overall? idfk
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
New
Card Sorting
1/87
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
1
New cards
Element
cannot be made simpler, building block of matter. Includes diatomics, atoms, and even polyatomic
2
New cards
Compound
Pure substances that can be broken down by chemical means ie. NaCl
3
New cards
Atoms
Neutral particles
4
New cards
molecules
Smallest physical unit, always neutral eg. a molecule of H2O
5
New cards
elements of a chemical formula
subscripts (number of atoms), superscript (charge), coefficient (# compounds), balanced
6
New cards
accurate
results close to the actual number
7
New cards
precise
results close to each other
8
New cards
Physical properties
appearance, smell, feel, melting point, density, etc
9
New cards
chemical properties
how things react ex. Mg burns in air
10
New cards
wtf is a barometer or a manometer
google it bitch
11
New cards
Methods of separation
decanting, filtration, distillation, evaporation
12
New cards
diatomics
H O N F I Cl Br
13
New cards
Ammonium
NH4 +
14
New cards
Hydroxide
OH -
15
New cards
Nitrate
NO3 -
16
New cards
Sulfate
SO4 2-
17
New cards
Carbonate
CO3 2-
18
New cards
Phosphate
PO4 3-
19
New cards
Diatomic tool
NICK the BABY CAMEL ate and INCH CLAM and CREPES for SUPPER in PHOENIX
20
New cards
Practice naming
don’t procrastinate
21
New cards
What is the number of protons
constant, atomic #
22
New cards
How to find neutrons
Mass-Protons/atomic #
23
New cards
Single replacement reaction
compound breaks apart and combines with the other reactant which is typically an element
24
New cards
Double replacement reaction
Both reactants break apart and recombine into two new parts
25
New cards
Synthesis/combination reaction
Several reactants combine to form a single product
26
New cards
decomposition reaction
a compound breaks down bc of a chemical change
27
New cards
Combustion reaction
tends to make H2O+CO2, reaction w/ O2 that produces light and heat
28
New cards
Group I solubility
soluble
29
New cards
NO3 - solubility
soluble
30
New cards
NH4+
soluble
31
New cards
Famous Precipitates
BaSO4 (white), PbI2 (bright yellow), AgCl, AgBr, AgI (white to pale yellow)
32
New cards
Precipitate Reaction
AB + XY = XB + AY (two ionics make at least one non soluble product)
33
New cards
Which are almost always (always when not with an always soluble) insoluble?
OH- (hydroxide), CO3 2- (carbonate), C2O4 2- (oxalate), PO4 3- (phosphate), "heavy metals"
34
New cards
electron configuration
1s2 2s2 2p5 etc (in order spdf)
35
New cards
What are orbital diagrams
the up down arrow ones
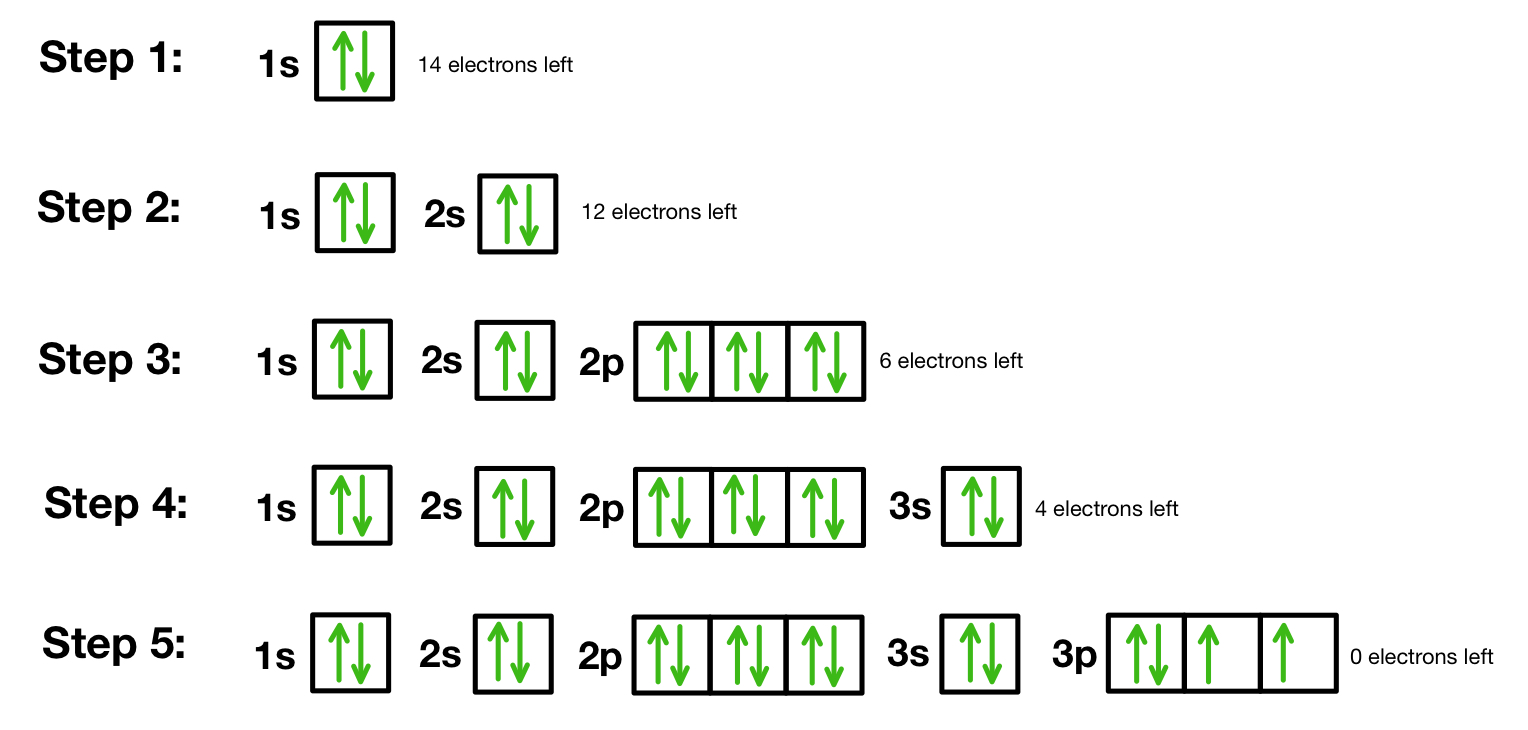
36
New cards
Coulomb's law
the force of attraction or repulsion between two charged particles is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the distance between them. F = (kq1q2)/dˆ2
37
New cards
As an electron moves away from the nucleus it's potential energy...
