Botany
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
153 Terms
3 cell types
-parenchyma
- collenchyma,
epidermis= 1 cell wall thick
-sclerenchyma ,
dead at maturity, lignin ( red color)
what is the difference between the periderm and the pericycle ?
The periderm is cork cambium,cork,phelloderm it divides
pericycle,functions to always divide
The life of a cell
1. interphase, cell is doing its function DNA is duplicated
2. Mitotic phase, mitosis ( division of nucleus and DNA) cytokinesis ( division of cytoplasm)
The life of a the cell
( 4 phases)
MITOSIS
(Interphase),is the majority of its life then it goes to its mitotic phase { nucleolus,cytoplasm,chromatin,cell wall and plasma membrane}
* Prophase { spindle forms, chromosomes form, nuclear envelope disapates}
*Metaphase { metaphase ( plate/ equatorial plane), spindle}
* Anaphase ( chromosomes separate and pulled to opposite ends of the cell by the spindle fibers) { spindle microtubules pull the genetically identical chromosomes, daughter chromosomes separate}
* telophase { cell plate, accomplishes cytoleinsis, nuclei form}
Plastids
3 basic types
* All related to each other from an evolutionary perspective
* all have 2 layers of membrane that surround them
- chloroplast { green because of chlorophyll (photosynthesis)
-chromoplast { yellow to red color from carotenoids, often attraction for animal seed disperseis or pollinators}
-plastids { naturally colorless,strach storage (leuroplast)
What does RAM stand for ?
Root Apical Meristem
RAM
( root apical meristem )
* divides off cells in 2 directions
Exterior cells = root cap
interior cells = 1 meristems > develop into 1 tissues
1. protoderm > epidermis
2. ground meristem > ground tissue
3. procambium > vascular tissue
Mitochondria
* have 2 layers of membrane
* fxn: cellular respiration
> how all cells get energy to power metabolism
What is the difference between the vascular cambium and the vascular cylinder?
*vascular cambium ,
creates second tissue
* vascular cylinder,
center colum,primary pholoem,xylem
What are vascular plants
* ferns
* conifers
* flowering plants
What is phyloroglucinol ?
reacts with lignin to turn pine/red
What is vascular tissue ?
Internal conclutive tissue
Development of tissues
Ground tissue, fill up the plant body and gives the plant shape and internal support
* help with nutrient production and storage
Development of tissues
Vascular tissue , made up of the xylem and phloem
Development of tissues
xylem, one way tube that carries water
Development of tissues
phloem, two way tube that carries food
Tissues of vascular plants
* epidermis
* ground tissue
* vascular tissue
3 cell types of vascular plants
* Parenchyma
* collenchyma
* sclerenchyma
Plastids
* 3 basic types
- all related to each other from evolutionary perspective
- all have 2 layers of membrane that surround them
- vary by color and function
Plastids ( leucoplasts)
Naturally colorless
fxns: starch storage, others make oil
plastids ( chromoplasts)
* yellow to red color from carotenoids
* fxns: often, attraction for animal seed dispersers or pollinators
The life of a cell
(Primary Growth )
Result in an increase in length
-new leaves and root form
the life of a cell
(secondary growth)
results in an increase in thickness
plastids ( chloroplast)
* green because of chlorophyll
* fxn: photosynthesis
the life of a cell
( root functions)
absorption, storage,anchorage,conduction
Difference between monocot and dicot root
MONOCOT ROOTS
Monocot roots,
1. xylem is polyarch
2. pith is usually large at the centre
3. Metaxylem vessels are generally circular in cross section
4. conductive tissue is sclerenchymatous in maize
5. there is no secondary growth
Difference between monocot and dicot root
DICOT ROOTS
1. xylem is usually tetrach
2. pith is usually absent
3.metaxylem vessels are generally polygonal in cross section
4. conjuctive tissue is usually parenchymatous
5. secondary growth is generally present
Summary of primary and secondary growth in a woody stem
PRIMARY MERISTEMS
* protoderm
* procambium
* ground meristem
Summary of primary and secondary growth in a woody stem
PRIMARY TISSUES
* epidermis
* primary phloem, primary xylem
* ground tissue { pith cortex}
Summary of primary and secondary growth in a woody stem
LATERAL MERISTEM
* vascular cambium
* cork cambuim ( periderm)
Summary of primary and secondary growth in a woody stem
SECONDARY TISSUES
*secondary phloem
* secondary xylem
* cork { periderm}
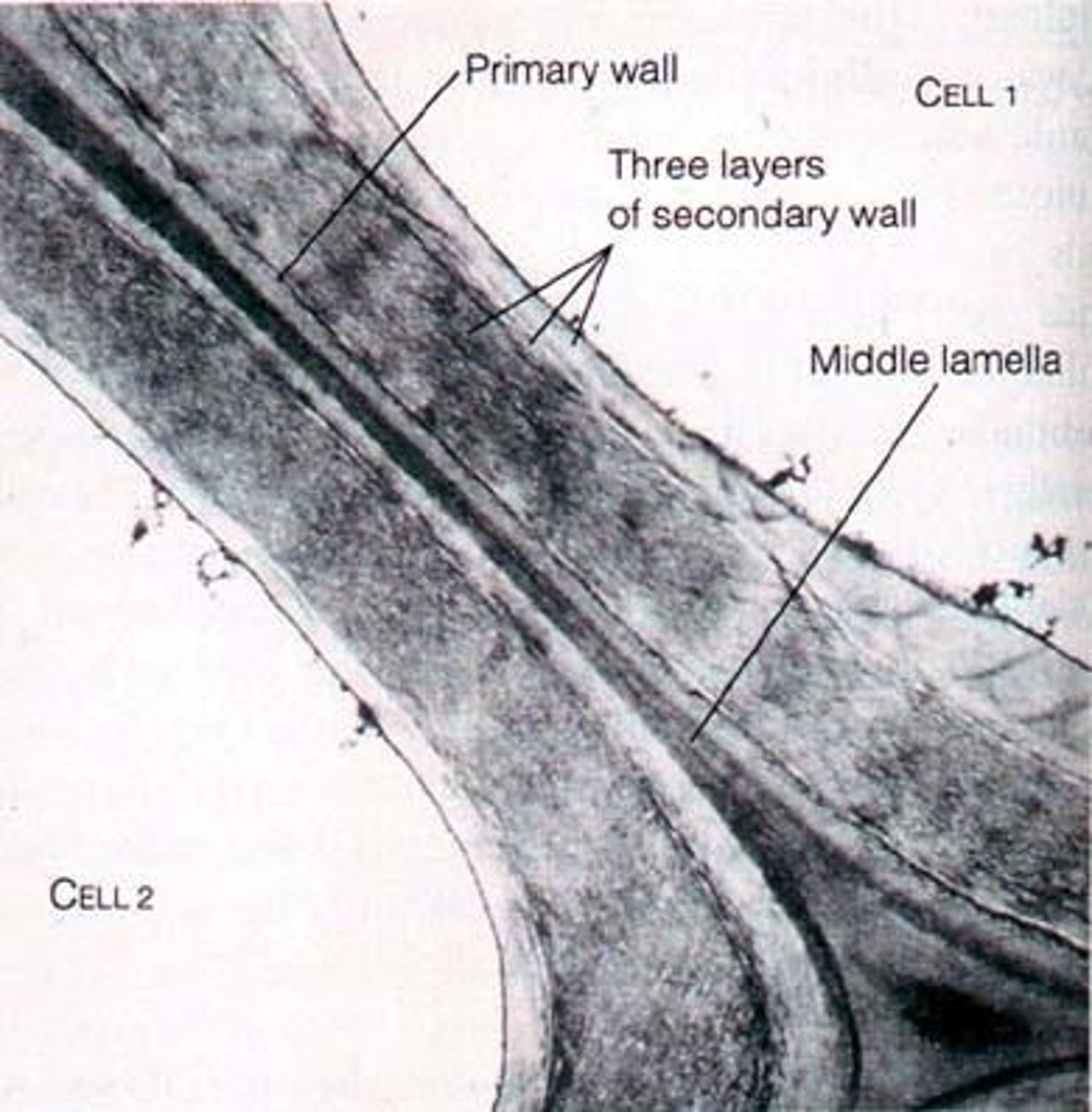
Middle Lamella
gives cells together
Plant tissues
* ( outside skin) Epidermis > always on the outside > made of parenchyma
ex: trichomes guard cells > modified epidermis cells
Phases of the cell cycle
* interphase
- primary growth
- genome replicated
- secondary growth
- mitosis
- cytokinesis
Simple leaf
- blade is 1 continuous piece

compound leaf
- blade is divided into leaflets pinnately compound leaf

Palmately compound leaf
the hand one
( node then at the end a compile pack of leaves)

