Polymerization & Dental Polymers
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
129 Terms
polymers are used extensively in dentistry and an understanding and review of the basic nature of polymers will aid in what?
aid in proper selection and use of polymeric dental materials
which 4 aspects of dentistry utilizes polymers frequently
prosthodontics: denture bases and teeth, custom trays, impression materials, etc
operative dentistry: dentin bonding agents, cavity filling materials, cements, etc
orthodontics: brackets, bracket bonding resins, elastics, etc
endodontic: root canal sealants, gutta-percha points, rubber dams, etc
other equipment: mixing bowls and spatulas, mouth guards, etc
what is a monomer
simplest repeating chemical structural unit from which the polymer is composed ("mer unit")
what is a polymer
consists of large, organic molecules built up by repetition of smaller and simpler chemical units
what is a copolymer
polymers prepared from a mixture of 2 different monomers
what is a block copolymer
mer units are arranged in a way that a large number of a mer type are connected to a large number of ANOTHER mer type

what is a stereospecific polymer
polymers in which mer units have a specific spatial arrangement with respect to adjacent units such as many natural and synthetic rubbers
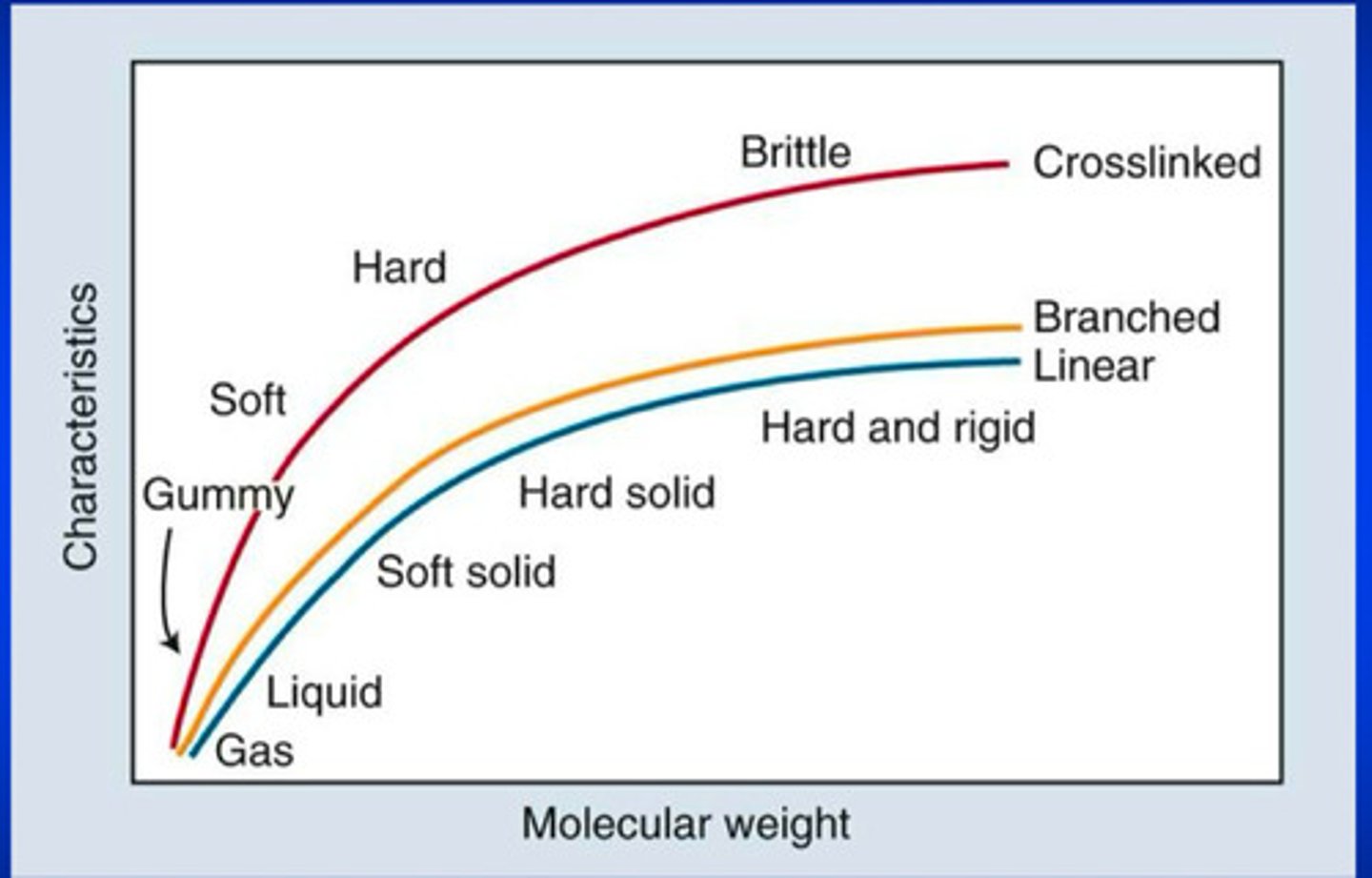
polymer chains are often connected together to form what 3 spatial structures?
a nonlinear, branched, OR cross linked polymer

crosslinking forms what kinds of bonds between the polymer chains and this dramatically increases what?
forms chemical bonds between the chains; increases molecular weight
physical and mechanical properties vary with what 2 qualities for a given polymer system
vary with composition and extent of crosslinking for a given polymer system
the 3-D network of crosslinked polymers increases what 2 things to solvents
increases rigidity and resistance
the longer the polymer chain, the greater ?
the greater the number of entanglements
the greater the number of entanglements in a polymer chain, the more difficult it is to what?
to distort the polymeric material
so what 3 properties increase with increasing chain length (as it is more difficult to distort the polymeric material with greater number of entanglements)
rigidity, strength, and melting temperature
what are thermoplastic polymers made of
made of linear and/or branched chains
thermoplastic polymers ______ when heating above the glass transition temperature
soften
what is the glass transition temperature
the temperature at which molecular motion begins to force the chains apart
once the thermoplastic polymers soften after being heated above the glass transition, the materials (such as dental waxes) can then be shaped and molded; and upon cooling, it will ?
will harden REVERSIBLY in this form
upon reheating, thermoplastic polymers will soften again and can be reshaped; why is this setting reaction reversible?
due to the relatively weak bonds among the molecular chains
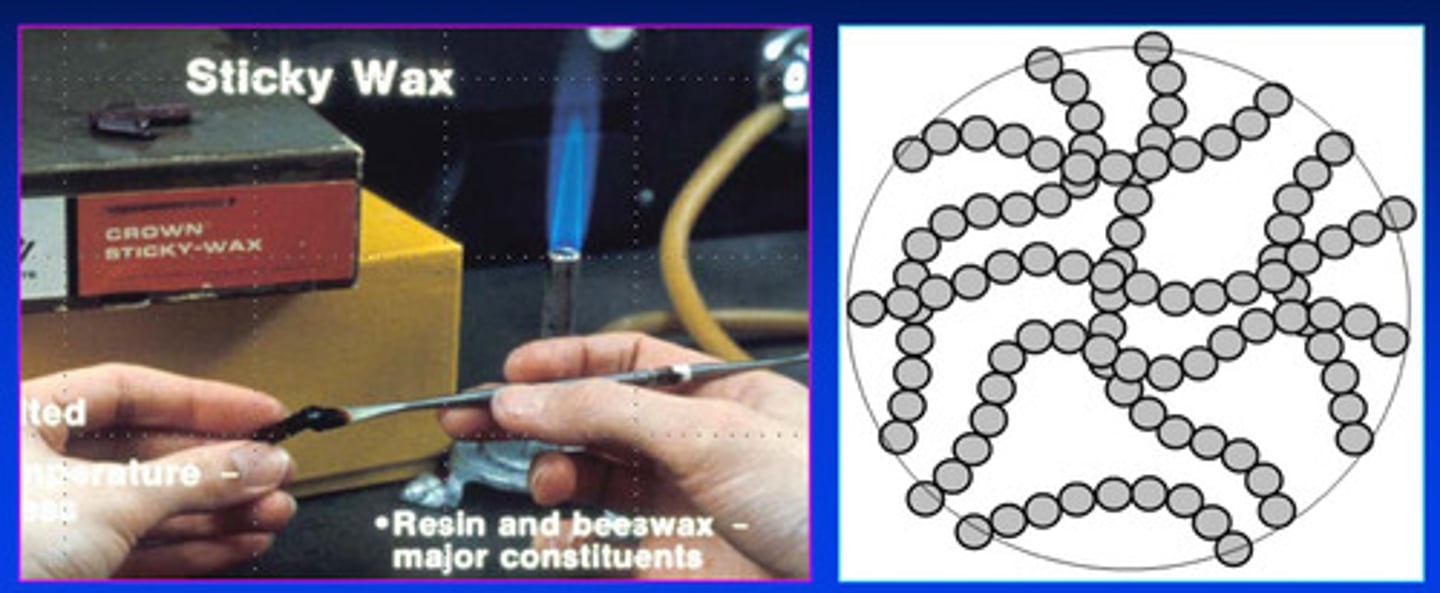
thermoPLASTIC polymers therefore undergo a ________ change
physical
what are the 4 characteristics of thermoSETTING polymers
1) undergo a chemical change during setting
2) are not softened by reheating
3) decompose rather than melt
4) are cross linked

the "mers" of the polymers are joined through what kinds of bonds?
