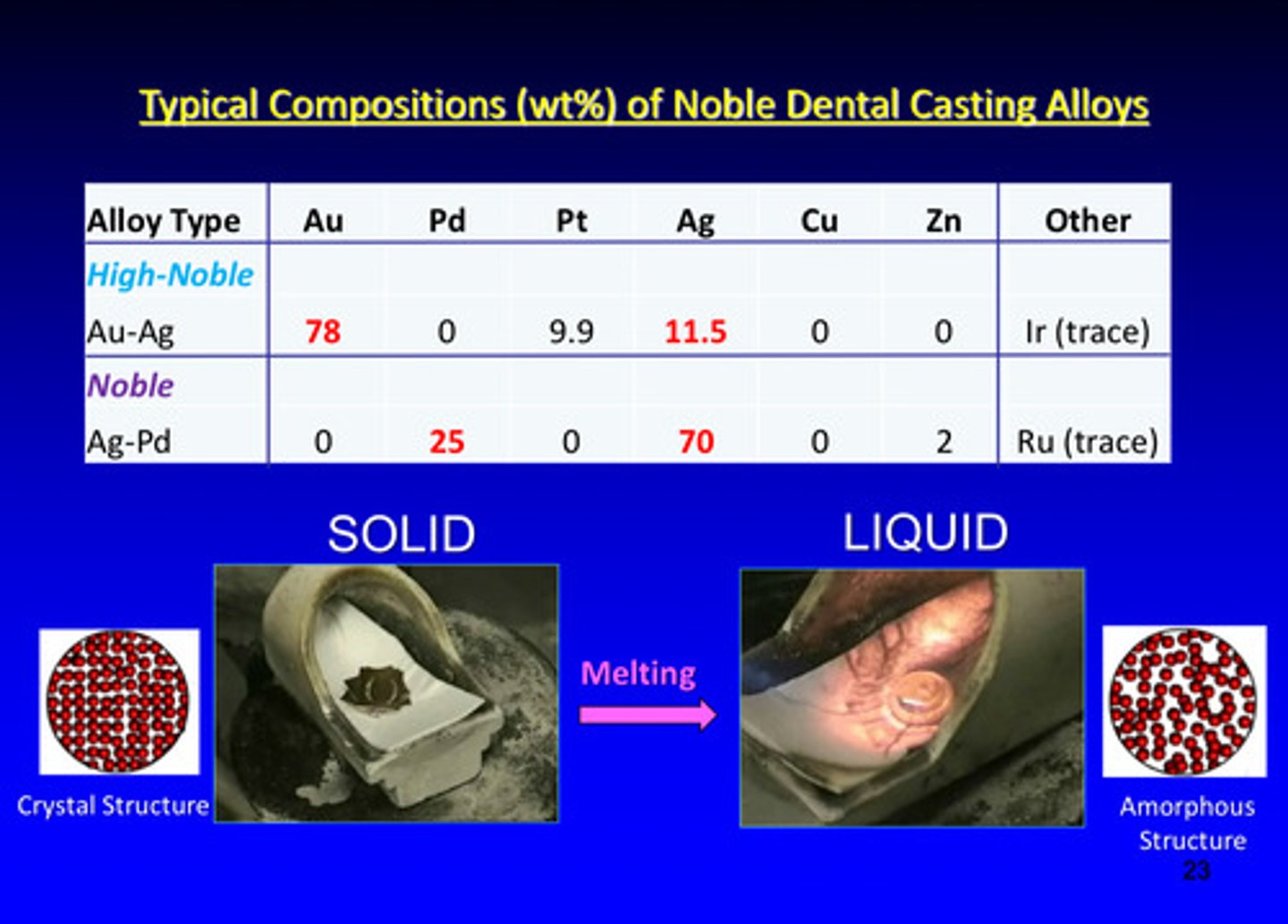
phase diagram for the noble alloy systems
in the solid state, what structure does the system have
crystal (3 types: hard ball model, unit cell, and single crystal with many unit cells)
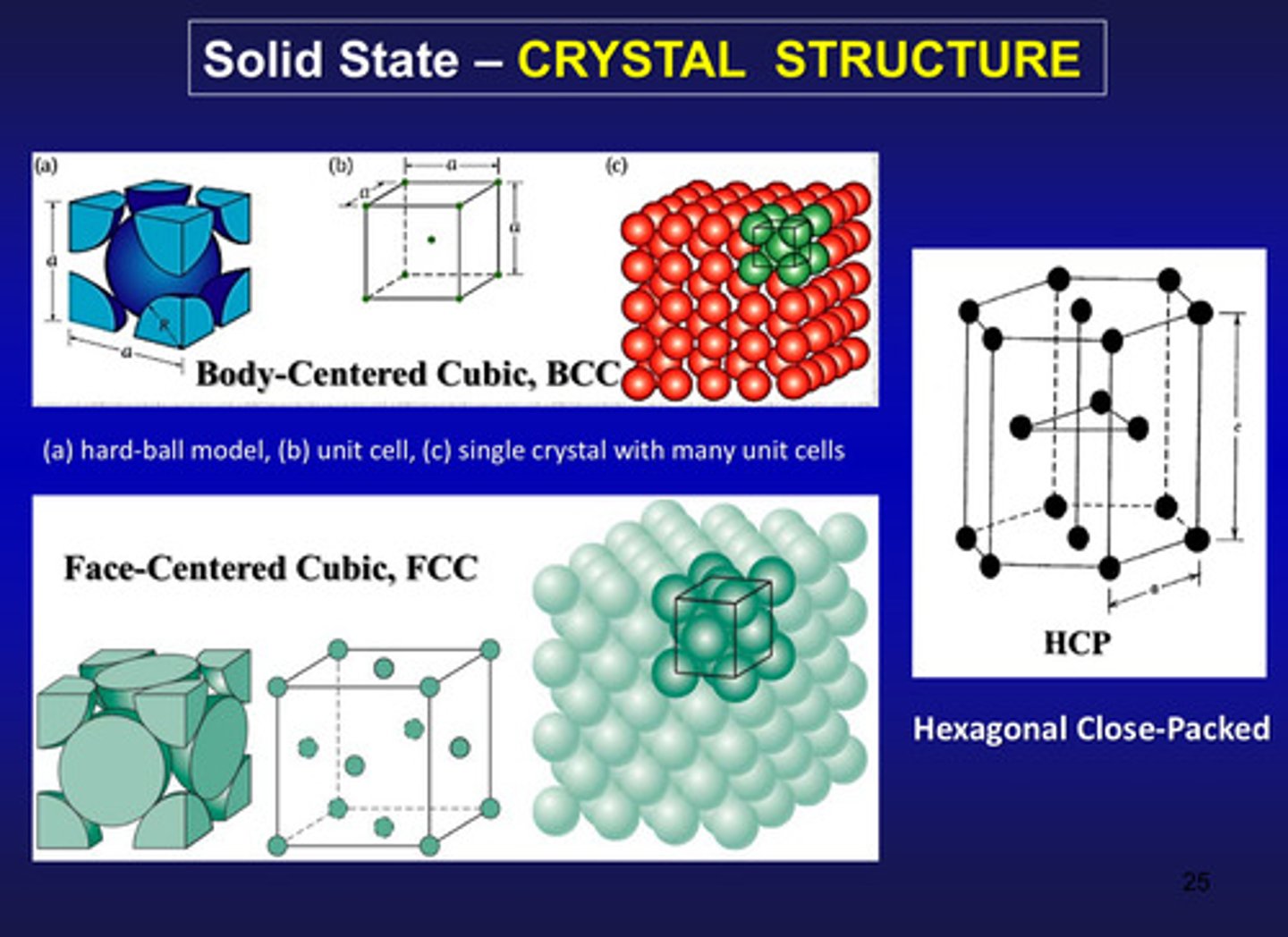
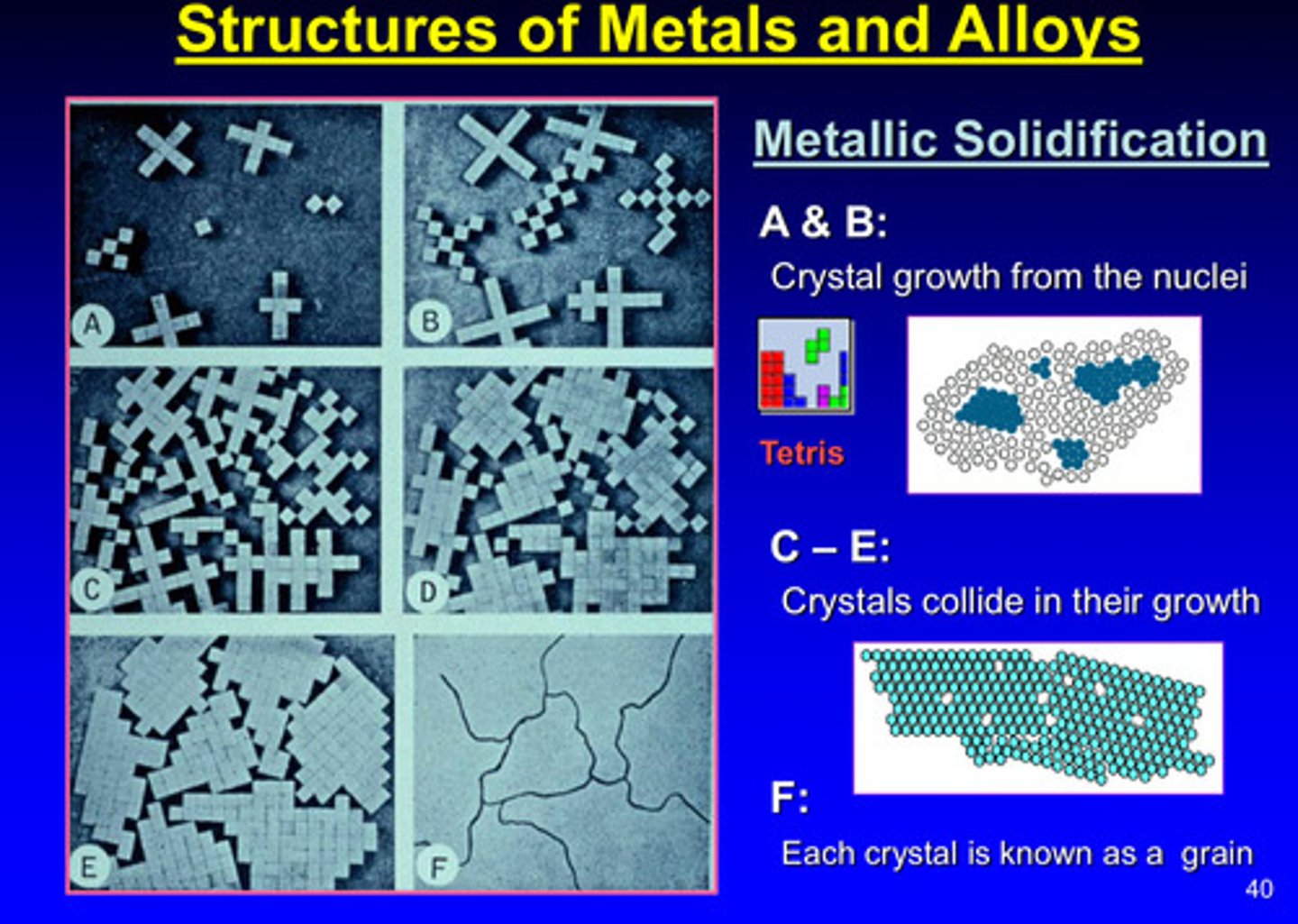
when a mixture of two or more metals is cooled, one of three possibilities may take place:
1) solid solution
2) compound
3) eutectic alloy
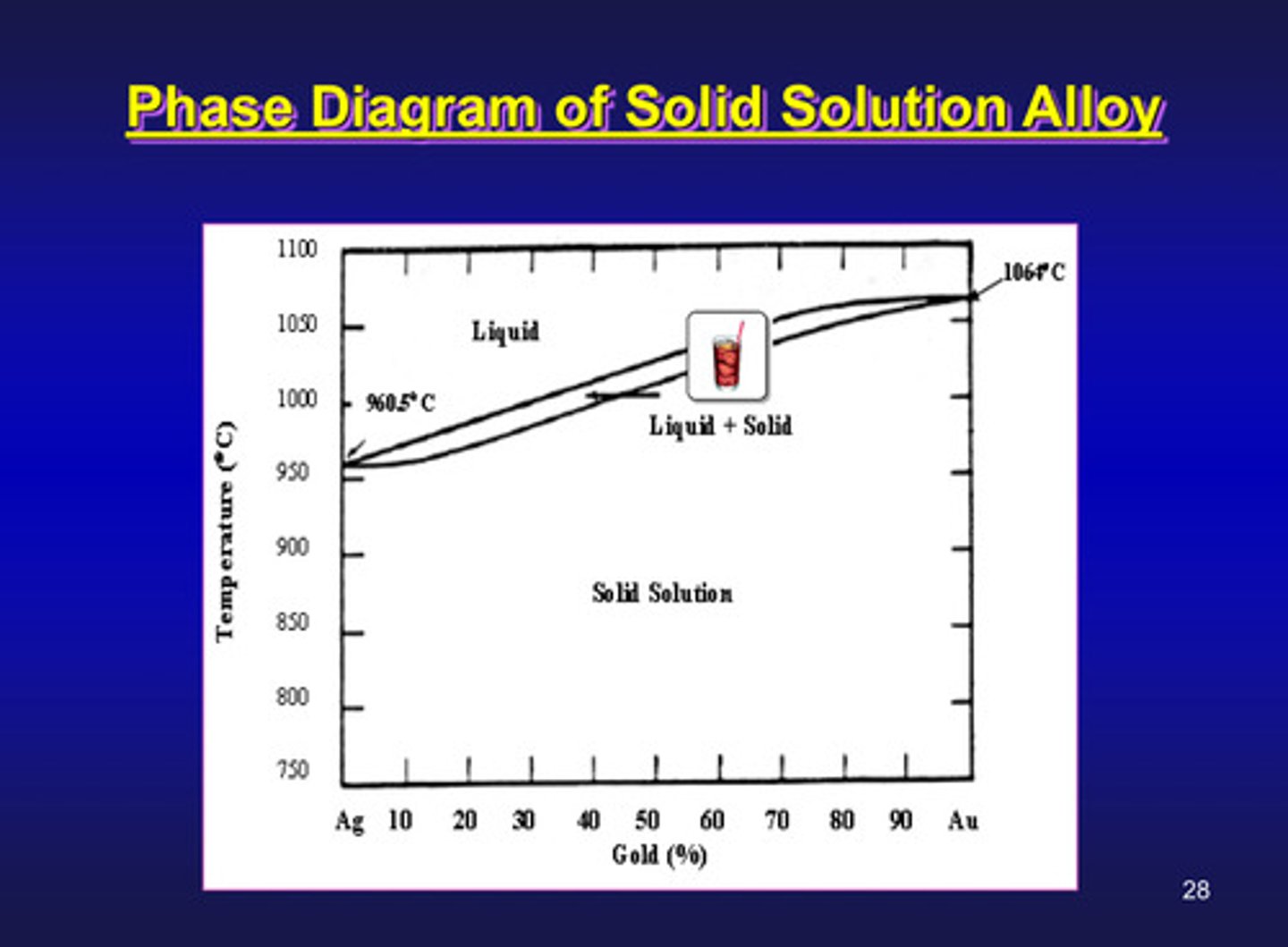
what is a solid solution alloy
a solid-state solution of one or more solutes (Ag, 11.5%) in a solvent (Au, 78%)
the crystal structure of the solvent in a solid solution alloy remains _________ by the addition of the solutes
unchanged
solid solution alloy: the solute may incorporate into the solvent crystal lattice substitutionally or interstitially: how?
