Bio Test Heredity
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Define heredity
Transmission of traits from parent to offspring.
What is a trait?
Genetically determined characteristics. Some we can see like hair color and others we can’t see like blood type.
Who was Gregor Mendel?
The first to develop a model explaining how the inheritance of traits works/model of dominant/recessive inheritance patterns.
What experimental organism did Mendel use and why?
Pea plants because they produce hundreds of offspring at a time, there’s a lot of variation in their characteristics, had either or variation (purple vs white), and could control fertilization.
Self fertilization
A plant fertilizes its own eggs with its own sperm
Cross fertilization
A sperm from one plant fertilizes the eggs from another plant.
Define true breeding
All offspring has the same trait as parent when parent self fertilizes.
Parental generation
True breeding plants that differed for a trait were crossed. Cross fertilization because sperm and egg come from different plants. Purple and White flowers.
F1 generation
F1 hybrids were allowed to self-fertilize because sperm and egg came from the same flower. All purple flowers.
F2 generation
¾ had one version of a trait while ¼ had the other version of a trait. ¾ were purple while ¼ were white.
4 components of Mendel’s theory of inheritance
Alternative forms of genes which account for variation in inherited characteristics called alleles, for each trait an individual receives two alleles one from each parent located on homologous chromosomes, alleles may be dominant or recessive (Dom always masks rec), and alleles for a trait separate during gamete formation (law of segregation which happens during meiosis).
Stamen
Male part of a flower. Contains the Filament and the Anther. The Anther produces pollen which contains plant sperm.
Carpel
Female part of a flower. Contains the Stigma, Style, and Ovary which produces eggs by meiosis.
Pollination
When pollen attaches to sticky stigma the sperm travels down the style of the carpel to fertilize eggs in ovule.
Seeds and Fruits
The fertilized egg becomes a seed which is a plant embryo with a food supply. The wall of the ovary then thickens becoming a fruit.
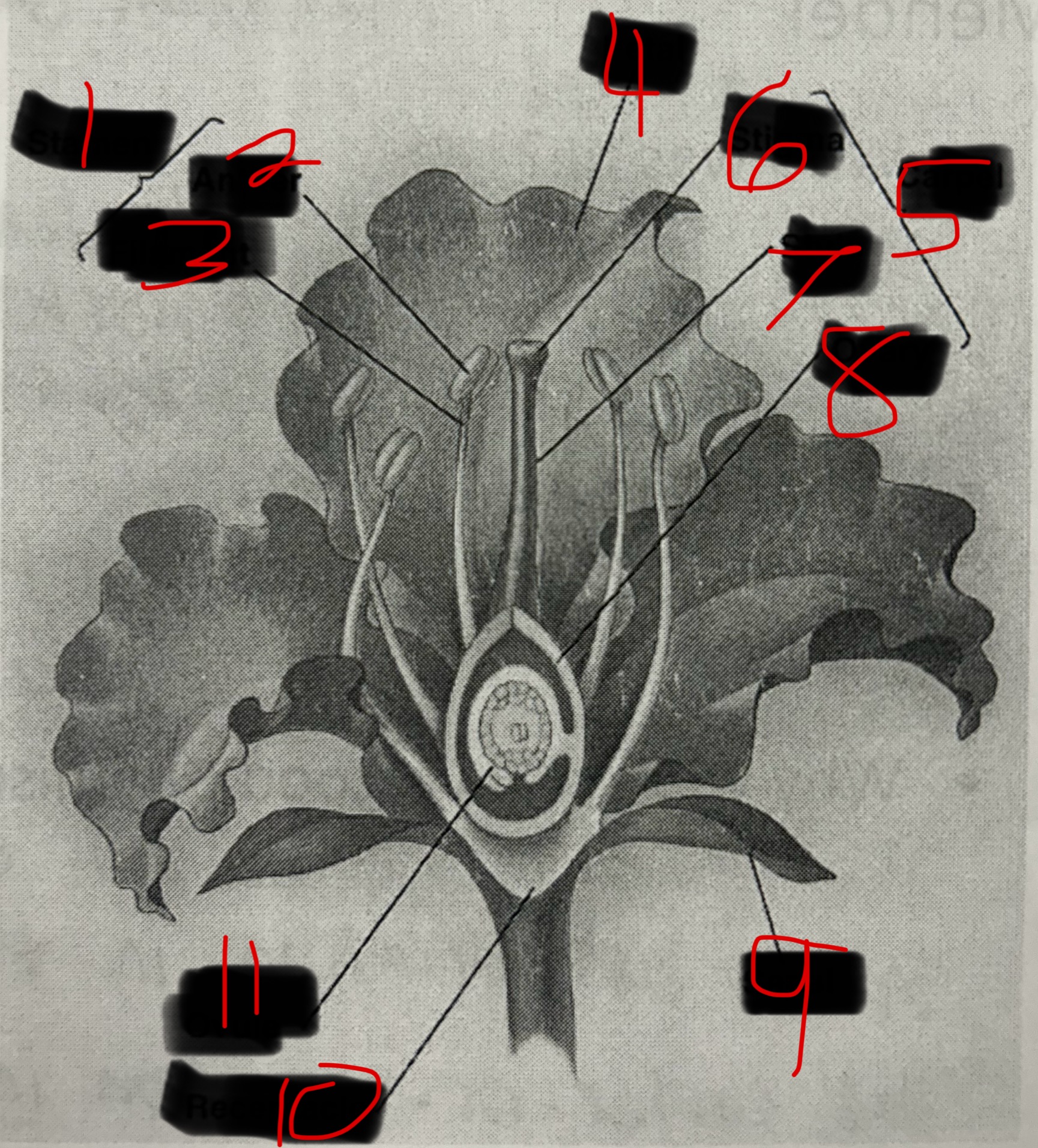
What is 1?
