Lecture 7: Cloning and Regenerative Medicine
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Define nuclear transfer
Introducing nucleus from a donor cell into an enucleated oocyte, creating an embryo that is genetically identical to the donor.
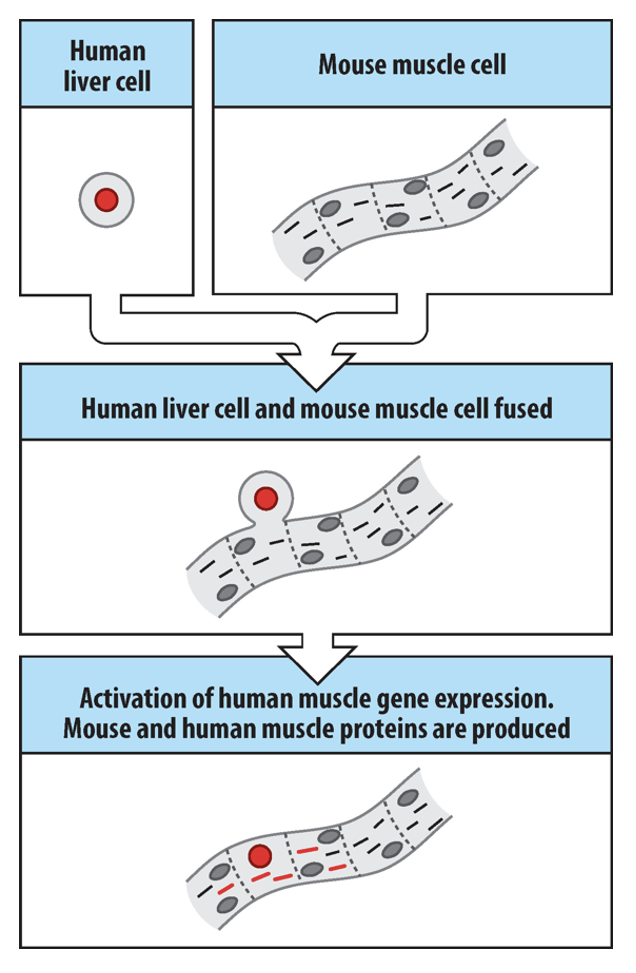
What does inter-species nuclear transfer allow?
For proteins to be easily analysed.
What does nuclear transfer show?
That terminal differentiation can be reversed.
What can induce reprogramming of cells?
Damage.
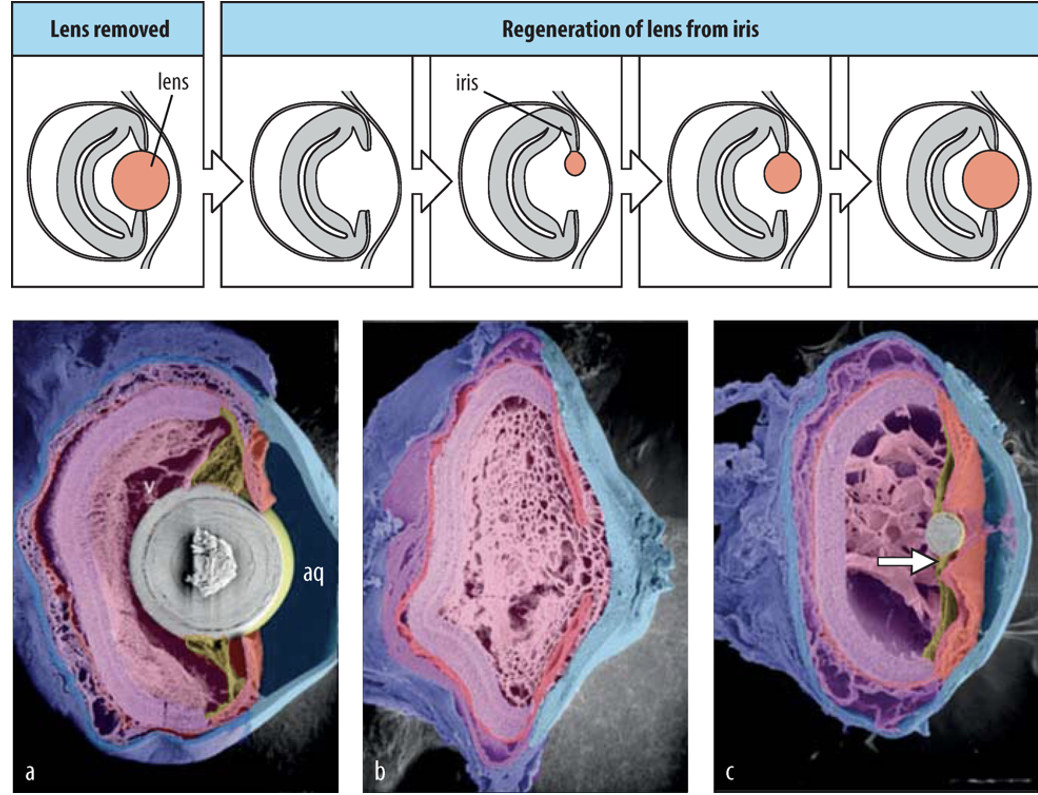
When the lens is removed or damaged from the eye of a newt, what happens?
