Pharm E2- Rheum
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
What is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by symmetrical joint involvement and extra-articular manifestations, with inflammation of synovial lining (pannus)?
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
What condition involves damage to articular cartilage, joint narrowing/erosion, and pain due to activation of nociceptive nerve ending in joint by mechanical/chemical irritants?
Osteoarthritis (OA)
What are non pharmacological treatment options for RA and OA?
PT/OT, wt loss, moist heat, ice, rest, surgery
The following treatment options are for RA or OA?
chronic: NSAIDs, low dose steroids
acute exacerbation: steroids
DMARDs
knee effusion: aspirate & steroid injection
RA
The following treatment options are for RA or OA?
chronic: APAP, NSAIDs, topical analgesics
acute exacerbations: opioid analgesics
knee effusion: aspirate & steroid injection
OA
What is the cornerstone of therapy for RA and should be initiated as early as possible?
disease modifying anti rheumatic drugs (DMARDs)
What are the traditional DMARDs?
MTX, HCQ, sulfasalazine, leflunomide
What biologic DMARDs are anti-TNF?
Infliximab
Certolizumab
Etanercept
Adalimumab
Golimumab
What biologic DMARD is a co-stimulation modulator?
Abatacept (Orencia)
What biologic DMARD is an IL-6 receptor antagonist?
Tocilizumab (Actemra)
What biologic DMARD is a CD20 inhibitor?
Rituximab (Rituxan)
What DMARD is a JAK inhibitor used in severe-moderate RA treatment when MTX therapy failed?
Tofacitinib (Xeljanz)
Which DMARDs have the best efficacy-toxicity ratios?
MTX and HCQ
What drug should be started first in most patients with RA?
MTX
Which has a faster onset of action- traditional DMARDs or biologic DMARDS?
biologic
What should be done before treatment for RA, especially if using biological DMARDs, due to immunosuppression?
test for TB & get up to date vaccines
Which vaccines can NOT be given to patients taking biologics?
live vaccines
The herpes zoster vaccine is normally recommended at age 60, but when should RA patients receive it?
50
What drug?
inhibits cytokine & purine biosynthesis, stimulates adenosine
analog of folic acid w/ high affinity for dihydrofolate reductase
(works against folic acid; stifles reproduction of immune cells & dec inflammation)
MTX (Trexall, Rheumatrex)
What SEs are seen with MTX?
BM suppression, stomatitis, GI / oral ulceration, N/V/D, hepatotoxicity, alopecia, pulm fibrosis, pneumonitis
*monitor renal function
What are CIs to MTX?
pregnancy, renal insufficiency (CrCl < 40), chronic liver dz, blood dyscrasias
What drug?
MC DMARD; tx for RA
fairly rapid onset of action (1-2mos)
acceptable incidence of SEs
monitoring - CBC, LFTs, SCr at baseline, monthly for 6 mos then every 1-2 mos
MTX
What should be given with MTX?
folic acid (1 mg daily or 7 mg once weekly)
What drug?
prodrug inhibits pyrimidine synthesis → dec lymphocyte proliferation
used in RA tx- benefits in 1 month
dec sx, inflammation, and joint damage
Leflunomide (Arava)
What drug has at the following adverse effects?
MC diarrhea
most significant: hepatotoxicity, immunosuppression, hematologic toxicity
**dont use w/ other hepatotoxins (ex- MTX)
teratogenic (need cholestyramine washout)
monitor- LFTs, CBC, pregnancy
Leflunomide
What drug?
least toxic & potent DMARD; less monitoring
no myelosuppression, hepatotoxicity, renal insufficiency
for mild RA dz or use in combo regimen
onset- 2-4 mos
Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ)
What drug has the following MOA?
inhibit neutrophil locomotion, chemotaxis eosinophils, & impairs complement dependent ag-ab rxns
(prevents ability of immune cells to get to site of inflammation → can’t cause inflammation → less joint damage over time)
HCQ
What SEs are seen with hydroxychloroquine (HCQ)?
GI: N/V/D (take w/ food)
retinopathy: blurry vision, scotomas, accommodation effects
derm: rash, alopecia, inc skin pigmentation
What drug?
DMARD used in RA tx
prodrug cleaved by colonic bacteria into sulfapyridine & 5 amino salicylic acid
unknown MOA- modulate inflam mediators, TNFi, see radical scavenger
onset 1-4 mos
Sulfasalazine
What SEs are seen with sulfasalazine?
