Early brain development
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Forebrain
the anterior part of the brain including the hemispheres and the central brain structures

Midbrain
The middle section of the brain forming part of the central nervous system
Hindbrain
The lower part of the brain forming part of the central nervous system
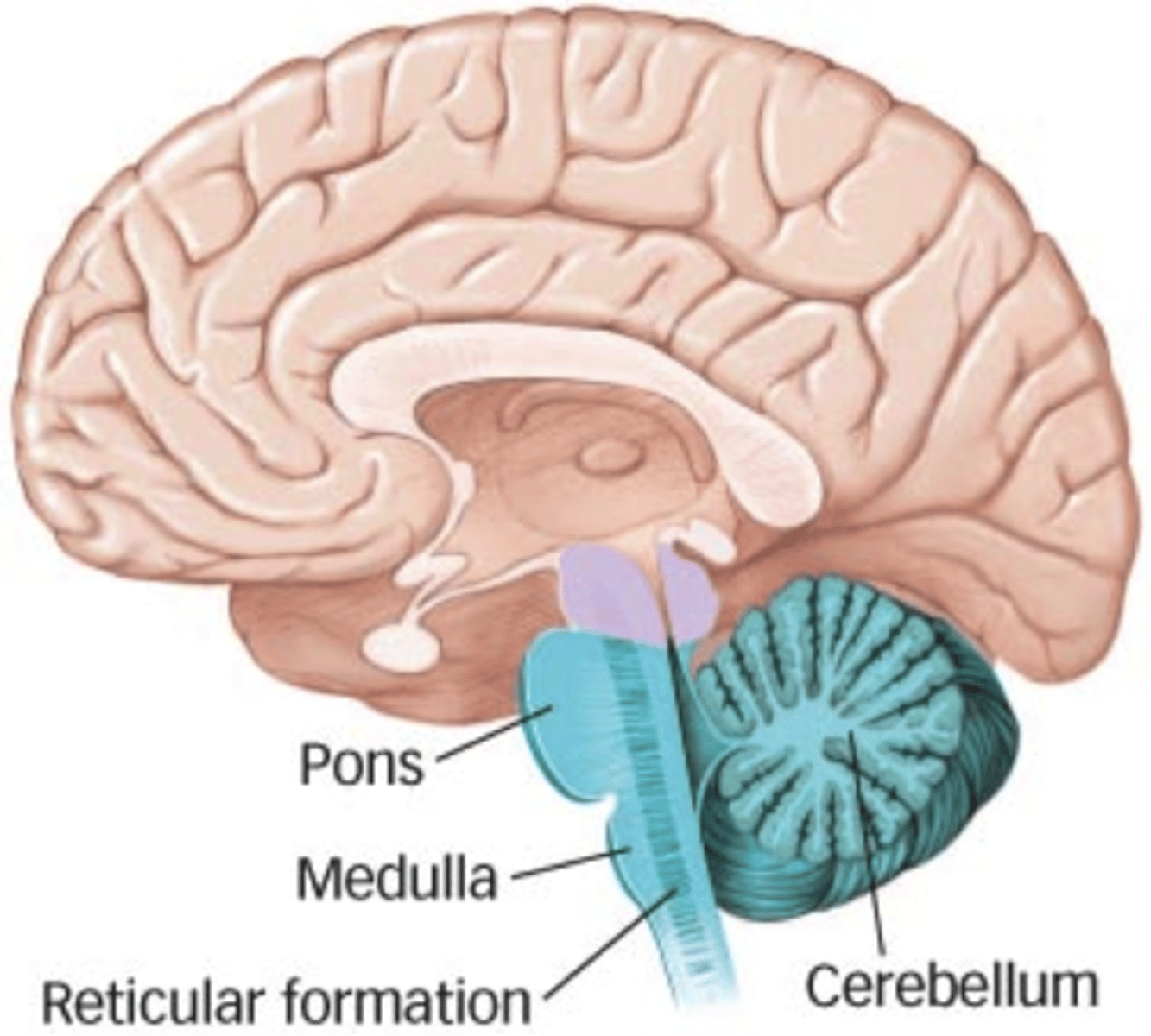
Anterior
towards the front
Posterior
towards the back
Cerebellum
Ensures that muscular contractions are controlled to produce smooth, accurately timed movements; it helps maintain equilibrium by predicting body positions ahead of actual body movements [Latin, literally: "little brain," diminutive of cerebrum]
![<p>Ensures that muscular contractions are controlled to produce smooth, accurately timed movements; it helps maintain equilibrium by predicting body positions ahead of actual body movements [Latin, literally: "little brain," diminutive of cerebrum]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1cf5e11a-04ed-41ef-b549-e2d3880be459.jpg)
Medulla oblongata
Connects the upper brain to the spinal cord and controls automatic responses

Involuntary response
A response to a stimulus that occurs without someone making a conscious choice. They are automatic, such as reflexes.
Neural connections
Links formed by messages passing from one nerve cell to another.
3 to 4 weeks old foetus
Long tube develops in the brain - divided from front to the back into forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain.
5 weeks old foetus
The forebrain and hindbrain split into two cavities: the forebrain splits into an anterior and a posterior section and the hindbrain splits through the middle.
6 weeks old foetus
The cerebellum can be seen. It will triple in size by the first year after birth.