Urbanization and Urban Models Overview
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Urbanization
The process of increasing population in cities and the expansion of urban areas. Example - The Industrial Revolution led to rapid urbanization as people moved to cities for factory jobs.
Multiple Nuclei Model
A city structure model where development is centered around multiple nodes, not just a single downtown. Example - Los Angeles has several business districts, such as Downtown LA, Hollywood, and Century City.
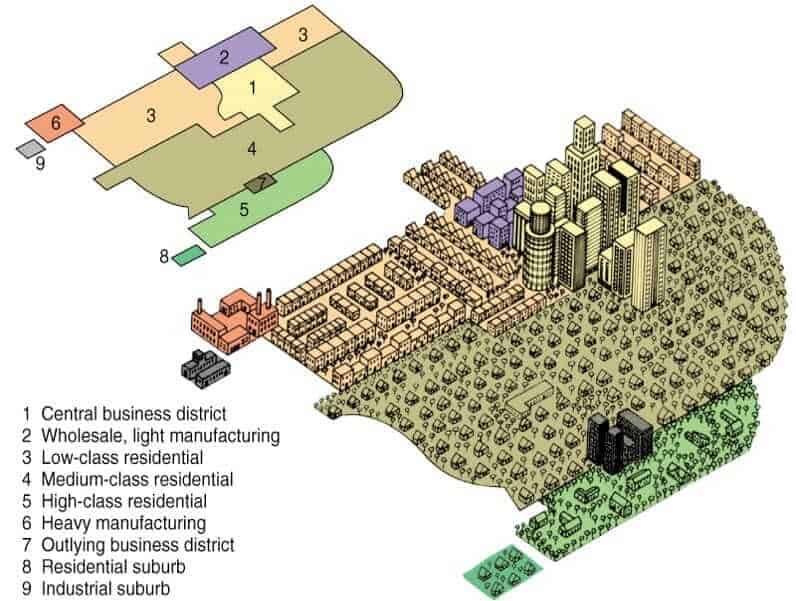
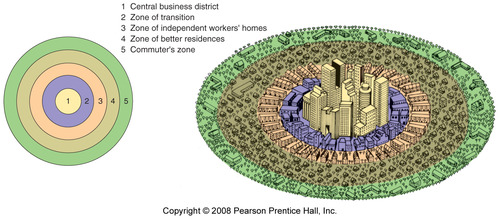
Concentric Zone Model
A model describing urban land use in rings, with the central business district (CBD) at the core. Example - Chicago in the early 20th century followed this model with wealthy areas further from the center.
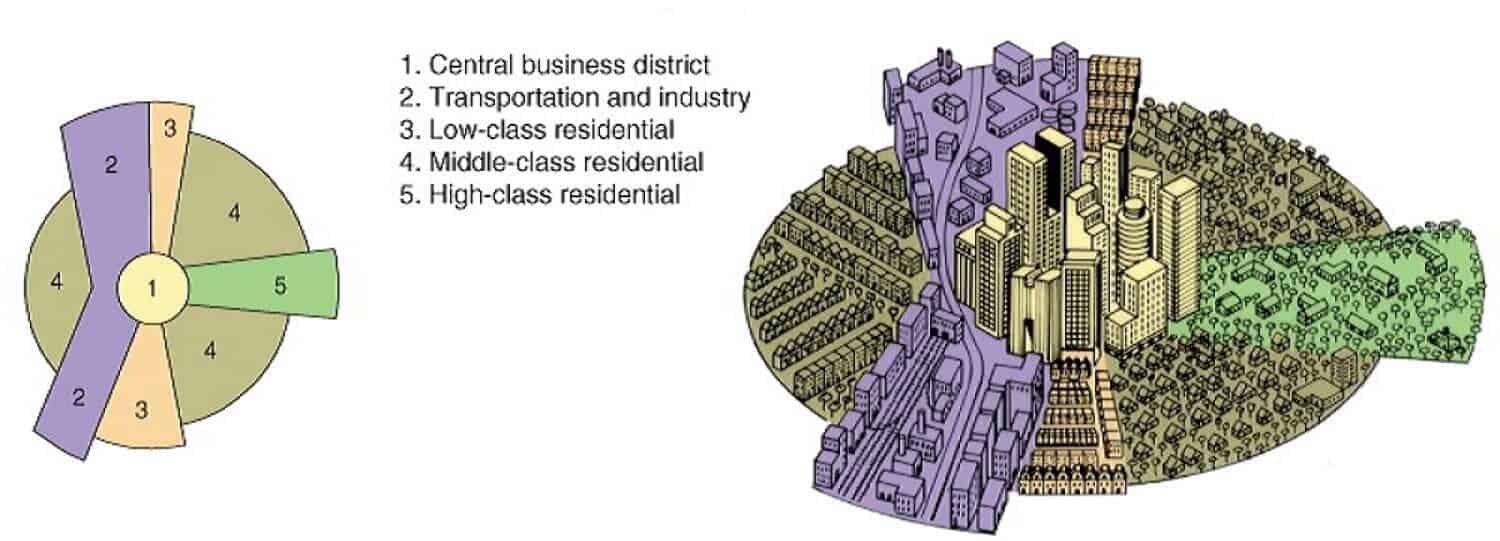
Sector Model
A city structure model where development expands in sectors from the CBD, often following transportation lines. Example - High-income housing often develops along desirable corridors, like waterfronts or highways.
