Genetics - Molecular Structure of Chromosomes (Chapter 10)
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Define genome.
The totality of all genetic material in a given organism.
Eukaryotic genome
1. Linear chromosomes
2. higher organisms with membrane-bound organelles
3. Linear chromosomes found in the nucleus
4. Chromosomes packaged into chromatin
prokarytoic genome
1. Circular chromosomes
2. Found in bacteria
3. Chromosomes found in the nucleoid
4. Packaged through supercoiling
What's similar about eukaryotic genome and prokaryotic genome?
You can find circular genomes in eukaryotes in mitochondria and chloroplasts.
What are four important processes chromosomes facilitate?
1. synthesis of RNA and cellular proteins
2. replication of chromosomes
3. proper segregation of chromosomes
4. compaction of chromosomes to fit in living cells
What are intergenic regions?
nontranscribed DNA between adjacent genes
What is the function of the origin of replication?
An initiation site for assembling proteins to begin the process of DNA replication.
How many origin of replications do bacteria chromosomes have?
one
how many origin of replication do eukaryotes have
multiple
What are the two steps of chromosomes condensation for bacteria?
1. microdomains
2. macrodomains
Microdomains
Loops of bacterial chromosomal DNA, tythat emanate from a central core
Macrodomains
Large contiguous regions on chromosomes that appear to act as independent units. Organize and further condense.
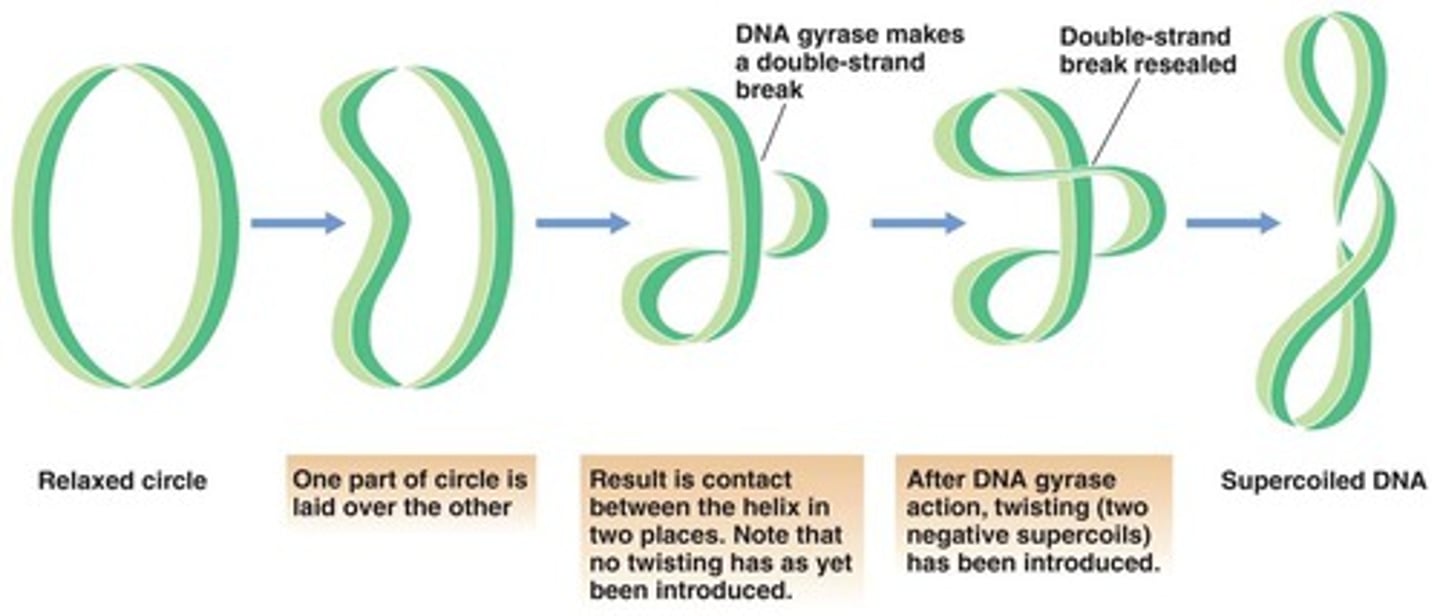
What is supercoiling?
Formation of additional coils within DNA due to twisting forces from already coiled DNA. Allows for strand separation.
What are nucleoid-associated proteins?
A set of DNA-binding proteins that form microdomains and marcodomains.
How does supercoiling promote strand separation? Why is that beneficial?
It increases the compaction of the chromosome. It allows for strand separation, which is important for replication and transcription to access the DNA sequence.