by replacing a solvent particle in the lattice OR by fitting into the space between solvent particles

the solid solution alloy mixture remains in a single _____________ phase
homogenous
phase diagram of solid solution alloy
solid solution alloys are dictated by hume-rothery rules, what are they?
a set of basic rules that describe the conditions under which an element could dissolve in a metal, forming a solid solution, if the solute and solvent have 4 particular characteristics
what are the 4 characteristics of the hume-rothery rules
1) atom radius: differed by <15%
2) valence: similar valency
3) chemical affinity: similar electro negativity
4) crystal structure: must match between solvent and solute

summary of solid solution alloys
1) when 2 metals are completely miscible in the liquid state and they remain completely mixed on solidification
2) they form a single-phase system
3) system is NOT mechanically separable
4) ordered solutions indicate higher hardness and strengths in properties

what are intermetallic compounds
2 metals are completely miscible in the liquid state and have a tendency to form unique chemical compounds on solidifying
intermetallic compounds are solid-state phase involving a more ________ structure and often a well-defined, fixed _____________
ordered; stoichiometry
in an intermetallic compound, the atoms of one metal occupy a ___________ position in the lattice space of another metal such as 73.2% Ag and 26.8% Sn
definite
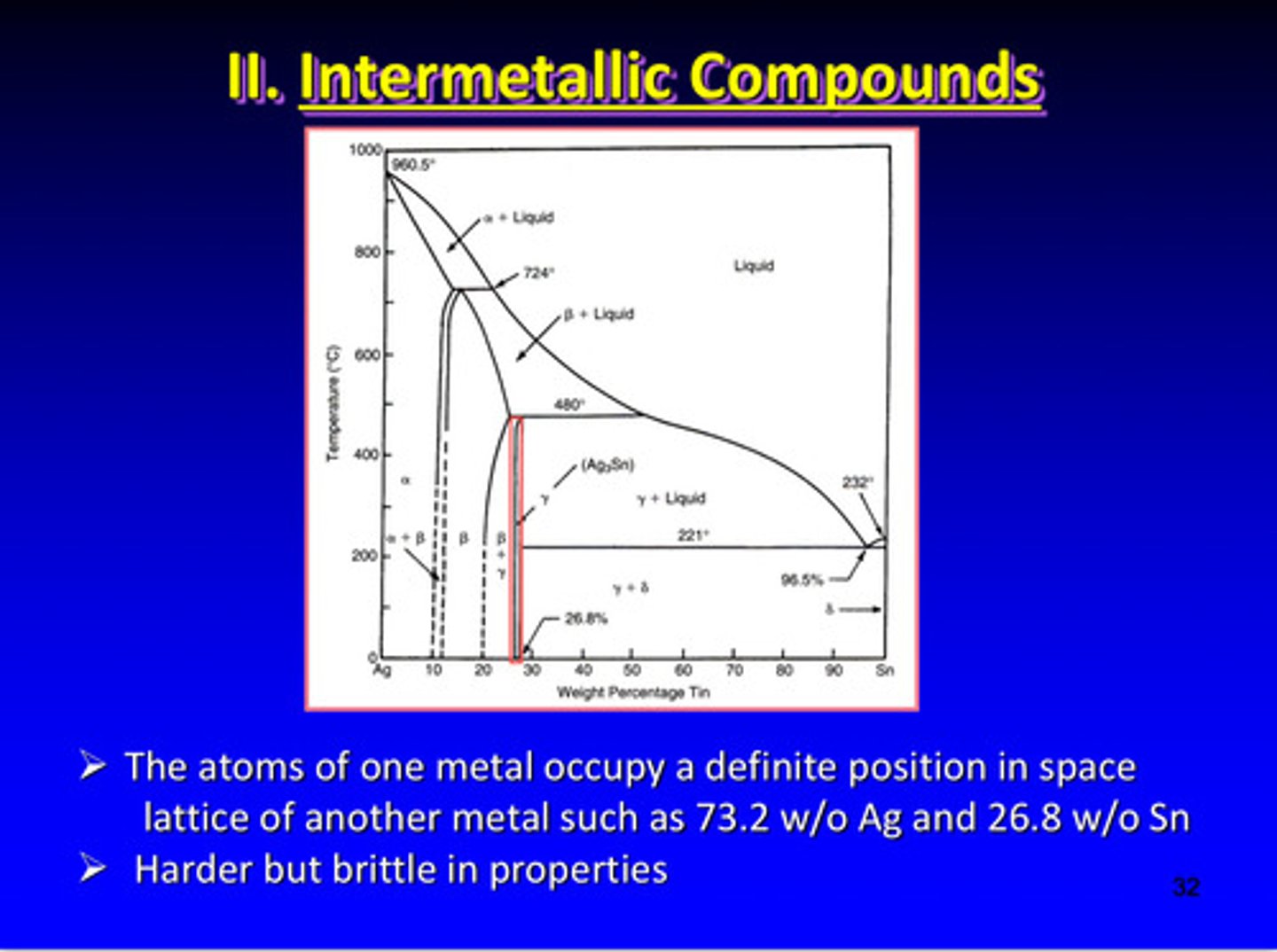
intermetallic compounds are harder but _______ in properties
brittle
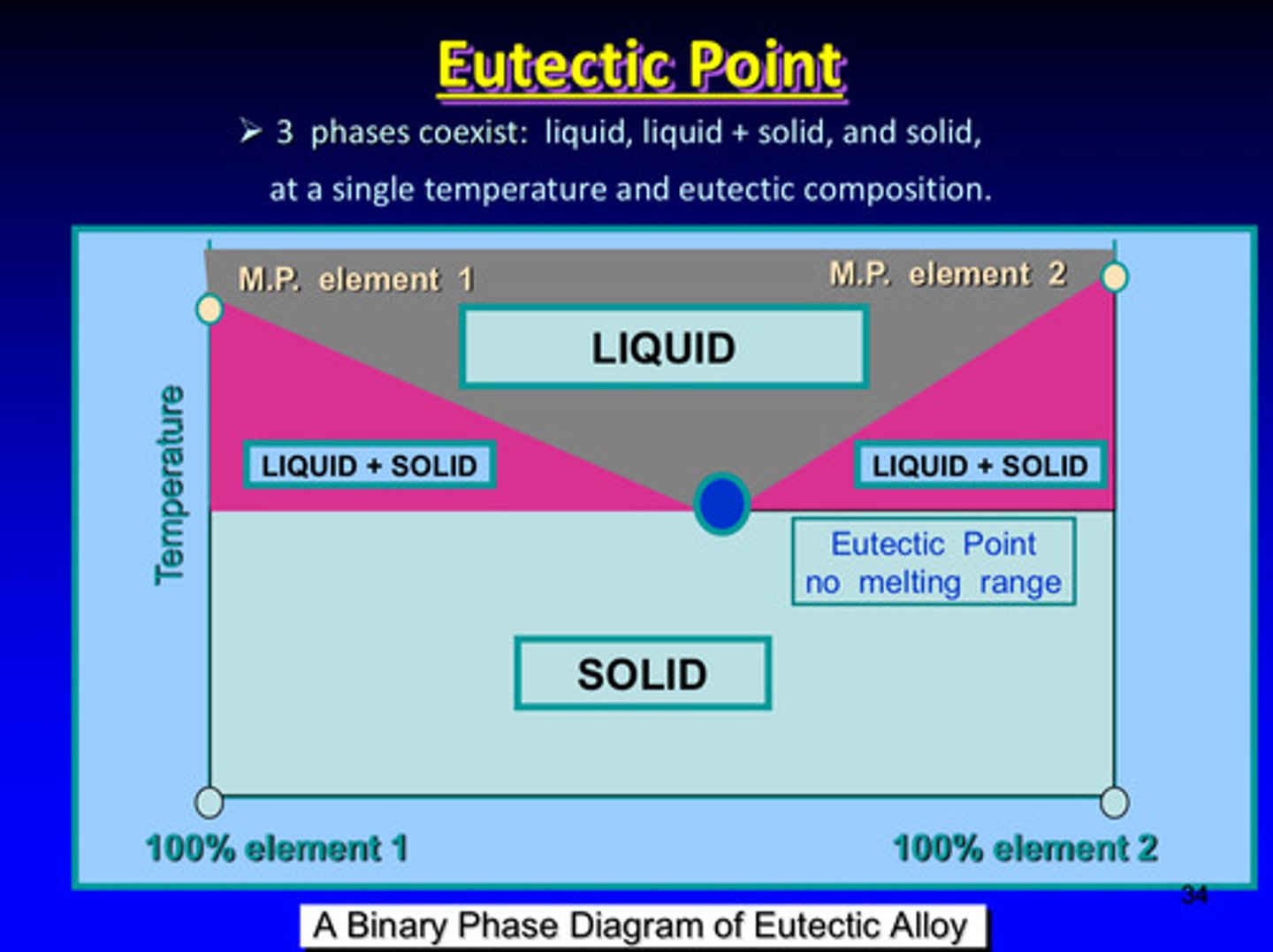
what are eutectic alloys
upon cooling or solidification, the liquid forms 2 separate solid phases
eutectic alloys are in _______ equilibrium and this means that the liquid and 2 solid solutions all ______ at the same time
coexist
eutectic alloys have _______ materials and have a eutectic composition
2+
when a eutectic alloy metals, it does so at a ______ and ______ temperature
single and sharp
eutectic reaction image

what is the eutectic point
the point in which all 3 phases coexist: liquid, liquid + solid, and solid —> all at a single temperature and eutectic composition
a eutectic alloy system AB with micro-structure representations of the various compositions at different temperatures
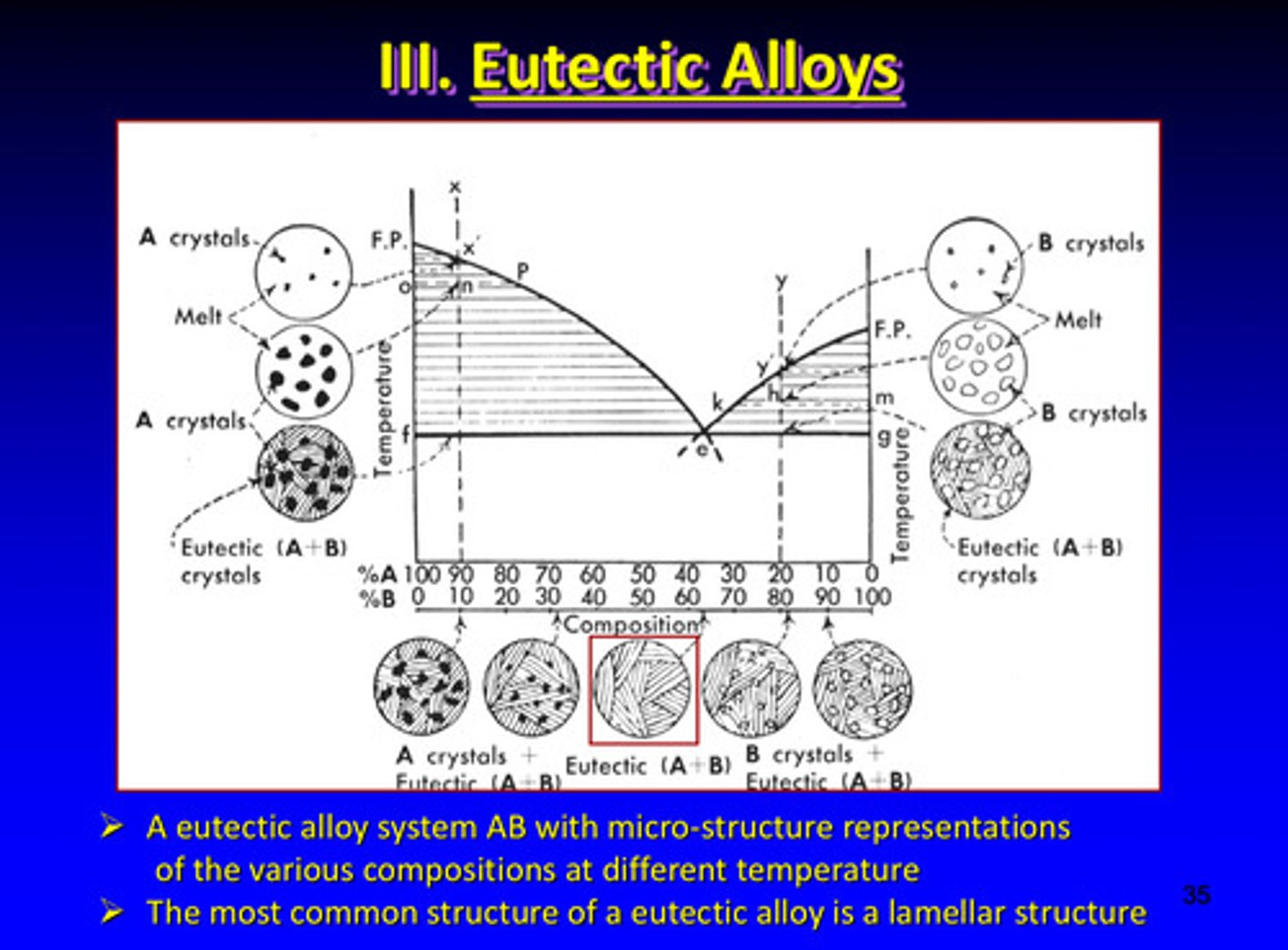
the most common structure of a eutectic alloy is a ?
