MMW - PATTERNS AND NUMBERS IN NATURE AND THE WORLD Mathematics in Our World
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
are regular, repeated, or recurring forms or designs.
patterns
comes from a Greek word meaning 'to measure together' and is widely used in the study of geometry. Mathematically, symmetry means that one shape becomes exactly like another when you move it in some way: turn, flip or slide. For two objects to be symmetrical, they must be the same size and shape, with one object having a different orientation from the first.
Symmetries
is a curve which emanates from a point, moving farther away as it revolves around the point. In the natural world, we find spirals in the DNA double helix, sunflowers, the path of draining water, weather patterns (including hurricanes), vine tendrils, phyllotaxis (the arrangement of leaves on a plant stem), galaxies, the horns of various animals, mollusc shells, the nautilus shell, snail shells, whirlpools, ferns and algae.
spiral
is one which refers to a winding curve or bend in a river. These are typical landforms at the middle and lower courses of a river. ALSO gradients are usually more gentle and they experience lateral (sideways) erosions which widen the channel of the river at the middle and lower courses of a river.
Meanders
is a physical phenomenon characterized by its frequency, wavelength, and amplitude. In general, waves transfer energy from one location to another, in which case they have a velocity. Standing waves may also occur; these have no net velocity and involve no net transfer of energy.
WAVES
is a substance made by trapping air or gas bubbles inside a solid or liquid. Examples of foams formed by gases in liquids include sea foams, fire retardant foam, and soap bubbles.
Foam
is tiling that uses shapes to cover a surface with no gaps or overlaps. Picture a kitchen floor with tiles. They can be any shape or any combination of shapes. And the shapes don't have to follow a particular pattern.
tessellations
occurs when the applied stress is sufficient to break the atomic bonds of the solid (Anderson,1995; Scholz, 2002).
Fractures or cracks
propagation may be described using the energy criterion theory (Griffith, 1920) which is based on thermodynamic and energy balance
Fractures or cracks
are made by series of bands or strips, often of the same width and color along the length. Nature’s love of stripes and spots extends into the animal kingdom like tigers and leopards, zebras and giraffes.
Stripes
is a never-ending pattern. ________ are infinitely complex patterns that are self-similar across different scales. They are created by repeating a simple process over and over in an on-going feedback loop.
fractal
It is a linear mapping method that preserves points, straight lines, and planes. The processes involved in affine transformations are rotation, reflection and scaling.
Affine Transformations
if an object is not symmetrical, it is called
asymmetric

Identify what type of pattern it is.
Symmetries

Identify what type of pattern it is.
Spiral

Identify what type of pattern it is.
Symmetries

Identify what type of pattern it is.
Spiral

Identify what type of pattern it is.
Spiral

Identify what type of pattern it is.
spiral

Identify what type of pattern it is.
Tesselattions

Identify what type of pattern it is.
Meanders

Identify what type of pattern it is.
Waves
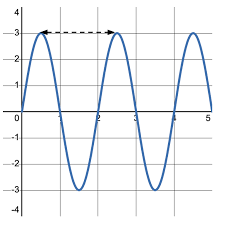
Identify what type of pattern it is.
Waves

Identify what type of pattern it is.
Foams

Identify what type of pattern it is.
Cracks

Identify what type of pattern it is.
Foams

Identify what type of pattern it is.
Tesselattions

Identify what type of pattern it is.
Cracks
Identify what type of pattern it is.
Waves

Identify what type of pattern it is.
Stripes
Identify what type of pattern it is.
Fractals
Identify what type of pattern it is.
Stripes

Identify what type of pattern it is.
Fractals

Identify what type of pattern it is.
Affine Transformations

Identify what type of pattern it is.
Fractals

Identify what type of pattern it is.
Fractals

Identify what type of pattern it is.
Affine Transformations