covalent C-C bonds
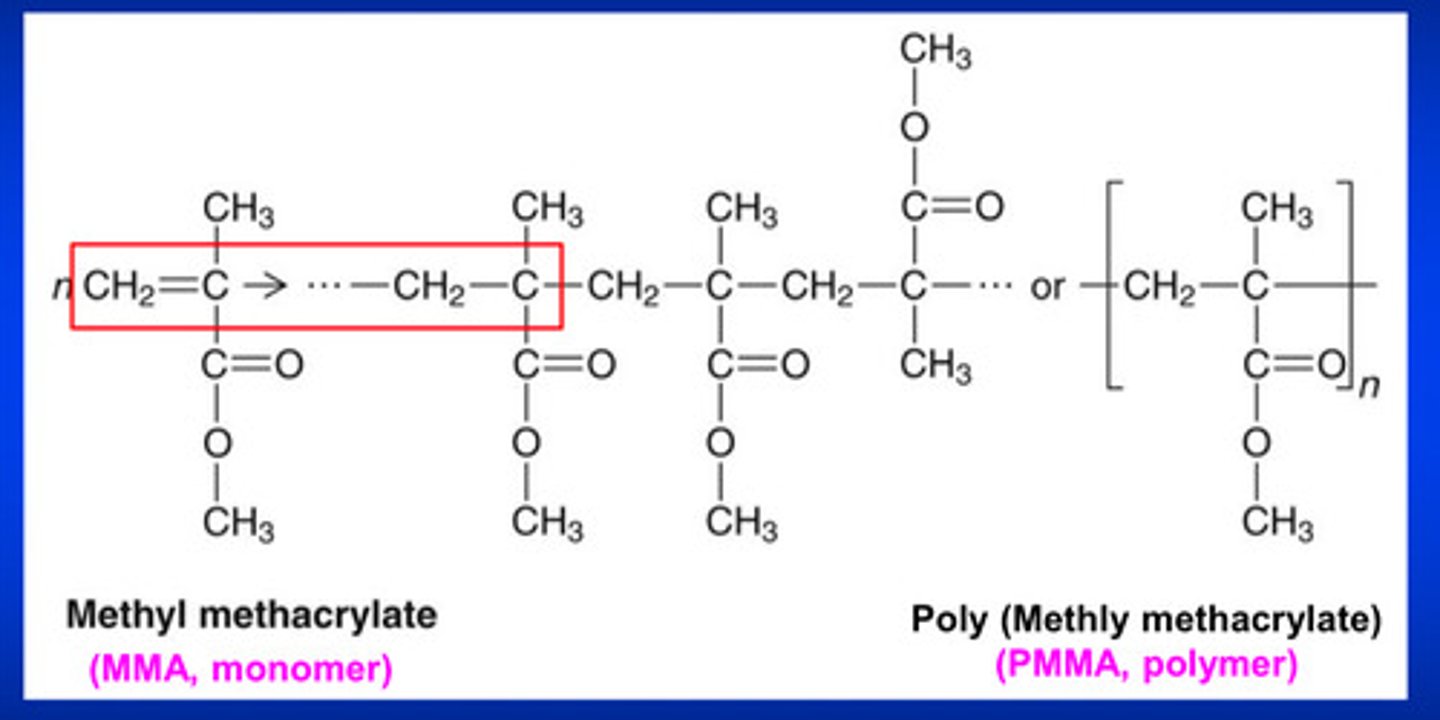
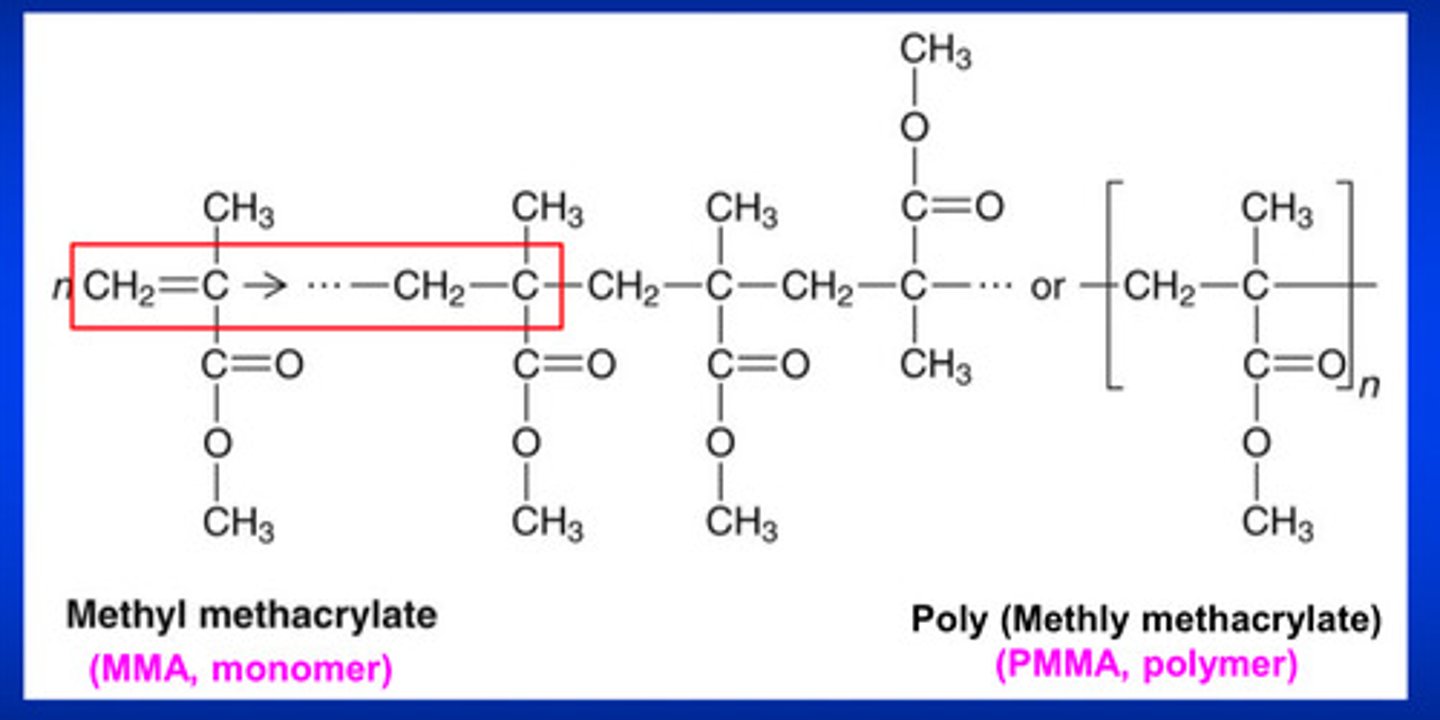
typically, during the polymerization process, C=C double bonds are converted to _____ _______ bonds and a "mer" is attached to one of the carbon atoms that was part of the C=C double bond
C-C single bonds
monomers may be joined together by means of either _______ or _________ reactions
addition or condensation
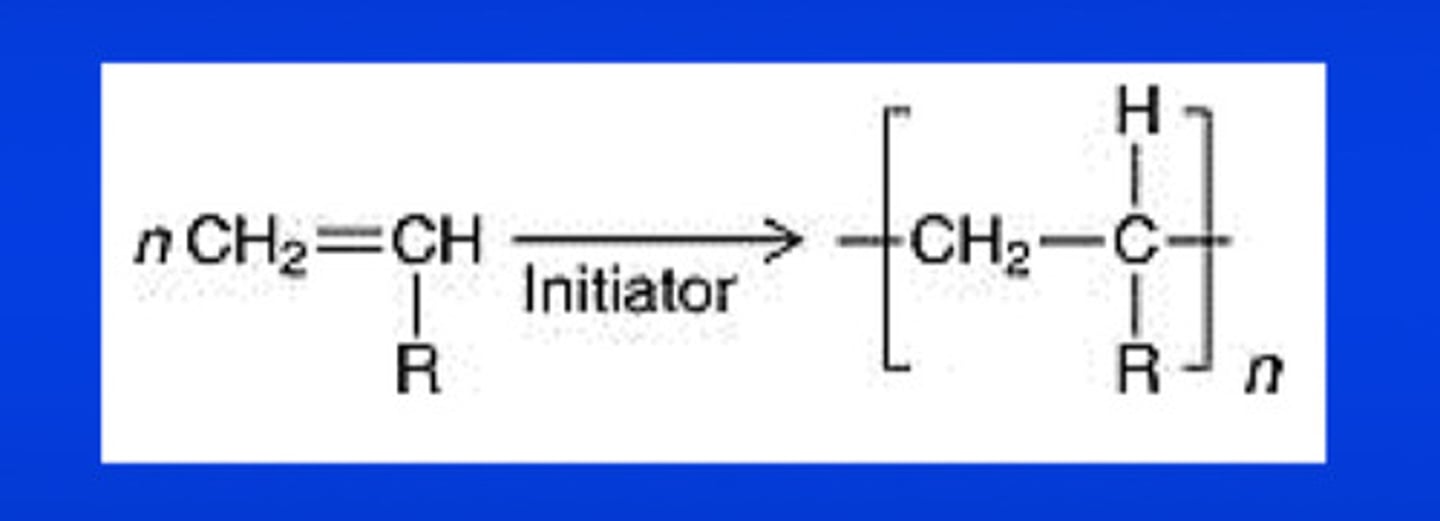
how does addition polymerization work
monomers are activated one at a time and added together in sequence to form a growing chain
what are examples of important additional polymerization reactions
free-radical and ring-opening reactions
how does condensation polymerization work
the components are di-functional and all are or become reactive simultaneously
the condensation polymerization reaction sometimes produces what kind of by-product?
a low molecular weight by product
what is condensation polymerization also known as
step growth polymerization
free-radical polymerization (a kind of addition polymer rxn) usually occurs with ____________ molecules containing ________ bonds
unsaturated molecules containing double bonds; in the equation, R represents any organic group, chlorine, or hydrogen
what are the 3 stages of the free-radical polymer rxn
initiation, propagation, and termination stages
the free-radical polymer rxn may be accelerated by what 3 things
chemical agents, heat, and visible light
in free-radical polymer rxn, is a byproduct obtained?
NO
free radical polymerization reactions can be inhibited by the presence of what
presence of any material or impurities in the monomer that will react with a free radical
when a free-radical polymerization rxn is inhibited, what may become decreased and what may become increased
decrease in the rate of initiation OR increase in the rate of termination
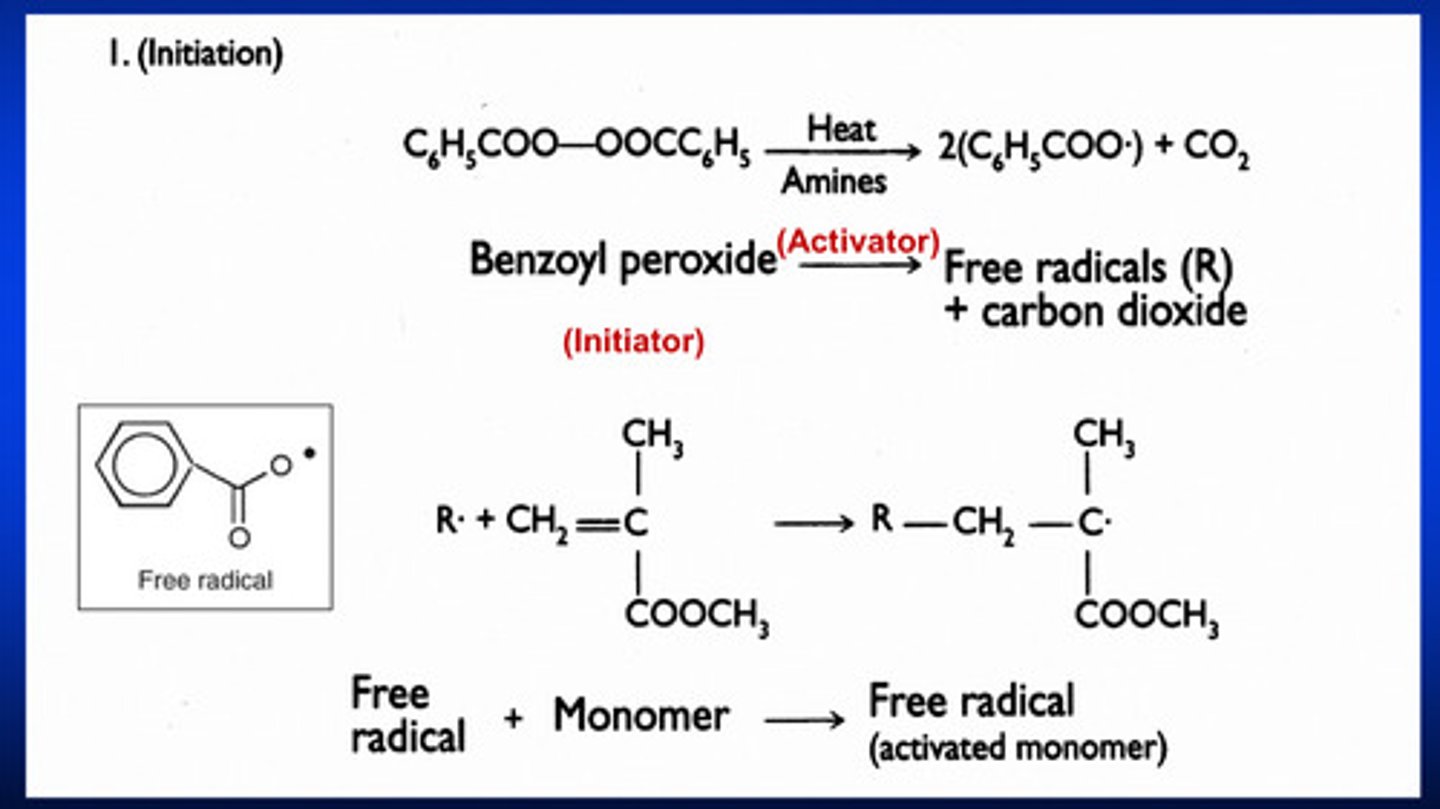
initiation stage of free-radical polymerization rxn
1) free radical bombards unsaturated double bond
2) activate the monomer which will start a chain reaction —> next stage of propagation
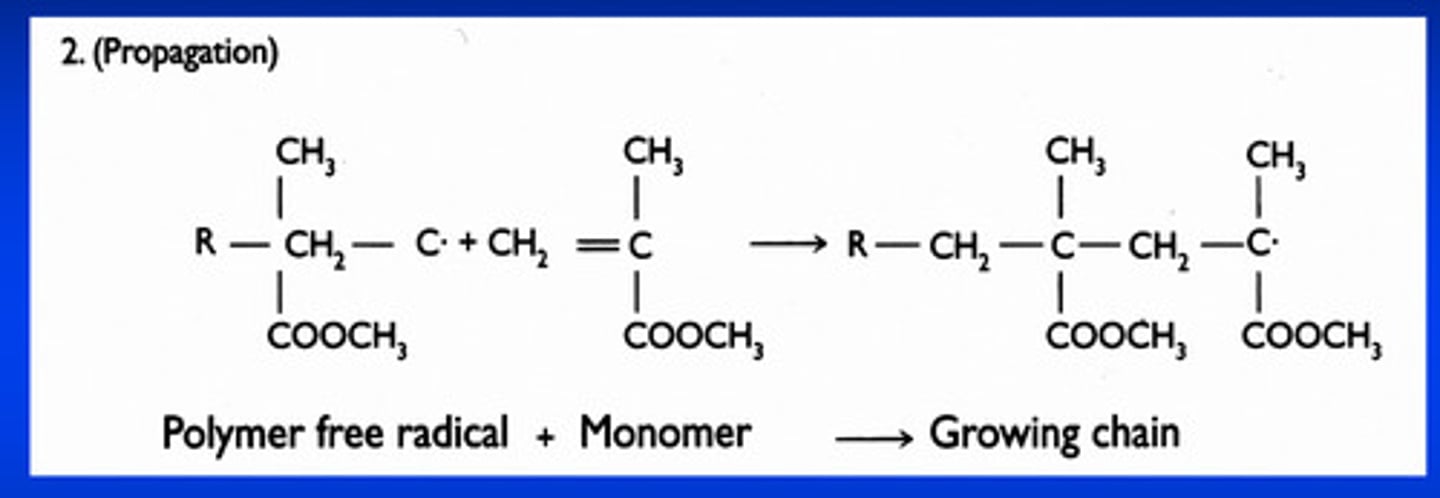
propagation stage of free-radical polymerization rxn
