Abdomen Pancreas
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
The pancreas initially arises from the _______________ as two buds on either side of the developing duodenum
endoderm
The ventral bud forms:
Pancreatic head
Uncinate Process
Main Pancreatic Duct
The Dorsal bud forms:
Portion of the head
Neck
Body
Tail
Portion of main pancreatic duct
Accessory pancreatic duct
True or false: the pancreas is a retroperitoneal organ
True; however a small portion of the tail lies within the peritoneal cavity
True or false: the pancreas doesn’t have a capsule
True
The pancreas is ___(1)______ to the stomach and it located between the _(2)__ loop of the ___(3)______ and the ____(4)______ hilum
1) posterior
2) C
3) Duodenum
4) Splenic
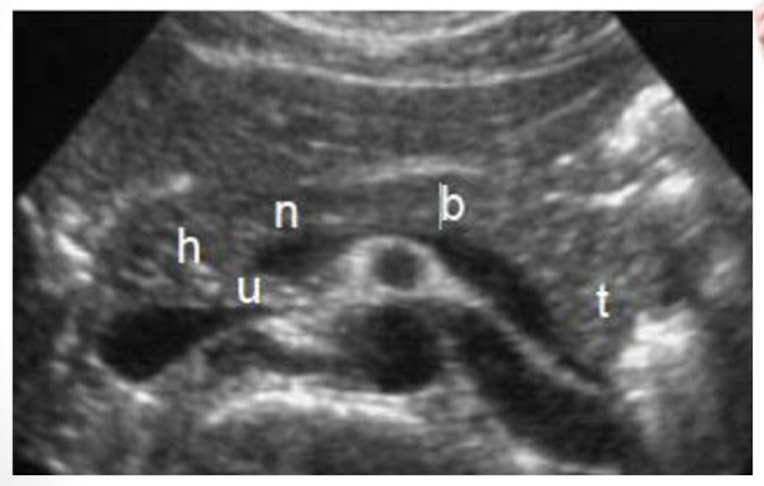
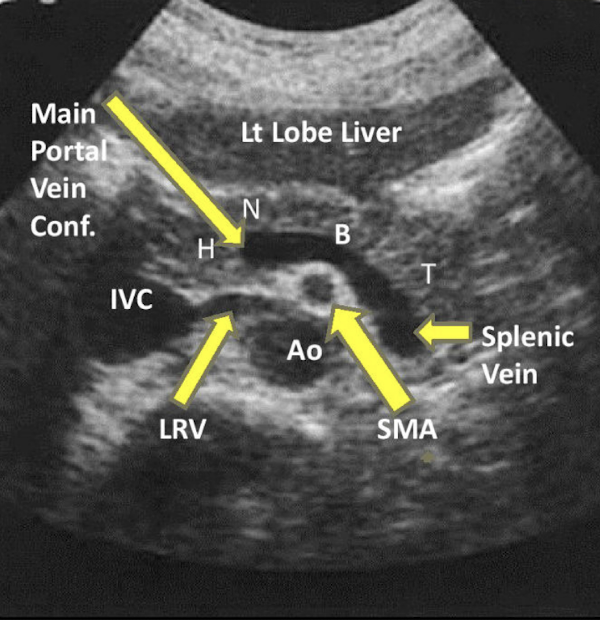
Be able to identify this image taken in a transverse plane
The pancreas sits horizontally in the abdominal cavity so in order to get a long axis image the sonographer must scan in the __________ plane
Transverse
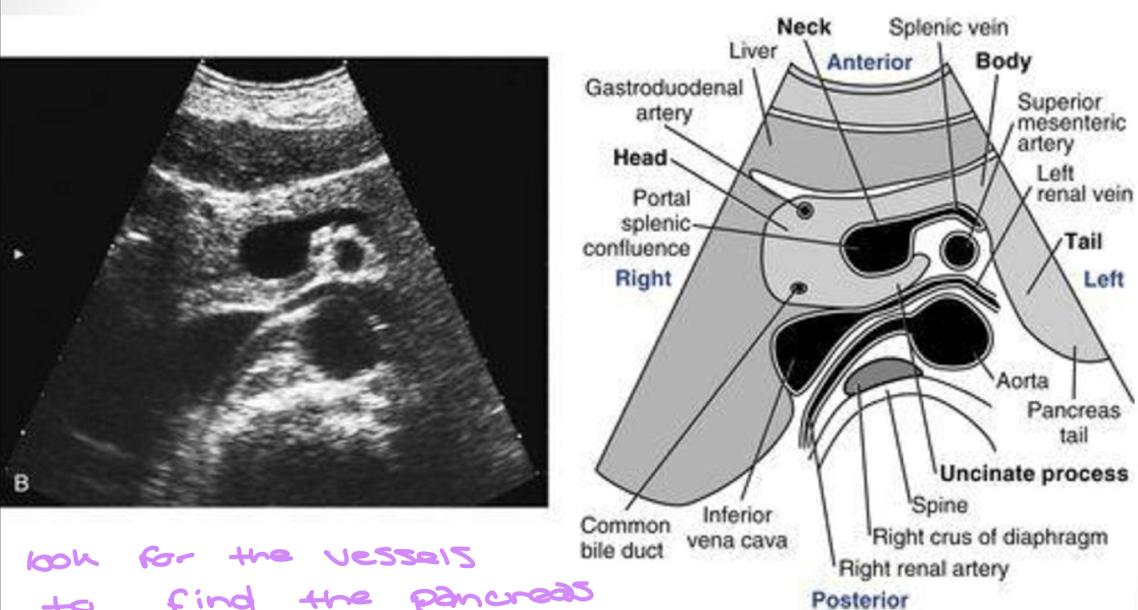
