A&P 2: EKG-One not from Quizlet
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Has the pictures from the lab pp
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
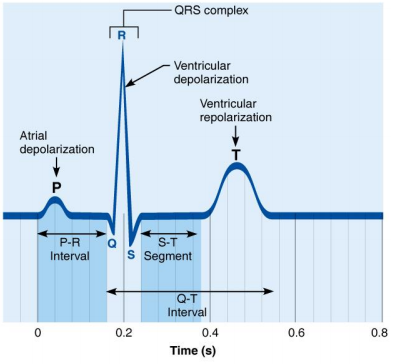
What does the P wave represent in an ECG?
Depolarization of the SA node and atria
What does the QRS complex represent in an ECG?
Ventricular depolarization and atrial repolarization
What does the T wave represent in an ECG?
Ventricular repolarization
What does the P-R interval indicate?
The time from the beginning of atrial excitation to the beginning of ventricular excitation
What does the S-T segment represent?
The entire ventricular myocardium is depolarized
What does the Q-T interval represent?
The time from the beginning of ventricular depolarization through ventricular repolarization
An ECG tracing
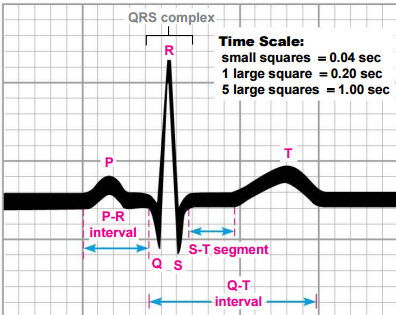