lamellar structure
the alloy components of eutectic alloys exhibit what easily
complete liquid solubility
eutectic alloys may be used in what kind of procedure
soldering
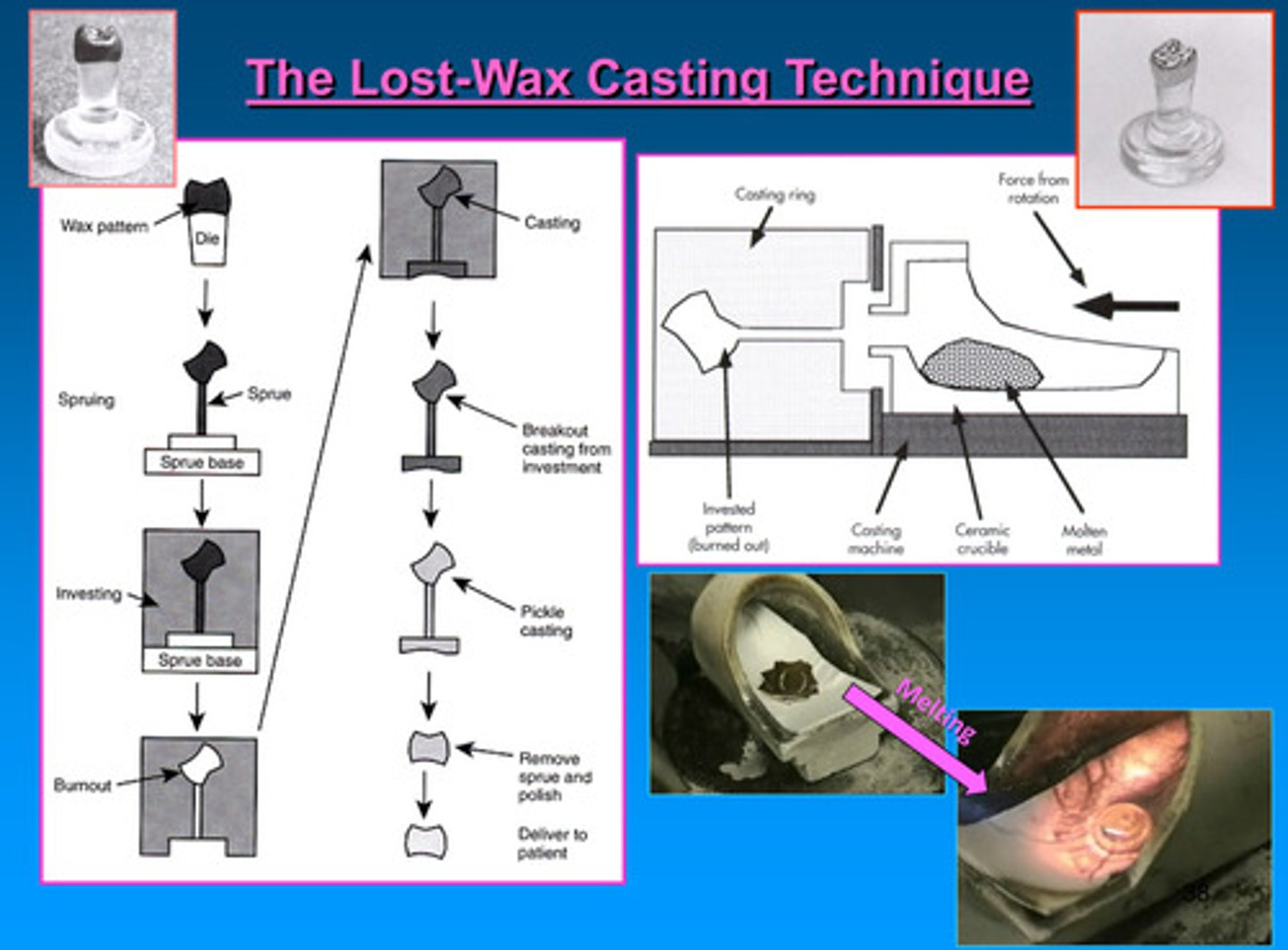
lost wax casting technique image
what are the 3 noble elements used in dental alloys
gold (Au), platinum (Pt), palladium (Pd)
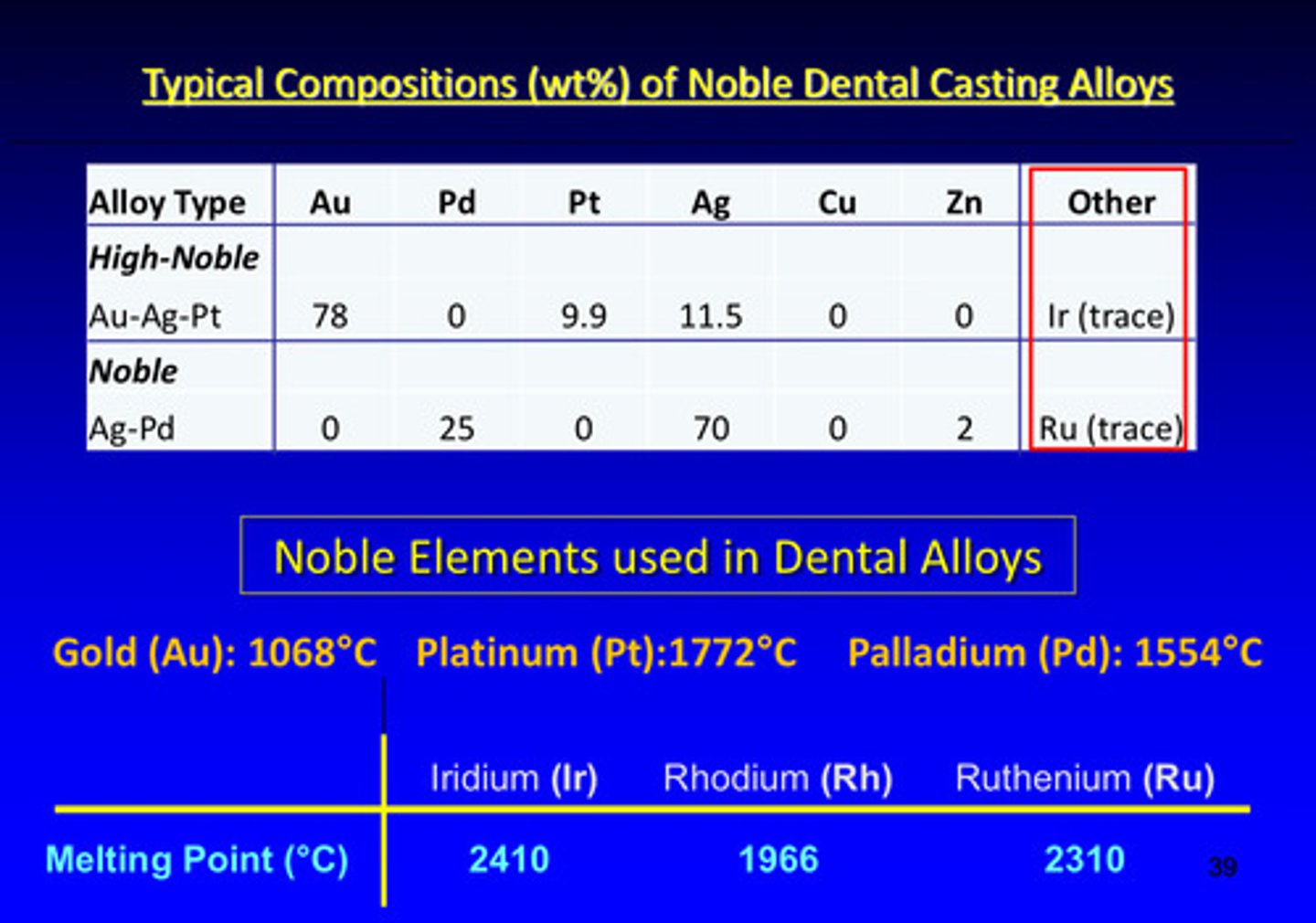
image of structures of metals and alloys in metallic solidification
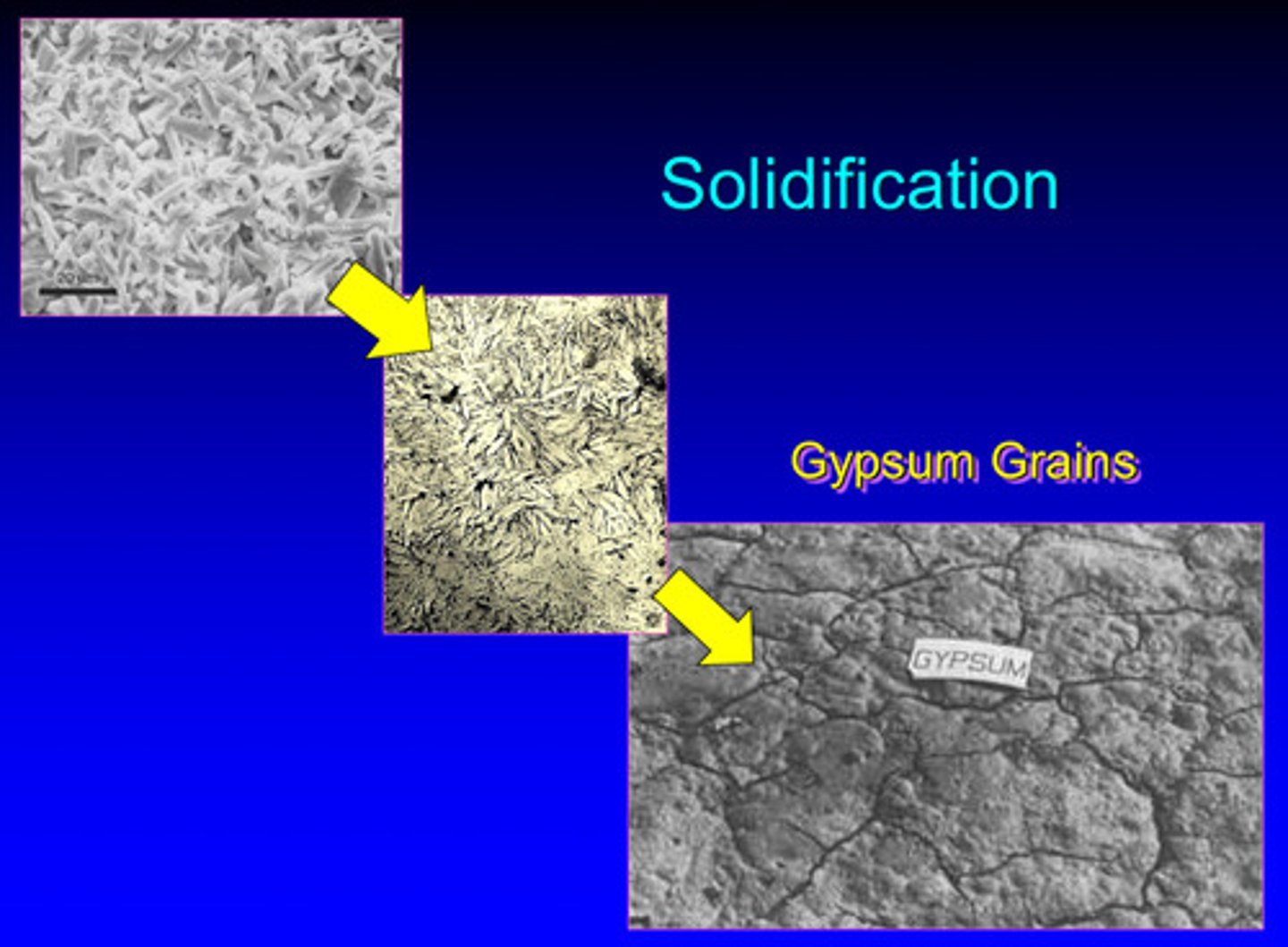
solidifcation image of gypsum grains
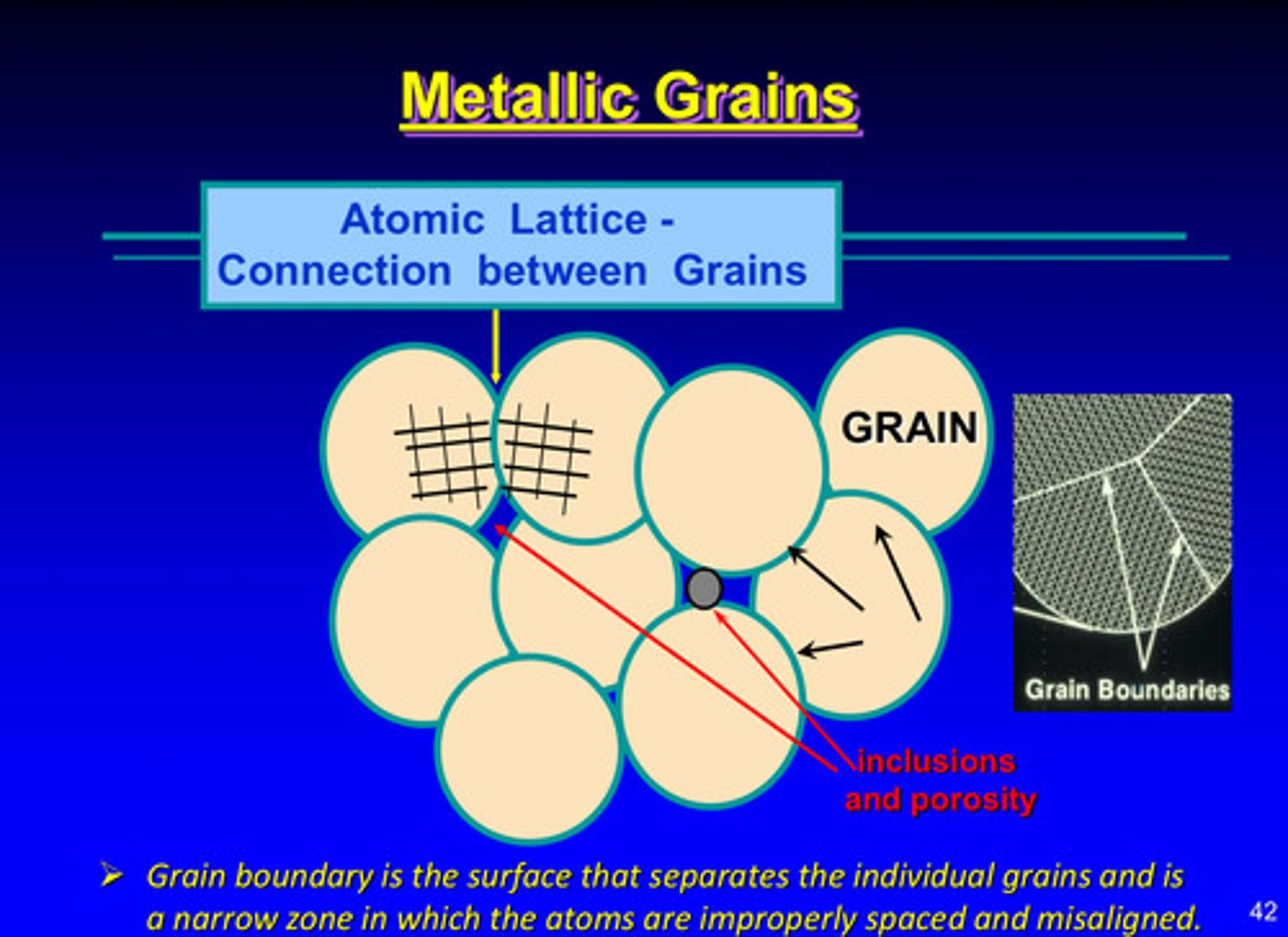
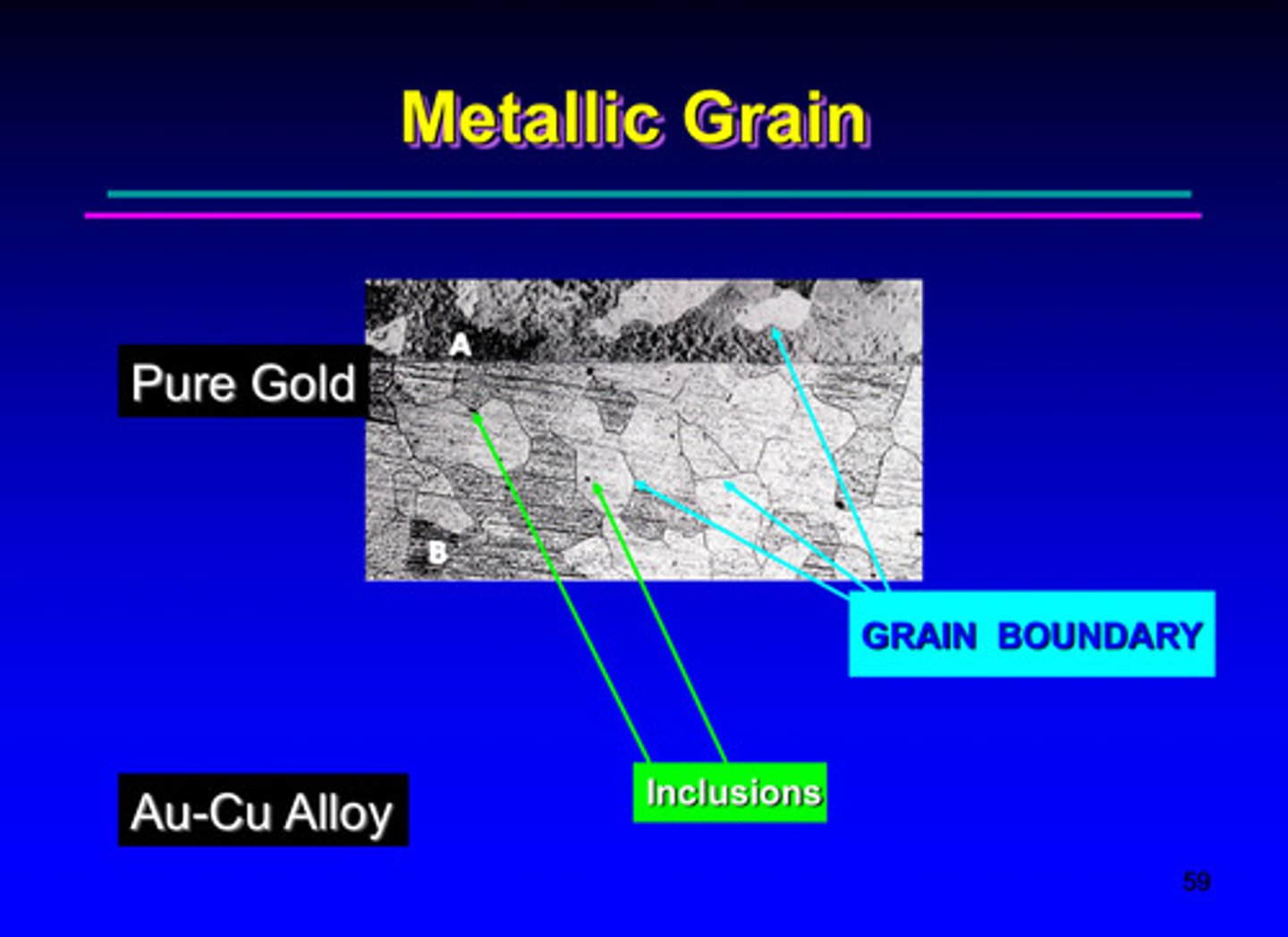
the atomic lattice is made by connections between ?
