Chordates, Chordate Evolution, and Vertebrate Story
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
(Lesson 2, 3 and 4)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Phylum Chordata = Chordates (Taxa)
Urochordates, Cephalochordates, and Vertebrates
Cephalochordates
Lancelets - 6-7cm, filter feeders
Urochordates
Sea Squirts/Tunicate - Larval chordate characteristics, keep pharyngeal slits
Vertebrates
Everything else - Very diverse
Notochord
Not a spinal cord, hydrostatic organ, elastic rod, flexes laterally, does not collapse
Pharyngeal Pouches
Endostyle
glandular groove on floor of pharynx, filter feeding, homology with thyroid
Thyroid
arises from floor of the pharynx, T3/T4, Calcitonin
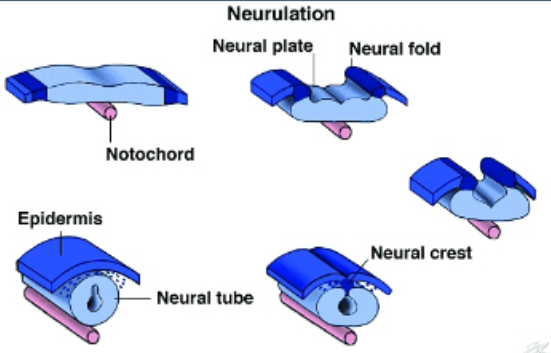
Dorsal Nerve Cord
Formed by invagination
• Embryonic process
• Surface ectoderm thickens into neural plate
• Folds/rolls inward from the surface to create a tube
Postanal Tail
Extension of the chordate locomotor apparatus
Agnathans and provide examples
Agnathans are jawless vertebrates, including lampreys and hagfish.
What are the two main groups of Gnathostomes?
Chondrichthyes (sharks, rays, chimaeras) and Osteichthyes (bony fish).
What are the two subclasses of Osteichthyes?
Actinopterygii (ray-finned fishes) and Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fishes).
What are the characteristics of Palaeonisciformes?
Living members include paddlefish, sturgeon, and bichirs; they have ganoid scales.

What are the characteristics of Neopterygii?
They have smaller scales for increased flexibility and include species like bass, perch, and trout.

