Visual Pathway
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
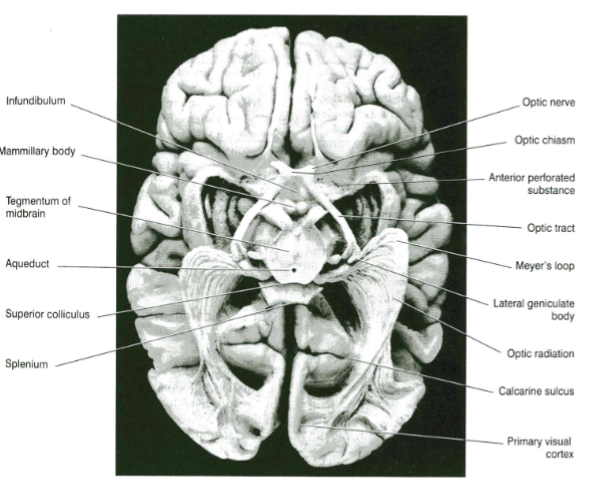
Primary visual cortex location (what surface of what lobe, surrounding what)
On the medial surface of the occipital lobe
Surrounding the calcarine sulcus
True'/False Visual info travels in crossed paths
Kind of true but visual information travels in both crossed and uncrossed paths
4 cells involved in conduction of visual impulses to visual cortex (pathway from eye to visual cortex)
Photoreceptor cells (rods and cones) → Bipolar neurons → Ganglion cells → Neurons of lateral geniculate body in thalamus → Primary Visual Cortex
Bipolar neurons connect what to what
Connect rods and cones to ganglion cells
Axons of the ganglion cells pass to where
Pass to thalamus
Where do axons of the neurons of lateral geniculate body in thalamus pass to
Axons pass to visual cortex
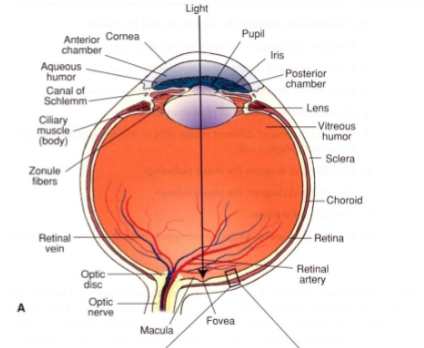
Light rays pass through the lens to the
Retina
Outmost layer of retina
pigment epithelial layer (single layer of cells containing melanin)
Role of the pigment epithelial layer
Pigment cells absorb light that passes through retina
Photoreceptors are a layer of the retina - They are made up of what types of cells
rods and cones
Human retina has how many rods & how many cones
110-125 million rods,
6-7 million cones
Role of cones
colour vision
Role of rods
vision in light of low intensity
Bipolar cells are found in the retina. What is their role
They serve as local circuit neurons connecting rods and cones to ganglion cells.
What interneurons are present in the retina?
Horizontal cells and amacrine cells
Axons of what cells form the optic nerve
Axons of ganglion cells form optic nerve
Are ganglion cells myelinated or unmyelinated
Unmyelinated until leave eye - an optical advantage as myelin is highly refractive
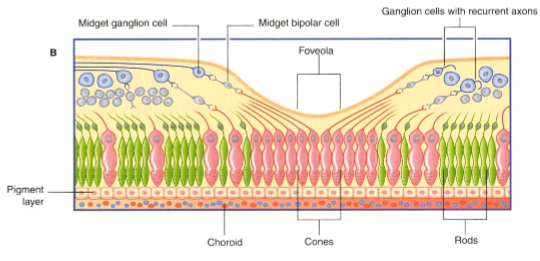
What is the fovea
An area of the retina that is structurally different & allows for acute (high-resolution) vision
How is the fovea built to allow for acute (high-resolution) vision
Contains only cones
Inner retinal layers are displaced to allow light to directly reach cones
What is the visual axis
The line connecting fovea with viewed object
What is the macula lutea?
The area surrounding the fovea.
Where is the blind spot of the eye
Optic disc (papilla)
What is the optic disc (papilla)?
The area where unmyelinated optic nerve fibres exit the retina - known as the blind spot because it lacks photoreceptors.
What happens to fibres after leaving the eye?
They become myelinated
Does the optic nerve have good regenerative capacity
No
What direction do light rays & visual impulse travel in the eye (external/internal → external/internal)
Light rays strike retina and travel from internal to external retinal layers
Visual impulses pass from external to internal retinal layers
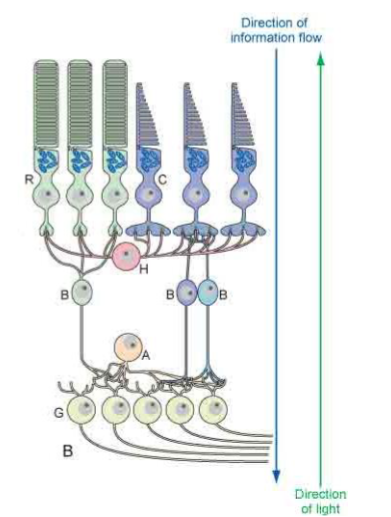
Describe the path of visual impulses
Rods and cones → Bipolar cells → Ganglion cells → Optic nerve → Optic chiasm → Thalamus → Visual cortex
What is binocular vision?