Stamen
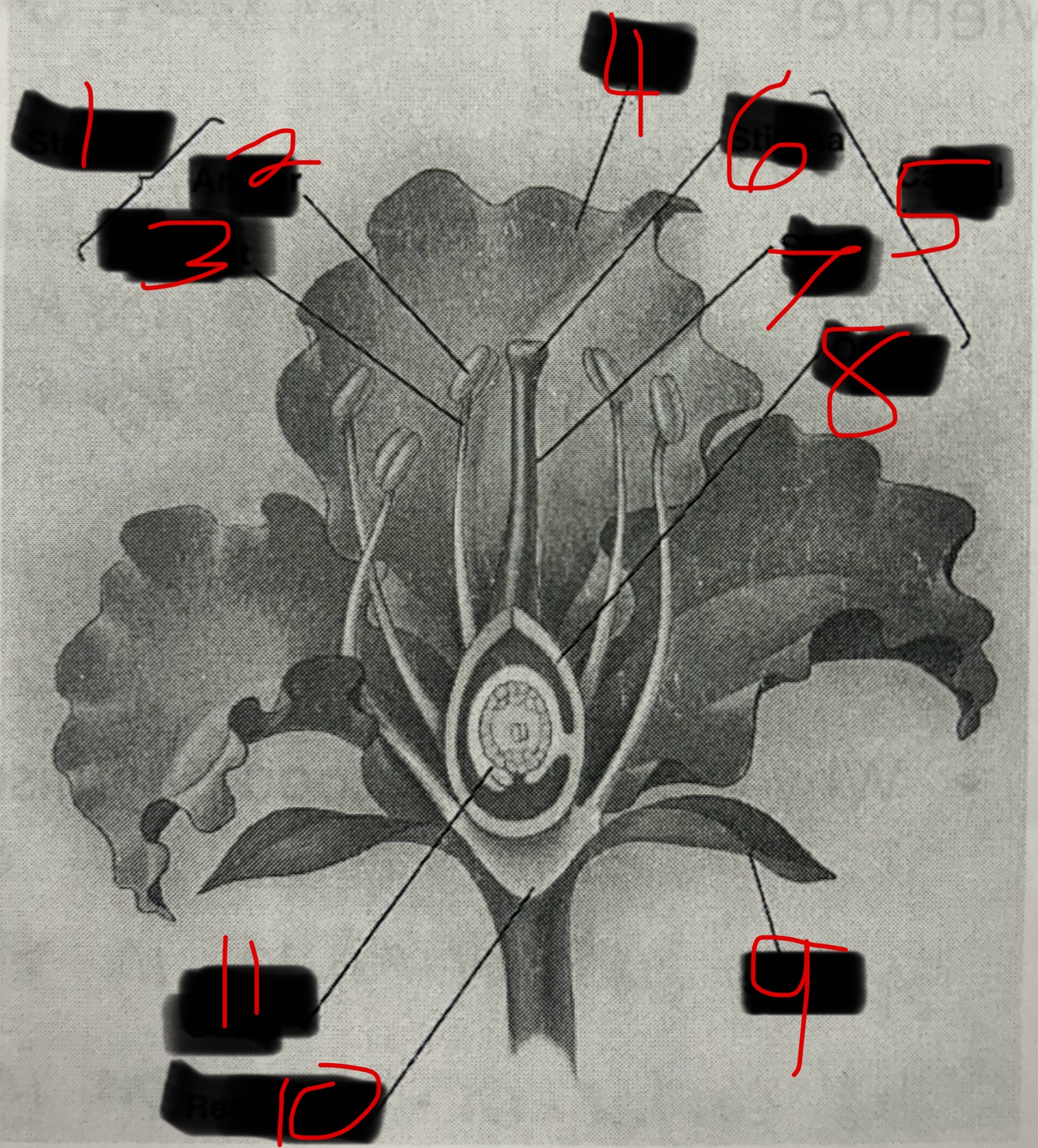
What is 2?
Anther
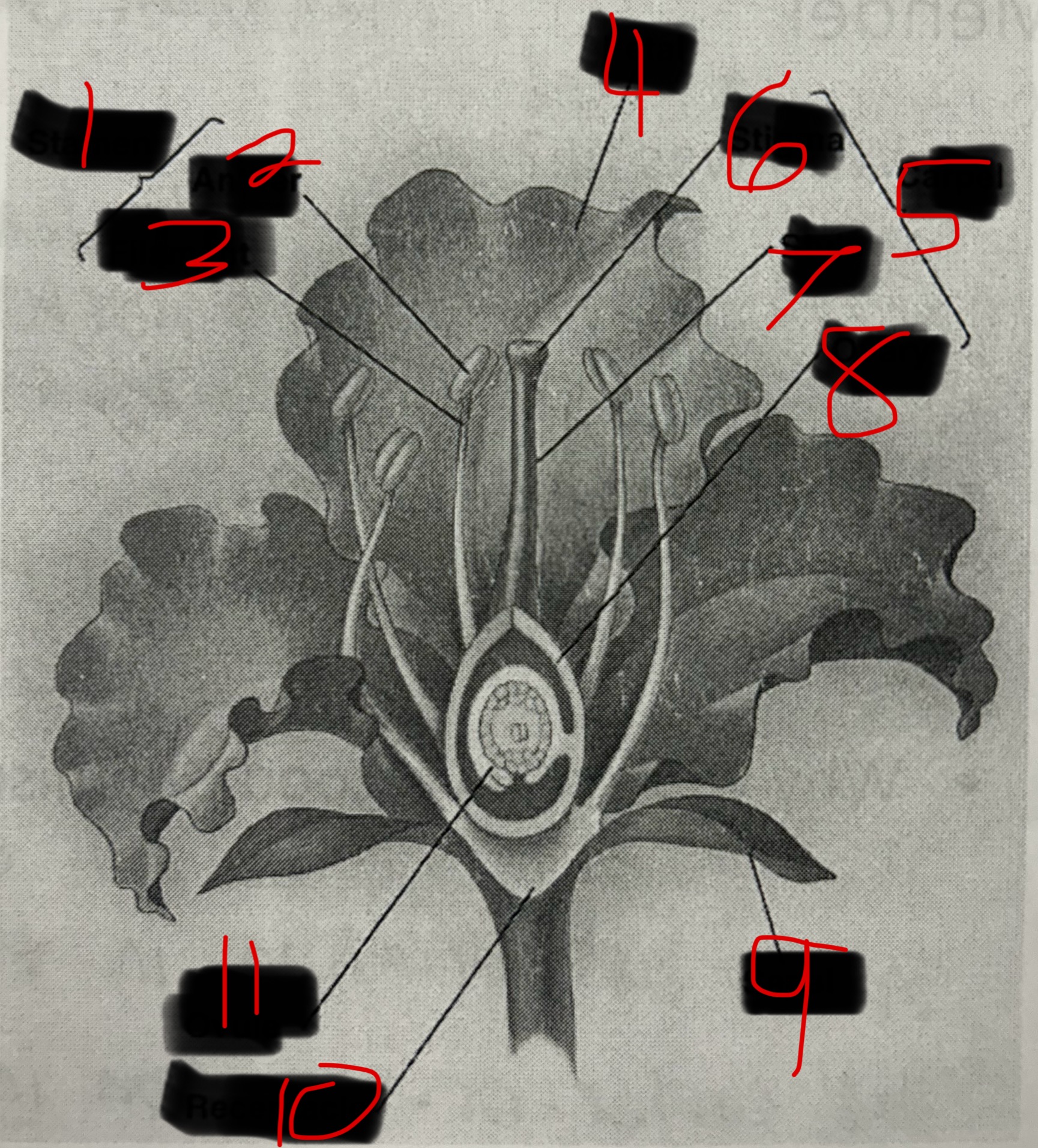
What is 3?
