lecture 2 Overview of Human Nervous System
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
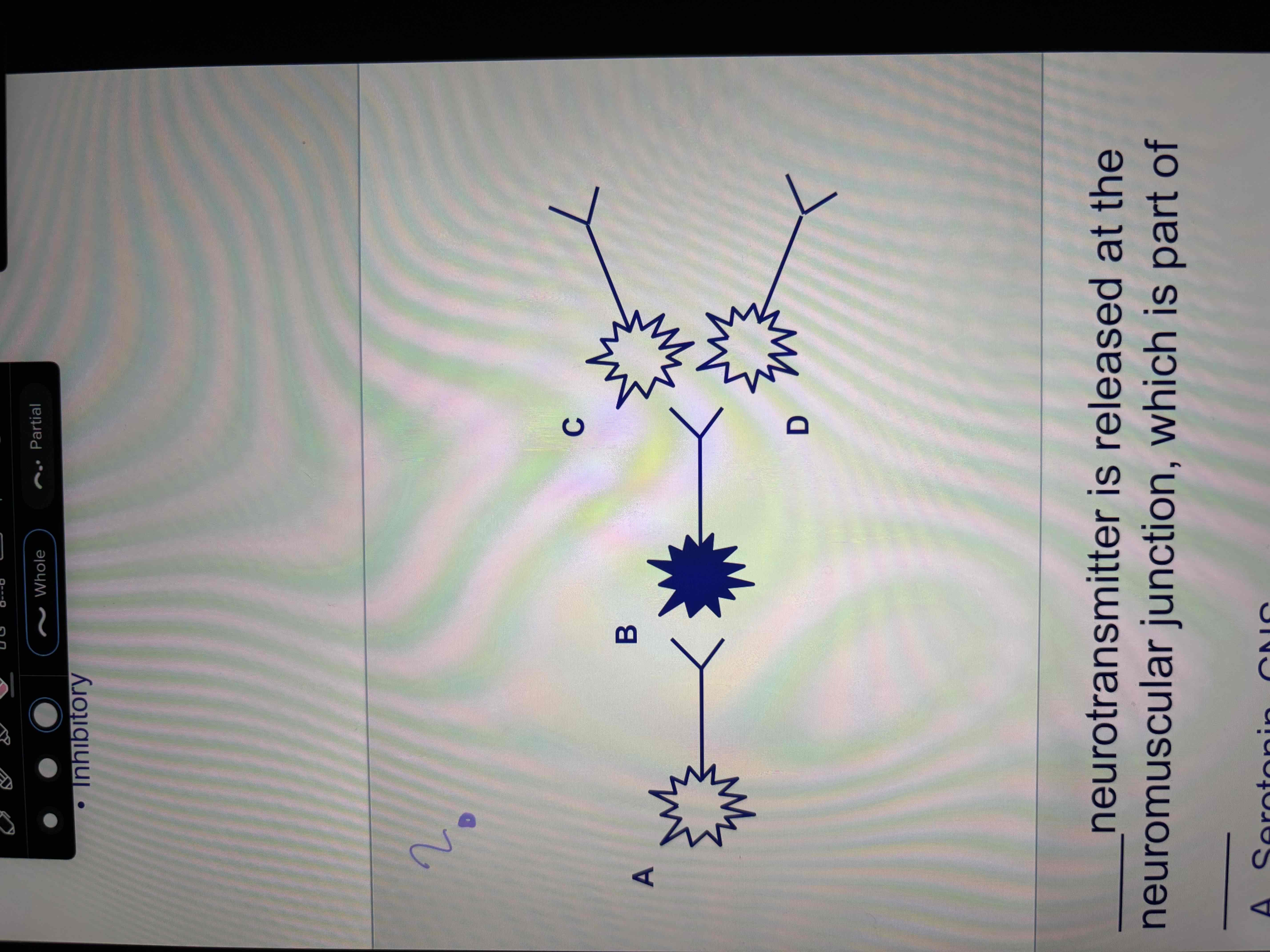
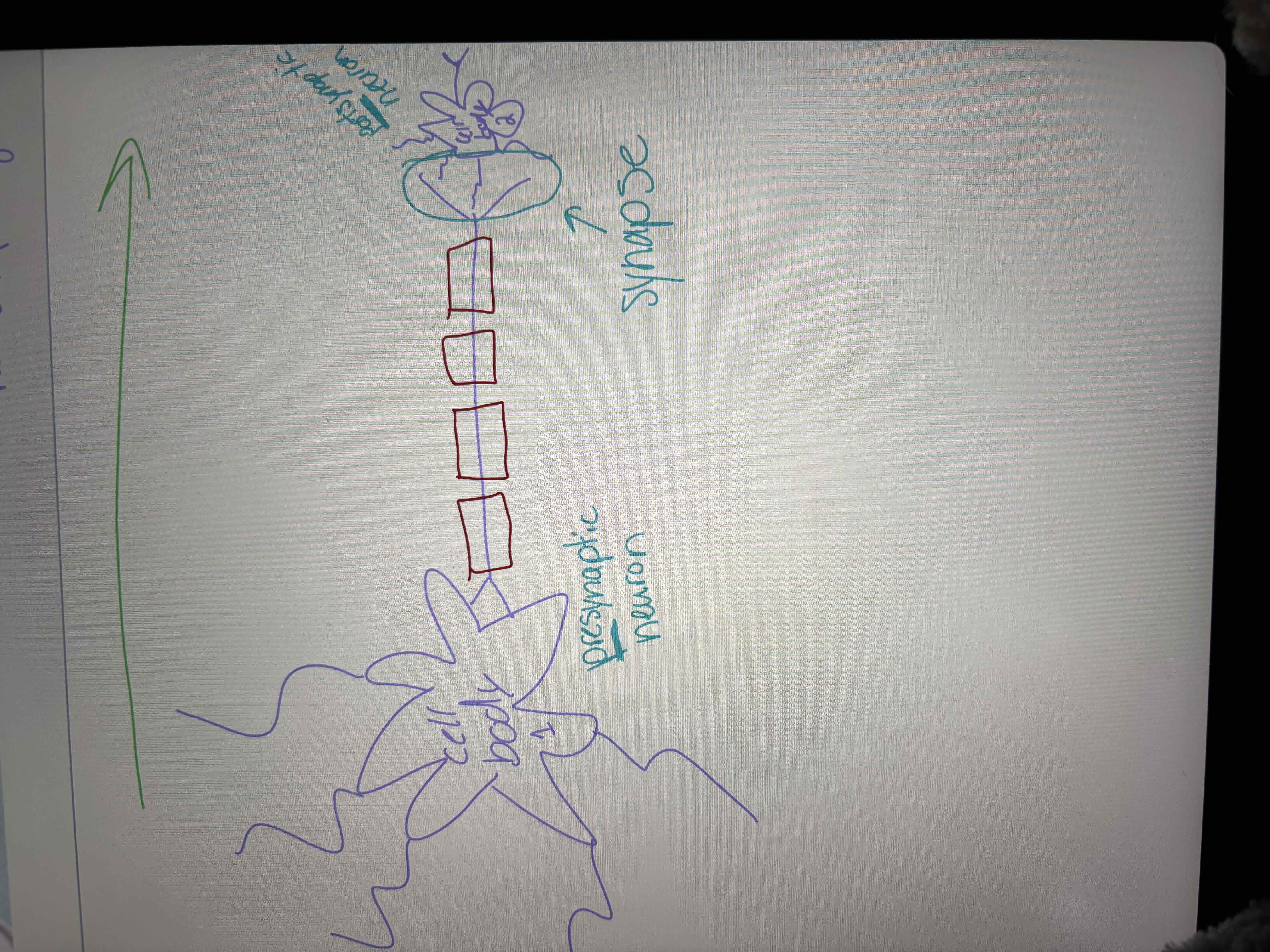
Structure of synapse
pre-synaptic cleft: before synapse, has message that needs sent
