Solid waste and soil pollution treatment
1/162
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Part 2 of Industrial Waste Management and Control
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
163 Terms
Solid waste
It refers to all the wastes arising from human and animal activities that are normally solid and are discarded as useless or unwanted.
Reduce
Reuse
Recycle
Recover
Residue
Enumerate the 5Rs in the hierarchy of waste minimization (from top to bottom).
FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.
Waste reduction
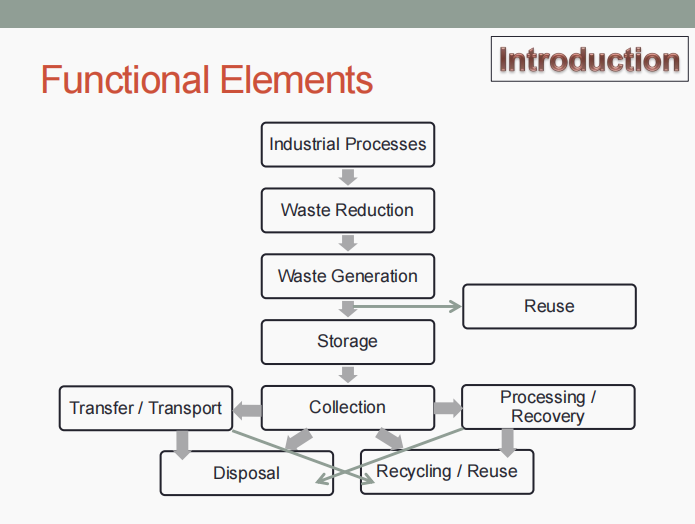
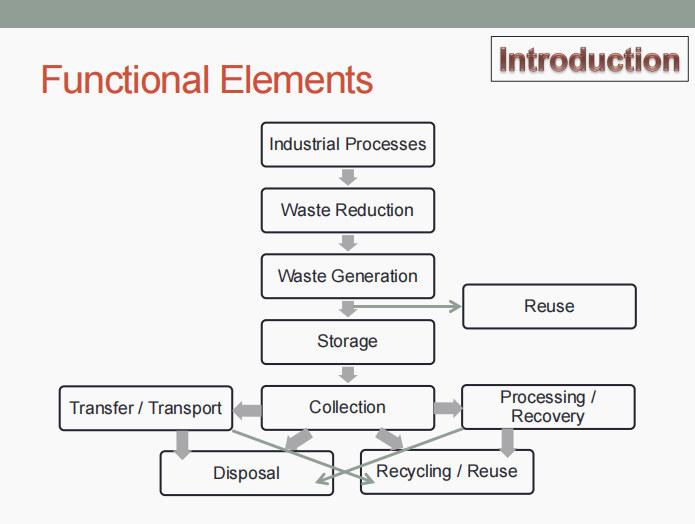
FUNCTIONAL ELEMENTS. Determine what is being described below.
Processes redesigned to reduce amount of waste generated
Waste generation
FUNCTIONAL ELEMENTS. Determine what is being described below.
Activities in which materials are identified as no longer being of value, and are either thrown away or gathered together for disposal
Reuse
FUNCTIONAL ELEMENTS. Determine what is being described below.
Waste may be diverted to reuse.
On-site handling, storage, and processing
FUNCTIONAL ELEMENTS. Determine what is being described below.
Of primary importance because of aesthetic, public health and safety, and economic considerations
Collection
FUNCTIONAL ELEMENTS. Determine what is being described below.
Gathering and hauling of solid wastes to a designed location (ex.: transfer station, processing station, or a landfill disposal site)
Transfer and transport
FUNCTIONAL ELEMENTS. Determine what is being described below.
(1) Transfer of wastes from the smaller container to the larger transport equipment, and
(2) Subsequent transport of the wastes, usually over long distances, to the disposal site
Processing and recovery
FUNCTIONAL ELEMENTS. Determine what is being described below.
All techniques, equipment, and facilities used both to improve the efficiency of the other functional elements, and to recover usable materials, conversion products, or energy from solid wastes.
Disposal
FUNCTIONAL ELEMENTS. Determine what is being described below.
Includes (a) wastes that are collected or transported directly to a landfall site, (b) semisolid wastes (sludge) from industrial treatment plants and air-pollution control devices, (c) incinerator residue, (d) compost, and (e) other substances from various solid waste processing plants that are of no further use.

FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.

Individual components
Density
Moisture content
Particle size
Enumerate the four (4) physical composition properties of solid wastes.
Moisture content
PHYSICAL COMPOSITION OF SOLID WASTE. Determine what is being described below.
It refers to the mass of moisture per unit mass of wet or dry material.