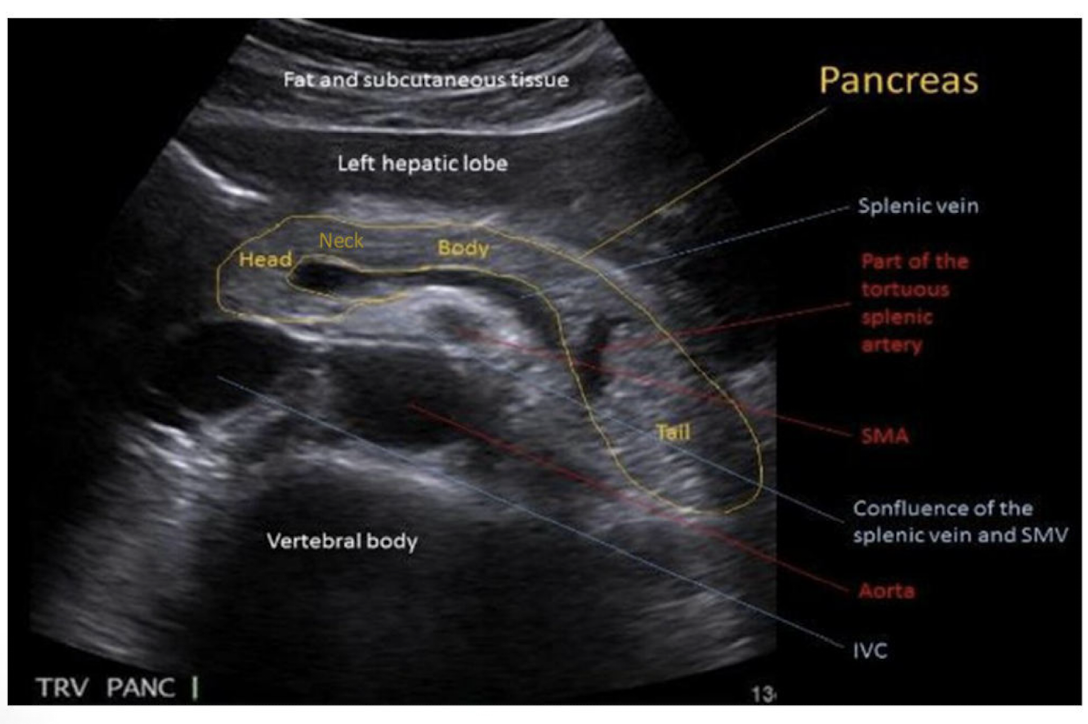
Look over this image
We look for the vessels to find the pancreas
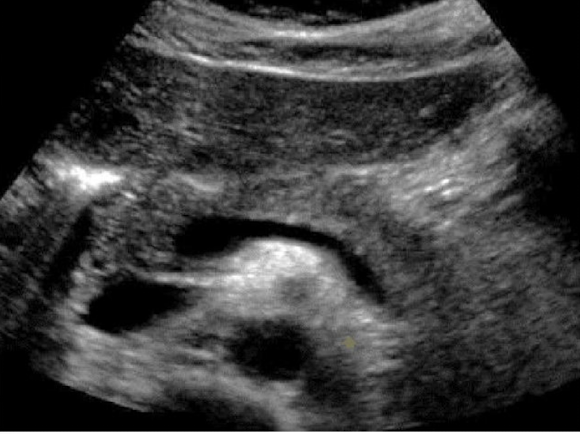
label this image
What are the five sections of the pancreas?
1) Uncinate Process
2) Head
3) Neck
4) Body
5) Tail
What is the uncinate process?
The section of the head of the pancreas that hooks towards the posterior aspect of the abdomen
It may or may not wrap around the SMA and SMV all variations are normal
This portion of the pancreas sits within the C loop of the duodenum
Pancreatic head
What occurs posterior to the neck of the pancreas?
The main portal vein confluence
This portion of the pancreas lies posterior to the stomach
Body
label
What are the measurements of the pancreatic Head?
2 - 3.5 cm AP
What are the measurements of the pancreatic neck?
1.5 - 2.5 cm AP
What are the measurements of the pancreatic Body?
2 - 3 cm AP
What are the measurements of the pancreatic tail?
1 - 2 cm
True or false: The pancreas is both an endocrine and exocrine gland
true
What is the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands?