1) as the activated monomer with an unpaired electron approaches the other methyl methacrylate molecule, one of the electrons in the double bonds is attracted to the free radical to form an electron pair AND a covalent bond between the free radical and the monomer molecule
2) the remaining unpaired electron makes the new molecule a free radical
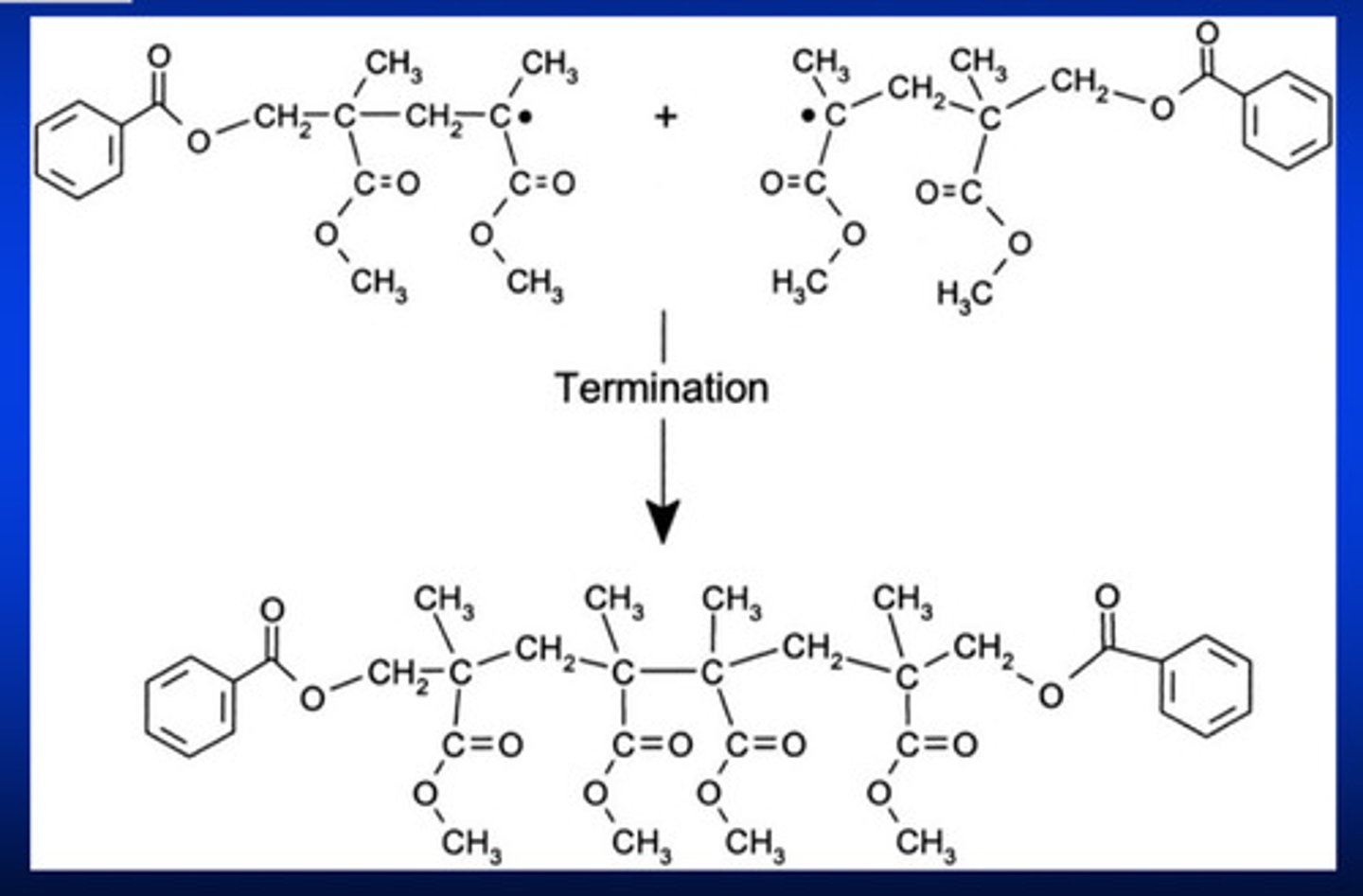
termination stage of free-radical polymerization rxn
occurs when two free radical interacts and form a covalent bond
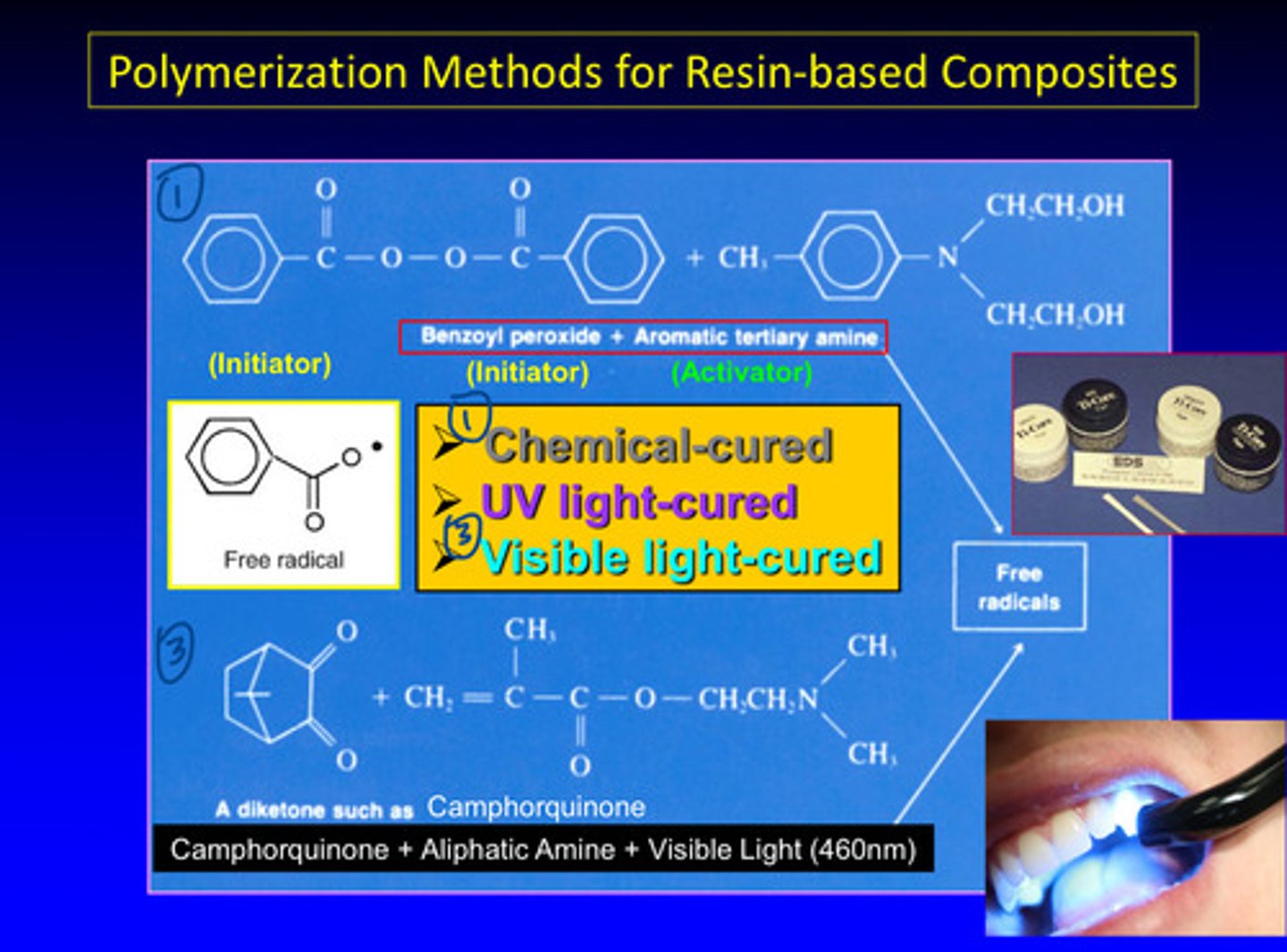
what are 3 polymerization methods for resin-based composites
1) chemical cured: use a chemical to activate or form the free radical; benzoyl peroxide as initiator and aromatic tertiary anime as activator and to produce a free radical —> will go through the 3 stages
2) UV light cured
3) visible light cured: use photons from visible spectrum to activate the aliphatic amine (activator) and camphorquinone acts as initiator to produce a free radical; especially blue light at 460 nm
decreasing the rate of initiation _______ the polymerization reaction
retards
increasing the rate of termination decreases what 2 things
decreases the degree of polymerization or the molecular weight of the final polymer
what 3 materials will inhibit or retard the polymerization?
hydroquinone, eugenol, or large amounts of oxygen
what is ring-opening polymerization (type of add poly rxn)
involves monomers with one or more three-atom end-group rings, which open and then join with other broken rings to form single bonds (similar to the way the C=C bonds open and link up to form C-C bonds)
condensation reactions result in
what are the 2 types of three-atom ring monomers that have found significant usage in dentistry
1) imines: with 2 carbons and a nitrogen
2) epoxies: with 2 carbons and an oxygen (example shown)
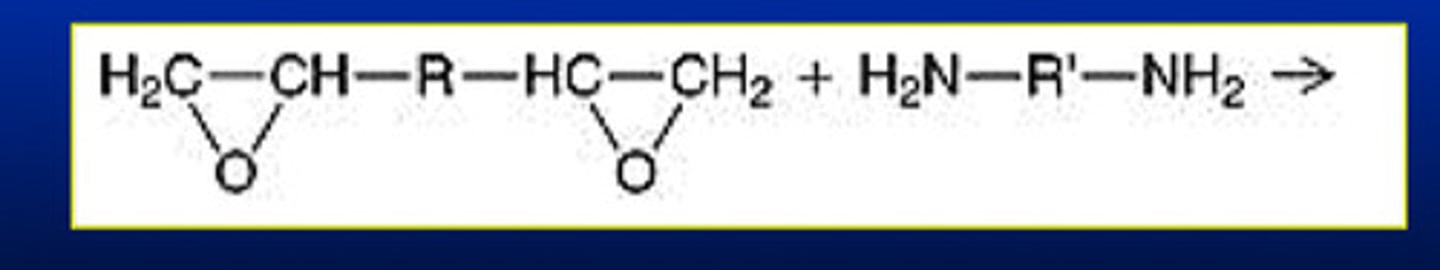
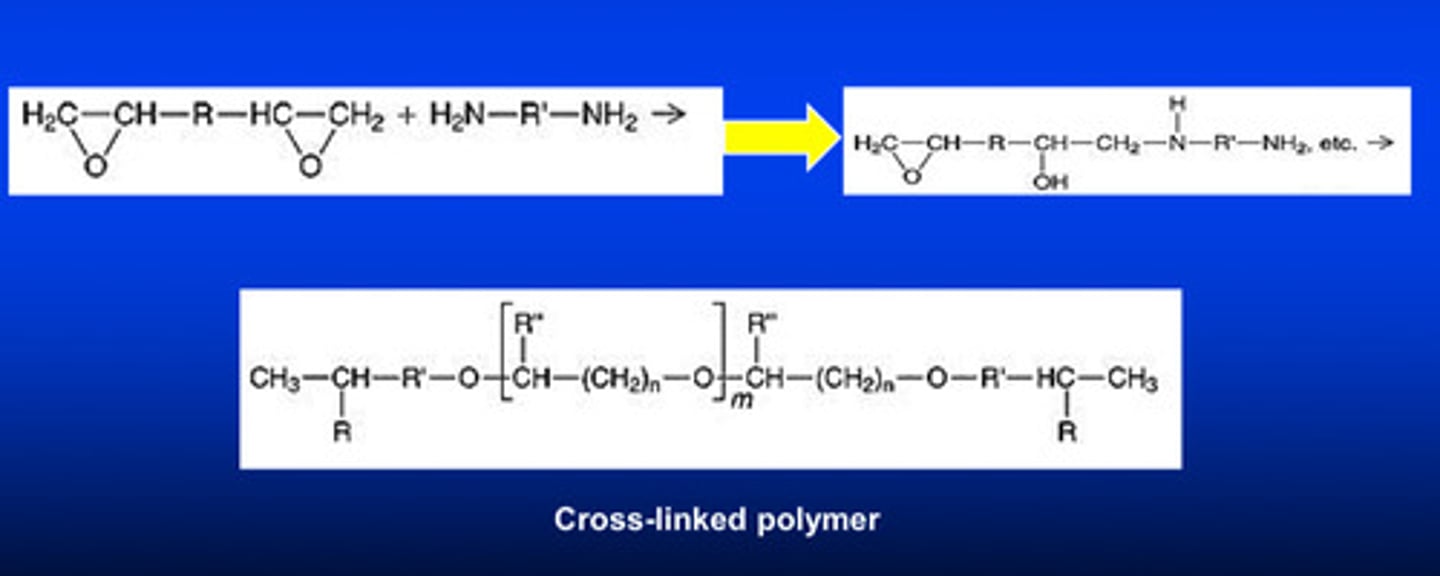
what are the 2 reactants for the epoxy system in a ring-opening polymerization reaction and what do they form
di-functional epoxide oligomer AND di-functional amine; form a cation
condensation reactions also result in polymerization plus the production of what kinds of by products?
