ESCI 274 Lecture 5: Atmospheric Changes
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
1
New cards
Pathways for climate change to impact health (similar to primary, secondary, tertiary)
1. Directly through weather variables such as storms
2. indirectly through natural systems such as disease vectors
3. pathways heavily mediated through human systems such as undernutrition.
2
New cards
Earth’s early atmosphere
* Early atmosphere
* Evolution of blue-green algae
* Photosynthesis reduces CO2
* O2 first tied up in rock cycle
* Rock O2 reservoirs saturated = free O2
\
* \~20% O2 optimal for life
* UV an issue
* Genetic materials of cells (DNA) susceptible to damage by UV light at certain wavelengths (\~25μm)
* Evolution of blue-green algae
* Photosynthesis reduces CO2
* O2 first tied up in rock cycle
* Rock O2 reservoirs saturated = free O2
\
* \~20% O2 optimal for life
* UV an issue
* Genetic materials of cells (DNA) susceptible to damage by UV light at certain wavelengths (\~25μm)
3
New cards
Earths atmosphere: Atmospheric Oxygen
* Atmospheric Oxygen
* Multiple mechanisms to balance O2
* Respiration - Photosynthesis
* Combustion (i.e. forest fires)
* Multiple mechanisms to balance O2
* Respiration - Photosynthesis
* Combustion (i.e. forest fires)
4
New cards
Earths atmosphere: Ozone
* Ozone
* In order to photosynthesize, organisms need access to sunlight, but also protection from UV radiation
* In order to photosynthesize, organisms need access to sunlight, but also protection from UV radiation
5
New cards
Permafrost link to atmosphere
* Warming → permafrost thaw → greenhouse gas emission → warming →
* “Permafrost will make it even harder to meet our emissions targets
* “Permafrost will make it even harder to meet our emissions targets
6
New cards
Air Pollution
Chemicals added to the atmosphere by natural events or human activities in high enough concentrations to to be harmful
7
New cards
Types of air pollution
1. Particulate matter
2. Fires
3. Carbon monoxide
8
New cards
Health impacts of air pollution
1. **Low level exposure**
* Irritates eyes
* Causes inflammation to upper respiratory tract
* Can develop to chronic respiratory issues
2. **High level acute exposure**
* Severe illness or death
3. **Impact depends on**
* Types of pollutants
* Pollutant concentration, duration of exposure
* Individual susceptibility
9
New cards
Air quality around the world
* 91% of the worlds population lives in areas with poor air quality (ambient)
* Total annual number of deaths by risk factor - air pollution = 6.67 million
* Total annual number of deaths by risk factor - air pollution = 6.67 million
10
New cards
Climate, air pollution, Covid impact
* Initial covid impact: dramatic fall in air pollution
* Exposure to low levels of air pollution increases covid-19 risk
* Air pollution and climate change: Allergens
= increased asthma and allergic respiratory issues
= increased allergic rhinitis
= increased conjunctivitis
= increased dermatitis
= increased ambulance calls for asthma and hospital visits for rhinitis
* Children are very susceptible
* Exposure to low levels of air pollution increases covid-19 risk
* Air pollution and climate change: Allergens
= increased asthma and allergic respiratory issues
= increased allergic rhinitis
= increased conjunctivitis
= increased dermatitis
= increased ambulance calls for asthma and hospital visits for rhinitis
* Children are very susceptible
11
New cards
Atmospheric future (IPCC projections)
* Dimming (earth reflecting less albedo, earthshine illuminating moon decreased from 1998-2017
* Climate change will affect future air quality (photochemical oxidant yes, fine particulates unsure)
* Increased urbanization, solid biomass fuels, industrial development in the absence of emission controls (all lead to O3 production (precursors), many lead to PM release
* Increased temperatures: expected to increase air pollutants effects (Canada/ USA mortality rate due to O3 expected to increase)
* Acute air pollution episodes: increased temperatures and droughts will increase wildfire incidents, particulate matter
* **Aeroallergens**: increased temperature, generally projected to increase production and release of airborne allergens (pollen, fungal spores), increase associated with respiratory illness
* Changes in wind and precipitation patterns may increase problems
* Summertime ozone is projected to change non-uniformly
* Climate change will affect future air quality (photochemical oxidant yes, fine particulates unsure)
* Increased urbanization, solid biomass fuels, industrial development in the absence of emission controls (all lead to O3 production (precursors), many lead to PM release
* Increased temperatures: expected to increase air pollutants effects (Canada/ USA mortality rate due to O3 expected to increase)
* Acute air pollution episodes: increased temperatures and droughts will increase wildfire incidents, particulate matter
* **Aeroallergens**: increased temperature, generally projected to increase production and release of airborne allergens (pollen, fungal spores), increase associated with respiratory illness
* Changes in wind and precipitation patterns may increase problems
* Summertime ozone is projected to change non-uniformly
12
New cards
Co-benefits of Reduction of Co-Pollutants
1. Improvement in energy efficiency will decrease CO2 and health damaging pollutants, provided energy demand does not increase (or is offset by carbon neutral sources).