N/V/D, rash, elevated LFTs, alopecia, leukopenia or thrombocytopenia (rare), yellow or orange urine/stools
What drug interactions are seen with sulfasalazine and should be separated out when taking?
abx, iron supplements, warfarin (protein binding)
What drug?
DMARD- available PO
RA monotherapy or in combo with other DMARDS
*dont use w/ biologics
dec dose w/ significant renal dysfunction, hepatic dysfunction, or CYP3A4 inhibitors
BBW: serious infx, lymphomas, malignancies
Test for latent TB before starting!
Tofacitinib
Which type of DMARDs?
very little monitoring needed
very expensive
inc risk of infx & TB (test before!!)
dont give live vaccines
discontinue while pt has infx
Biologics
What BBW is seen with TNF-⍺ inhibitors?
lymphoproliferative cancer
What are relative CIs to TNF-⍺ inhibitors?
CHF (EF < 50% or NHYA class II or IV) & MS (can induce sx)
What drug?
bind & inhibit TNF linked to Fc fragment of IgG → dec sx, inflammation, and joint damage
2nd line DMARD in RA; use alone or w/ MTX
inc risk of infx & injection site rxns
Etanercept (Enbrel)
What drug?
chimeric ab that binds & inhibits TNF-⍺ → dec sx, inflammation, & joint damage
2nd line for RA if MTX inadequate
combo w/ leflunomide
combo w/ MTX to prevent infusion rxn to foreign protein (flu like sx, rash, etc) & improve efficacy
Infliximab (Remicade)
What should be used as pretreatment prior to an infusion of chimeric proteins like Infliximab?
antihistamine/bendaryl, corticosteroids, tylenol
(have EPI on hand in case of reaction)
What drug?
human monoclonal ab binds & inhibits TNF → dec sx, inflam, & joint damage
human = less allergy risk
monotherapy for RA if inadequate response to other DMARDs
SQ injection at home
SE: infx, injection site rxn, rash, HA, pruritus, N, V
Adalimumab (Humira)
What drug?
mod-severe RA tx when other therapies failed
binds to CD80-CD86 receptions → prevent interactions bt ag presenting cells & T cells → prevent T cell activation
weight based design q 4 wks
SE: HA, infx, injection rxn, extremity pain
Abatacept
What drug?
chimeric antibody against CD20 protein on B cells → binding almost completely depletes B cells → dec ag presentation to T cells
RA tx when MTX or TNFi failed
needs to be pretreated!
Rituximab (Rituxan)
What drug?
humanized mab against IL-6 (promotes inflammation in RA)
used after TNFi failure
SE: infusion rxn, infx, hyperlipidemia, elevated transaminases, GI perforation
CYP3A4 inducer
(lowers levels of other drugs like warfarin, birth control, statins, etc)
Tocilizumab (Actemra)
If biologic agents fail, can you use a combination of biologics?
no- too much immunosuppression
What should be done if biological agents fail in RA treatment, either primary lack of efficacy (no response in 3-6 mos, never really worked) or secondary lack of efficacy (failure after initial response, neutralizing abs formed against drug & stopped working)?
add on non biological DMARD or switch between MOAs
What drug?
used in RA treatment- antiinflammatory & immunosuppressive
chronic tx, bridge therapy (allow DMARD to start working), & disease flare ups
interfere w/ ag presentation to T cells
inhibit free radical generation
impair cell migration & chemotaxis
corticosteroids
What dosage form of corticosteroids allows for a natural taper and less withdrawal / adrenal insufficiency?
intramuscular long acting depot
What dosage form of corticosteroids is good for a small number of joints but should not be administered more than 2-3x per year due to joint destruction and tendon atrophy?
intra-articular injection
What SEs are seen with corticosteroids?
HPA axis suppression, osteoporosis (give Ca and vit D), myopathies, cataracts, hirsutism, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, ulcers, infx
What drug?