production of low molecular weight by products such as water and lead sulfide
what kinds of rubbers are formed by a condensation reaction
polysulfide rubbers
describe how the condensation polymerization reaction works in 2 steps
1) SH groups interact with oxygen released from lead dioxide
2) completion of the condensation reaction results in water as a by product (so when the water evaporates, there is a porosity left inside the polymer material)
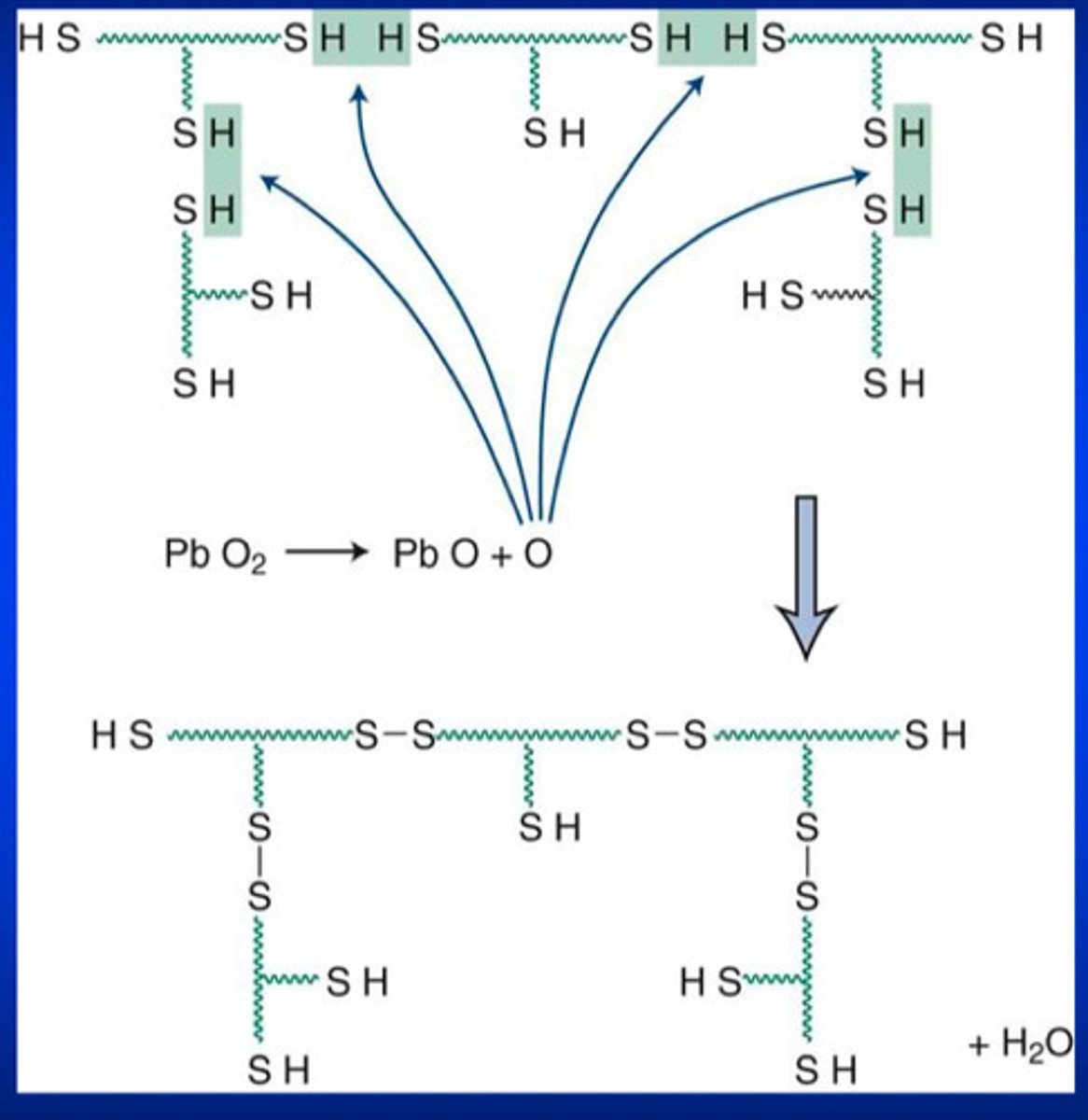
what is the most general kind of condensation reaction that forms polysulfide rubbers
reaction between low molecular weight polysulfide polymers that have mercaptan (-SH) groups AND lead dioxide (catalyst)
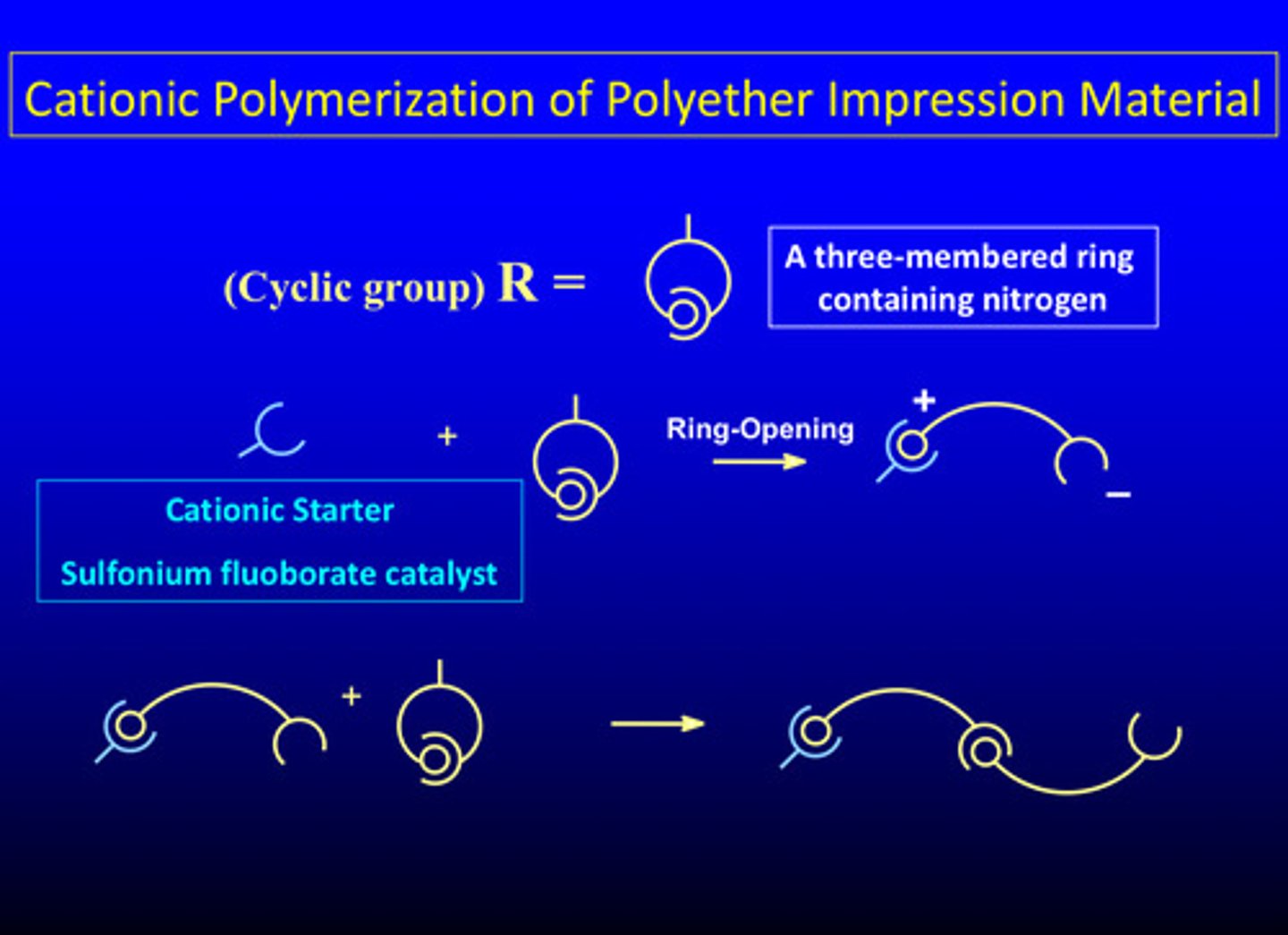
cationic polymerization of polyether impression material (aka ring-opening)
1) cation is formed from the 2 reactants
2) ring opens
3) a chain reaction is formed
4) cross linking network is formed for the final material
in condensation poly rxns, pendant -SH is for _______________ and terminal -SH is for _______ ________________ of the polymer
cross-linking; chain lengthening of the polymer
what are type 1 denture base resins
heat-polymerization polymers (vast majority of dentures made today are fabricated from heat-cured polymers (methyl methacrylate) and rubber reinforced polymers (methyl methacrylate)
what are class 1 and class 2 specifications of type 1 denture base resins
class 1: powder and liquid
class 2: plastic cake (related to CAD/CAM manufacturing)
what are type 2 denture base resins
auto-polymerizable polymers
what are class 1 and class 2 specifications of type 2 denture base resins
class 1: power and liquid
class 2: powder and liquid pour-type resins
what are type 3 denture base resins
thermoplastic blank or powder
what are type 4 denture base resins
light-activated materials
what are type 5 denture base resins
microwave-cured materials
is the powder a polymer or a monomer
polymer
is the liquid a polymer or a monomer
monomer
the powder requires what 2 things
initiator: benzoyl peroxide
plasticizer: dibutyl phthalate to decrease polymerization and strength
the liquid requires what 3 things
inhibitor: hydroquinone necessary to prevent premature polymerization bc monomers are very active molecules (increases shelf life of monomer)
plasticizer: added to produce a softer and more resilient polymer but it may leach out
cross-linking agent: glycol dimethacrylate yields a network structure and provides resistance to crack
powders have pink dyed organic fibers that helps to simulate what
blood vessels in the denture base
mixing the powder with the liquid, what starts
the polymerization reaction
the main ingredient inside the powder and the liquid is the?