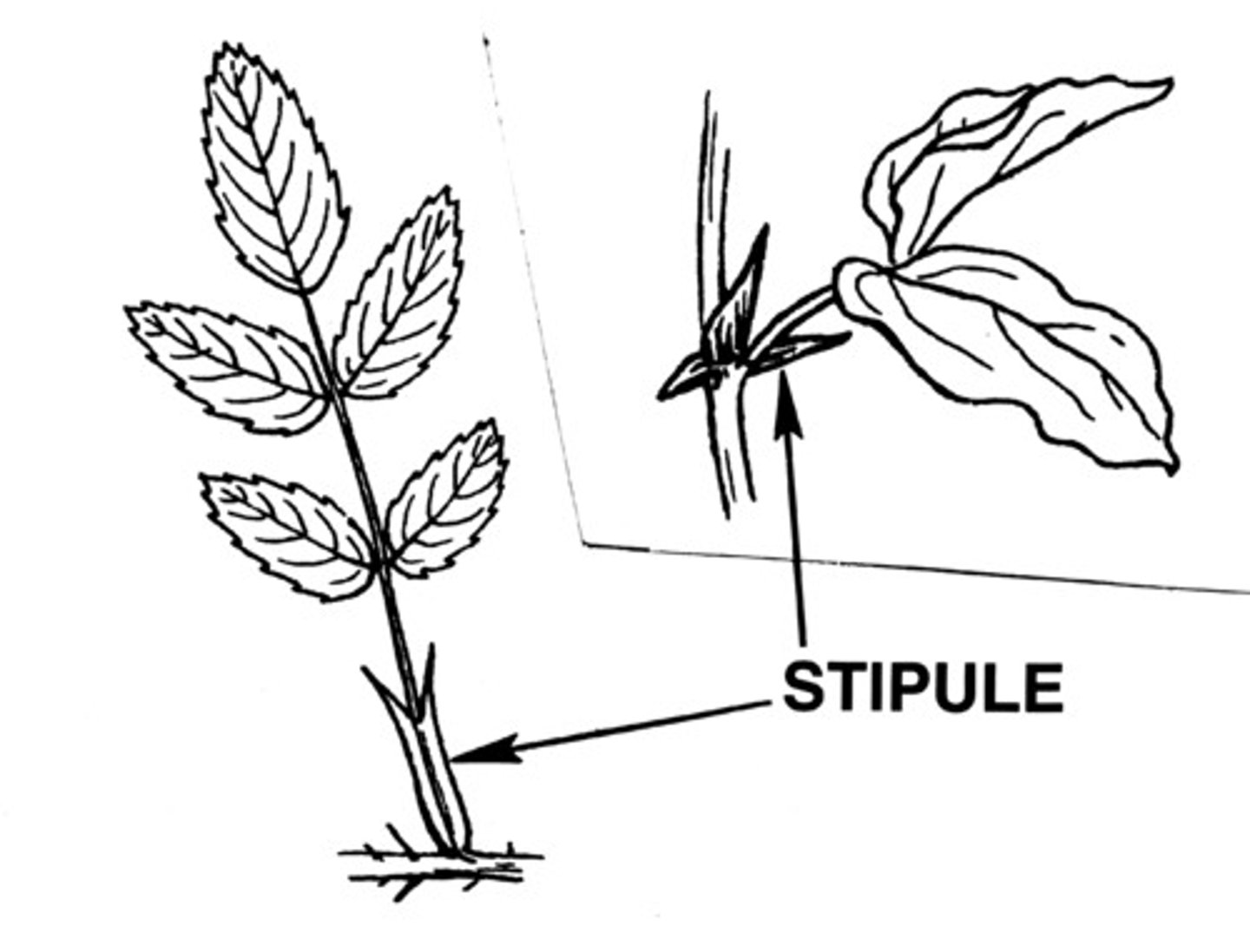
Stipules
- paired leaf appendages found at the base of the petiole
petiolate leaf
has a petiole
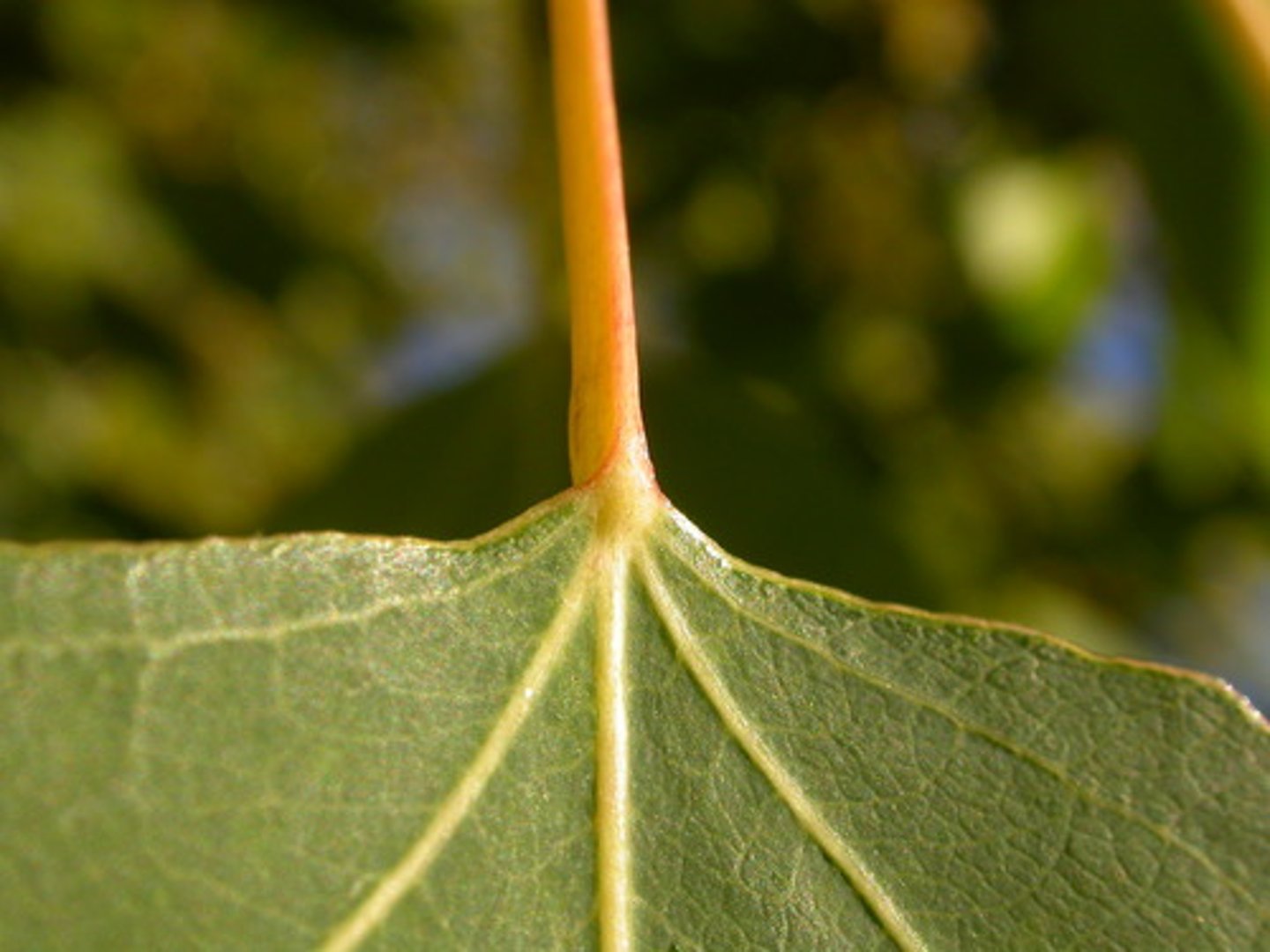