grains
what are grain boundaries
the surface that separates the individual grains and is a narrow zone in which the atoms are improperly spaced and misaligned
what are dislocations
the misaligned lattice points within the crystal and at the grain boundaries
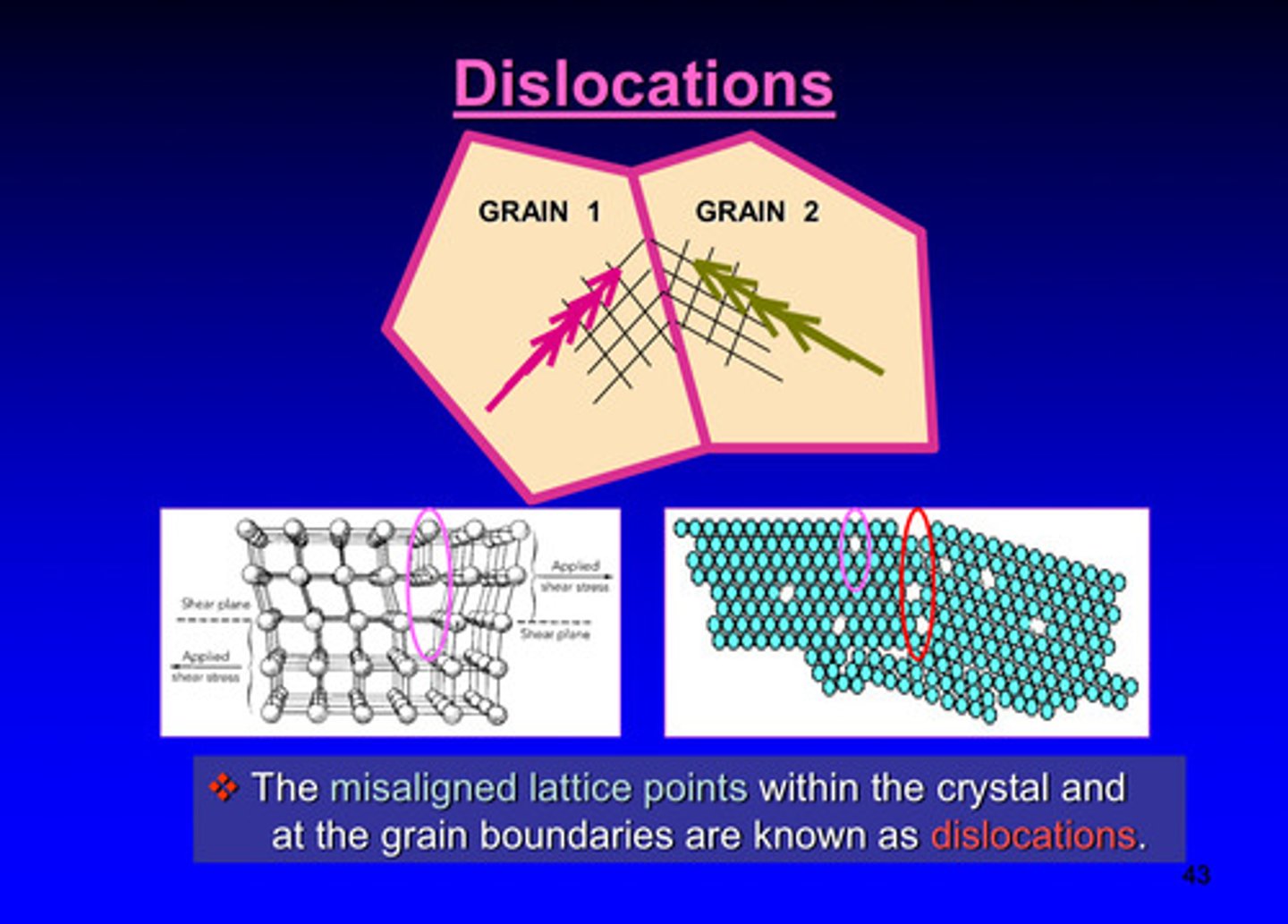
atomic plans are _________ at grain boundaries
discontinuous
slip in each grain stops where
at grain boundaries
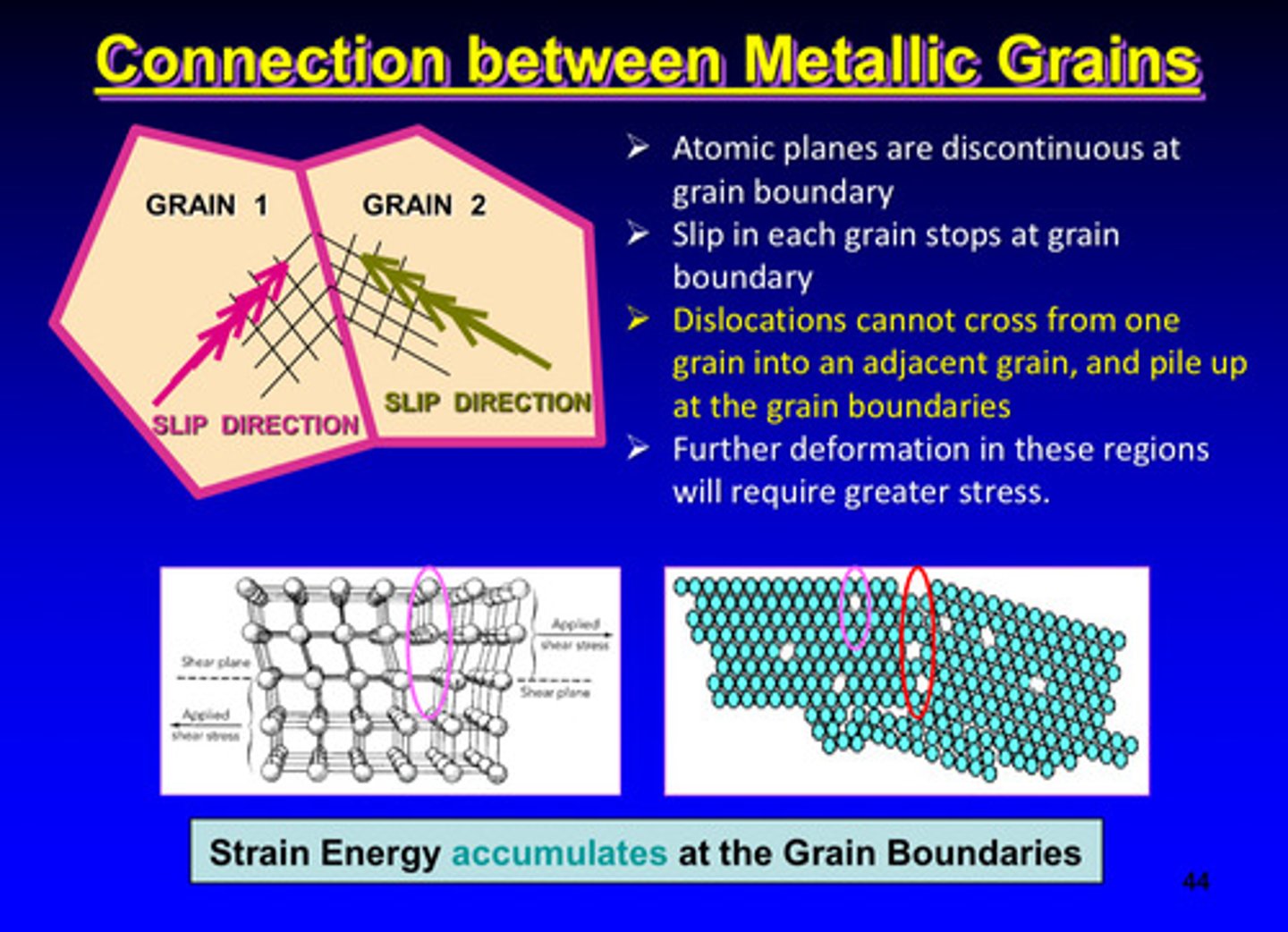
dislocations cannot cross from one grain into another adjacent grain, so they ?