DNA gyrase (topoisomerase II)
introduces negative supercoils; underwinding; relax positive supercoils
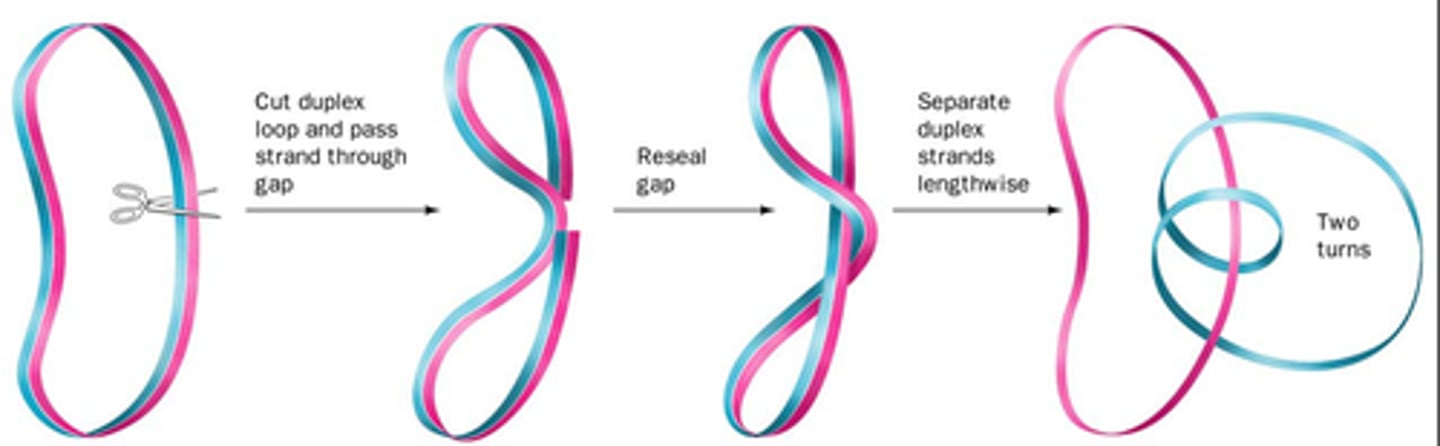
Topoisomerase I
relaxes negative supercoils; overwinding
Do eukaryotes or prokaryotes have more spaces in between genes?
Eukaryotes
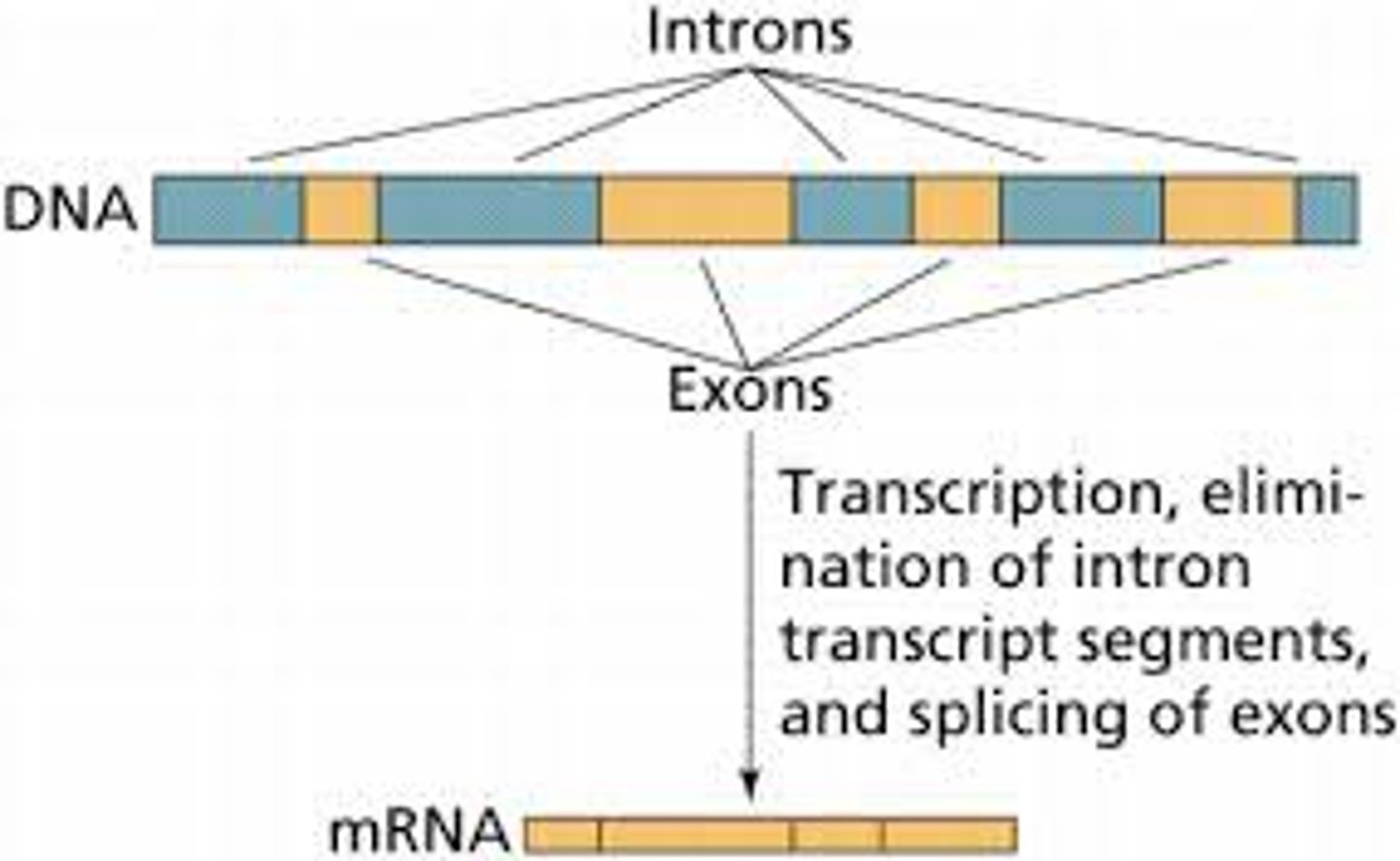
introns
Noncoding segments of nucleic acid that lie between coding sequences.