sessile leaf
lacks a petiole
Modified roots
adventitious roots

pheumatophores
roots for gas exchange
shoot
stem + leaves
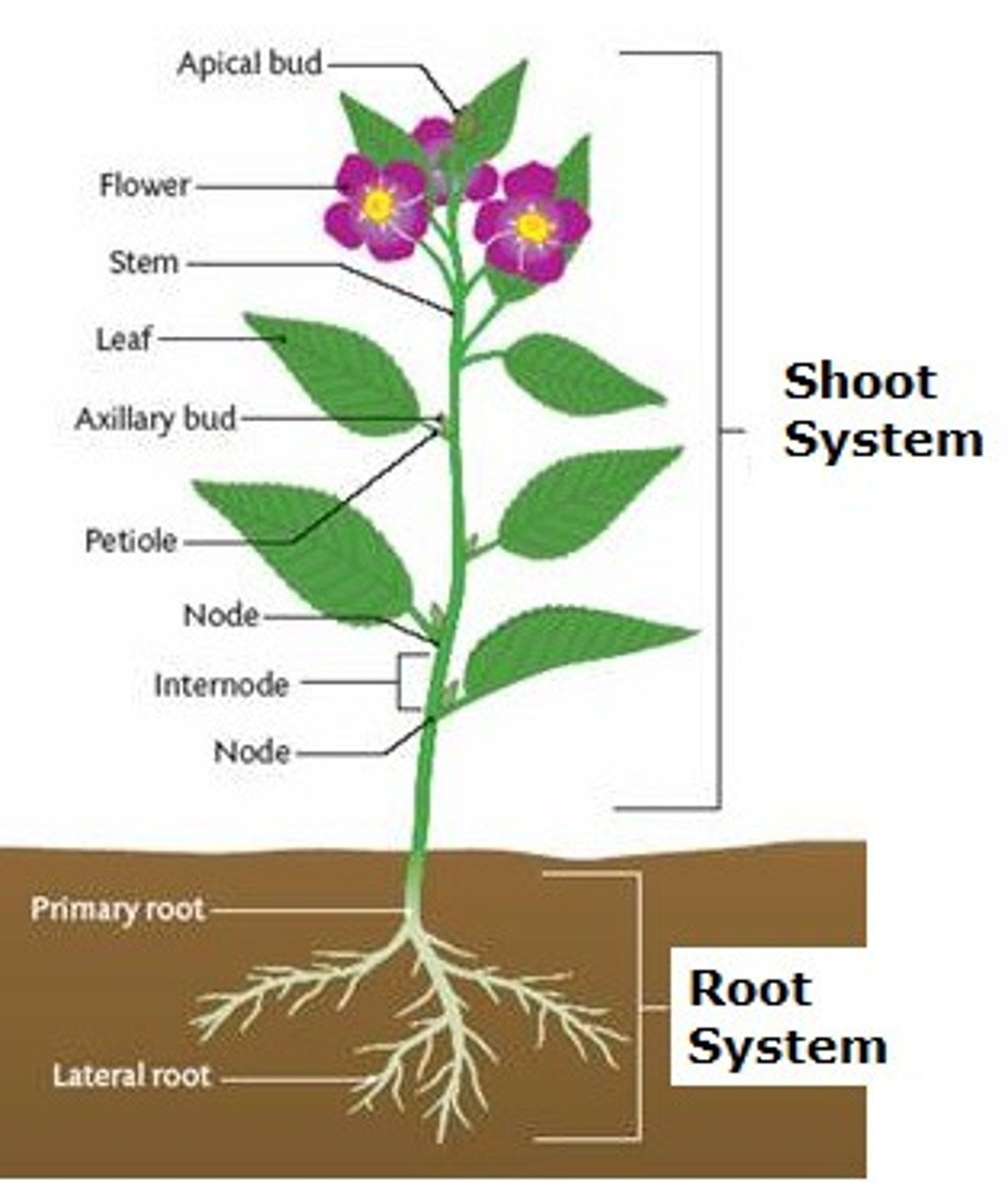
Node
Section of stem where leaves attach
Leaf venation
* parallel
- typical of moncots
* netted
- typical of eudicots
Leaf arrangement
* Alternate, 1 leaf per node
* opposite, 2 leafs per node
* whorled, 3+ leaves per node
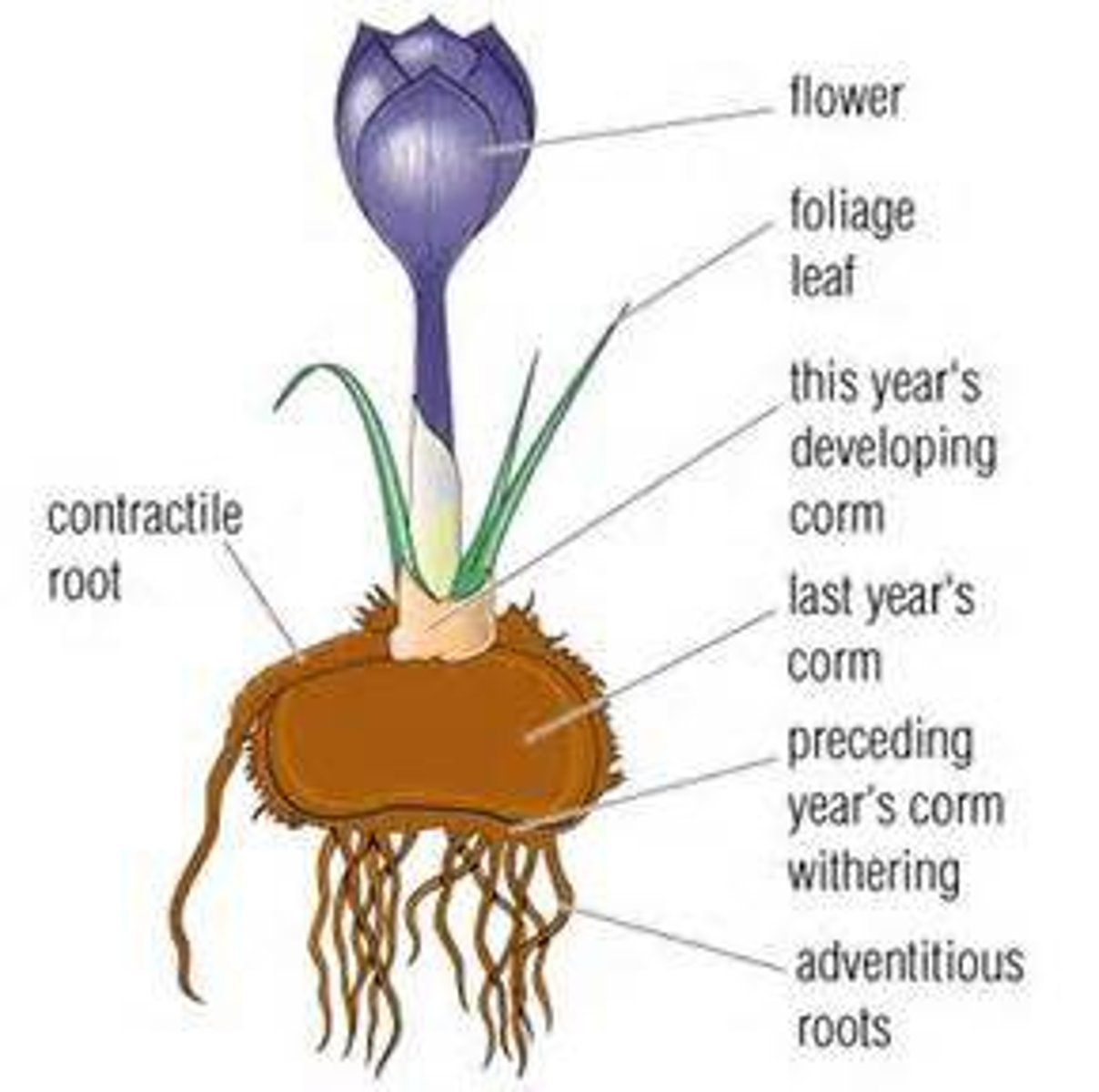
BULB
ex. Onion
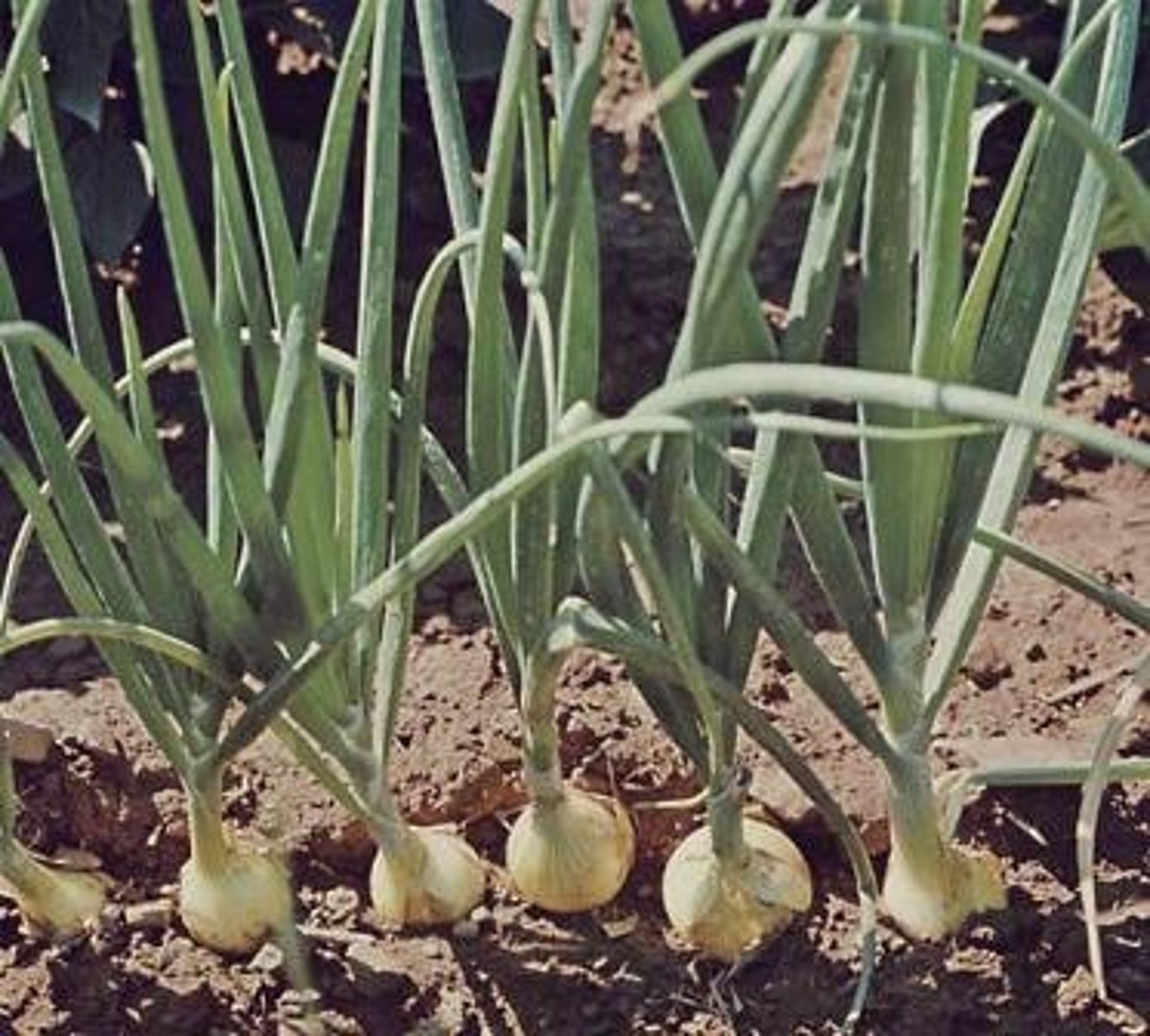

CORM
ex. green onion, chive, leek
( basil plate)
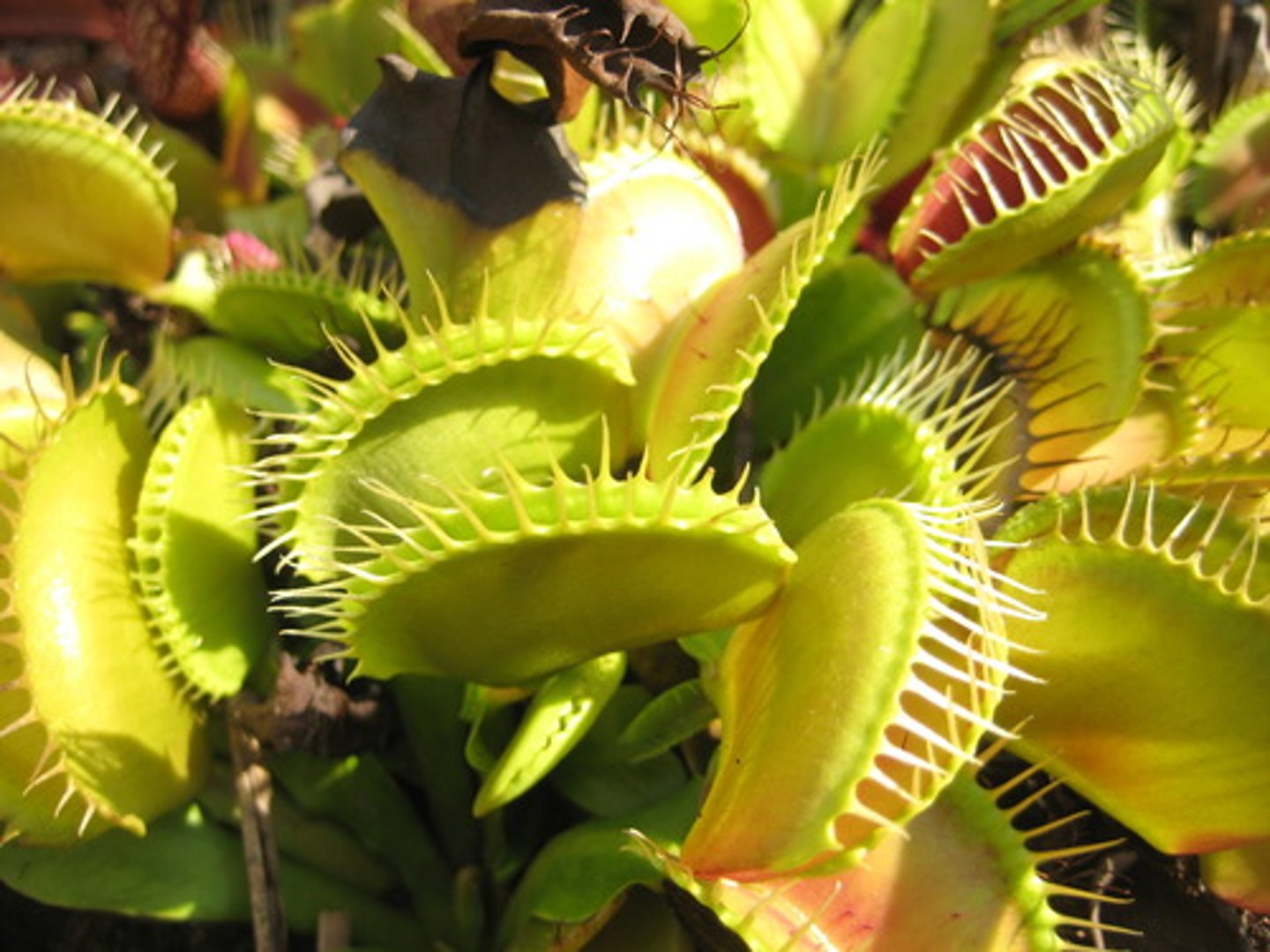
CLADODE + TRAP
ex. fanged pitcher, venus fly trap
( flattened stem for photosynthesis, carnivorous part of leaf)