Endocrine glands are ductless and drain directly into bloodstream. Exocrine glands release product into a ductal system
Islets of Langerhans are clusters of cells that carry out the __________ functions of the pancreas
Endocrine
What are the 4 cells that make up the islets of Langerhans
Alpha
Beta
Delta
F (AKA: PP - pancreatic polypeptide
____(1)_________ cells produce glucagon which acts on the liver and stimulates the conversion of ____(2)_______ into ____(3)_______ which is then released into the blood stream ___(4)_____ blood glucose levels
1) Alpha cells
2) Glycogen
3) Glucose
4) raising
Which endocrine cell lowers blood sugar levels by producing and releasing stored insulin
Beta cells
Which endocrine cells produce the hormone somatostatin?
Delta Cells
Which hormone acts as an inhibition to other hormones so that if blood sugar levels drop this hormone will be released in increased amounts
Somatostatin
Which endocrine cells produce Pancreatic Polypeptide?
F cells
________________ which inhibits gallbladder contraction and the secretion pancreatic digestive juices
Pancreatic polypeptide
List the cells that make up the Islets of Langerhans and which hormone they are each associated with
Alpha cells - Glucagon
Beta Cells - Insulin
Delta cells - Somatostatin
PP or F cells - Pancreatic Polypeptide
Which function of the pancreas is an exocrine function?
It’s involvement in the digestive process
These cells in the pancreas are responsible for exocrine functions
Acinar cells
The enzymes released by the _________ cells are responsible for the breakdown and digestion of fat, carbs, protein and acids
acinar cells
Amylase, lipase, sodium bicarbonate, Trypsin, Chymotripsin, Carboxypeptidase, Nucleases are ______(1)___________ released by __(2)______
1) digestive enzymes
2) Acinar cells
Enzymes, along with pancreatic juices, drain into the ductal system of the pancreas. Microscopic ducts merge along the length of the pancreas, forming the _____________ AKA ______________
Main pancreatic duct AKA duct of wirsung
Most of the population also has an accessory duct AKA _____________
Duct of Santorini
________________ is the most common pancreatic anomaly
Pancreatic Divisum - failure of fusion of the ventral and dorsal pancreatic ducts
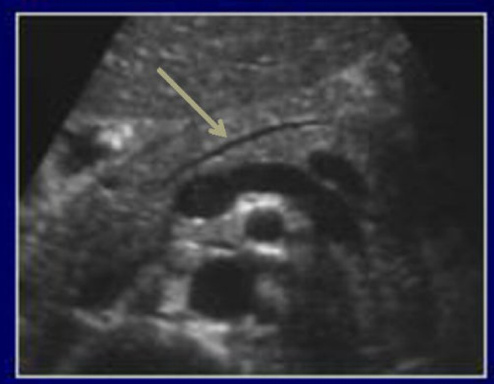
What is this image pointing to?
The pancreatic duct

This anomaly is more common in males and has been associated with complete or partial absence of the duodenum
Annular Pancreas
When pancreatic tissue is located in other organs. This anomaly is known as:
Ectopic Pancreatic Tissue
The pancreatic head recieves blood via the:
Gastroduodenal artery (GDA) & Superior Mesenteric Artery (SMA)
The ___________ further branches into anterior and Posterior Inferior Pancreaticduodenal artery
SMA
The ___________ further branches into anterior & posterior superior pancreaticduodenal artery
gastroduodenal artery (GDA)
The body and tail of the pancreas recieve blood from the:
Splenic artery
__________ has many branches supplying blood as it travels the length of the pancreas superiroly
Splenic artery
Blood is drained from the pancreas body and tail via the:
Splenic vein & eventually SMV
Pancreatic blood drainage is into the:
Portal venous system
pancreas laboratory values: If which two enzymes increase does it mean there is a problem within the pancreas?
Amylase & Lipase
What does Amalyse help digest? What does Lipase help digest?
Amylase = carbs
Lipase = fats
Techniques to implement to try to troubleshoot overlying bowel gas
have the patient push their belly out
Ask the patient to take a deep breath
Give the patient 3 - 4 small glasses of water assuming NPO is not needed
Turn patient to LLD position
True or false: The normal pancreas should visualize as homogenous with medium to bright echotexture
True
This duct may be visualized and noted if dilated. Typically measures 2mm or less
Main pancreatic duct
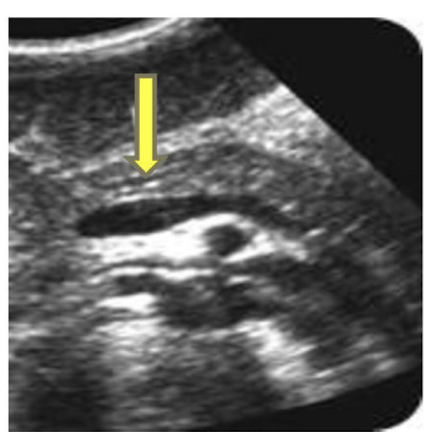
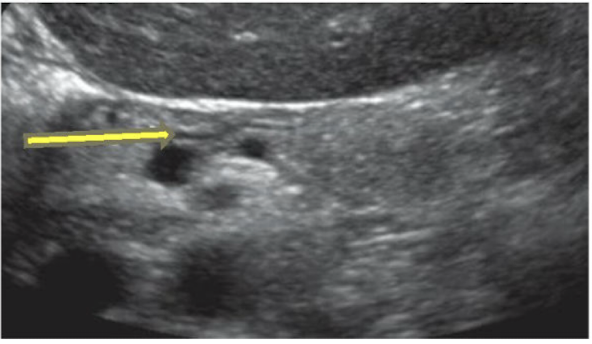
What is the yellow arrow pointing to?