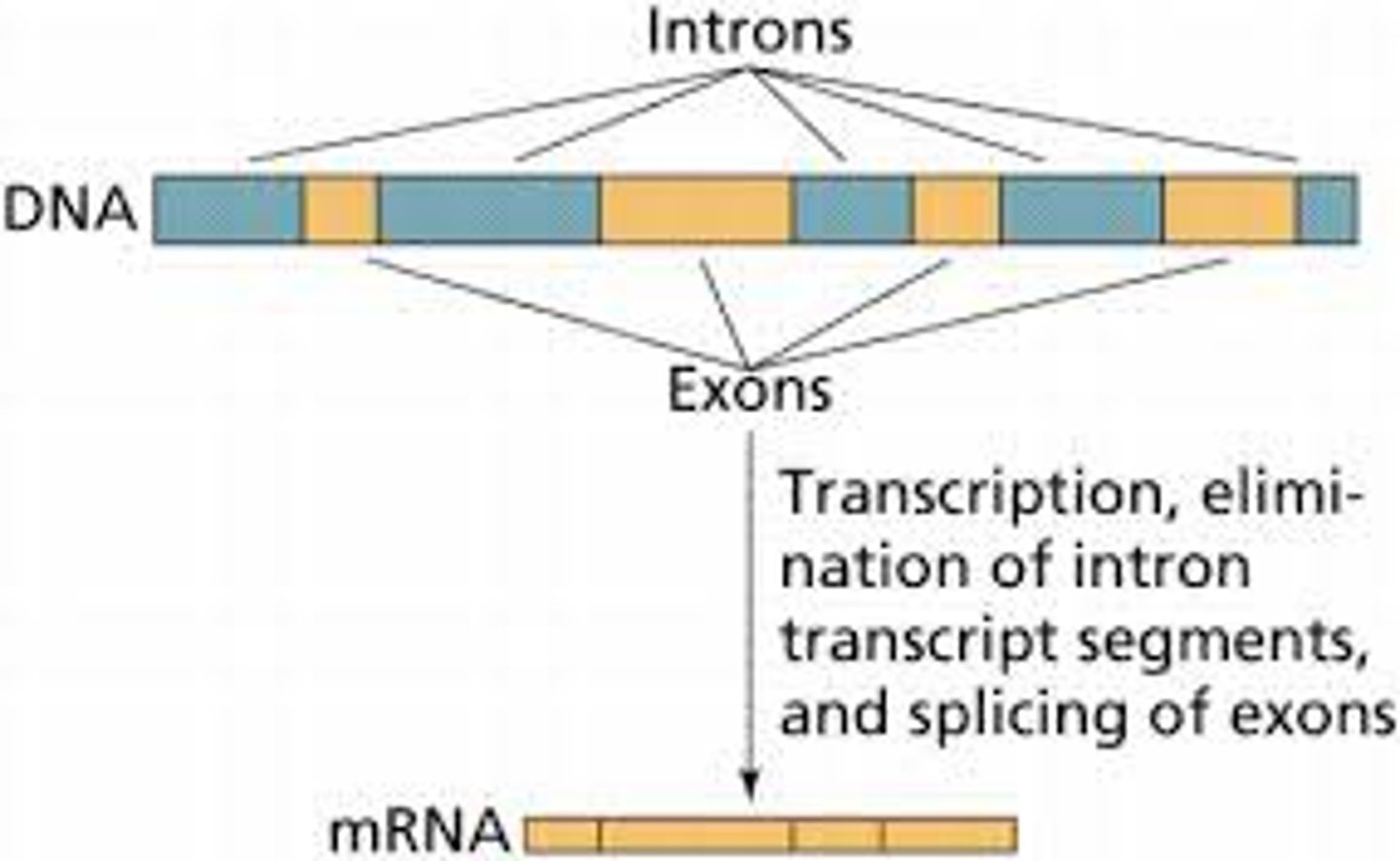
exons
Coding segments of eukaryotic DNA.
Are exons and introns found in eukaryotes or prokaryotes?
Eukaryotes
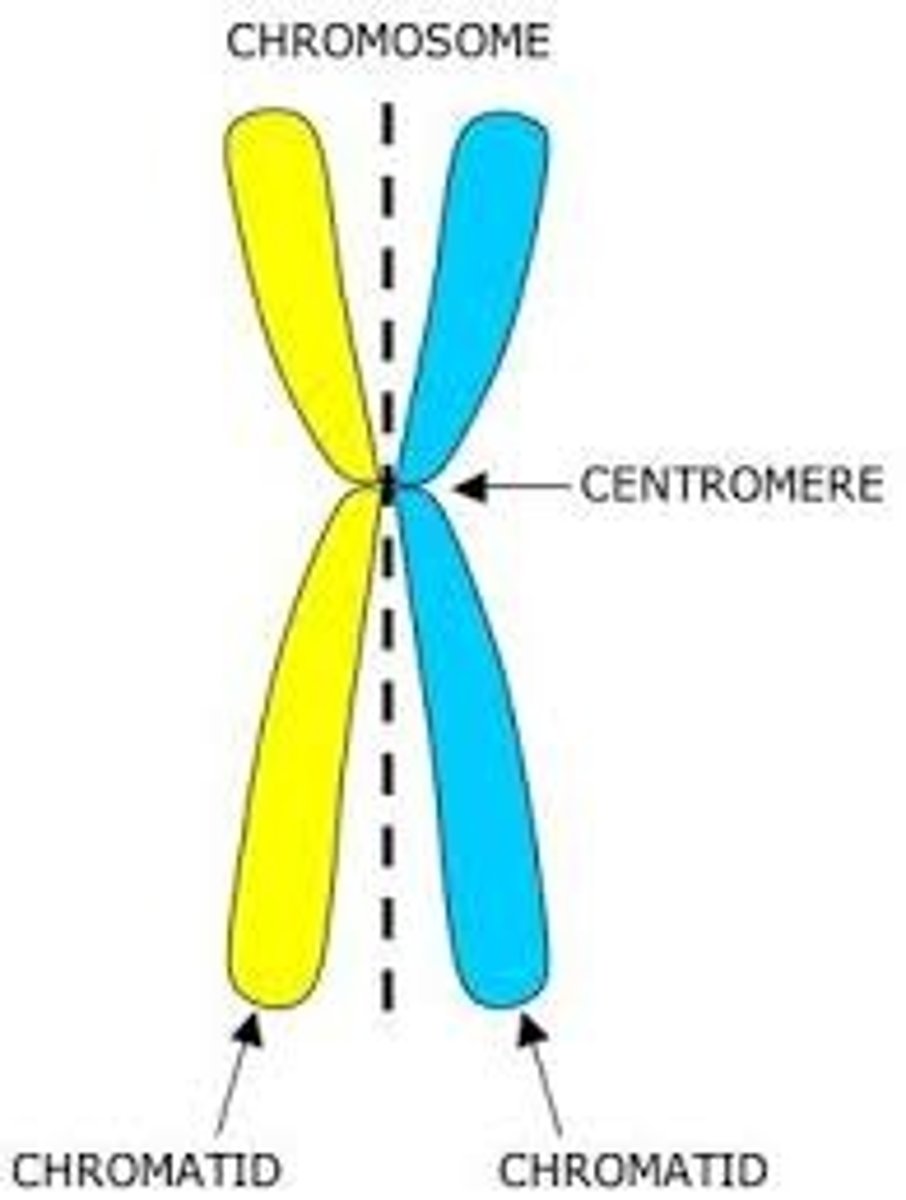
Centromeres
areas that play a role in the proper segregation of chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis. One per chromosome. Eukaryotic structure.
