OCR GCSE Biology: B1
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
How does the temperature effect the rate of photosynthesis?
At low temperatures, the enzymes work at a slower pace and at high temperatures the enzymes will denature- the rate of reaction decreases rapidly.
What is the ideal temperature needed for photosynthesis?
45 degrees.
How does carbon dioxide effect photosynthesis?
The amount of carbon dioxide will only increase the rate of photosynthesis up to a certain point. After reaching the point, carbon dioxide is no longer the limiting factor.
How does light level effect photosynthesis?
If the light level is raised, the rate of photosynthesis increases steadily to a certain point. Overall, it does not make much of a difference.
What are the two main stages of photosynthesis?
Energy transferred by light is used to split water into oxygen gas and hydrogen ions. Carbon dioxide then combines with the hydrogen ions to make glucose.
What time of reaction is photosynthesis?
Endothermic
What is the balanced symbol equation for photo synthesis?
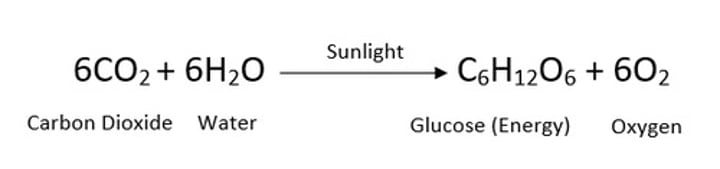
Where does photosynthesis occur?
Photosynthesis happens inside chloroplasts- they contain chlorophyll which absorbs the light.
What is glucose used for in plants?
Some of the glucose is used to make larger, complex molecules that the plants need to grow. These make up the organism's biomass.
What happens during photosynthesis?
Photosynthetic organisms (e.g green plants and algae) use the energy from the sun to make glucose.
How are lipids broken down in the body?
Lipids are broken down by enzymes in the small intestine.
What do lipids contain?
Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen atoms.
What are lipids made up of (in regards to fats and oils)?
Glycerol and 3 fatty acids.
How are proteins broken down in the body?
Proteins are broken down by enzymes in the stomach and small intestine.
What are amino acids made of?
Carbon, Nitrogen, Hydrogen and Oxygen atoms
What are proteins made of?
Proteins are polymers that are made up of long chains of monomers called amino acids.
How are carbohydrates broken down in the body?
Carbohydrates are digested/broken down by enzymes in the mouth and small intestine.
How can polymer molecules be broken down back into sugars?
When the chemical bonds between the monomers are broken.
How are carbohydrates made?
Monomers (simple sugars e.g glucose or fructose) can be joined together in long chains, polymers, to make large, complex carbohydrates.
What are carbohydrates made up of?
Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen.
What is the equation for anaerobic respiration in plants and fungi?
Glucose --> Ethanol + Carbon Dioxide.
Why do plants sometimes have to resort to anaerobic respiration?
If the soil is water-logged, plant root cells respire anaerobically as there is little to no oxygen.
What is the word equation for anaerobic respiration in animals?
Glucose --> Lactic Acid
What is anaerobic respiration?
'Anaerobic' means "without oxygen".
What is the equation for aerobic respiration?
Glucose + Oxygen --> Carbon Dioxide + Water
What is aerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration is what happens when there's plenty of oxygen available. It is the most efficient way to transfer energy from glucose.
How can cells respire?
Cells can respire using glucose as a substrate, but organisms can also break down other organic molecules (e.g carbohydrates, proteins and lipids) to use as substrates for respiration.
How is respiration controlled?
Respiration is controlled by enzymes.
What can effect the rate of respiration?
The rate of respiration can be effected by temperature and pH.
What type of reaction is respiration?
Exothermic (because it transfers energy to the surroundings).
How does substrate concentration effect the rate of reaction?
The higher the substrate concentration, the faster the reaction but only to a certain extent.
How does enzyme concentration effect the rate of reaction?
Increasing the concentration of the enzyme increases the rate of reaction but in some cases there are more than enough enzyme molecules to deal with the available substrate, so adding more enzymes would have no further effect.
How does pH effect enzymes?
If the pH is too high or too low, it interferes with the bonds holding the enzyme together which changes the shape of its active state- causing it to denature.
What is the optimum pH for enzymes?
The optimum pH is often 7 but not always, e.g pepsin is an enzyme used to break down proteins in the stomach and it works best at a pH of 2.
What is an enzymes optimum temperature?
37 degrees (body temperature).
How does temperature effect enzymes?
A higher temperature increases the rate at first.
What happens if an enzyme loses its shape?
It cannot catalyse the reaction.
What makes up a cell's metabolism?
Respiration, photosynthesis and protein synthesis and these reactions need to be carefully controlled.
How can you speed up the reactions which occur in a cell's metabolism?
Usually, you can speed up the reaction by raising the temperature.
How are enzymes specific?
They have an active site where it joins on to its substrate. They all have their own specific substrate.
What happens if an enzyme's active site does not match the substrate?
The reaction will not be catalysed.
What is the term used to describe an enzyme's active site bonding to its substrate?
Lock and Key hypothesis.