Duct of Wirsung
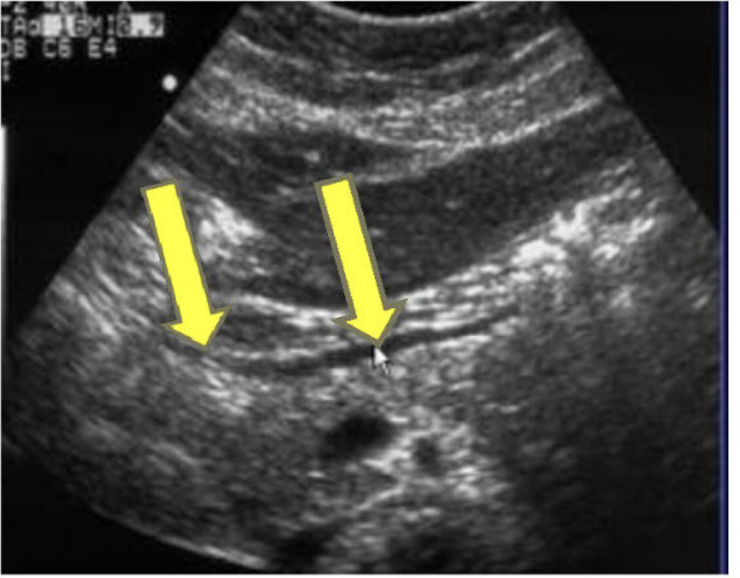
What are the yellow arrows pointing to?
Posterior wall of stomach (BE CAREFUL not to confuse with MPD)
In order to obtain a longitudinal image of the pancreas the probe is positioned in the ___________ scan plane at the level of the _____________
Transverse; xiphoid process
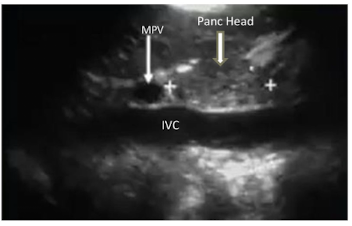
Which round anechoic structures can be visualized within the pancreatic head
Gastroduodenal artery (GDA) & Common Bile Duct (CBD)
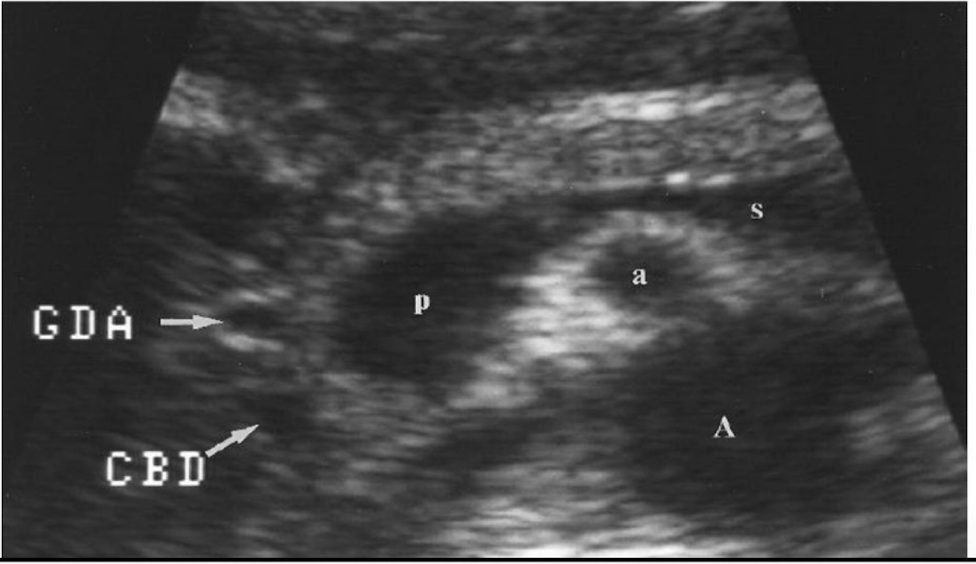
Usually within the pancreatic head the gastroduodenal artery is ___(1)________ and the common bile duct is _____(2)______. But, if you are unsure which is which what is an easy solution?