Telomeres
Found at the end of chromosomes. Functions in replication and stability. Eukaryotic structure.
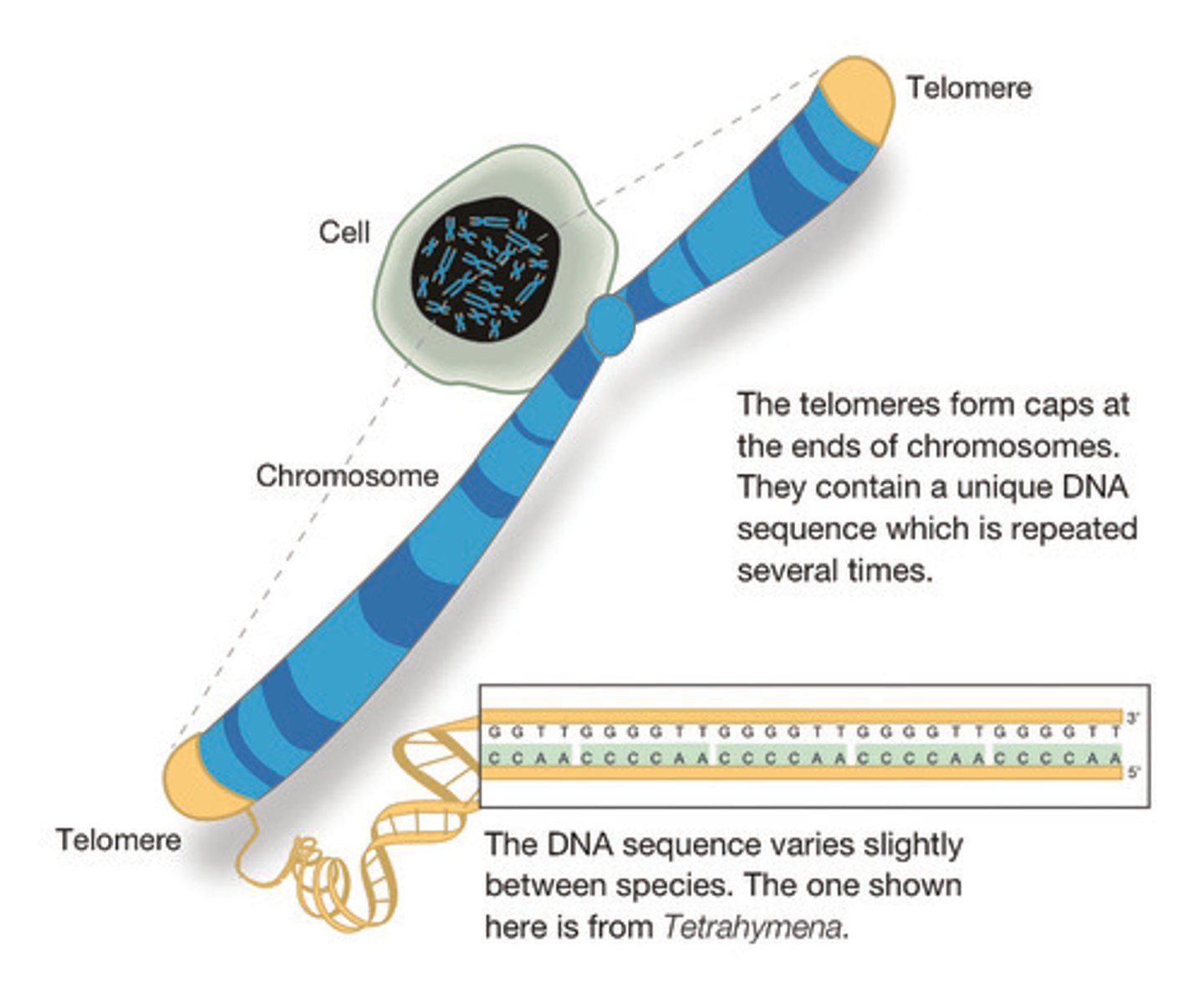
True or false. Scientists do not understand the exact purpose of repetitive DNA.