The time scale for an ECG
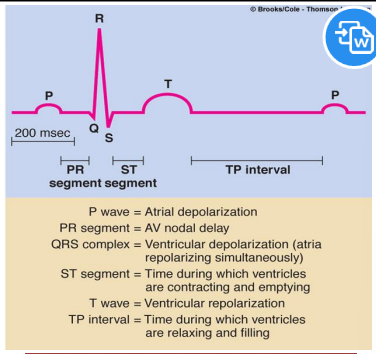
EKG wave differentiation-Recorded potential
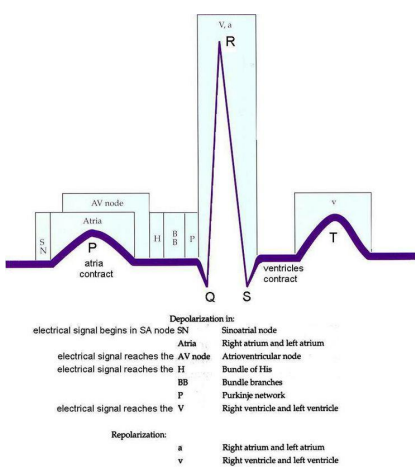
EKG-wave differentiation (Depolarization)
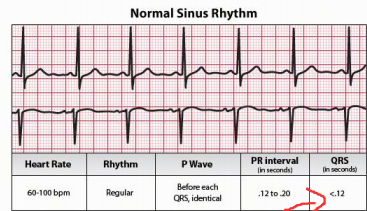
Normal Sinus rhythm
Common ECG rhythms
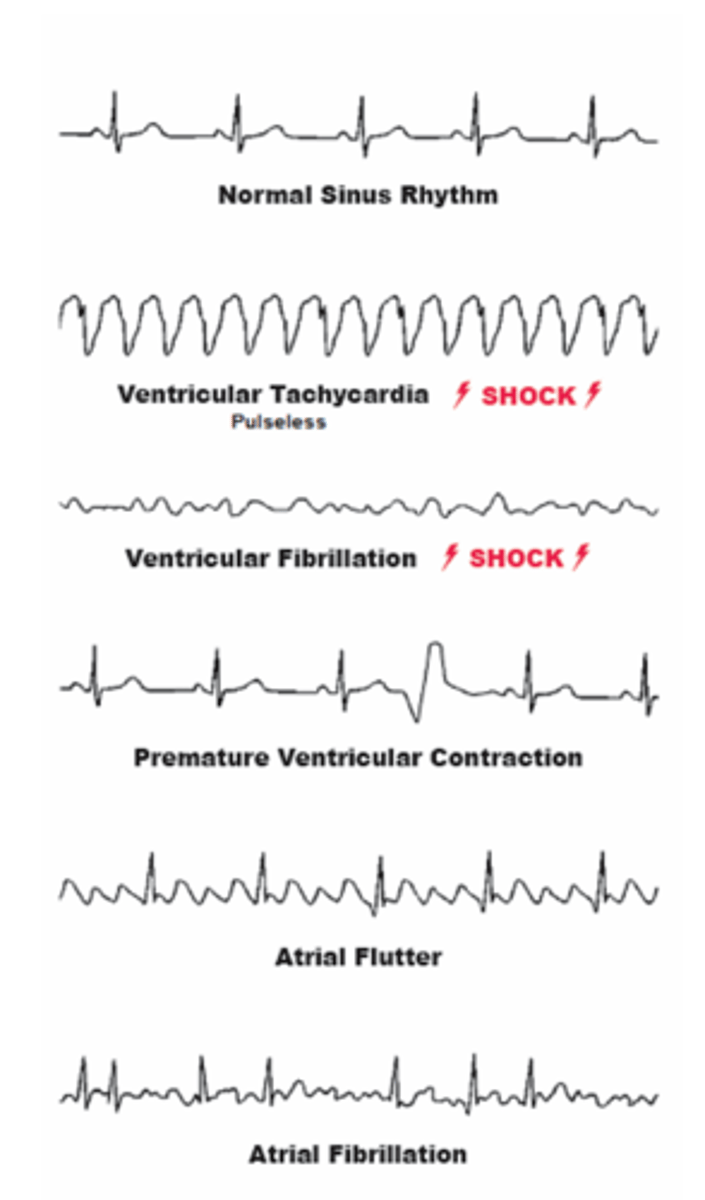
What is Atrial Fibrillation (A-Fib)?
Atrial Fibrillation is a condition characterized by uncoordinated impulses for contraction that spread over the atria and ventricles.
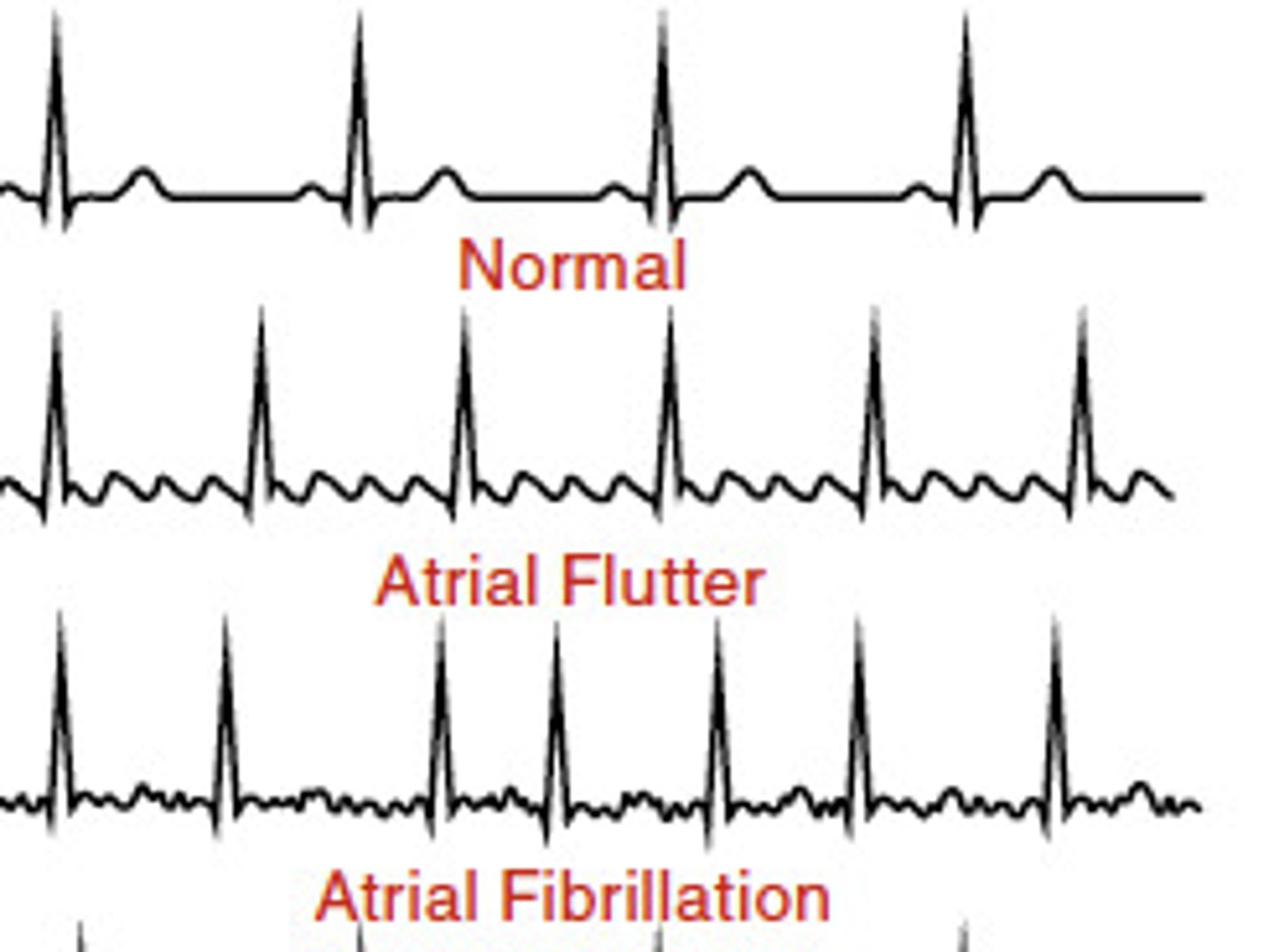
How do the atria behave during Atrial Fibrillation?
The atria quiver instead of beating.
What is a common characteristic of both Atrial Fibrillation and Atrial Flutter?
Both Atrial Fibrillation and Atrial Flutter involve very fast impulses.
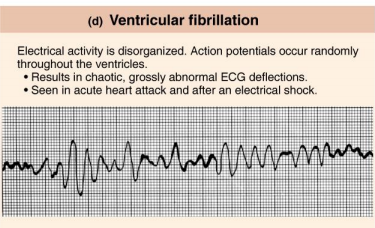
What is ventricular fibrillation?
A series of uncoordinated impulses spreads over the ventricles.
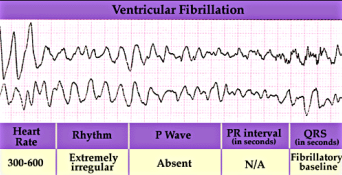
What happens to the ventricles during ventricular fibrillation?
They twitch or quiver instead of contracting.
What is the effect of ventricular fibrillation on blood circulation?
No blood is pumped from the heart.
What type of medical emergency is ventricular fibrillation?
It is a form of cardiac arrest.
What must be done immediately in the case of ventricular fibrillation?
Immediate attempts at resuscitation must be made or the patient will expire.
What can result from prolonged ventricular fibrillation?
Permanent damage to other organs, particularly the brain due to decreased blood supply.
Why is ventricular fibrillation considered potentially fatal?
Because it leads to ineffective coordinated contractions of the heart.
