Honors When Good Cells Go Bad
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Mutation
change in a DNA sequence that affects genetic information
missense mutation
A base-pair substitution that results in a codon that codes for a different amino acid.
nonsense mutation
A mutation that changes an amino acid codon a stop codon, resulting in a shorter and usually nonfunctional protein.
silent mutation
A mutation that changes a single nucleotide, but does not change the amino acid created.
frameshift mutation
involves the insertion or deletion of a nucleotide in the DNA sequence
cancer cells
Do not have a properly functioning cell-cycle system; instead, they divide excessively and can invade other tissues of the body
tumor suppressor genes
make proteins that stop cell division and kill cells
Proto-oncogenes
the corresponding normal cellular genes that are responsible for normal cell growth and division
Apoptosis
programmed cell death
DNA repair
Term for the processes that correct changes to a DNA molecule.
checkpoints
3 points (g1, G2, M) where regulatory proteins (enzymes) determine if cell is ready to proceed in cell cycle
G1 phase
stage of interphase in which cell grows and performs its normal functions
S phase
DNA is replicated during interphase
G2 phase
stage of interphase in which cell prepares to divide
Protein
A polymer made of monomers of amino acids.
multi-hit model
multiple mutations are usually required to convert a normal cell to a malignant one
cell cycle
series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide
Mitosis
division of the nucleus
Cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm
G0 phase
a non dividing state occupied by cells that have left the cell cycle, sometimes reversibly
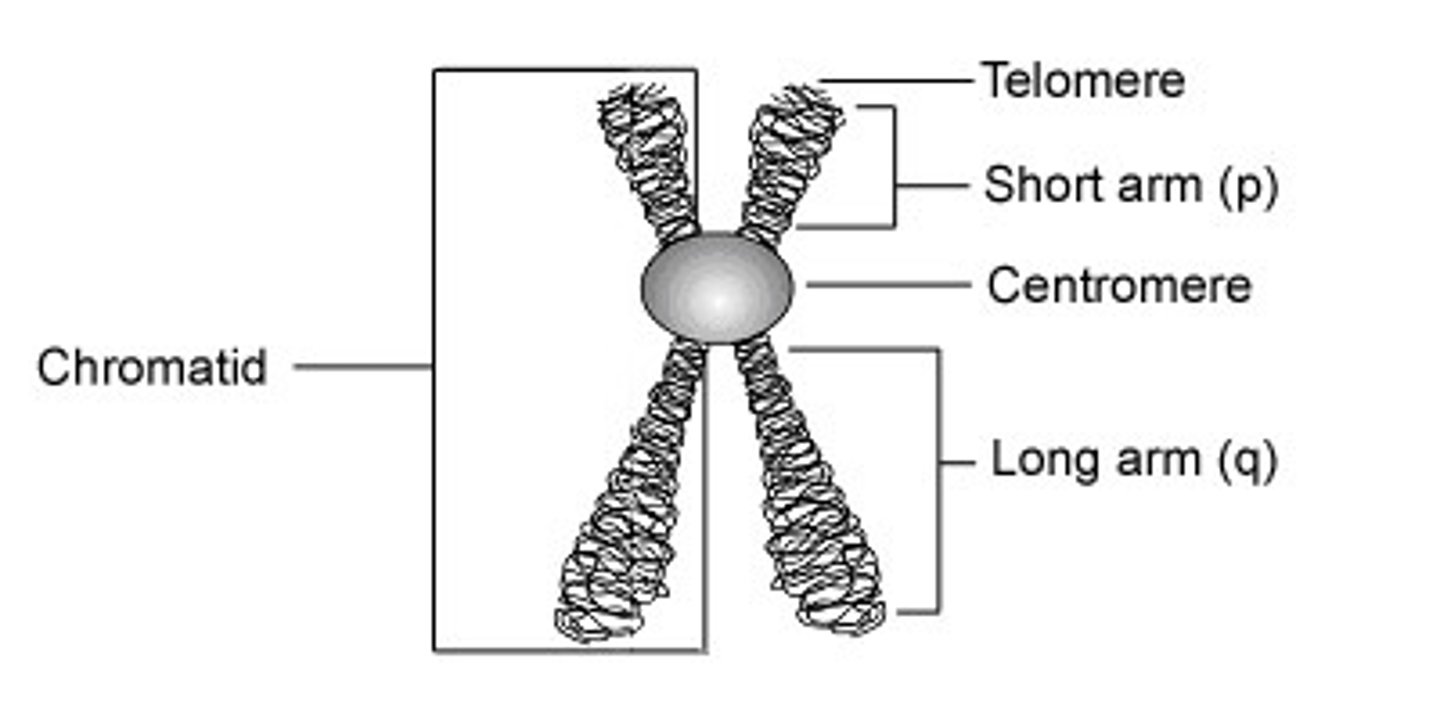
sister chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome; full sets of these are created during the S subphase of interphase.