Particle size
PHYSICAL COMPOSITION OF SOLID WASTE. Determine what is being described below.
The material handling properties of solid wastes depend on this property.
Proximate analysis
Fusion point of ash
Ultimate analysis (CHONS)
Heating value
Organic chlorine
Organic sulfur
Enumerate the six (6) chemical composition properties of solid wastes, if they are to be used as fuel.
Extent of salvage and recycle operations
Company attitudes
Legislation and regulations
Enumerate the three (3) factors that affect industrial solid waste generation rates.
On-site handling
This refers to activities associated with handling of solid wastes until they are placed in storage containers before collection.
From office containers to large storage containers, compactors used with large containers, stationary compactors, and other processing equipment
ON-SITE HANDLING. Determine what is being described below.
How are conventional solid wastes being handled?
Hazardous Waste Operations and Emergency Response (HAZWOPER) training
ON-SITE HANDLING. Determine what is being described below.
How are hazardous wastes being handled?
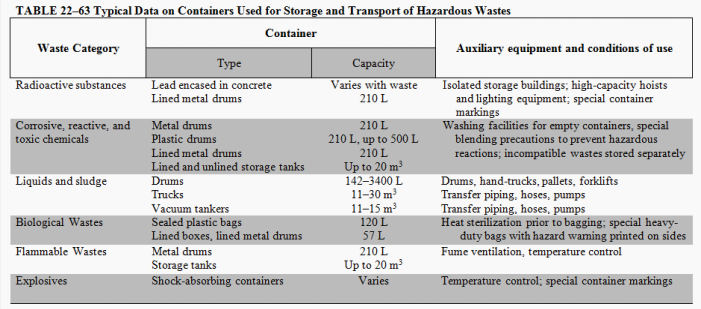
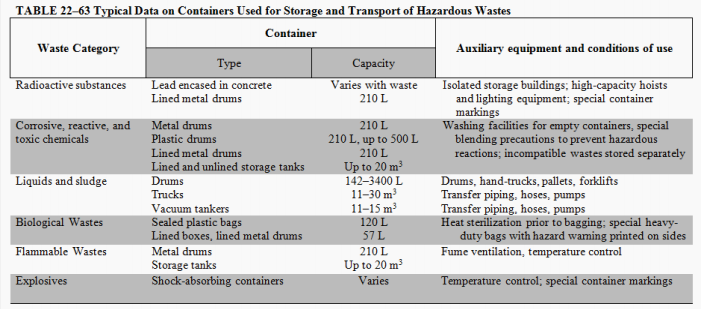
Container type
Container location
Public health and aesthetics
Collection method
Future transport method
Enumerate the five (5) factors to be considered in on-site storage.
Characteristics of solid waste
Collection frequency
Available space
The type and capacity of containers depend on (3):
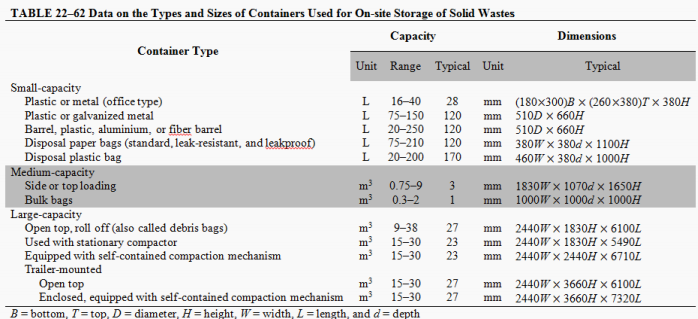
FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.
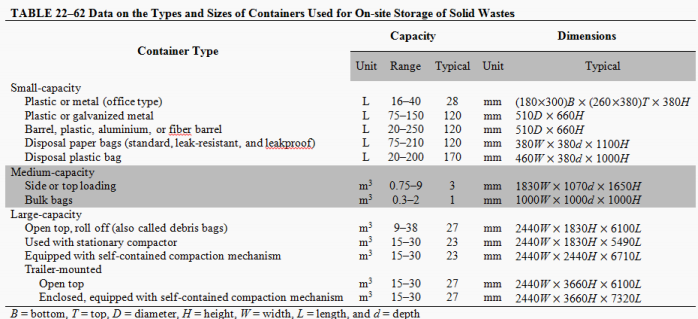
Types and amounts of hazardous wastes generated
Time period over which waste generation occurs
Containers for hazardous wastes are a function of (2):
FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.
Location of available space
Service-access conditions
Container location depends on (2):
Containers
These are usually owned by the collection agency.
Space
It is usually owned by the commercial or industrial organization.