2. Increase in combustion efficiency will decrease incomplete combustion products, this is positive regardless of energy efficiency change.
3. Increased use of non-combustion sources (wind, solar, tidal, wave, geothermal) will reduce emissions of CAPs and health damages.
13
New cards
Air pollution diagram
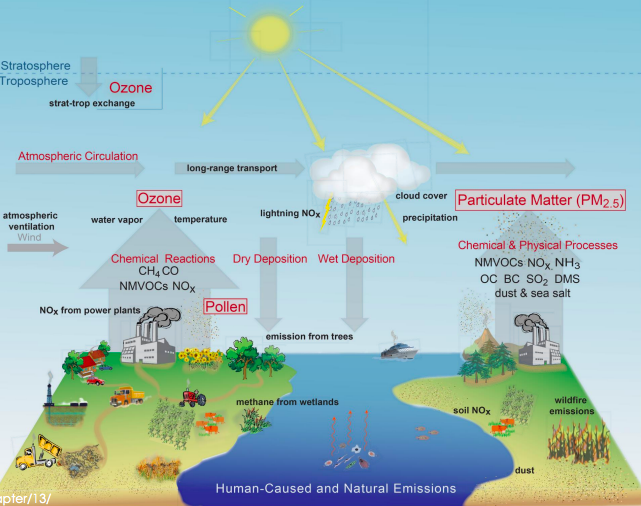
14
New cards
Classifying pollutants diagram

15
New cards
Signs of carbon monoxide poisoning diagram

16
New cards
Why smog is harmful diagram
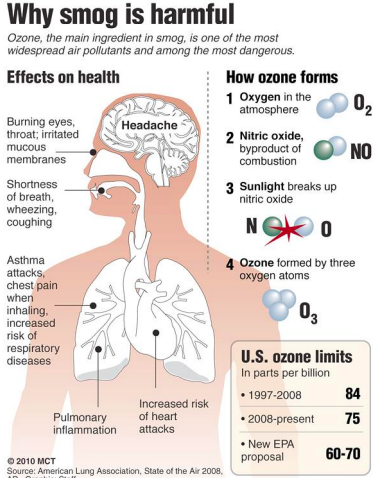
17
New cards
Air pollution and climate change diagram
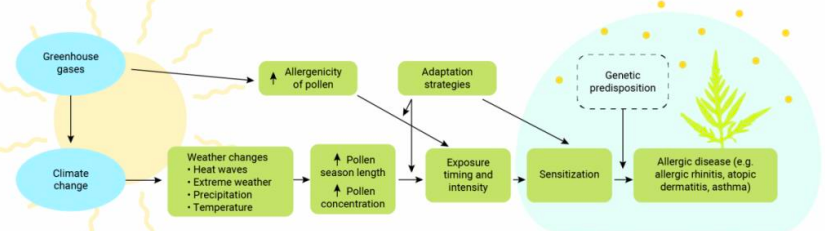
18
New cards
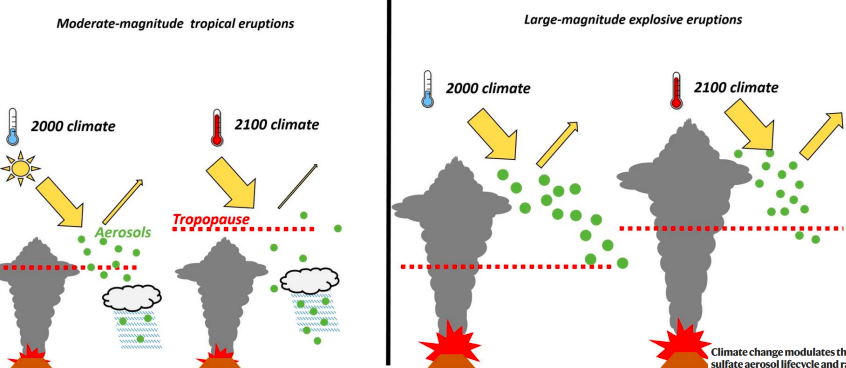
Climate change and volcanic eruption diagram