synaptic cleft: space b/w 2 neurons/nerve cells
post-synaptic terminal: after synapse, receives message
synapse: point of connection b/w 2 neurons in pathway
Excitatory
“yes” send our message
glutamate: to brain cells (CNS)
acetycholine: to muscle cells (PNS)
Inhibitory
“stop” don’t send message
GABA (gamma aminobutyric acid): tells next neuron in process to stop (CNS and PNS)
Anterograde
action potentials, neurotransmitters
forward

Retrograde
waste products, toxins, viruses
gets in through permeable shield
backwards

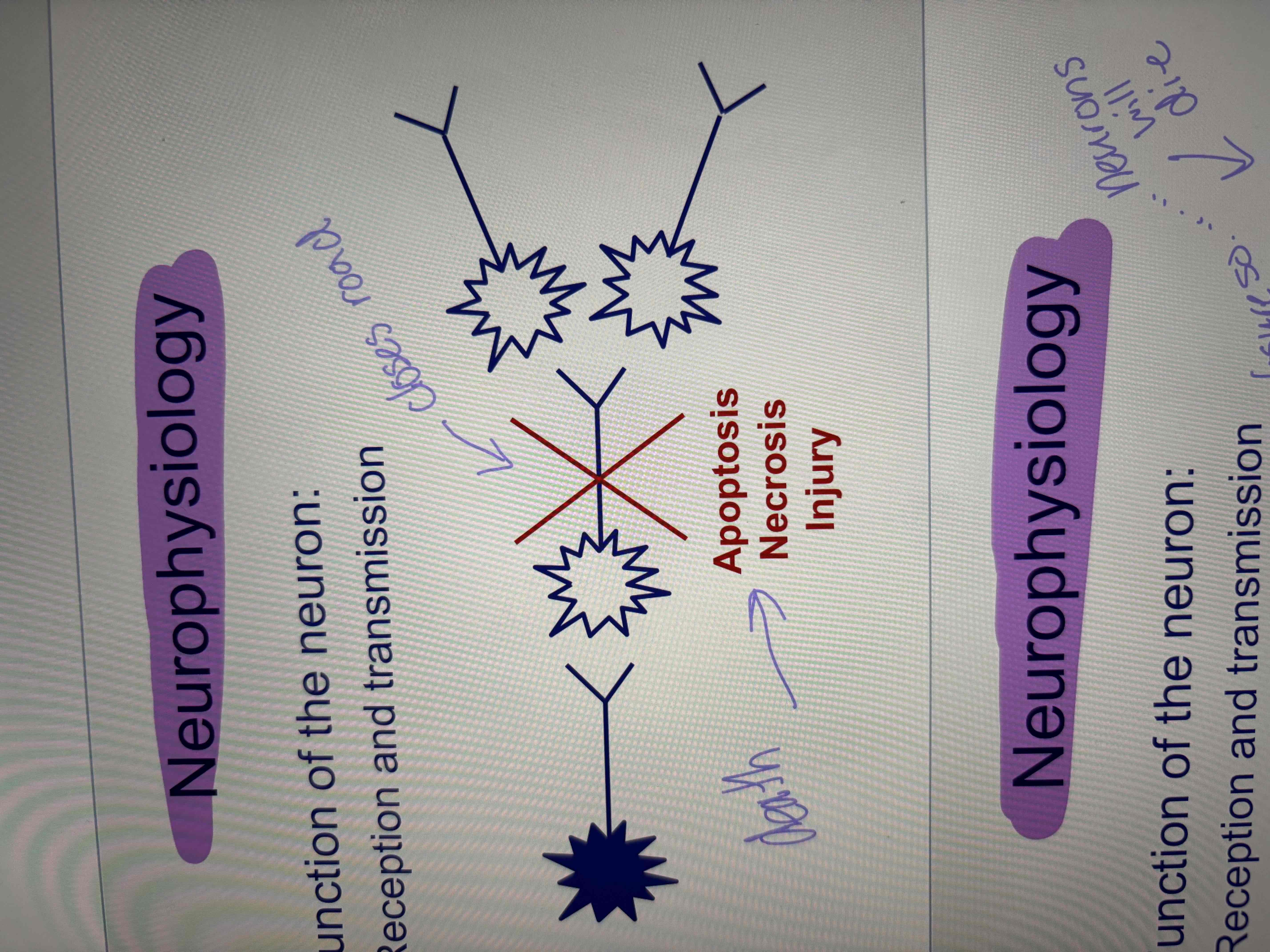
apoptosis necrosis injury
death