On-site processing
It is done to recover usable materials, remove volume, or alter the physical form of solid wastes.
Manual sorting
Compaction
Incineration
Enumerate the three (3) most common on-site processing operations.

FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.

READ.
Processing and resource recovery includes:
Processing techniques for solid waste
Processing techniques for hazardous wastes
Materials-recovery systems
Recovery of biological conversion products
Thermal processes
Waste-to-energy systems
READ.
Processing and resource recovery includes:
Processing techniques for solid waste
Processing techniques for hazardous wastes
Materials-recovery systems
Recovery of biological conversion products
Thermal processes
Waste-to-energy systems
READ.
Processing techniques for solid waste are done to:
Improve the efficiency of the systems
Recover resources (usable materials)
Prepare materials for recovery of conversion products and energy
READ.
Processing techniques for solid waste are done to:
Improve the efficiency of the systems
Recover resources (usable materials)
Prepare materials for recovery of conversion products and energy
Manual component separation
Storage and transfer
Mechanical volume reduction
Chemical volume reduction
Mechanical size alteration
Mechanical component separation
Magnetic and electromechanical separation
Drying and dewatering
Bulking of liquid wastes
Enumerate the nine (9) important techniques for solid waste processing.
Component separation
It is the heart of recycling.
READ.
Processing of hazardous waste is to:
Recover useful materials
Reduce the amount of wastes disposed in landfills
Prepare the wastes for ultimate disposal
READ.
Processing of hazardous waste is to:
Recover useful materials
Reduce the amount of wastes disposed in landfills
Prepare the wastes for ultimate disposal
Physical
Chemical
Thermal
Biological
(ADDITIONAL: Physical, chemical, and thermal techniques are most commonly used.)
Enumerate the four (4) processing techniques for hazardous waste.
FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.
Identification of waste constituents
It is considered the key item in any processing (and disposal) scheme and a responsibility of the waste generator.
Paper
Rubber
Plastics
Textiles
Glass
Metals
Organic and inorganic materials
Enumerate the seven (7) principal recoverable materials in industrial solid wastes.
Process performance efficiency
Reliability and flexibility
Ease and economy of operation
Aesthetics
Environmental controls
Enumerate the factors for design and layout of physical facilities.
Refuse-derived fuel (RDF)
Light combustible materials are often identified as ___.

FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.

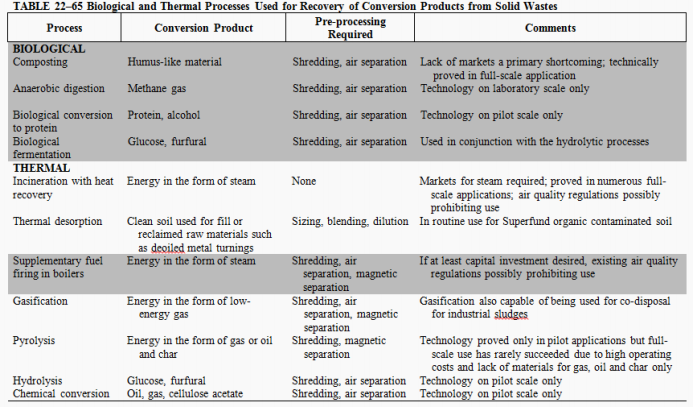
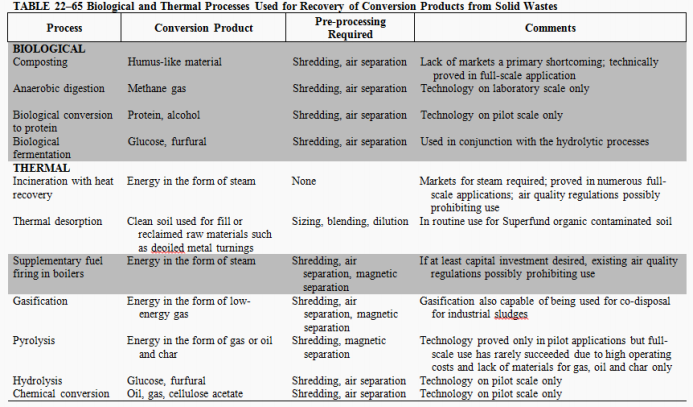
Composting
Anaerobic digestion
What are the two (2) most highly developed processes to produce biological conversion products?
Composting
HIGHLY DEVELOPED PROCESSES FOR BIOLOGICAL CONVERSION. Determine what is being described below.
It is the process involving both separation and bacterial conversion of organic wastes.
Compost or humus
HIGHLY DEVELOPED PROCESSES FOR BIOLOGICAL CONVERSION. Determine what is being described below.
