PAS407 - Updated Study Material on Ocular Anatomy and Associated Nerves
1/164
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
165 Terms
superior wall of orbit:
frontal bone and lesser wing of sphenoid
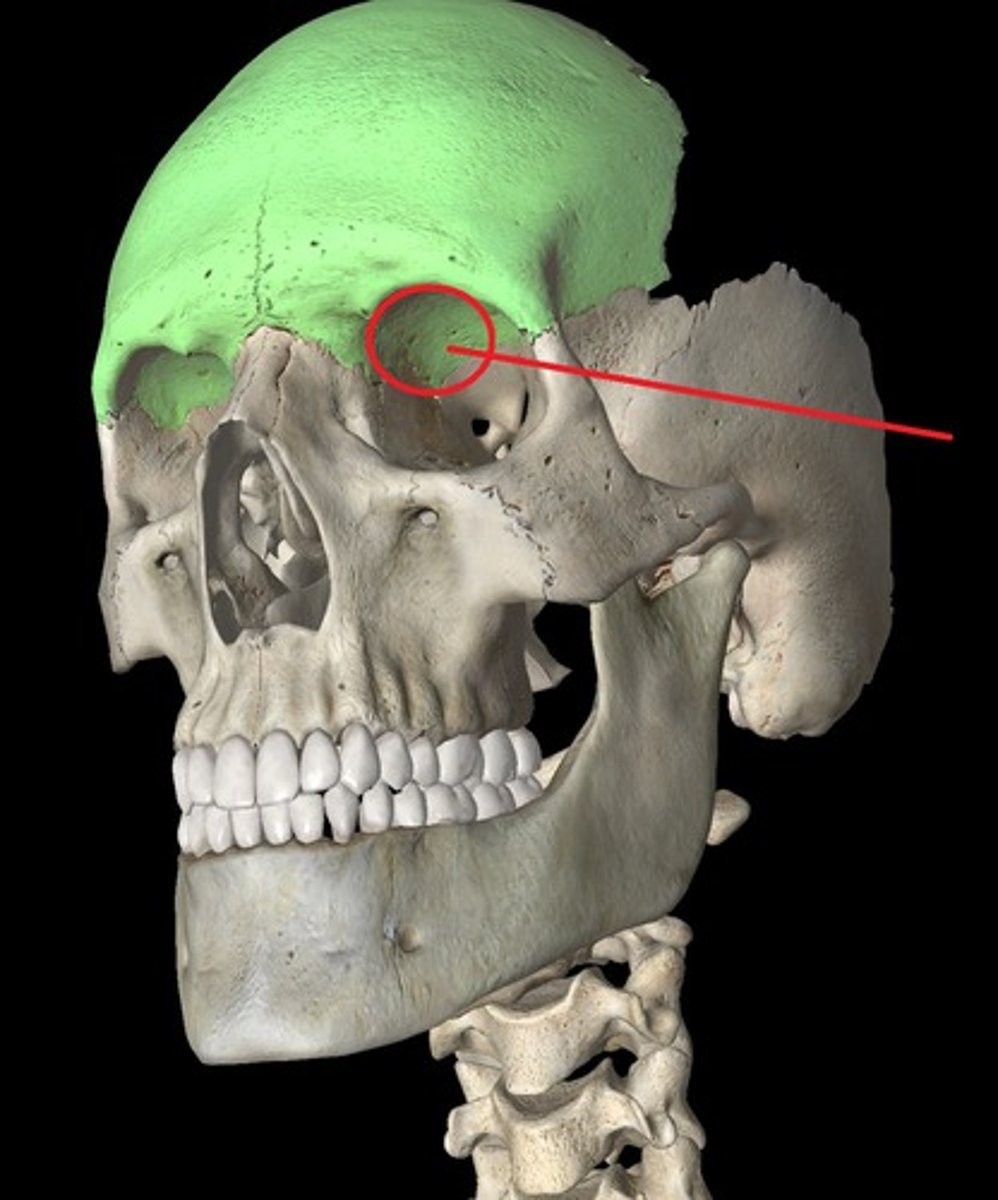
medial wall of orbit:
ethmoid bone, maxilla, lacrimal, sphenoid bones
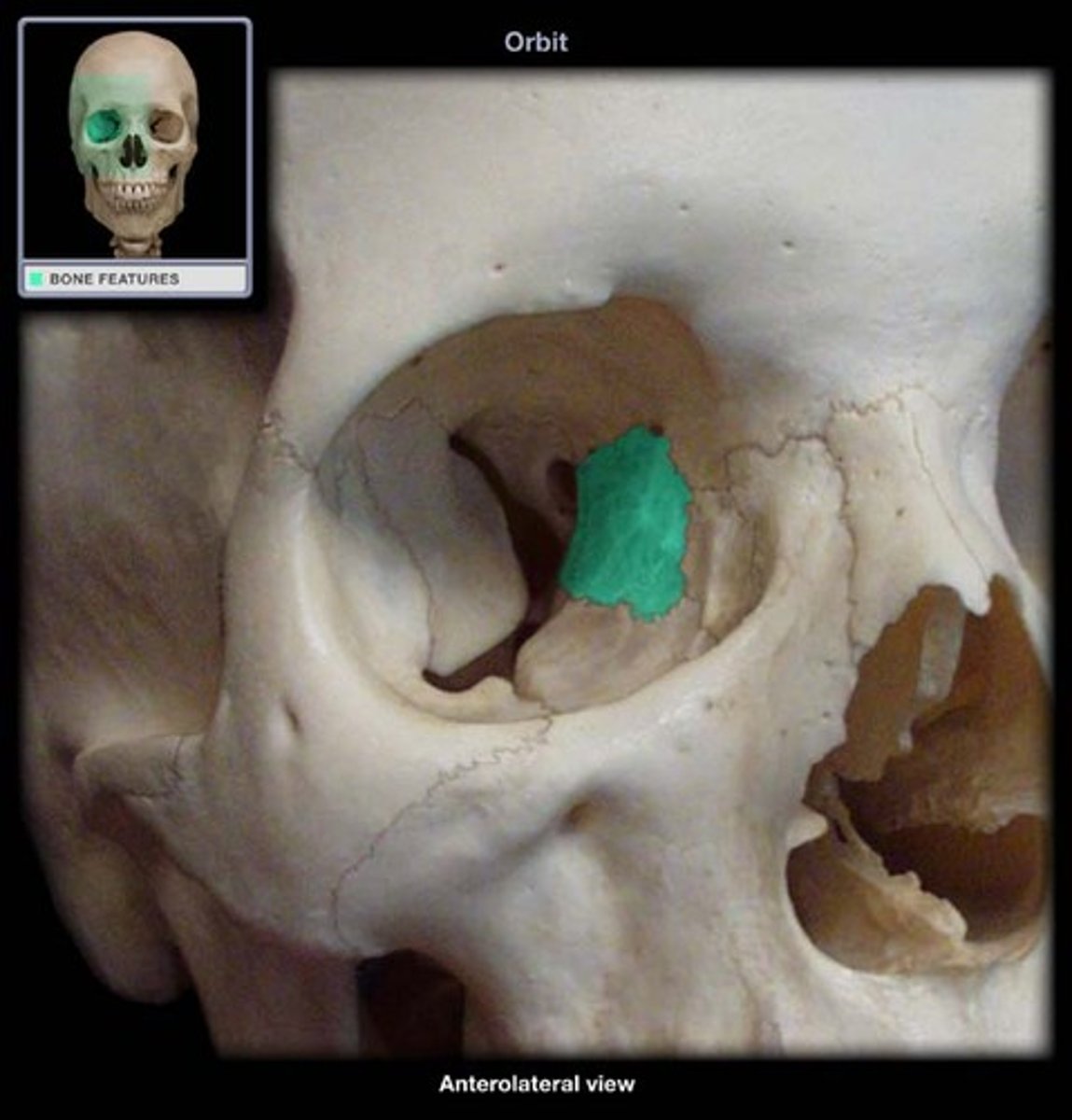
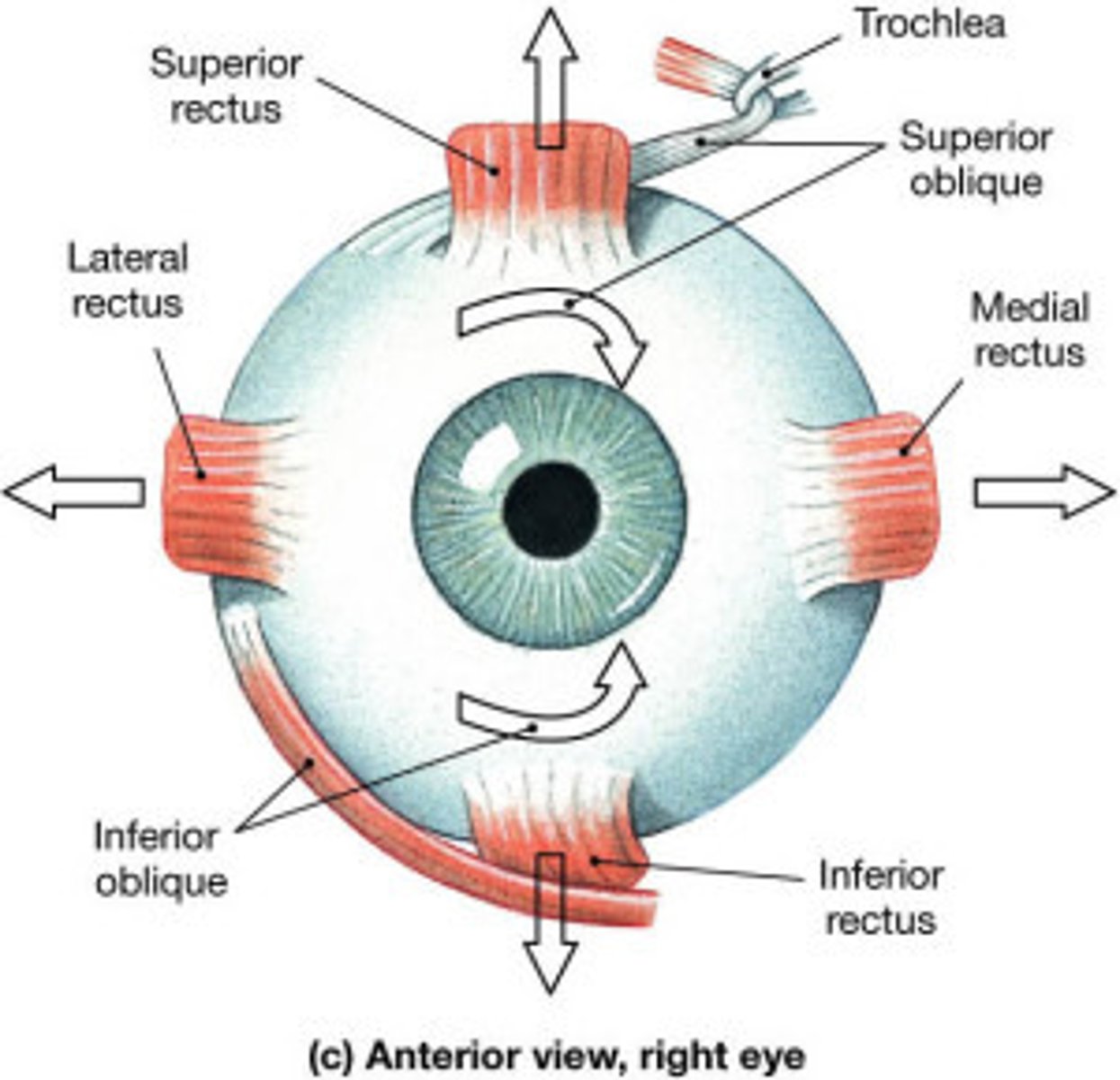
the trochlea is found in?
medial wall, superiorly
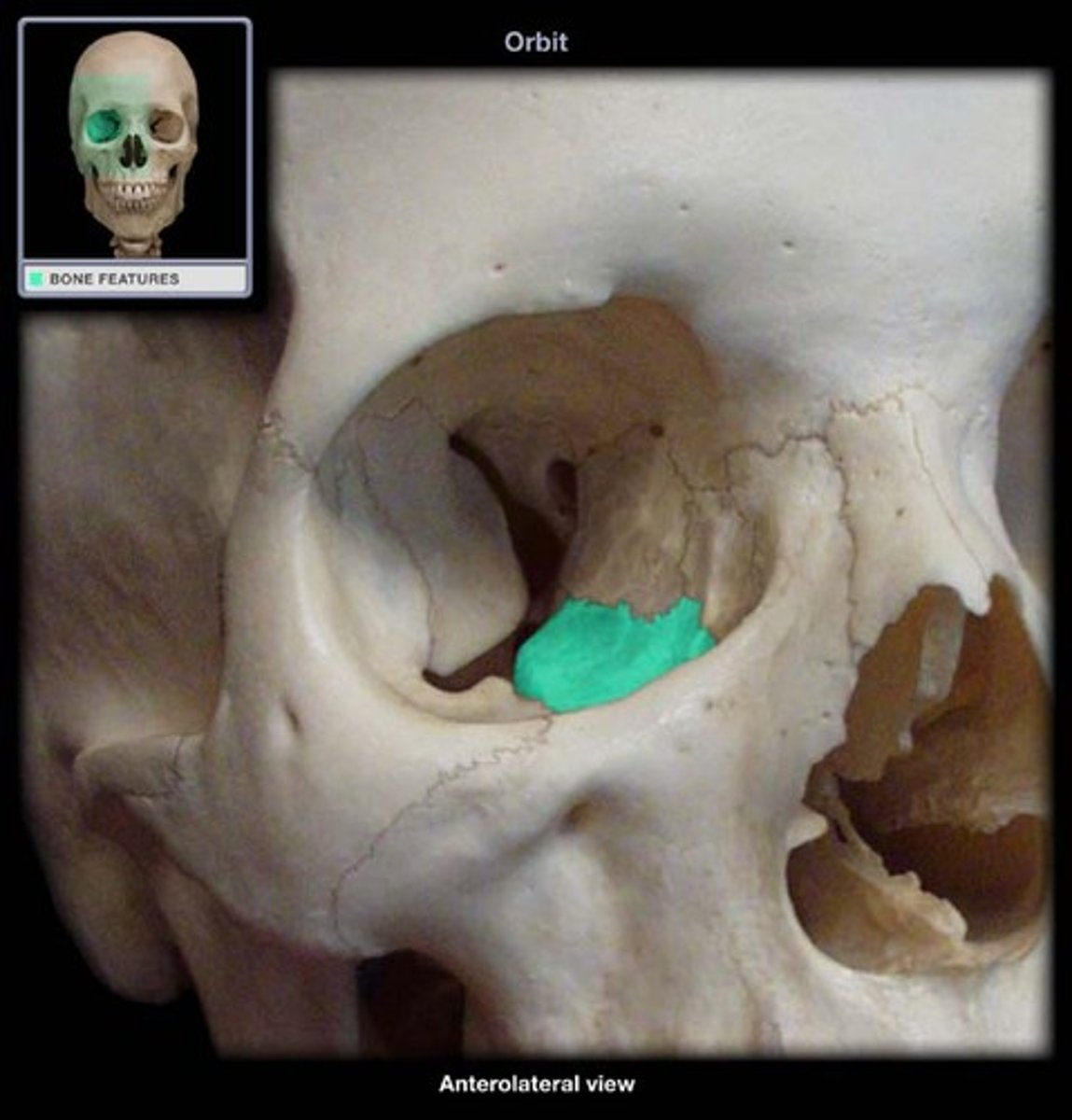
inferior wall of orbit:
maxilla, zygomatic, palatine bones
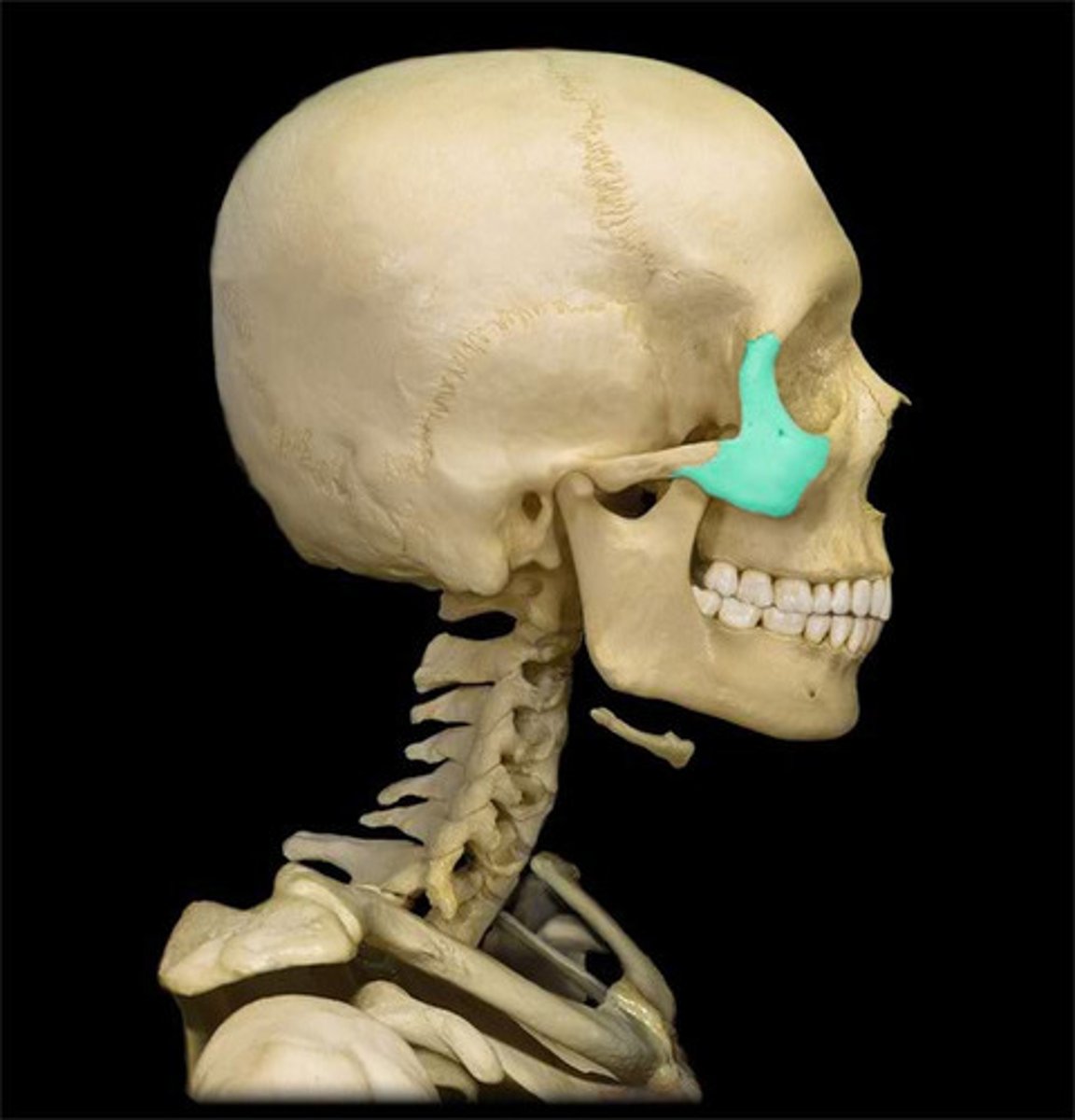
lateral wall of orbit:
formed by zygomatic, sphenoid
o strongest, thickest wall
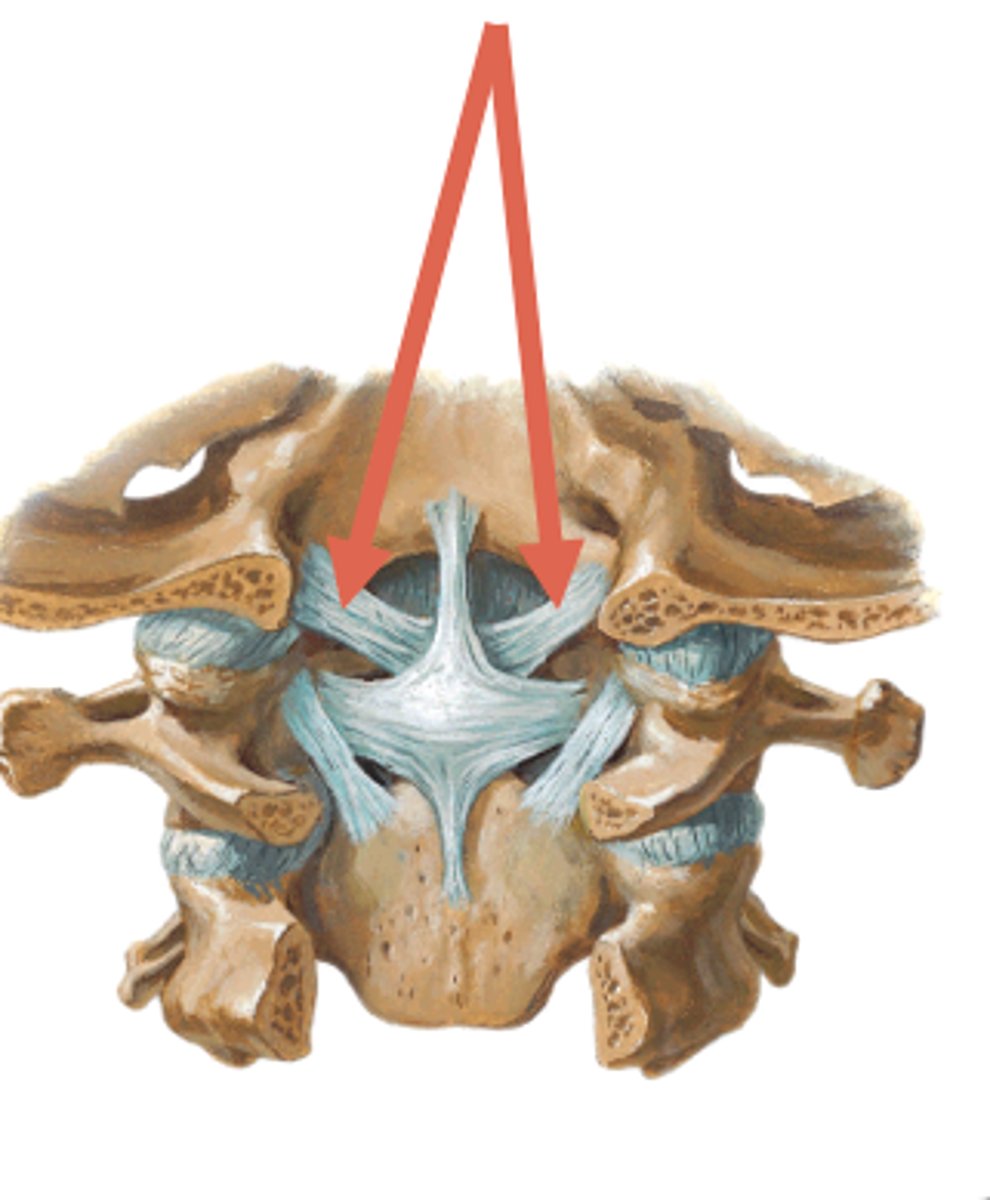
what are the 3 supporting apparatuses of the eye?