they pile up at the grain boundaries
further deformation in grain boundaries will require greater ________
stress
what kind of energy accumulates at the grain boundaries
strain energy
example of strain energy accumulating at grain boundaries
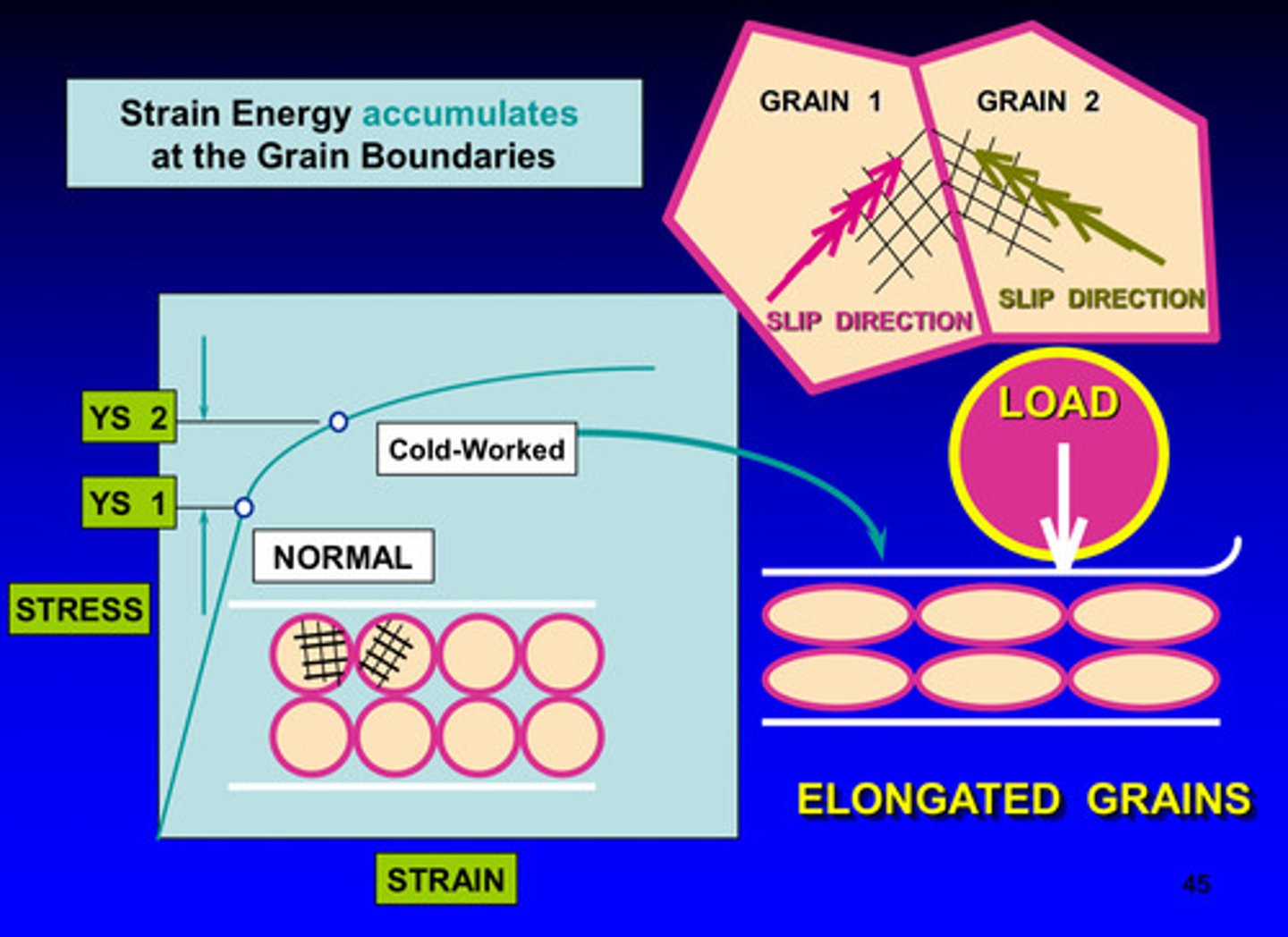
deformation from loading is viewed in the form of what
form of dislocations moving to the grain boundaries (more grain boundaries = higher strength)
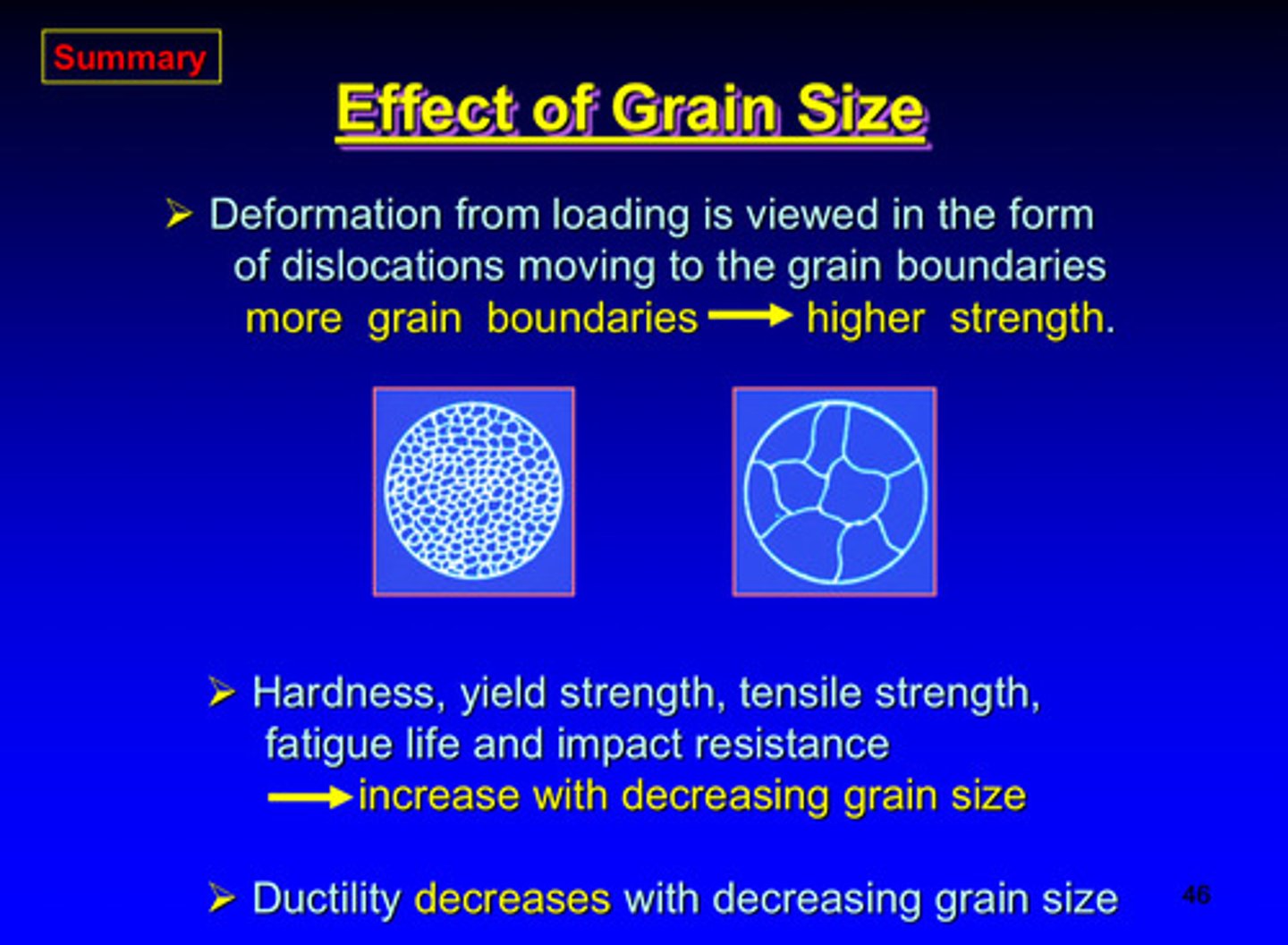
what 5 characteristics increase with decreasing grain size
1) hardness
2) yield strength
3) tensile strength
4) fatigue life
5) impact resistance
what characteristics decreases with decreasing grain size
ductility
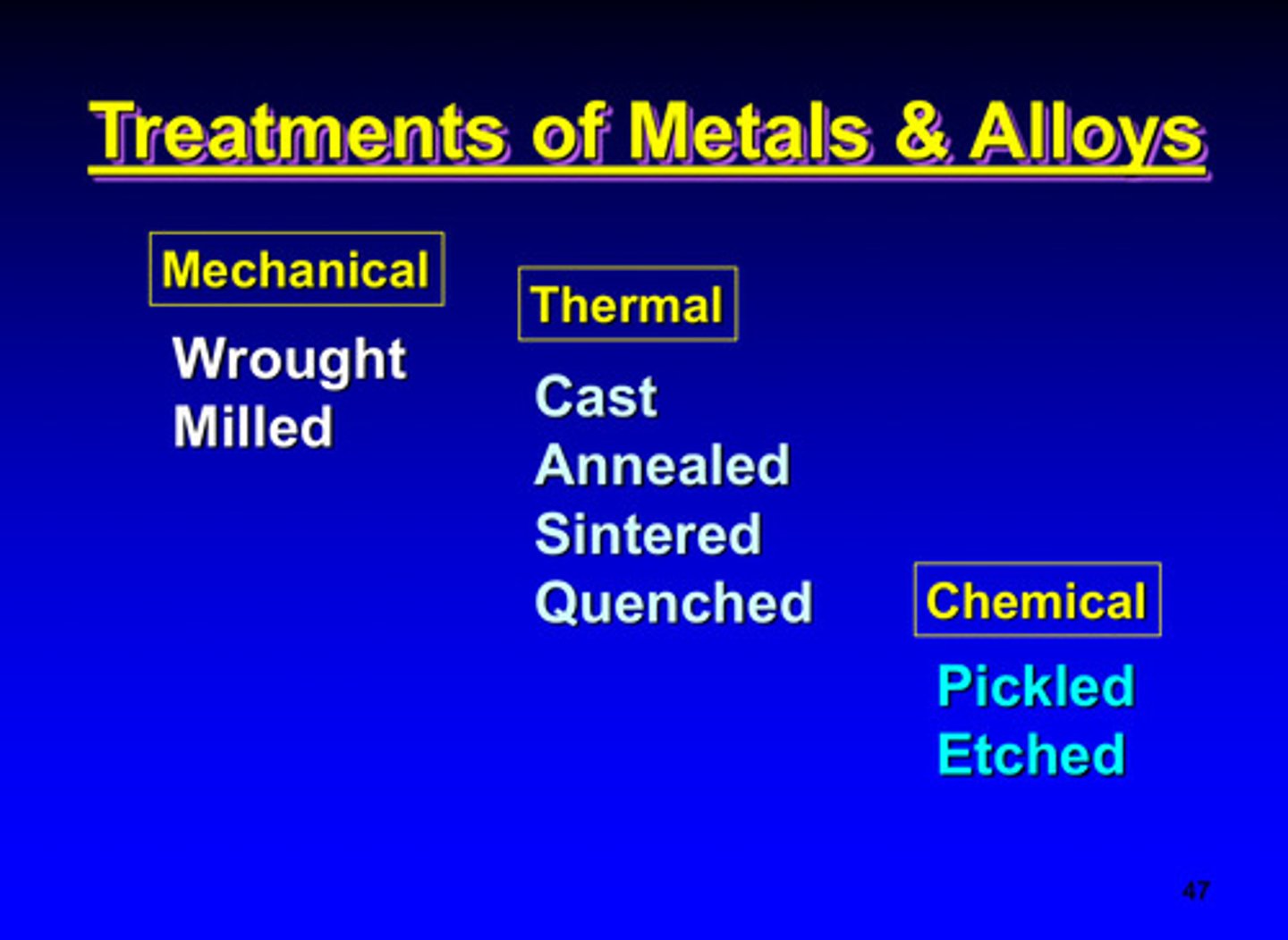