It is the end product remaining after dissimilatory and assimilatory bacterial activity.
Anaerobic digestion
HIGHLY DEVELOPED PROCESSES FOR BIOLOGICAL CONVERSION. Determine what is being described below.
It is the process used for the production of methane from solid wastes.
Anaerobic fermentation
HIGHLY DEVELOPED PROCESSES FOR BIOLOGICAL CONVERSION. Determine what is being described below.
Anaerobic digestion is also called as ___.
Composting
HIGHLY DEVELOPED PROCESSES FOR BIOLOGICAL CONVERSION. Determine what is being described below.
It may be accomplished either aerobically or anaerobically.
Composting
HIGHLY DEVELOPED PROCESSES FOR BIOLOGICAL CONVERSION. Determine what is being described below.
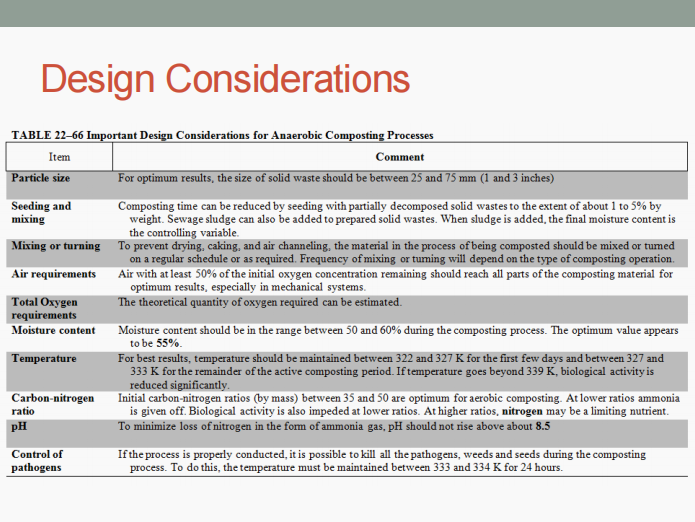
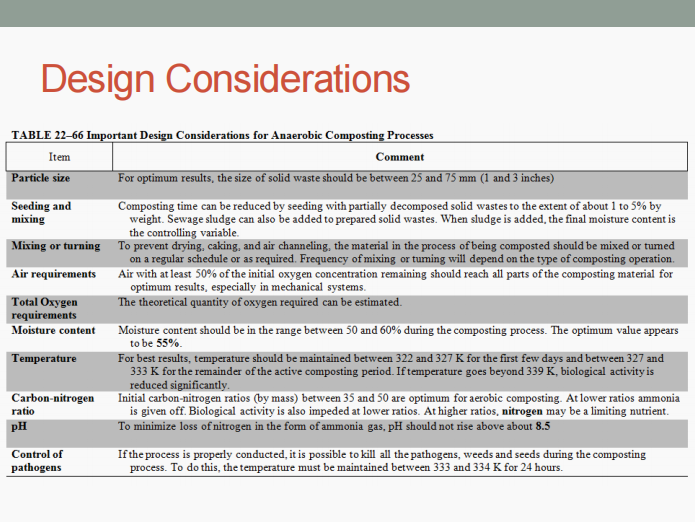
Its three (3) basic steps include:
Preparation of solid wastes (with moisture and nutrient addition)
Decomposition of solid wastes
Size reduction
Anaerobic digestion
HIGHLY DEVELOPED PROCESSES FOR BIOLOGICAL CONVERSION. Determine what is being described below.
Its three (3) basic steps include:
Preparation of the organic fraction of the solid wastes
Addition of moisture and nutrients, blending, pH adjustment (≈6.7), heating of the slurry (327-333 K), anaerobic digestion in a well-mixed continuous flow reactor (8-15 days)
Capture, storage, (if necessary) separation of gas components
Disposal of digested sludge
FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.
Incineration with heat recovery
Combustion
Gasification
Pyrolysis
Enumerate the four (4) thermal processes mentioned in the module.
Incineration with heat recovery
THERMAL PROCESSES. Determine what is being described below.
Includes:
In existing incinerators
In water-wall incinerators (internal walls of combustion chamber lined with boiler tubes)
Combustion
THERMAL PROCESSES. Determine what is being described below.
It is the process of burning something; an exothermic process.
Mass-burn
Modular
RDF-fired facilities
THERMAL PROCESSES. Determine what is being described below.
Enumerate three (3) types of combustors.
Gasification
THERMAL PROCESSES. Determine what is being described below.
Partial combustion of a carbonaceous or hydrocarbon fuel to generate a combustible fuel gas rich in carbon monoxide and hydrogen
Pyrolysis
THERMAL PROCESSES. Determine what is being described below.
