Nutrient Cycling & Climate Change
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Nutrient cycles
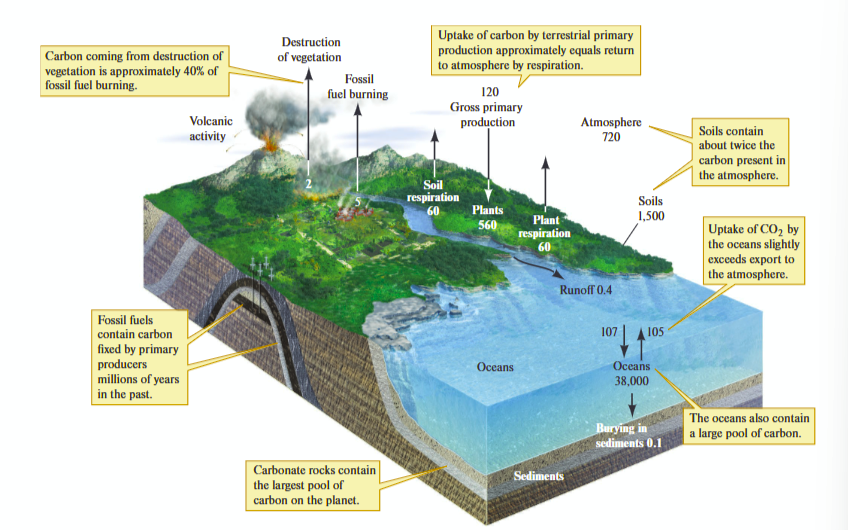
involve the storage (pools or reservoirs) and movement (flux) of nutrients in an ecosystem
carbon cycle
is the process by which carbon is exchanged among the atmosphere, land, and oceans, involving photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, and fossil fuel combustion.
key points - carbon cycle
moves between organisms and atmosphere
photosynthesis removes CO2 from atmosphere
Respiration by primary producers, consumers, decomposers, returns carbon to atmosphere
Some carbon cycles rapidly between organisms and atmosphere like
photosynthesis by plants, respiration by animals and decomposition by microbes.
Some carbon cycles are unavailable for long periods of time
carbonate rocks, carbon in soil, fossil fuel
In aquatic ecosystems,
CO2 first dissolves in water before being used by aquatic producers. Once dissolved CO2 enters chemical equilibrium with bicarbonate and carbonate. Carbonate may precipitate out of solution as calcium carbonate may be buried in ocean sediments.
greenhouse effect
caused by radiatively active gases (RAGs) “greenhouse gases”
what are the greenhouse gases
water vapor
carbon dioxide
methane
ozone
nitrous oxide
chlorofluorocarbons
what is the greenhouse effect
gases that absorb infrared radiation emitted by a solar-heated earth and reemit that energy back to earth, trapping heat and raising earth’s temperature
The most abundant radiatively active gas in the atmosphere is
water vapor (60%-80% warming)
If water vapor is the most important greenhouse gas, why are scientists so much more concerned about CO2 and CH4?
There’s a limit to how much water can be held in the atmosphere before it precipitates. That’s not true of CO2 and CH4.
Humans have much more control over emissions of CO2 and CH4 than they do over the amount of water vapor.
After water vapor, what are the next most important RAGs
CO2 and CH4
What other factors beside the greenhouse effect also influence climate?
variation in solar activity
changes in earth’s orbit and rotation
volcanic activity
ocean currents and other natural factors
Other factors affecting climate change
axial wobble and variation of tilt - earth’s axis is not stable causing wobbling and tilt change over time. This alters amount of sunlight received by different parts of earth (occurs over 100,000 years)
climate
The long-term average of weather patterns in a specific area, including temperature, humidity, and precipitation.
weather
The day-to-day state of the atmosphere in a specific area, including temperature, humidity, precipitation, and wind.
Current climate models suggest
global warming is being produced by natural and anthropogenic processes, but humans are having a larger effect than natural processes.
How have humans altered carbon cycles?
Destroying vegetation = carbon released is then 40% fossil fuel burning
Approximately 15,000 years ago, much of the earth (including the area that is now Massachusetts) was covered by glaciers. The difference in global mean temperature between that “ice age” and today was:
approximately 5°C
How have humans altered the global carbon cycle?
Increasing the rate at which carbon enters the atmosphere
Assuming greenhouse gas emissions continue at current rates, the climate in MA at the end of this century is expected to be most similar to the current climate of:
South Carolina - hotter summers
Ocean acidification is a potentially serious problem because:
It will make it difficult for many marine organisms to produce their exoskeletons.
agricultural Implications
can adjust to climate change by moving crops around and adaptive management
though some areas can become non-productive from insufficient soil moisture
While increased CO2 increases photosynthetic rates and growth of plants
it also increases the ratio of carbohydrates to other nutrients reducing food nutrition
gulf stream
a warm and swift Atlantic Ocean current that follows the eastern coastline of the US and Canada before crossing the Atlantic Ocean towards Europe. It ensures that the climate of Western Europe is much warmer than it would otherwise be.
Climate change can disrupt gulf stream and result in
Warmer waters: Rising temperatures make ocean waters warmer and lighter.
Freshwater influx: Melting ice sheets and glaciers add freshwater to the North Atlantic, making the water less salty and less dense.
Reduced circulation: If the water isn't heavy enough to sink, the circulation stops
decrease in dissolved oxygen in oceans
significant impacts on marine life and ecosystems,
hurt fish population and disrupt food web
Things to reduce the net emissions of RAGs
Decrease the use of fossil fuels:
- reduce the overall use of energy by reduction & conservation
- displace fossil fuels with other sources of energy, preferably renewable ones
Stop or decrease the conversion of high-C ecosystems into low-C ones:
conserve existing forest and grassland; these ecosystems store more C than agricultural or urban systems
afforestation - increase carbon storage in ecosystems
What if nothing is done to stop emission of RAGs
eventually fossil fuels will run out = carbon emissions will decrease
excess carbon will be absorbed by the oceans, leading to increased ocean acidification
ocean acidification effects (pg 508)
skeletal damage
food web disruption
ecosystem changes
harmful algal blooms