AP Chapter 11: The Efferent System - ANS
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Somatic Nervous System
Voluntary control of Skeletal Muscles
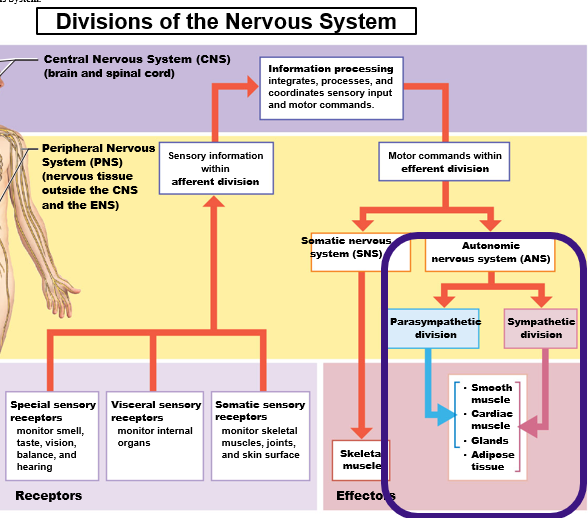
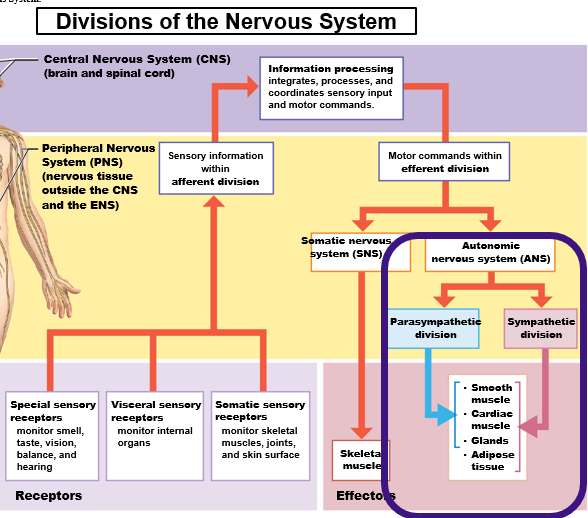
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
Involuntary control of visceral effectors (organs)
Smooth muscles, glands, cardiac muscle, adipocytes
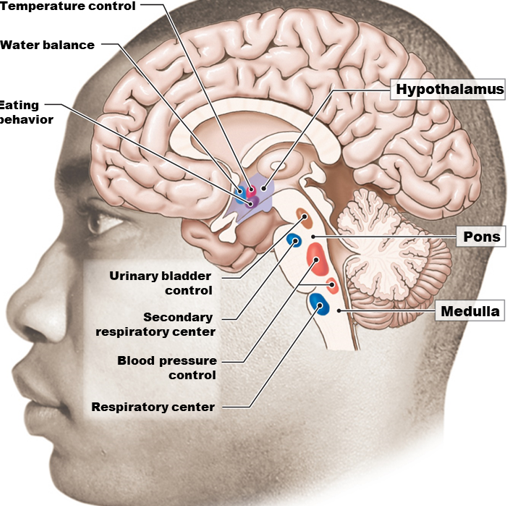
Hypothalamus contains __________ centers
Integrative (Reflex Actions)
Neurons comparable to upper motor neurons in the SNS (Skeletal Muscles)
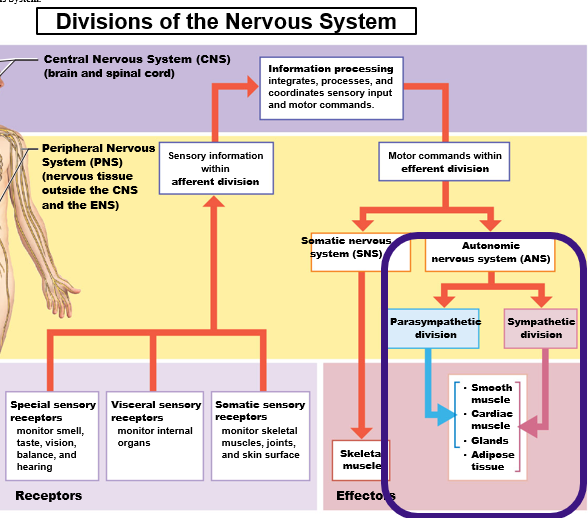
Two Subdivisions of the ANS
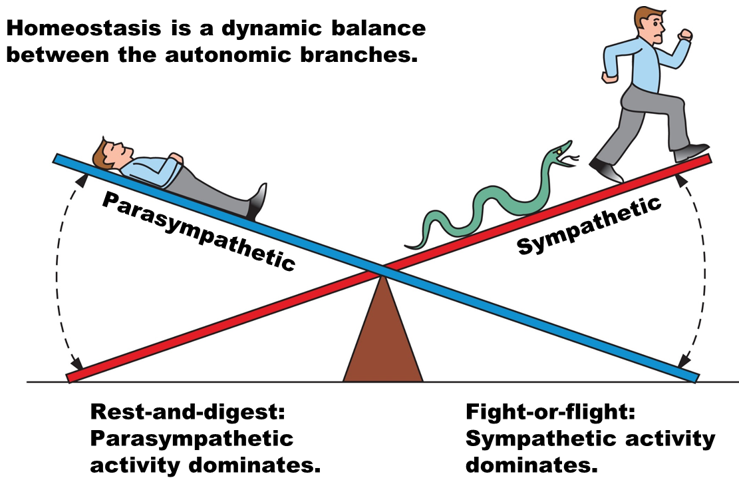
Sympathetic Branch (“Fight-or-Flight”)
Parasympathetic Branch (“Rest-and-Digest)
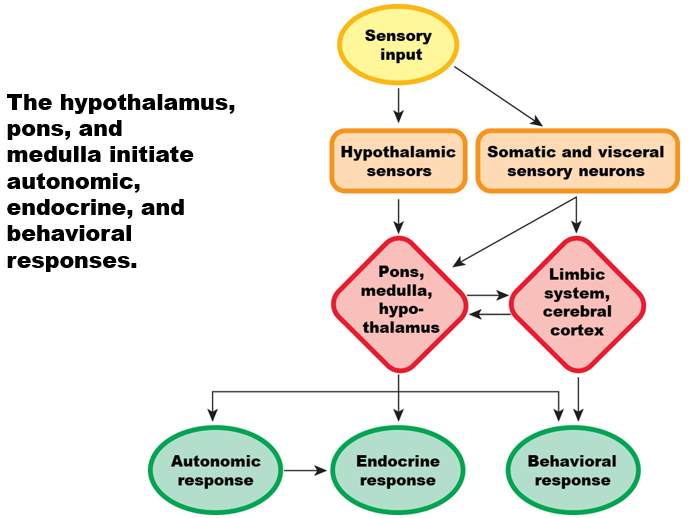
What responses do hypothalamic and Somatic/Visceral sensory neurons?
The hypothalamus, pons, and medulla initiate:
autonomic
endocrine
behavioral responses.
Antagonistic Control
Goes against the branch in action
One autonomic branch is excitatory
The other branch is inhibitory
What are some exceptions to dual antagonist control?
Sweat glands and smooth muscles in most blood vessels
Only sympathetic innervation; tonic control
Cooperative Control
Work on different tissues to achieve common goal
Sympathetic Branch
Fight or Flight
Dominates in stressful situations
Ex. Controls blood flow to the tissues, provides energy for escape
Parasympathetic Branch
Rest or digest
Dominates in times of calm and rest
Ex. Relaxes the muscles, reduces respiration, slows down heart rate