1. fascial sheath
2. check ligaments
3. retrobulbar fat
what envelops the eyeball?
fascial sheath
o forms actual socket for eyeball
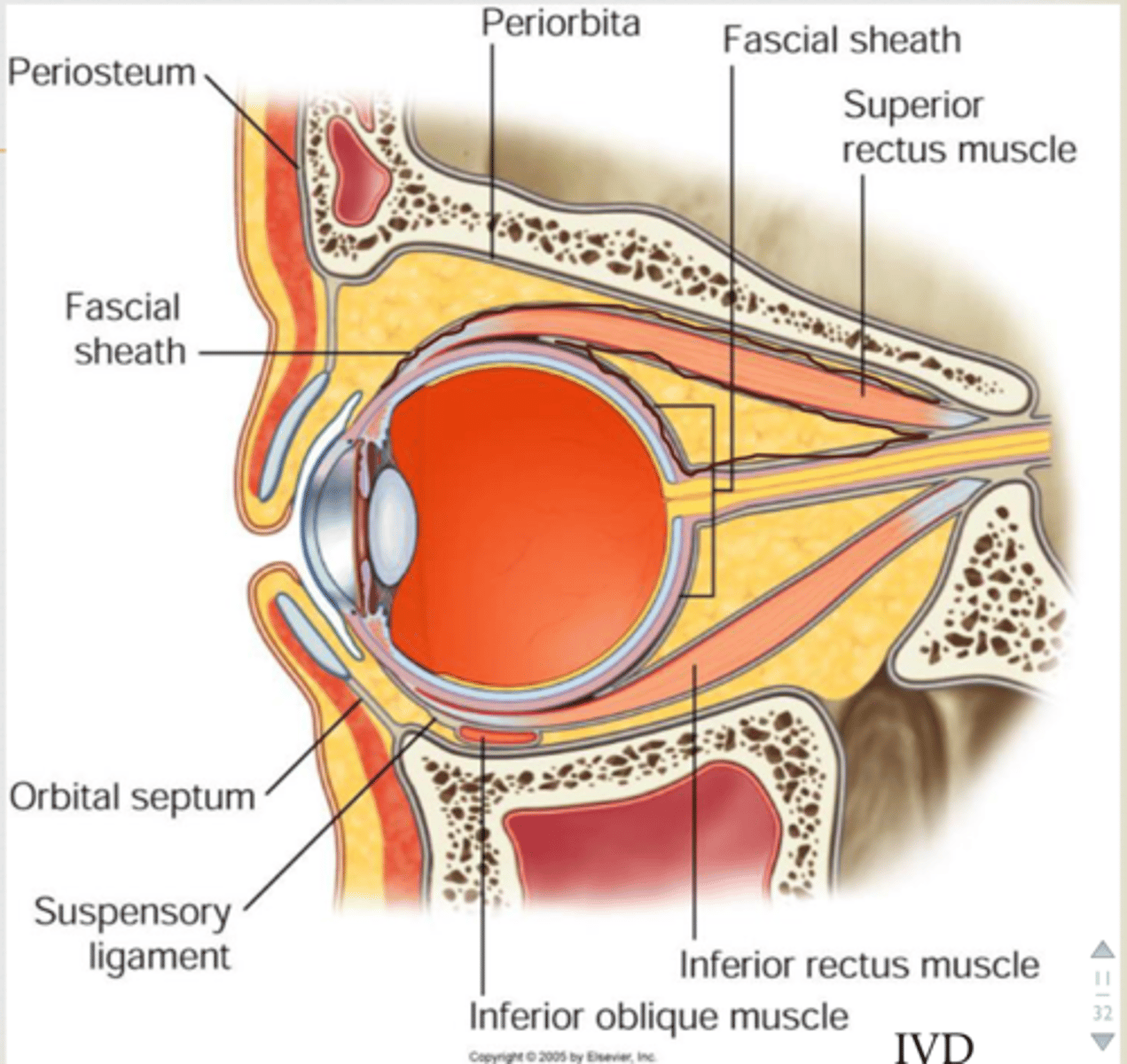
what does the fascial sheath of the eyeball do passively?
passively elevate/depress superior/inferior eyelids during upward/downward gaze
what helps with stabilization of the eye?
check ligaments
- limit abduction, adduction
what is the retrobulbar fat of the eye?
provides padding, support to resist posterior movement of eye during compression, muscle contraction
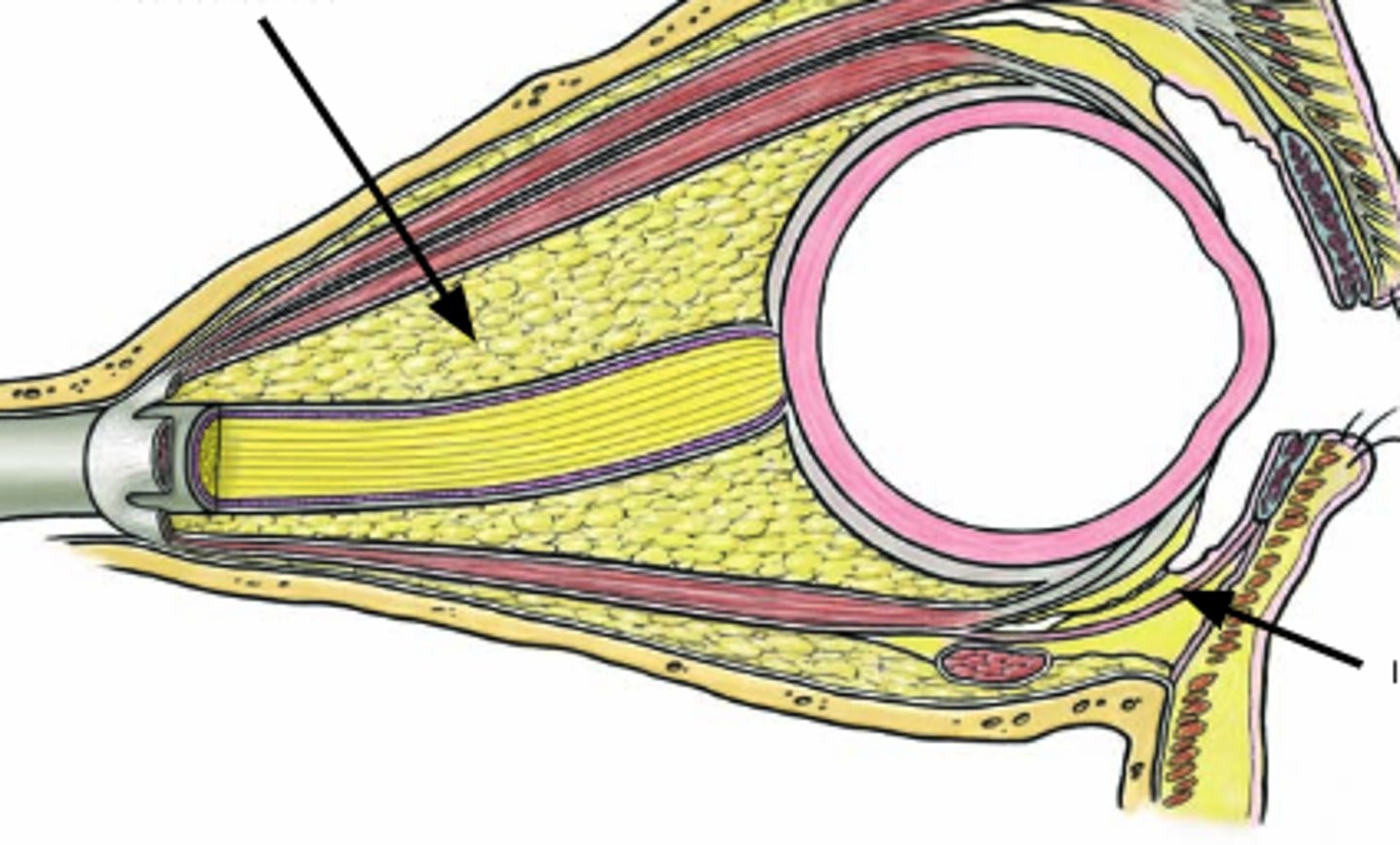
inophthalmos: what is it?
retraction of eyeball into orbit during periods of starvation, due to shrinking of retrobulbar fat
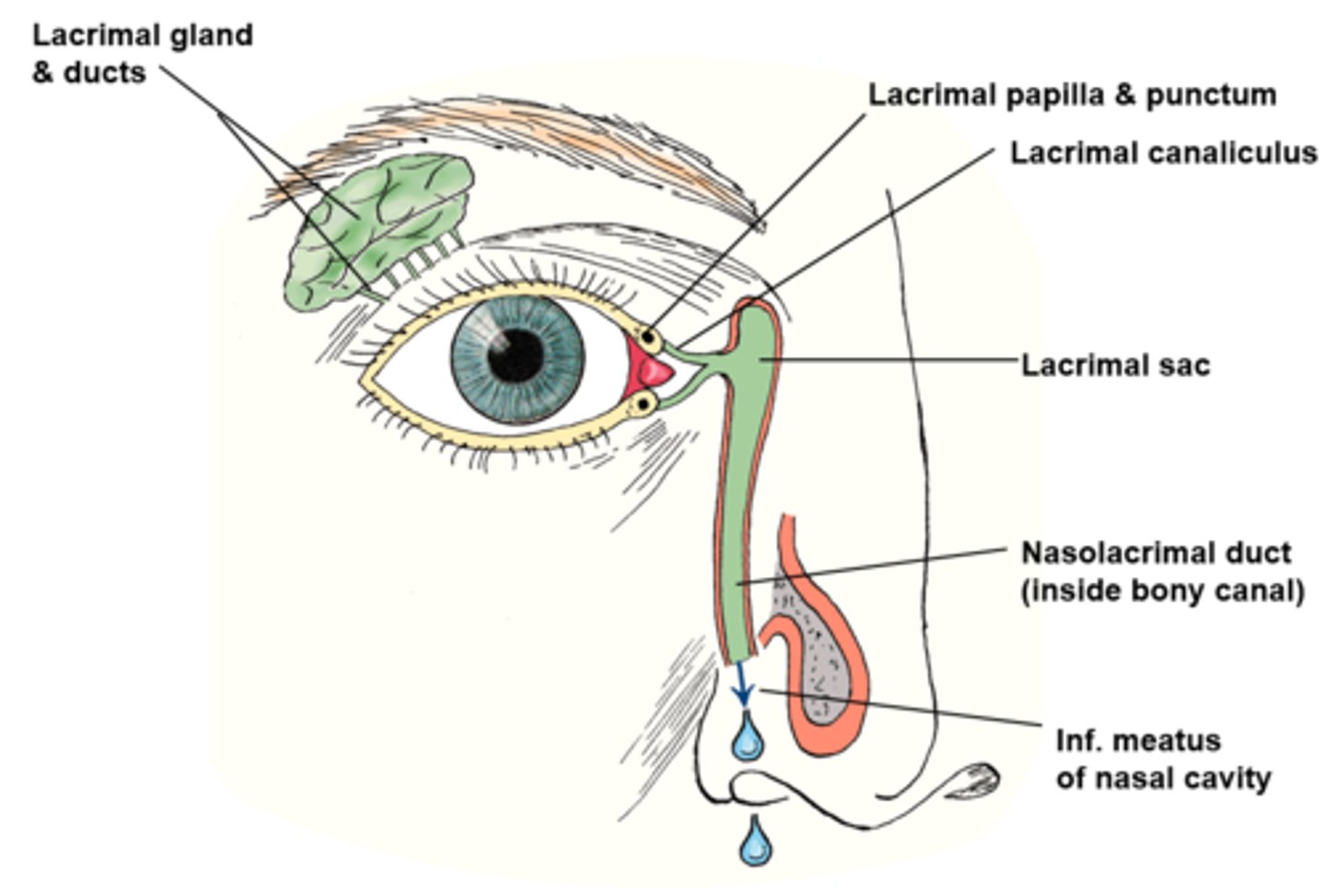
What is the lacrimal apparatus?
produces, distributes, and removes tears
what are the portions of the lacrimal apparatus? (3)
1. lacrimal gland
2. lacrimal canaliculi
3. nasolacrimal duct
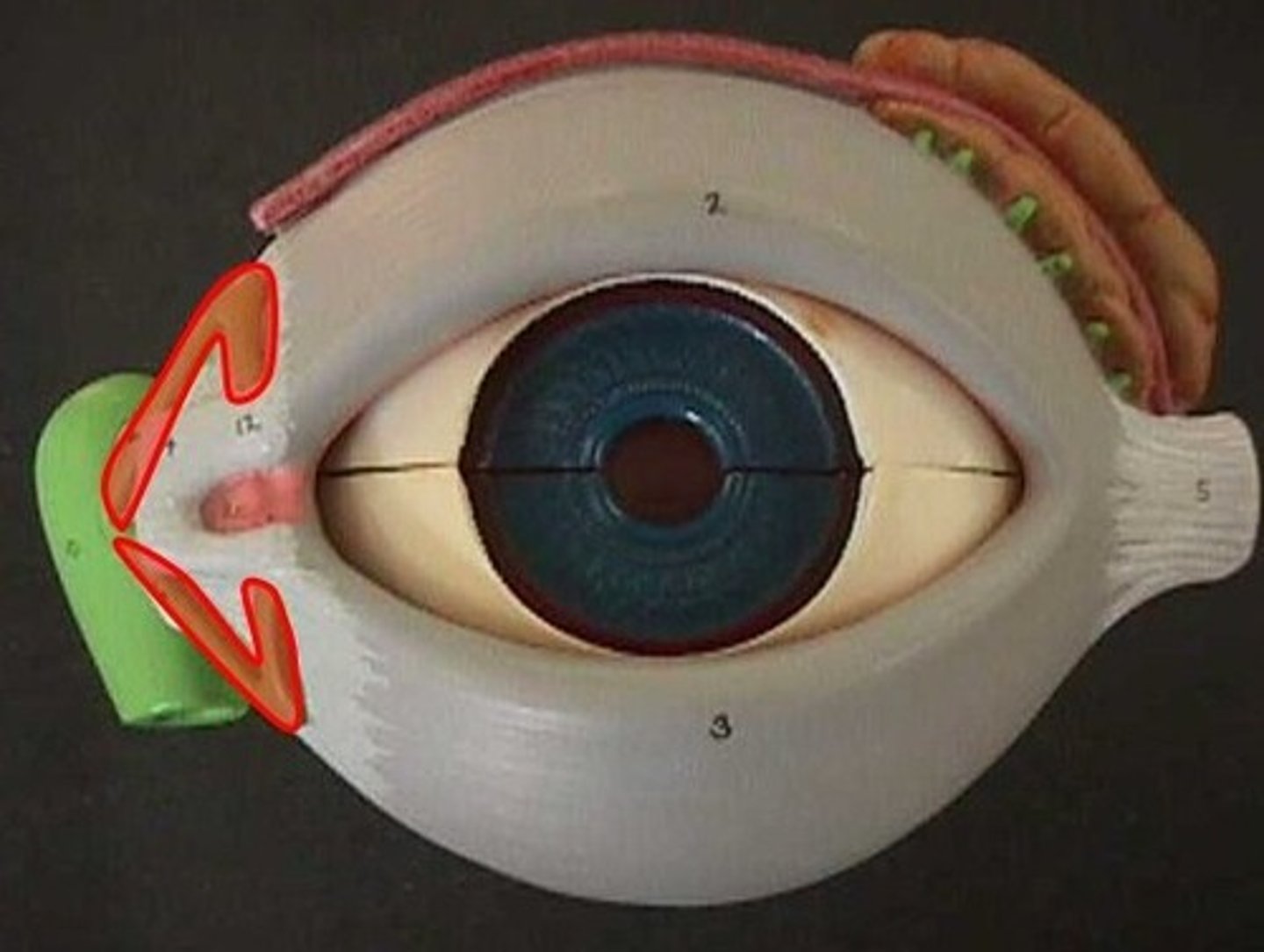
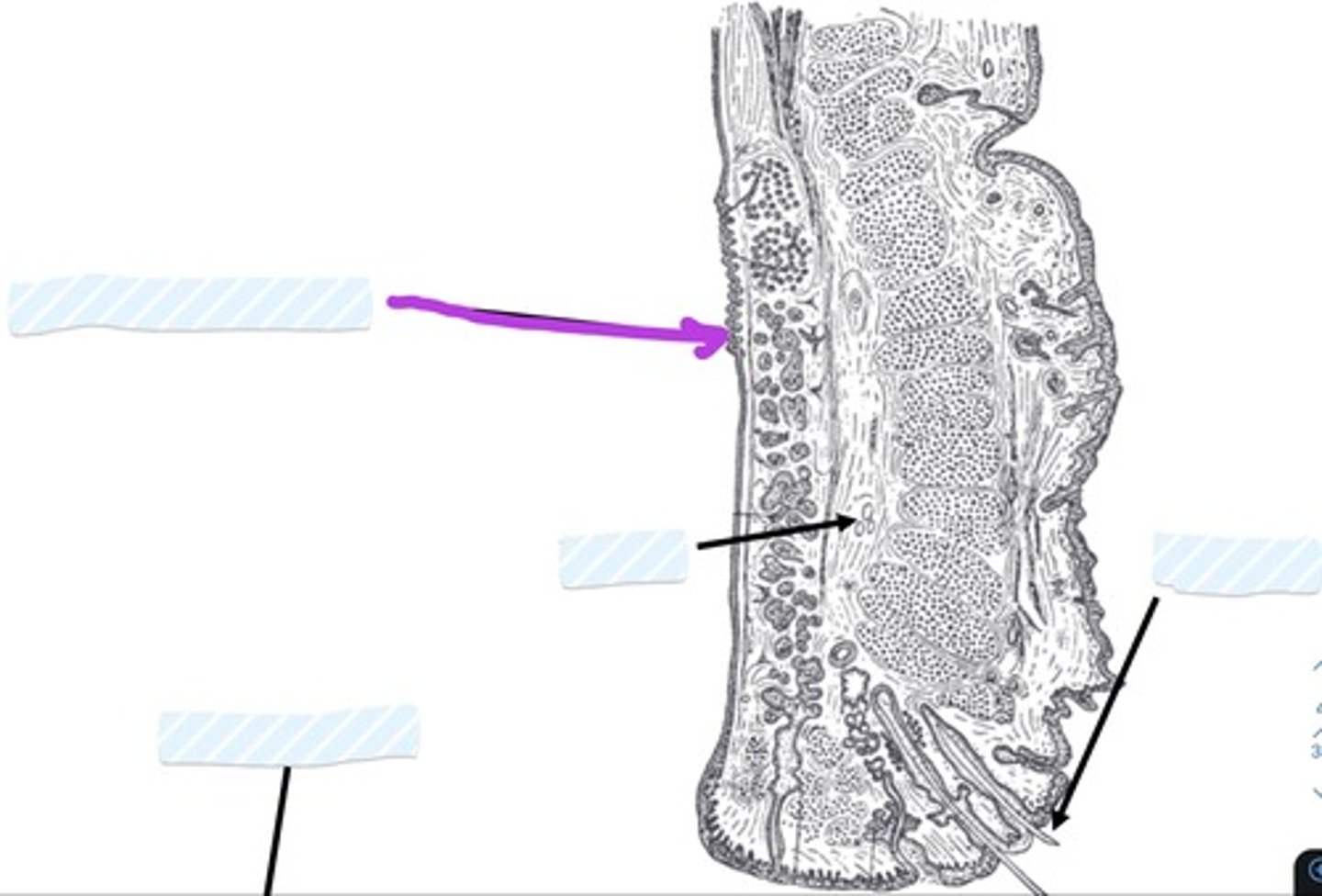
what is the lacrimal gland?
Almond shaped gland tucked in superolateral lacrimal fossa
secretes lacrimal fluid
· watery physiological saline
· moistens, lubricates surfaces of conjunctiva, cornea
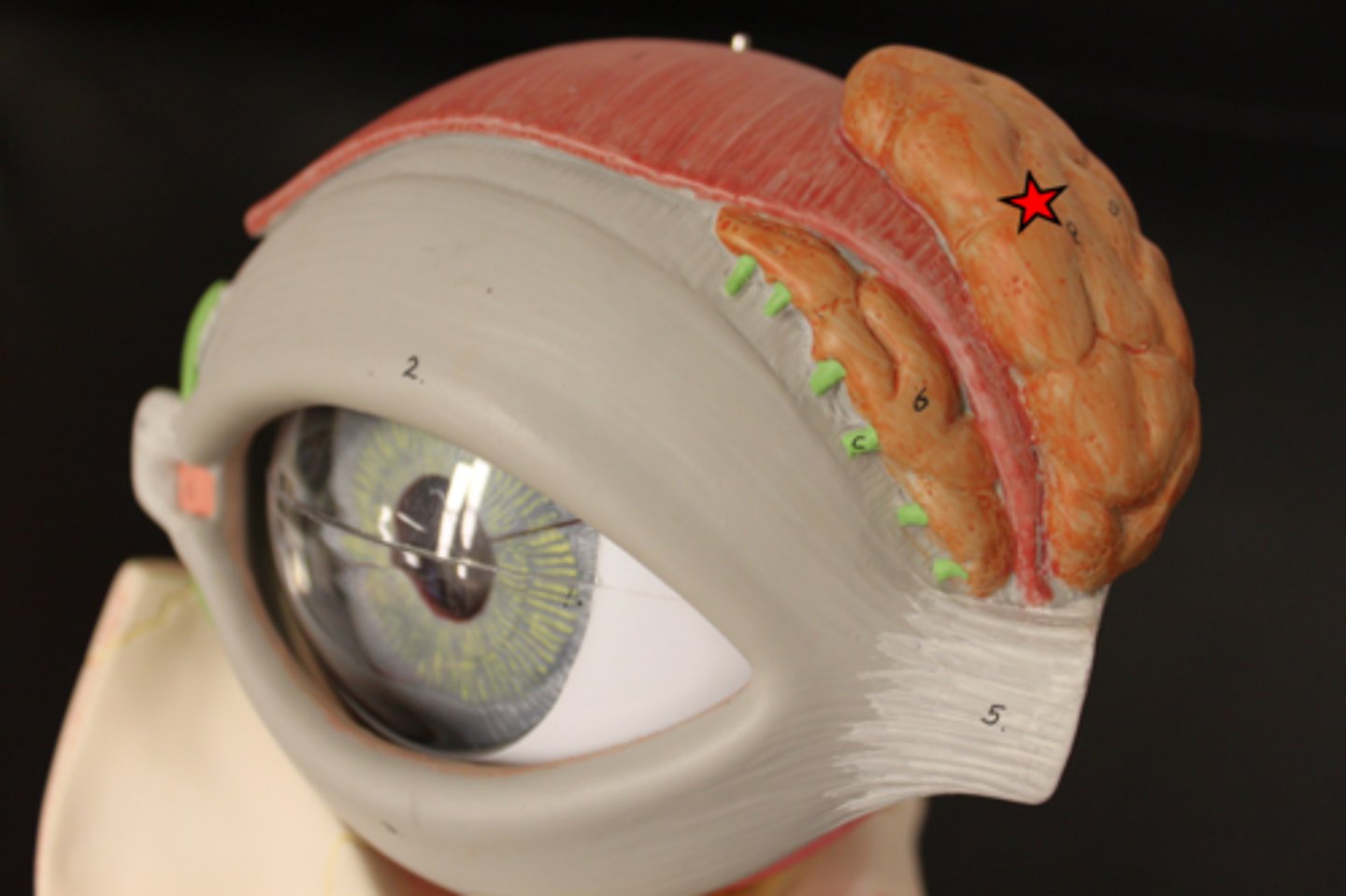
what is the lacrimal canaliculi?
drain lacrimal fluid to lacrimal sac (dilated superior part of nasolacrimal duct)
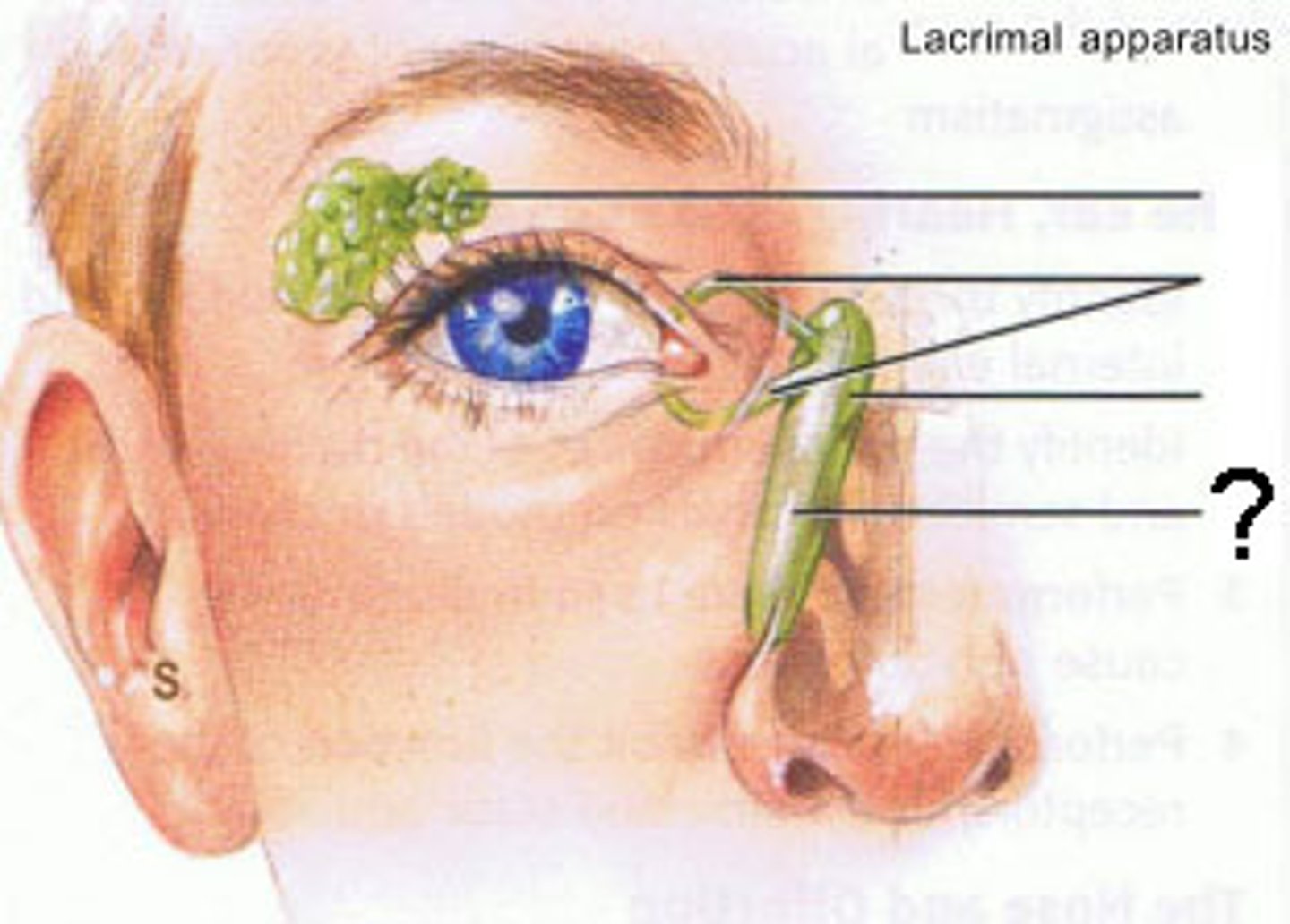
what is the nasolacrimal duct?
conveys lacrimal fluid to inferior nasal meatus in nasal cavity
describe the flow of fluid/tear production (5)
1. fluid production stimulated by parasympathetic impulses from facial nerve
2. eyelids come together in lateral-to-medial sequence, pushing fluid medially over cornea
3. drains by capillary action through lacrimal puncta, lacrimal canaliculi to lacrimal sac
4. fluid passes to inferior nasal meatus of nasal cavity through nasolacrimal duct.
