imaging midterm review
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
image identification
owner, patient, ID, date of examination, name, location, DVM
radiographic checklist
Is the image labeled and legible?
Are positional lead markers present?
Do you have good exposure with appropriate contrast and density?
Is your image properly centered?
Is the body part properly positioned, with no rotation?
Are the appropriate borders included, and is there evidence of collimation?
Is there no evidence of a human exposure, such as a glove?
Is the film properly processed (if applicable)?
Have artifacts been kept to a minimum to prevent interference with the image?

x-ray tube. Cathode and anode
what is the arrow pointing at? What does it consist of?

cathode
negatively charged

anode
positively charged
stationary anode
stays still,
Heat is always dissipated in the same spot causing machine damage over time
rotating anode
Disperses heat more evenly keeping dose efficacy and image quality in tact
rotates around anode
Anode heel effect
intensity of the radiation is greater on the cathode side than on the anode side.
thicker end of animal should be placed on…
head side
the cathode side to take advantage of the greater amount of radiation at that end.
Line focus principle:
describes how the electrons interact with the anode and change direction, so the x-rays are directed toward the patient being radiographed.

wall switch
Before the on/off switch for the x-ray unit itself is the wall switch.
4 important factors involved in transmitting electicity to the x-ray tube
current
voltage
resistance
time
current (I)
Milliamperage (MA) is the unit used to measure the electric current that activates the x-ray tube.
voltage (V)
the speed with which the electrons in the electric current transfer energy along the circuit. High voltage (kV) produces short-wavelength/high-frequency, highly penetrating x-rays.
resistance (R)
the factor that slows the current as it travels through a wire. A wire that is large in diameter will have low resistance. A wire that is small in diameter will have high resistance. Very large diameter or long cables that are used in the x-ray unit will “leak” electric current. This is known as line loss.
time (s)
A timer controls the length of time that the x-rays are produced. This is determined by the setting on the control panel.
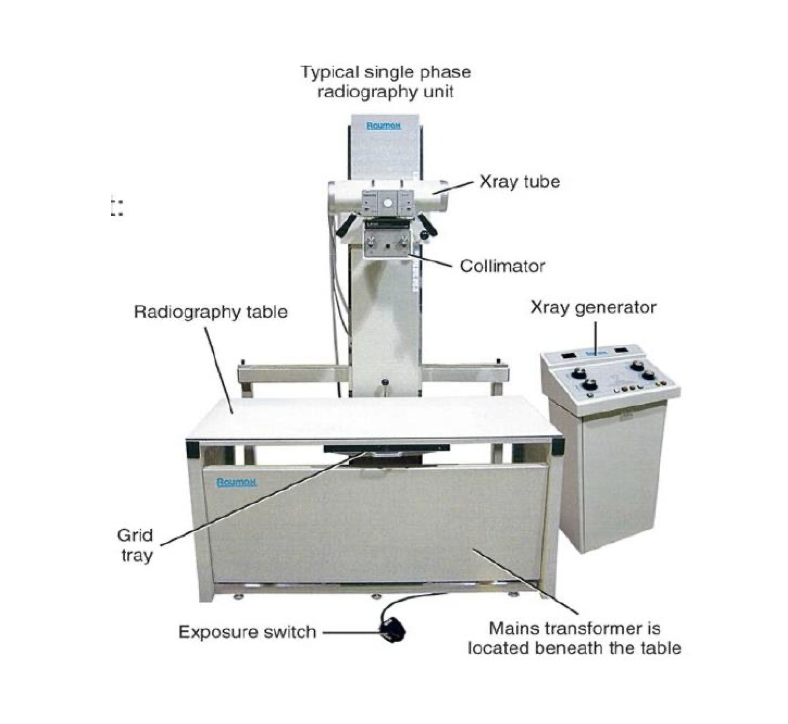
different parts of the x-ray machine
x-ray tube, collimator, table, grid tray, exposure switch, cassette, generator
process of developing an x-ray
developer
silver halide crystals
fixer
removes unexposed silver halide, “fixes” image
H2O bath
stops all processes
dryer
PPE used during radiography
lead apron
lead thyroid shield
lead googles
lead gloves
dosimeters
radiopaque
metal, bone, water soft tissue
radiolucent
air, gas, fat
artifact
anything that decreases the quality of the radiograph resulting in difficult evaluation and interpretation
what does CR stand for
computerized radiography
what does DR stand for?
digital radiography
2 differences between CR and DR
image capture method/speed
efficiency
define latent image
the x-ray before processing
what is an automatic processor?
runs the x-ray automatically, thought developer, fixer, wash
label the bones of the front limb from proximal to distal
scapula
humerus
radius/ulna
carpus
metacarpals
phalanges
label the bones of the hind limb from proximal to distal
pelvis
femur
patella
fibula/tibula
tarsus
metatarsals
phalanges
name of instrument that we use to measure the part that we are imaging
caliper
5 things included or performed in a diagnostic x-ray
positioned properly
x-ray centered
no human exposure
minimal artifacts
lead labels