Filament
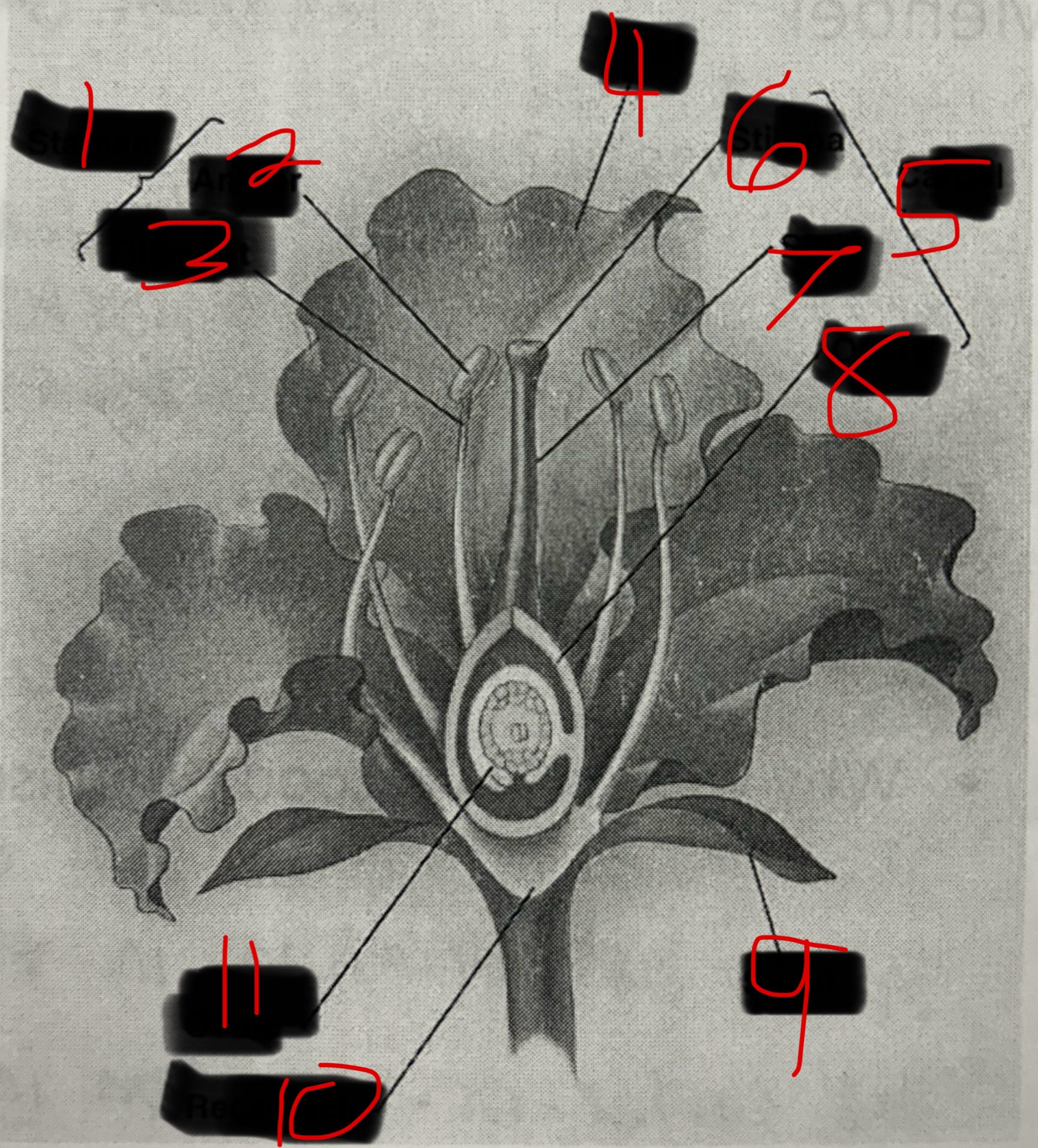
What is 4?