5. drain posteriorly across floor of nasal cavity, eventually swallowed
what is the lacrimal sac?
provides passage of lacrimal fluid towards nasal cavity
what are the extraocular muscles of the orbit? (7)
Levator Palpebrae Superioris
lateral rectus
medial rectus
superior rectus
inferior rectus
inferior oblique
superior oblique
what do these muscles primarily work to do? where do they mostly originate?
· seven muscles work together to move superior eyelids, eyeballs.
· Most originate off common tendinous ring - fibrous cuff that surrounds optic canal, part of superior orbital fissure at apex of orbit
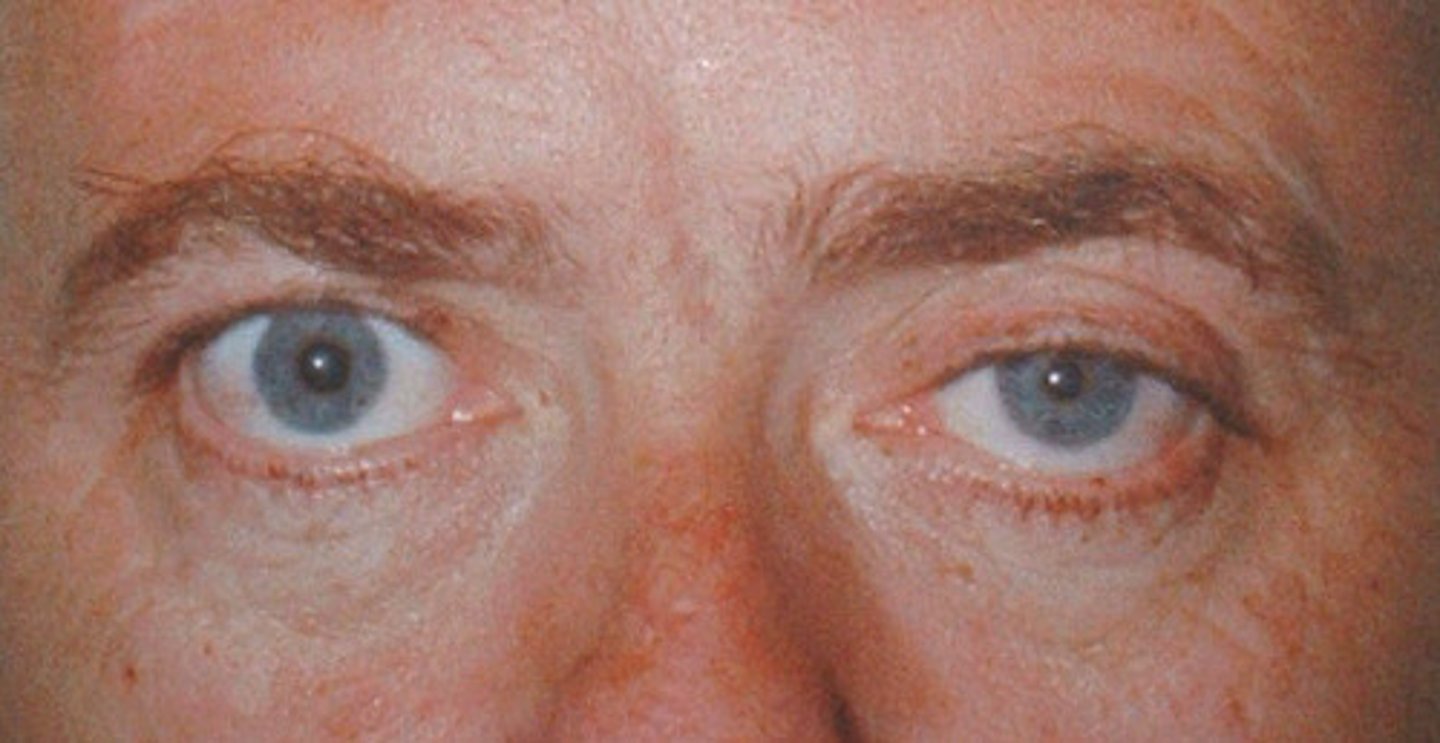
what muscle is associated with Horner's syndrome? (ptosis of the eyelid due to loss of sympathetic tone)
levator palpebrae superioris
this is because this muscle's primary function is to keep the eyelids open
levator palpebrae origin
roof of orbit
levator palpebrae insertion
upper eyelid
levator palpebrae action
elevates superior eyelid
levator palpebrae innervation
oculomotor nerve (CNIII)
lateral rectus origin
common tendinous ring
lateral rectus insertion