treatments of metals and alloys
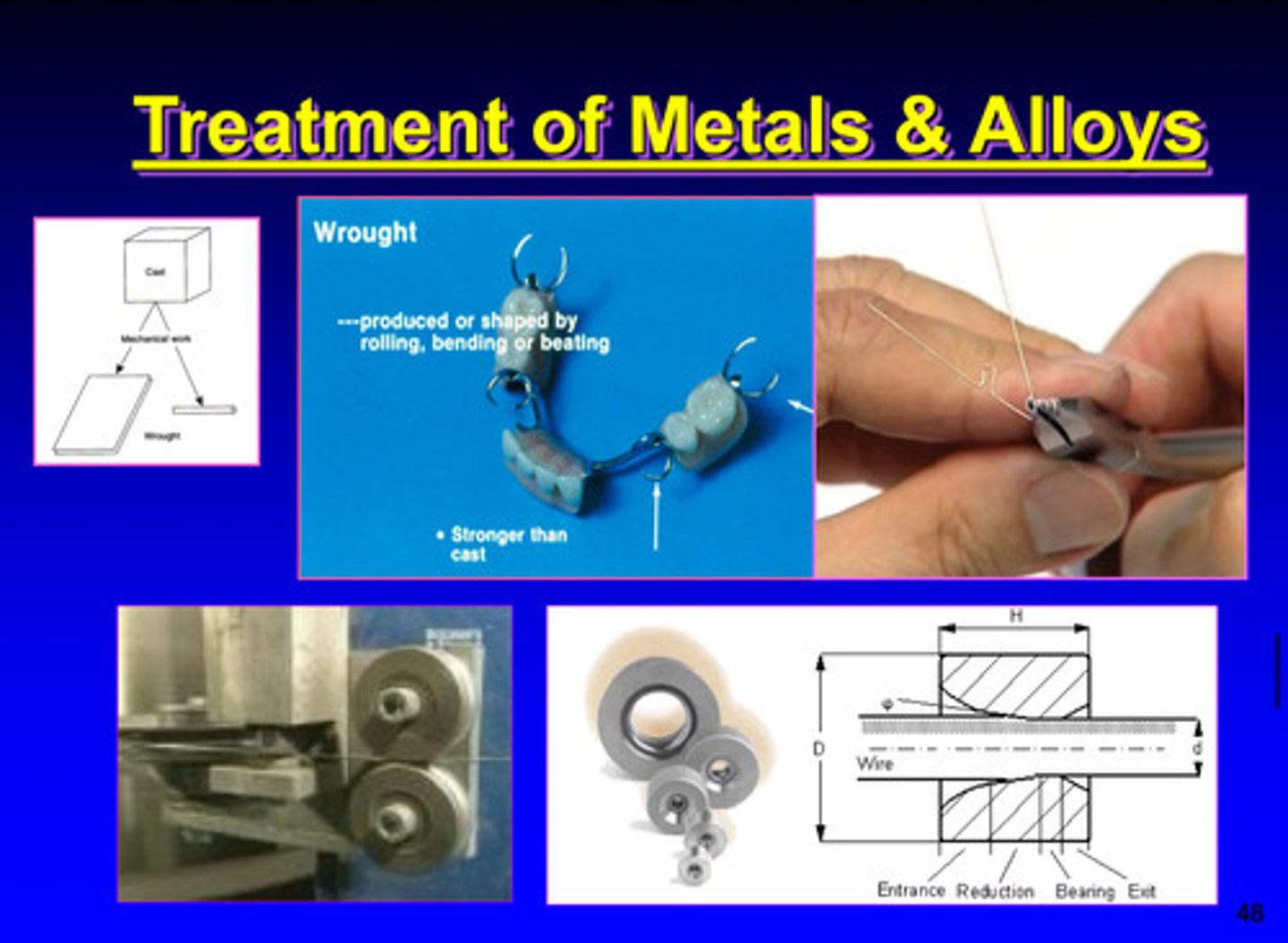
mechanical wrought treatment of metals and alloys
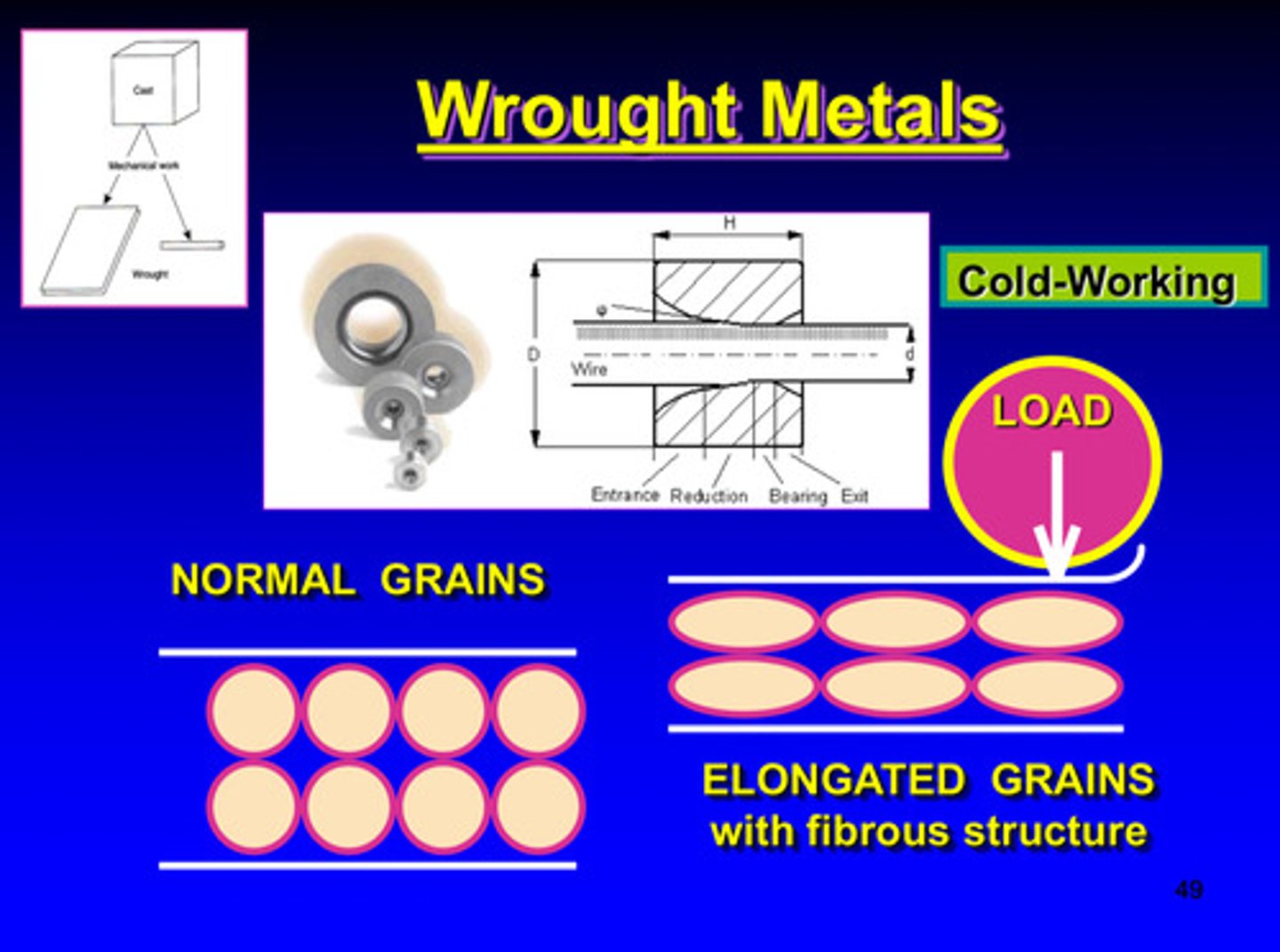
wrought metals image
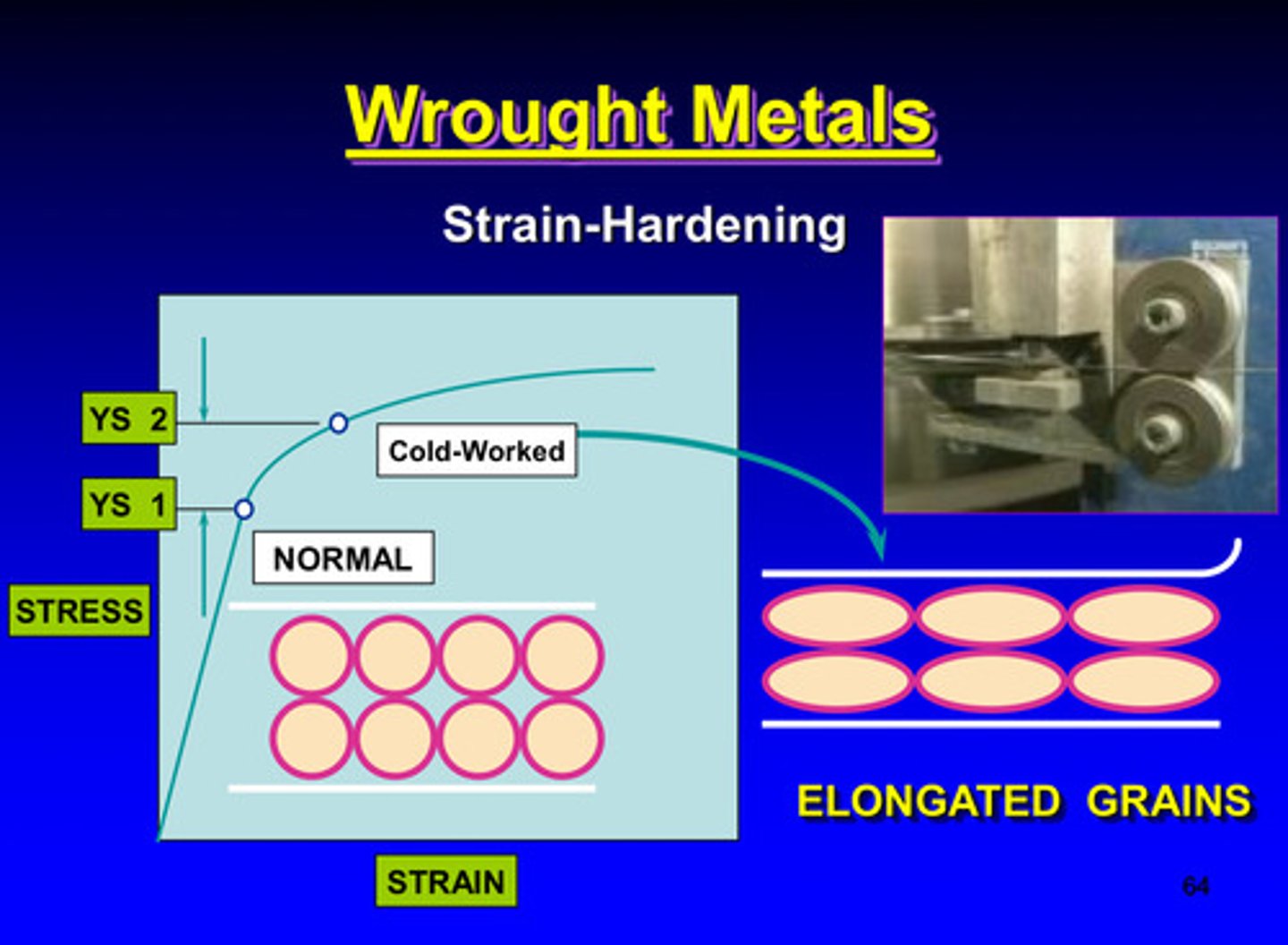
wrought metals and strain-hardening
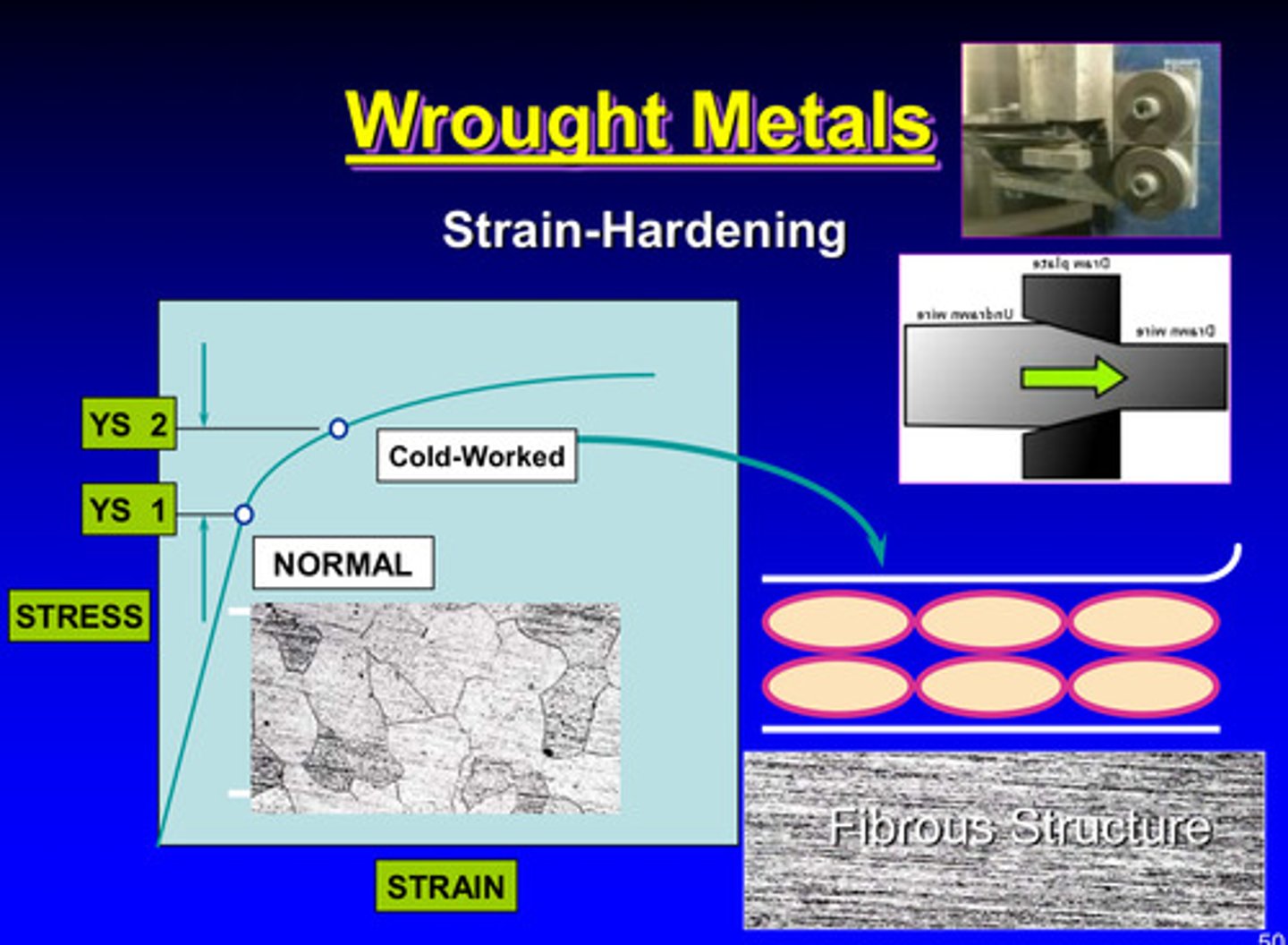
deformation of a metallic specimen is performing below what temperature
the recrystallization temperature
metals are cold worked in a high energy state due to what
the mechanical energy is absorbed in the plastic deformation
the mechanical energy absorbed in plastic deformation is attributed to the _____ concentration of dislocations in the crystal lattice and grain boundary
high
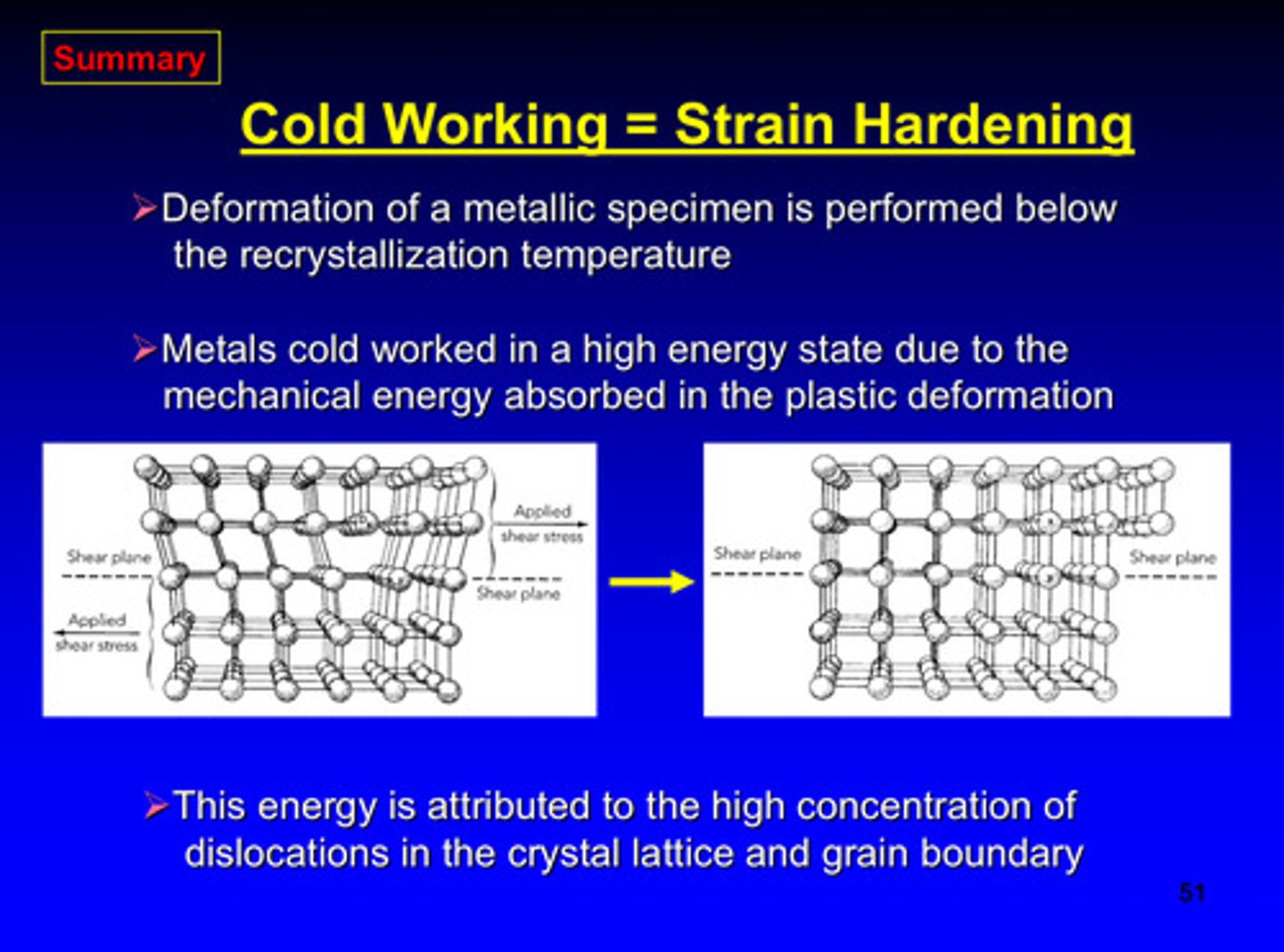
cold working = ?