Petal
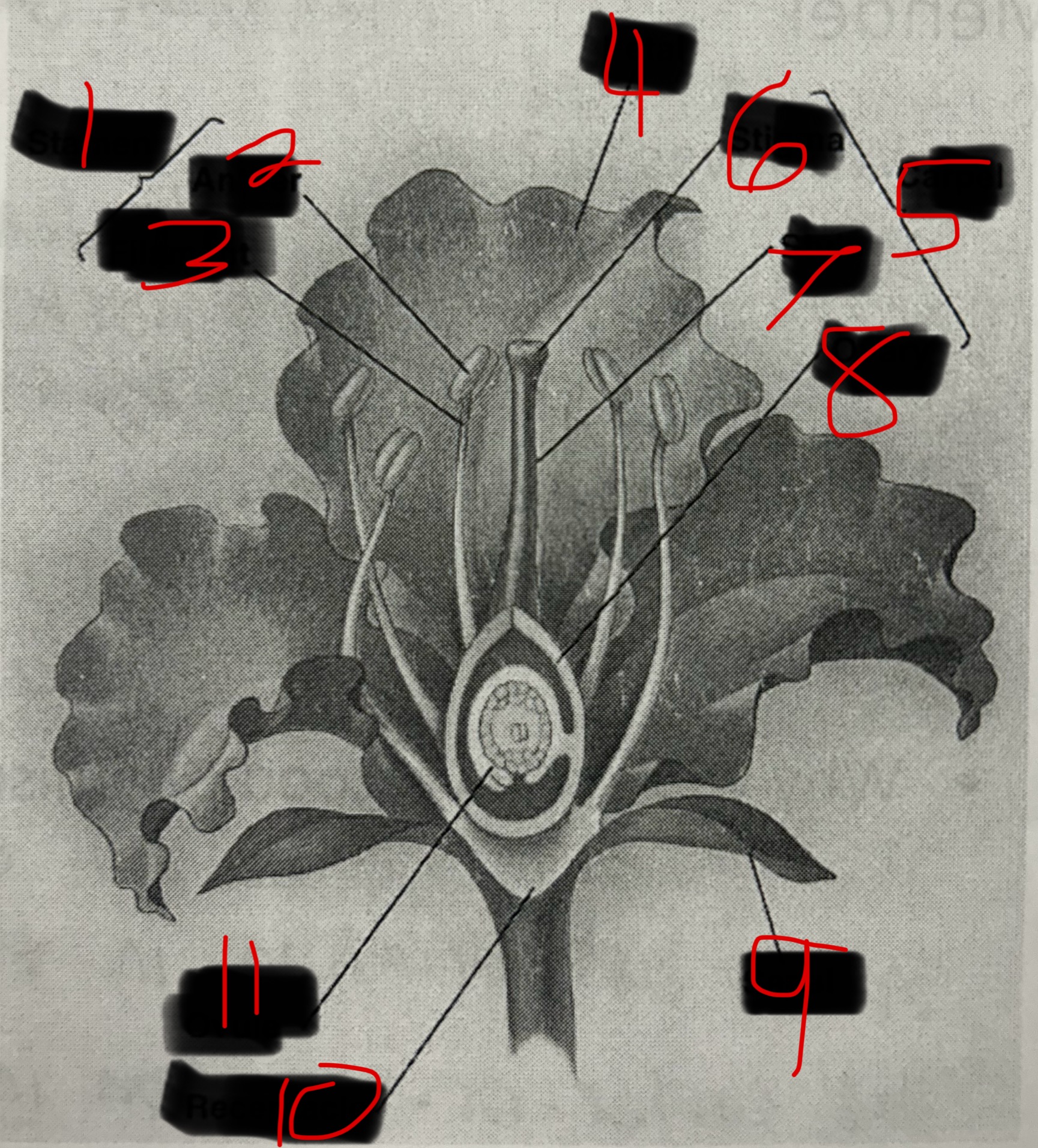
What is 5?
Carpel
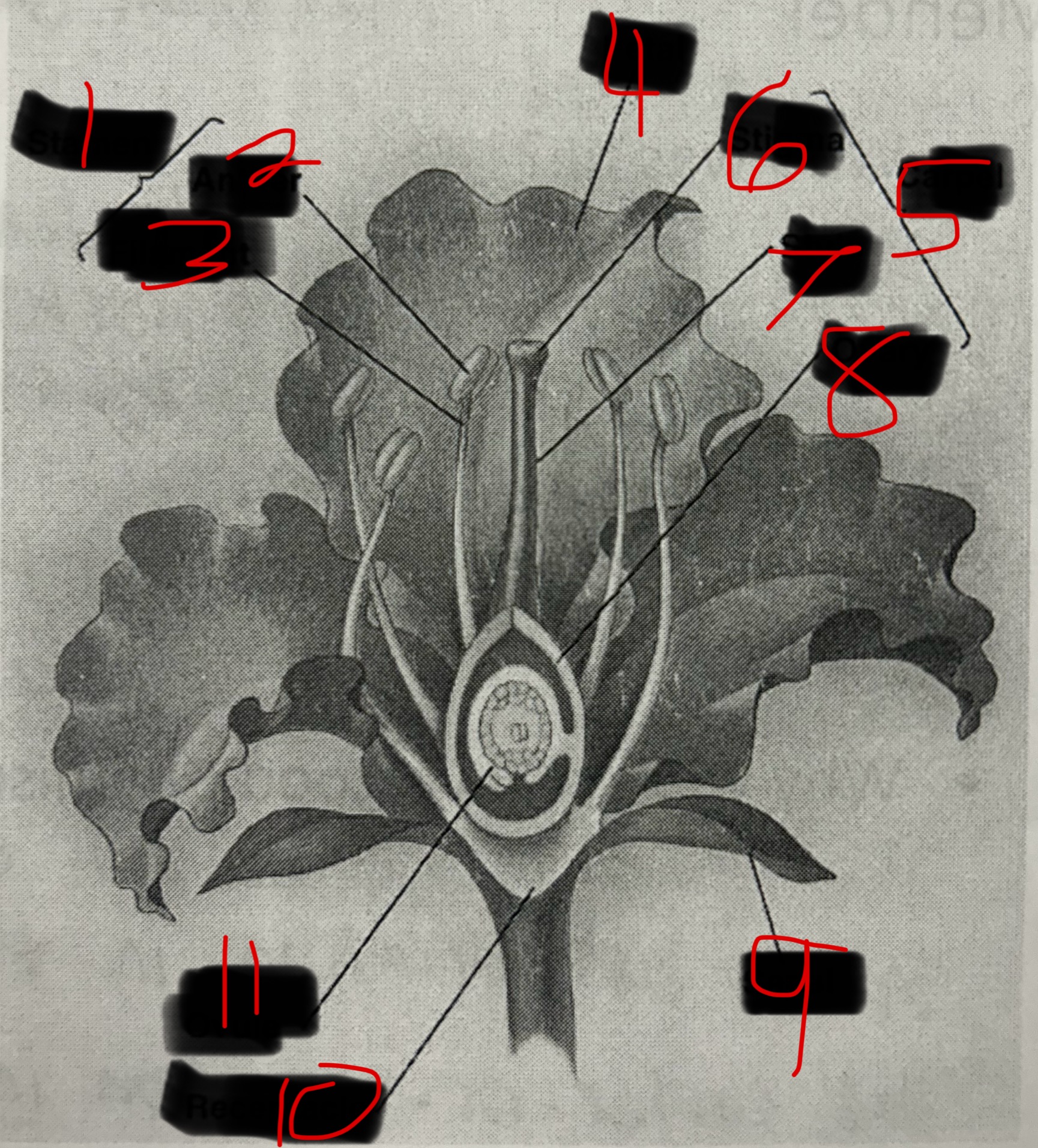
What is 6?