lateral surface of eye
lateral rectus action
abduction
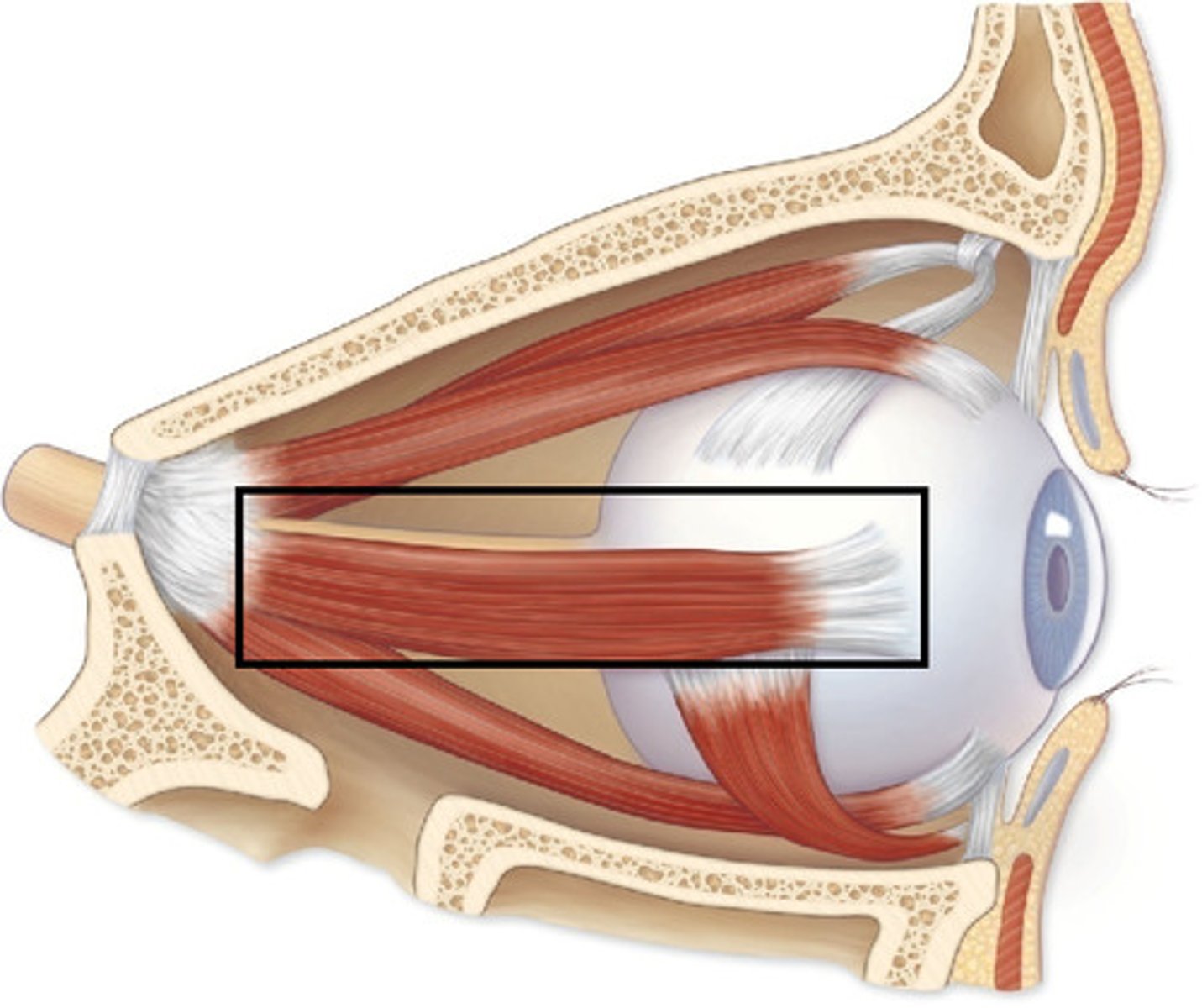
lateral rectus innervation
abducens nerve
medial rectus origin
common tendinous ring
medial rectus insertion
medial surface of eyeball
medial rectus action
adduction
medial rectus innervation
Oculomotor nerve (CN III)
superior rectus origin
common tendinous ring
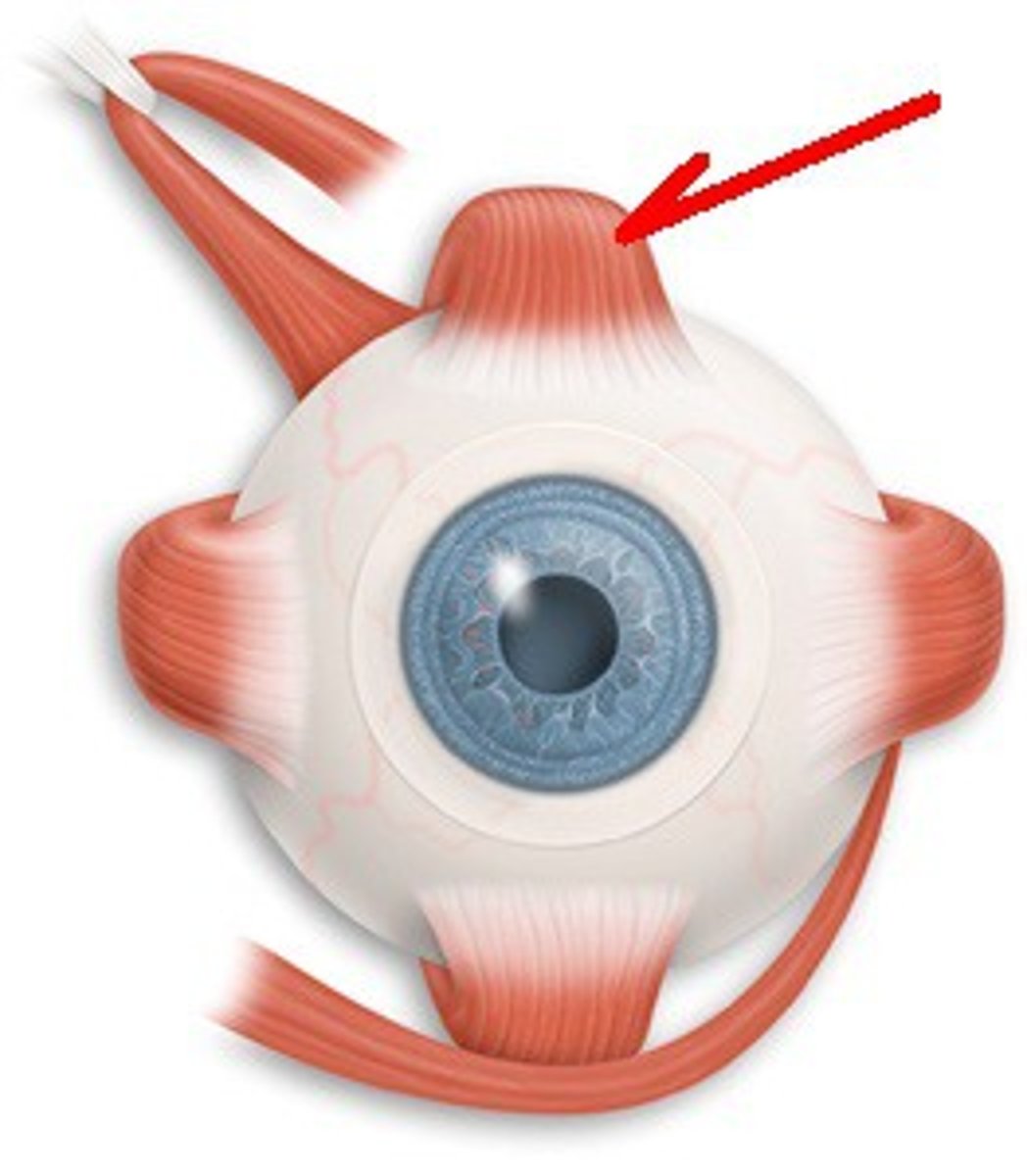
superior rectus insertion
superior surface of eyeball
superior rectus action
turns eyeball superiorly
superior rectus innervation
Oculomotor nerve (CN III)
inferior rectus origin
common tendinous ring
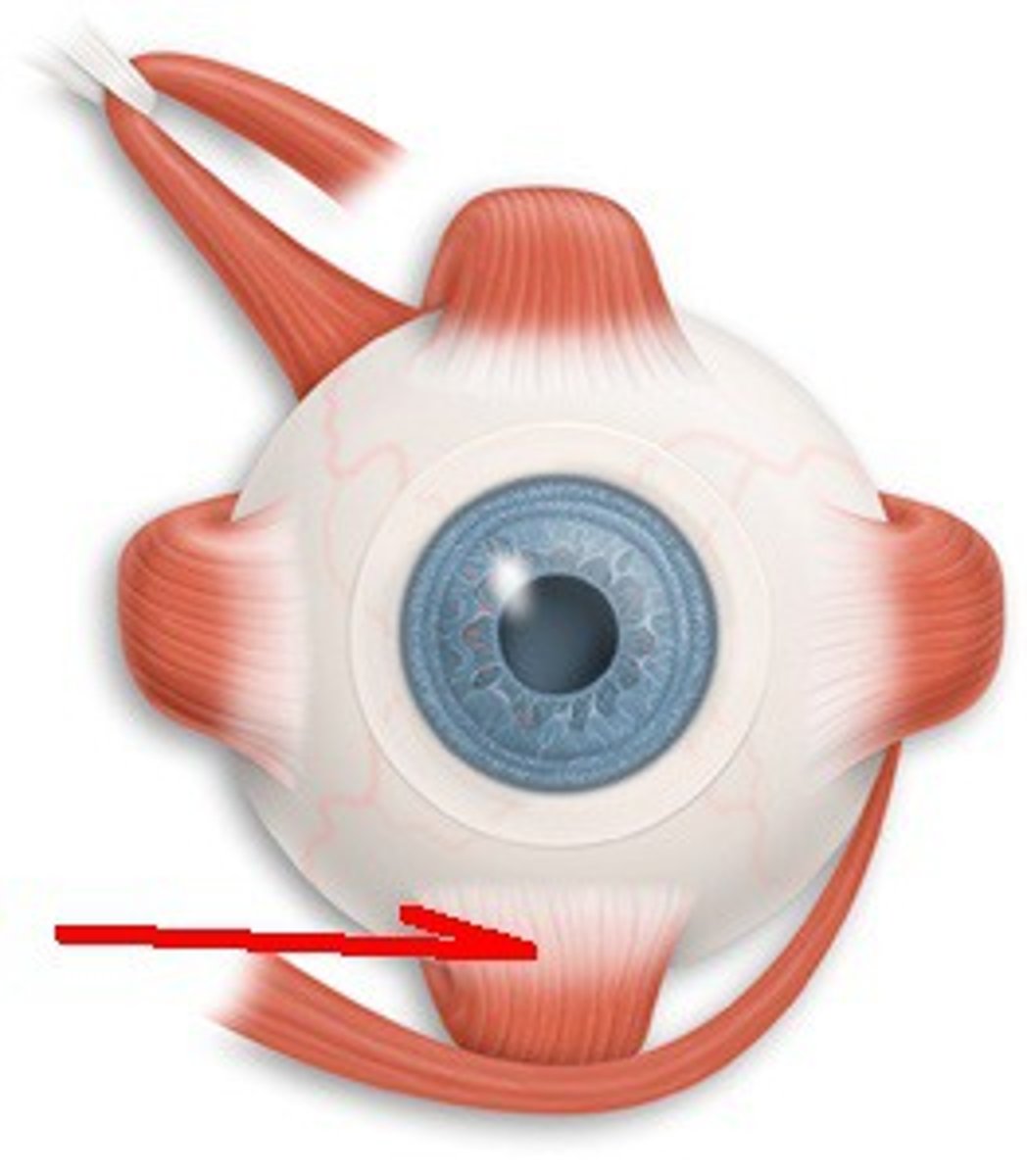
inferior rectus insertion
inferior eye
inferior rectus action
depresses eye
inferior rectus innervation
Oculomotor nerve (CN III)
inferior oblique origin
anteromedial floor of orbit
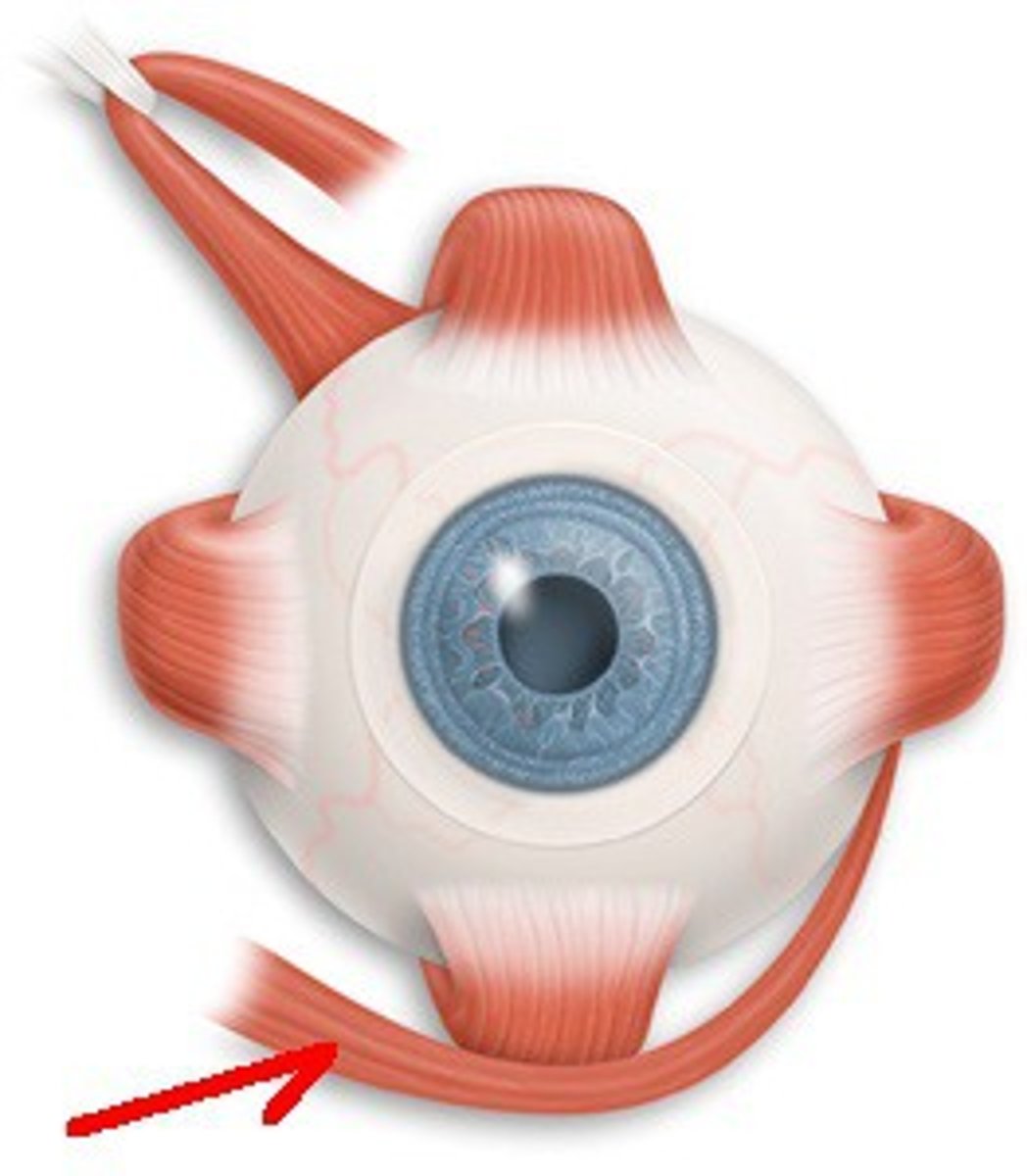
inferior oblique insertion
inferior, lateral surface of eyeball
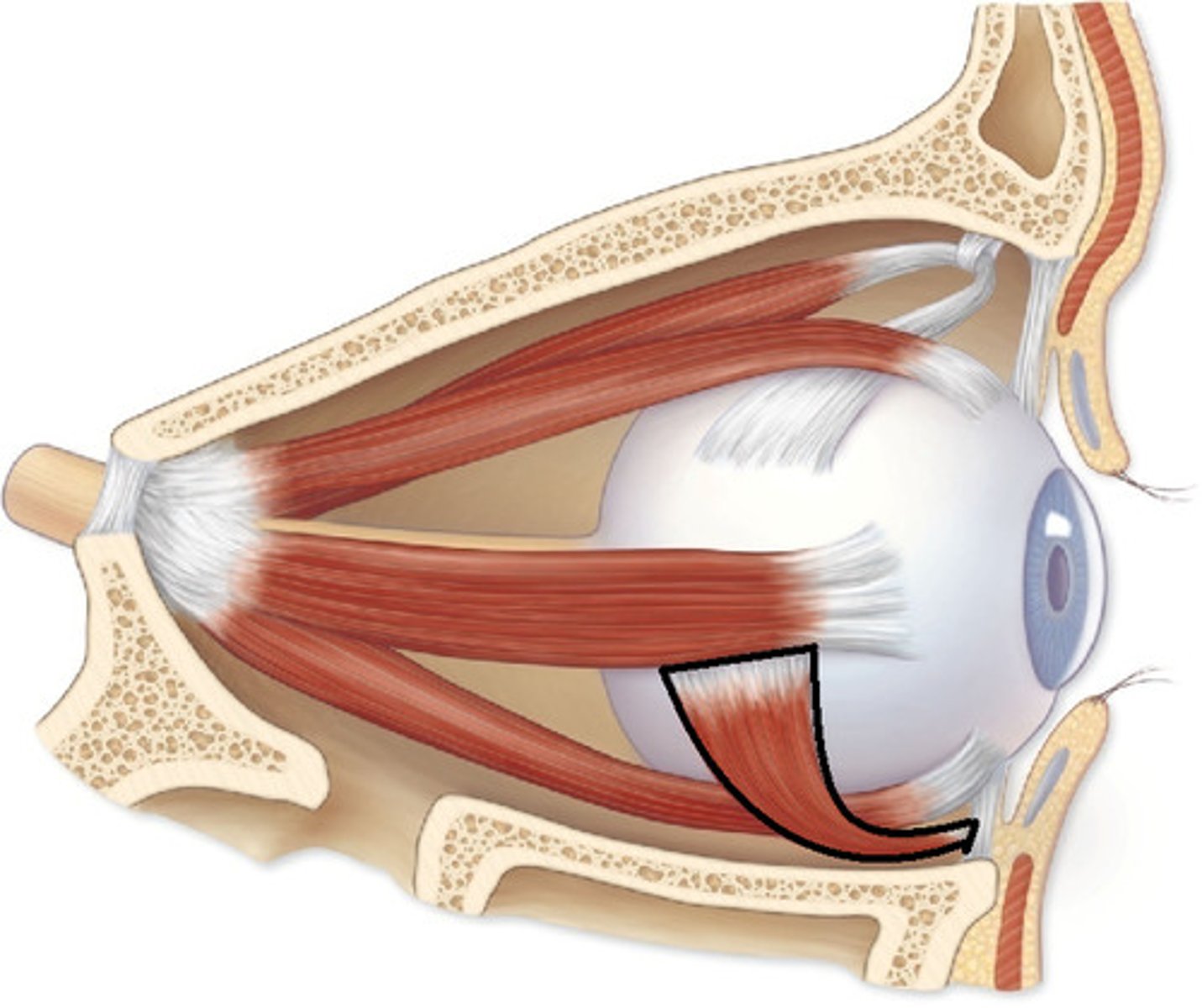
inferior oblique action
Abducts, elevates, externally (extorsion) rotates the eye
inferior oblique innervation
oculomotor nerve