strain hardening
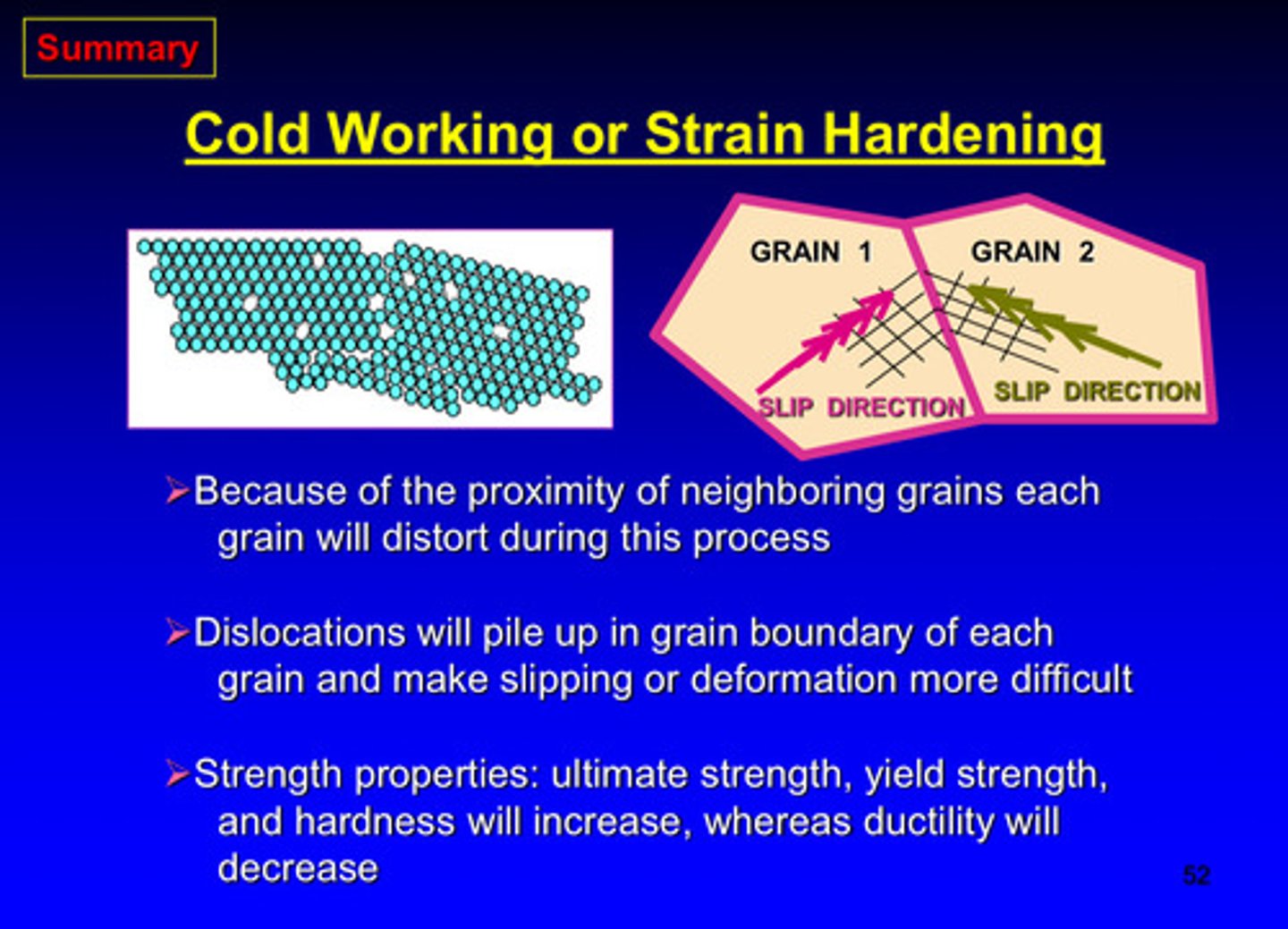
in cold working, because of the proximity of neighboring grains each grain will _______ during this process
distort
dislocations will pile up in grain boundary of each grain and makes ________ or _________ more difficult
slipping or deformation
what properties will increase and which property will decrease in cold working
ultimate strength, yield strength, and hardness will increase & ductility will decrease
milling treatment of metals and alloys (mechanical)
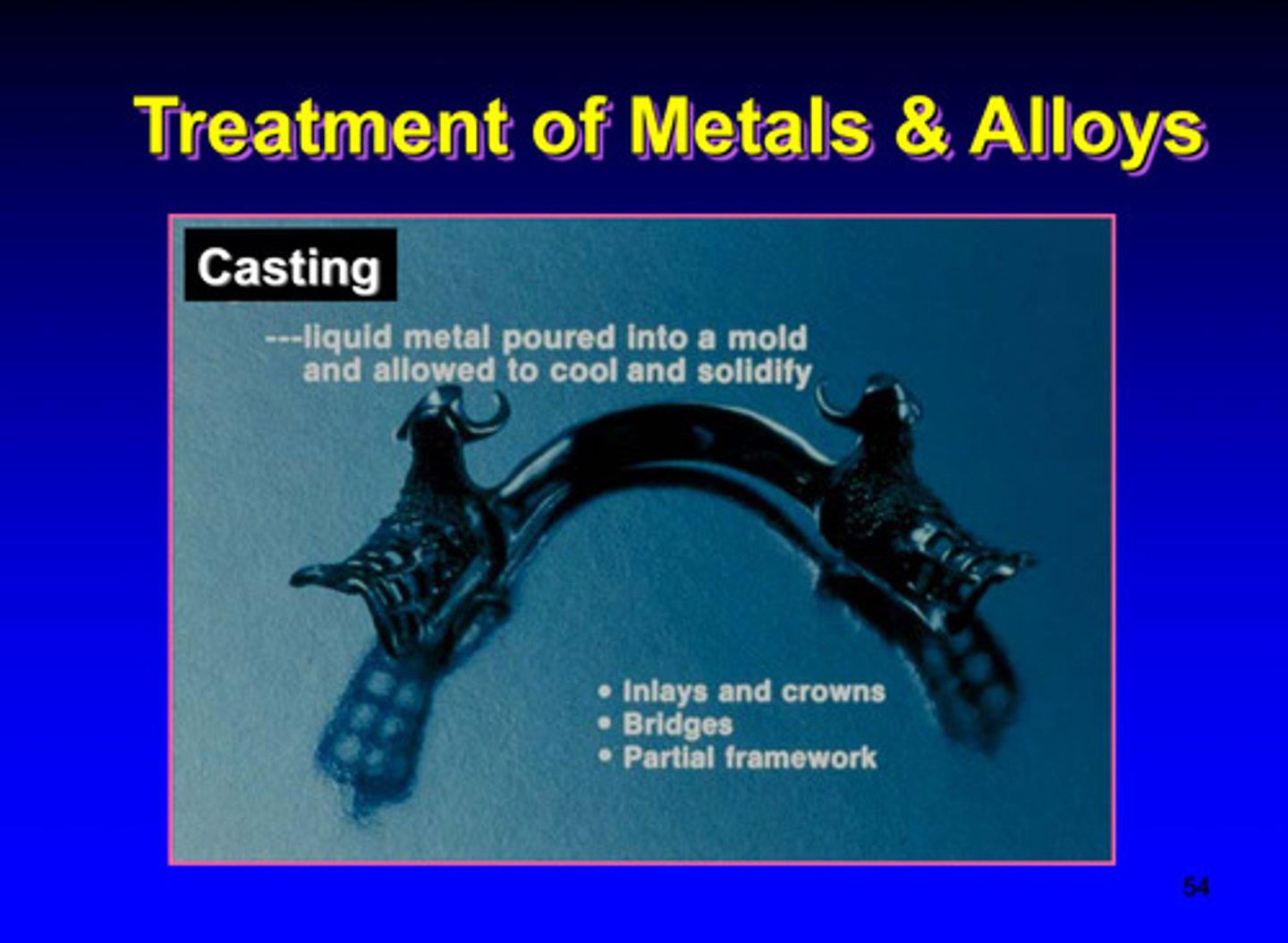
casting treatment of metals and alloys (thermal)
annealing treatment of metals and alloys (thermal)

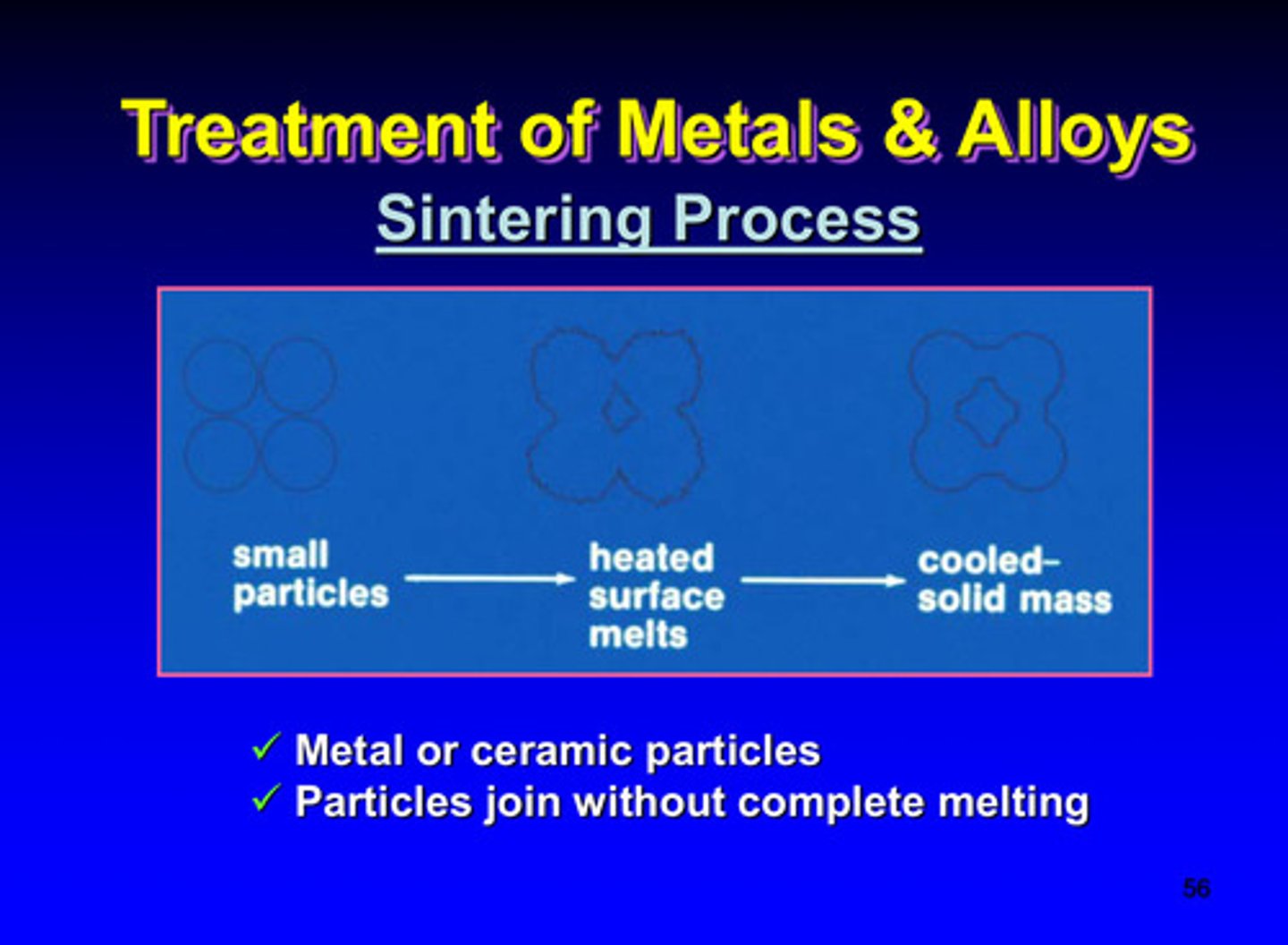
sintering process of metals and alloys (thermal)
uses metal or ceramic particles; particles join without complete melting
quenching process of metals and alloys (thermal)
cooled rapidly in order to freeze the microstructure; to gain the described strength and hardness