plasticizer; we add this in a high enough amount to make the denture have good impact strength
what are the 8 components of the powder
1) polymer beads
2) initiator
3) rubber
4) plasticizer
5) inorganic particles
6) dyed organic fibers
7) pigments
8) opacifiers
powder polymers beads result in what 2 properties
decreased shrinkage and increased strength
powder initiator results in what
initiates polymerization
powder rubber results in what 2 properties and what is the chemical used for it
increased resilience and increased impacts; butadiene-styrene
powder plasticizer results in what property
increased resilience
picture of powder stuff woohoo
powder to liquid is 3:1 ratio

powder inorganic particles result in what 2 properties
increased stiffness, and decreased TEC (thermal expansion coefficient)
powder opacifiers result in what 2 properties
decreased translucence and increased radiopacity (you cannot find denture without opacifier through an x-ray)
what are the 5 components of the liquid
1) monomer
2) inhibitor
3) accelerator
4) plasticizer
5) cross-linking agent
liquid monomer results in what property and what is the chemical
increased strength; MMA
liquid inhibitor results in what property and what is the chemical
increased shelf life; hydroquinone
type 1 class 1 compression molding techniques
1) wax up denture base with baseplate wax
2) create teeth and put in correct position
3) embed the denture into plaster
4) we soften the wax; one side of the plaster holds the denture teeth and is detached from the base
5) clean up and add separator
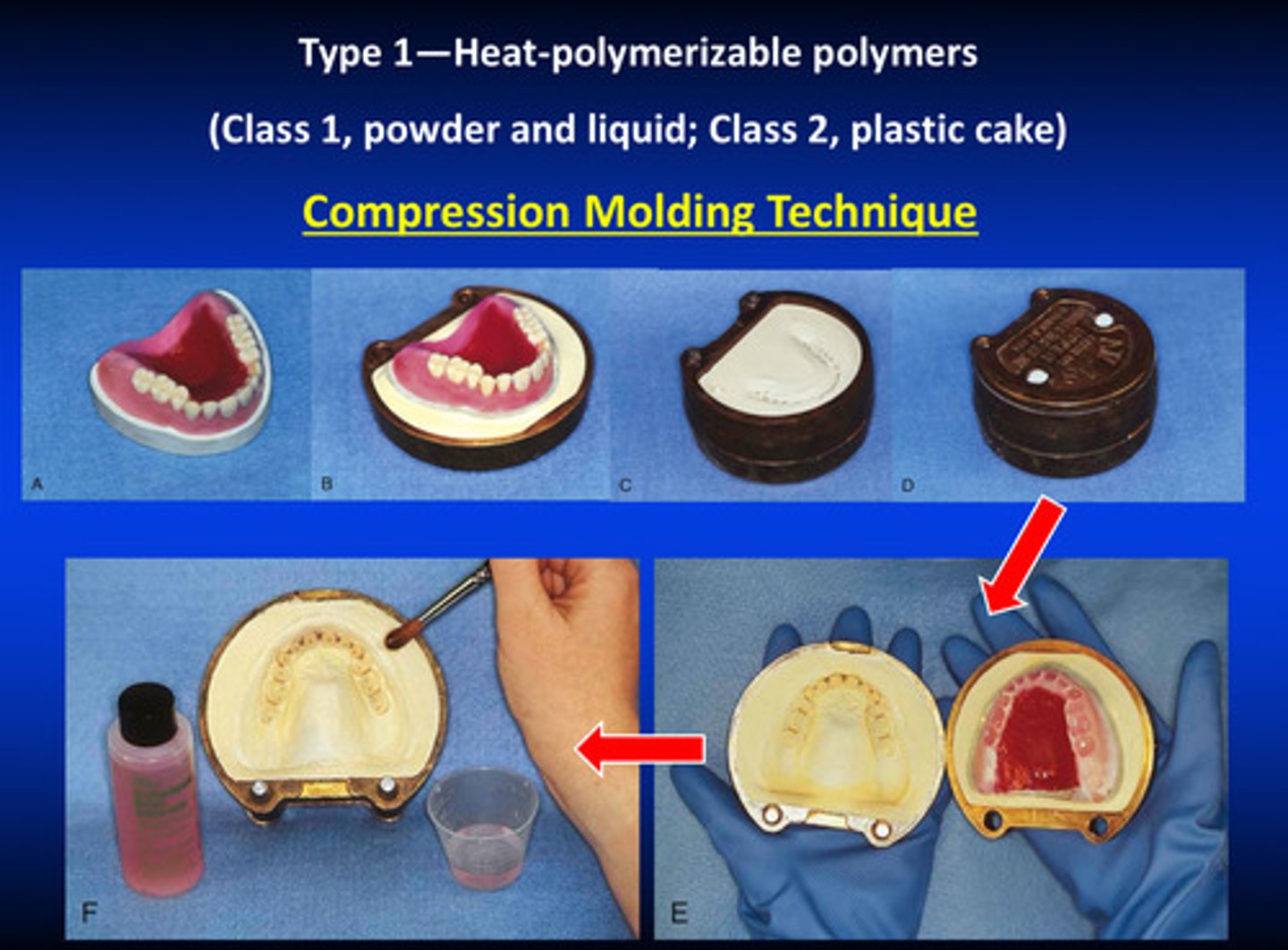
type 1 compression molding techniques
milling technique is used for plastic cake (class 2) instead of compression method; material mixing is used for powder and liquid (class 1)