True
Unique sequences
sequences found once or a few times within a genome
moderately repetitive sequences
found a few hundred to several thousand times in the genome
highly repetitive sequences:
sequences that are found tens of thousands or even millions of times throughout the genome
Tandem array
a short nucleotide sequence that is repeated many times in a row
chromatin
Substance found in eukaryotic chromosomes that consists of DNA tightly coiled around histones
what makes up a nucleosome?
histone octet w/ DNA wrapped 1.65 times around it
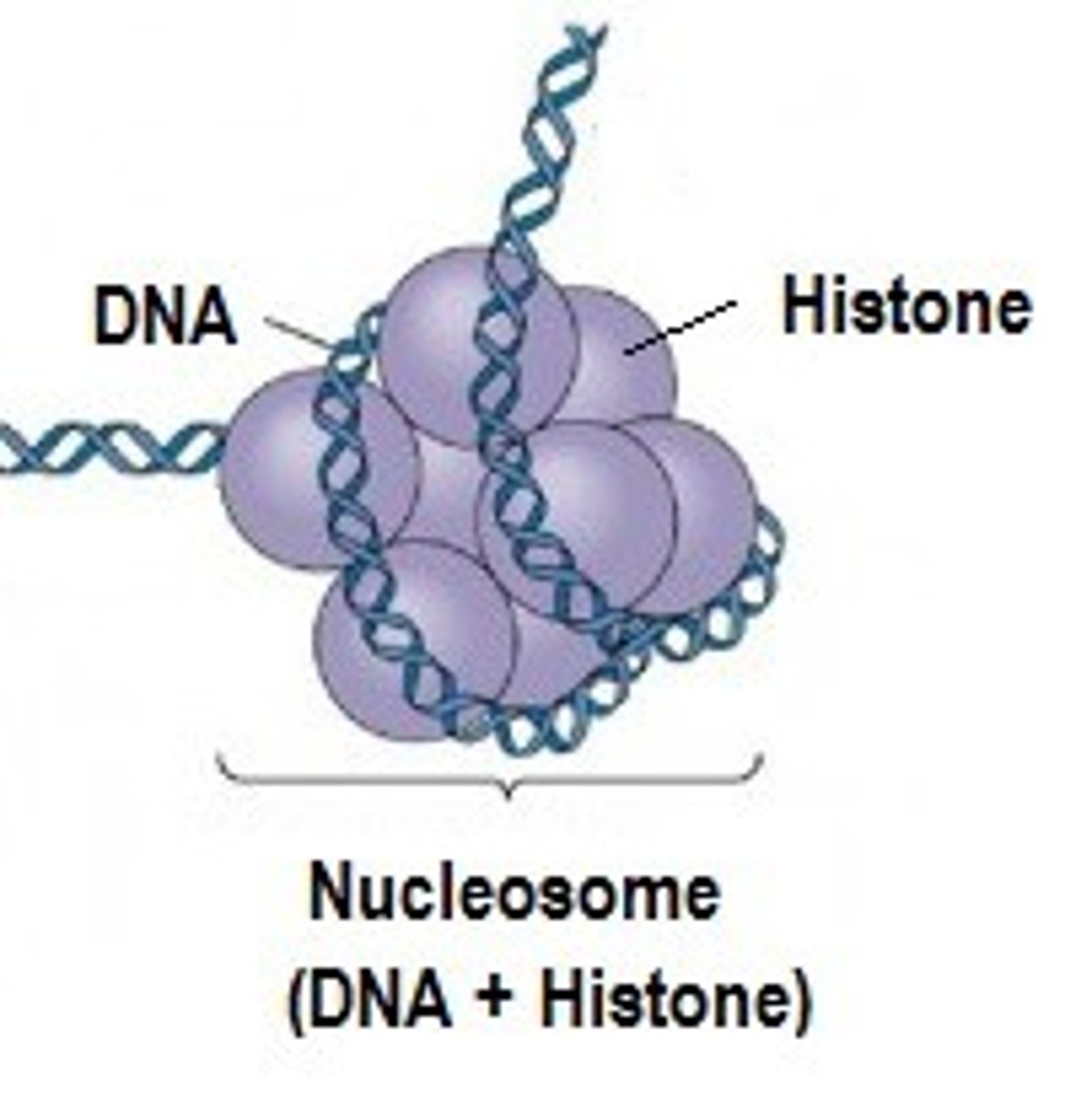
what proteins are found in a nucleosome?
histones
What are the components of a single nucleosome?
A. About 147 bp of DNA and four core histone proteins
B. About 147 bp of DNA and eight core histone proteins
C. About 200 bp of DNA and four core histone proteins
D. About 200 bp of DNA and eight core histone proteins
B. About 147 bp of DNA and eight core histone proteins
Why are the bands in Noll's agarose gel so large?
There are bands in 400 and 600 because incomplete digestion of DNA is why we get larger sizes of DNA
Extra base pairs are the linker regions themselves
Why is it important that histone proteins contain a lot of arginines and lysines?
They form electrostatic and hydrogen-bonding interactions with the phosphate groups alone the DNA backbone.