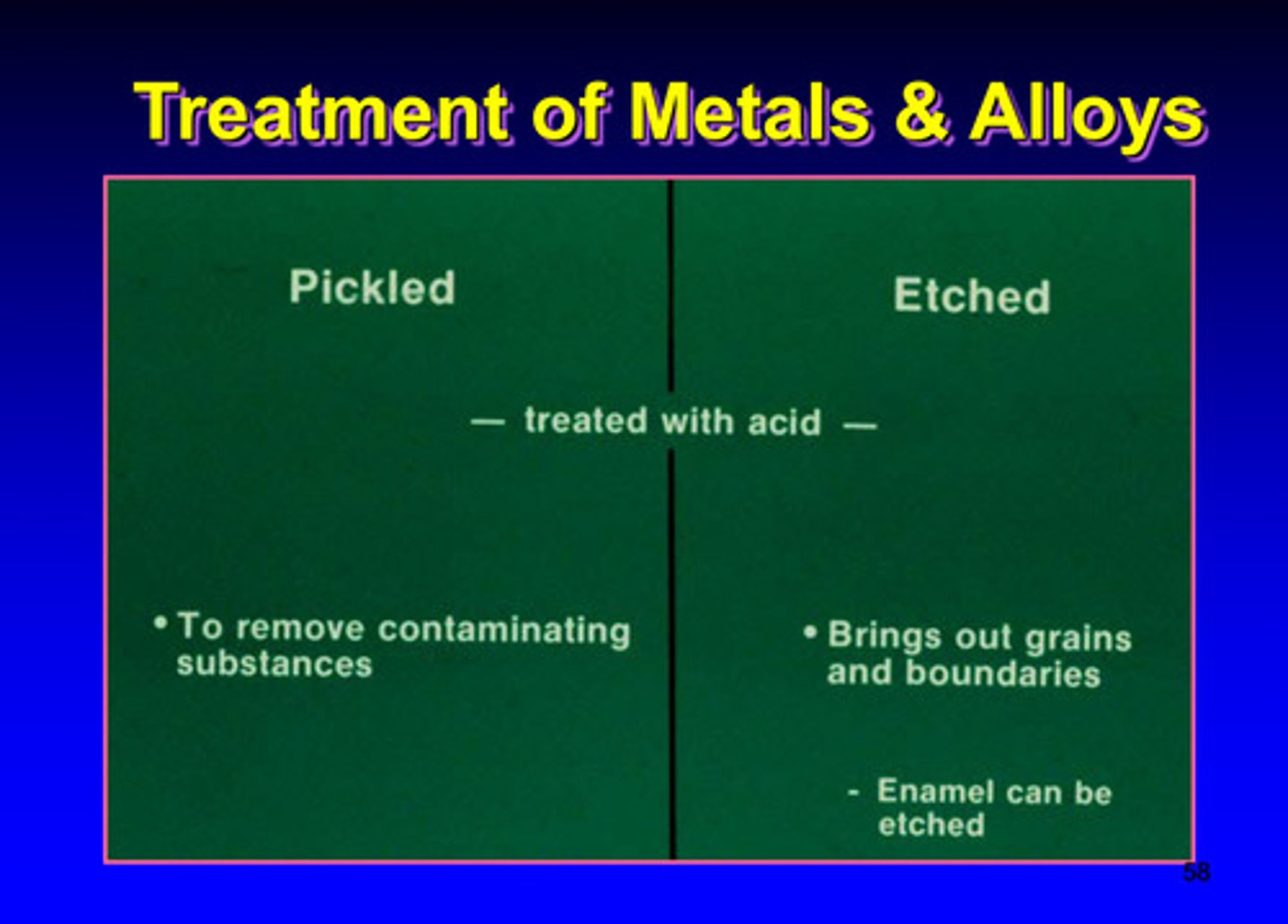
pickled and etched treatment of metals and alloys (chemical)
both treated with acid
pickled: to remove contaminating substances
etched: brings out grains and boundaries
metallic grain image of pure gold
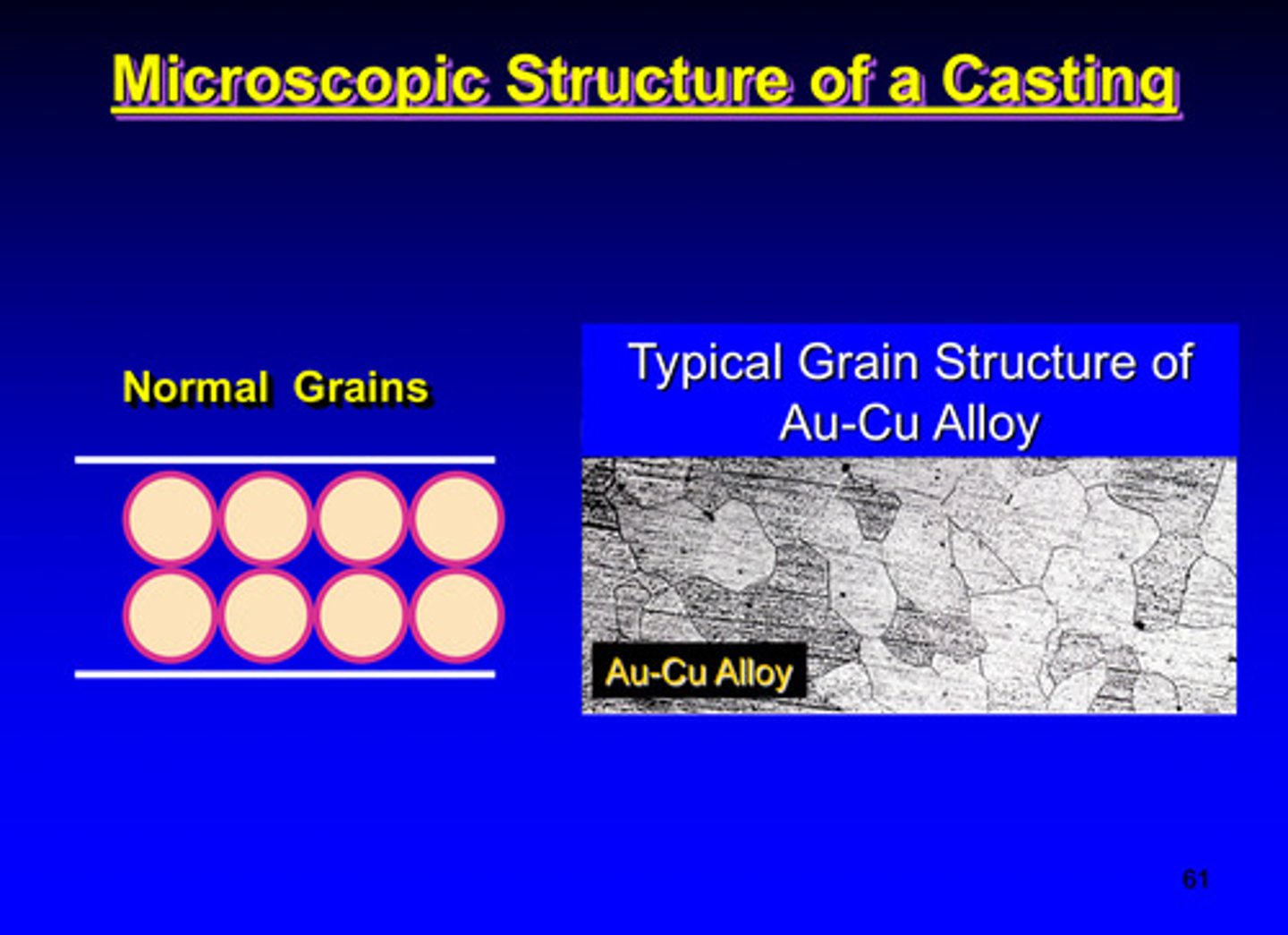
microscopic structure of a casted metal
microscopic structure of a wrought metal
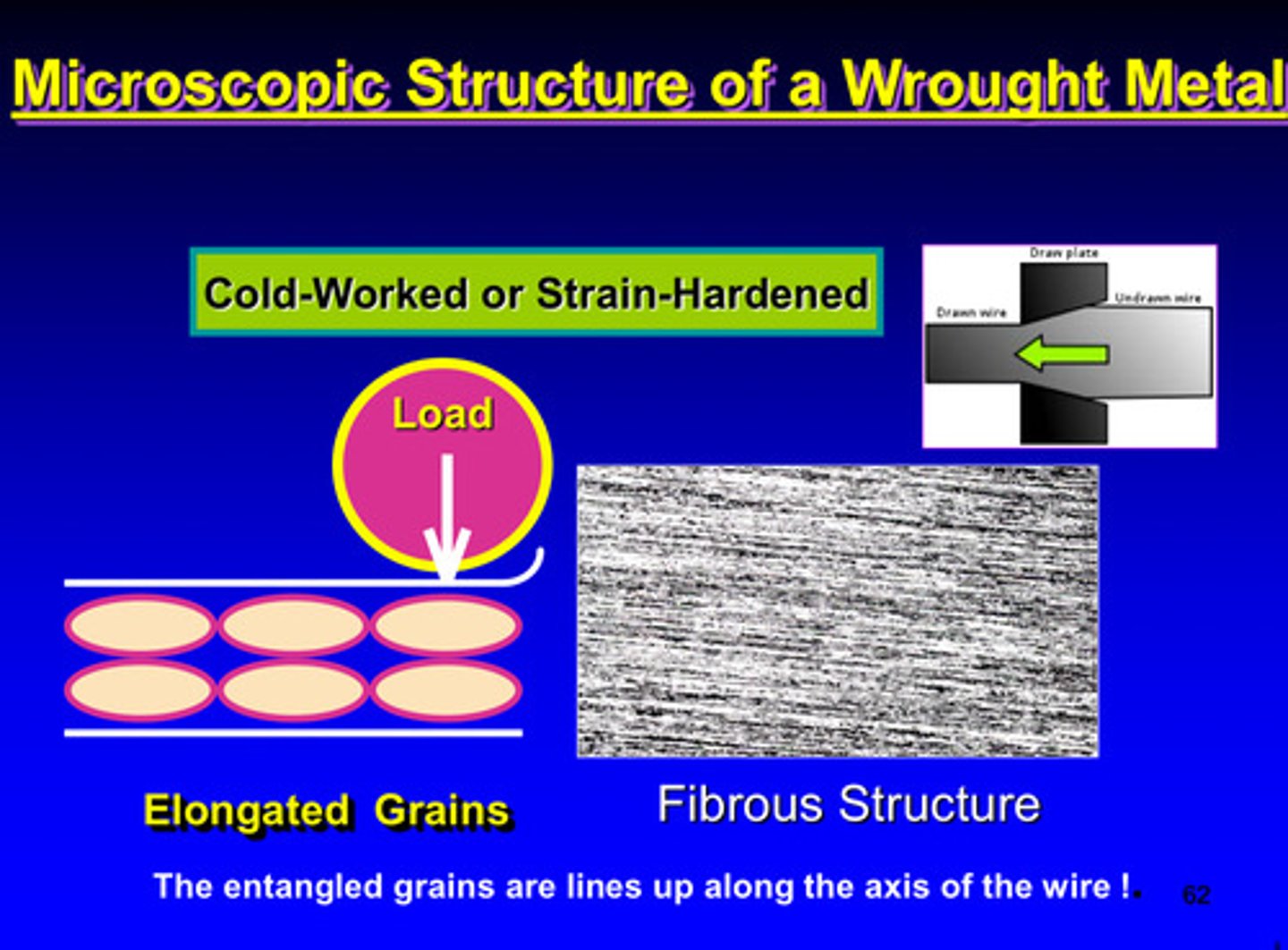
change in thickness during cold working

strain hardening of wrought metals
what is annealing
controlled heating or cooling to remove or prevent stresses
annealing is similar to that of __________ heat-treatment
softening
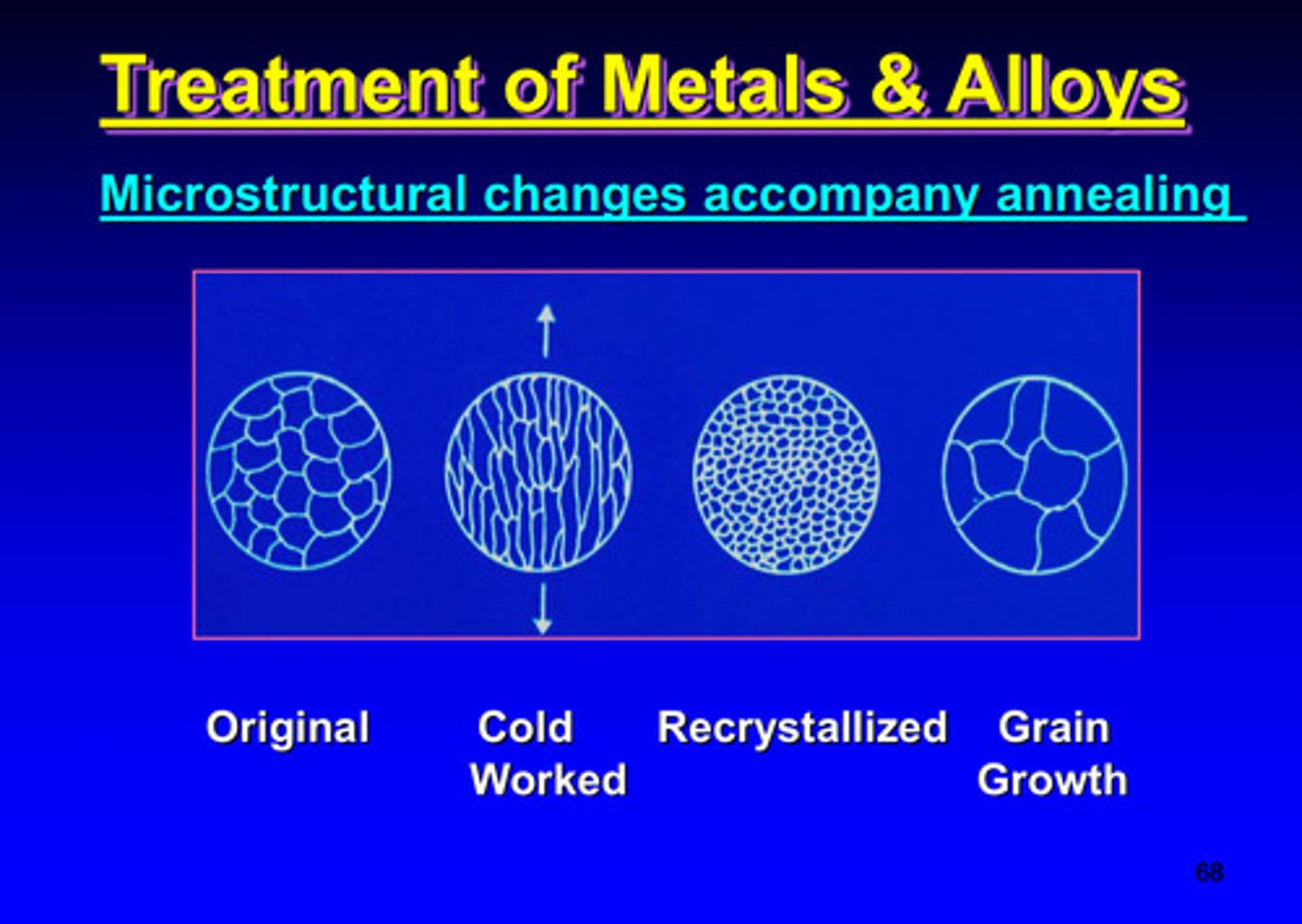
what is the goal of annealing
to form new stress-free crystals in a work-hardened metal through a controlled heat-treatment process

cold working of titanium vs annealing of titanium
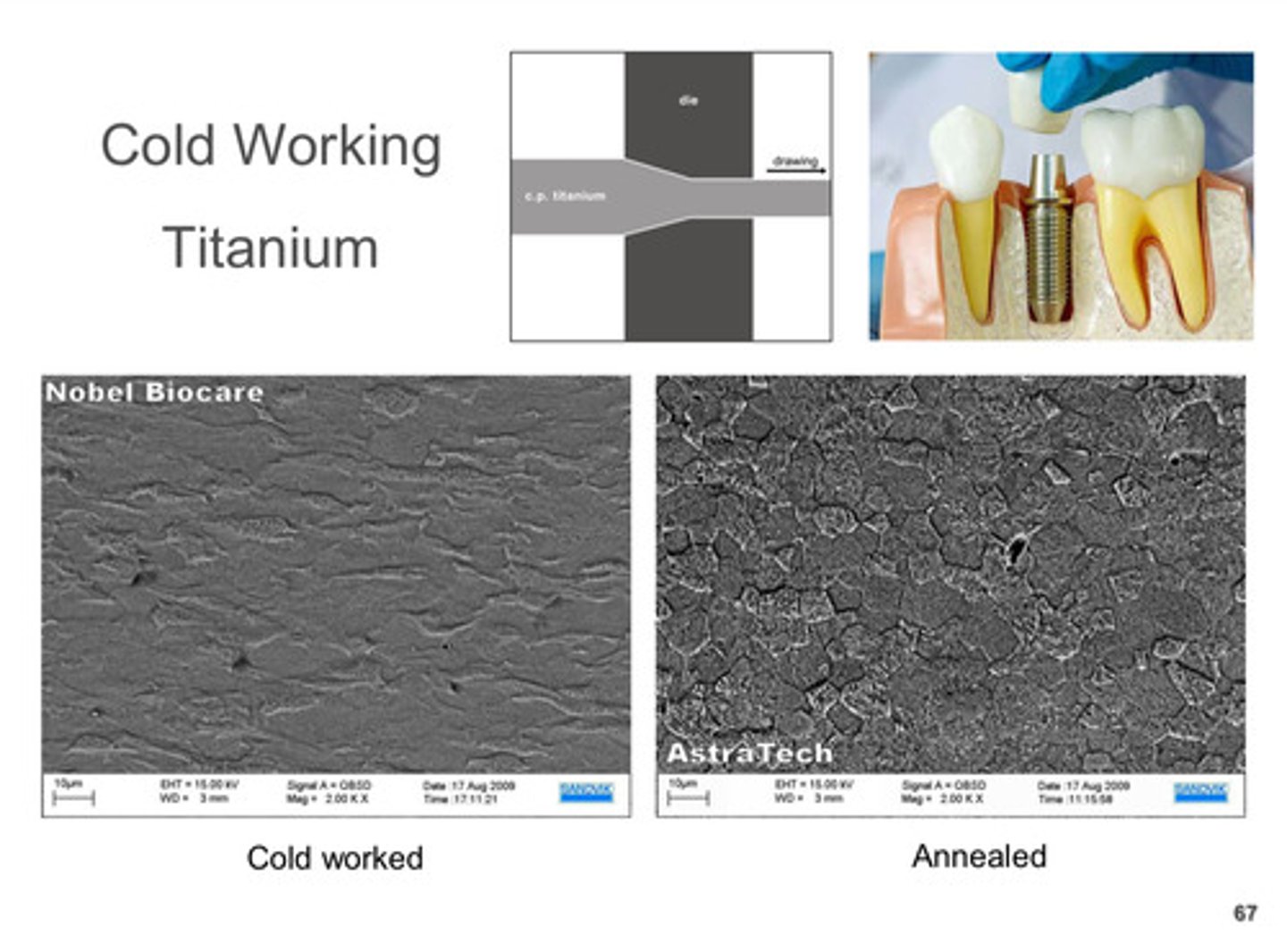
_____________ changes accompany annealing
microstructural