THORN
modified branch
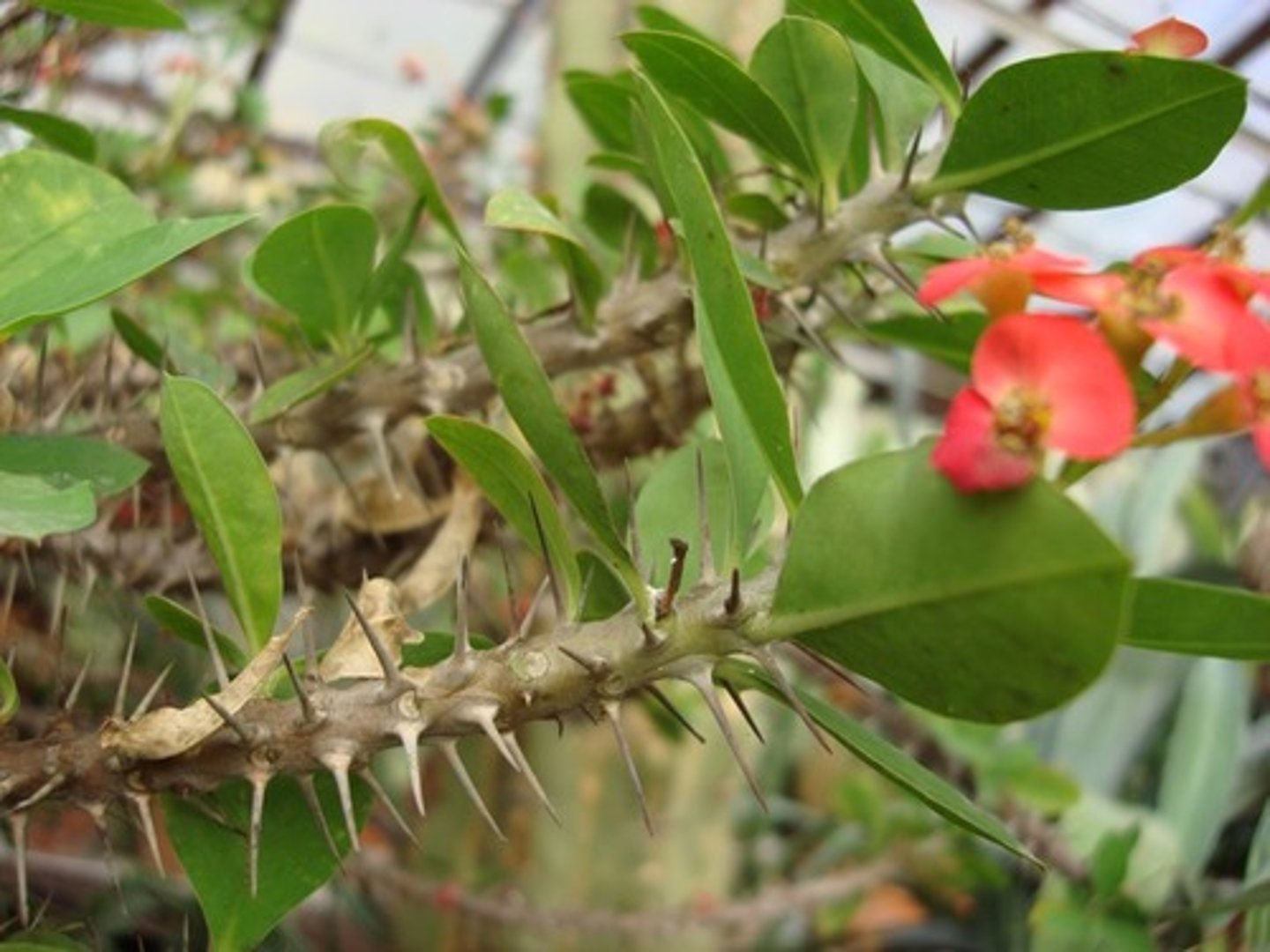

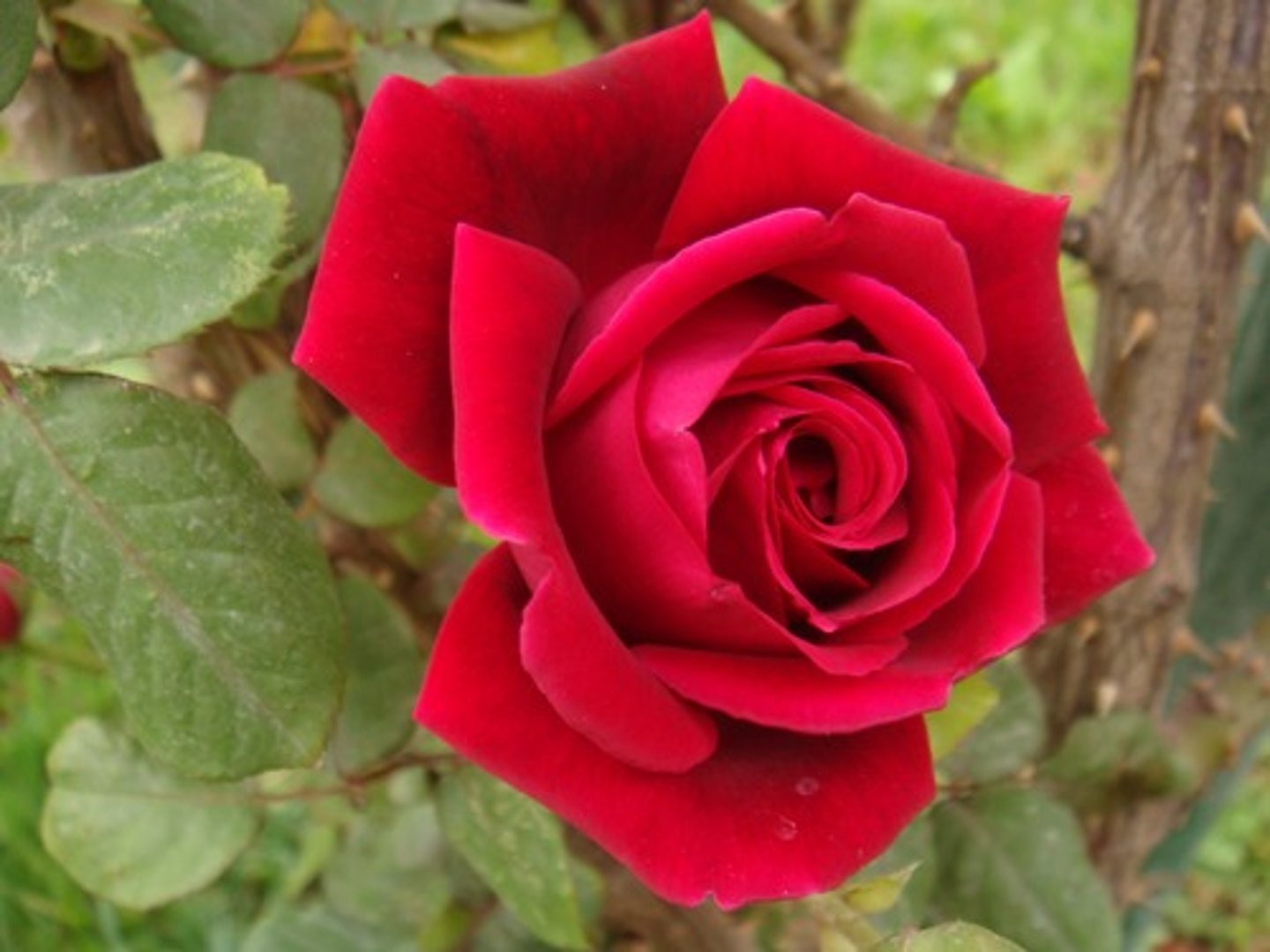
PRICKLE
extension of epidermis
ex. rose

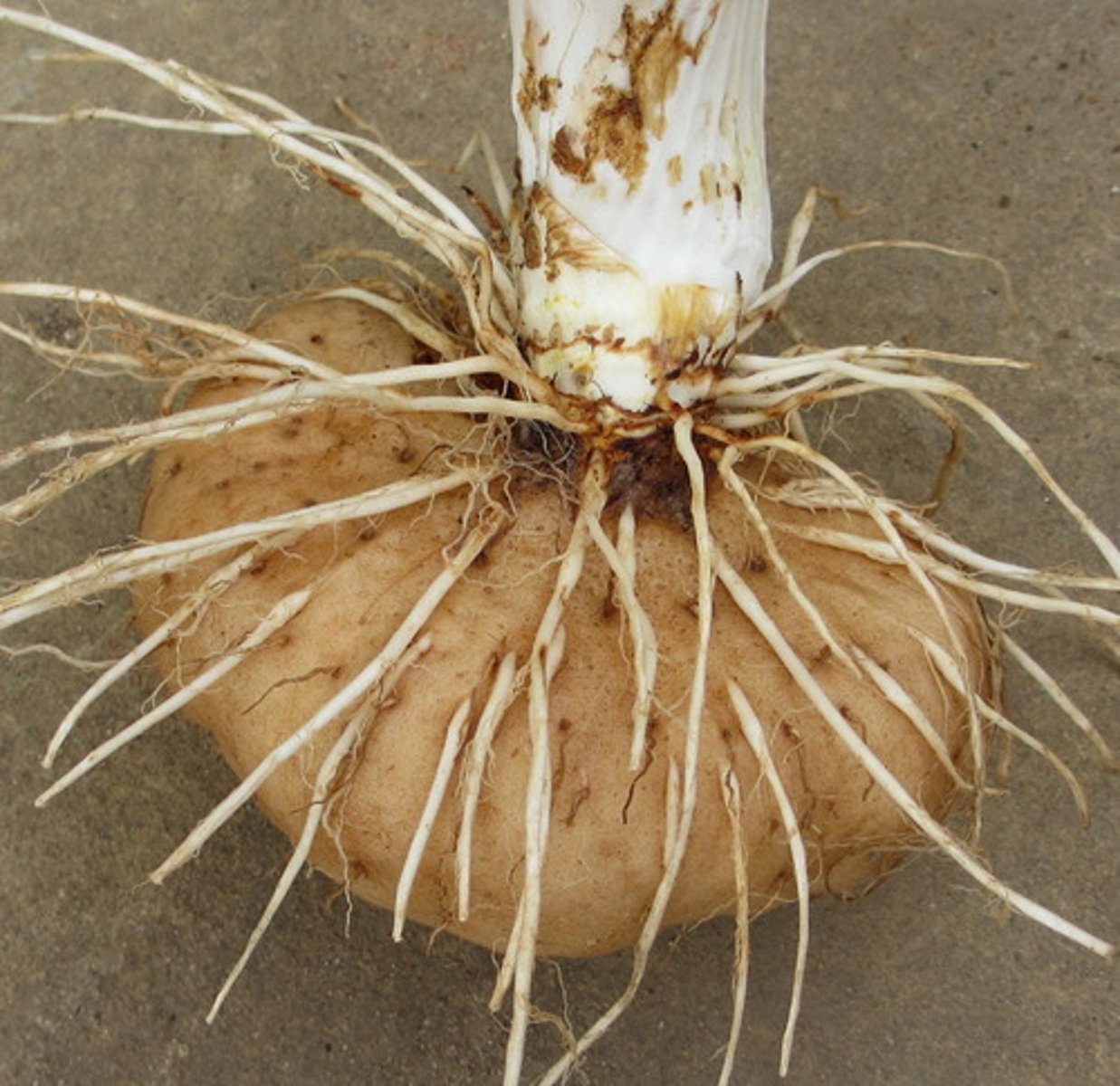
TUBER
swollen underground stem
ex.potato