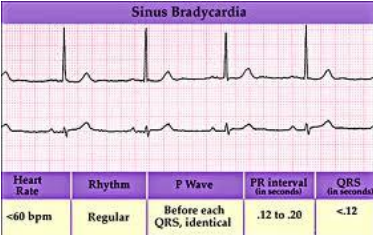
Sinus Arrhythmias-Bradycardia
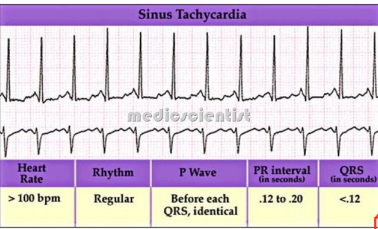
Sinus Arrhythmias-Tachycardia
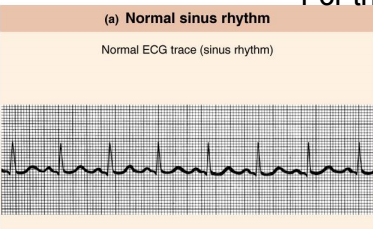
Normal Sinus Rhythm
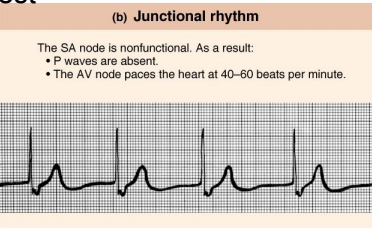
Junctional Rhythm
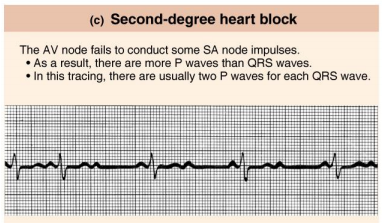
Second-degree heart block
Ventricular fibrillation
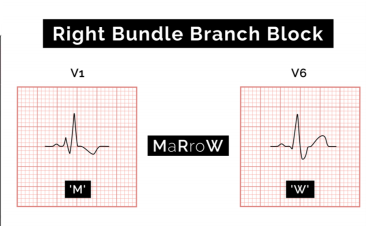
Right Bundle branch block
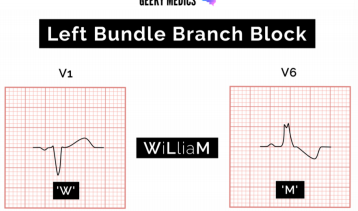
Left Bundle branch block
Systole
contraction & emptying
Diastole
relaxation & filling
What is cardiac output?
The amount of blood that the heart can pump out in one minute.
What is stroke volume?
The volume of blood ejected with each beat.
What is preload?
The volume of blood leading to ventricular stretch at the end of diastole.
What is afterload?
The amount of resistance the heart must overcome to open the aortic valve and push the blood volume out into systemic circulation.
What does EDV stand for?
End-Diastolic Volume
What is EDV?
The amount of blood in the heart at the end of diastole.
Which ventricle has the most amount of blood at EDV?
Left Ventricle (LV)
What does ESV stand for?
End-Systolic Volume
What is ESV?
The amount of blood in the ventricle once systole has ended.
Which ventricle has the least amount of blood at ESV?
Left Ventricle (LV)
What is intrinsic control of stroke volume (SV)?
It refers to the mechanisms within the heart that regulate stroke volume without external influences.
What is venous return?
The amount of blood returning to the heart from the veins.
What is the length-tension relationship of cardiac muscle?
It describes how the force of contraction of cardiac muscle is related to its initial length.
What is the Frank-Starling Law of the Heart?
It states that the strength of the heart's contraction is directly related to the degree of diastolic filling.
What happens to contractility with larger end-diastolic volume (EDV)?
Greater EDV leads to greater contractility.
What is an advantage of intrinsic control of stroke volume?
It ensures equality of output from the right and left ventricles.
What is the effect of sympathetic stimulation on heart contractility?
It increases heart contractility, leading to more complete ejection.
What do norepinephrine (NE) and epinephrine (EPI) trigger in the heart?
They trigger more calcium to be released.
How does sympathetic stimulation affect the Frank-Starling curve?
It shifts the Frank-Starling curve to the left.
What role does venoconstriction play in venous return?
Venoconstriction helps to move blood toward the heart.
Cardiac Reserve
difference btwn resting CO & maximal CO