Transport of oxygen by haemoglobin
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What does the oxygen dissociation curve look like?
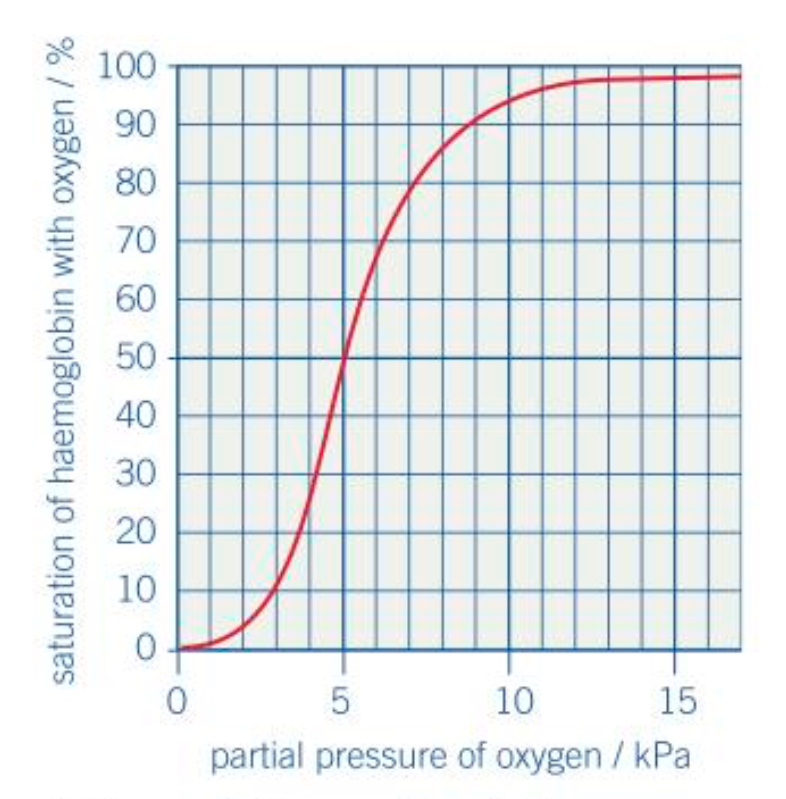
Why is the gradient of the curve initially shallow?
It’s difficult for the 1st oxygen molecule to bind to one of the sites because the polypeptide chain are closely united
Why does the gradient of the curve become steeper?
The binding of the 1st oxygen molecule changes the quaternary structure and so causes it to change shape.
UNCOVERS ANOTHER BINDING SITE
It takes a smaller increases in the partial pressure of oxygen to bind the second and third oxygen: positive cooperativity
Why does the gradient once against become less steep?
It’s harder for the 4th oxygen molecule to bind as there are more sites occupied so its less likely to find and empty site to bind to
What does it mean if the curve is further to the left?
There is greater affinity of haemoglobin for oxygen: loads oxygen readily
What does it mean if the curve is further to the right?
There is a lower affinity of haemoglobin for oxygen: unloads oxygen readily
At the gas-exchange surface, will the curve be shifted to the right or left?
CO2 concentration is low so the affinity of haemoglobin for oxygen is increased: curve shifts to the left
In rapidly respiring tissues does the curve shift to the right or left?
CO2 concentration is high so the affinity of haemoglobin for oxygen is reduced: curve shifts to the right
The more active a tissue, the more oxygen is unloaded. How does this work?
Higher respiration rate → more CO2 produced → lower pH → greater haemoglobin shape change → more readily oxygen is unloaded → more oxygen for respiration
Where does the curve shift for a llama?
High altitudes → lower partial pressure of oxygen → shifts to the left
Species that live in an environment with a lower partial pressure of oxygen will have their curve shifted to the left or right?
Left: haemoglobin is loaded with oxygen even when there’s little available
What does the Bohr effect refer to?
Shifts to the oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve: increase in ppCO2 will shift curve to right, decrease shifts curve to the left