What are enzymes mainly used for?
They are biological catalysts, which means they speed up a reaction without being used up themselves. They can build up larger molecules from smaller ones and break down bigger ones from smaller ones.
What happens in protein synthesis?
In the nucleus, the two DNA strands unzip around the gene. The DNA is used as a template to make mRNA. Base pairing ensures it is complementary. This is transcription. The mRNA molecule moves of of the nucleus into the cytoplasm. Amino acids that match the triplet codes on mRNA join together. This makes the protein coded for by the gene. This is called translation.
What is transcription?
Translation is the process in which protein is made. The mRNA attaches itself to the ribosome and the nucleotide sequence of 3 is interpreted and what protein is made is decided by the code. The ribosome reads the nucleotides on the mRNA in groups of 3. The groups are called base triplets or codons. Each triplet codes for a specific amino acid. For example CGU codes for a different amino acid to ACG. The ribosome continues to read the triplet code adding more and more amino acids. The amino acids join together in a chain and produce a protein.
What is translation?
Translation is a step in protein biosynthesis wherein the genetic code carried by mRNA is decoded to produce the specific sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
Where are proteins synthesised?
Proteins are synthesised in the cytoplasm.
What are proteins made from?
Proteins are made from chains of molecules called amino acid. Each protein has its own specific number and order of amino acids.
What is a polymer?
A polymer is a large complex molecule composed of long chains of monomers joined together.
What is a monomer?
Monomers are small, basic molecular units.
What are the 3 things that make up a nucleotide?
A sugar called deoxyribose, a phosphate group and a base.
What are the 4 bases?
Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine
What shape is DNA?
A double helix.
What are the two DNA strand made up of?
The two DNA strands are made up of nucleotides joined together in a long chain called polymers.
What do animal cells contain?
Nucleus, Cytoplasm, Mitochondria, Cell Membrane
What is the function of a nucleus?
It contains DNA and controls the cell's activity.
What is the function of cytoplasm?
Cytoplasm is a gel like substance where chemical reactions occur.
What is the function of the mitochondria?
It is the site of cellular respiration and it contains enzymes which are needed for chemical reactions.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
It holds the cell together and controls what goes in and out of the cell by providing a selective barrier. They contain receptor molecules that are used for cell communication.
What is a prokaryote?
Prokaryotes are smaller and simpler cells.
What is a eukaryote?
Eukaryotes are complex cells.
What is the equation for magnification?
Magnification=image size/real size.
What are chromosomes?
Chromosomes are long molecules of coiled up DNA. The DNA is divided up into short sections called genes.
What do bacterial cells contain?
Chromosomal DNA, Plasmids and a Cell Membrane.
What is the function of chromosomal DNA?
It is one long circular chromosome which controls the cells activities and replication. It floats in the cytoplasm.
What is the function of a plasmid?
A plasmid is a small loop of extra DNA that is not a part of the chromosome. Plasmids contain genes for things like drug resistance and it can be passed on between bacteria.
What do plant cells have that animal cells do not?
Cell wall, chloroplasts.
What is the function of the cell wall?
It provides support and it is made up of cellulose.
What are the functions of chloroplasts?
They carry out photosynthesis (it's where it occurs) and they contain chlorophyll.
What is a light microscope used for?
To observe small structures in detail
How does a light microscope work?
The microscope passes the light through an object placed on a slide on the stage, then through two glass lenses- the objective lens and the eyepiece lens. The lens magnifies the object, so when you view it through the eyepiece you can easily see the cell in detail.
Why stain cells?
Most cells are colourless so they are stained to make them easier to observe
Common types of stain?
Methylene blue, Iodine, Crystal violet
What is electron microscopy?
It uses beams of electrons instead of light for a higher magnification
What are the two types of electron microscopy?
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM)
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
How does TEM work?
An electron beam is passed through an extremely thin section of the specimen. You will get a two-dimensional cross-section of the specimen.
How does SEM work?
-beam of electrons onto surface of specimen from above not below
-beam passed back and forth across portion of specimen in a regular pattern
-electrons scattered by specimen
-then can build up 3D image by a computer analysis based on pattern and secondary electrons produced
What are the differences between SEM and TEM?
TEM produces a 2D image but has a higher magnification.
SEM produces a 3D image
Light microscopy is...?
Cheap to buy and operate. Small and portable. Simple to prepare a sample. The natural colour of the sample is seen unless staining is used. Specimens can be living or dead. Resolution is up to 0.2µm (2x10^-7m).
Electron microscopy is...?
Expensive to buy and operate. Large and difficult to move. Sample preparation is complex. Black and white images are produced. Specimens have to be dead. Resolution up to 0.1nm (1x10^-7m)
Where is DNA stored?
In the nucleus
What happens after transcription?
The strand of mRNA detaches itself from the DNA template and the DNA zips back up. The mRNA then moves out of the nucleus and travels to subcellular structures called ribosomes in the cytoplasm. This is where the protein is made.
Why is mRNA made?
Because DNA is too big to leave the nucleus
What are the complementary pairings of the bases?
Adenine - Thymine
Cytosine - Guanine