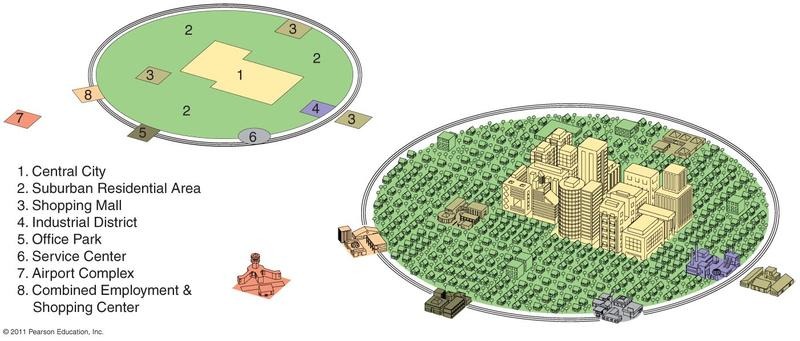
Galactic City Model
A modern urban model describing cities with multiple decentralized business areas due to suburbanization. Example - Cities like Detroit have edge cities around the main urban center.
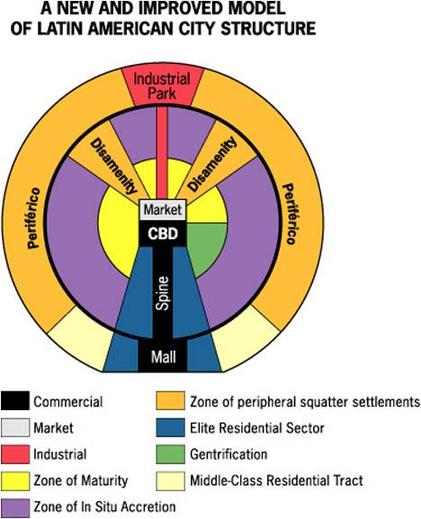
Griffin-Ford Model
A Latin American city model with a spine extending from the CBD and squatter settlements on the outskirts. Example - Mexico City has a well-developed commercial sector along a main boulevard.
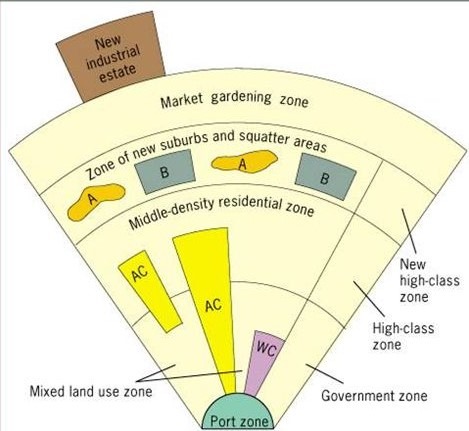
McGee Model
A Southeast Asian city model with no clear CBD, but with a port serving as the economic hub. Example - Jakarta, Indonesia, follows this model with its economy focused on its port.
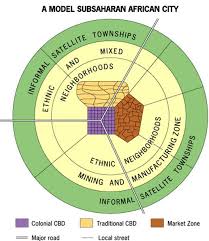
Sub-Saharan Africa Model
A city model featuring multiple CBDs, influenced by colonialism, with informal settlements on the periphery. Example - Nairobi, Kenya, has a colonial CBD, a traditional market CBD, and informal settlements.
Edge City
A large center of business, retail, and entertainment outside of a traditional downtown. Example - Tysons Corner, Virginia, is an edge city outside Washington, D.C.