The overlap of right and left visual fields so both eyes project portions of each field onto both retinas, allowing depth perception
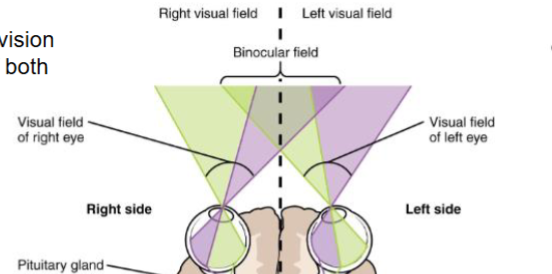
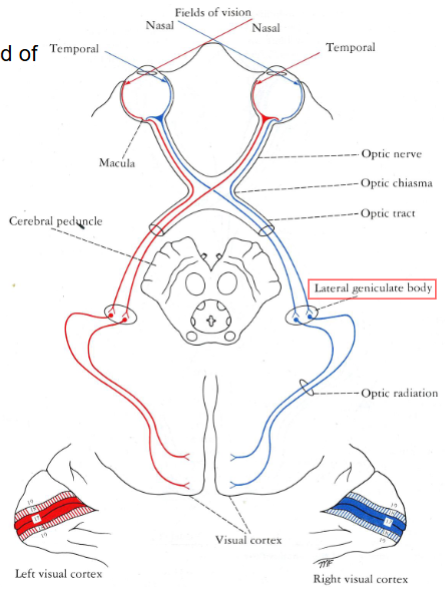
How is the right visual field projected on the retina
Nasal (medial) half of the right retina
Temporal (lateral) half of the left retina
Where is the right field of vision processed in the brain
In the left visual cortex
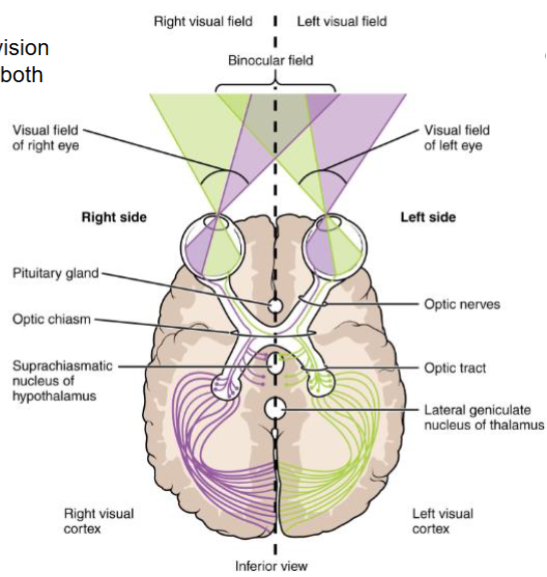
What fibres cross in the optic chiasm
Fibres from the nasal (medial) halves of both retinas
What fibres do not cross the optic chiasm
Fibres from the temporal (lateral) halves → continue in the optic tract of the same side
Where do most fibres terminate
In the lateral geniculate body of the thalamus
What arises from the lateral geniculate body
Optic radiation (Loop of Meyer), projecting to the primary visual cortex on the walls of the calcarine sulcus.
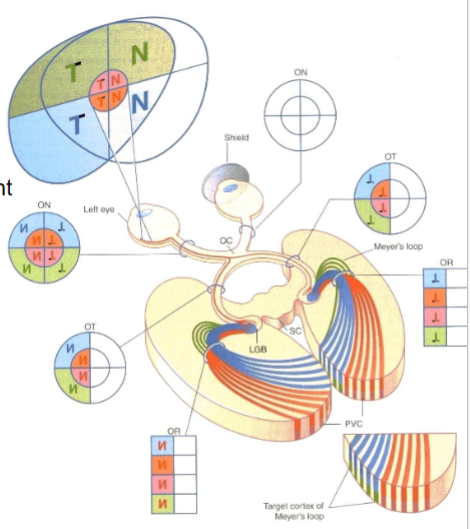
How are visual field quadrants arranged on the retina?