Preganglionic Neuron
Originates in the CNS and projects to an autonomic ganglion
Later synapses with the postganglionic neuron
Postganglionic Neuron
Cell body in autonomic ganglion and projects its axon to the target tissue
Synapses with target cell
Ganglion
A cluster of nerve cell bodies that lie outside the CNS
Acetylcholine
Binds to cholinergic nicotinic and muscarinic receptors
Stimulates action potentials in the postganglionic neuron then goes into the skeletal muscles
Inside the parasympathetic division
Norepinephrine
Binds to adrenergic receptors
Inside the sympathetic division
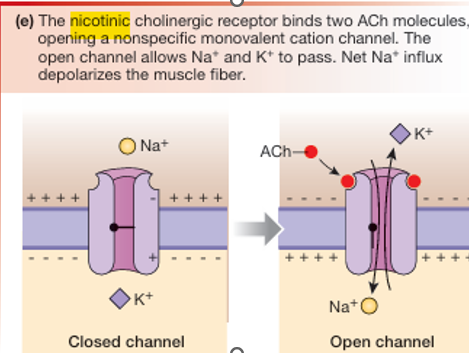
Nicotinic cholinergic receptors
Chemically gates ion channels with two binding sites for ACh
Parasympathetic
ionotropic, ions channels for Na+ and K+
Muscarinic Cholinergic Receptors
Ach Neurotransmitters
Where most postganglionic parasympathetic neurons secrete ACh onto
Metabotropic, GPCR (Location: smooth muscles, glands, autonomic division of CNS/PNS
Adrenal Medulla
Secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine hormones into the blood
Releases large amounts of epinephrine (fight or flight response)
Controlled by sympathetic preganglionic neurons
B1-receptors
Respond equally strongly to norepinephrine and epinephrine
B2-receptors
Sensitive to epinephrine than to norepinephrine
Not innervated (No sympathetic neurons terminate near them, limits exposure to norepinephrine)
B3-receptors
Found primarily on adipose tissue
Innervated and more sensitive to norepinephrine than epinephrine