1) anterior
2) posterior
*Turn on color doppler if you are unsure which is which. GDA should appear red
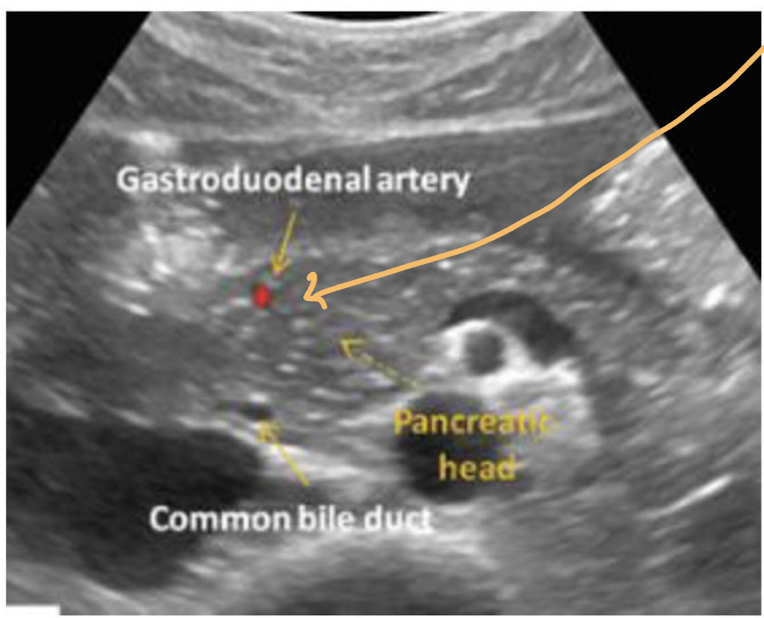
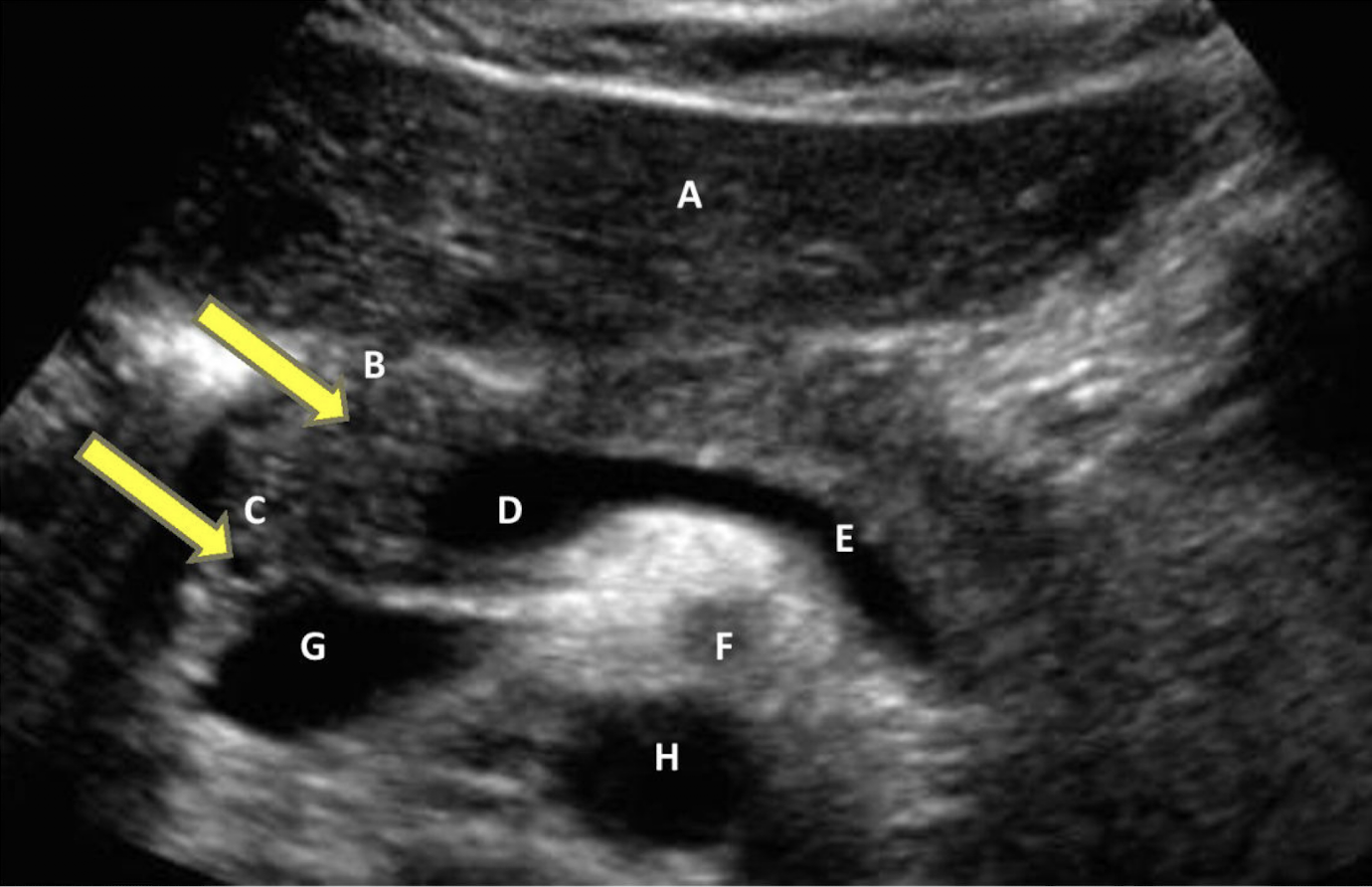
identify all structures
A) left liver lobe
B) gastroduodenal artery
C) common bile duct
D) Main portal confluence
E) Splenic vein
F) SMA
G) IVC
H) Aorta
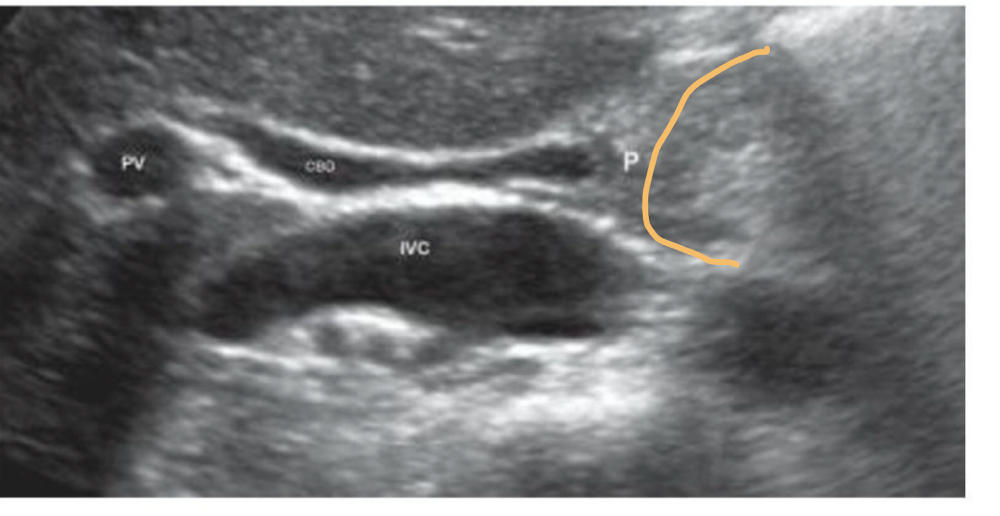