road closes
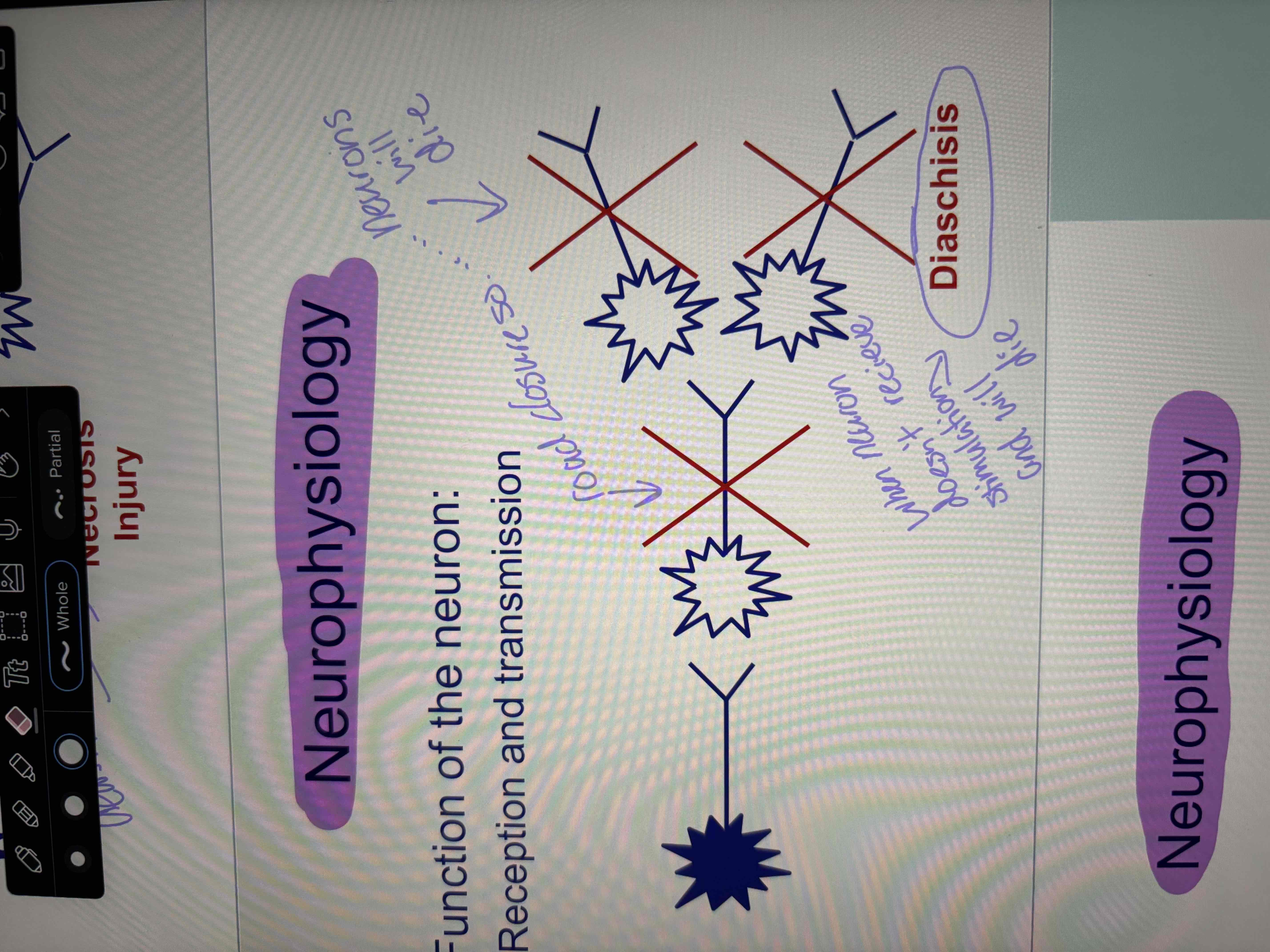
diaschisis
when neuron doesn’t receive stimulation and will die
Excitation
excitatory message keeps going
“feed forward excitation”

Inhibition
Inhibitory message keeps going
“feed forward inhibition”

transmission patterns (networks)