superior oblique origin
posterior orbit
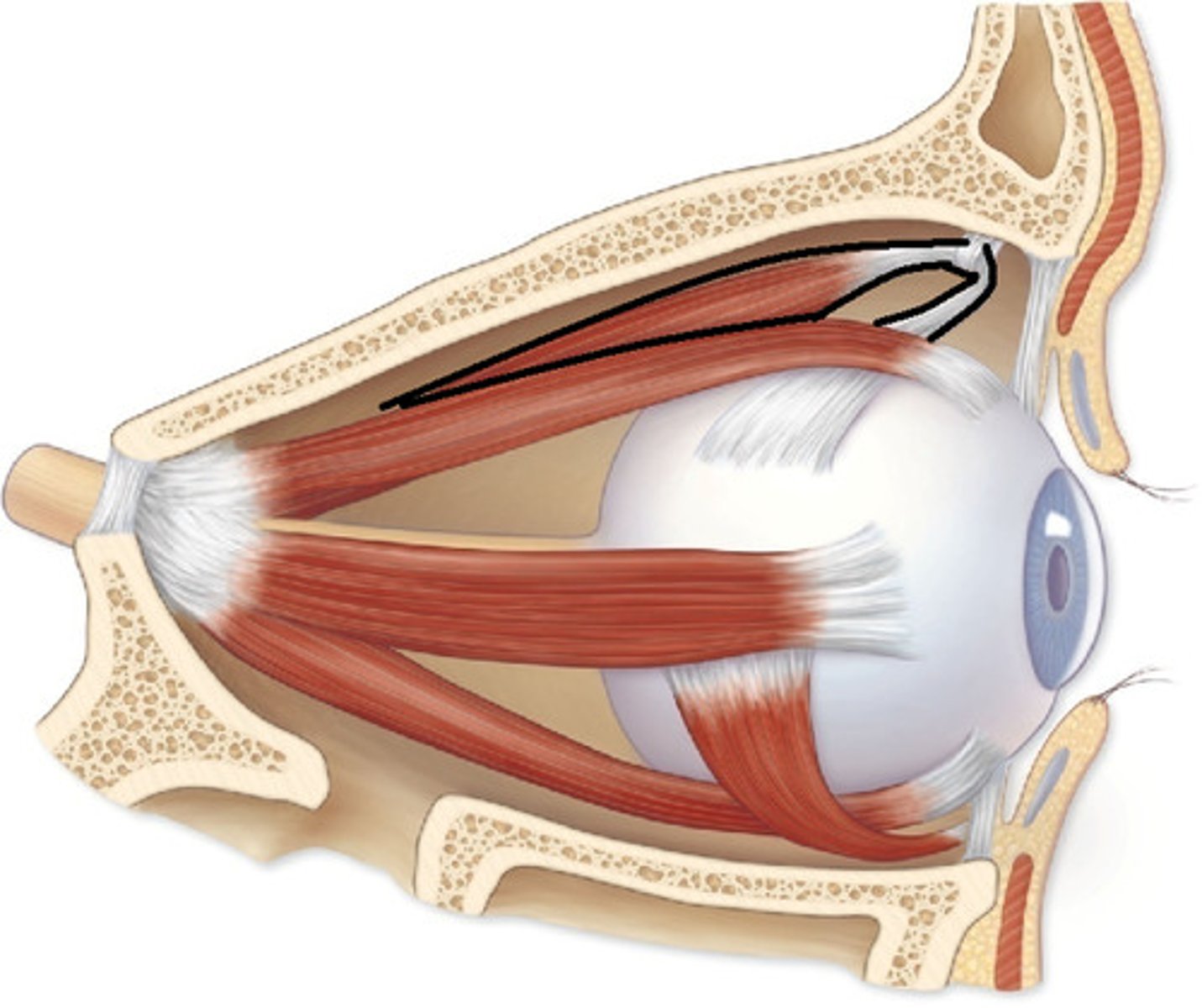
superior oblique insertion
superior, lateral surface of eyeball
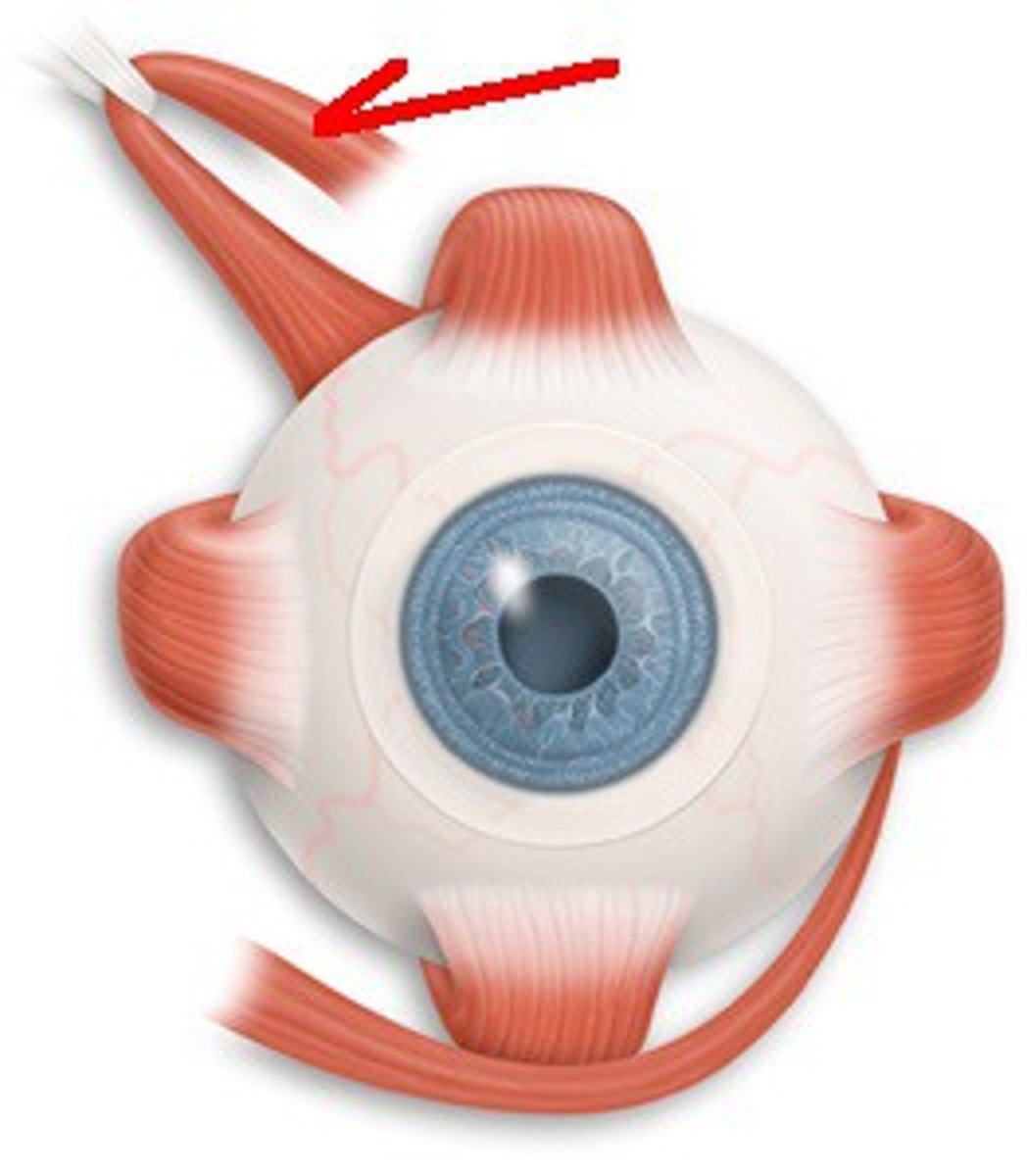
superior oblique action
abducts, depresses and internally (intorsion) rotates the eye
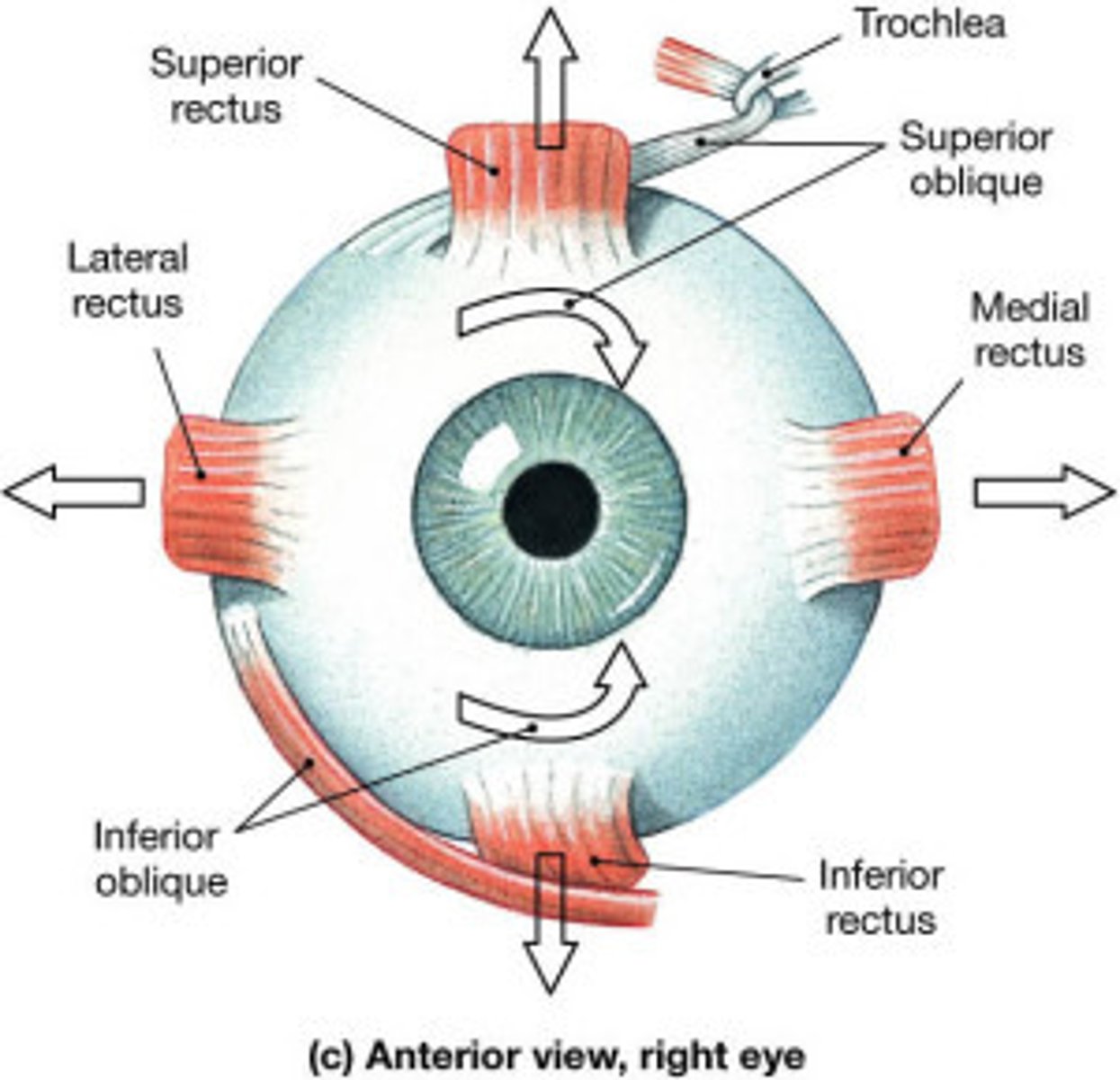
superior oblique innervation
trochlear nerve
what are the ocular muscles not innervated by the oculomotor nerve?
1. superior oblique m. -> trochlear n.
2. lateral rectus m. -> abducens n.
what are the main nerves of the orbit? (5)
1. optic nerve
2. oculomotor nerve
3. abducens nerve
4. trochlear nerve
5. opthalmic nerve
what does the oculomotor nerve do?
controls eye movement
what are the divisions of the oculomotor nerve and what do those divisions do? (2)
1. superior division
- supplies superior rectus, levator palpebrae superioris
2. inferior division
- supplies medial, inferior rectus, inferior oblique
- carries presynaptic parasympathetic fibers to ciliary ganglion, postsynaptic parasympathetic fibers to eye
where does the trochlear nerve pass?
medial surface of superior oblique muscle