..increases
38
New cards
what is special about transition metal ions?
they lose electrons from the s sublevel before d
39
New cards
isometric
same electron configuration (K+, Cl-, S2-, Ar)
40
New cards
periodic groups are...
...columns, # of electrons in outer shell
41
New cards
periodic periods are...
...rows, # of shells
42
New cards
transition element properties
conductive, malleable, for ions with variety of positive charges, act as good catalysts, often form colored compounds, form variety of alloys
43
New cards
valence electrons
outermost electron ring (highest energy level)
44
New cards
core electrons
\n all non valence electrons
45
New cards
effective strength formula
proton # - # core electrons = strength of + on valence e-
46
New cards
electronegativity/electron affinity
how much an element will attract electrons. increases (+ charge increases) across the periodic table, and decreases (greater atomic radii) descending
47
New cards
ionization energy (IE)
energy required to remove an electron. increases across (+ charge increases) and decreases descending periodic table (more barriers)
48
New cards
Evaporation is endothermic or exothermic
endothermic, need to GIVE it heat
49
New cards
cation
positive, metal
50
New cards
anion
negative, non-metal
51
New cards
Order of IMFs (least to greatest)
Disperson, dipole-dipole, hydrogen
52
New cards
Trigonal pyramidal
4 e- pairs, 3 bonds, 1 lone pair
53
New cards
Tetrahedral
4 e- pairs, all bonds
54
New cards
Octahedral
6 e- pairs, all bonds, x,y,z
55
New cards
Trigonal planar
3 e- pairs, all bonds, flat
56
New cards
Linear
2 e- pairs, all bonds, a line
57
New cards
Bent
4 e- pairs, 2 bonds, 2 lone pairs, angle
58
New cards
Water's normal boiling point is 100˚C, why can water evaporate at 20˚C?
Because of random velocities of water molecules causing some to have a high enough kinetic energy to escape from the surface.
59
New cards
What havens to water vapor pressure in a container with ice melting at room temp?
Increases rapidly, then more slowly until reaching equilibrium
60
New cards
What happens to the rate of condensation?
Increases until it equals the rate of evaporation and then remains constant.
61
New cards
What are the affects of temp, IMFs, and molar mass on the vapor pressure of a substance?
Vapor pressure increases with an increase in temp and a decrease in strength of IMFs and molar mass.
62
New cards
When, in general, does a liquid begin to boil?
\n When the vapor pressure equals the outside pressure
63
New cards
Why does ice have a lower density than water>
**than water>**
**Because of the crystal structure formed by hydrogen bonds and its open structure.**
**Because of the crystal structure formed by hydrogen bonds and its open structure.**
64
New cards
hydrogen bonds occur when hydrogen is bonded to which elements
F, O, N
65
New cards
kinetic molecular theory
gas molecules are in constant random motion, when they collide energy is not lost, do not attract each other, far apart, same temp, same average kinetic energy
66
New cards
kinetic energy formula
KE=1/2mvˆ 2
67
New cards
pressure and force formula
p=f/a
68
New cards
Formula for pressure, volume, and temp
pv/t = pv/t
69
New cards
Dalton's law of partial pressures
Since gas pressure depends on # of molecules not their mass or size, it is easy to see that each gas in a mixture contributes pressure according to the number of molecules present.
70
New cards
Graham's Law
small particles diffuse faster
71
New cards
˚ C to K
\+273
72
New cards
atm to mmHg
atm x 760
73
New cards
How do gasses exert pressure?
Tiny molecules colliding with every pinhead-sized area of any surface. # of collisions is identical, forces add up for exert a force on the whole surface, creating a uniform "pressure".
74
New cards
Which is larger: proportional more collisions or harder collisions
samsies
75
New cards
mole to liter (for gasses)
1 mol = 22.4L
76
New cards
molar mass
g/mol
77
New cards
particles / mol
6\.02x10ˆ 23
78
New cards
Relative atomic mass
average atomic mass of all isotopes based on how common they are: (mass(%)+mass(%))/100
79
New cards
percent composition by mass
mass/total mass
80
New cards
density=
m/v
81
New cards
molarity
mass of solute per solution: moles of solute/liters
82
New cards
Dilution rule
concentration 1(volume 1) = concentration 2(volume 2)
83
New cards
Ideal gas law
PV = nRT
84
New cards
When will something produce a smell
when it is polar
85
New cards
When something has a charge, the polarity is…
Not applicable
86
New cards
manometer gas pressure shit
if gas is lower than outside: atmosphere pressure - height (mm) = gas pressure (mmHg)
\
If gas is greater than out side side: atmosphere pressure + height (mm) = gas pressure (mmHg)
\
If gas is greater than out side side: atmosphere pressure + height (mm) = gas pressure (mmHg)
87
New cards
percent error
(|accepted-measured| x 100) / accepted
88
New cards
is phase change a physical or chemical change
physical