Which is shown in this image?
a longitudinal view of the CBD entering the pancreatic head. Pancreatic head outlined in orange
The pancreas should be evaluated in both the transverse and sagittal planes. How are sagittal sections of the pancreas evaluated?
by sweeping through the pancreas from right to left
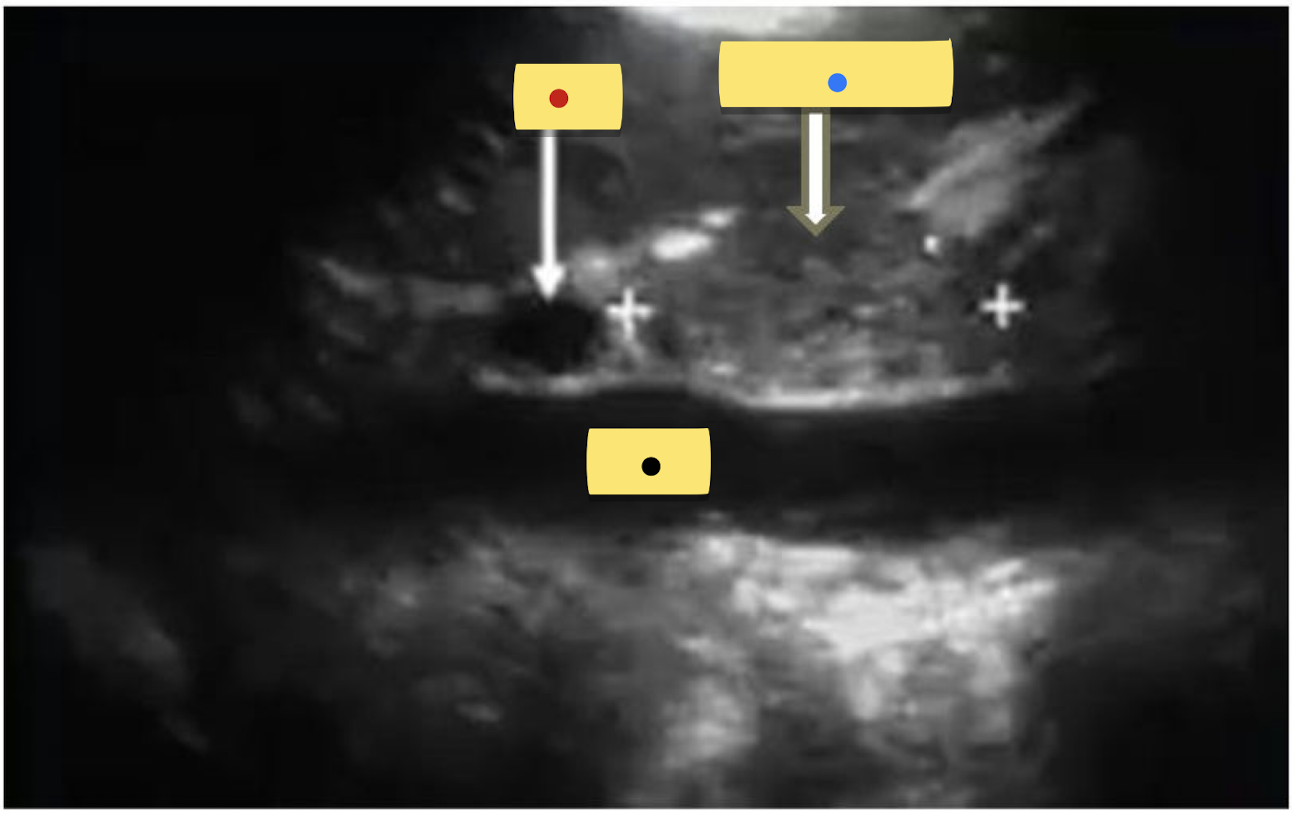
identify the sagittal image.