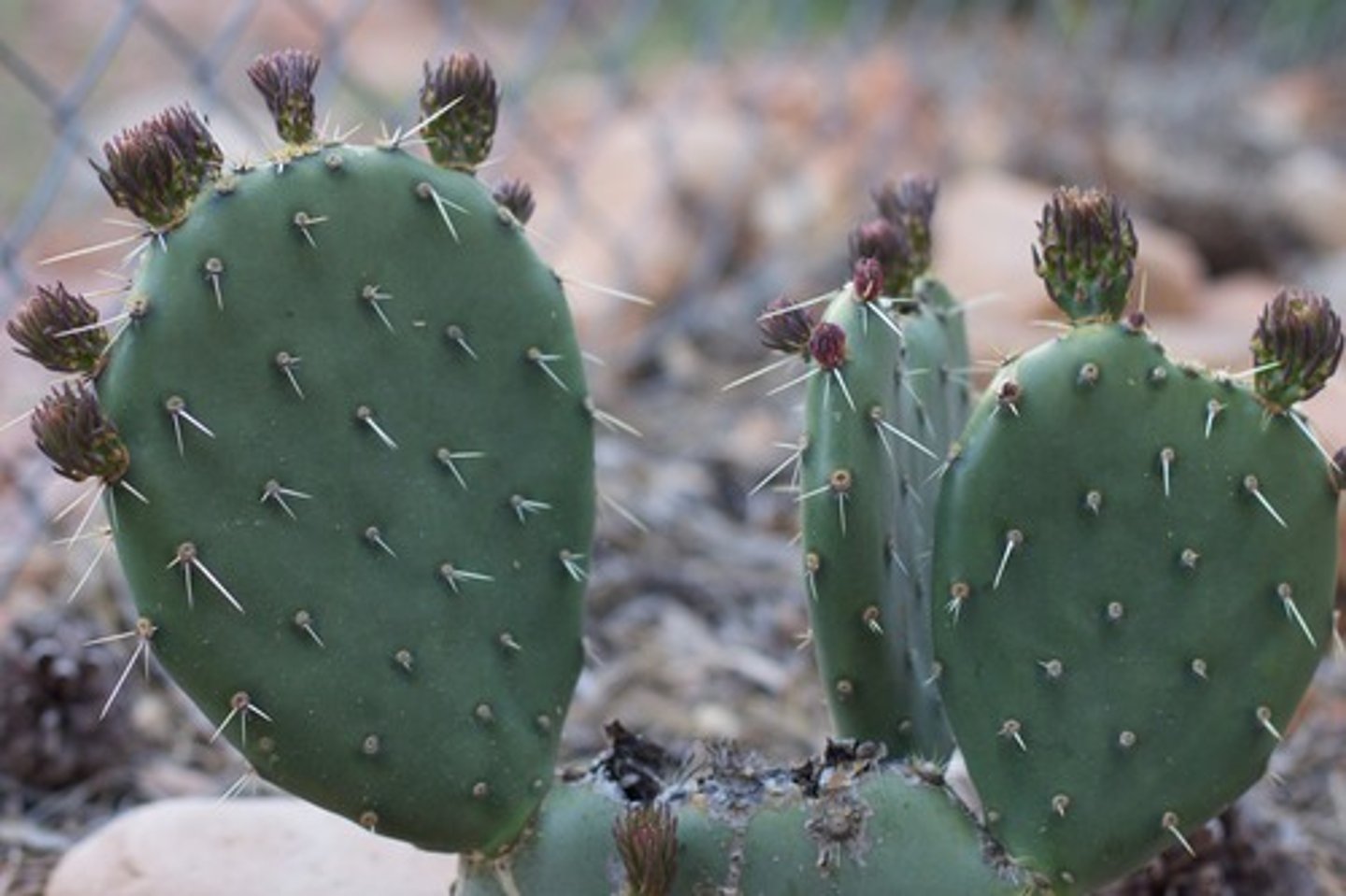
PHYLLODE
Spines, flattened stem for storage
ex. nopal

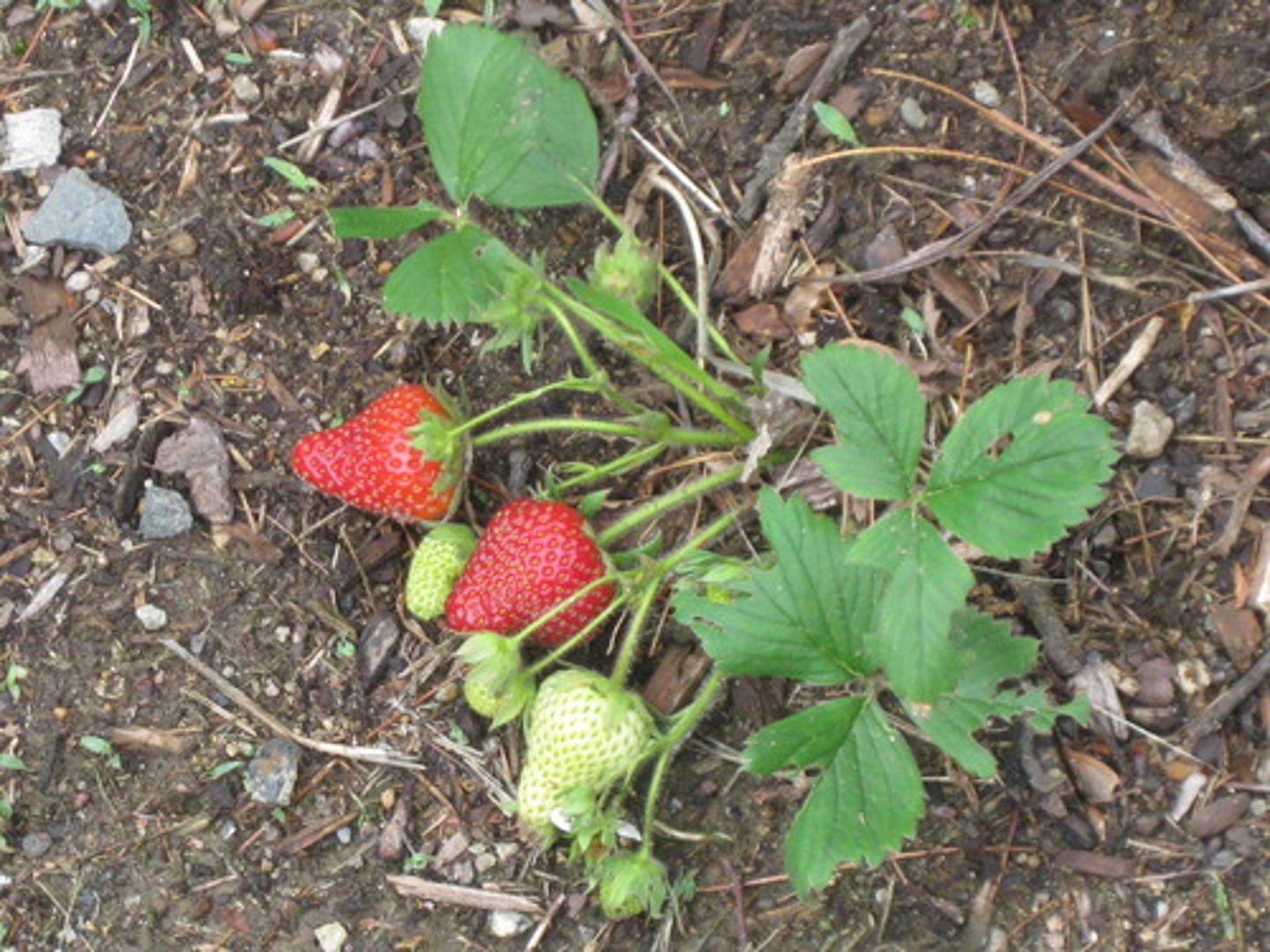
STOLEN
Above ground stem lying on ground
ex. strawberries

