BIOL 2030: Module 4
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Linkage and Mapping in Eukaryotes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Independent assortment
haploid set of 23 genes from mother + haploid set of 23 genes from father
DNA synthesis ‘scrambles’ these genes resulting in a combination of a new set of gametes, come containing exact matches of the parental generation, and some that do not match the parental haploid set
genes on different chromosomes assort into haploid gametes independent of eachother
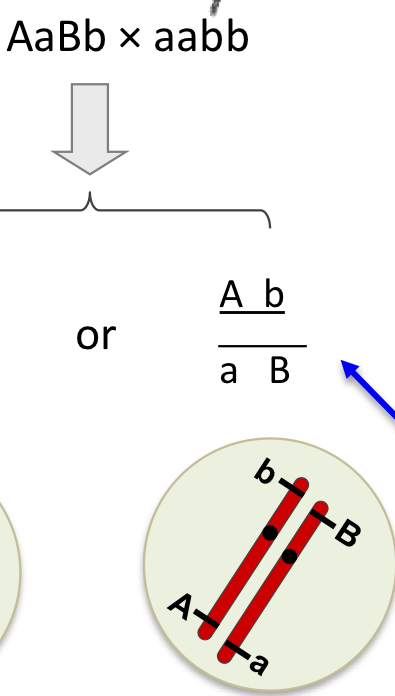
Linkage
a group of genes that do not assort independently into gametes because they are located on the same chromosome
not all linkage groups are the same
strong linkage: physically close loci
weak linkage: physically distant loci
independent assortment: loci too far apart for linkage
degree of linkage varies from Mendelian principles
Degree of linkage
if you have 2 genes on the same chromosome, they are linked
they move to the next generation together
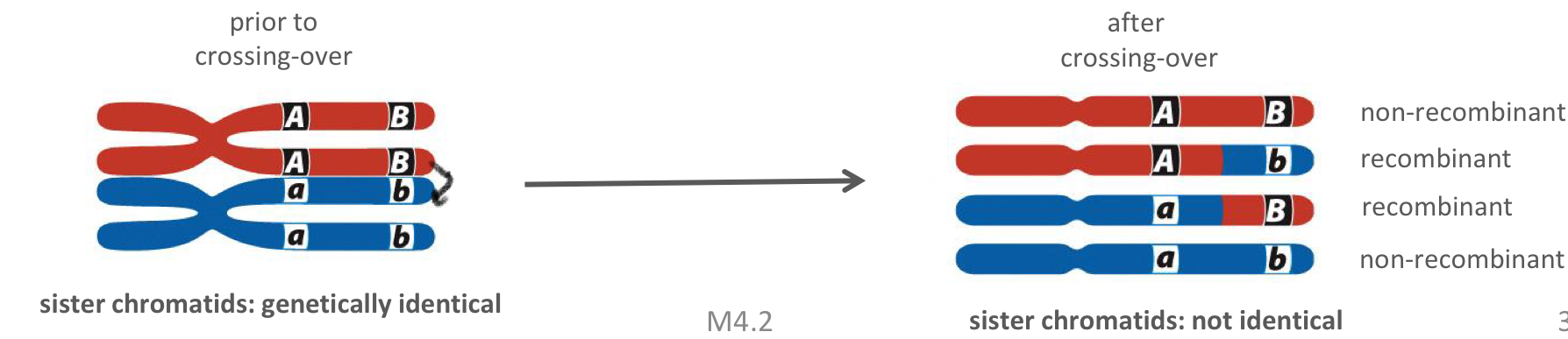
Crossing over
farther apart genes = higher likelihood for crossover event
for a single crossover event;
½ chromatids are non-recombinant
½ chromatids are recombinant
Recombinant
assortment of alleles into non-parental combinations
less common
never on the outside
Inter-chromosomal recombination
on different chromosomes for different genes
assortment of alleles for genes on different chromosomes into novel combinations
on different chromosomes for different genes