Chromatin
uncondensed DNA
chemotherapy
treatment of cancer with drugs that target rapidly dividing cells
spindle fibers
Protein structures which move the chromosomes during cell division.
causes of mutations
Copying Errors and Exposure to Chemicals & UV radiation
Prophase
Chromosomes become visable, nuclear envelop dissolves, spindle forms
Metaphase
phase of mitosis in which the sister chromatides line up across the center of the cell
Anaphase
the third phase of mitosis, during which the chromosome pairs separate and move toward opposite poles
Telophase
phase of mitosis in which the distinct individual chromosomes begin to spread out into a tangle of chromatin
Oncogenes
genes that cause cancer by blocking the normal controls on cell reproduction
Image of interphase
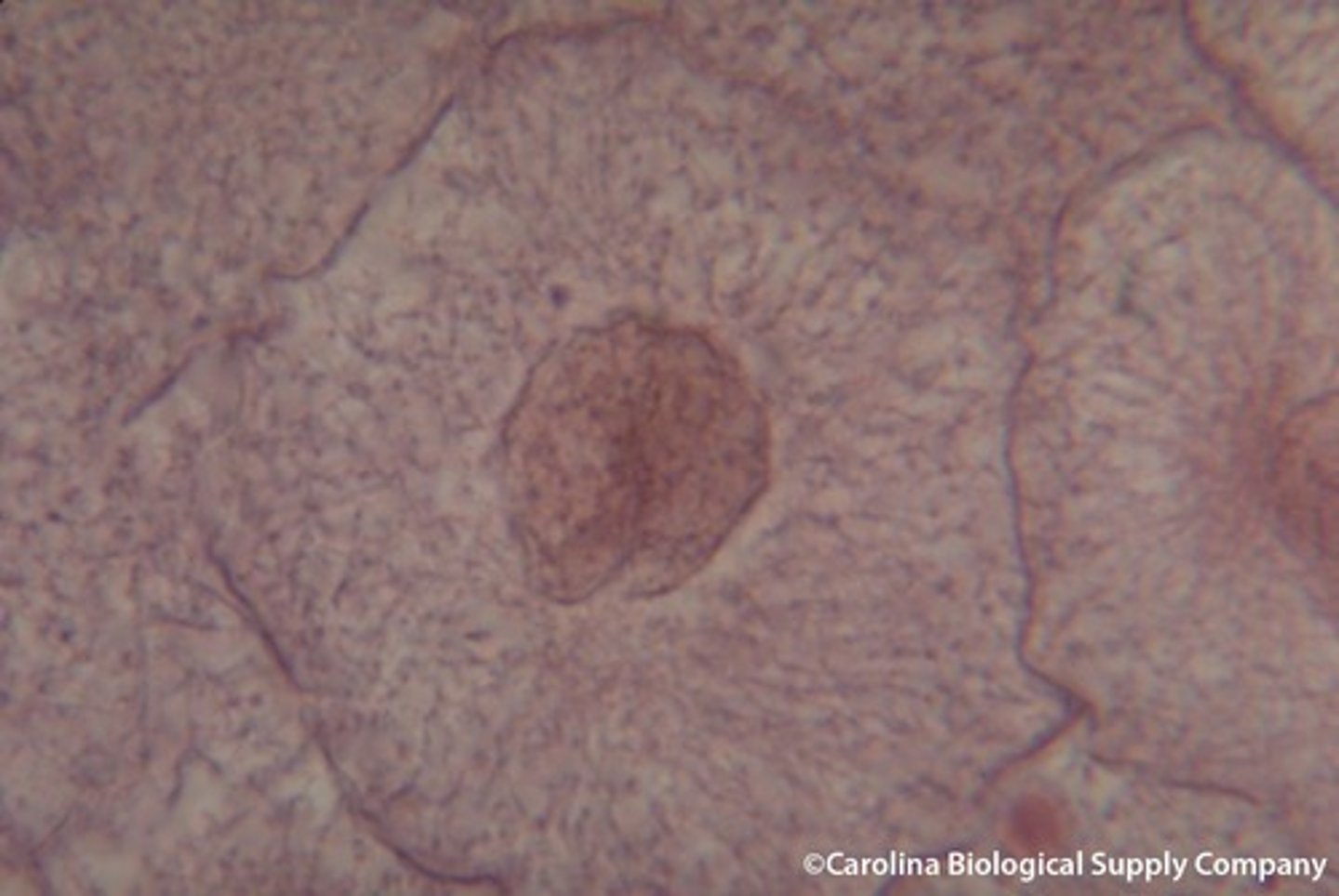
Image of prophase
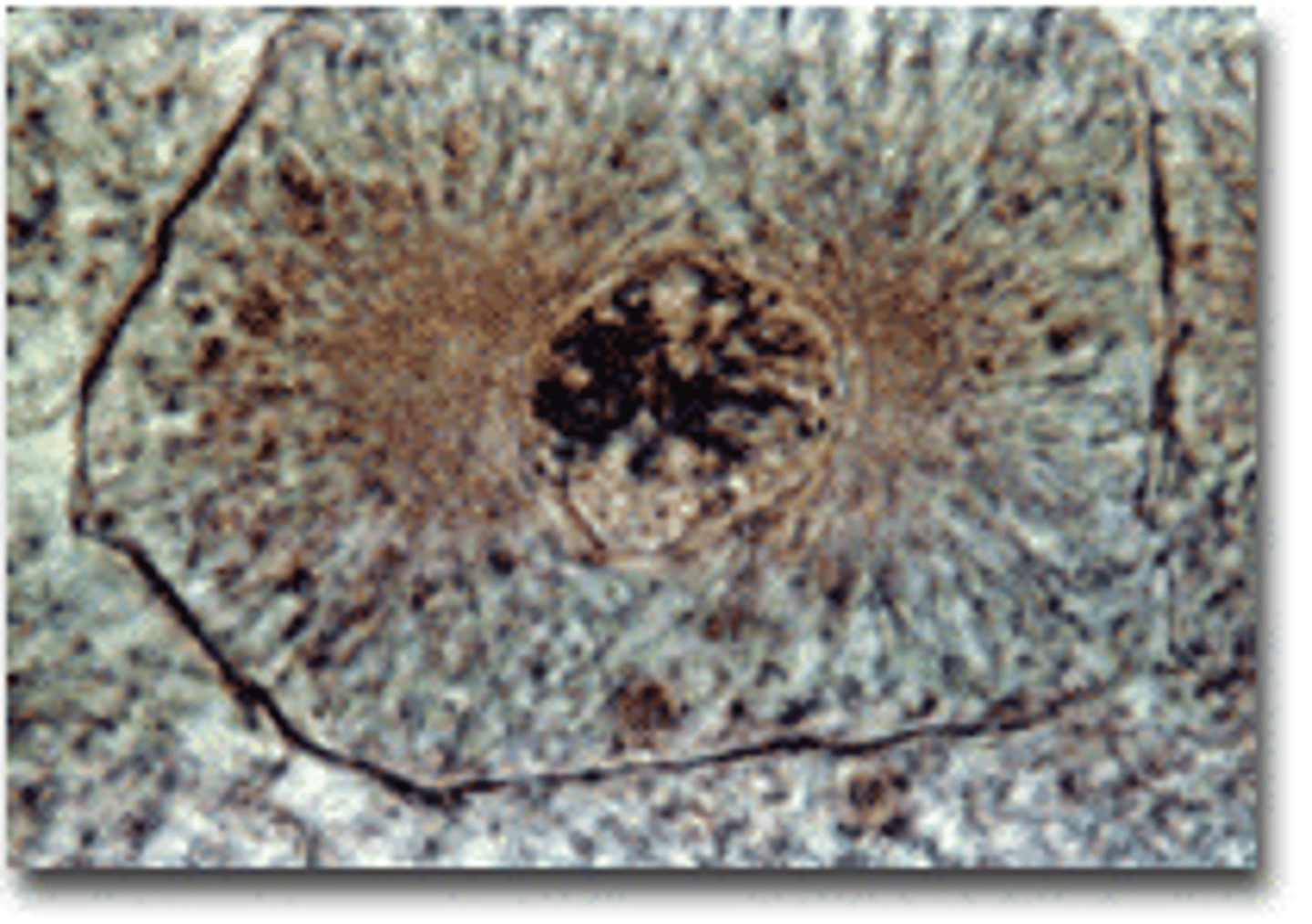