Iris cells transdifferentiate into lens cells to regenerate the missing tissue,
Define clone
Group of identical cells that share a common ancestry.
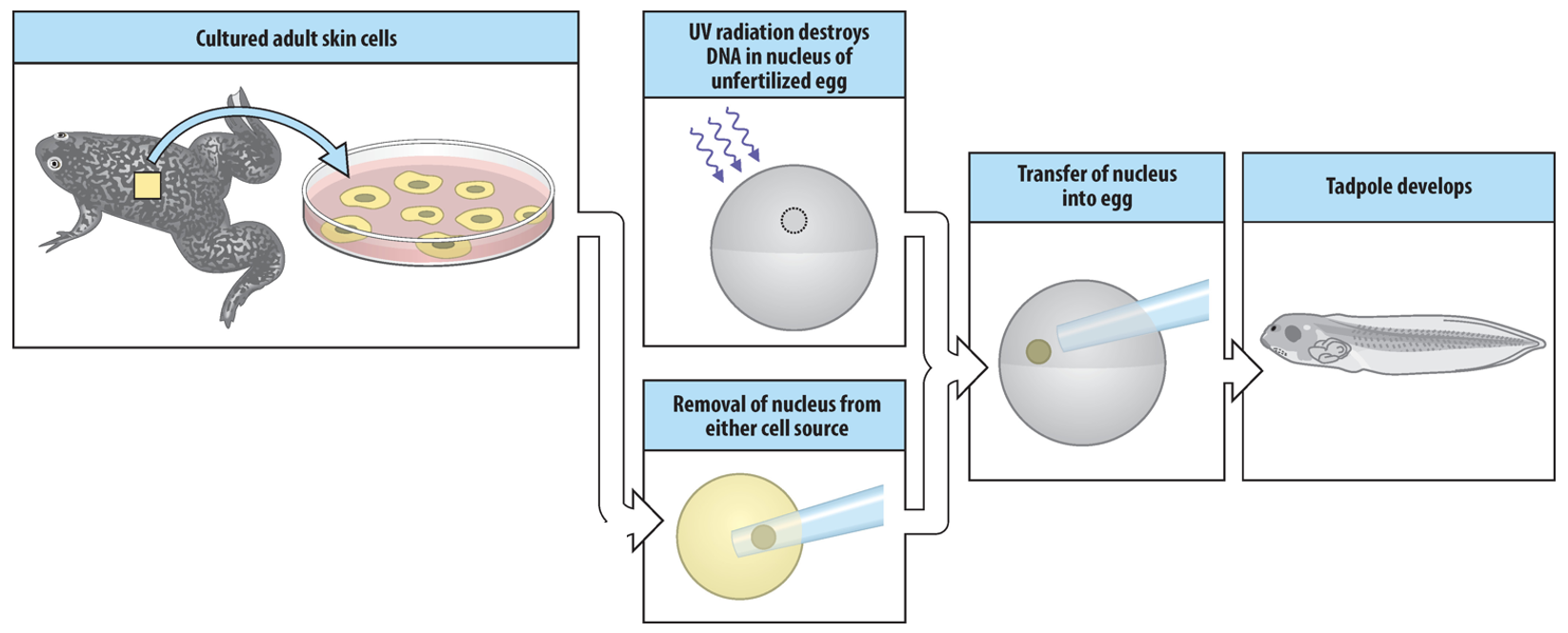
What was the first evidence of totipotency?
Cloning of frogs using tadpole gut cells (1962). The nucleus couldn’t produce an adult frog, only tadpole.
The fact that blastula nuclei were more successful in cloning frogs suggests what?
That younger cells are more stem cell like. Suggests as nuclei gets older it loses it ability to revert to stem cell fate.
Describe the process used to clone the first mammal
Take unfertilised egg from host + removed nucleus. Take mammary epithelial cells from donor + culture in low serum so cells exit mitotic cycle into G0. Fuse the egg without a nucleus + mammary epithelial cells using electric current. Nucleus of mammary cell inside egg. Culture the embryo. Transfer to foster mother.
What does regenerative medicine focus on?
Using in vitro technology to improve health.
What does regenerative biology focus on?
In vivio approaches.
Describe scaffolds
Made out of biodegradable material to support 3D growth of cells.
Why should stem cells come from the patient?
To avoid tissue rejection.
State 3 different methods of creating insulin producing cells
Somatic cell nuclear transfer, induced pluripotency, transdifferentiation in vivo.