Decomposition brought about by high temperatures
Destructive distillation
THERMAL PROCESSES. Determine what is being described below.
Pyrolysis is also called as ___.
Waste to Energy systems
It refers to the use of high-pressure or high-temperature stream to drive turbines and produce shaft horsepower for prime movers at industrial plants or to generate electricity.
True
TRUE OR FALSE. Disposal on/in Earth’s mantle is, at present, the only viable method for long-term handling of (1) solid wastes collected that are of no further use, (2) residue after solid waste processing, (3) residue after recovery of conversion products and/or energy.
Dump
What is considered the most common disposal method?
Dump
It refers to the accumulation of refuse and discarded materials; a disorderly, slovenly, or objectionable place.
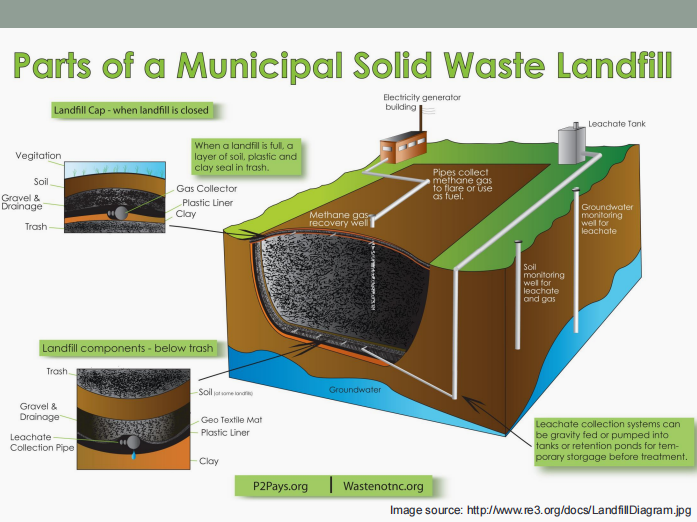
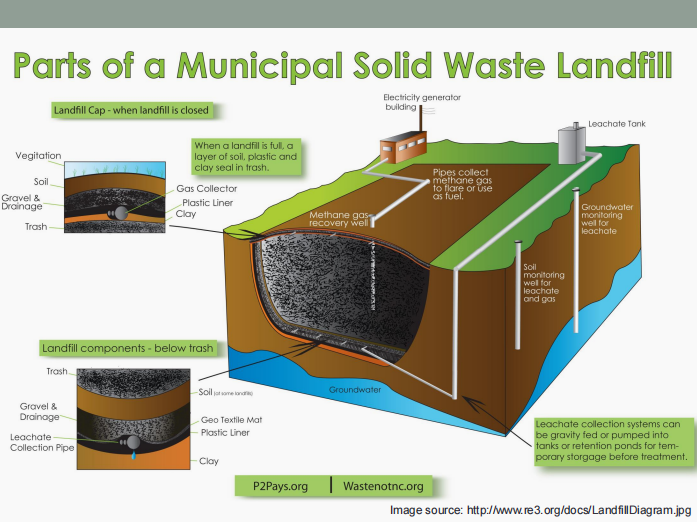
Landfill
Landfarm
Deep-well injection
Enumerate three (3) land disposal methods.
False
(EXPLANATION: In reality, incineration is a processing method.)
TRUE OR FALSE. In reality, incineration is considered a disposal method.

FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.

Dumpsite
DUMPSITE VS LANDFILL. Determine what is being described below.
It is an excavated piece of land used as storage for waste materials.
Dumpsite
DUMPSITE VS LANDFILL. Determine what is being described below.
It produces toxic gases and a hazard because it can be located anywhere.
Landfill
DUMPSITE VS LANDFILL. Determine what is being described below.
It is an excavated piece of land for waste storage but is regulated by the government.
Dumpsite
DUMPSITE VS LANDFILL. Determine what is being described below.
It does not have leachate collection and treatment systems.
Landfill
DUMPSITE VS LANDFILL. Determine what is being described below.
It might produce toxic gases which are released into the air and ground because waste materials cannot rot.
Landfill
DUMPSITE VS LANDFILL. Determine what is being described below.
It is covered daily with soil to deter pests and prevent bad smells from being released into the air.
Dumpsite
DUMPSITE VS LANDFILL. Determine what is being described below.
It has no liner at the bottom to catch the liquid produced by solid waste.
Landfill
DUMPSITE VS LANDFILL. Determine what is being described below.
It is larger in scale.
Dumpsite
DUMPSITE VS LANDFILL. Determine what is being described below.