Image of metaphase
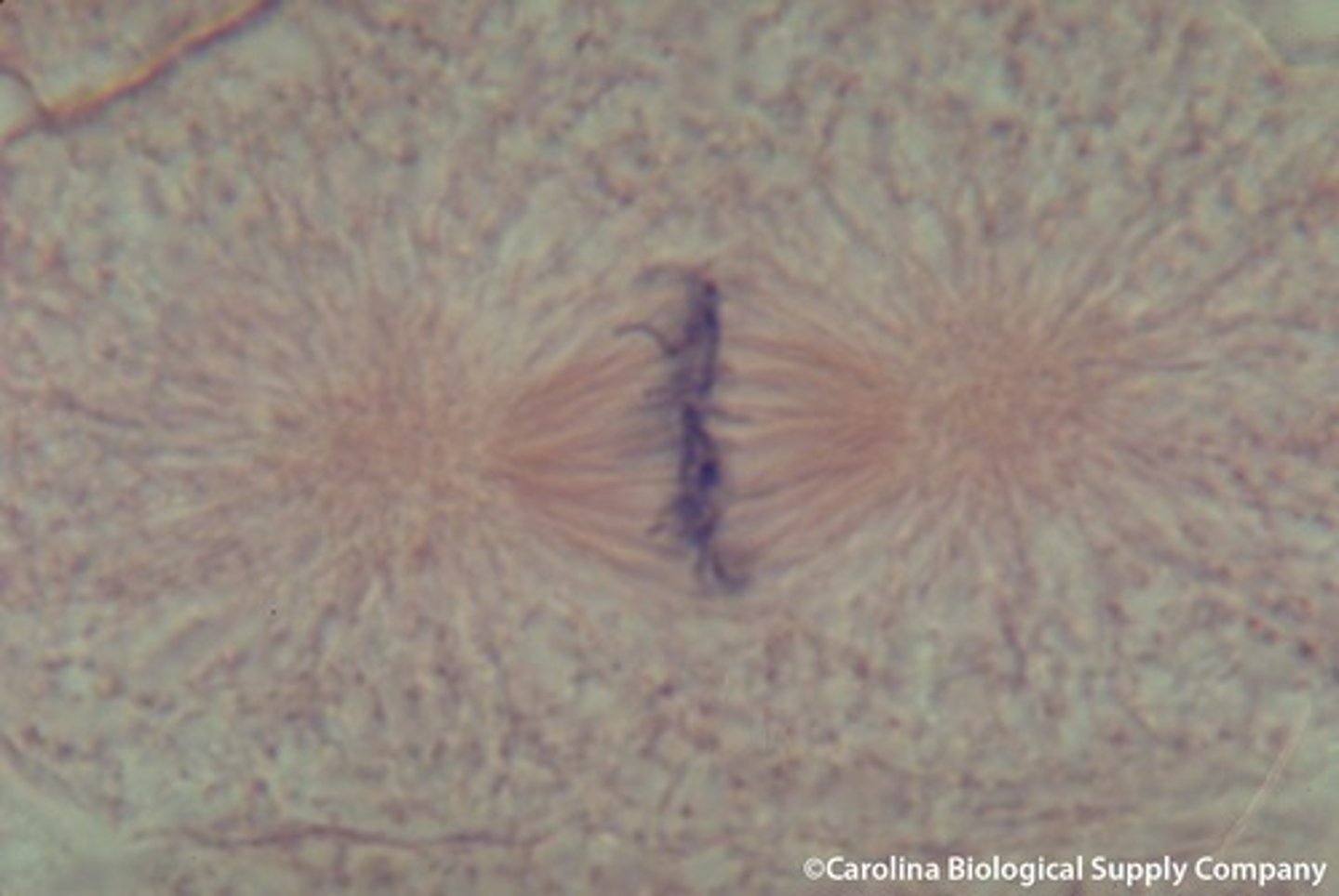
Image of Anaphase
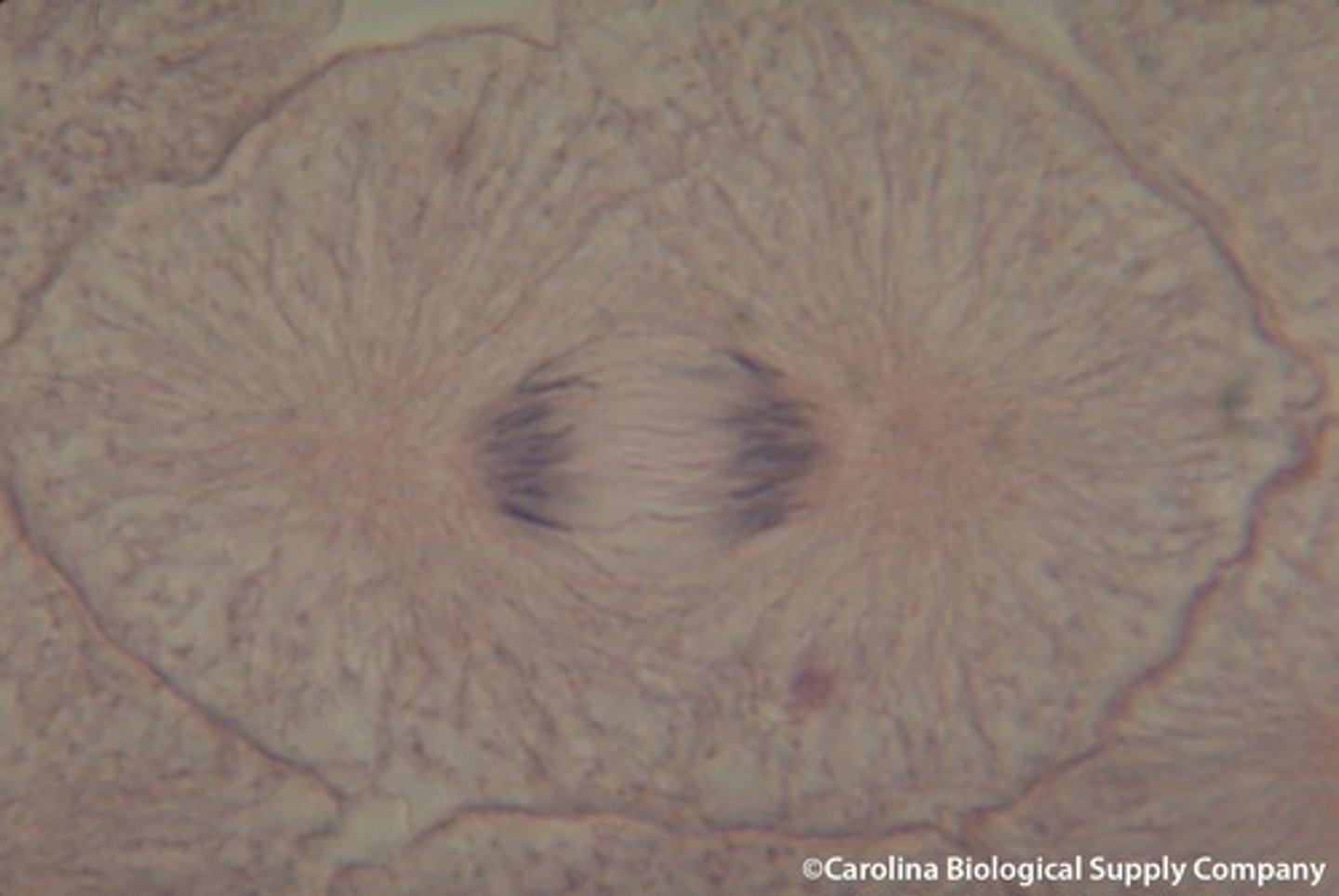
Image of telophase/cytokinesis
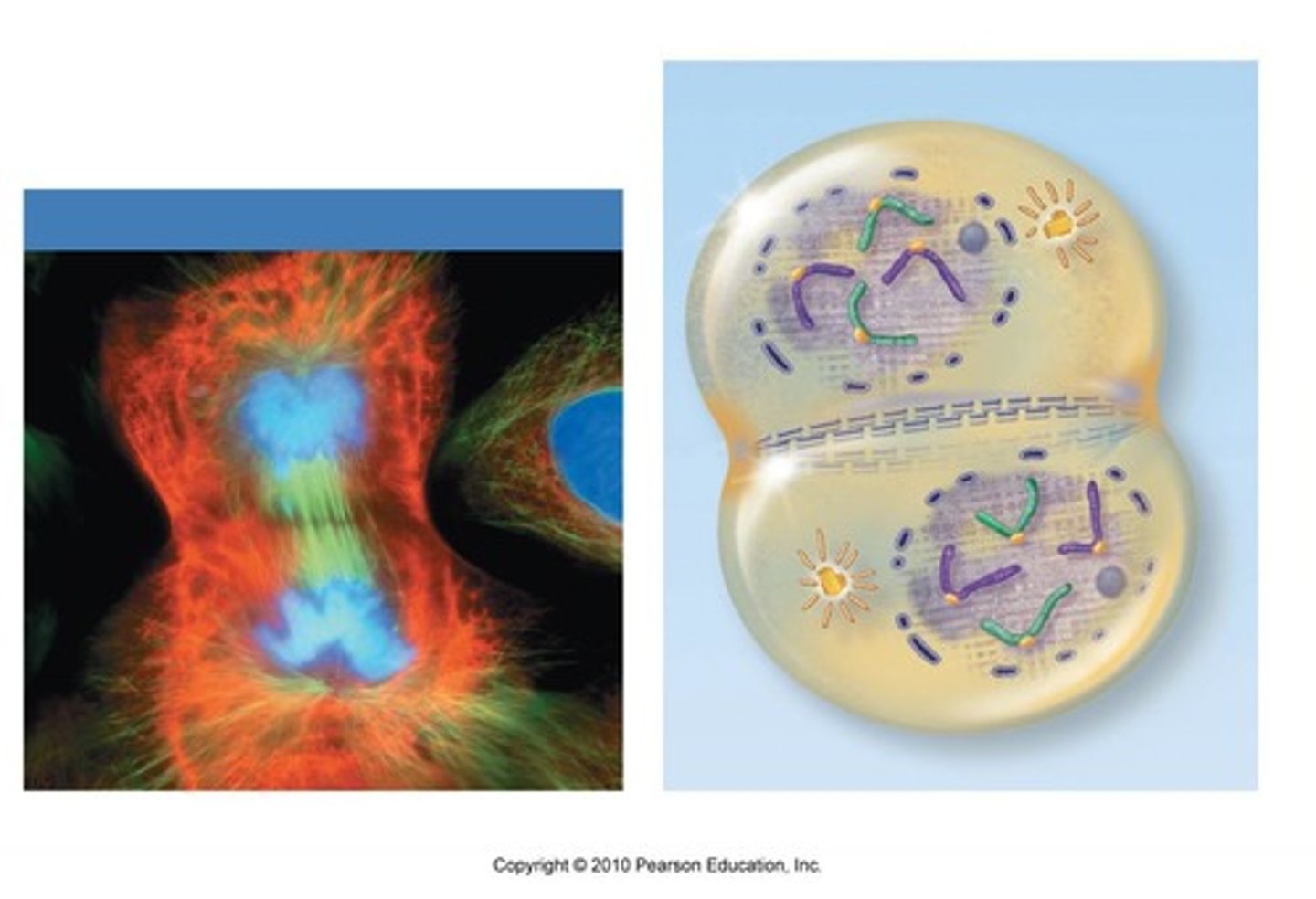
Image of sister chromatids