CAD-CAM denture materials with class 2 type 1 polymers
compression molding techniques continued for class 1 type 1
1) after mixing, the materials go through chemical setting reaction
2) place the materials in the space where the base plate wax was initially
3) compress the materials to fill the cavity but to also make the materials become more solid (eliminates all air left inside the materials)
4) after removing excess material, you use a special frame and flask to put the denture into the curing machine
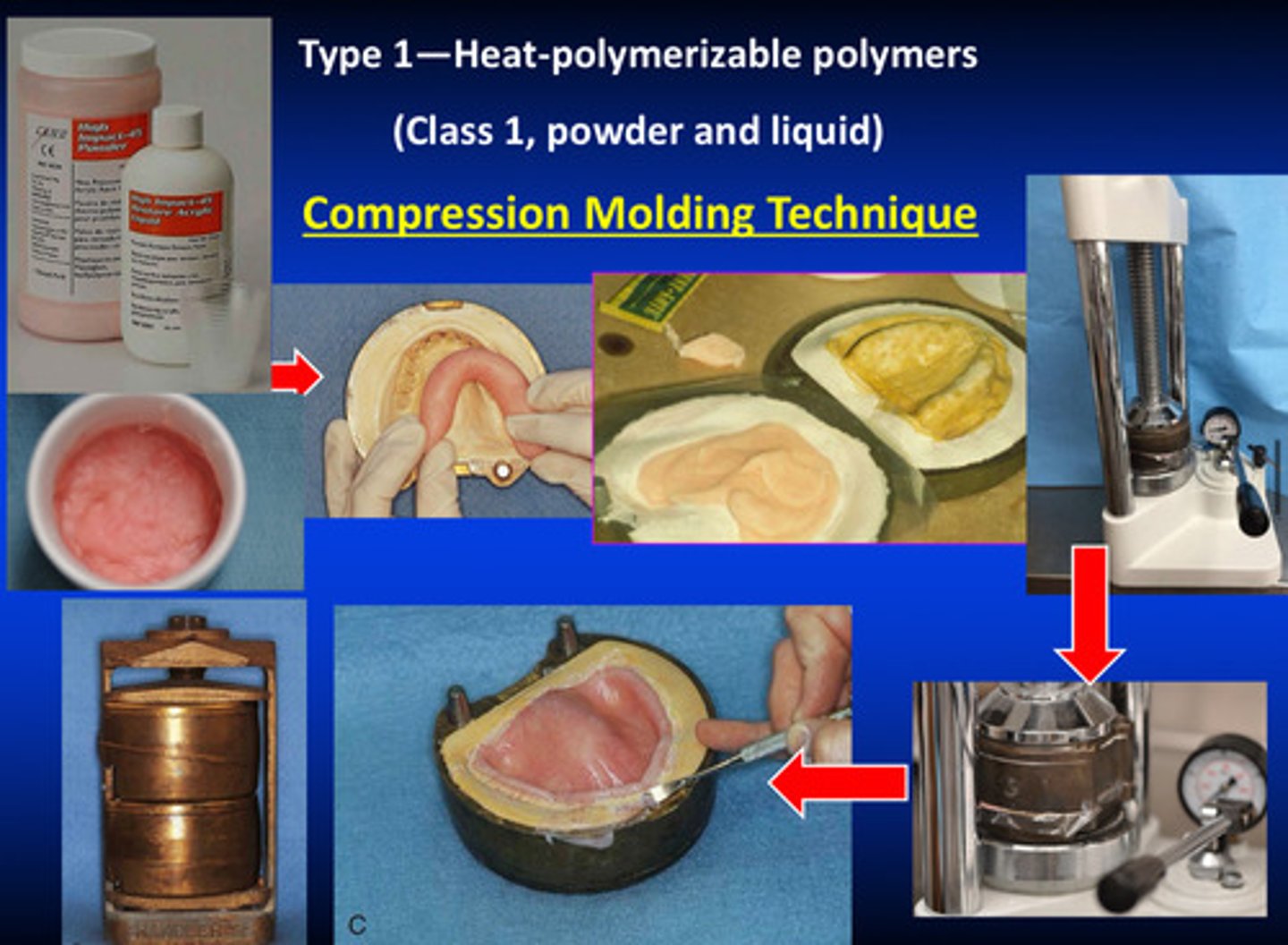
compression molding techniques continued for class 1 type 1; heat processing
1) process the denture base resin in a constant-temp water bath at 74 degrees C for 8 hours or longer with NO terminal boiling treatment (long-term)
OR
2) process the resin at 74 degrees C for 2 hours and increase the temp of the water bath to 100 degrees C and process for 1 hour (short-term and most common procedure)

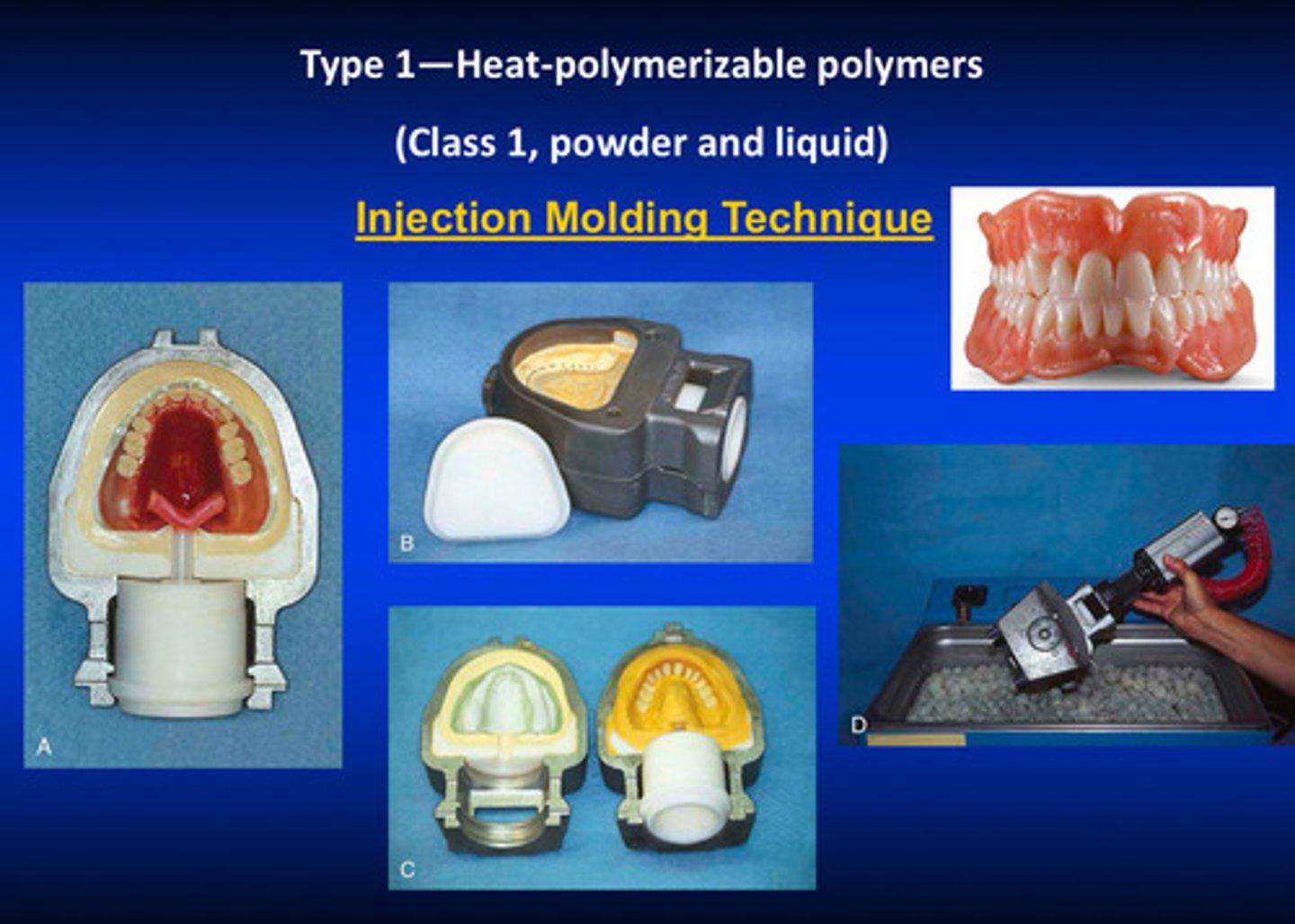
type 1 class 1 injection molding technique
uses injection instead of compression
1) inject flowable resin
2) use a special flask to put the base under pressure under a water bath
3) ^^ starts polymerization reaction
type 2 auto-polymerization polymers, fluid resin technique
used for class 1 (powder and liquid) and class 2 (powder and liquid pour-type resins) for type 2
resin is very flowable and can fill the cavity in between the denture teeth and the cast

liquid plasticizer results in what property
increased resilience
in type 3 (thermoplastic blank or powder), we have ________ denture bases
flexible
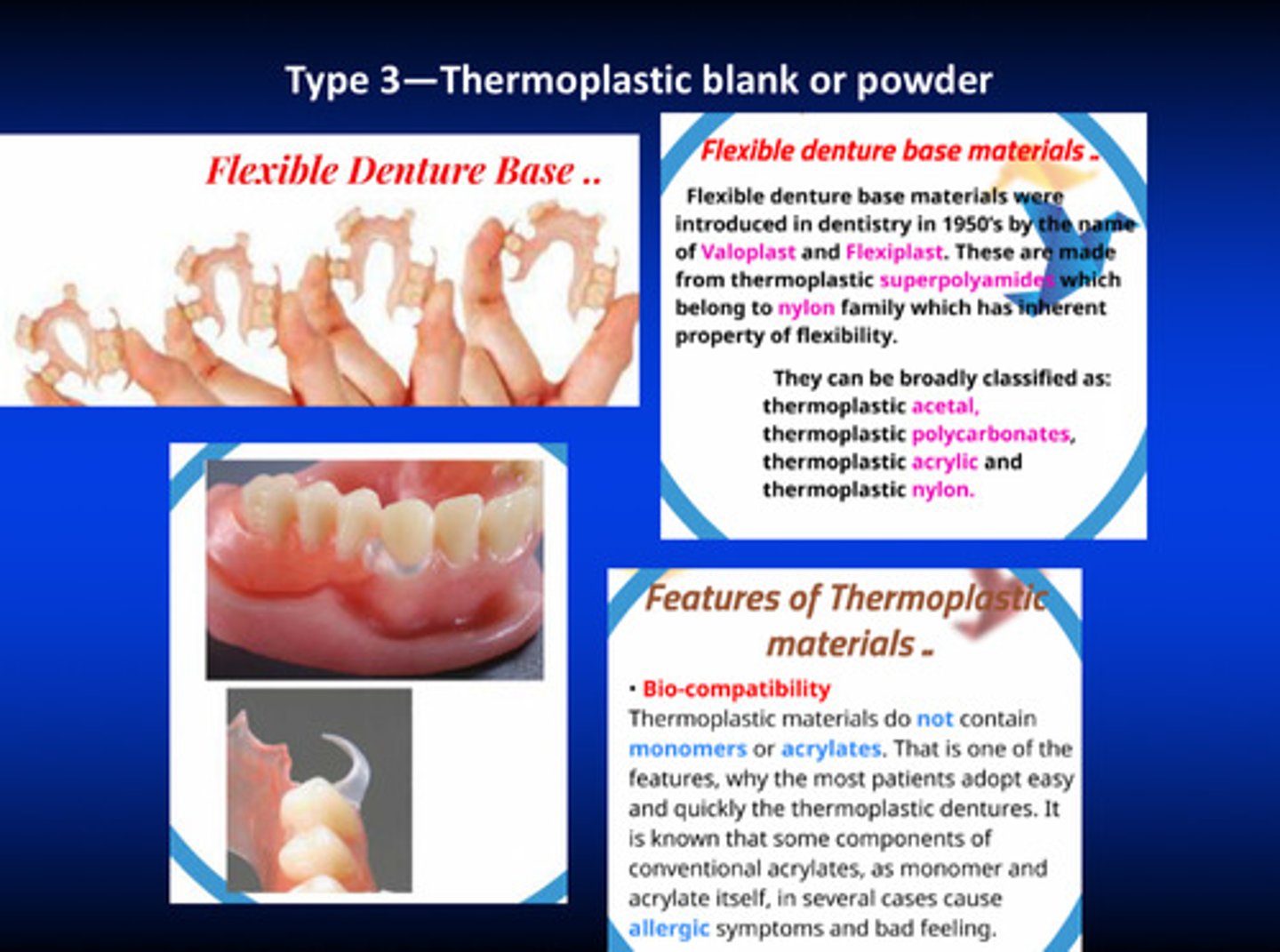
why are type 3 flexible denture bases not really taught or used widely