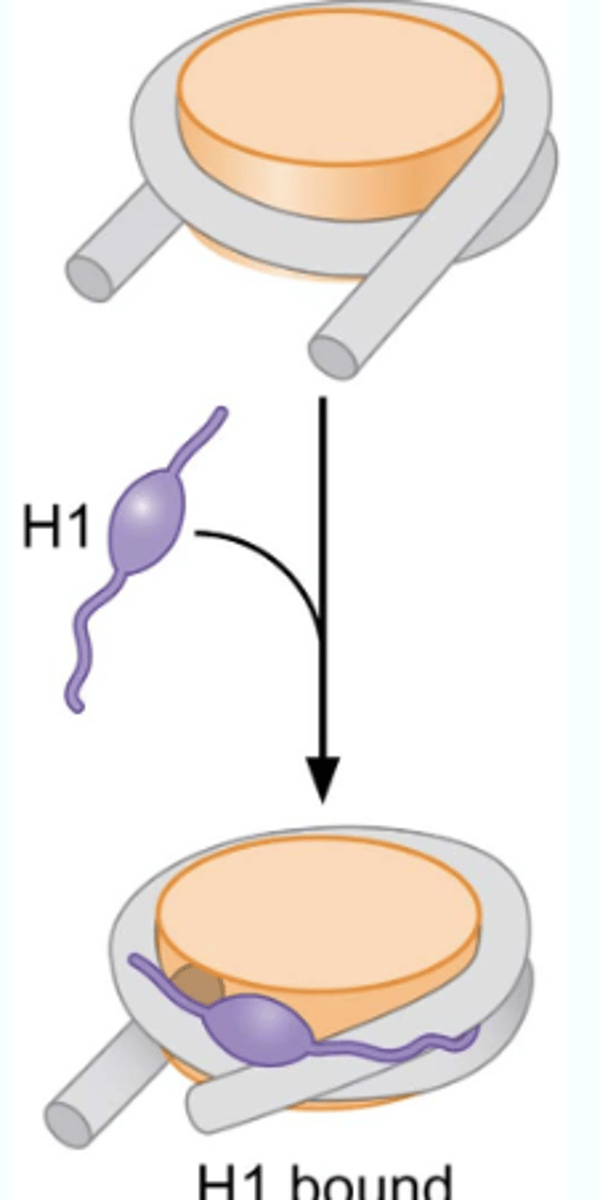
H1 histone
By binding to DNA in the linker region between nucleosomes, it helps organize adjacent nucleosomes.
DNase
a protein that cuts a part naked DNA;DNA backbone
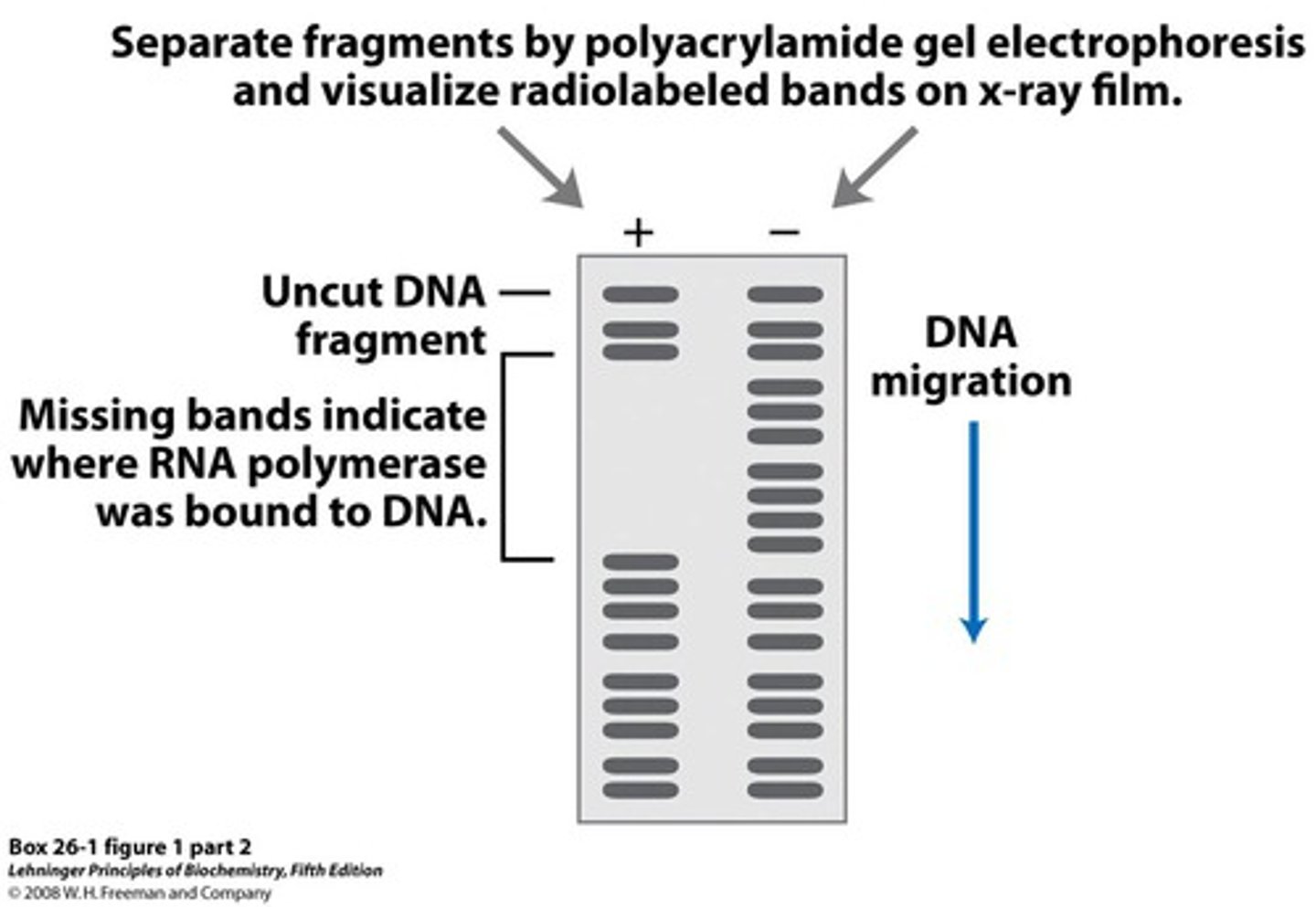
Noll's experiment
determine the size of the DNA complex
Noll tested Kornberg's model of nucleosomes
digested chromatin with the enzyme DNase I, which cuts the DNA backbone → accurately measured the molecular mass of the resulting DNA fragments by gel electrophoresis
hypothesis for Noll's experiment
hypothesis for Noll's experiment
results of Noll's experiment
Low concentration of DNase I- some linker regions remained uncut, produced fragments unequal in lengthHigher concentrations of DNase I- mostly cut DNA into fragments of 200bp, consistent with the beads on a string model
What evidence proves histone H1 helps package the nucleosomes more compactly?