feedforward
feedback
lateral
convergence
divergence
Excitation
Feedback: excites neuron EARLIER in circuit
Feedforward: excites neuron LATER in circuit

Inhibition
Feedback: inhibits neuron EARLIER in circuit
feedforward: inhibits neuron LATER in circuit
lateral: inhibits neuron in adjacent circuit (more common)
Disinhibition: activates neuron by inhibiting an inhibitory neuron

Lateral Inhibition
picture
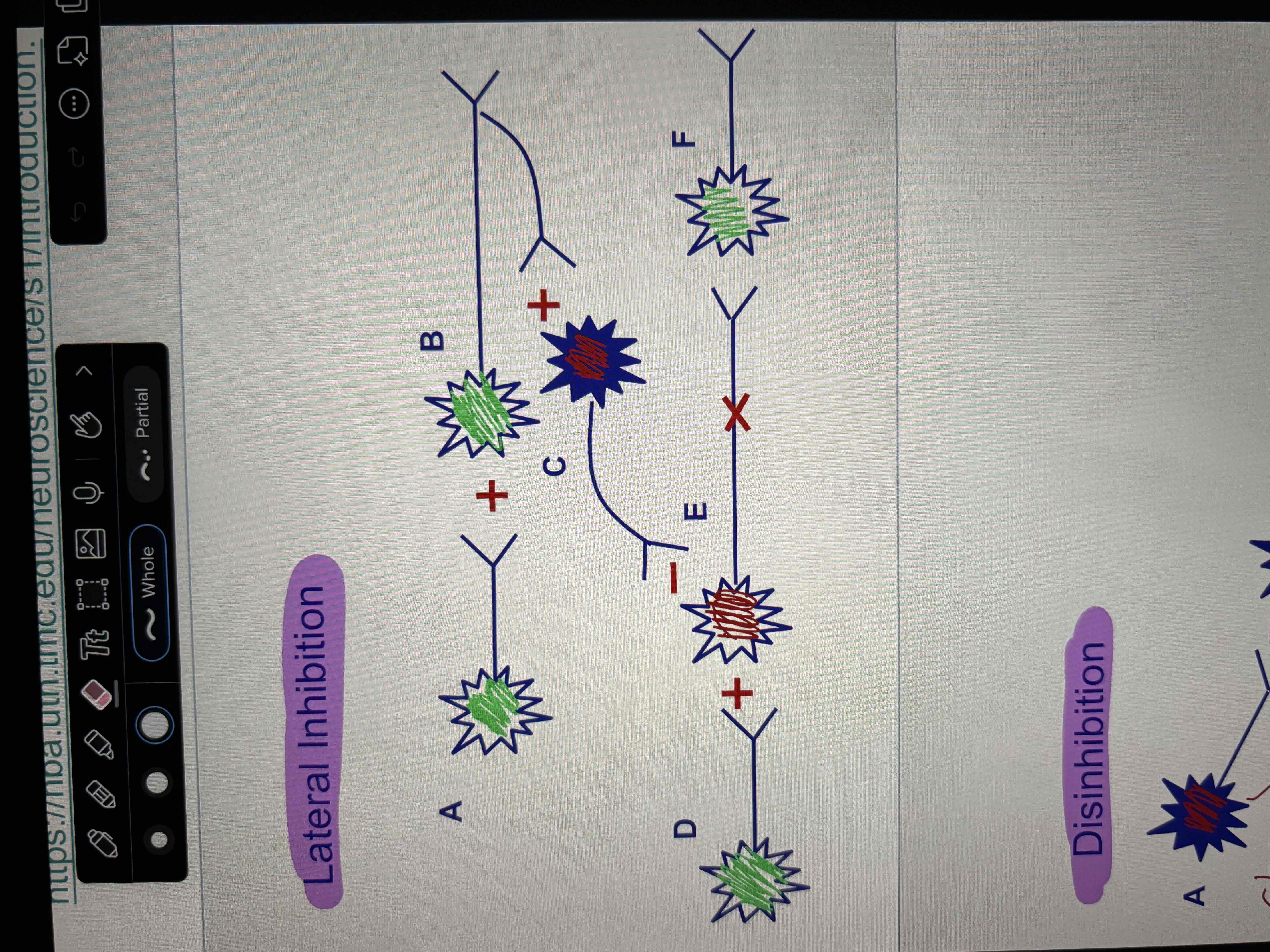
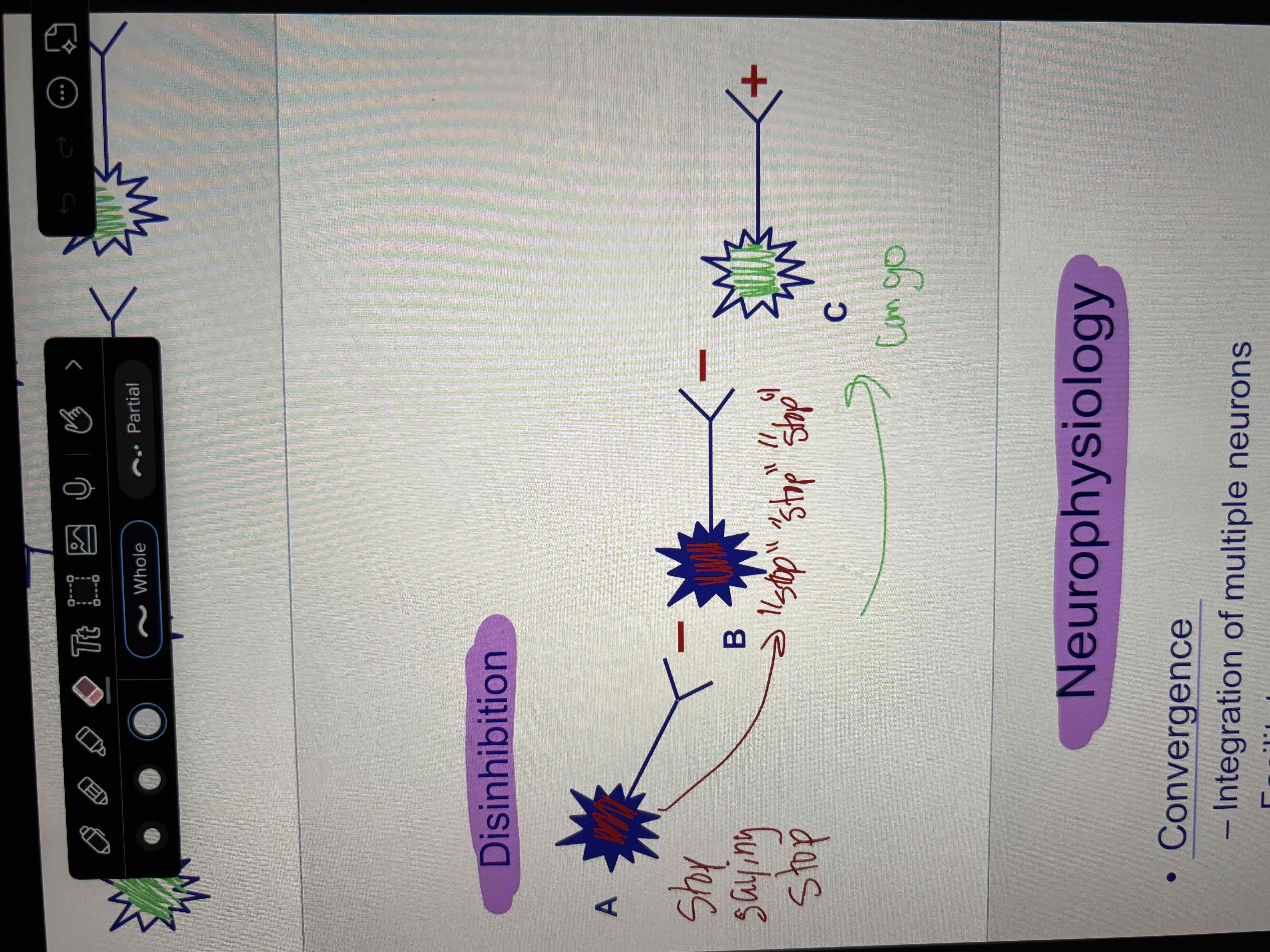
Disinhibition
“stop stop stop”
stop saying stop
can go
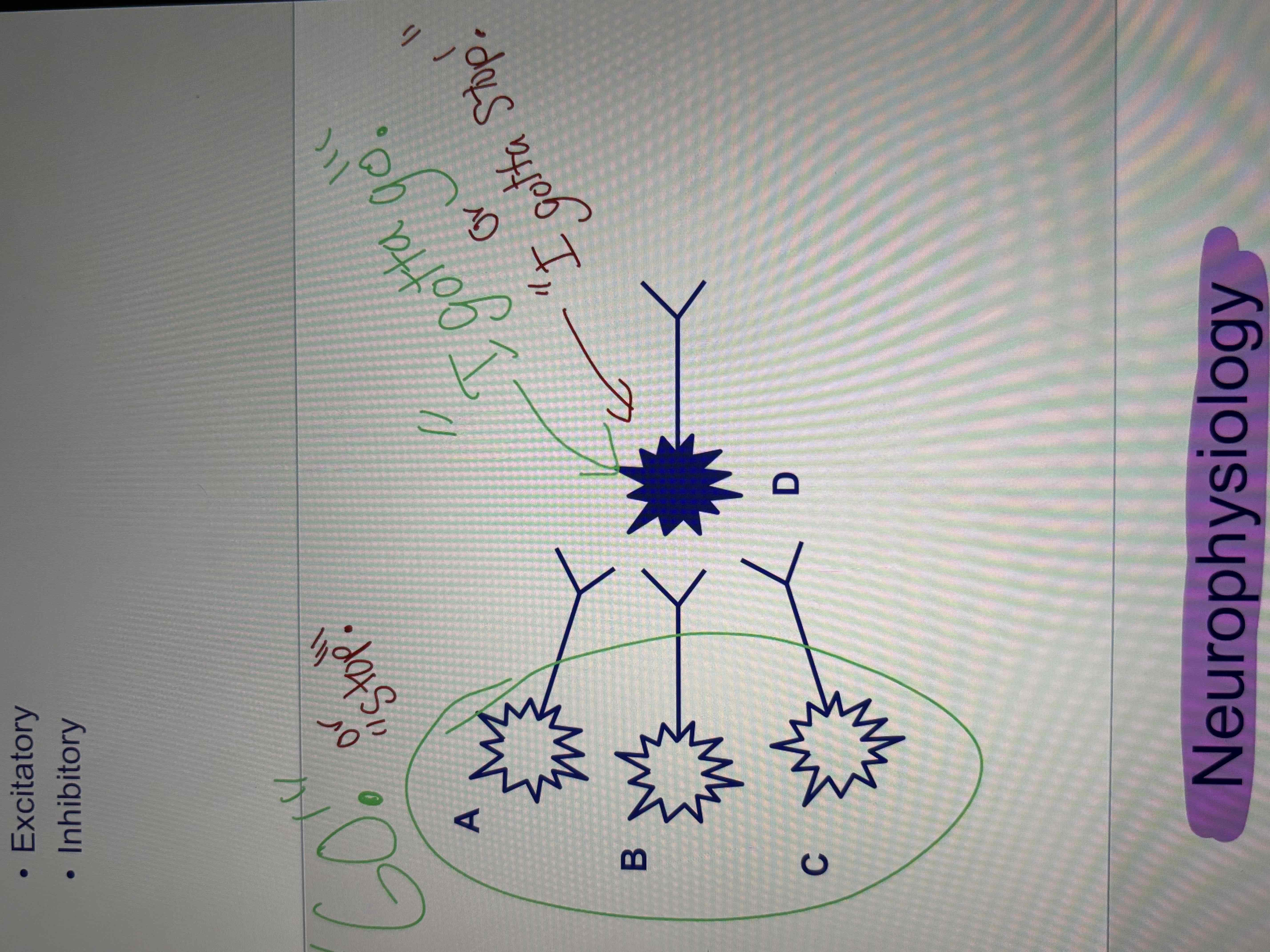
convergence
integration of multiple neurons
facilitates propagation of single signal transmission (increases likelihood of neuronal firing)
excitatory and inhibitory
Divergence
coordination of signal transmission from single neuron to multiple neurons
excitatory and inhibitory