Stigma
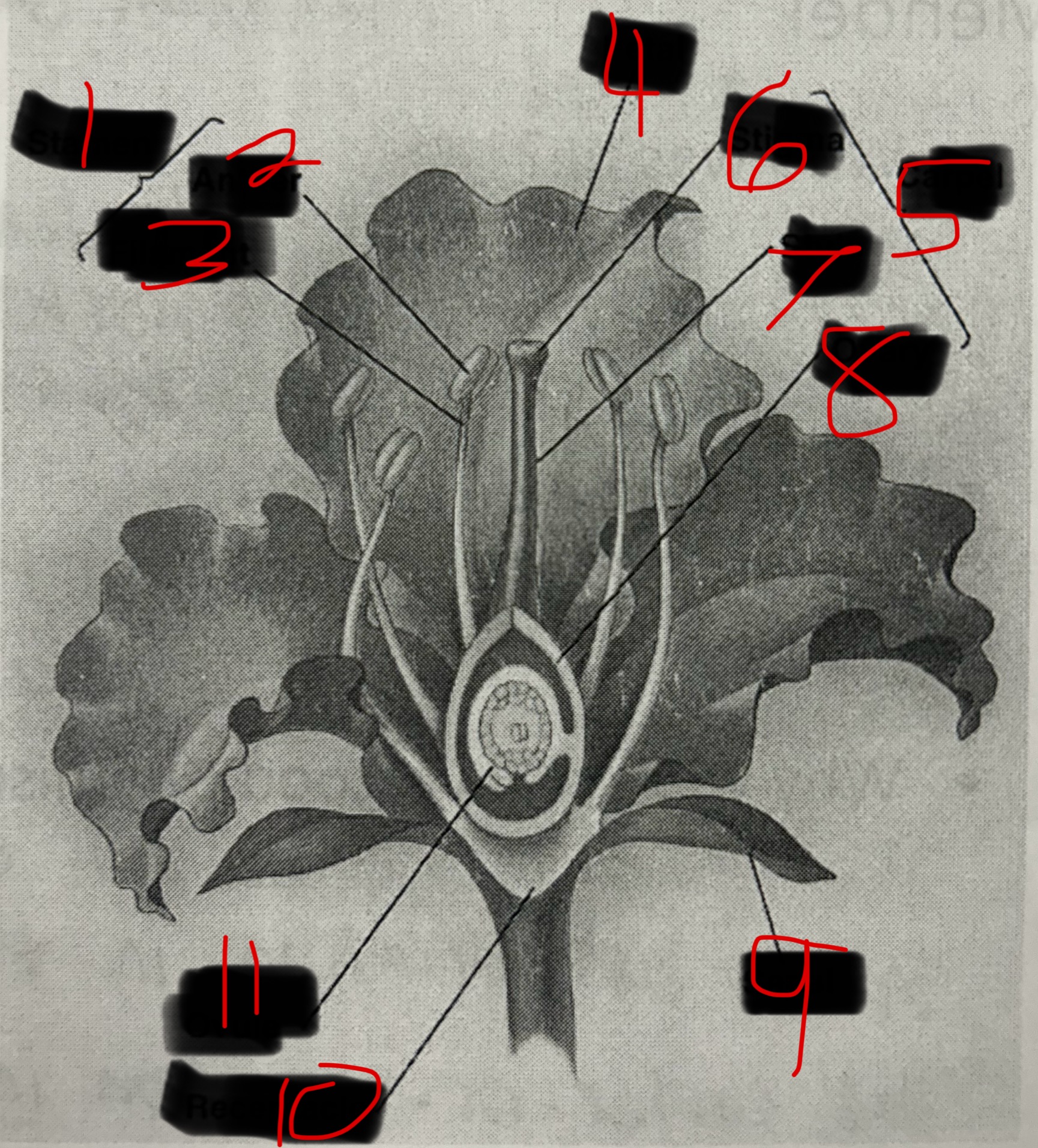
What is 7?