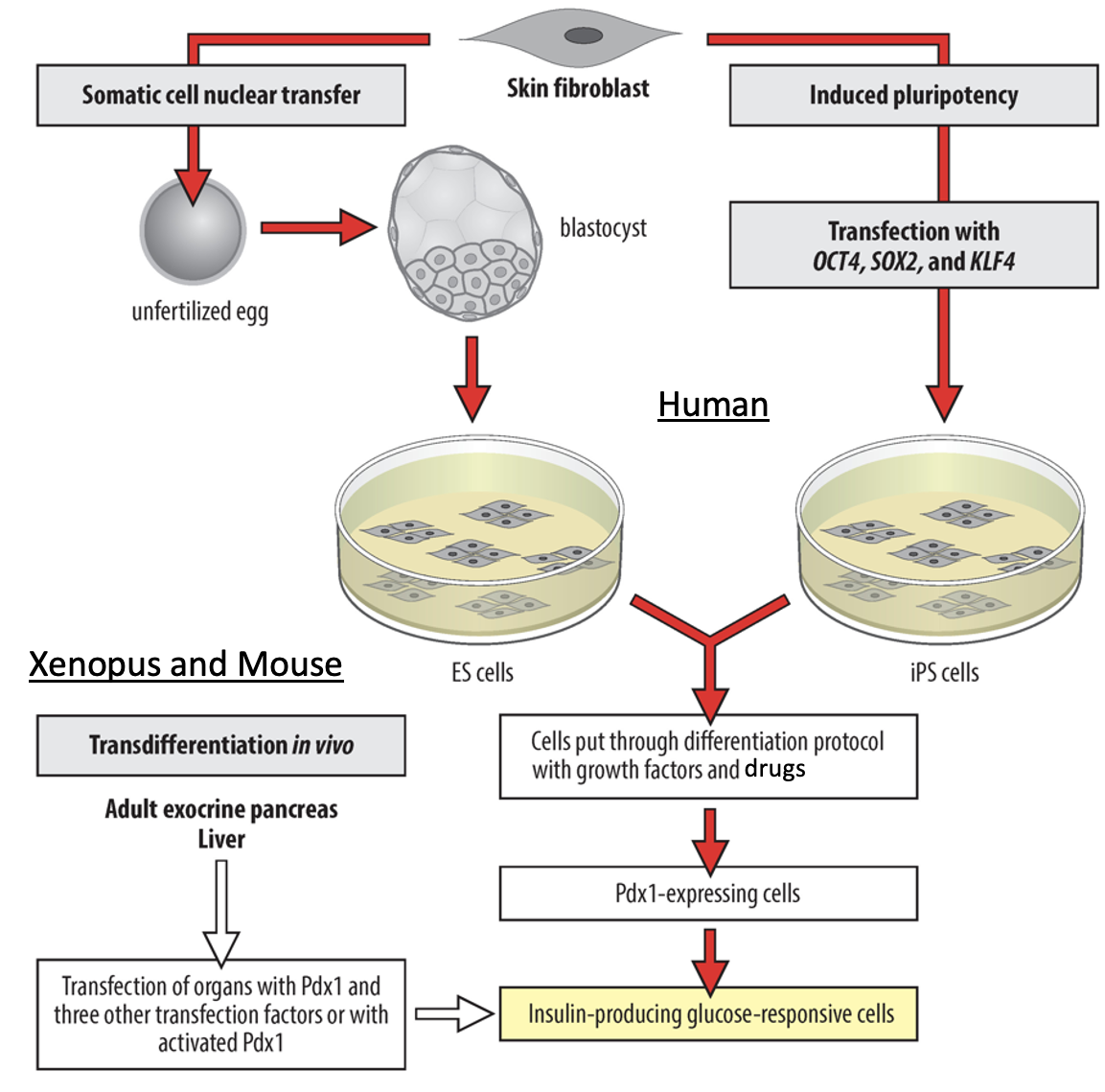
How does transdifferentiation work when producing insulin producing cells?
Causes liver cells to transdifferentiate into pancreas cells. Overcomes issues of transplanting cell into the correct place.
What are advantages + disadvantages of stem cell therapies based upon iPS cells?
Advantages: correcting genetic defects (like junctional epidermolysis bullosa). Replacing simple tissues or single cell types (bladder, retinal cells). Testing how cells will respond to different pharmaceuticals (personalised medicine).
Disadvantages: transplantation could be difficult. Organogenesis is very complex, tissue engineering scaffolds have had limited success.
How was it discovered that cells can self-organise?
Wilson dissociated sponges by putting them through a fine sieve then observed them reorganised themselves into intact sponges. Adhesion molecules + cell signalling play a role in this process.
Briefly state how organoids are formed
By stem cells when cultured in special media.
State different types of organoids that have been generated from iPS cells
Cerebral cortex (2008), intestine (2009), gastric + renal (2010), retinal (2011), inner ear + liver + pancreas (2013), lung + prostate (2014), fallopian tube + kidney + mammary gland (2015), endometrium (2017), placenta + hepatocyte (2018) etc.