Urban Sprawl
Unplanned, uncontrolled expansion of cities into rural areas. Example - The growth of suburbs around Atlanta has led to traffic congestion and loss of green space.
Redlining
The discriminatory practice of denying financial services to certain neighborhoods based on race. Example - In the 20th century, Black communities in Chicago were denied home loans.
Gentrification
The process where wealthier people move into poorer urban areas, leading to displacement of lower-income residents. Example - Brooklyn, New York, has seen increased property values and displacement of longtime residents.
Blockbusting
A practice where real estate agents encourage homeowners to sell cheaply due to racial fear, then resell for profit. Example - In the 1960s, realtors in Detroit used blockbusting to manipulate housing prices.
McMansions
Large, mass-produced suburban homes that are often considered oversized for their lots. Example - Many McMansions were built in U.S. suburbs during the early 2000s housing boom.
Shantytowns / Informal Settlement
Poorly built housing communities often lacking basic services, typically found on the outskirts of cities. Example - Dharavi in Mumbai is one of the largest informal settlements in the world.
New Urbanism
A movement promoting walkable neighborhoods, mixed-use development, and reduced car dependence.
Smart Growth
A planning strategy focused on sustainable and efficient land use to reduce sprawl.
Gated Communities
Residential areas with restricted access, often featuring security measures.
Trade Area
The region from which a city draws customers for its goods and services.
Rank-Size Rule
A pattern where the second-largest city is half the size of the largest, the third is one-third, etc.
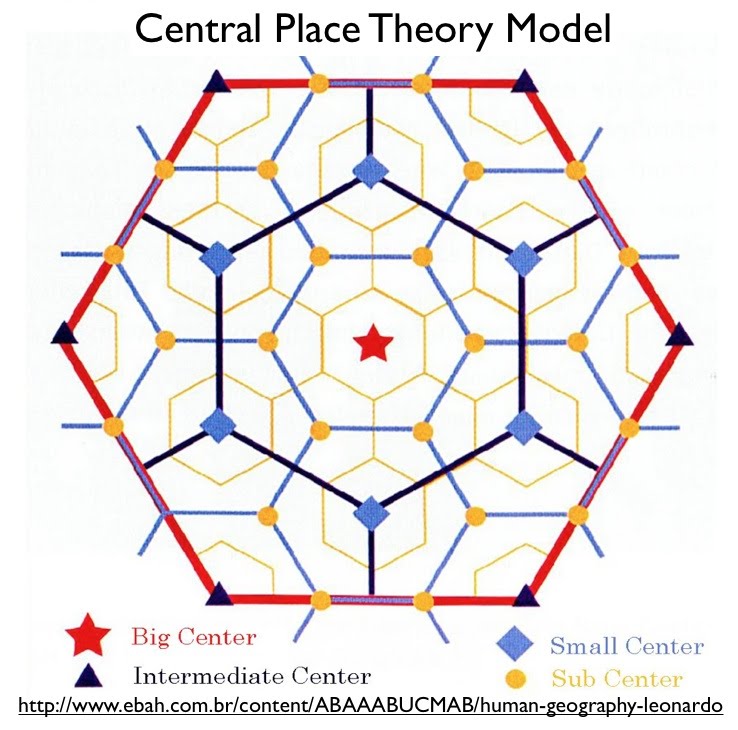
Central Place Theory
A model explaining how cities serve as centers of economic activity and provide goods/services to surrounding areas.
Threshold
The minimum number of people needed to support a business or service.
Range
The maximum distance people are willing to travel for a good or service.
Primate City
A city that is disproportionately larger and more important than any other city in a country.
Spaces of Consumption
Areas designed to attract people for shopping and entertainment.
1st Urban Revolution
The first historical shift to urban living, associated with the rise of ancient cities.
2nd Urban Revolution
The urbanization that accompanied industrialization, leading to massive city growth.
Situation
The relative location of a place based on its surroundings.
Site
The physical characteristics of a place, such as climate and natural resources.
Functional Zonation
The division of a city into areas for specific purposes, like business, industry, or residential use.
Suburbanization
The movement of people from cities to surrounding suburban areas.
Metacity
A city with over 20 million people.
World City / Global City
A city with major influence in global finance, politics, and culture.
Megacity
A city with more than 10 million people.
Urbicide
The deliberate destruction of urban areas, often during war or conflict.
Central Business District (CBD)
The commercial and business center of a city.