Style
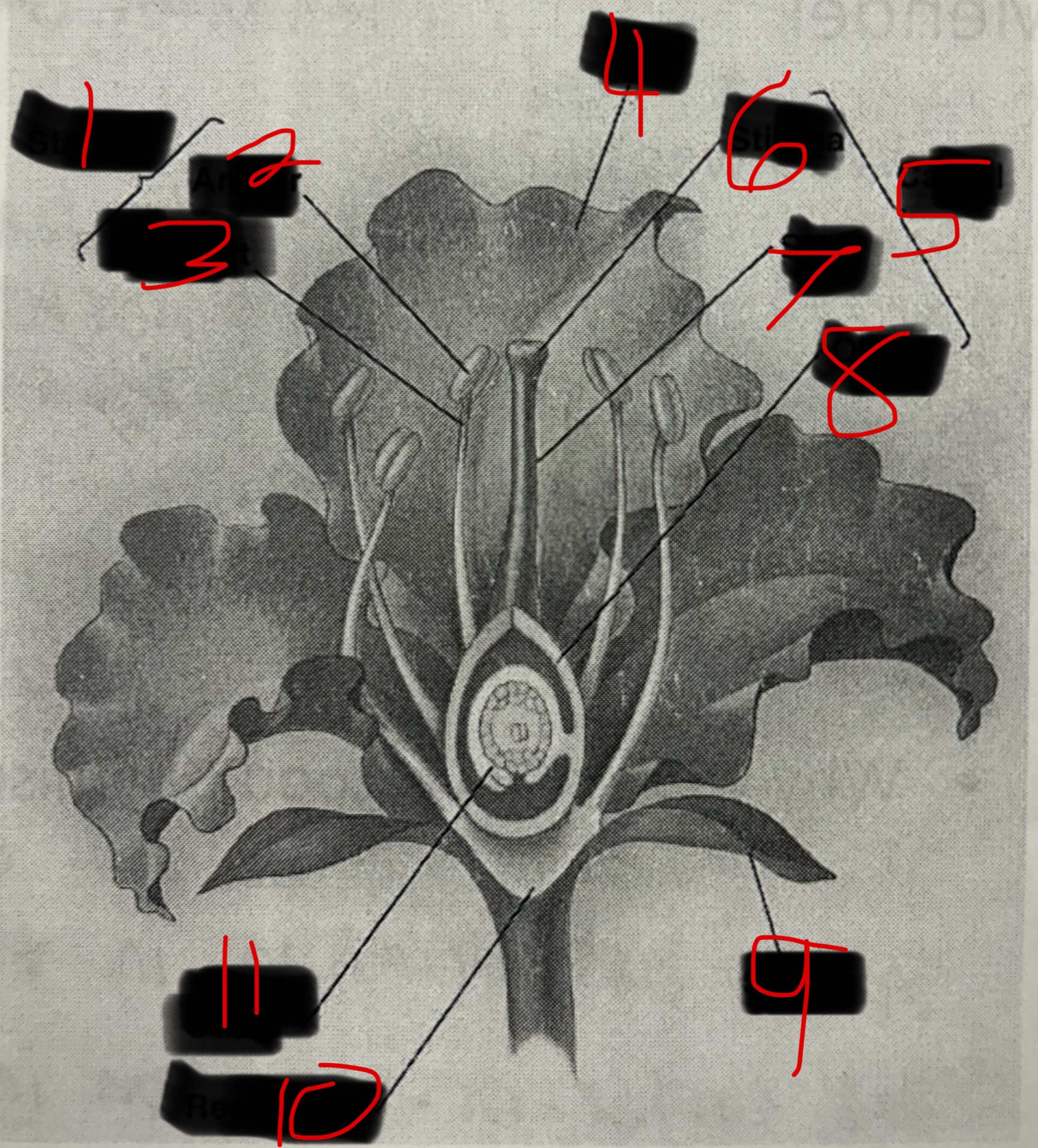
What is 8?
Ovary
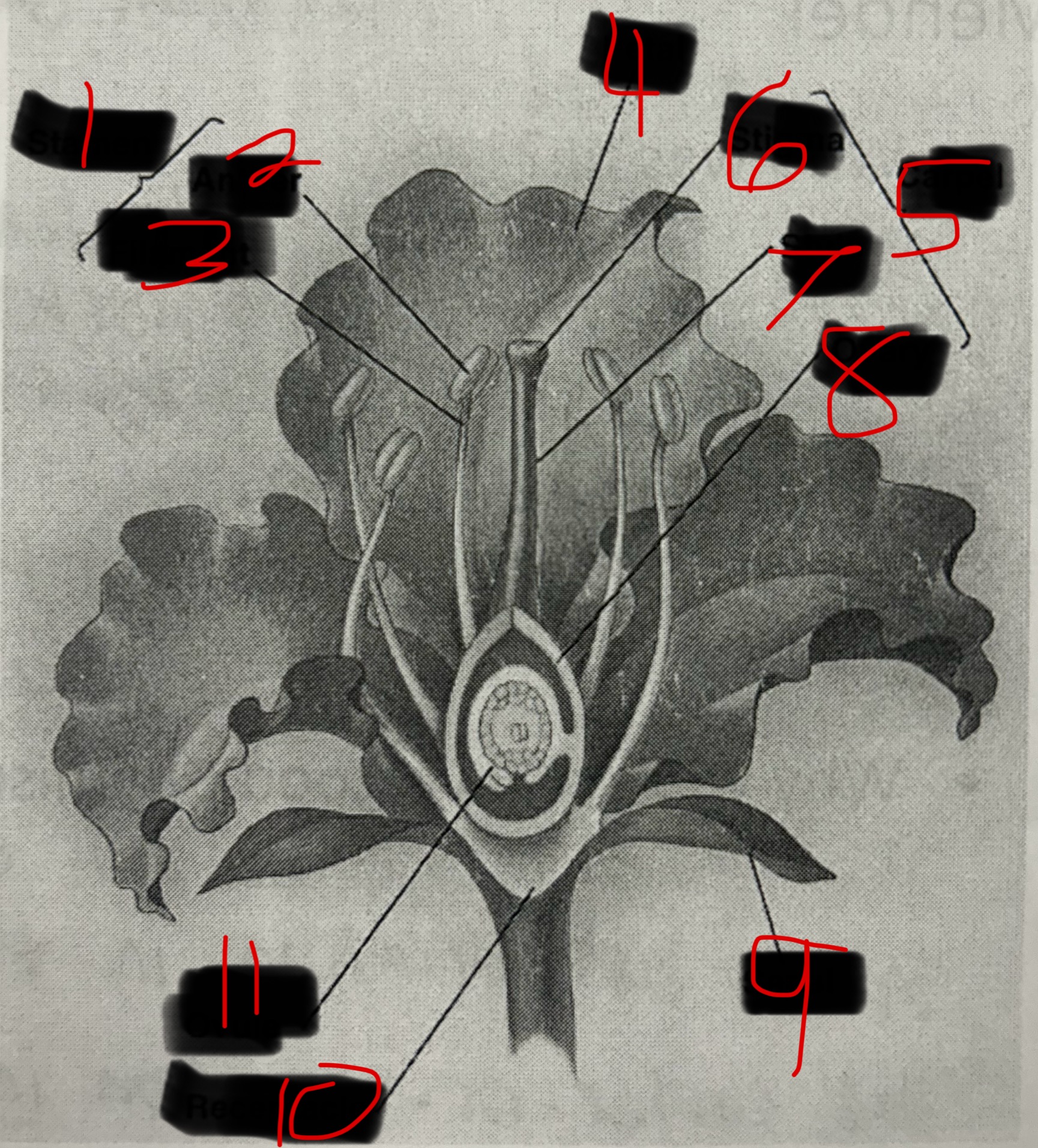
What is 9?