where does the abducens nerve pass?
directly to inferior rectus muscle
what 3 branches does the Opthalmic nerve divide into, in the orbit? (Remember, the Opthalmic nerve is a branch of the trigeminal nerve)
1. frontal
2. nasociliary
3. lacrimal
where do the frontal, nasociliary, and lacrimal nerves pass through?
superior orbital fissure
what do the frontal, nasociliary, and lacrimal nerves supply?
supply structures related to anterior orbit (e.g., lacrimal gland, eyelids, face, scalp)
what artery mainly supplies the orbit?
Opthalmic artery
the ophthalmic artery branches from what?
internal carotid a.
what are the sub-arteries of the orbit? (3)
1. infraorbital a. (from external carotid)
2. central artery of retina (from ophthalmic artery)
3. short and long ciliary arteries
the venous drainage of the orbit is done through what veins?
1. superior ophthalmic vein
2. inferior opthalmic vein
where do the superior and inferior ophthalmic veins pass through?
superior orbital fissure
where do the superior and inferior vena cava veins empty?
cavernous sinus
Opthalmic nerve:
what two branches come off the frontal branch of the Opthalmic nerve?
1. supraorbital
2. supratrochlear
what does the Opthalmic nerve and its frontal branches supply?
skin of the forehead
Opthalmic nerve:
what branches come off the nasociliary branch of the Opthalmic nerve?
1. posterior ethmoidal
2. anterior ethmoidal
3. infratrochlear
what does the opthalmic nerve and it's nasociliary branches supply?
ethmoidal air cells, external nose, cutaneous bridge of nose
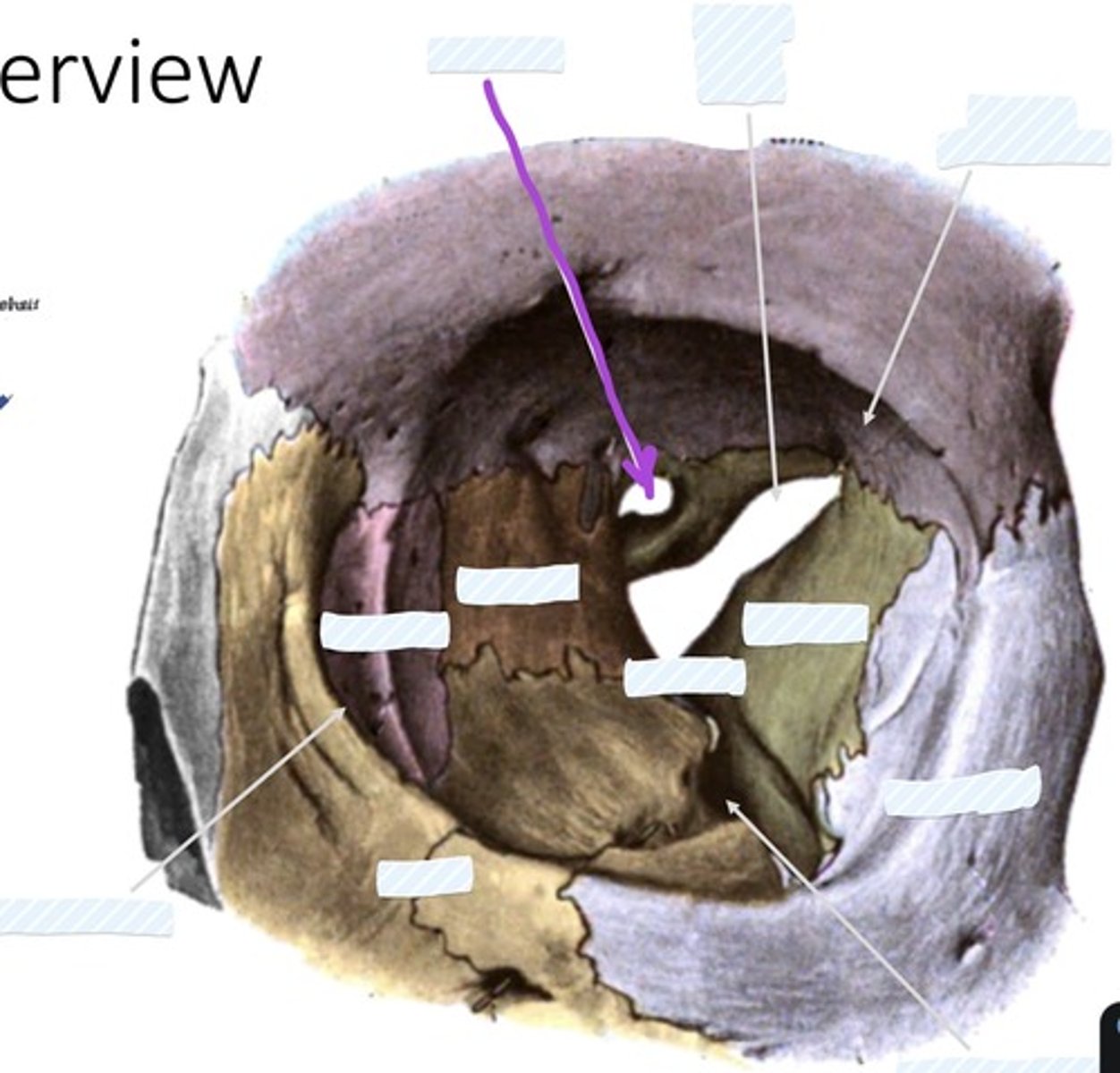
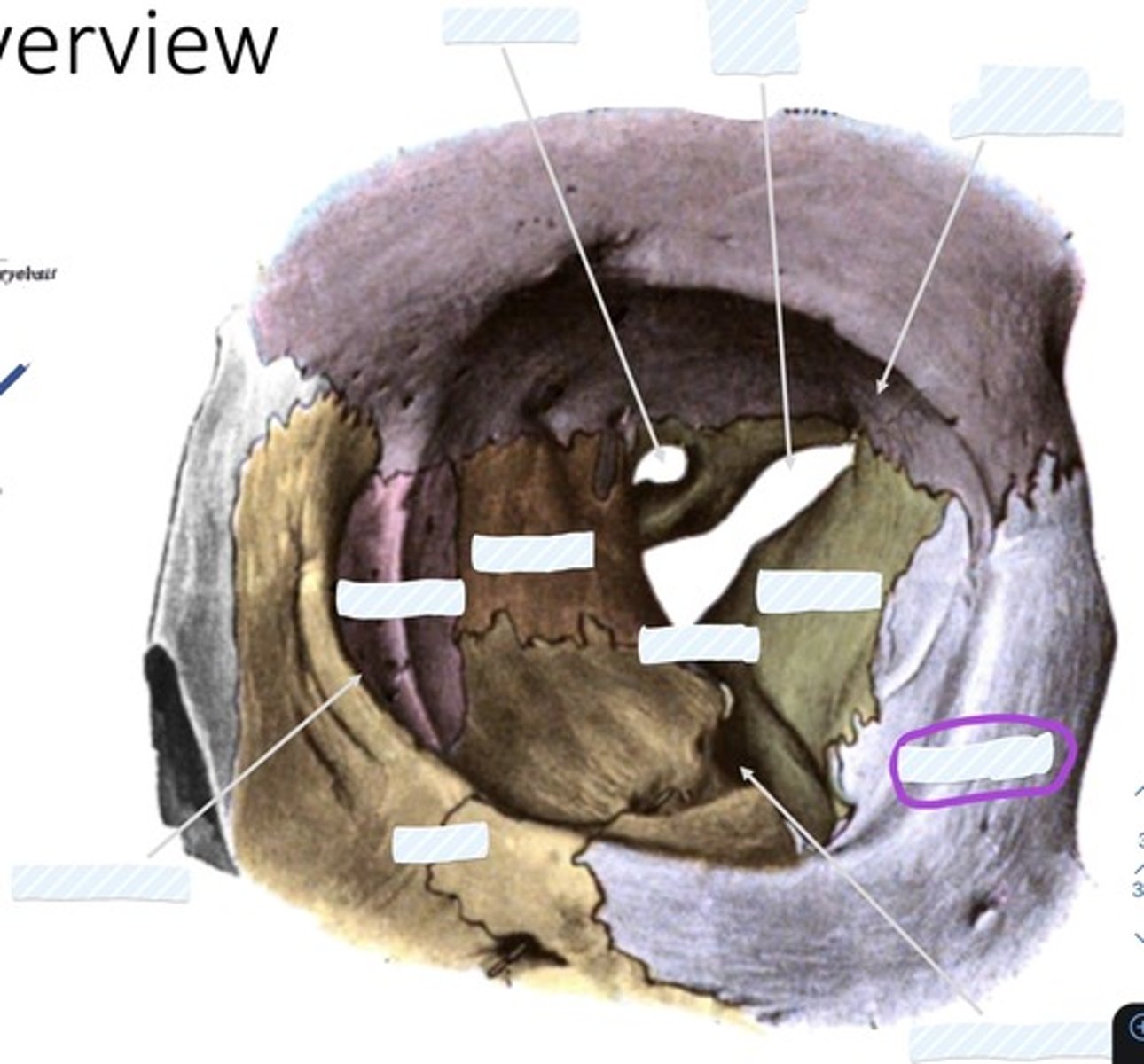
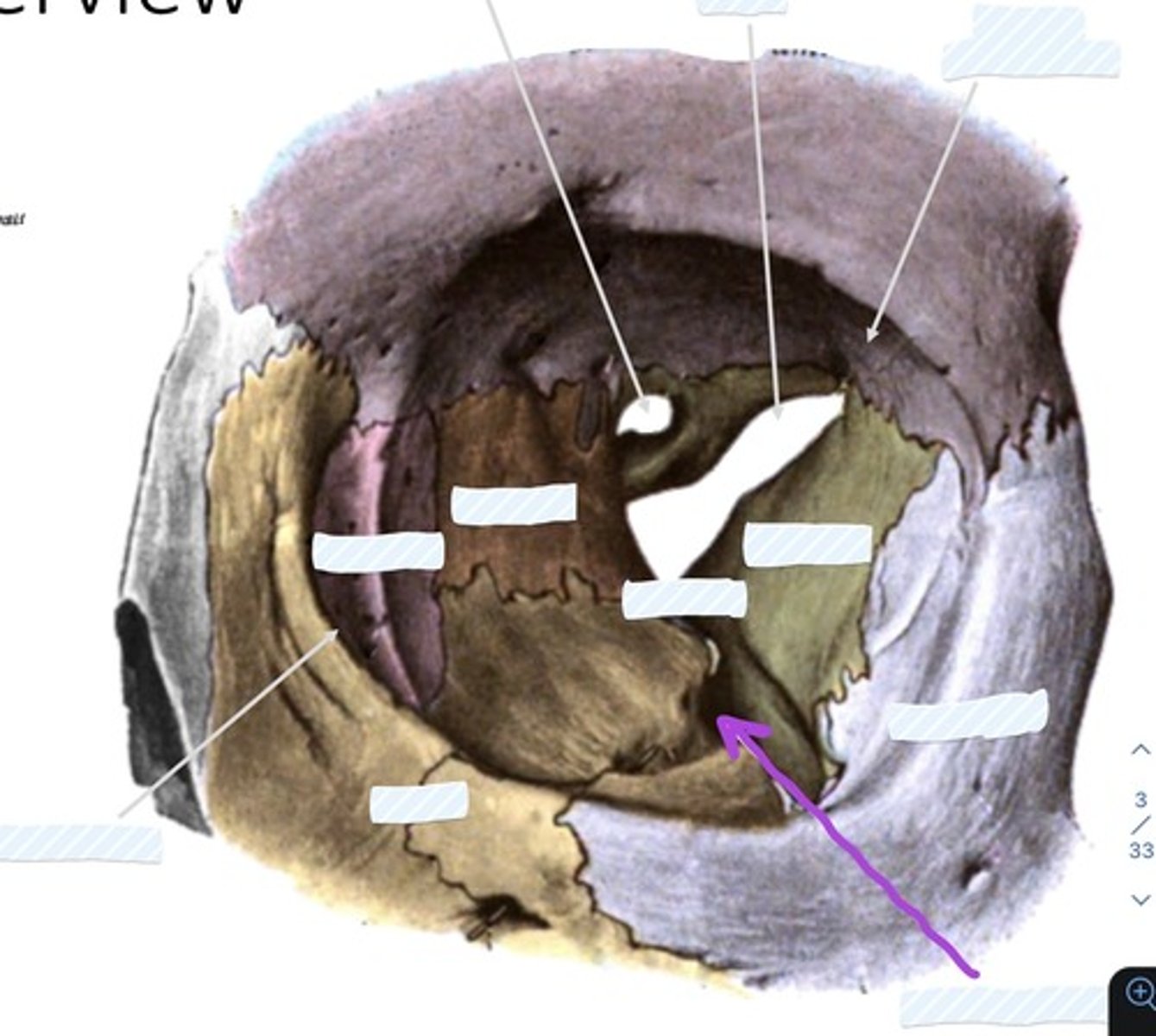
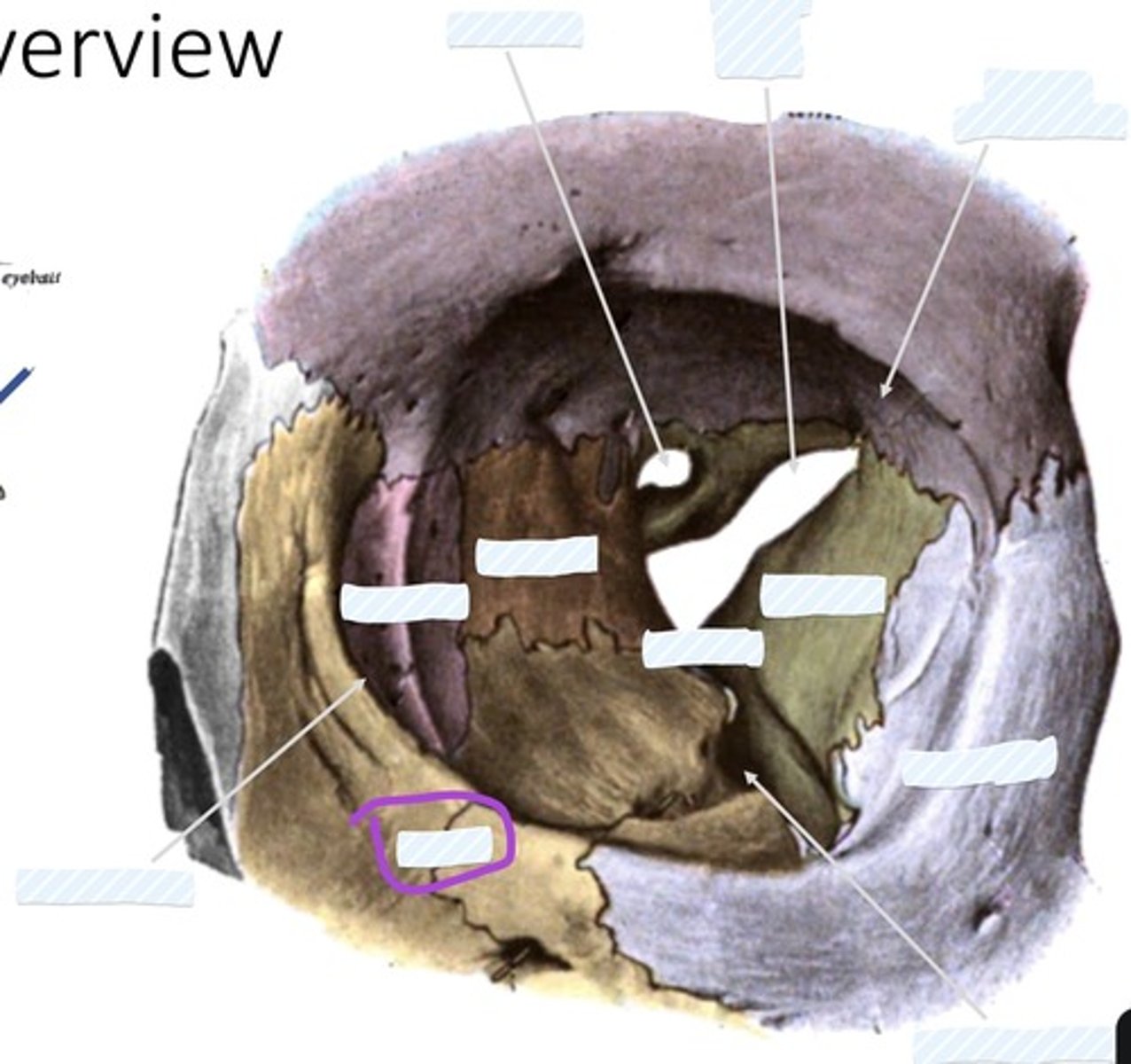
Optic canal
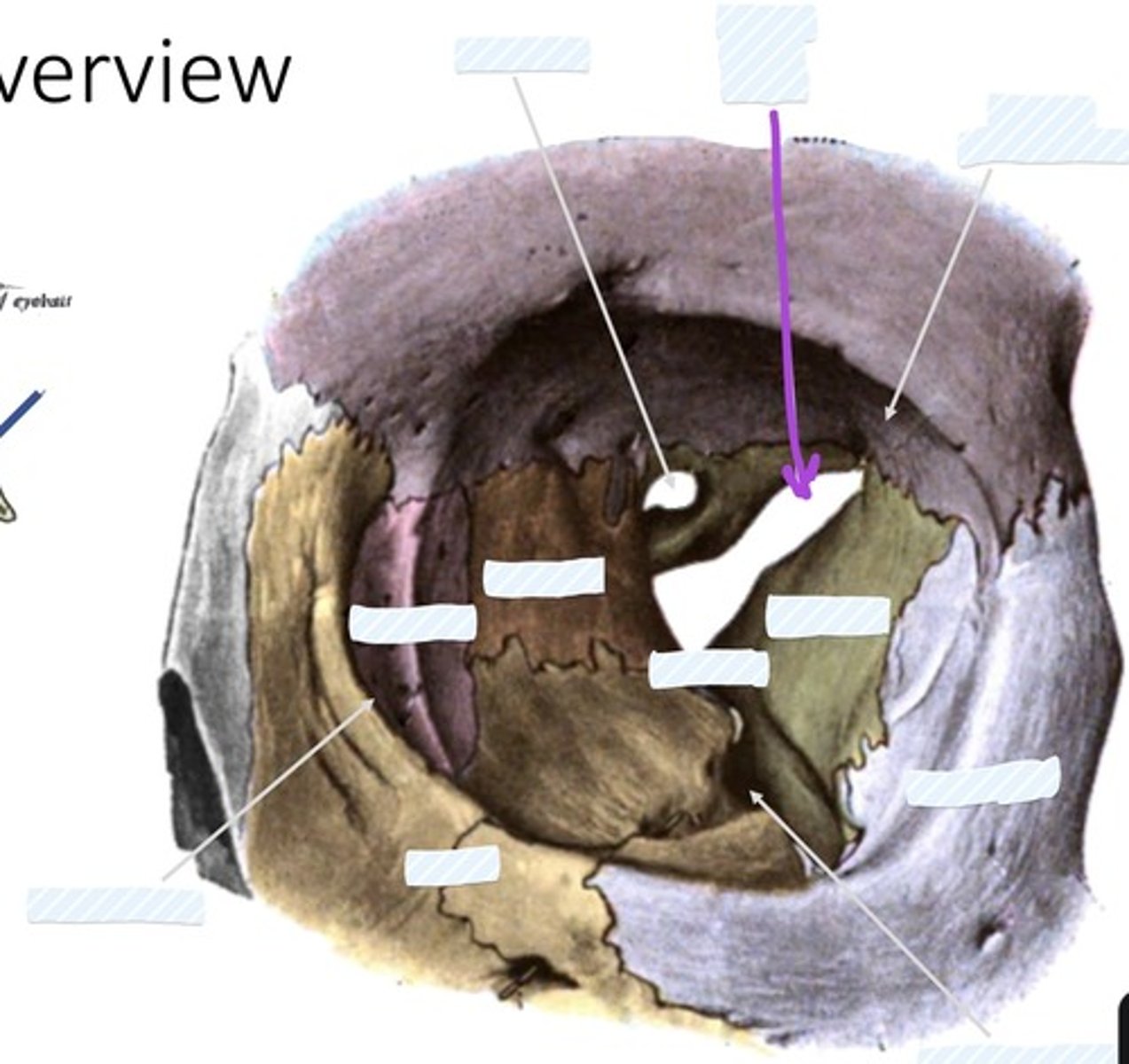
Superior orbital fissure
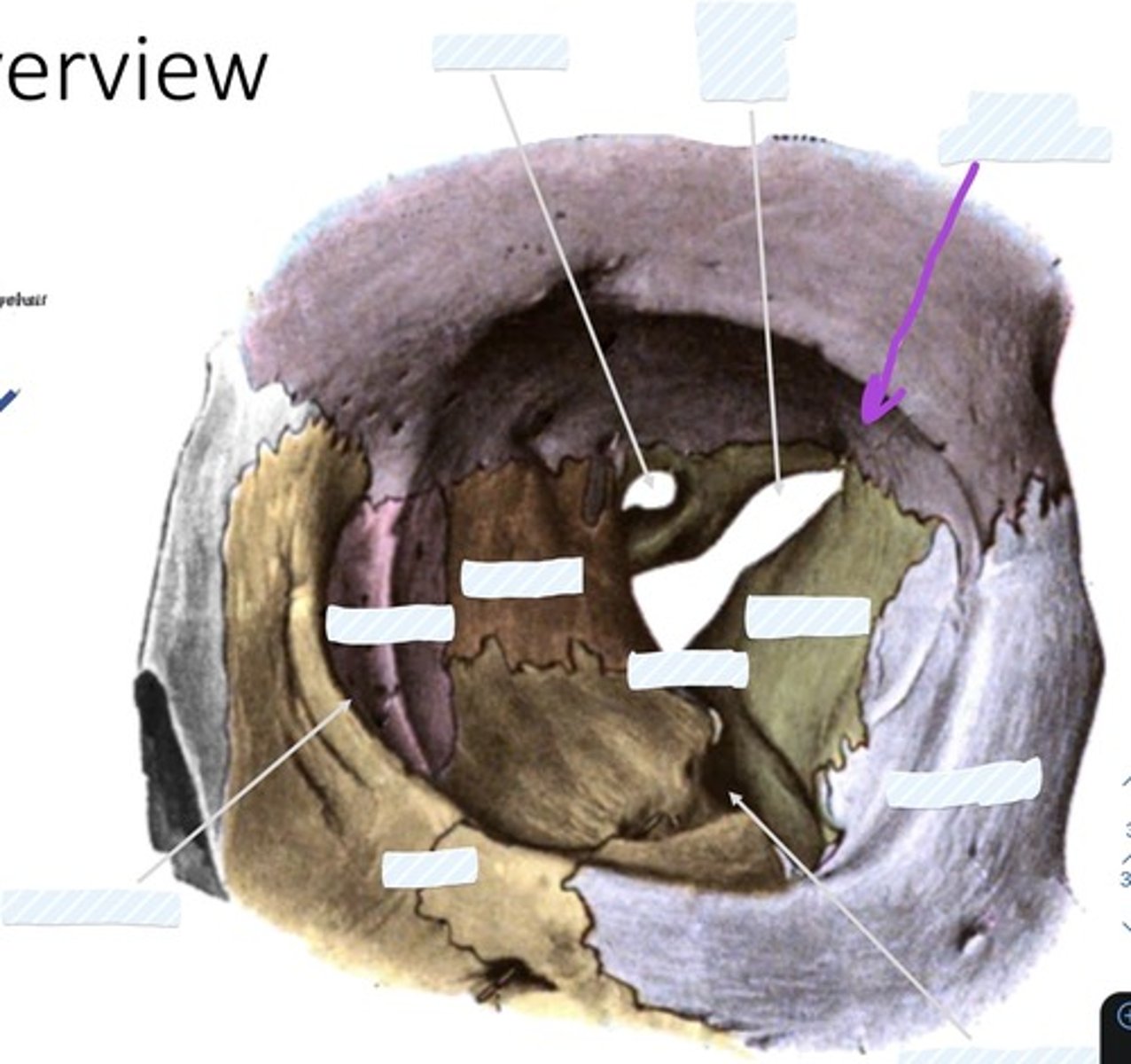
Fossa for lacrimal gland
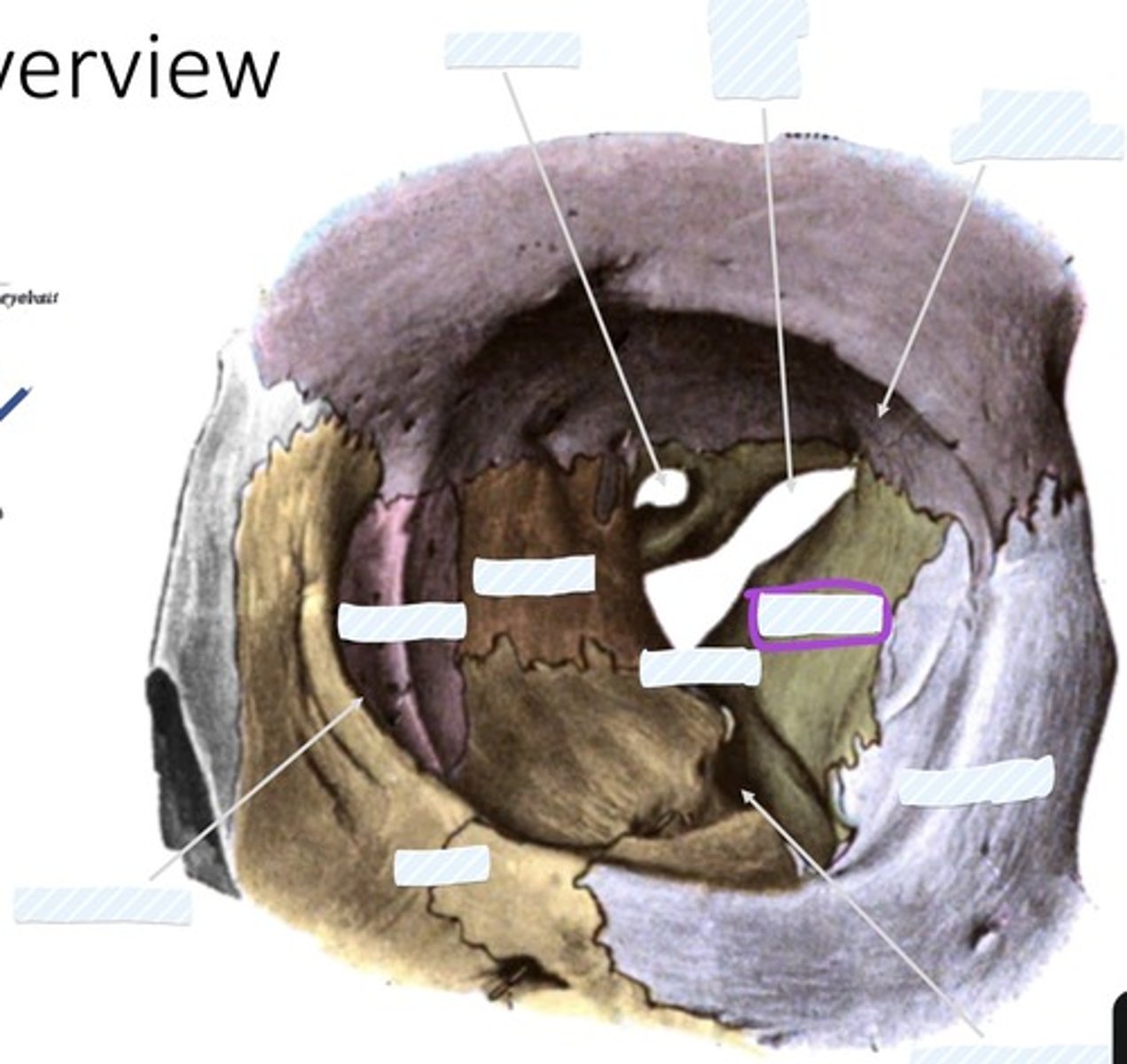
Sphenoid bone
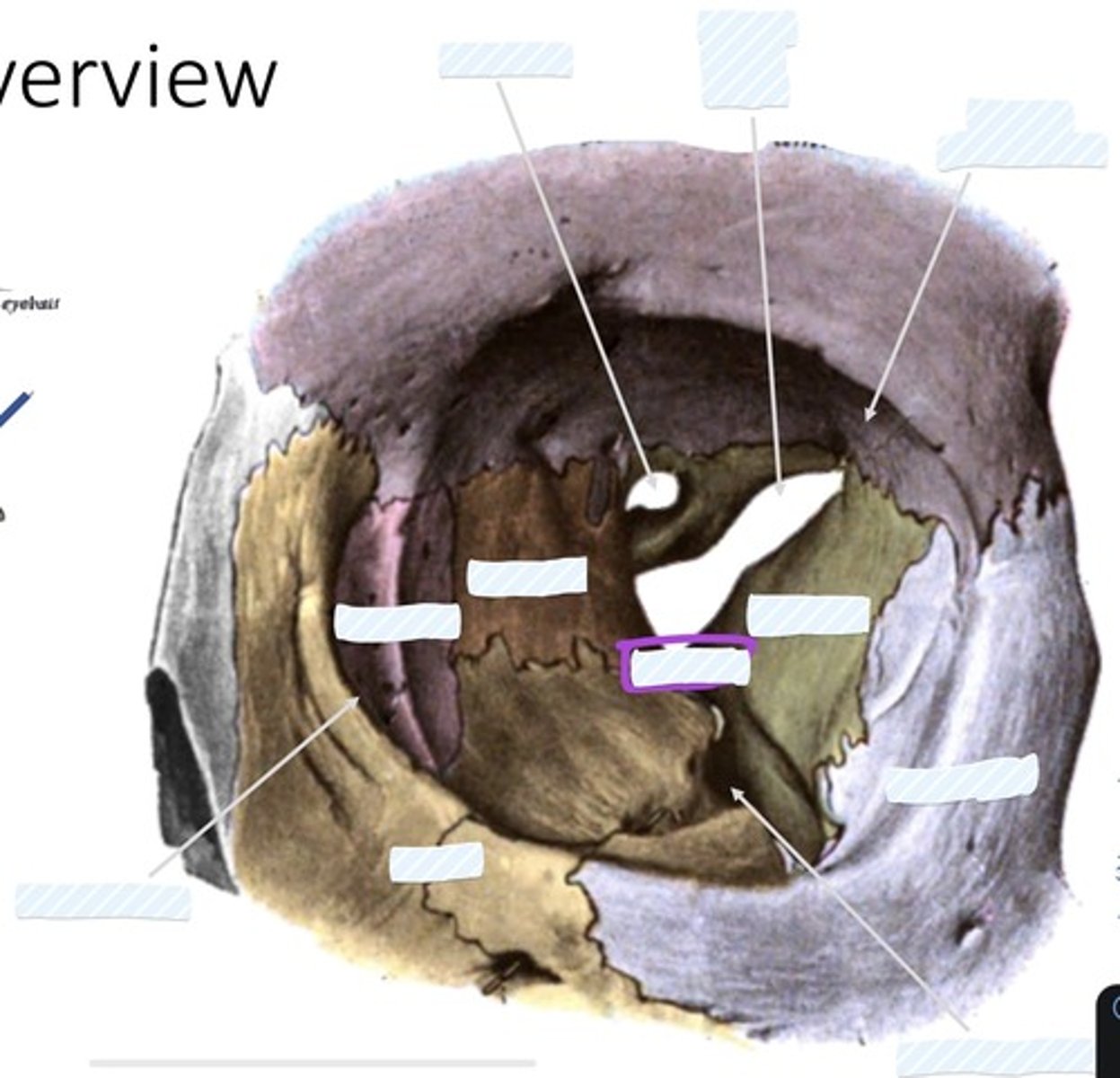
palatine bone
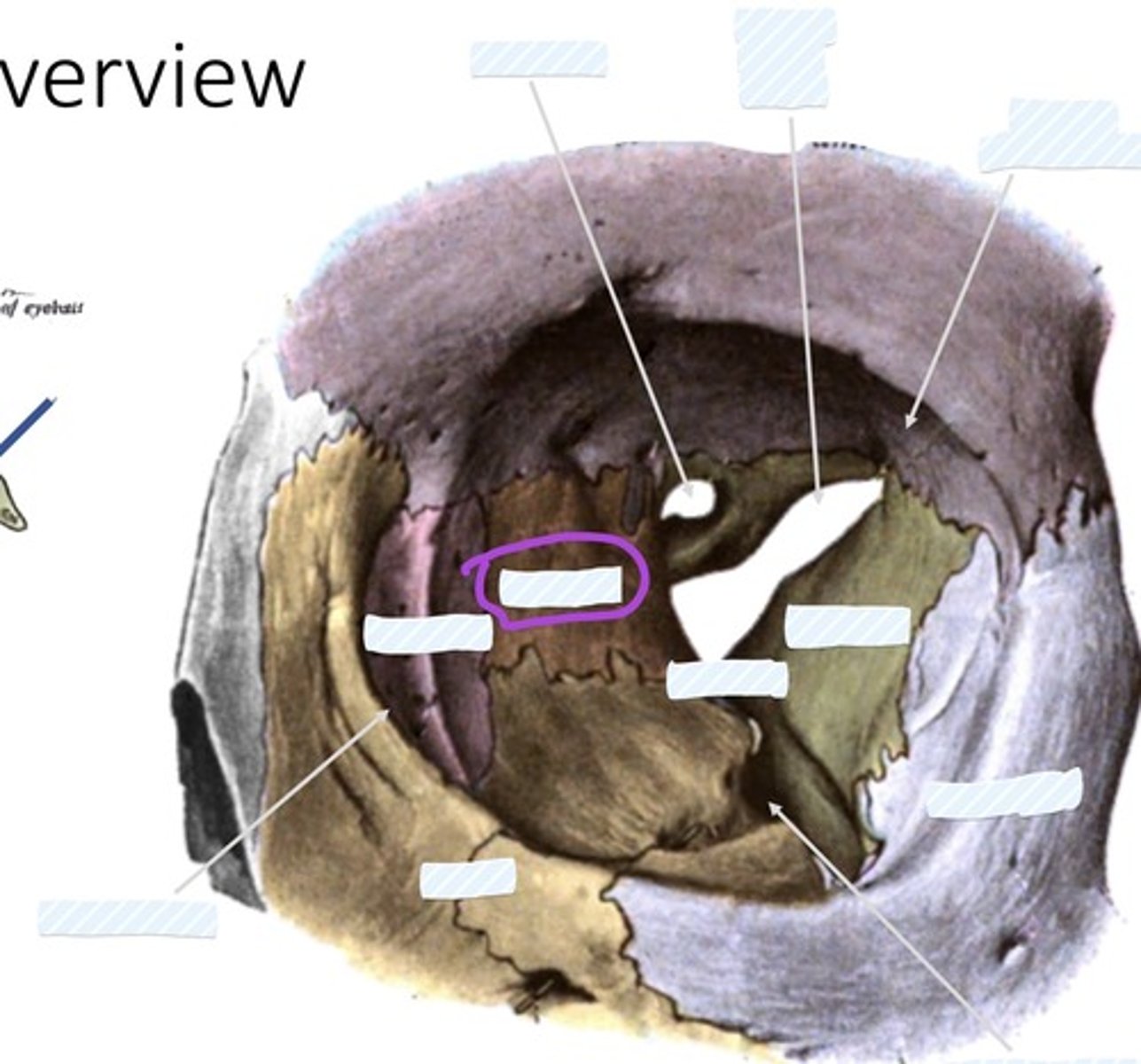
Ethmoid bone
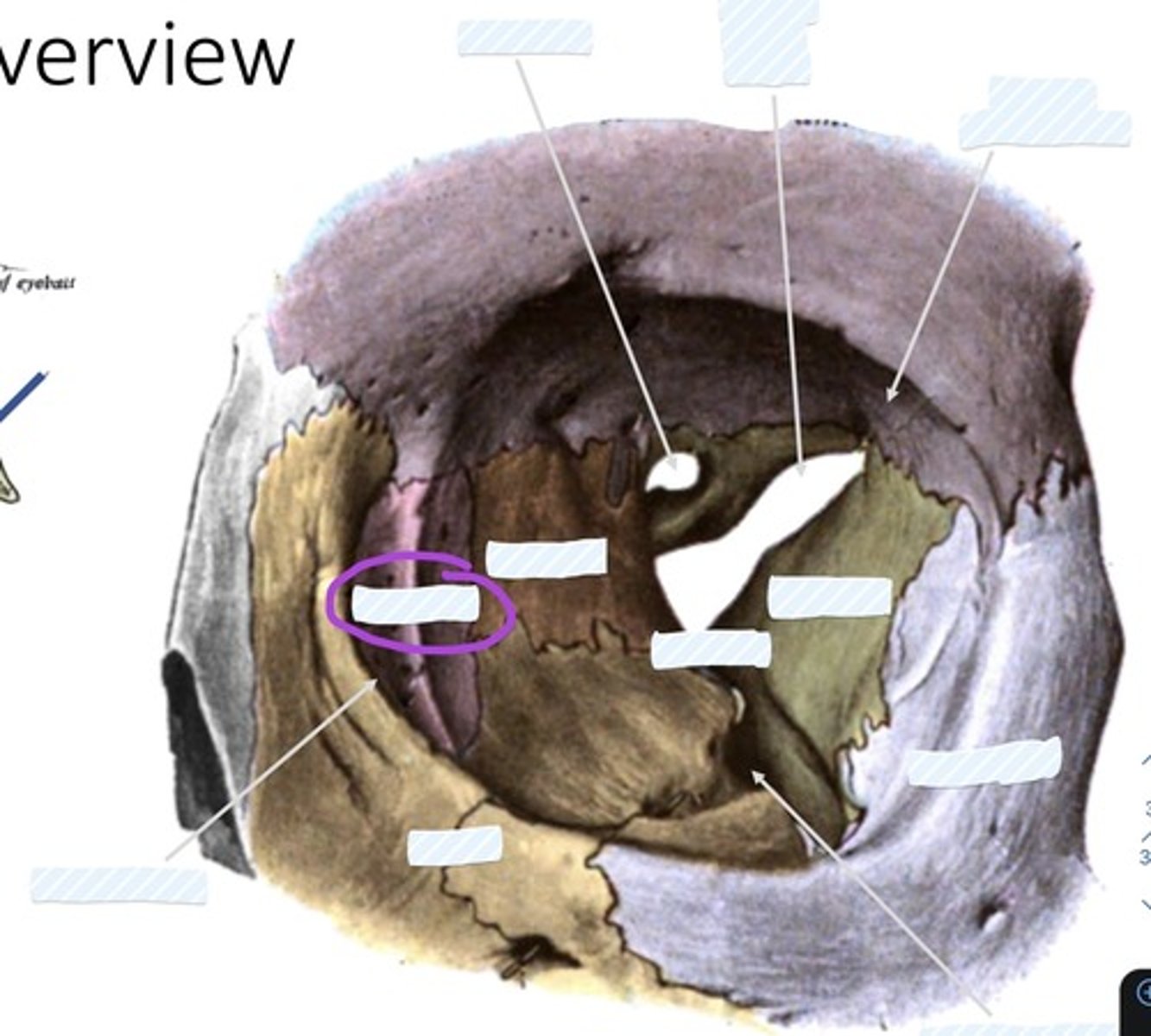
Lacrimal bone
Zygomatic bone
Inferior orbital fissure
Maxilla
Palpebral Conjunctiva
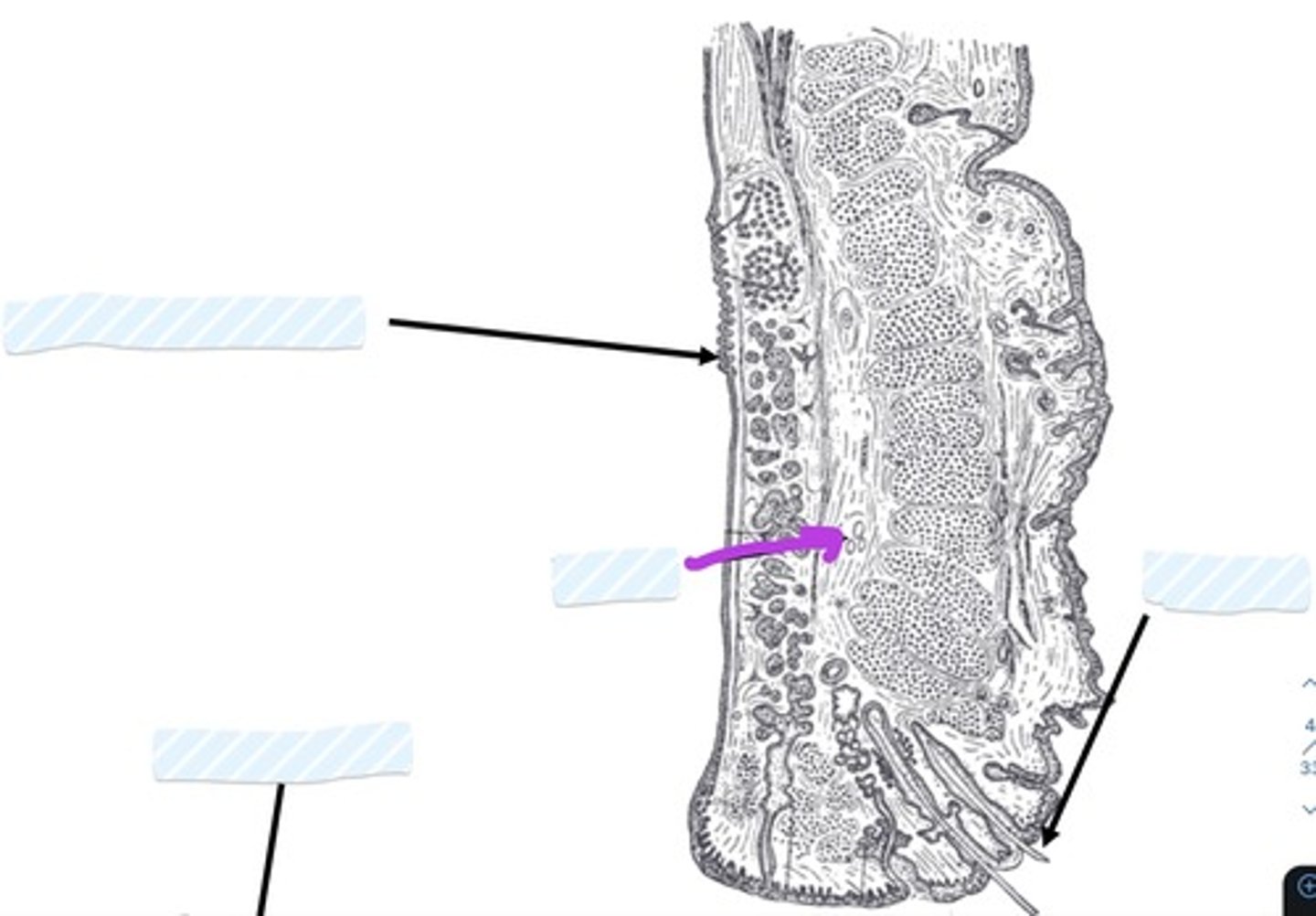