Intra-chromosomal recombination
assortment of alleles for genes located on the same chromosome into novel combinations
within same chromosome
Non-recombinant
parental
more common
always on the outside
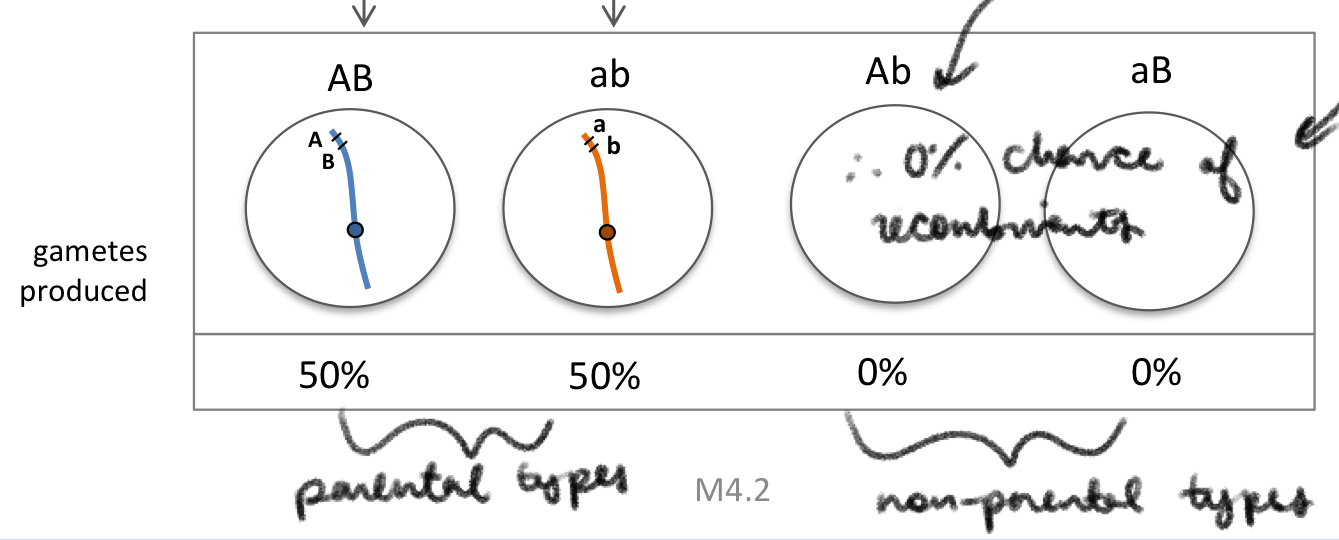
2 genes very close together on the same chromosome
crossing over will not occur
2 genes close on the same chromosome
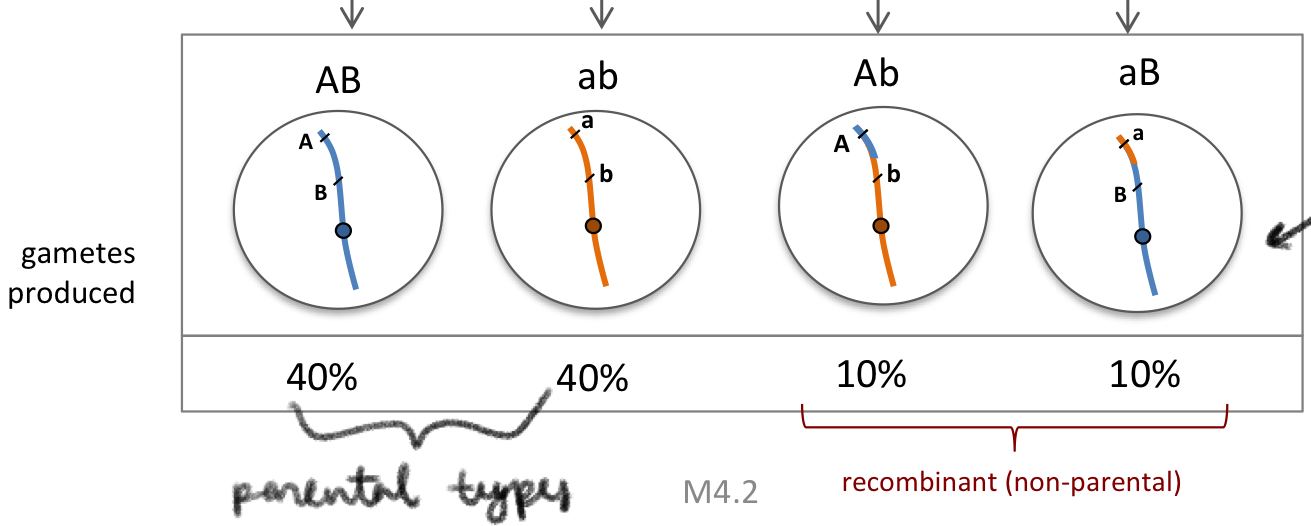
because they are slightly far away, there is a small chance of recombination between genes
more opportunities for crossover to produce Ab and aB
2 genes very far apart on the same chromosome
if far enough apart, crossover occurs in every meiosis event
equal 25% chance for all potential gametes
Genes are independent (unlinked) if…
they are located on different chromosomes
located very far apart on the same chromosome
Complete linkage
only parental gamete types are produced
no recombinant gametes
crossing over never occurs
genes must be very close
Independence
parental and recombinant gametes are produced with equal frequencies
crossing over occurs in every meiosis
genes must be very far apart
Incomplete linkage
parental gametes are produced with greater frequency than recombinant gametes
crossing over occurs in some meioses
frequency of crossing over depends on distance
Coupling
same dominance with same dominance
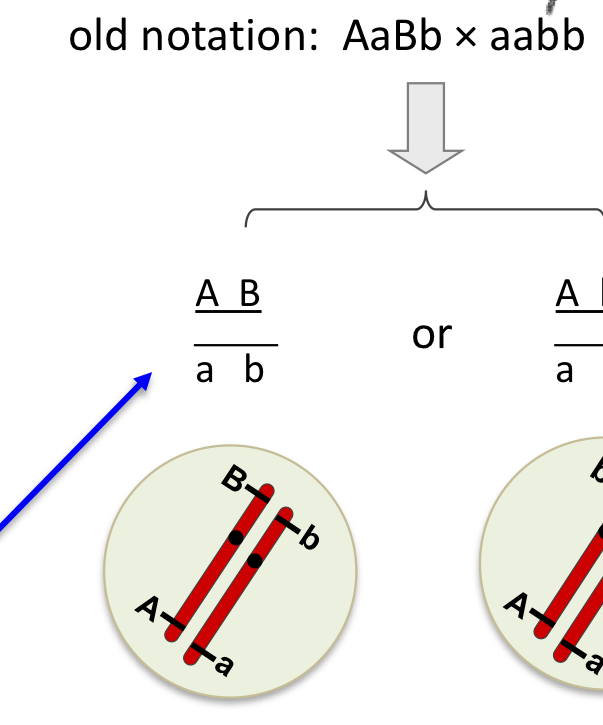
Repulsion
mixed up dominance with recessive
Recombination frequency
# of recombinant progeny/total # of progeny
Recombination/map unit
1% of recombination = 1 m.u.