Without H1, the nucleosomes are classic beads-on-a-string, but with H1, it its more compacted together.
Mechanisms that compact eukaryotic DNA:
1. wrapping DNA within nucleosomes
2. arrangement of nucleosomes to form a 30-nm fiber
3. formation of loops
loop domains
a segment of chromatin that is organized into a loop; the 30-nm fiber folded into loops
CTCF
binds to 3 regularly spaced repeats; promoting the formation of a loop domain
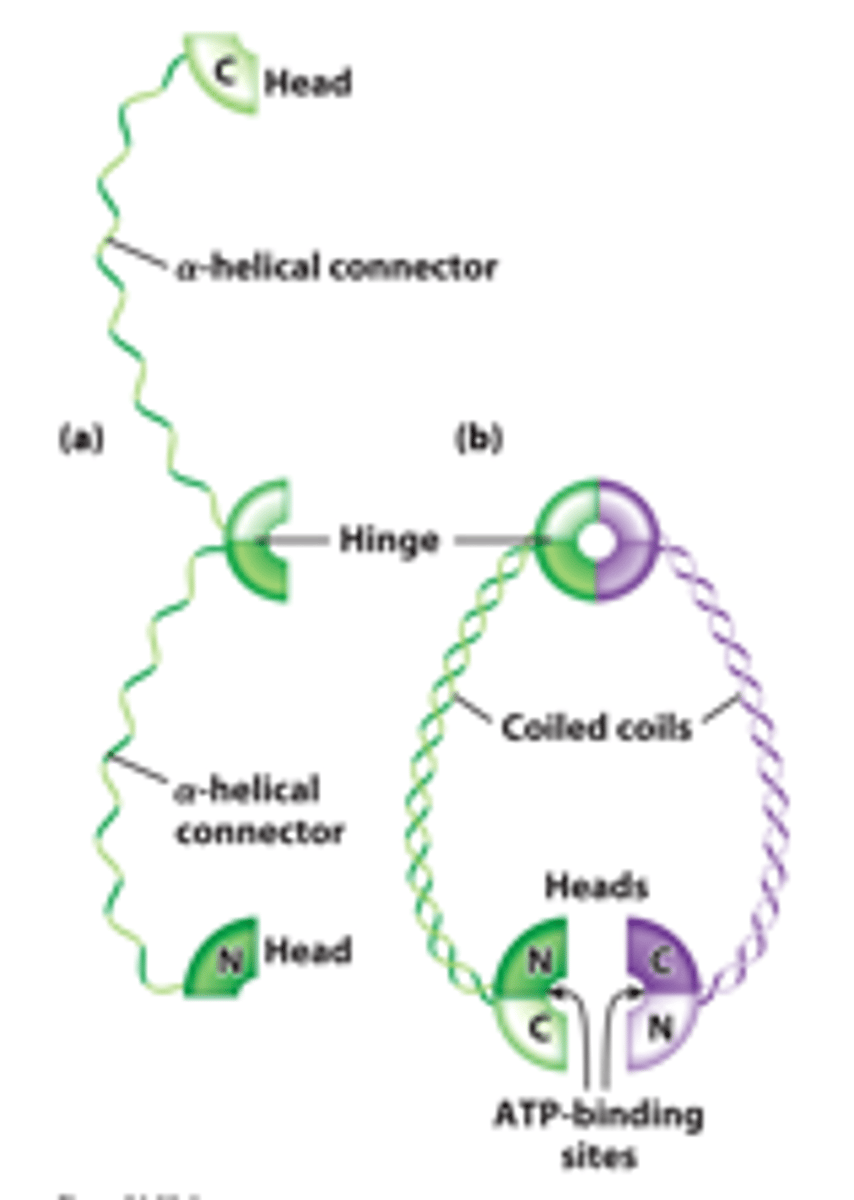
SMC
forms a dimer that can wrap itself around two segments of DNA to create a loop.
True or false. chromosomes are distributed randomly around the nucleus.
False.
heterochromatin
Eukaryotic chromatin that remains highly compacted during interphase and is generally not transcribed.
euchromatin
The less condensed form of eukaryotic chromatin that is available for transcription.
when are chromosomes most highly condensed?