they are completely different from the MMA/PMMA conventional materials: if it is used for esthetics in anterior it is good; but when used for posterior, under the occlusal forces, the denture will move and compress the tissue and push the adjacent teeth —> whole bunch of problems!

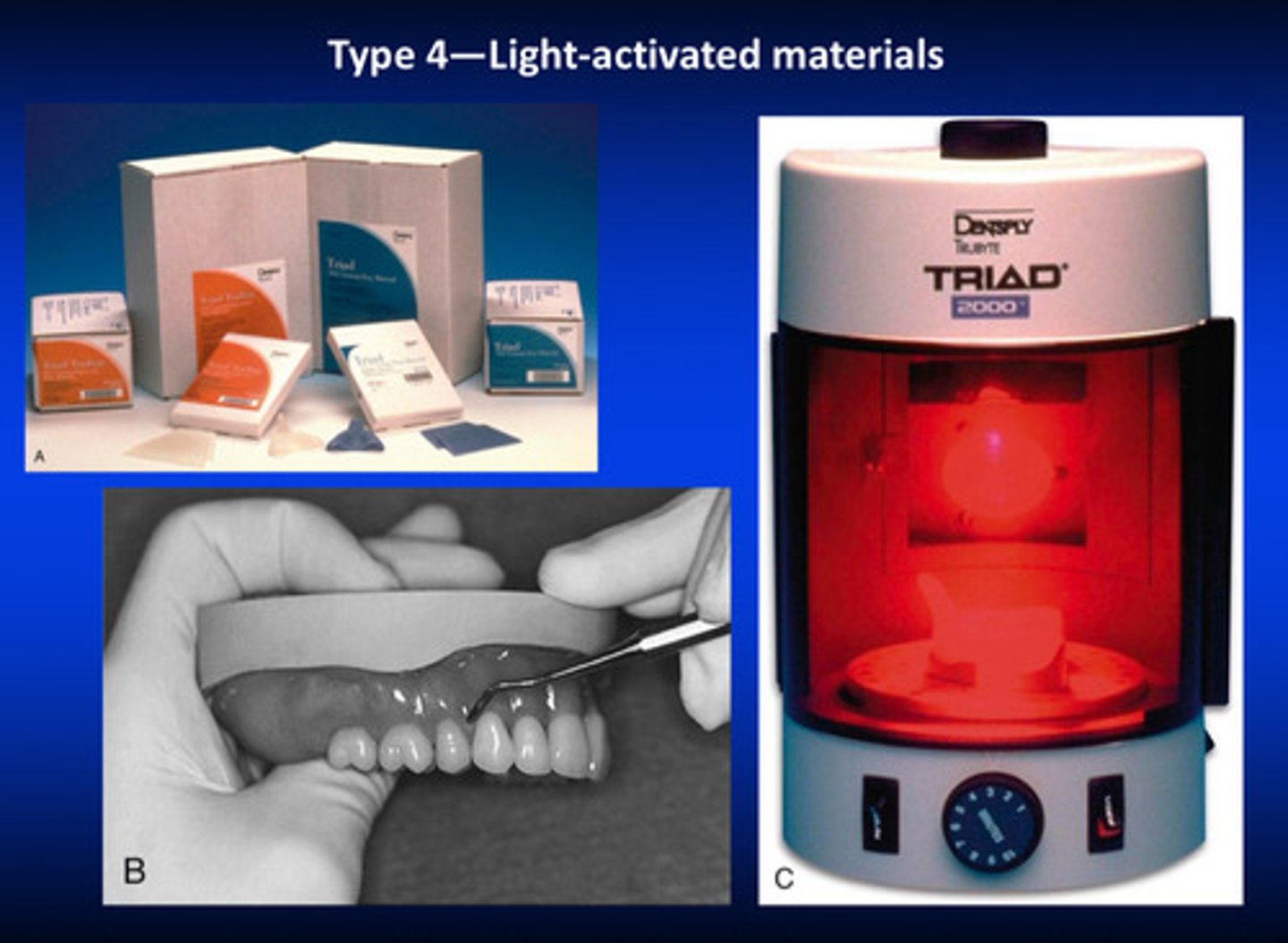
type 4 (light activated materials) use what kind of technique
use the relevant materials like wax, beautify it, add teeth, and put into special curing unit for a couple of minutes and the final denture is ready
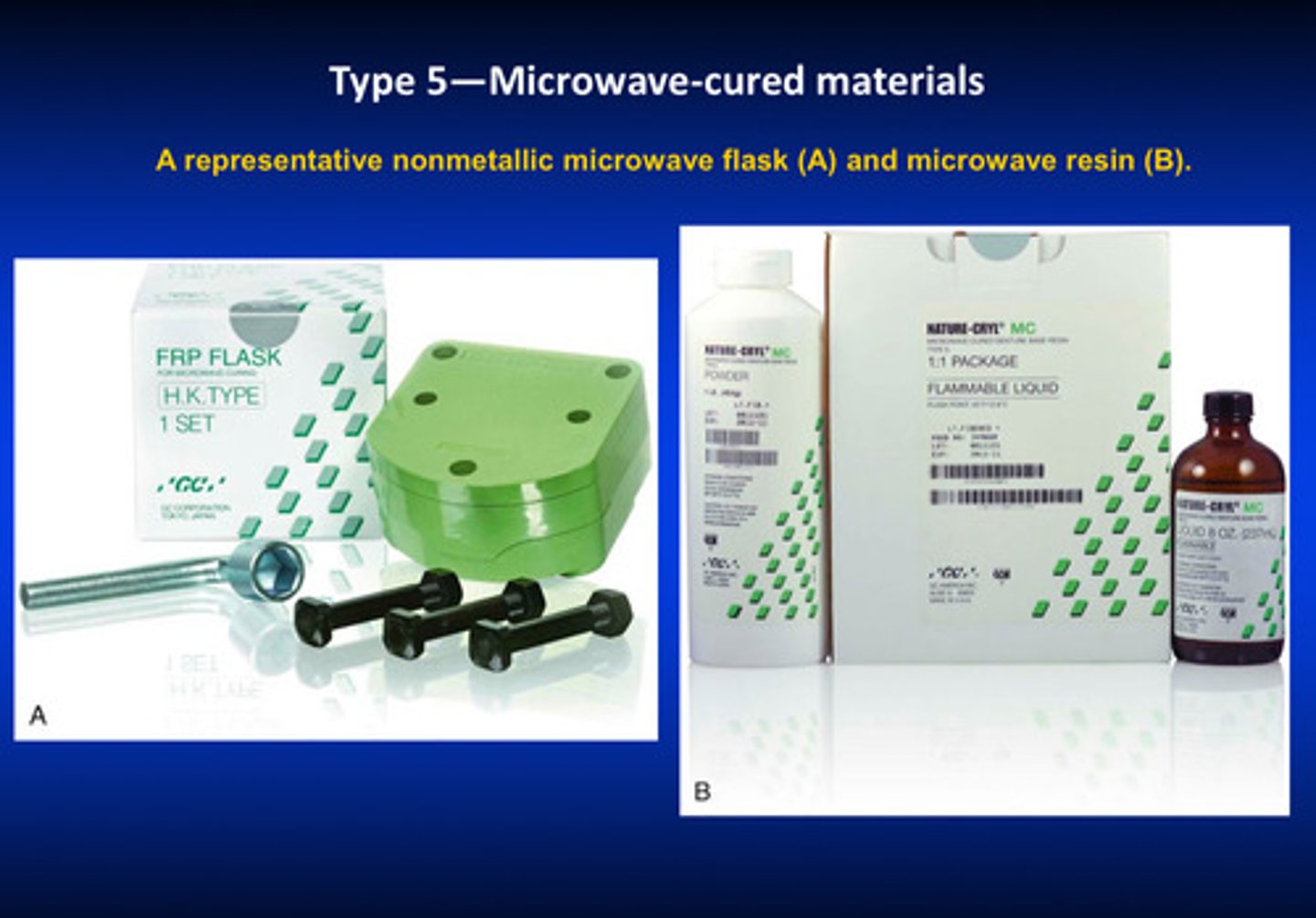
type 5 (microwave cured materials) use what kind of technique
use a representative NONmetallic microwave flask (A) and microwave resin (B) —> use fiber reinforced polymer as a flask bc metal will cause boom boom explosion
liquid cross-linking agent results in what 2 properties
increased stiffness and increased strength
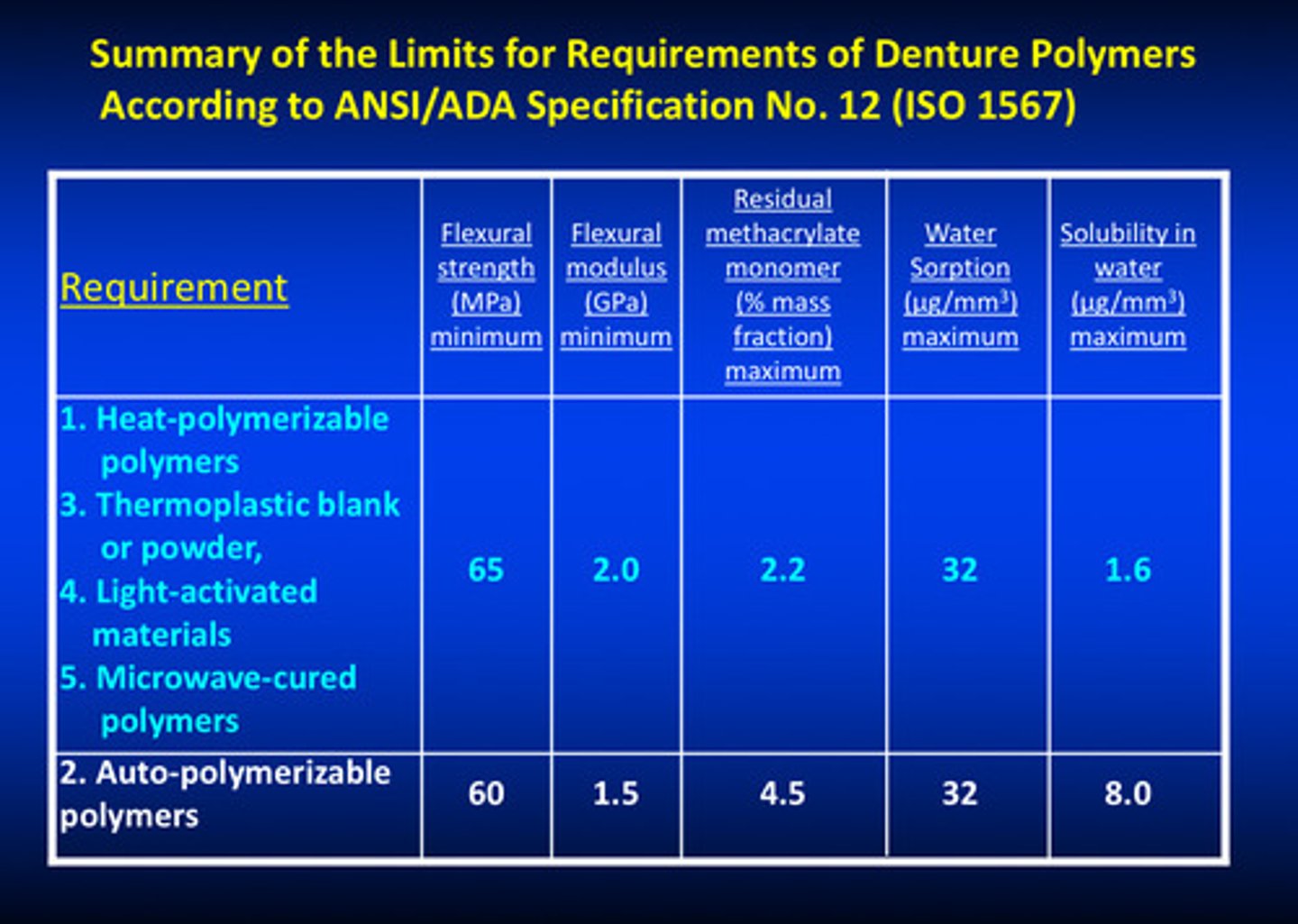
summary of the limits for requirements of denture polymers
types 1, 3, 4, and 5 have same limits; type 2 have lower limits because it uses mixing of powder and liquid and completion of the rxn on the bench instead of under pressure or using heat processing —> may have more voids, flaws, porosities, etc
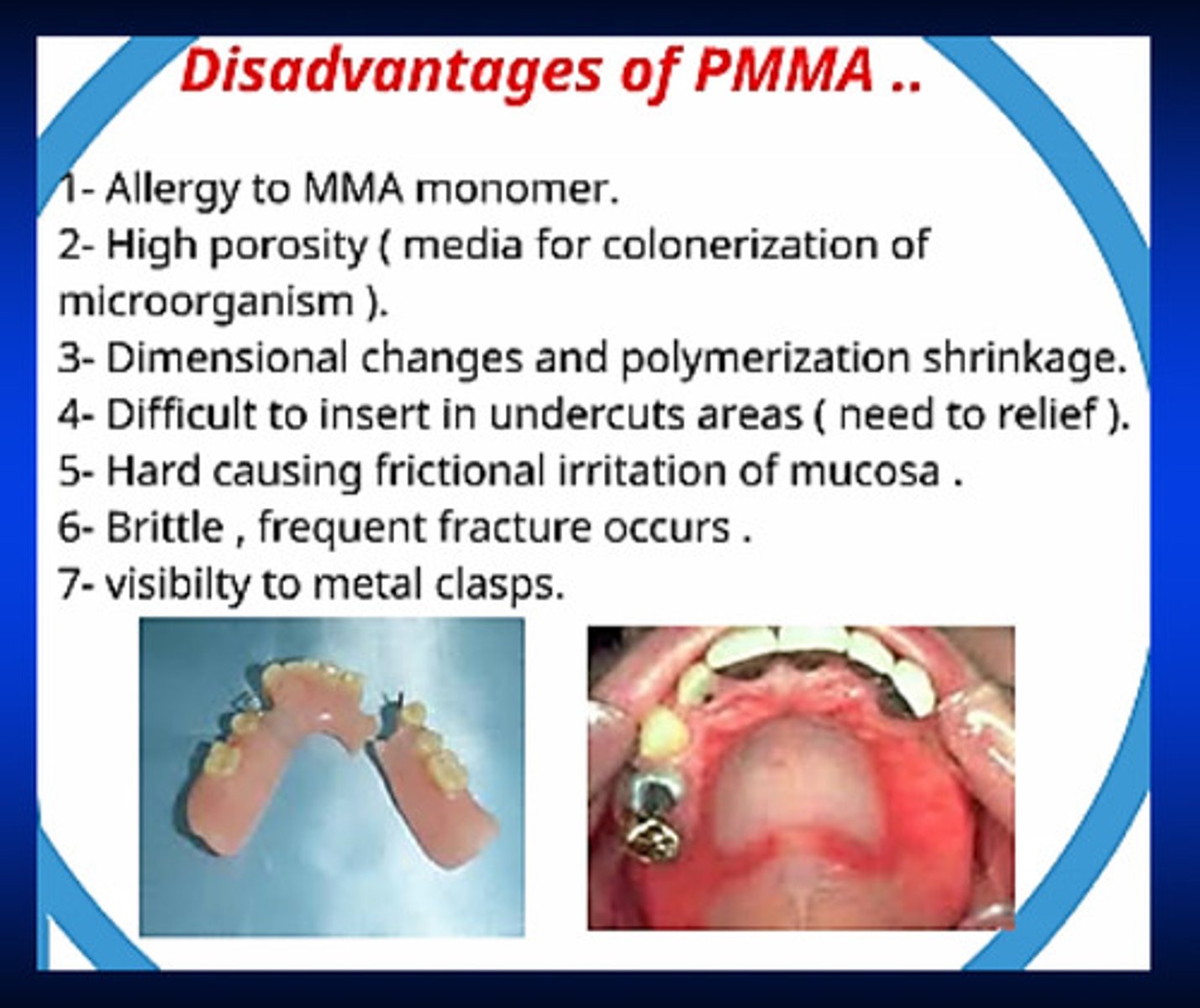
what are 7 disadvantages of PMMA
1) allergies to MMA monomer
2) high porosity (microorganisms can colonize in the porosities)
3) dimensional changes and polymerization shrinkage
4) difficult to insert in undercut areas
5) hard: causes frictional irritation of mucosa
6) brittle, frequent fracture occurs
7) visibility to metal clasps
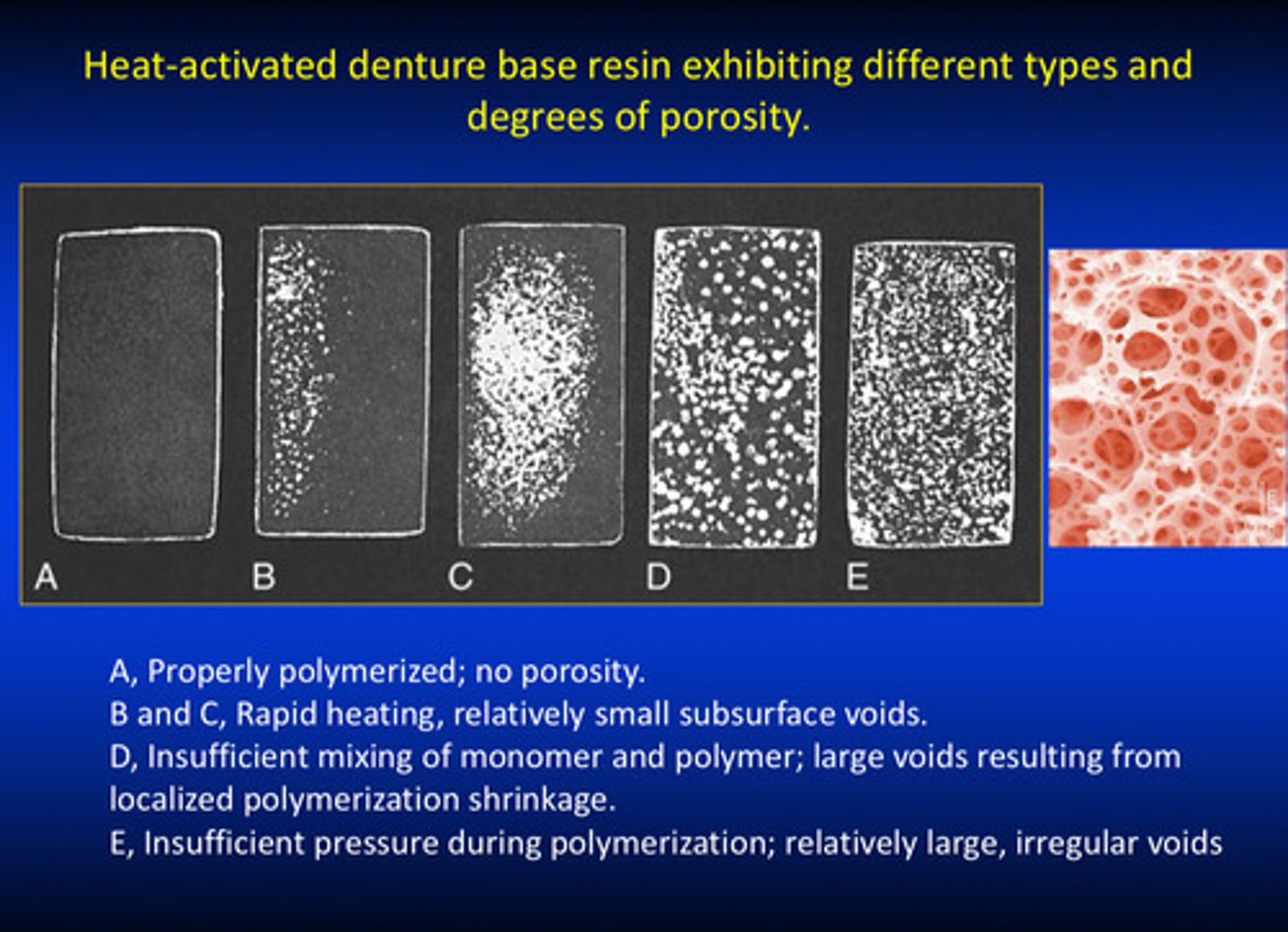
examples of heat activated denture bases resins (type 1) exhibiting different types and degrees of porosity