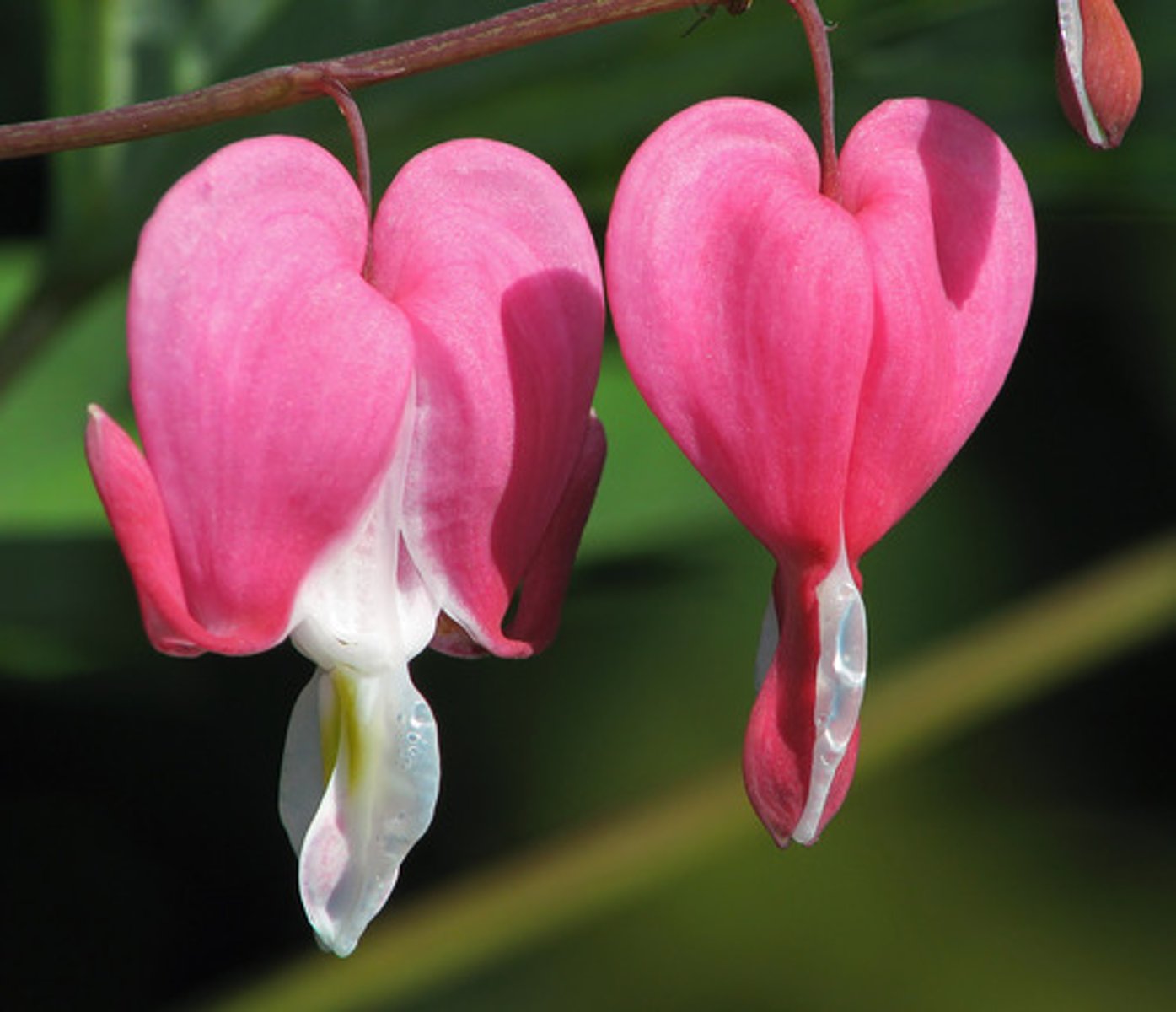
RHIZONE
Below ground stem
ex. bleeding heart