RA- mainstay of chronic tx
OA- adjunctive to analgesics or used alone
does not modify dz progression
NSAIDs
RA algorithm
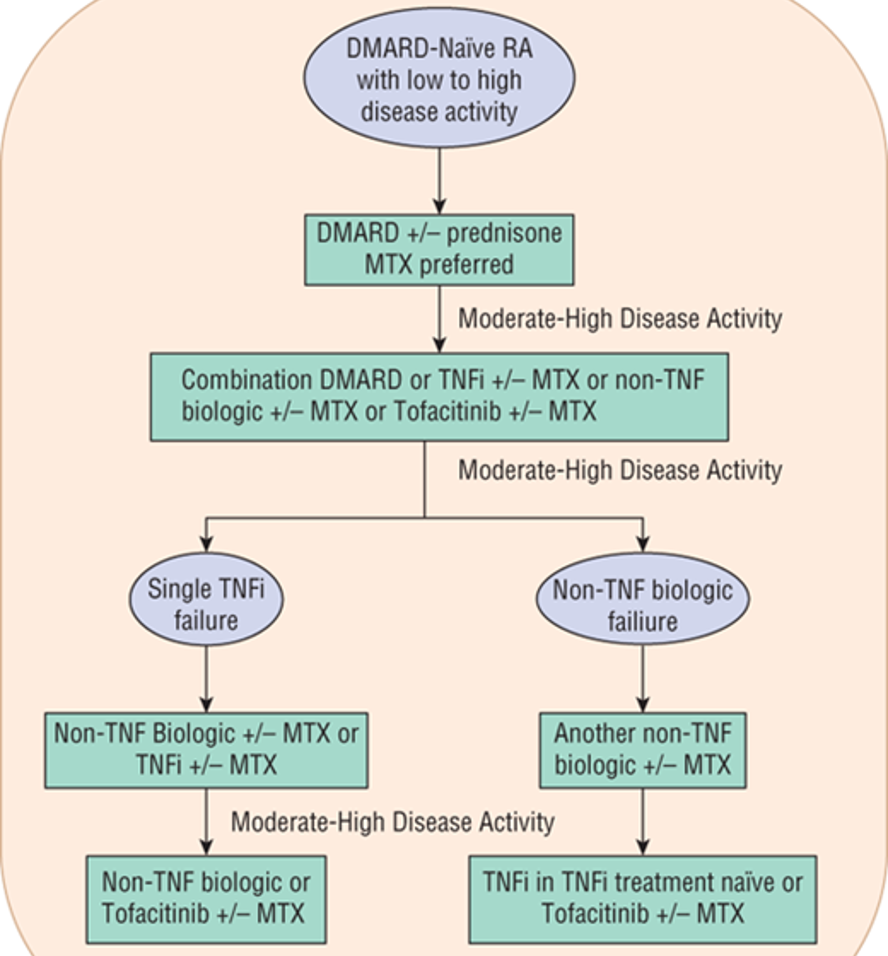
What DMARD combinations are acceptable for treatment of RA?
(*** Test Q)
2 Traditionals
Traditional + Biologic
Traditional + Jak inhibitor
What combination of DMARDs should be AVOIDED in RA treatment due to high risk of hepatotoxicity?
(***Test Q)
MTX + Leflunomide
What DMARDs combos should be avoided due to high infection risk?
2 biologics
Jak inhibitor + biologics
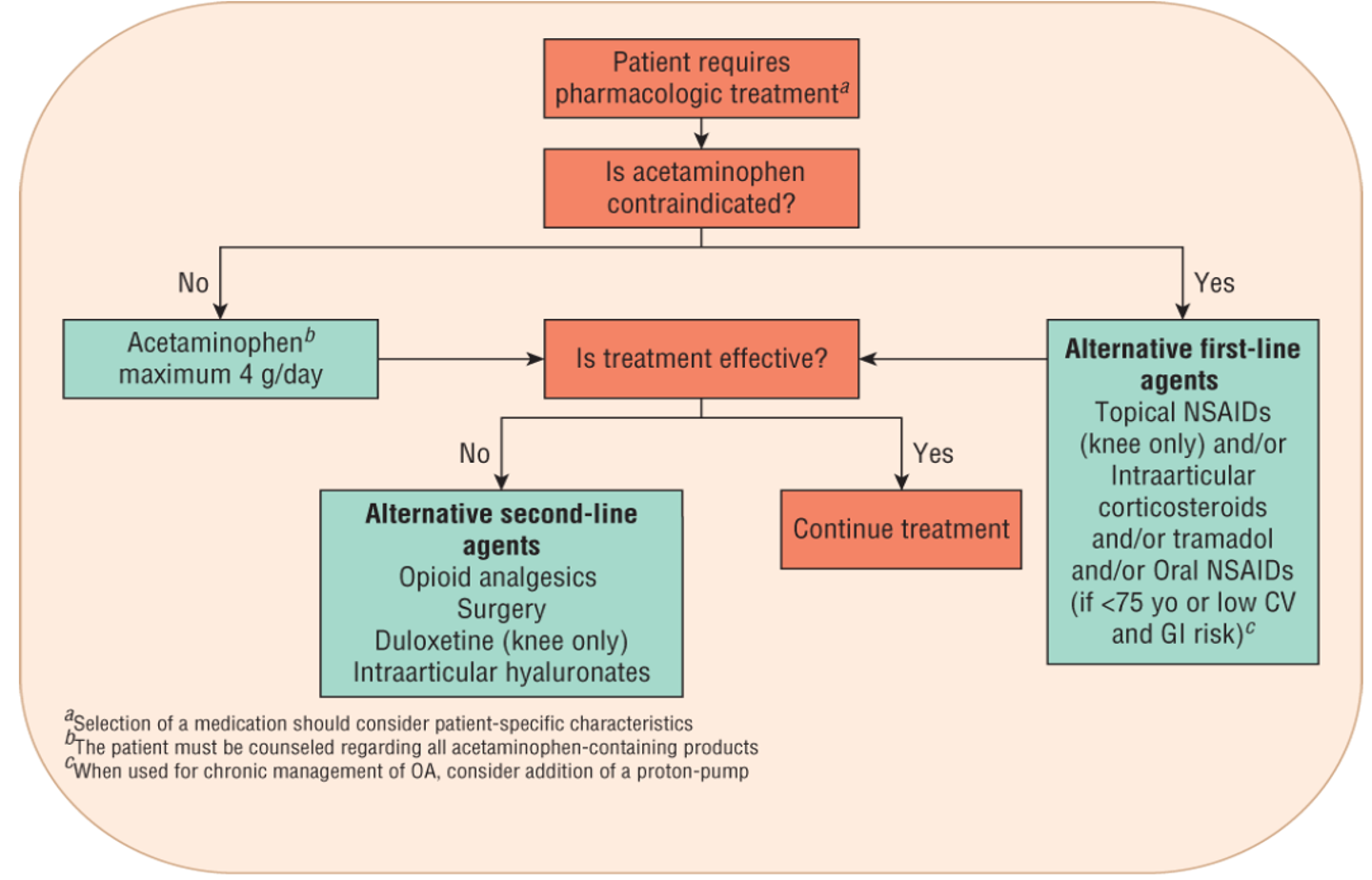
What is the max dose of acetaminophen per day?
4 g
What drug?
first line for OA
(not good for RA bc no anti-inflammatory properties)
less effective than NSAIDs but also less toxic
hepatotoxicity, inc bleeding risk if taken w/ warfarin
Acetaminophen (APAP)
What drug?
first line for knee OA if APAP failed
fewer systemic SEs
Topical NSAIDs (Diclofenac, Aspercreme, etc)
Which is preferred in OA patients over age 75?
Topical NSAIDs
What drug?
topical analgesic used in adjunct to analgesics & NSAIDs in OA treatment
need to be consistent- results in several weeks after depletion of substance P
wash hands w/ soap & water after
Capsaicin
What are examples of counter-irritants used in OA treatment that work by creating cold/heave over the sore surface drawing the pain?
menthol, camphor, oil of wintergreen
What is the alternative first line tx for knee and hip OA when uncontrolled by NSAIDs & APAP?
(*dont give more than every 3 mos - tendon atrophy)
Intraarticular corticosteroids
What is second line tx for OA and should be used short term for pain?
Opioids
What dietary supplement (found in cartilage and synovial fluid) can be given for OA & work by increasing proteoglycan synthesis in articular cartilage to repair and prevent further breakdown?
Glucosamine & Chondroitin
What is a contraindication to glucosamine and chondroitin?
shellfish allergy
What drug?