It may or may not be covered with soil.
Landfill
DUMPSITE VS LANDFILL. Determine what is being described below.
It has a liner at the bottom to catch the liquid produced by solid waste.
Landfill
DUMPSITE VS LANDFILL. Determine what is being described below.
It has leachate collection and treatment systems.
FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.
Landfill
It is a large-scale operation with the controlled disposal of solid wastes on or in the upper layer of the Earth’s mantle.
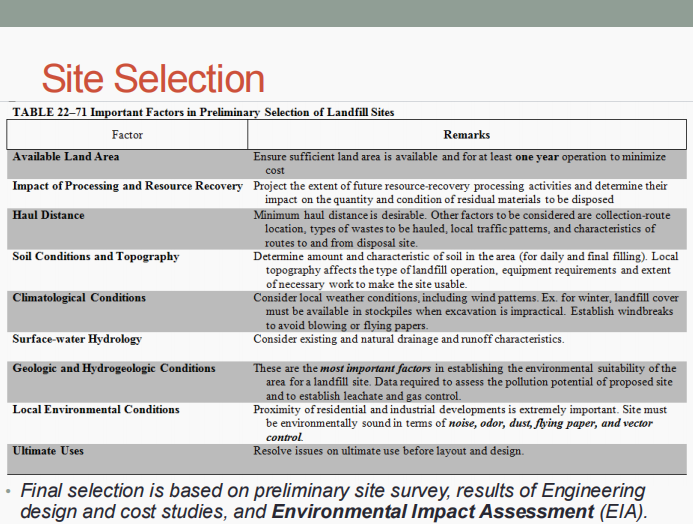
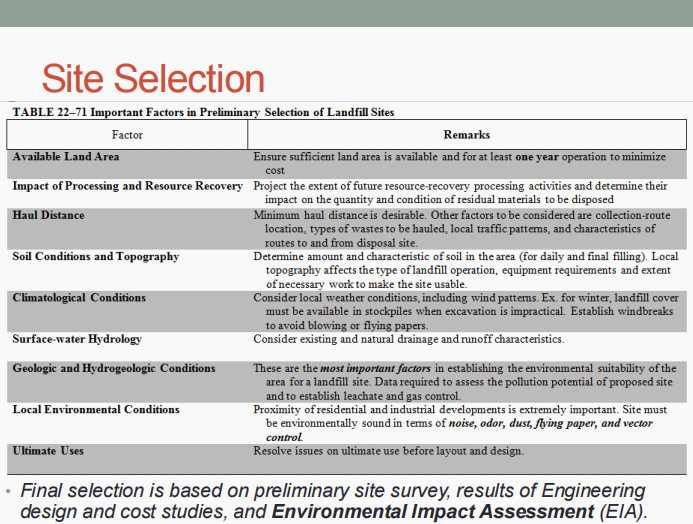
Site selection
Methods and operations
Occurrence of gases and leachates
Movement and control of gases and leachates
Landfill design
Enumerate the five (5) important aspects of sanitary landfills.
FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.
Depression (trench) method
Area method
Enumerate the methods and operations used in a landfill for dry areas.
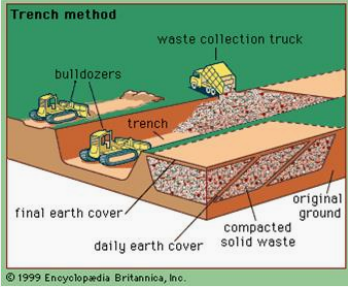
Depression (trench) method
METHODS AND OPERATIONS FOR DRY AREAS. Determine what is being described below.
This is used for locations where natural or artificial depressions exist.
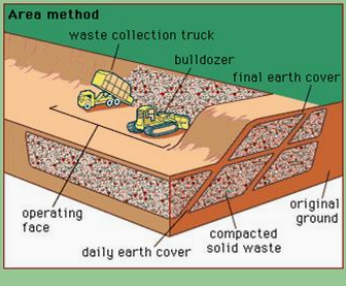
Area method
METHODS AND OPERATIONS FOR DRY AREAS. Determine what is being described below.
This is used when the terrain is unsuitable for excavation of trenches in which to place solid wastes.
READ.
Under area method operation,
Begin with building of earthen levee, against which wastes are placed in thin layers and then compacted.
Each layer is compacted as the filling progresses until the thickness of the compacted wastes reaches a height varying from 2 to 3 m (6 to 10 ft).
At the end of each day’s operation, a 150 to 300 mm (6 to 12 inch) layer of cover material (hauled from adjacent land or borrow-pit areas) is placed over the completed fill.