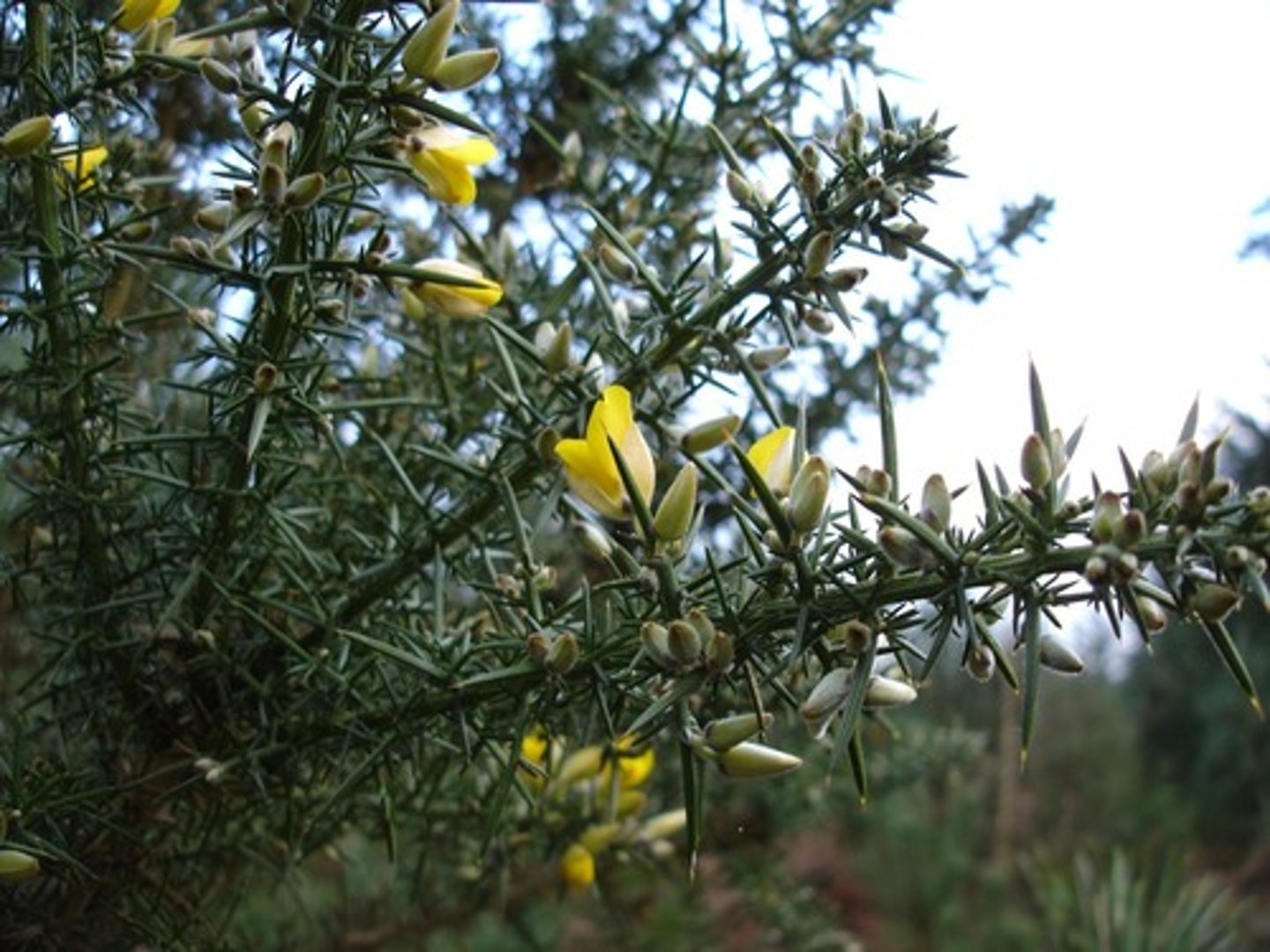
SPINES
modified leaf
ex. ulex europaeus

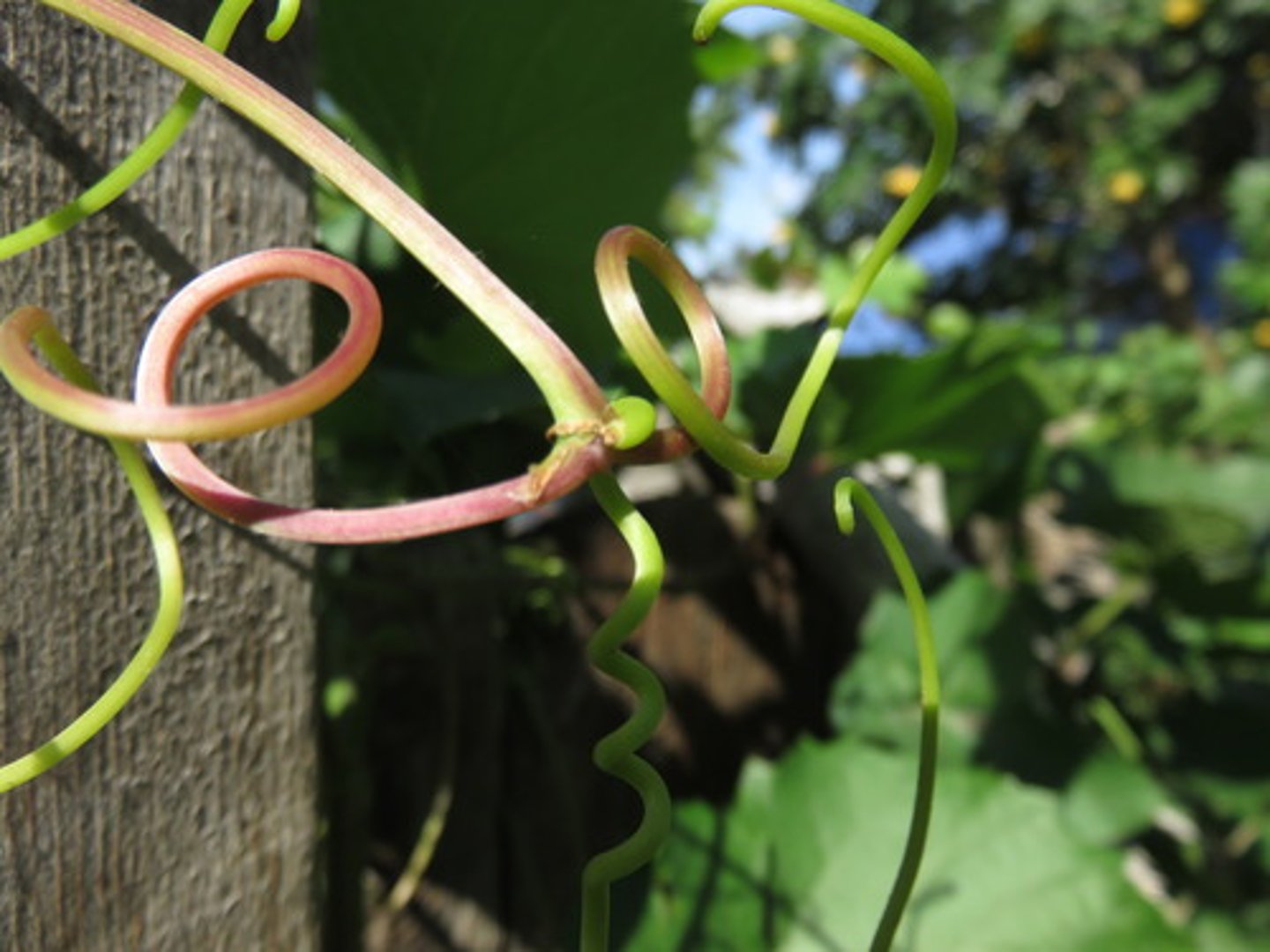
TENDRIL
modified plant
ex. pea plant

Ancestral
describes a character state that is the same as a group's common ancestor
Character
a trait used to decipher evolutionary relationships. these inches but are not limited to an organism's morphology reproduction structures, and DNA sequences
Character Matrix
a table showing the characters and character states for a given group of organisms
Character state
the form of a character. For example if out character was flower color in a particular group of organisms the possible character states might be red,orange or blue
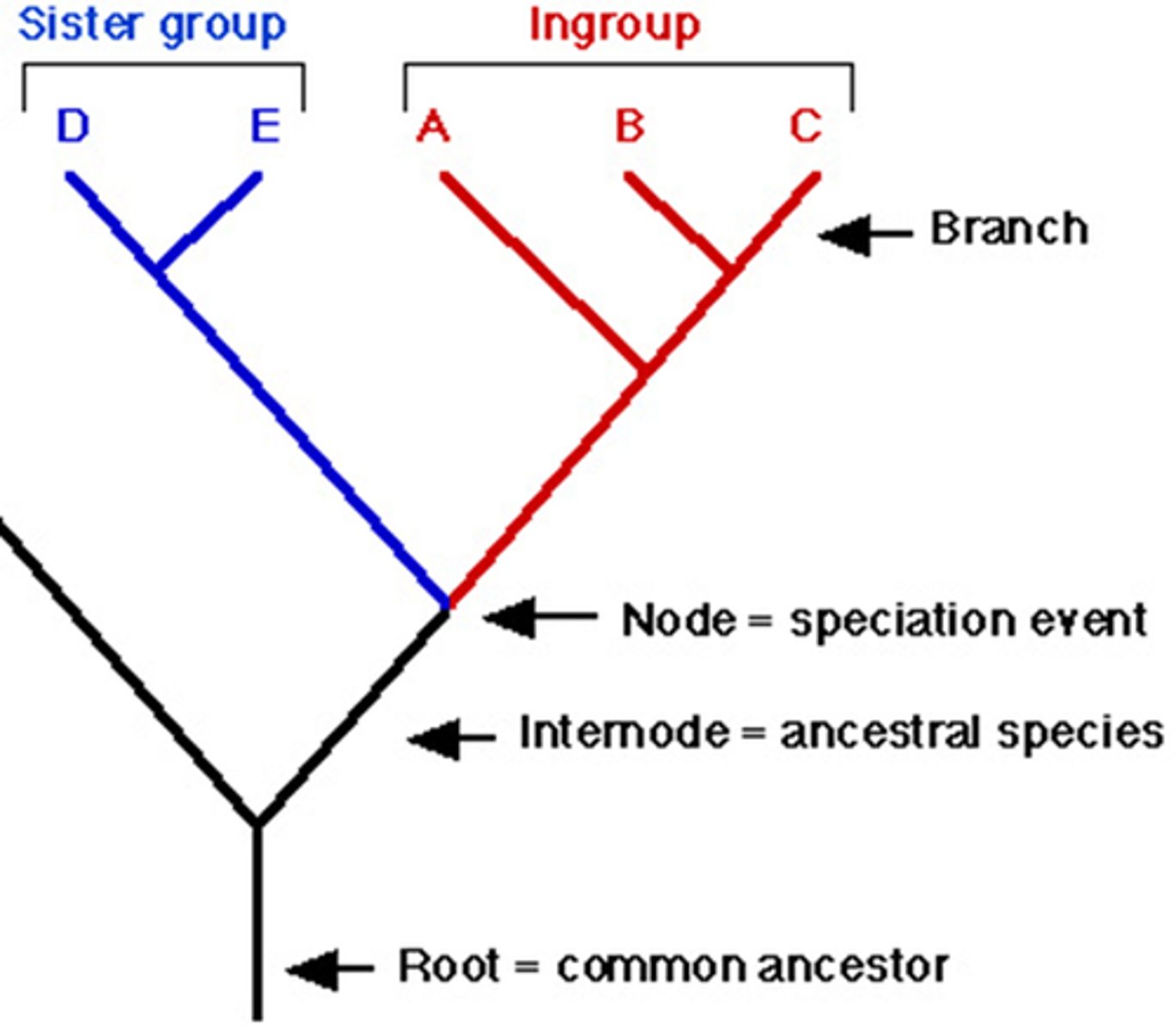
Cladogram
a diagram illustrating the branching patterns of evolution for a particular group. also called phylogenetic trees
Derived
a character state that is different from a groups common ancestor
Group of interest
a term used to describe the groups of organisms for whom you are trying to determine their evolutionary relationship
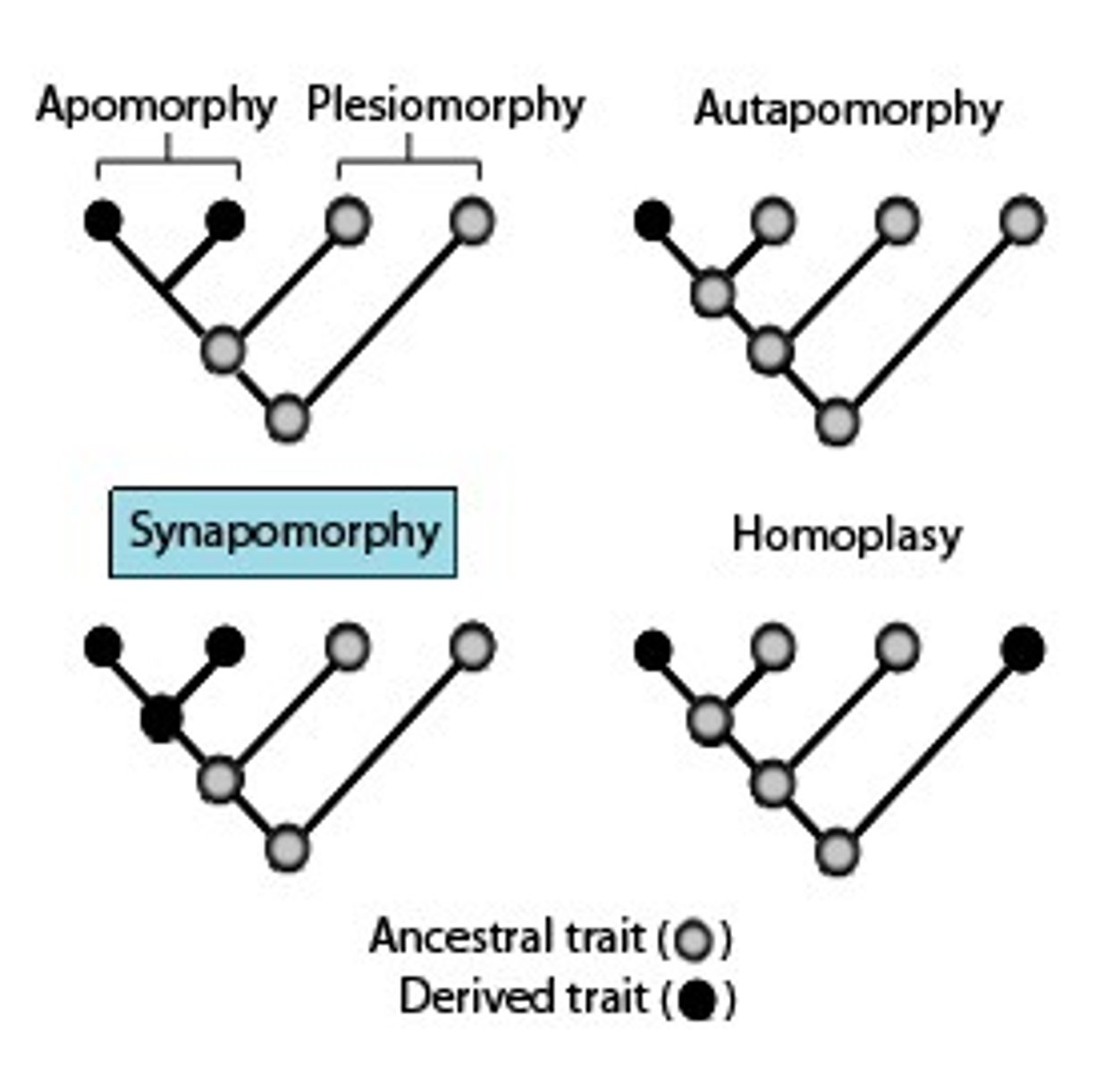
Homoplasy
a shared character state due to convergent evolution
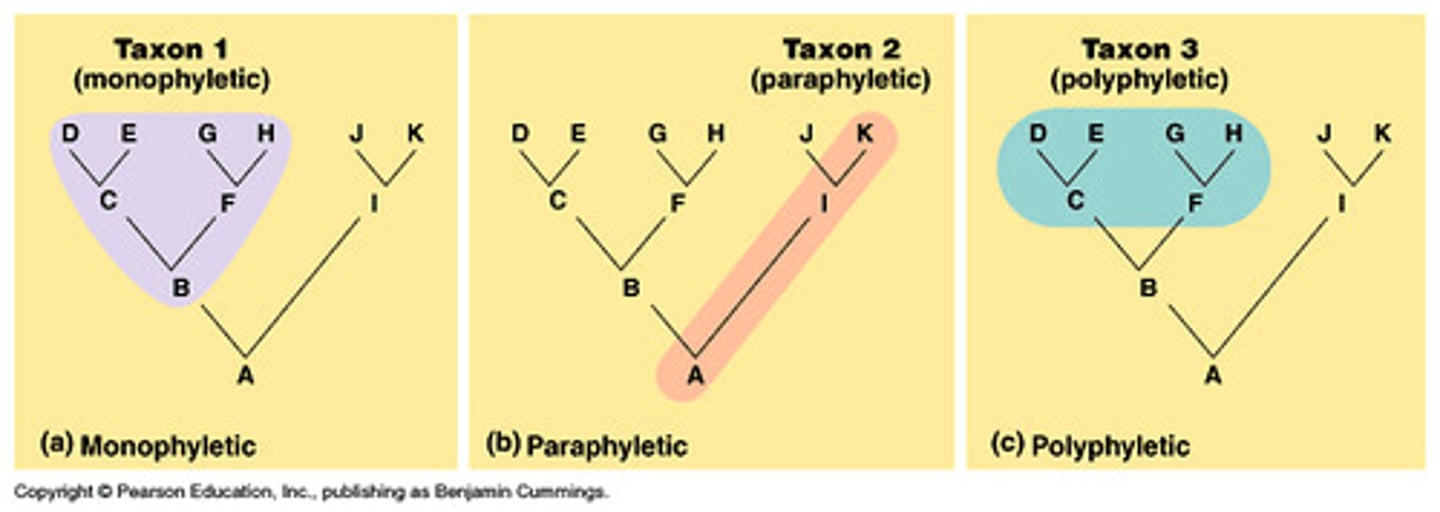
Monophyletic group
a taxonomic group that shares a common ancestor and all of its descendants. defined by synapomorphies
Node
A branch point on a cladogram, represents the most recent common ancestor of all taxa above the node
Ockham's razor
a rule used throughout science stating " do not generate a hypothesis any more complex than is demanded by the date"
Outgroup
a group outside of you're group of interest. An outgrip is used to determine which character states are ancestral and which are derived
Paraphyletic group
a taxonomic group that includes a common ancestor and some, but nit all of its descendants
Parismony
a principle used to decipher evolutionary relationships based upon they deal that the simplest explanation of a dataset is the one most likely to be true. parsimonios trees minimize the number of a character changes to explain the data set. based upon ockham's razor
Polyphyletic
a taxonomic group from 2 or more ancestral sources
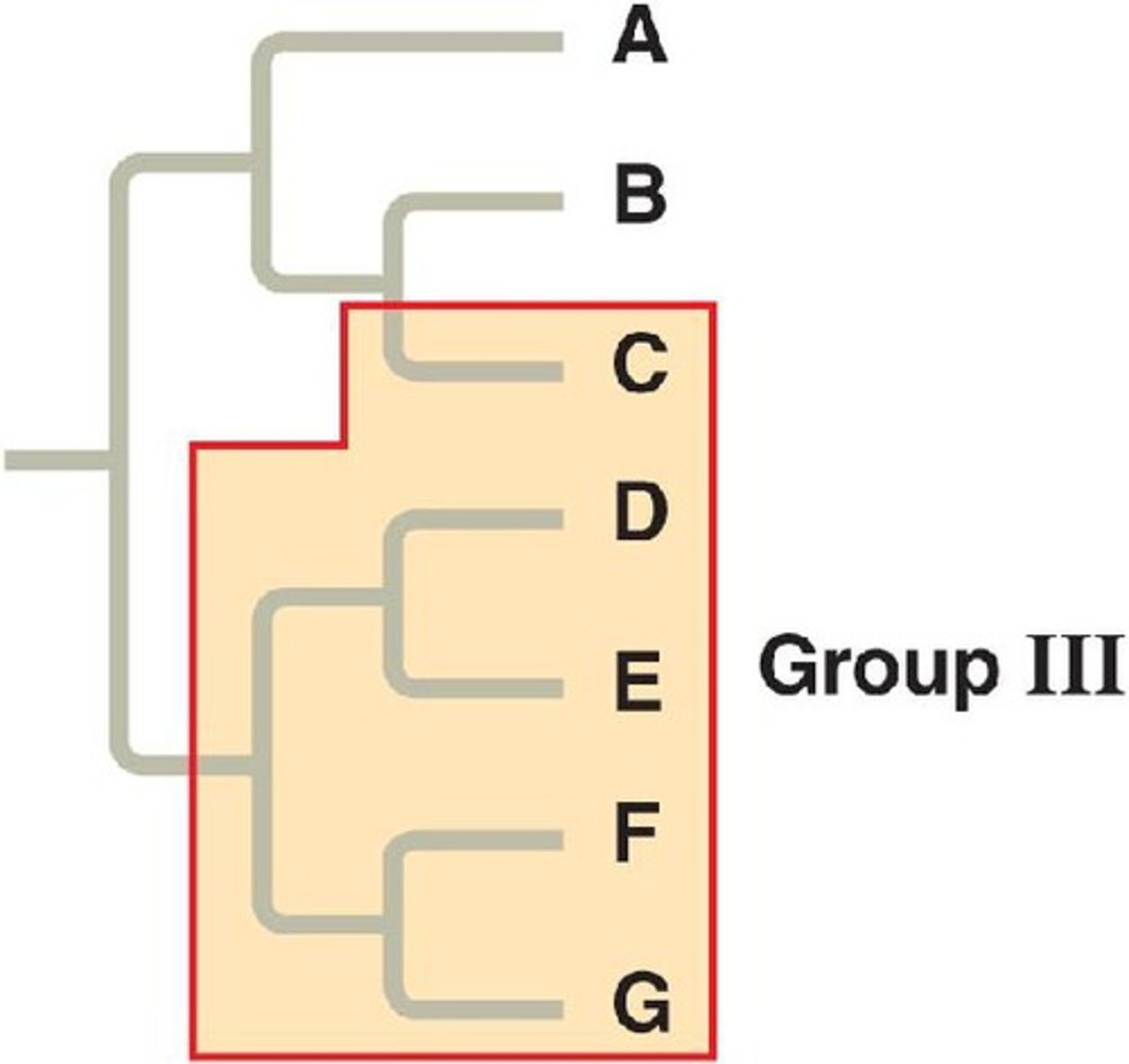
Symplesiomorphy
A shared, ancestral character state
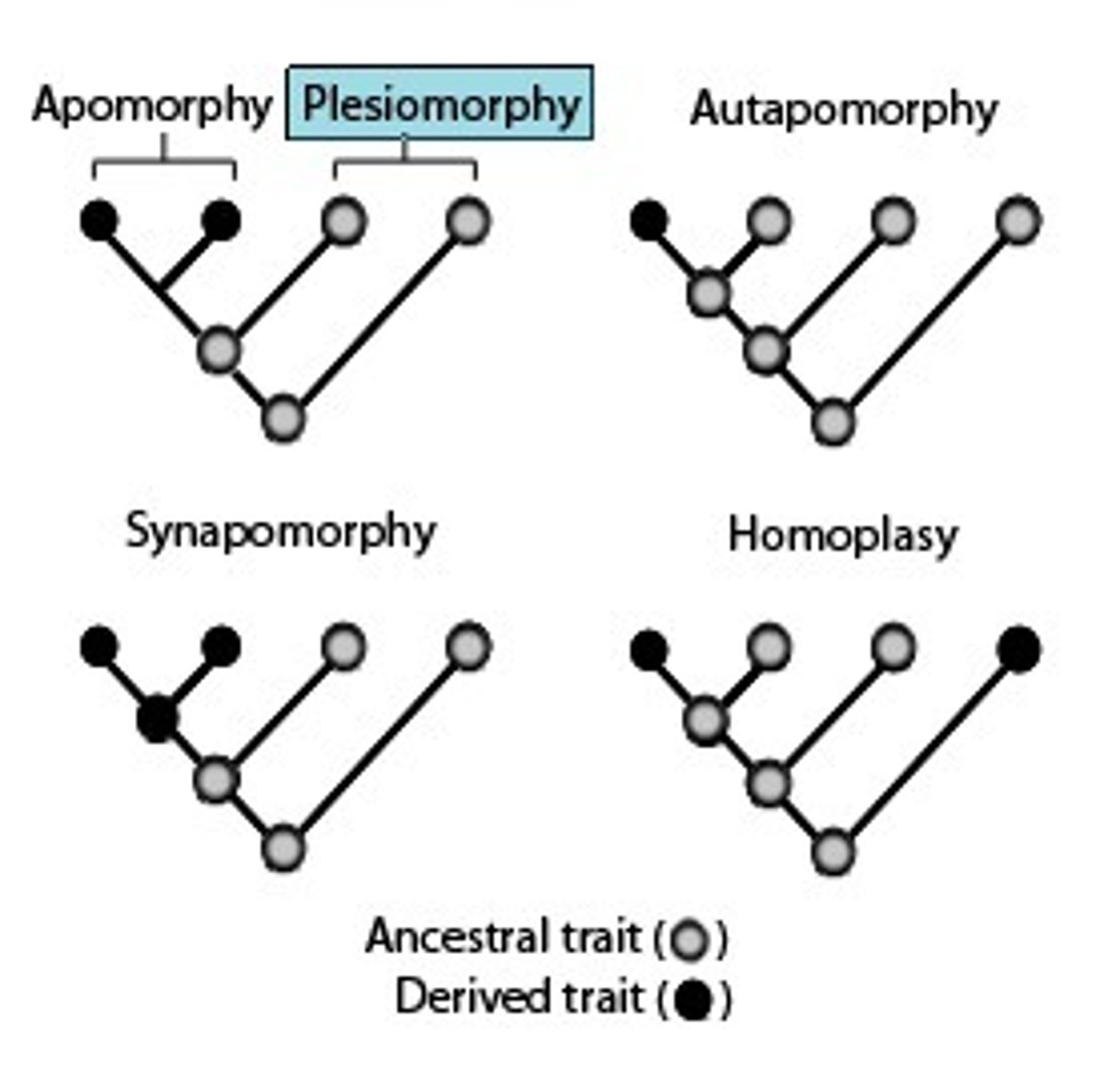
Synapomorphy
a unique shared, derived character state
Taxon
a named group of organisms
plural = taxa
How can you tell the difference between an asexual sporangium and a zygosporangium ?