Sepal
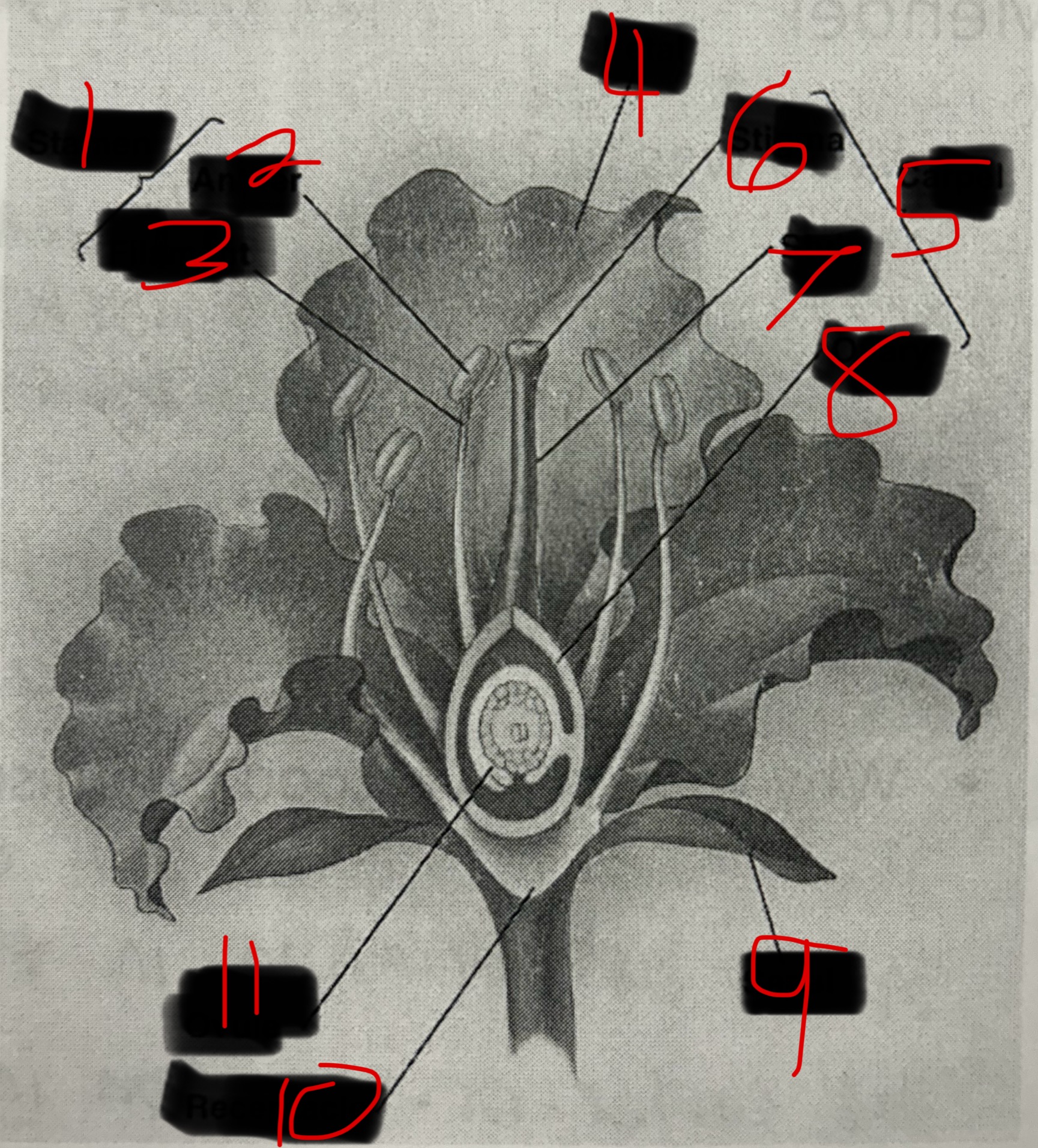
What is 10?