constituent of synovial fluid; used for pain associated with knee OA
antiinflammatory, reduces pain, & improves jt mobility
relatively free of SEs
Hyaluronate injections
Hip & Knee OA algorithm
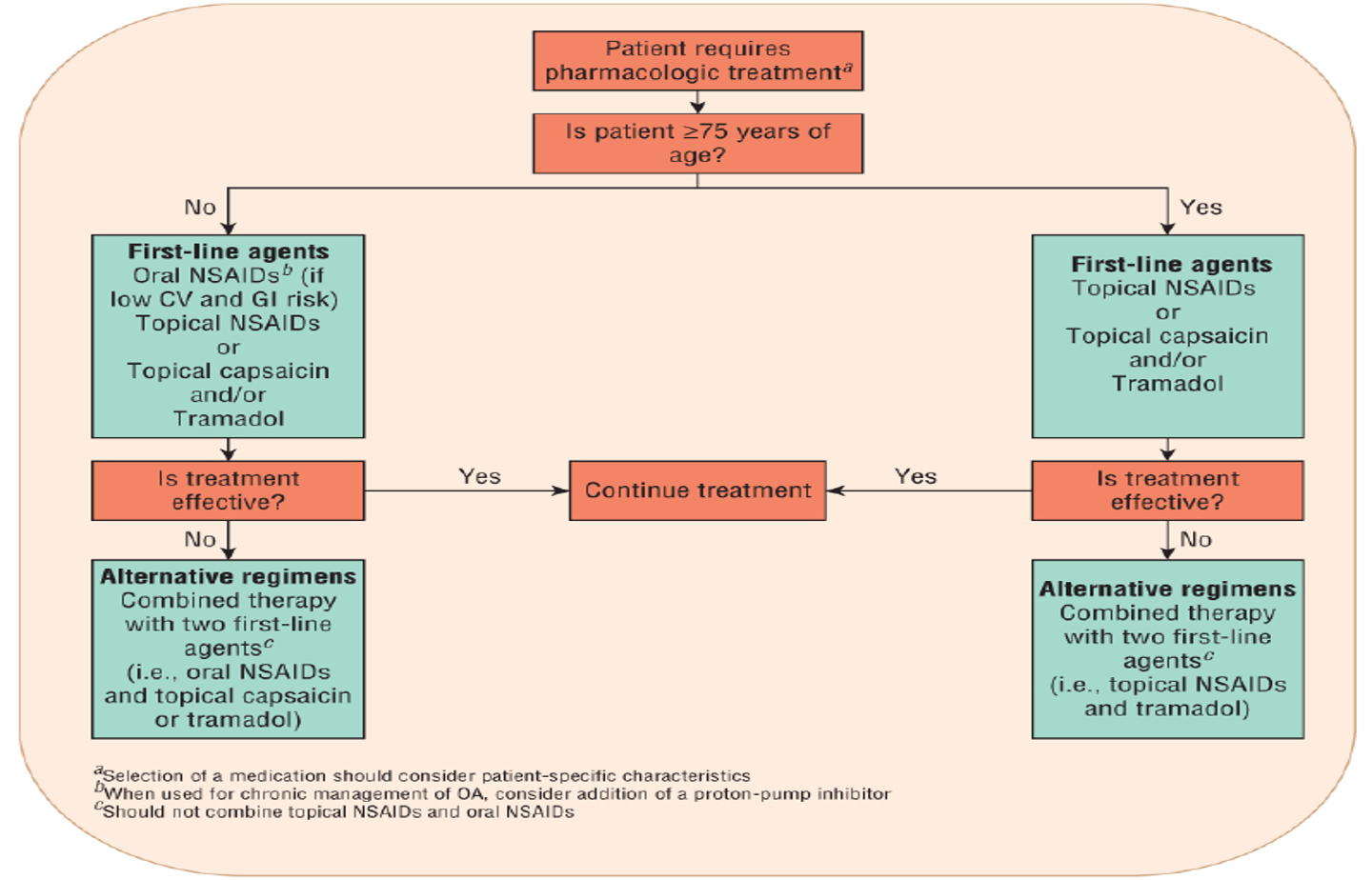
Hand OA algorithm
What bone disorder is characterized by low bone density, impaired bone architecture, & compromised bone strength?
Osteoporosis
What drugs are associated with osteoporosis?
aromatase inhibitors (dec estrogen), long term PO glucocorticoids (inc bone resorption & dec formation), long term PPIs (Ca malabsorption)
Estrogen & testosterone increase bone ______ ; PTH increases bone ______
formation ; resorption
What is the active form of vit D (activated in liver & kidneys) that stimulates Ca absorption/retention?
Calcitriol (1,25 dihydroxy)
What factors are seen in the pathophysiology of osteoporosis?
low vit D → low serum Ca → parathyroid releases PTH → stimulates Ca resorption in kidney & osteoclast activity (bone resorption)
estrogen deficiency → inc osteoclast activity
What are non pharmacological options for osteoporosis?
Calcium (carbonate, tums) & Vitamin D
What SEs are seen with calcium?
constipation, hypercalcemia, nephrolithiasis, can bind to other drugs (iron, thyroid supplements, FQs, tetracyclines, bisphosphonates)
What patients would vitamin D supplementation not be efficient?
hepatic / renal impairment (can’t activate)
Who is prescription tx for osteoporosis prevention recommended in?
postmenopausal women or men > 50 y/o with
osteoporosis
low bone mass + 10 yr hip fx risk ≥3%
10 yr risk of any osteoporosis related fx ≥20%
Are the following drugs antiresorptive or anabolic?