In some newer landfill operations, reusable geotextile covers are used instead of soil.
READ.
Under area method operation,
Begin with building of earthen levee, against which wastes are placed in thin layers and then compacted.
Each layer is compacted as the filling progresses until the thickness of the compacted wastes reaches a height varying from 2 to 3 m (6 to 10 ft).
At the end of each day’s operation, a 150 to 300 mm (6 to 12 inch) layer of cover material (hauled from adjacent land or borrow-pit areas) is placed over the completed fill.
In some newer landfill operations, reusable geotextile covers are used instead of soil.
Depression method operation
METHODS AND OPERATIONS FOR DRY AREAS. Determine what is being described below.
Used in canyons, ravines, dry borrow pits, quarries
Depression method operation
METHODS AND OPERATIONS FOR DRY AREAS. Determine what is being described below.
In this method, the technique varies with geometry of the site, characteristics of the cover material, hydrology and geology of the site, and access of the site.
READ.
Under depression method,
In canyons, filling starts at the head end of the canyon and ends at the mouth to prevent accumulation of water behind the landfill.
Wastes are deposited in the canyon floor, pushed against the canyon face at a 2:1 slope to achieve high degree of compaction.
READ.
Under depression method,
In canyons, filling starts at the head end of the canyon and ends at the mouth to prevent accumulation of water behind the landfill.
Wastes are deposited in the canyon floor, pushed against the canyon face at a 2:1 slope to achieve high degree of compaction.
READ.
For methods and operations for wet areas,
Problems include contamination of local ground water, odors, and structural stability.
Operation includes: (1) drain the site and line the bottom with clay liner or other appropriate sealants, and (2) continuous drainage operation for clay liner to avoid uplift pressures that cause liner rupture from heaving.
READ.
For methods and operations for wet areas,
Problems include contamination of local ground water, odors, and structural stability.
Operation includes: (1) drain the site and line the bottom with clay liner or other appropriate sealants, and (2) continuous drainage operation for clay liner to avoid uplift pressures that cause liner rupture from heaving.
Air
Ammonia
Carbon dioxide
Carbon monoxide
Hydrogen
Hydrogen sulfide
Methane
Nitrogen
Oxygen
Gases in landfills include (9):
Carbon dioxide
Methane
Principal gases produced from anaerobic decomposition include (2):
READ.
Under biological, physical, or chemical activities of gases and leachate in landfills,
Biological decay of organic materials (aerobic or anaerobic) with evolution of gases and liquids
> Initially under aerobic conditions because air is trapped within the landfill, but oxygen in trapped air is exhausted within days, and long-term decomposition occurs under anaerobic condition
Chemical oxidation of waste materials
Escape of gases from the fill
Movement of liquids caused by differential heads
Dissolving and leaching of organic and inorganic materials by water and leachates moving through the fill
Movement of dissolved material by concentration gradients and osmosis, and
Uneven settlement caused by consolidation of material into voids.
READ.
Under biological, physical, or chemical activities of gases and leachate in landfills,
Biological decay of organic materials (aerobic or anaerobic) with evolution of gases and liquids
> Initially under aerobic conditions because air is trapped within the landfill, but oxygen in trapped air is exhausted within days, and long-term decomposition occurs under anaerobic condition
Chemical oxidation of waste materials
Escape of gases from the fill
Movement of liquids caused by differential heads
Dissolving and leaching of organic and inorganic materials by water and leachates moving through the fill
Movement of dissolved material by concentration gradients and osmosis, and
Uneven settlement caused by consolidation of material into voids.