Red = ?
Blue = ?
Black = ?
Red = MPV
Blue = pancreatic Head
Black = IVC
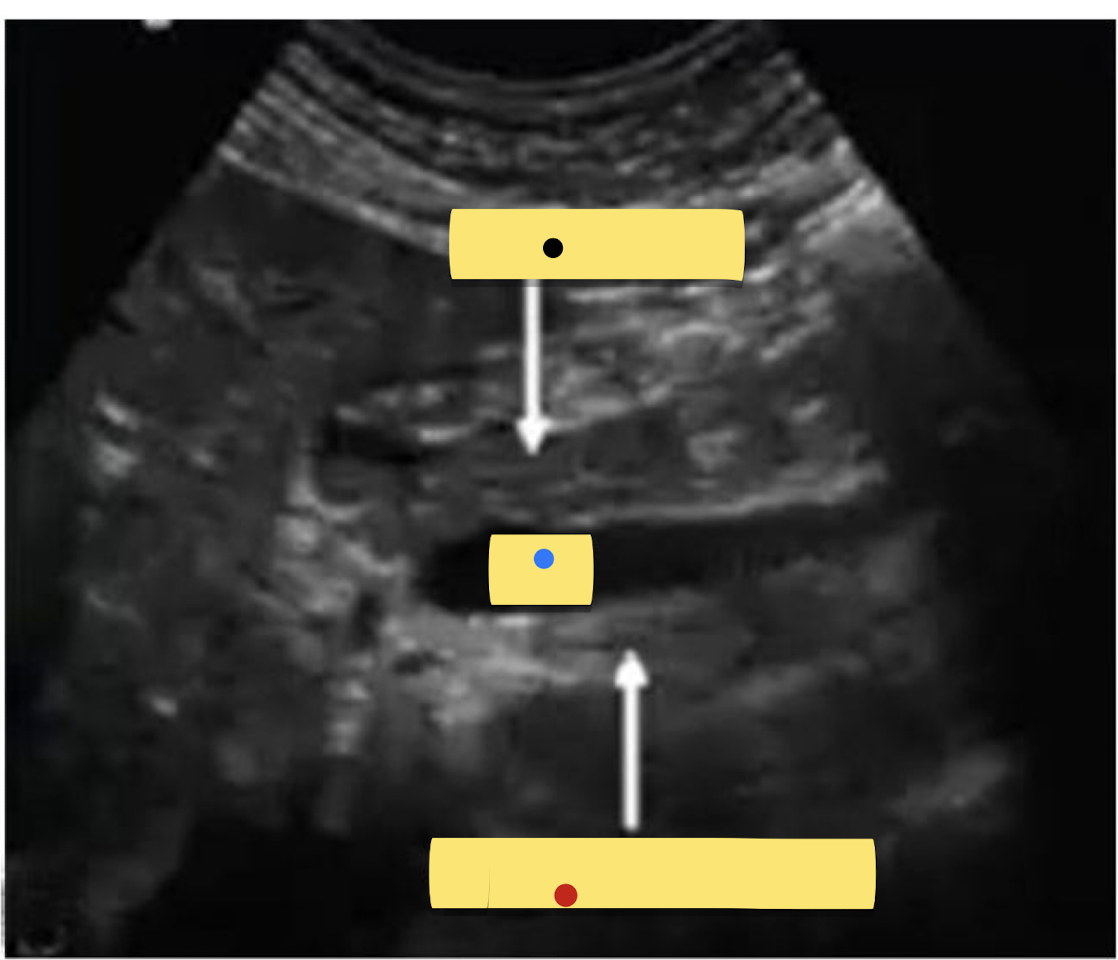
Label the Sagittal Image
Black = ?