Tarsus
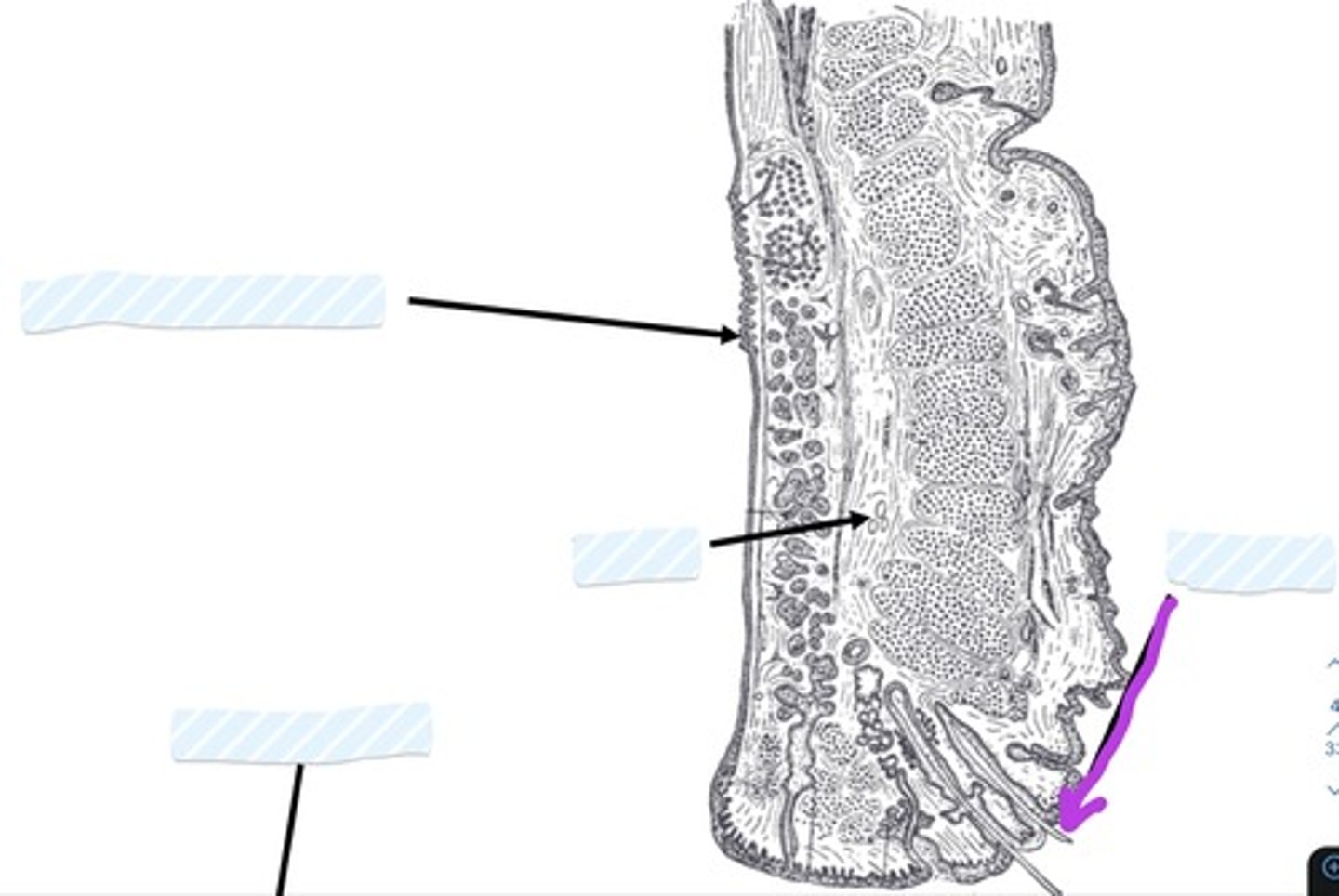
Eyelashes
Orbital septum
Medial palpebral ligament
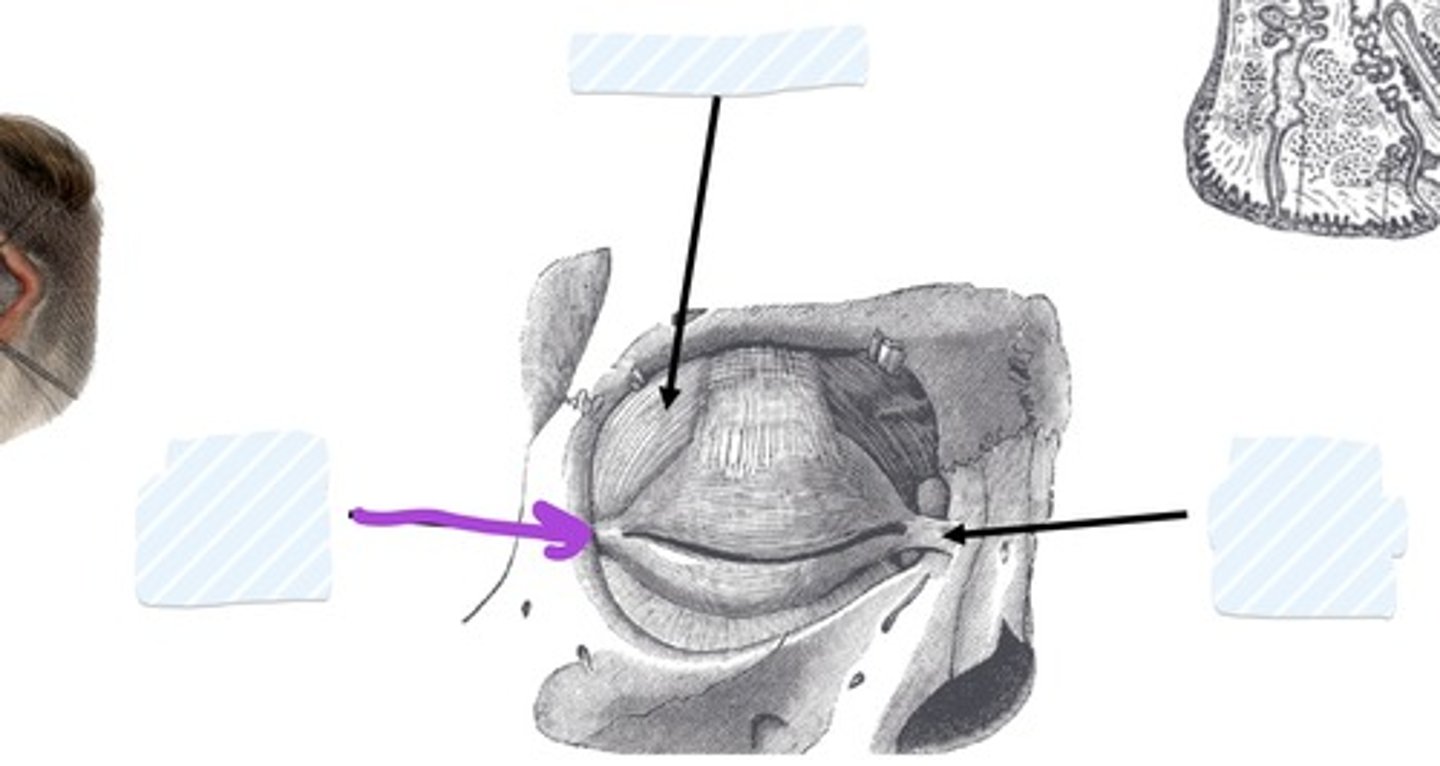
Lateral palpebral ligament
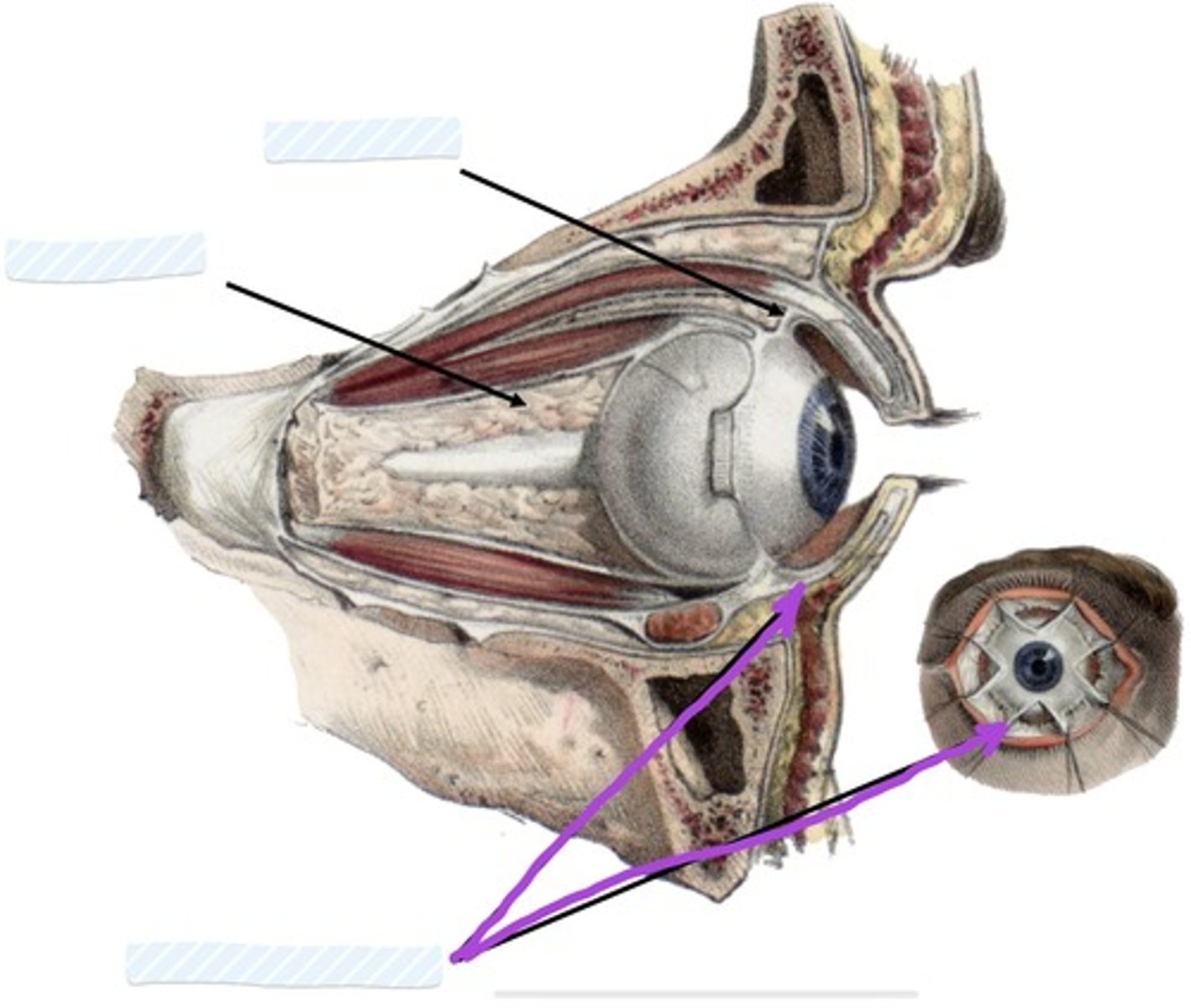
Inferior check ligament
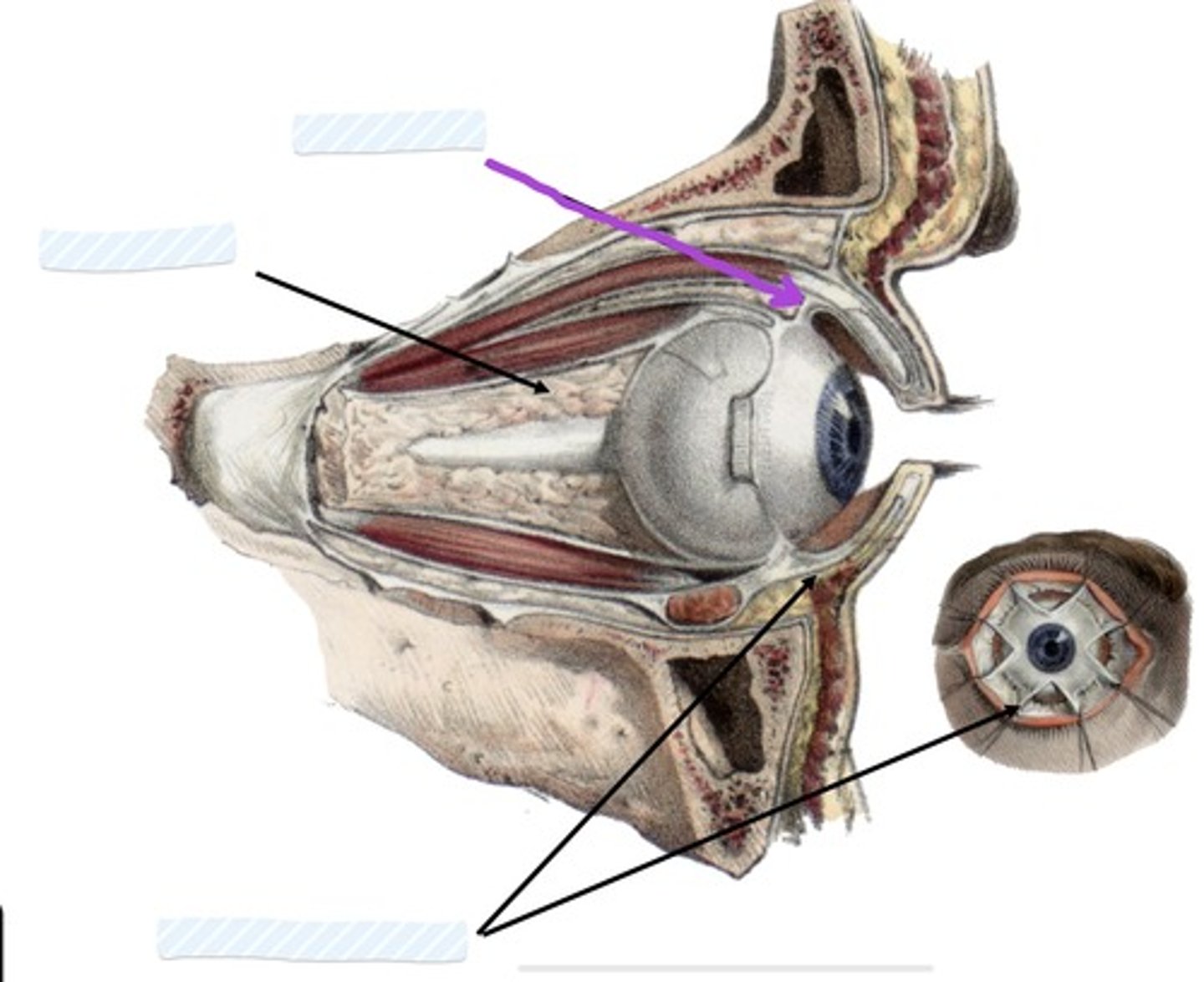
Facial sheath
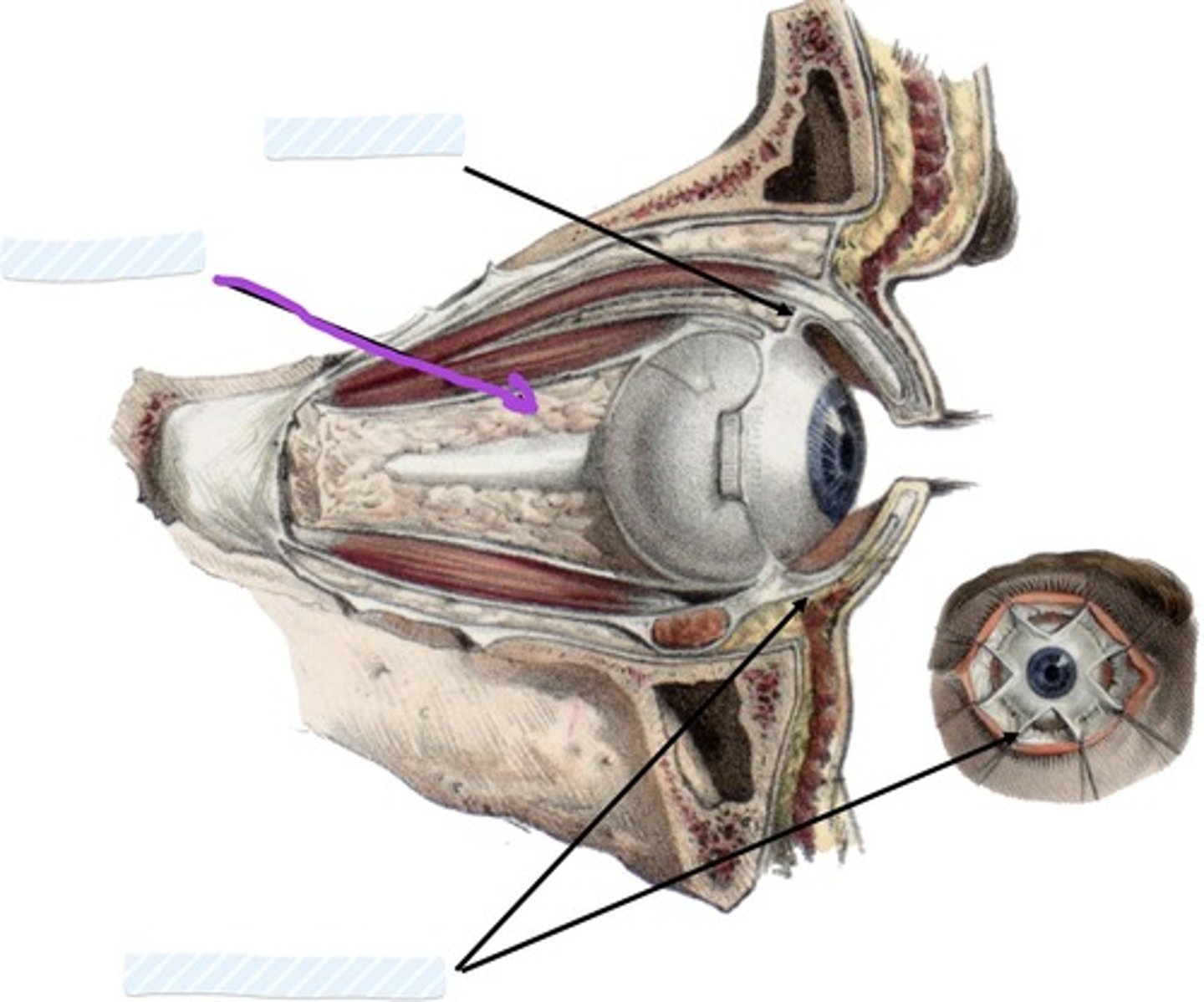
Retrobulbar fat
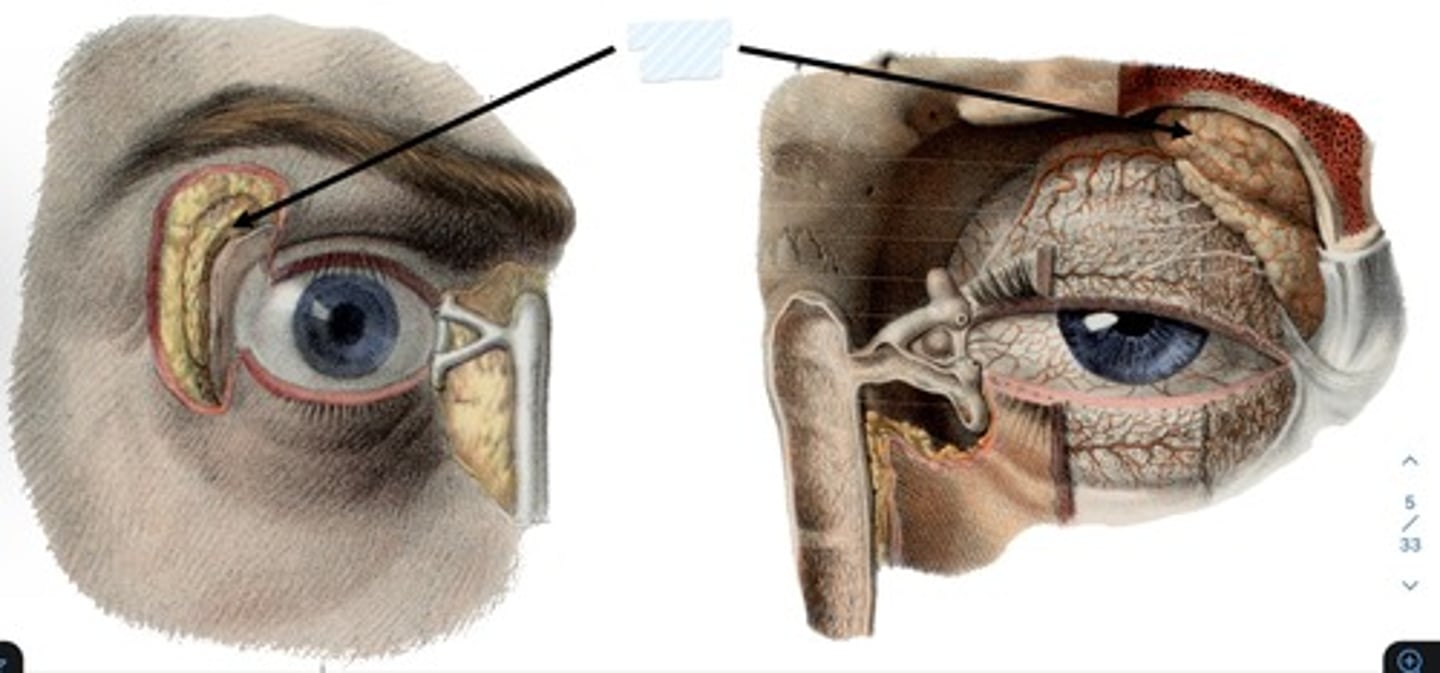
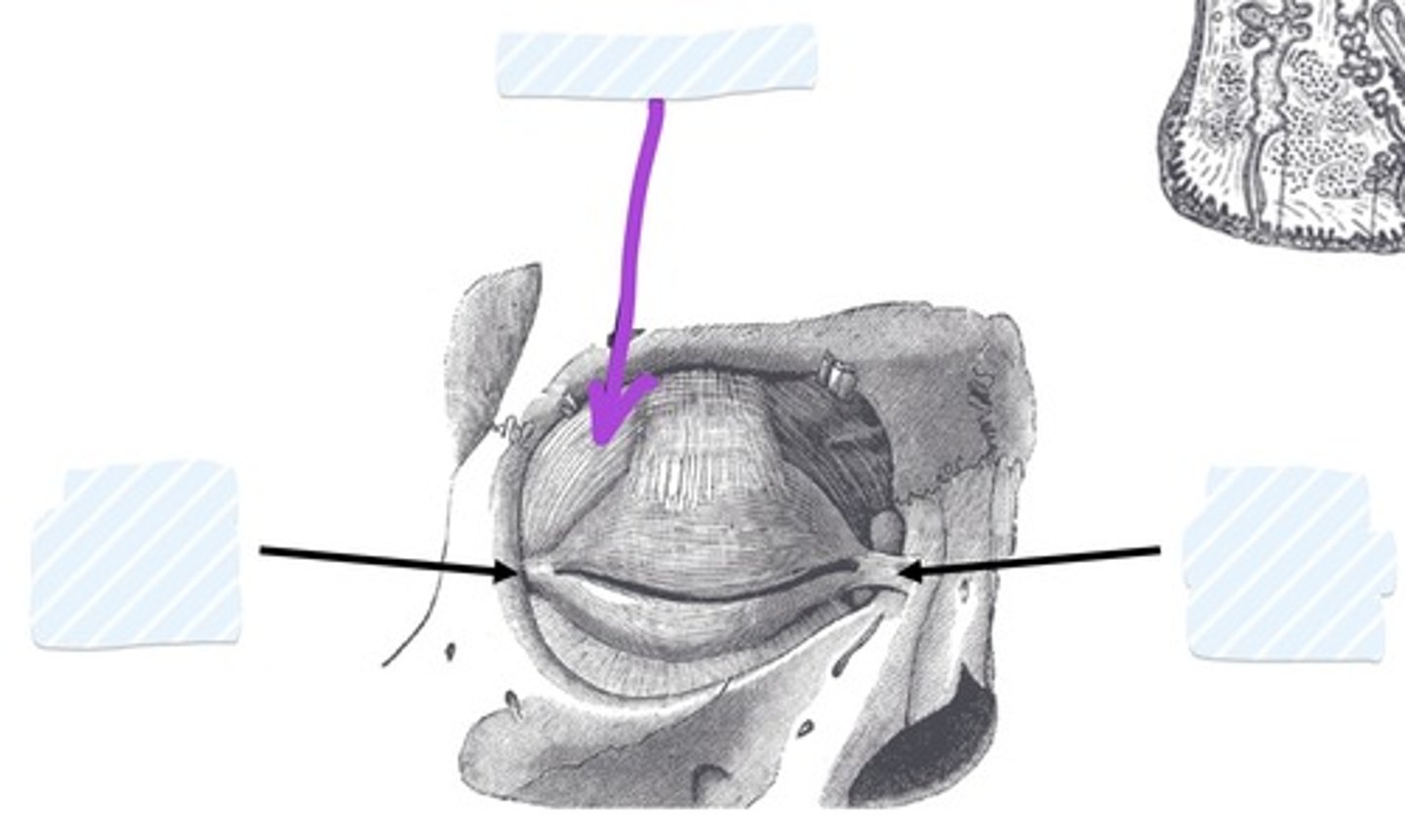
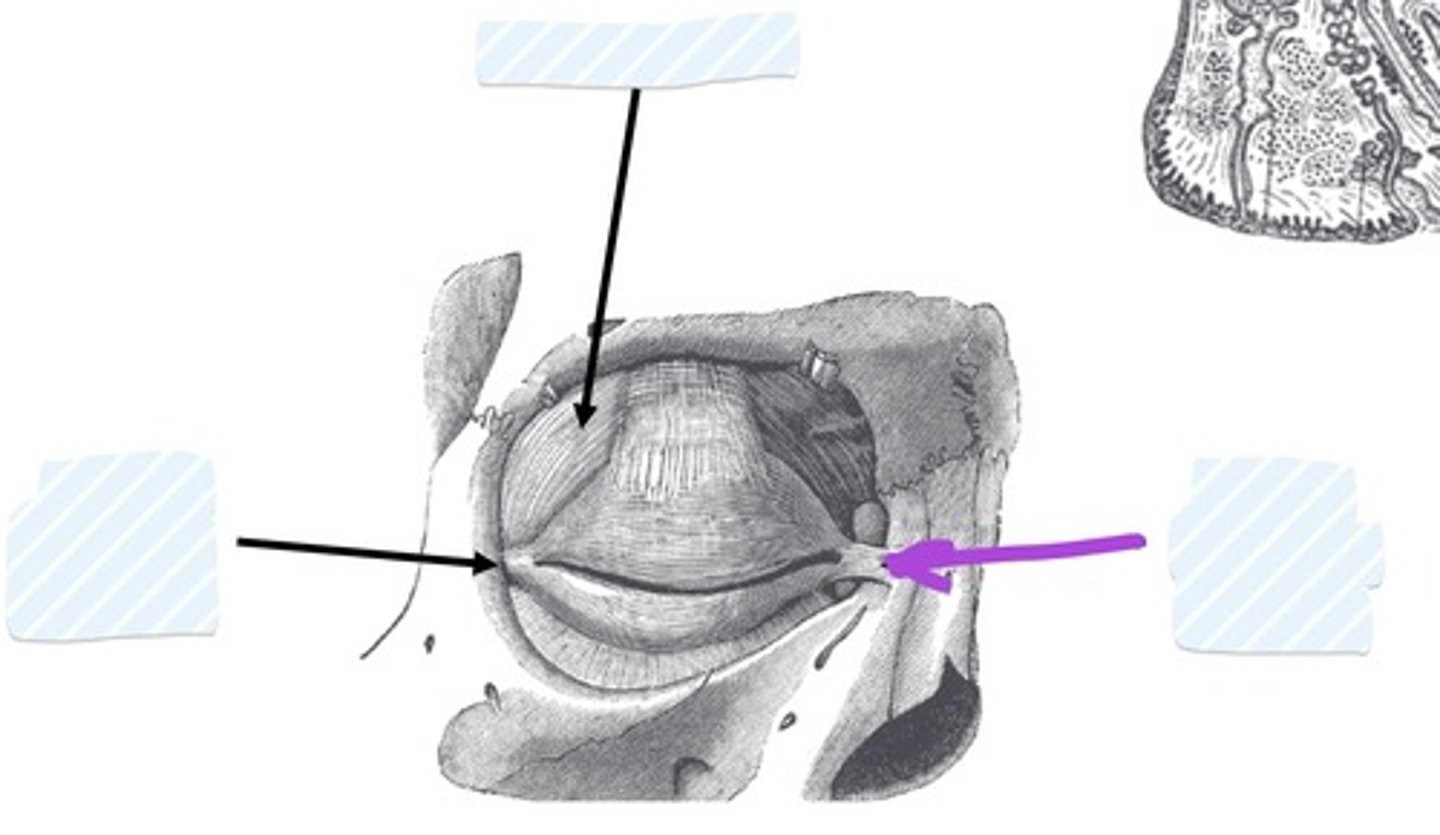
Lacrimal gland
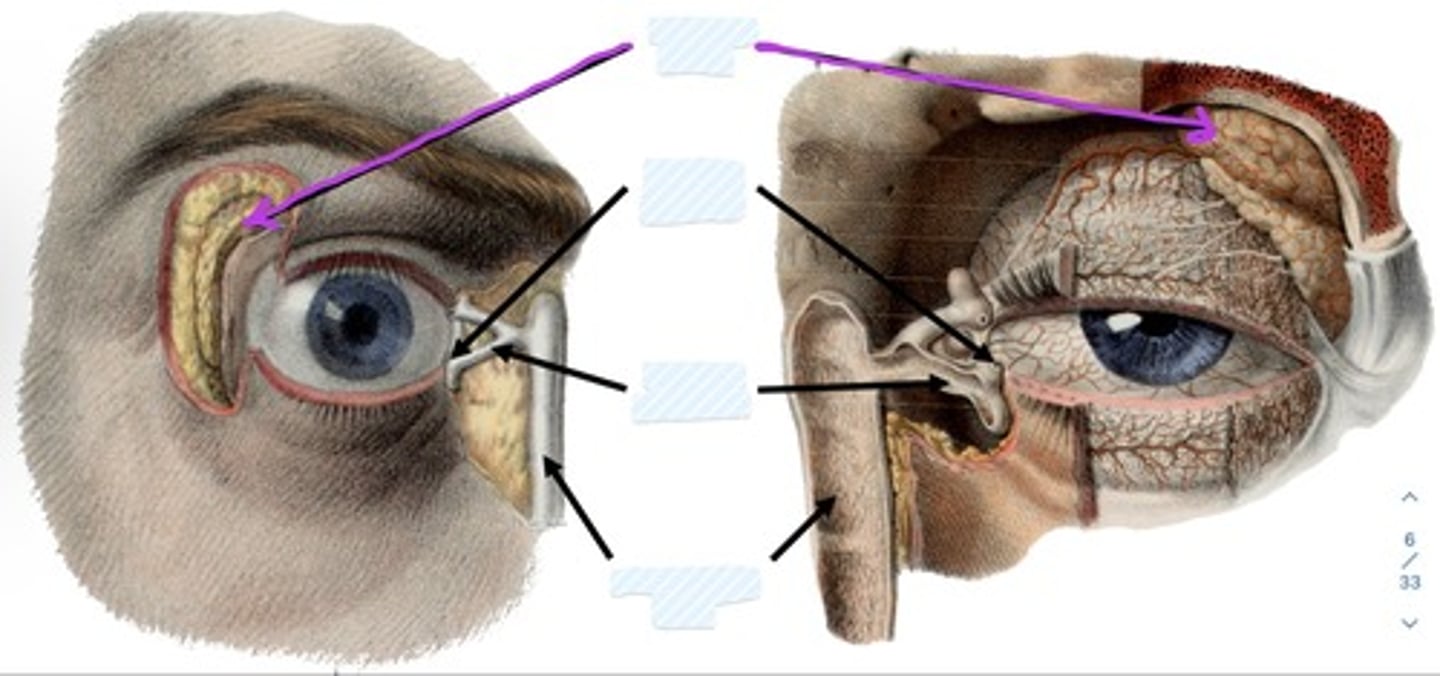
Lacrimal gland
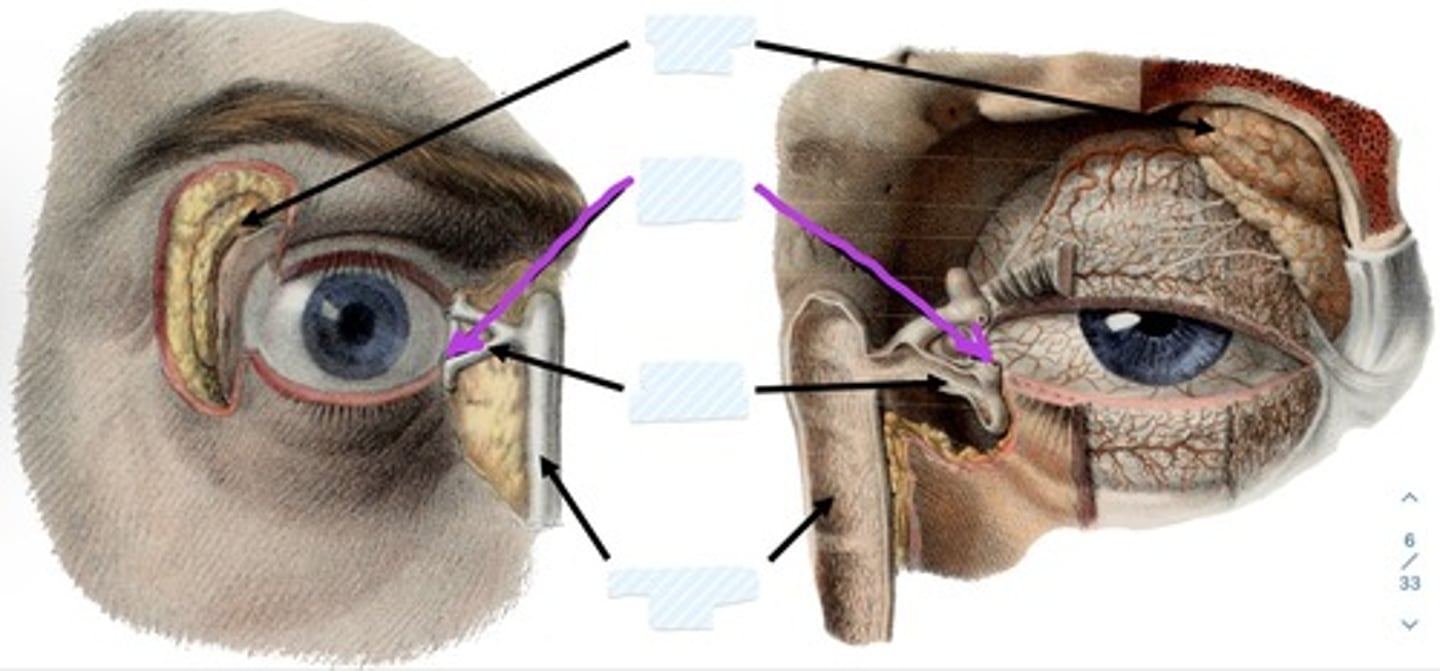
Lacrimal punctum
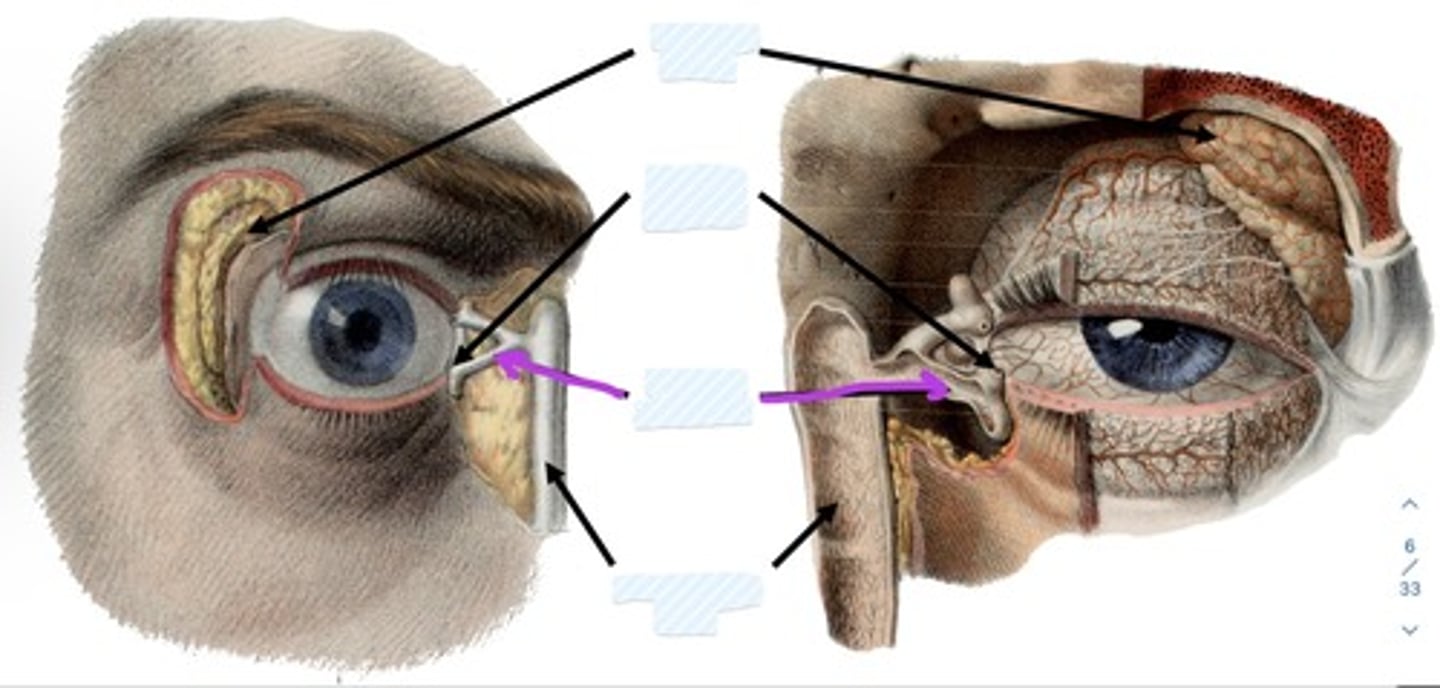
Lacrimal canaliculi
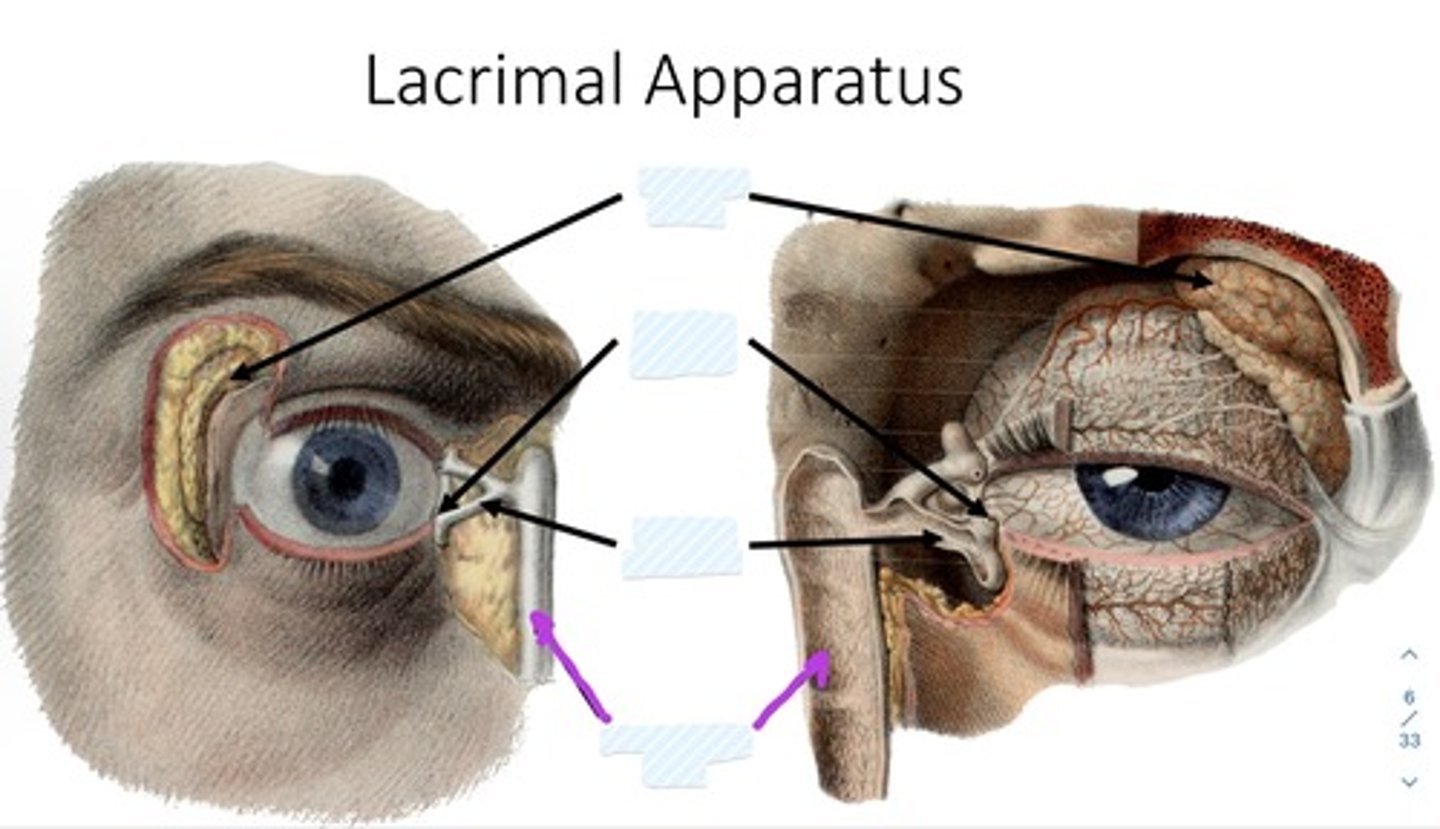
Nasolacrimal duct
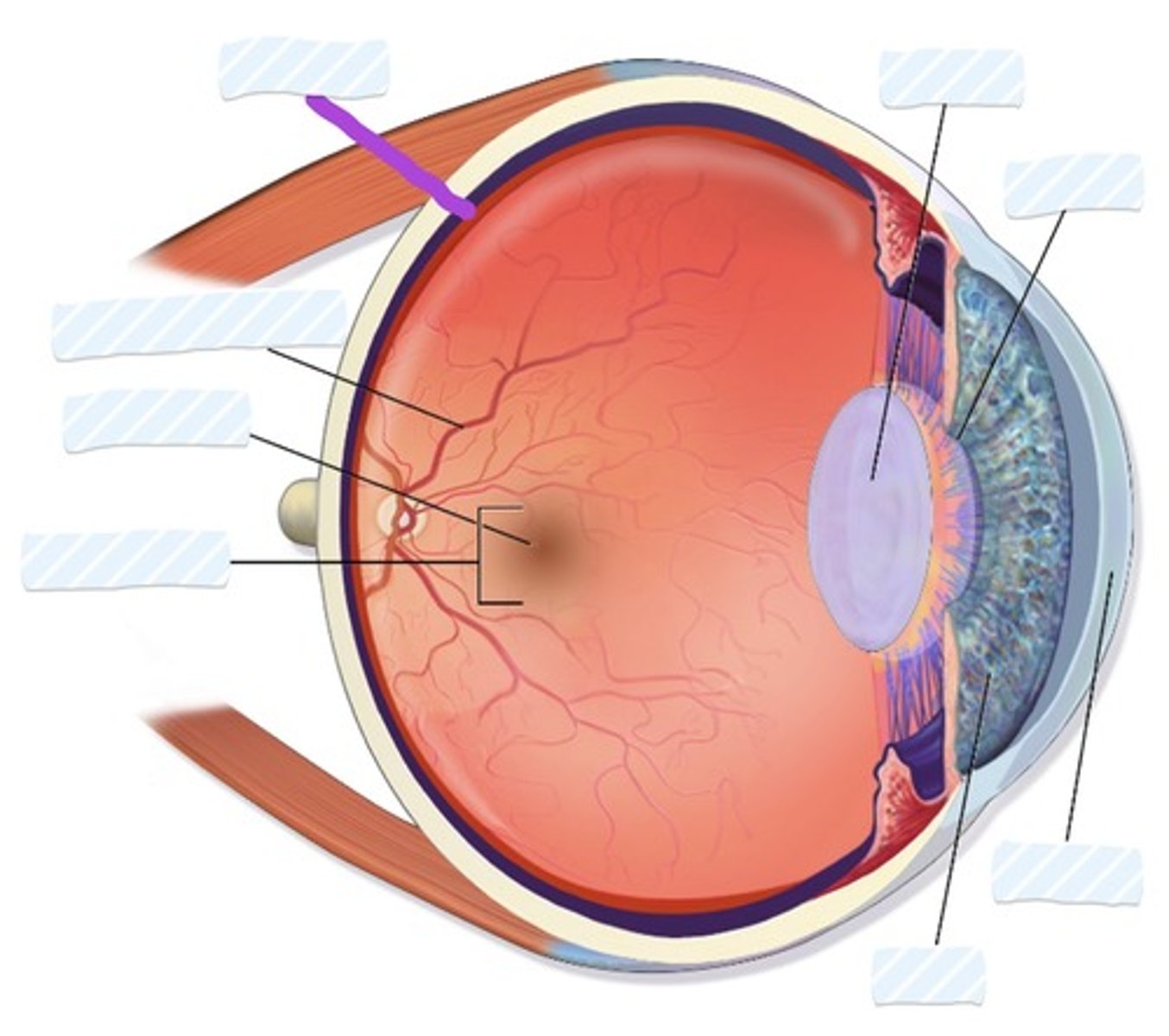
Retina
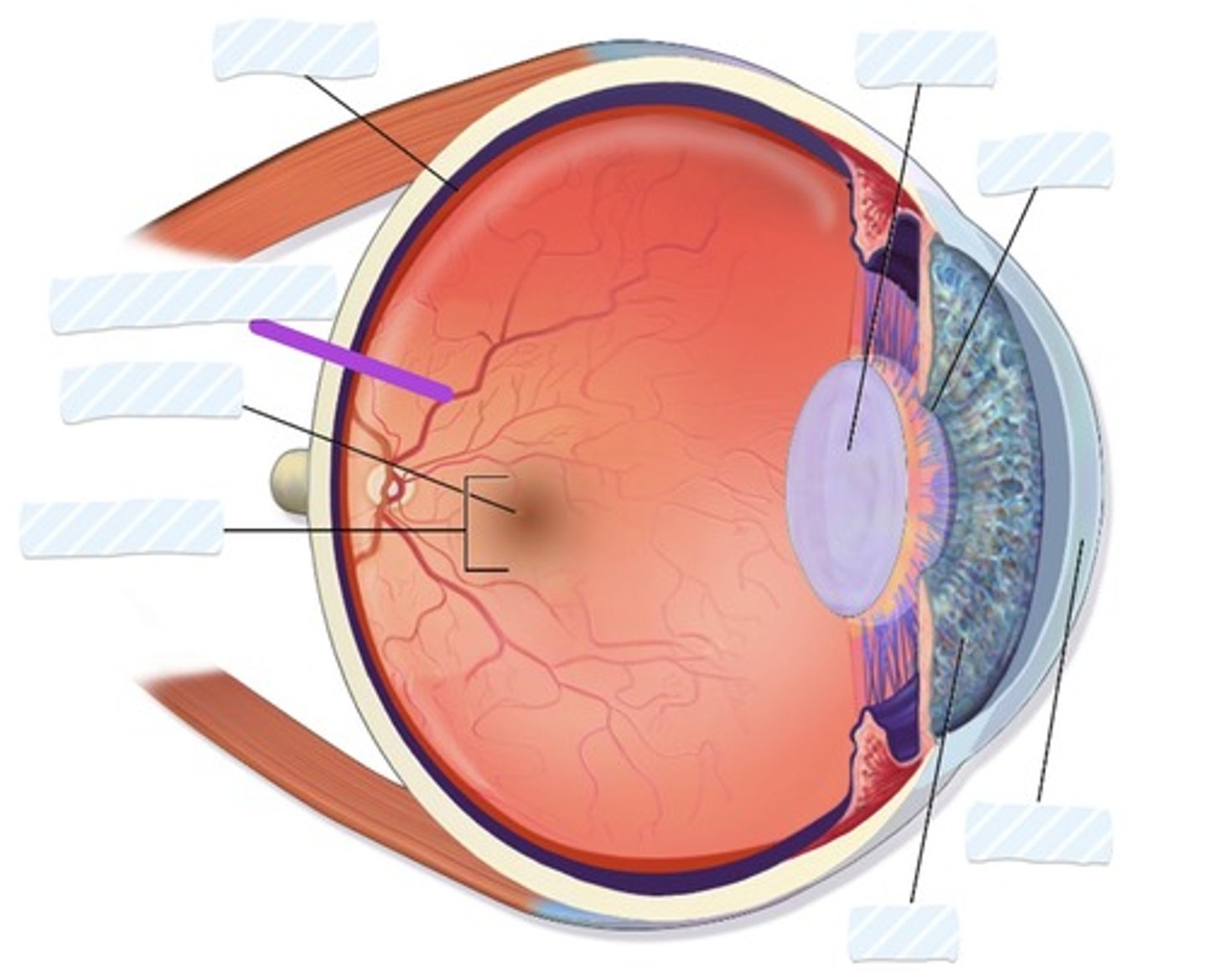
Blood vessels
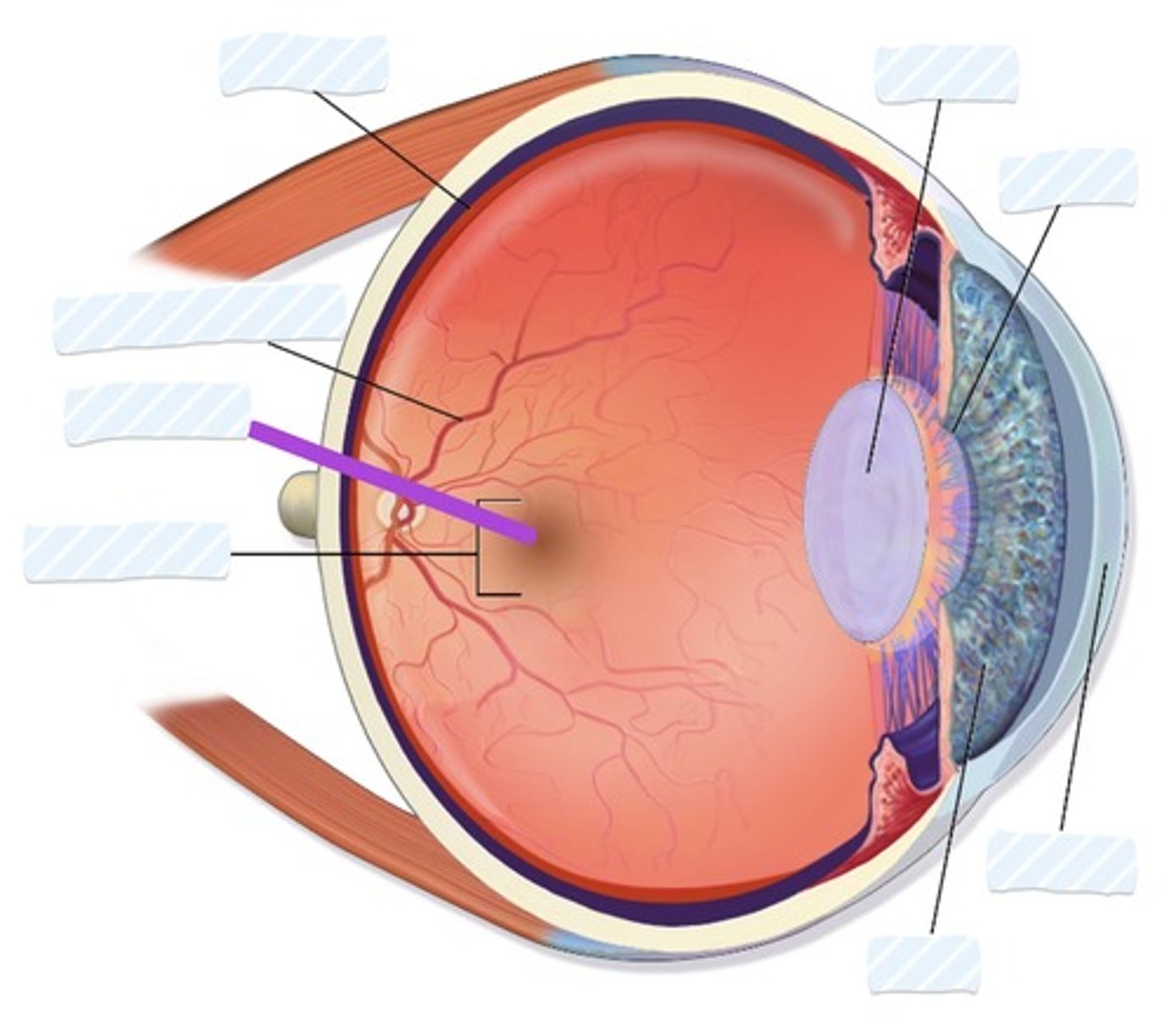
Fovea
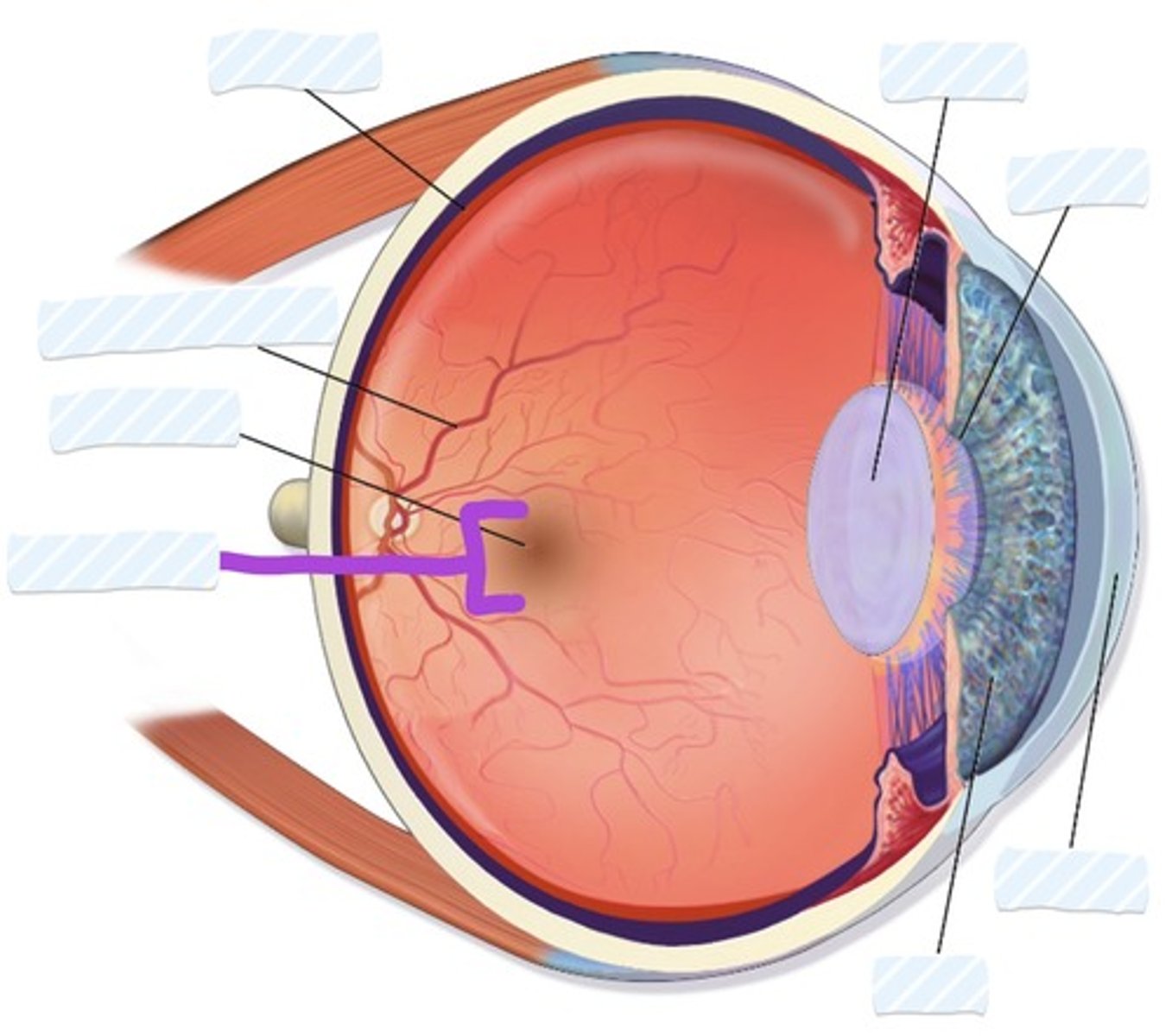
Macula
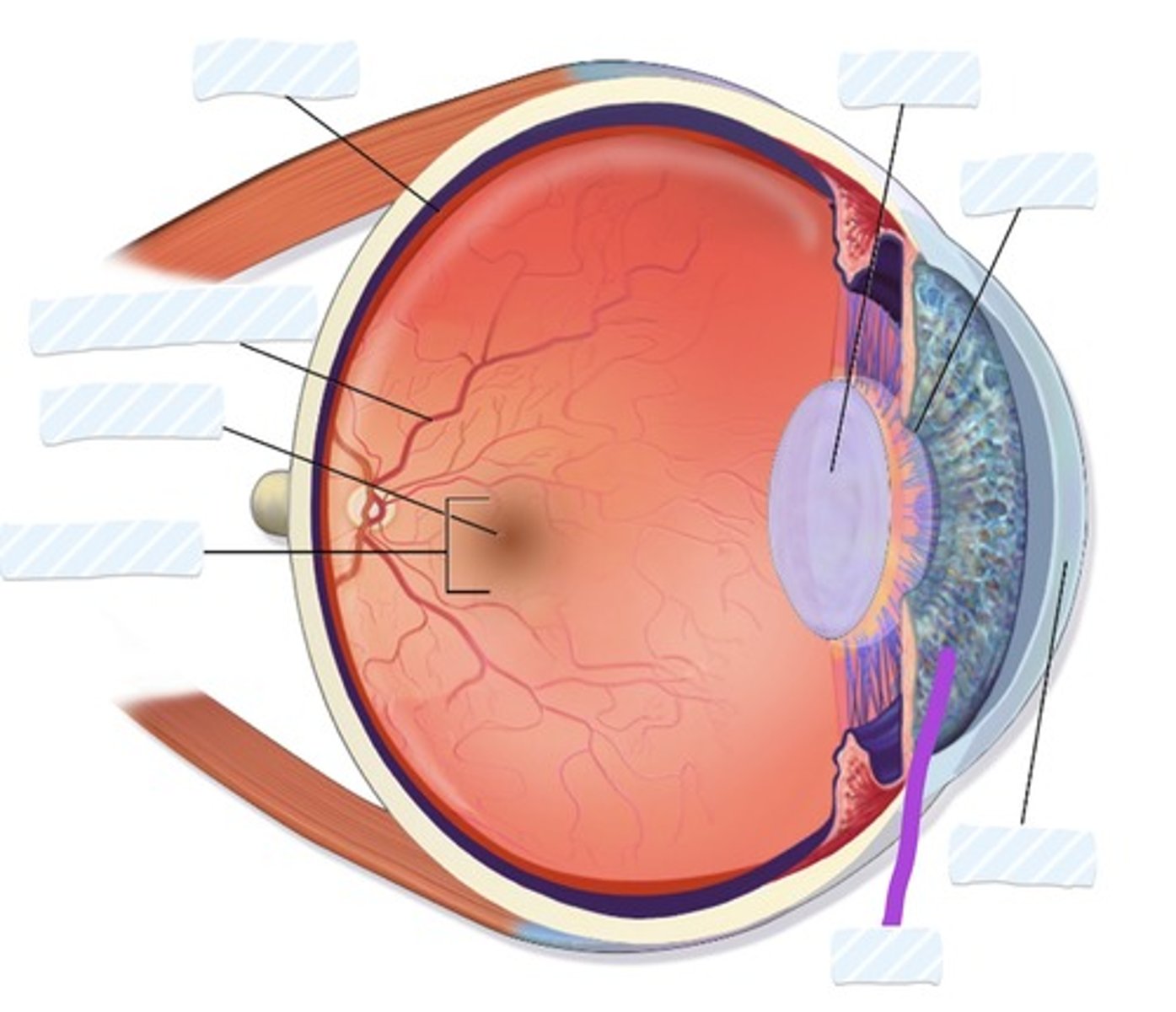
Iris
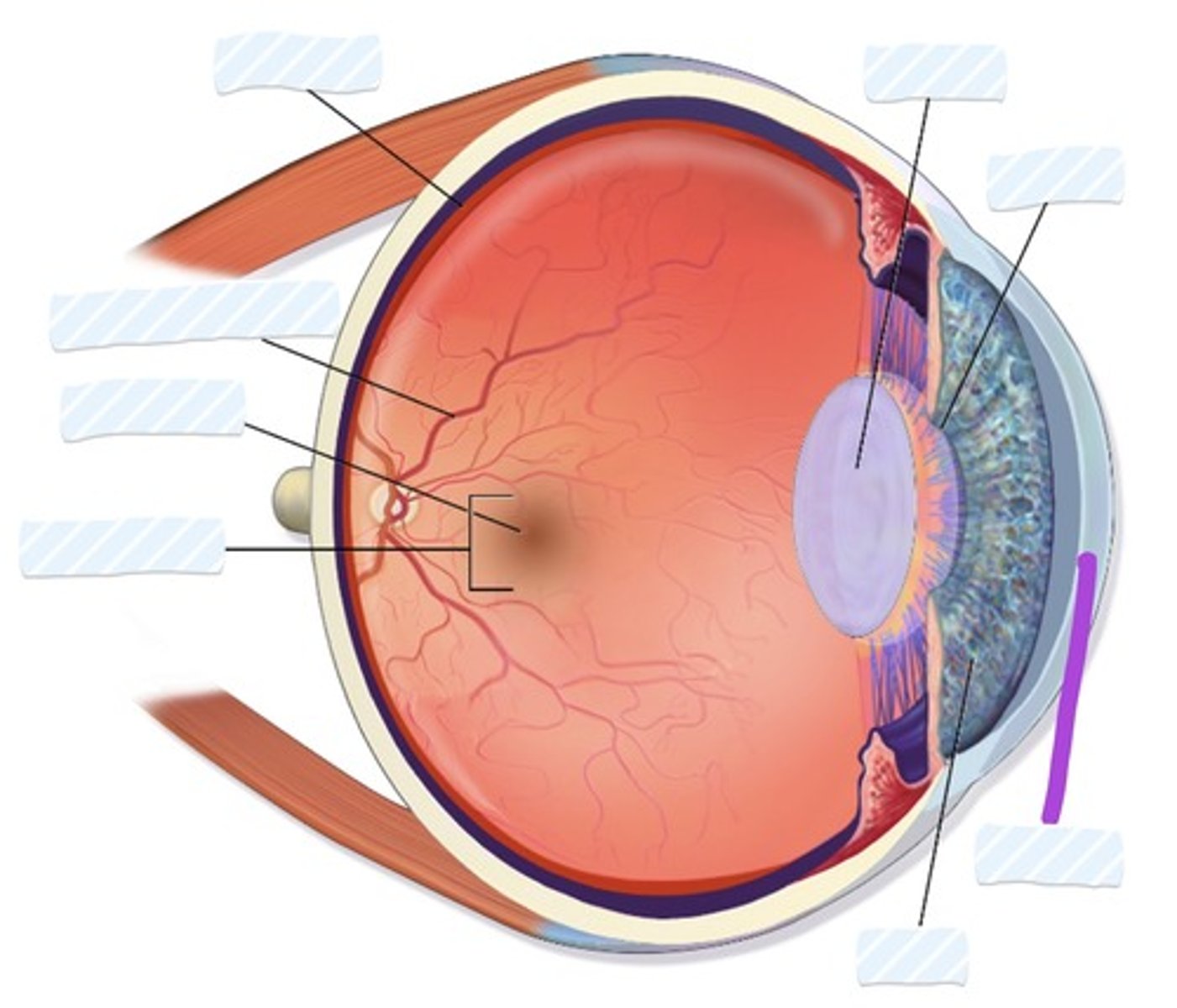
Cornea
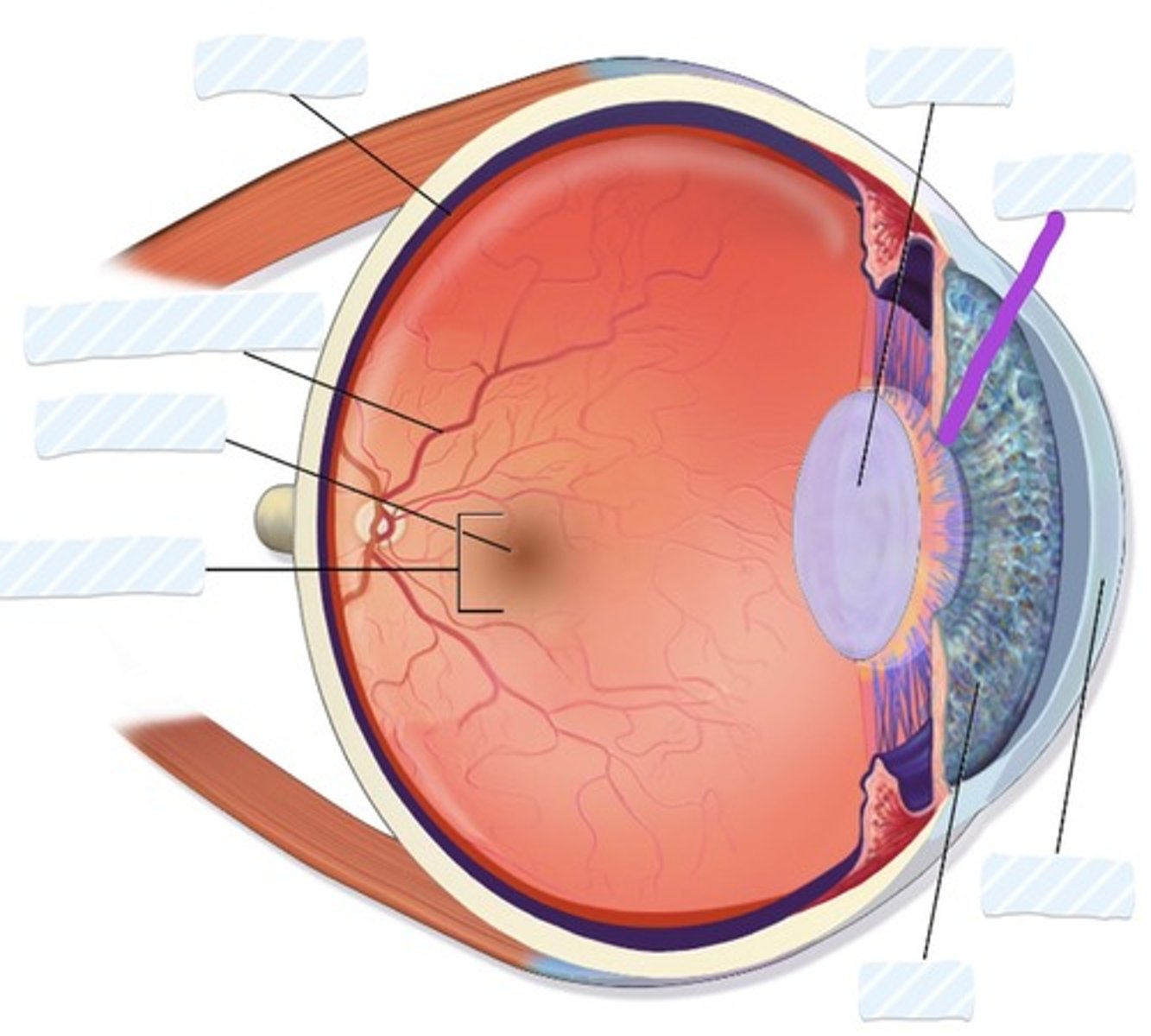
Pupil
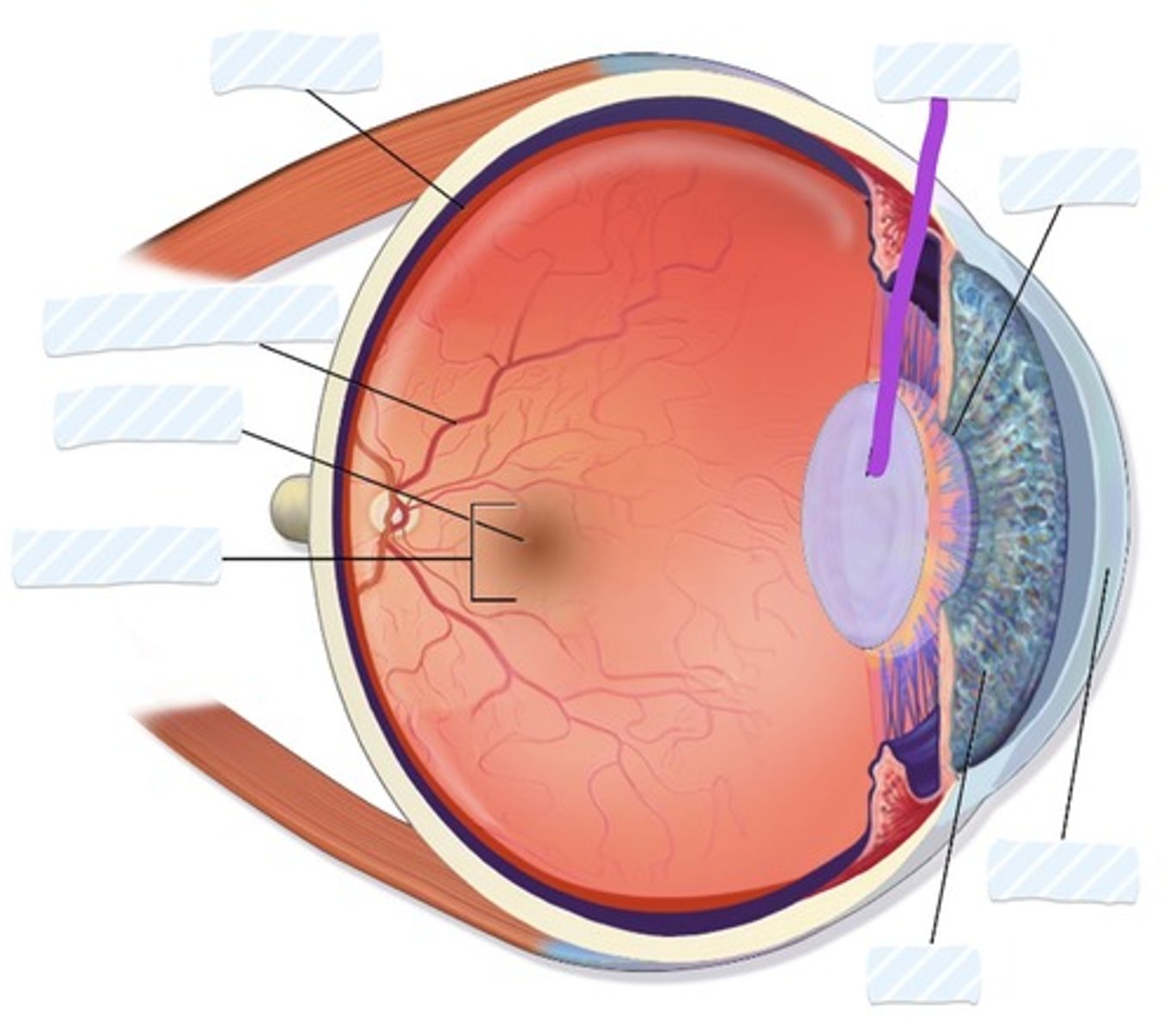
Lens