Zygospargia are DIPLOID and formed by conjugation off and mycelium while Asexual sporangium are HAPLOID and form a zygus paradigm with a long sporangiosphore.
ZYGOSPARGIA
THEY ARE DIPLOID
ASEXUAL SPORANGIUM
THEY ARE HAPLOID
A. PHYLUM ZYGOMYCOTA
What is the ploidy of nuclei in the zygospore ?
Nuclei in the zygospore are Zn
Are the spores produced by the sporangia on the sporangiophore mitospores or meiospores ?
Mitospores
Which type of sporangium produces spores that are genetically different from each other ? the one that germinates out of a zygospore or the asexual sporangia ?
The one that germinates out of a zygospore
B. PHYLUM ASCOMYCOTA
How many ascospores are present in each ascus ?
8 ascospores are present in each ascus
What events take place in the ascus ?
karygogamy ,meiosis and mitosis
Are the hyphae of sordaria septet or non-septate ?
Septate
Are the mature ascospores haploid, dikaryotic or diploid ?
Mature ascospores are haploid
How do apothecia differ from perithecia ?
Apothecia are cup-shaped and the hymenium is COMPLETELY EXPOSED , while perithecia have a hymenium that is MOSTLY ENCLOSED.
What is the ploidy or plodies of the cells within the ascocarp ?
The ploidy of the most cells within the ascocarp is dikaryotic
C. CONIDIAL FUNGI
What type of cell division produces conidia ?
Mitosis
What is the ploidy of conidia ?
Haploid
Can you see differences in the shape and organization of conidiophores in penicillium vs aspergillus ?
In penicillin both the hypa and conidiophore are septate aspergillum has just a septet hyphae
Are sexual reproductive structures present ?
No conidial fungi have lost the ability to sexually reproduce
What is the functional advantage of reproducing exclusively by asexual spores ?
Better survival of genetically favorable offspring
What might be a long term disadvantage or reproducing entirely asexually ?
Less adaptable to changes in the environment
( observe the variety of conidial fungi in the laboratory)
Would you say that conidial fungi contribute to breakdown of organic matter in compost piles?
YES
Ploidy
The number of sets of chromosomes
Diploid
two sets of chromosomes (2n)
Haploid
one set of chromosomes (n)
Homologous Chromosomes
Contain the same genes but not identical
Meiosis
two sets of divisions
- 1 (2n) parent cell that divides 4 (n) daughter cells that divides 4n daughter cells
Meiosis 1
homologous chromosomes separate