Ca, Vit D, bisphosphanates, SERMs, calcitonin, denosumab, estrogen, testosterone
Antiresorptive
What agents are bisphosphonates?
Alendronate (Fosamax)
Ibandronate (Boniva)
Risedronate (Actonael)
Zoledronic acid (Recast) - IV
What agents mimic pyrophosphate (endogenous bone resorption inhibitor) and reduces osteoclast maturation, number, adhesion, & lifespan to allow osteoblasts to function?
Bisphosphonates
What drugs require specific administration for absorption to occur due to < 1 % oral bioavailability; but has a half life of up to 10 years once absorbed?
Bisphosphonates
What SEs are seen with bisphosphonates?
GI (heartburn, dyspepsia), esophageal erosion/ulcer, osteonecrosis of jaw
How should oral bisphosphonates be administered?
take tablet w/ 6 oz water (no other liquid) atleast 30 min before consuming other foods or liquids
remain upright for atleast 30 min
Which bisphosphonate can be dosed yearly?
Zoledronic acid
Which drug?
binds to RANKL → prevents binding on surface of osteoclast precursor cells → never gets signal to mature, fewer osteoclasts resorbing bone
25 day half life; peak concentration 10 days
dosed every 6 mos
ADR: local derm rxn, skin infx, bone turnover suppression
Denosumab (Prolia)
What mixed estrogen agonist/antagonist (SERM) can be used for treatment and prevention of osteoporosis in women?
Raloxifene (Evista)
What drug?
endogenous hormone released from thyroid gland when Ca elevated (opposes actions of PTH)
produced from salmon sperm
Intranasal administration
not recommended osteoporosis but can be used if other tx not appropriate
only evidence for vertebral fx reduction, not hip fx
Calcitonin
What drug?
used in osteoporosis pts who are high risk for fx but failed bisphosphonates
mimics PTH - stimulate bone formation, remodeling rate, osteoblast number & activity (anabolic agent)
REMS program- bone cancer risk; take less than 2 years
Teriparatide (Forteo)
What are treatment options for acute gouty arthritis?
Ice, NSAIDs, corticosteroids, colchicine
begin w/in 24 hrs; combo if severe
When would systemic steroids be used instead of intraaritcular injections (kenalog) for acute gouty arthritis?
> 2 joints are affected
When do corticosteroids need to be tapered?
duration > 1 wk
What drug?
antimitotic - prevents cell replication in rapidly dividing cells
in gout- binds microtubule proteins in neutrophils inhibiting migration & limiting inflam response
only used for acute gouty arthritis w/in 36 hours or will lose efficacy
Colchicine (Colcrys)
What SEs are seen with colchicine?
dose dependent GI sx (N/V/D), axonal neuromyopathy, neutropenia
What are non pharmacological options to prevent recurrent gout attacks?
maintain lower uric acid levels, limit alcohol intake, limit meds that raise uric acid (thizaide/loop diuretics, niacin, low dose ASA)
What treatment options for hyperuricemia are considered with two or more gout attacks per year, one or more typhus is present, chronic kidney disease, or history urolithiasis?
urate lowering therapy (XOIs or uricosurics)
What drugs?
lowers uric acid- impairs xanthine oxidase to convert hypoxanthine → xanthine & xanthine → uric acid
most widely used for prevention of gouty attacks
Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors (XOIs)
What drugs are XOIs?
Allopurinol & Febuxostat
what SEs are seen with allopurinol?
rash, leukopenia, GI upset
rare- TEN, exfoliative dermatitis
what SEs are seen with febuxostat?
N, arthralgias, transaminitis
What drug?
uricosuric: inc renal clearance of uric acid by inhibiting post secretory renal tubular absorption
ADR: nephrolithiasis, rash, GI sx, precipitation of gouty arthritis
may inc levels of drugs by inhibiting renal secretion (extending half life)
PCNs, cephalosporins
CI in renal impairment (*watch kidneys)
Probenecid
What drug?
recombinant form of urate oxidase → catalyzes breakdown of uric acid into soluble allantoin
reserved; used for tumor lysis syndrome
can form abs that make drug less effective if given again or develop allergy
SE: may cause hemolysis and methemoglobinemia (blue/cyanotic look) in patients w/ G6PD deficiency
Rasburicase (Elitek)