Blue = ?
Red = ?
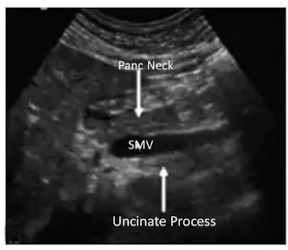
Black = Pancreatic Neck
Blue = SMV
Red = Uncinate Process

Label the sagittal image
Black = ?
Blue = ?
Red = ?
Yellow = ?
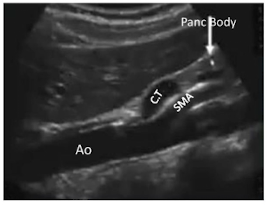
Black = Pancreatic body
Blue = SMA
Red = Celiac trunk
Yellow = Aorta
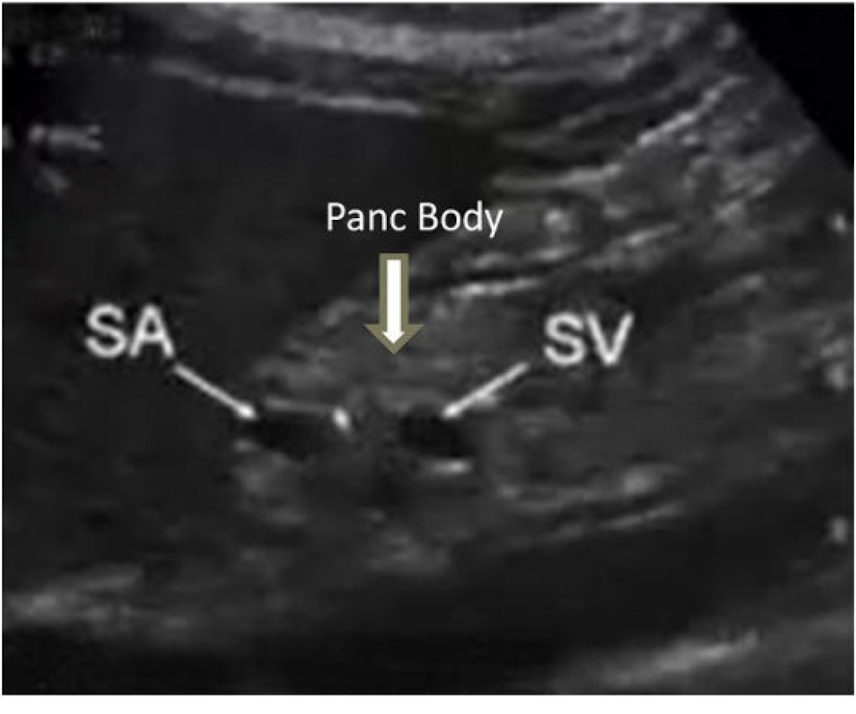
Where was this image taken from?
Shows sagittal pancreatic body more towards patients left
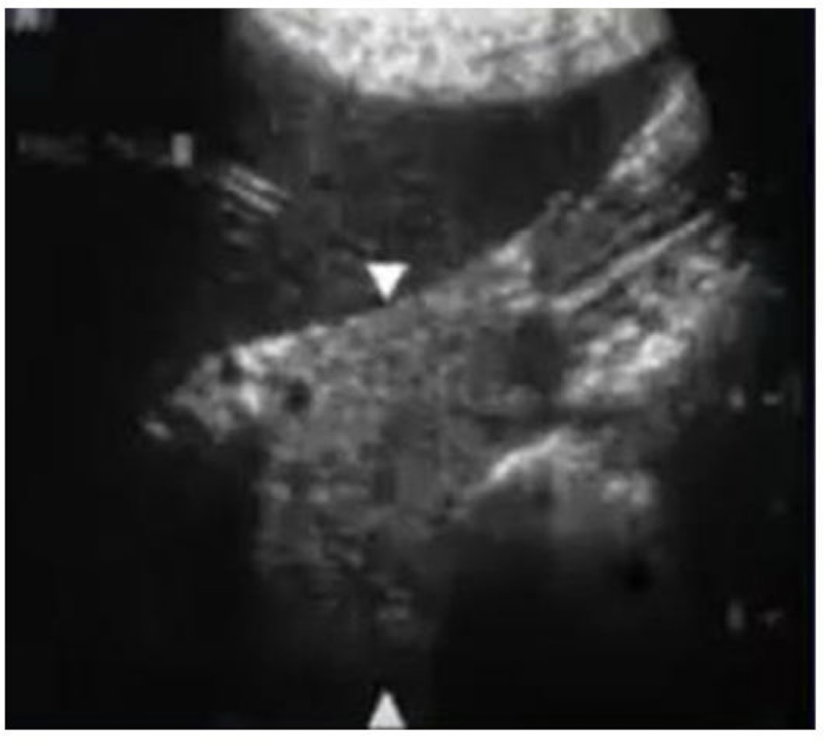
What is this image showing?
Sagittal pancreatic tail