They are reversed and inverted — upper visual fields project onto lower retina and vice versa
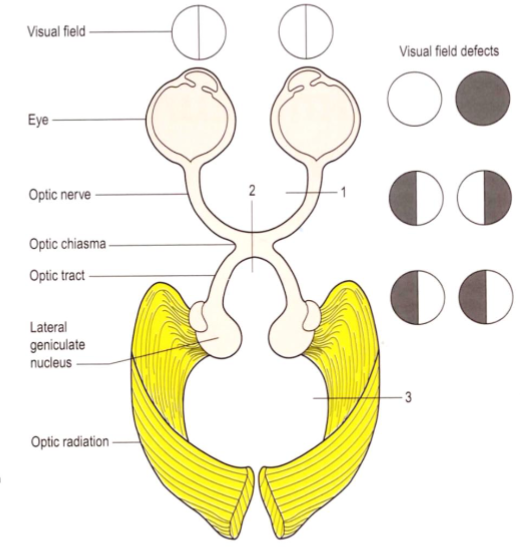
What is the relationship of the optic chiasm to the pituitary gland?
(clinical significance?)
The optic chiasm lies just above the pituitary stalk - a pituitary tumour can damage the median portion of the chiasm → Bitemporal hemianopia
What structure lies lateral to the optic chiasm
(clinical significance?)
The internal carotid arteries — aneurysm here can damage the lateral part of the chiasm → Monocular blindness
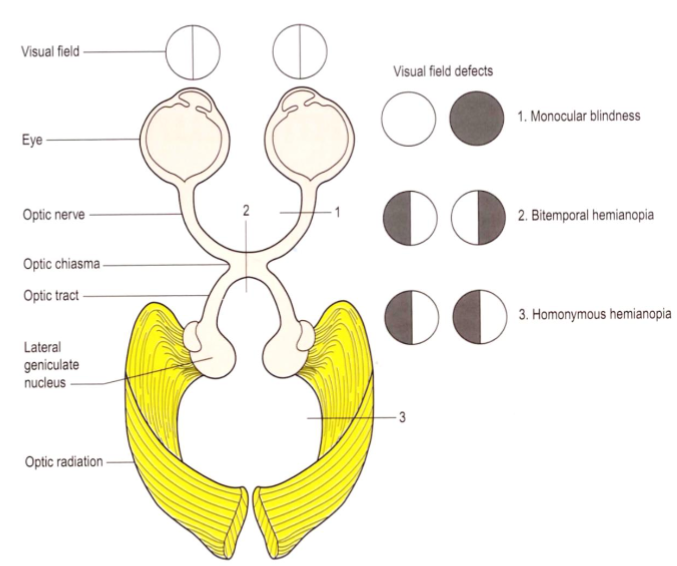
Damage to the area of which number correlates with which visual field defect
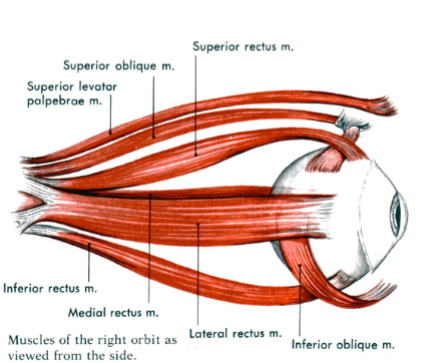
Name the 3 Cranial Nerves responsible for controlling extraocular muscles
CN III (Oculomotor)
CN IV (Trochlear)
CN VI (Abducent)
What specific movements do each of the 3 Cranial Nerves control
CN III (Oculomotor): All other eye movements
CN IV (Trochlear): Turns the eye downward and laterally (says this in slides, but should be medially)
CN VI (Abducent): Abducts the eye laterally
Where do fibres go that mediate light reflexes?
Some optic tract fibres pass from the lateral geniculate nucleus to the pretectal nucleus in the midbrain
Describe the direct and consensual light reflexes
Direct reflex: Pupil constricts in the eye directly exposed to light
Consensual reflex: Pupil of the opposite eye also constricts
What muscle is responsible for constricting the pupils
Pupillary constrictor muscle
Outline the neural pathway for the light reflex
Light stimulus → Optic nerve → Optic chiasm → Optic tract → Synapse in pretectal nucleus near the superior colliculus → Edinger-Westphal nuclei (Parasympathetic nuclei of CN III (oculomotor nerve)) → Ciliary ganglion → Short ciliary nerves → Constrictor pupillary muscles of the iris → Both pupils constrict
What triggers the accommodation reflex
Shifting gaze from a distant to a near object
What muscles are involves in the Accommodation reflex
Contraction of medial rectus muscle on both sides
What changes happen in the eye as a result of the accommodation reflex
Causes convergence of eyes
Lens thickens to increase refractive power by contraction of cillary muscle
Pupils constrict to restrict light waves to central part of lens
How does the accommodation reflex pathway work?
Impulses pass from retina → Visual cortex
Visual cortex connects to frontal eye field
Fibres descend to oculomotor nuclei in midbrain
CN III activates:
Medial recti → Convergence
Parasympathetic fibres → Pupil constriction