What is the function of the swim bladder in fish?
It helps with buoyancy control.
What are the two types of swim bladders?
Physoclistous (derived, more prone to barotrauma) and Physotomous (primitive, allows gulping air).
What adaptations do lungfish have?
Lobed fins, a prominent notochord, paired lungs, and alternating fin movement.
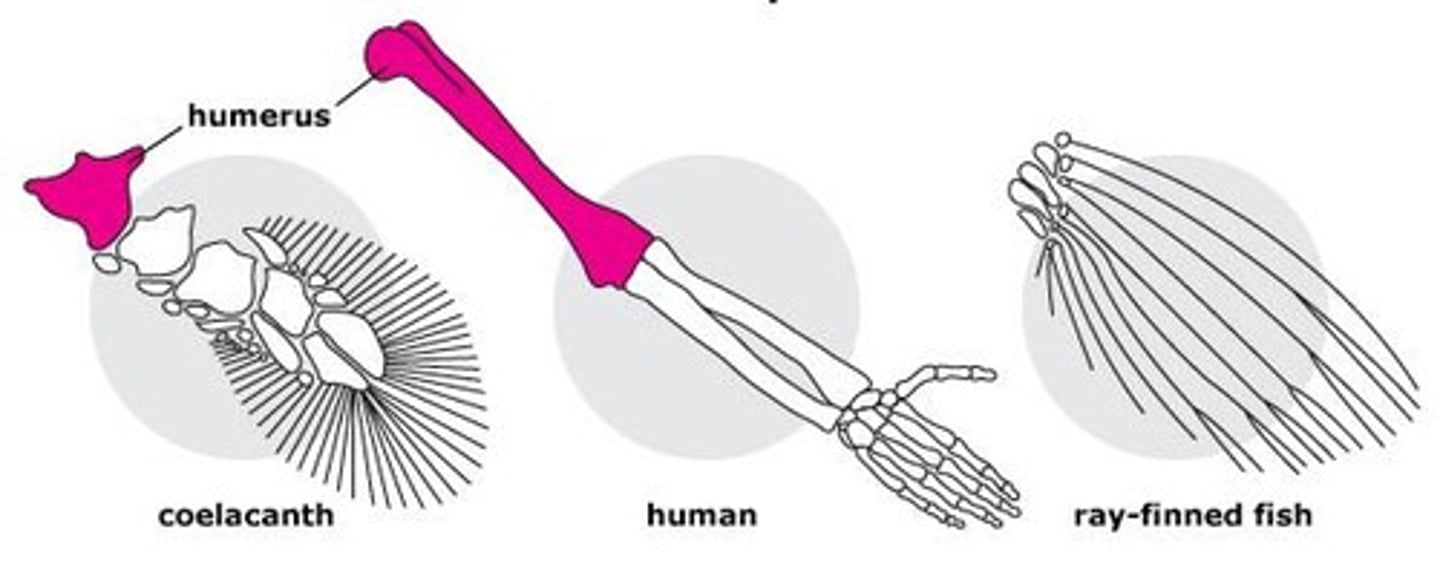
What is Tiktaalik roseae and why is it significant?
A transitional fossil showing features between fish and tetrapods, such as robust pectoral fins.
Lissamphibia (Examples and characteristics)
Includes salamanders, frogs, toads, and caecilians; they often have paired lungs and lack scales.
Types of Lissamphibia
Anurans, Urodela, Apoda
Anurans
Frogs and Toads, tympanum present and prominent
Paired limbs
No tail in adults
Urodela
Salamanders, Paired limbs
• Lungs reduced or absent
• Long tail
Apoda
Caecilians
Wormlike burrowers
• No limbs (or girdles)
• Reduced eyes
What are the two main lines of Amniotes?
Sauropsida (birds and reptiles) and Synapsida (mammals).
What are the four primary skull types in amniotes?
Based on temporal fenestra and arches: Synapsid (mammals) and Diapsid (birds and reptiles), with turtles being Anapsid.
What are the key characteristics of mammals?
Hair, mammary glands, non-nucleated red blood cells, and a single jawbone (dentary).
What are the three groups of mammals?
Monotremes (egg-laying), Metatherians (marsupials), and Eutherians (placental mammals).
What are some examples of mammal diversity?
Cetaceans (whales), Sirenia (manatees), Chiroptera (bats), and Primates.
What is the significance of surface area in biological functions?
Surface area affects heat loss, fluid absorption, respiration, and metabolism.
What are the three primary germ layers in organogenesis?
Ectoderm, Endoderm, and Mesoderm.
What are the four tissue types found in adults?
Epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue.
What is the role of the ectoderm in development?
It forms the epidermis and nervous tissue.
What is the role of the endoderm in development?
It forms the digestive and respiratory linings, including organs like the liver and pancreas.
What is the role of the mesoderm in development?
It forms skeletal muscles, circulatory components, kidneys, and connective tissue.
Cranium
Protection for evolving sensory structures
• Bone/Cartilage
• Cranial portion of neural tube
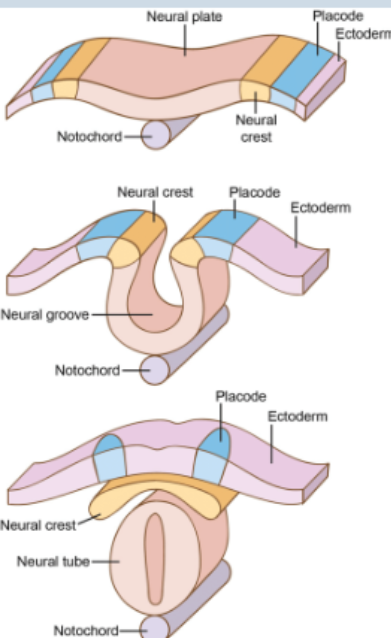
Neural Crest Cells
Stem cells located at the side of the neural tube after neurulation that migrate throughout embryo and give rise to a range of cell types
Epidermal (ectodermal) placodes
Localized thickenings of ectoderm just
lateral to neural plate border that give rise
to cells that make up many of the sensory
components in the vertebrate head
Steps in Vertebrate Development
1) “Prevertebrate"
2) Agnathan
3) Gnathostome

Prevertebrate
Transition from solely ciliary feeding
Muscular pump → increased feeding and respiration efficiency → increased size
Agnathans (General ans examples)
Jawless fish - Hagfish and Lampreys

Hagfish
Slime predator defense, Two pairs of tooth-like rasps on top of “tongue, Adult hagfish: no true vertebrae

Lampreys
Vertebrae are cartilaginous, many are parasitic
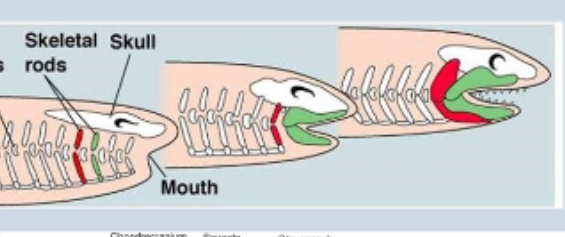
Gnathostomes
Development of jaws from rostral pharyngeal arches, Paired pectoral fins, paired pelvic fins
3 divisions of Gnathostomes
Placoderms, Chondrichthyes, and Teleostomi
Placoderms
Extinct species, 380–360 million years ago
Chondrichthyes
Chimera, no scales, fused upper jaw to brain case
No swim bladder - Oily livers
Vertebral column- cartilage with some calcium
2 types of Teleostomi
Acanthodii and Osteichthyes
Acanthodii
EXTINCT
Osteichthyes
Characteristics:
• Persistent presence of bone
• Development of swim bladder (vs. oily liver)
• Operculum is bony (vs. skin)
2 types of Osteichthyes
Actinopterygii and Sarcopterygii
Actinopterygii
Ray-finned fishes
Sarcopterygii
Fleshy-finned fishes /lobe-finned fishes