metaphase
condensin
proteins that cause greater compaction of the loop domains starting at M phase
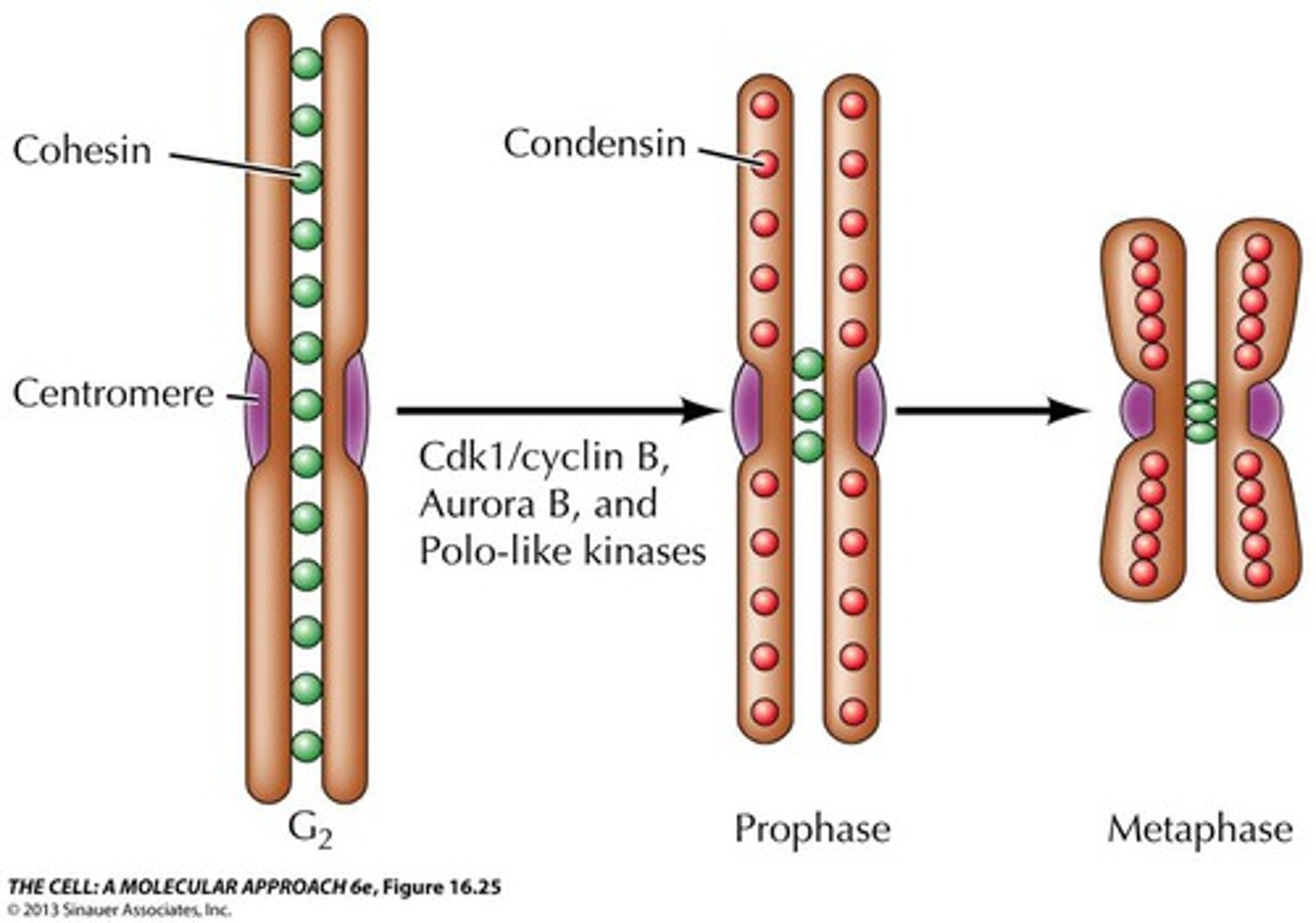
cohesion
protein that sticks the sister chromatids together starting at the end of S phase
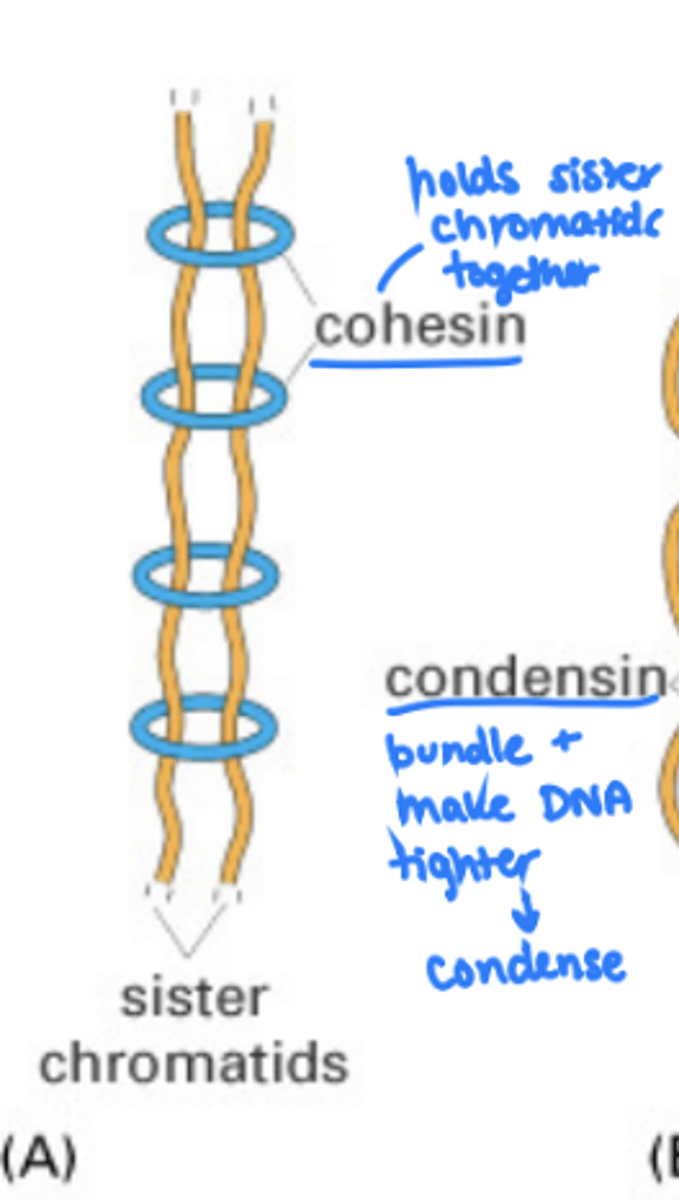
Condensin I can only bind to chromatin after the nuclear envelope breaks apart. What part of the cell cycle does it play a role in?
Metaphase