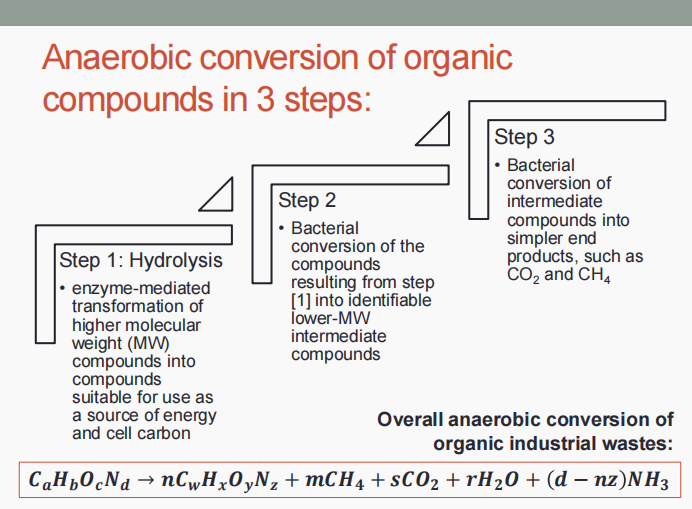
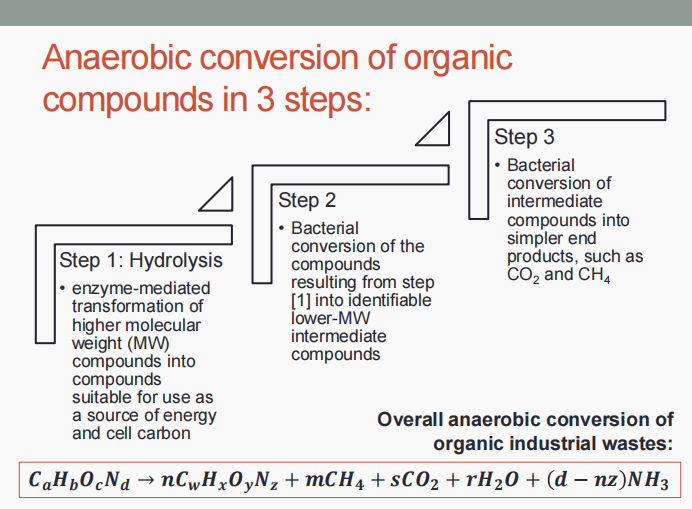
Hydrolysis
Bacterial conversion of the compounds into identifiable lower MW intermediate compounds
Bacterial conversion of intermediate compounds into simpler end products, such as CO2 and CH4
The anaerobic conversion of organic compounds occur in three (3) steps which are:
FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.
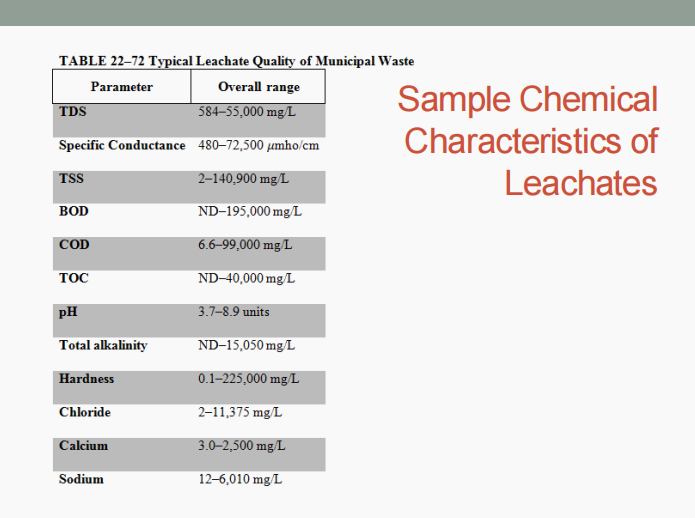
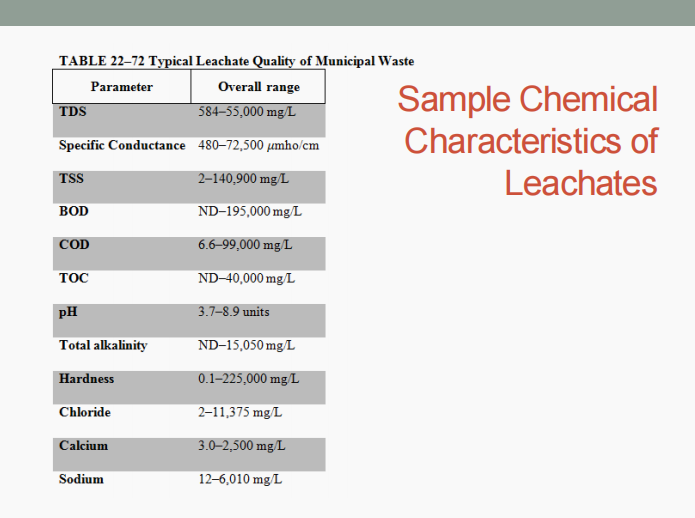
Leachate
It is the liquid that has percolated through solid waste and has extracted dissolved or suspended materials from it.
Leachate
It consists of (1) liquid produced from the decomposition of the waste, and (2) liquid that has entered the landfill from external sources (ex.: surface drainage, rainfall, groundwater, water from underground springs).
FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.

FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.

Carbon and methane
GAS MOVEMENT IN LANDFILLS. Determine what is being asked below.
These gases are over 90% of the gas volume and contribute to greenhouse effect.
Methane
GAS MOVEMENT IN LANDFILLS. Determine what is being asked below.
Most of this gas escapes to the atmosphere, but some accumulate below buildings or in other enclosed spaces.