porosities usually caused by insufficient techniques such as mixing or insufficient pressure
examples of impact strength for various denture base resin materials
different materials may have different impact strengths; impact strength is one of the most imp mechanical properties of denture base materials
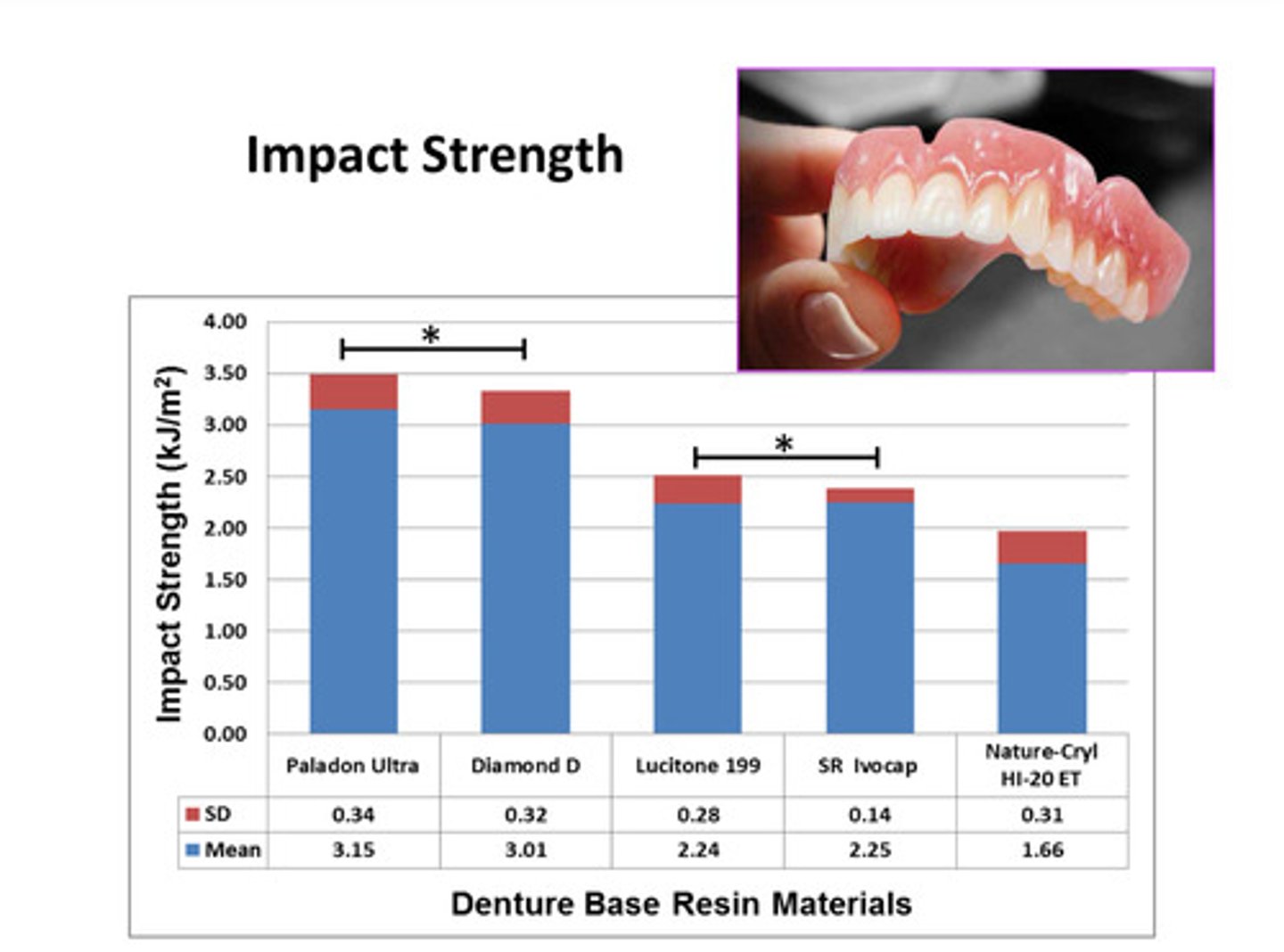
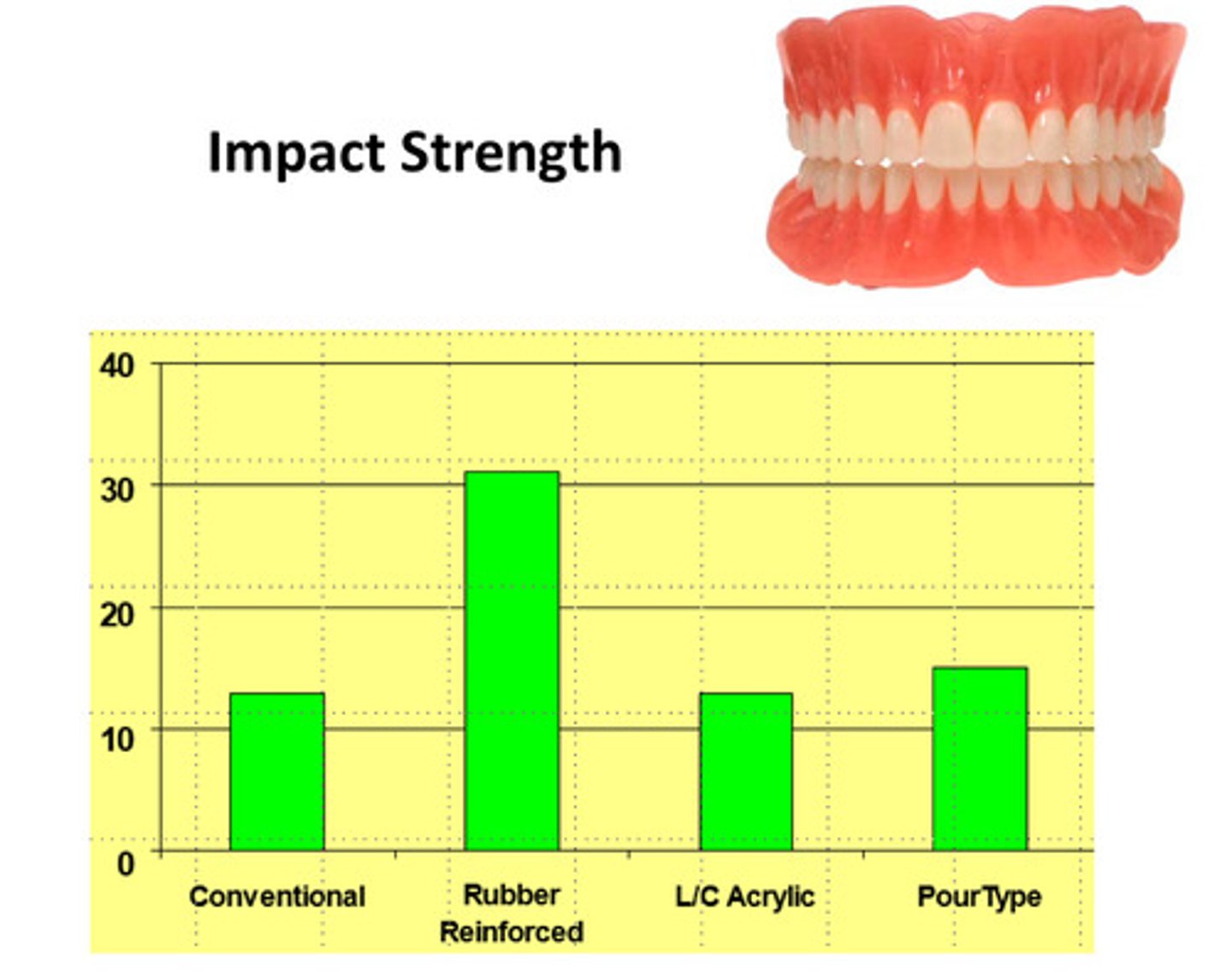
examples of impact strength of denture materials with rubber reinforcement
any rubber reinforcement increases impact strength much more than other materials
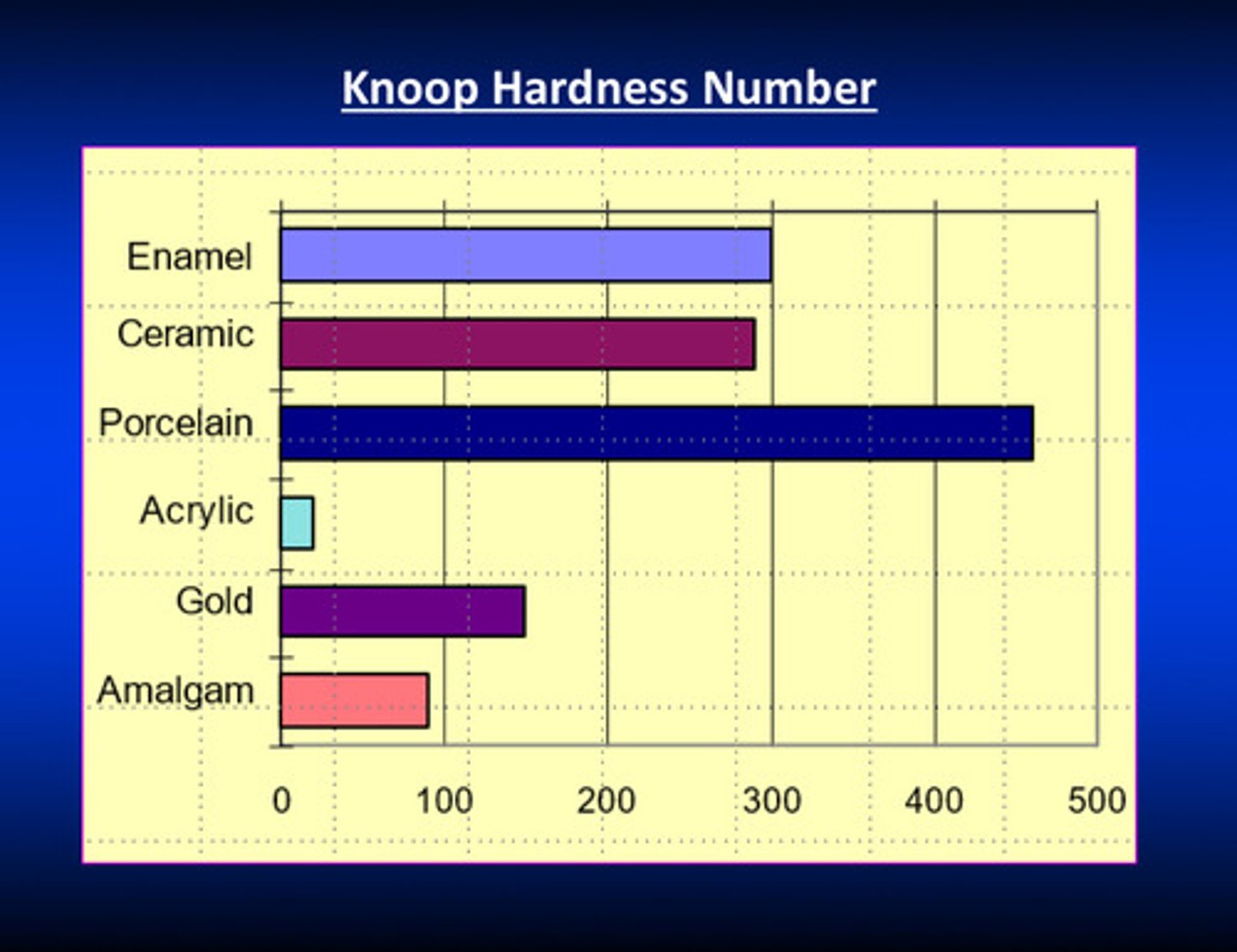
knoop hardness number examples
porcelain has the highest hardness number (recall hardness is resistance to scratching or indentation); denture brushes under water are recommended to clean acrylic dentures due to low hardness AND you must leave acrylic denture out of your mouth while sleeping
"auto" in auto-polymerization polymers (type 2) means what
chemical
what are the 12 requirements for a clinically acceptable denture base material
1) strength and durability
2) satisfactory thermal properties
3) processing accuracy and dimensional stability
4) chemical stability (for both unprocessed and processed material)
5) insolubility in and low sorption of oral fluids
6) absence of taste and odor
7) biocompatible
8) natural appearance
9) color stability
10) adhesion to plastics, metals, and porcelain
11) ease of fabrication and repair
12) moderate cost
the density of methyl methacrylate monomer is only 0.945 g/cm^3 compared to 1.16 to 1.18 for polymer methyl methacrylate, as a result what happens as the monomers polymerize
a volumetric decrease of almost 20% occurs in some dental polymers
as the volumetric decrease occurs, either the mass ______ or internal stresses ______
mass shrinks OR internal stresses accumulate