Receptacle
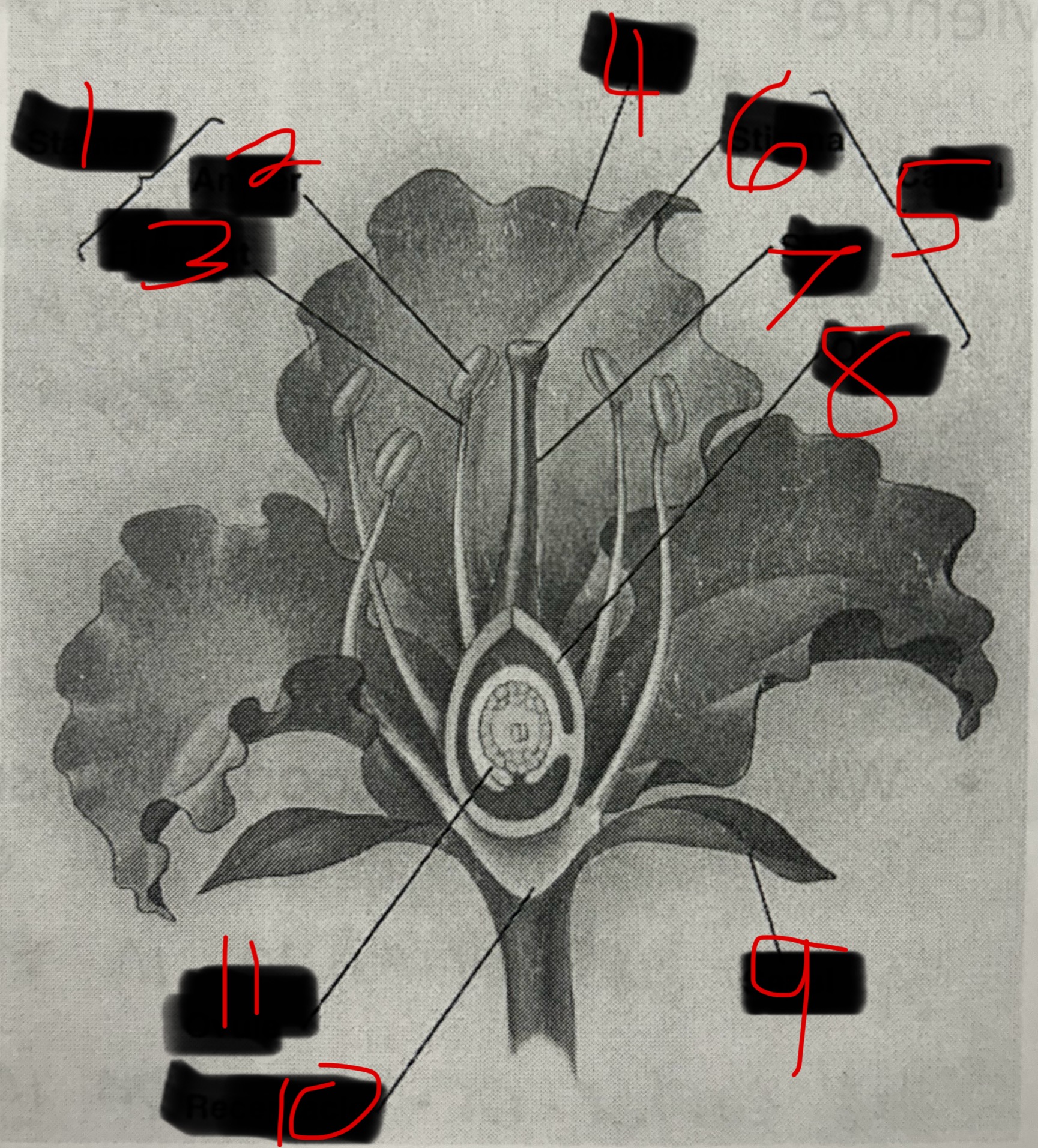
What is 11?
Ovule
Law of segregation and when in meiosis?
The 2 alleles for a given gene are separated during the Anaphase of meiosis and packaged into different gametes.
What is a genotype?
The alleles inherited from parents
Homozygous
Homozygous genotypes have 2 of the same alleles.
Heterozygous
Heterozygous genotypes have 2 different alleles.
Phenotype
Phenotype is the resulting appearance or the expression of the alleles.
What is a test cross and when would one do a test cross?
A test cross is when Mendel observed a dominant trait in one of his plants but he didn’t know if the plant was homozygous or heterozygous.
What do the ABO blood groups tell us about our blood.?
The blood groups refer to glycoproteins on the membranes of your red blood cells and tells us which antibodies are present.
What are antibodies?
Proteins in our blood that mark foreign invaders for destruction by immune system.
What is multiple allele inheritance?
Multiple allele inheritance is when there are more than 2 alleles for a gene.
Why are ABO blood groups an example of multiple allele inheritance?
A and B are dominant while O is recessive.
What is co-dominance?
When 2 dominant alleles are both fully expressed, neither masks the other.
Why are ABO blood groups an example of co-dominance?
AB blood has both glycoproteins.
What glycoproteins, antibodies, and alleles does type A blood have?
Type A blood has A glycoproteins on the surface of the red blood cells, they make anti-B antibodies, and the alleles are either AA or AO.
What glycoproteins, antibodies, and alleles does type B blood have?
Type B blood has B glycoproteins on the surface of the red blood cells, they make anti-A antibodies, and the alleles are either BB or BO.
What glycoproteins, antibodies, and alleles does type AB blood have?
Type AB blood has both A and B glycoproteins on the red blood cells, no antibodies are made, and the alleles are AB.
What glycoproteins, antibodies, and alleles does type O blood have?
Type O blood has neither glycoproteins on the red blood cells, they make anti-A and anti-B antibodies, and the alleles are OO.
Which blood type is the universal donor? Why?
O blood because it has neither A or B glycoproteins so no blood types reject it.
Which blood type is the universal recipient? Why?
AB blood because they make no antibodies.
On what chromosomes would you find genes for sex-linked traits?
X chromosomes
Why do males suffer from recessive sex-linked disorders more frequently than females?
Males only have one X chromosome so they only need one recessive allele to have it while females have 2 X chromosomes so they need 2 recessive alleles to have it.
3 sex-liked disorders.
Hemophilia - When injured, blood is slow to clot, Muscular Dystrophy - Gradual weakening of skeletal muscle, Red green color blindness - Difficulty identifying and distinguishing between reds and greens.
Independent assortment
During Metaphase 1 each pair of chromosomes can line up on the metaphase plate in either the maternal or paternal orientation. The orientation they line up in is random and independent of every other pair. This determines the combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes in the gametes.