Attribute Data
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Title
The name of the data table.
Records
The OBJECTID of the rows; numbered 1, 2, 3, …
Field
The name of the data column.
Field defintions
Control the type of data that can be stored in a field.
Attribute table
Stores attributes of map features. Associated with spatial data layer. Has special fields for spatial information.
Standalone table
Stores any tabular data. Not associated with spatial data. OID instead of FID.
Database management systems
Dedicated systems for managing tables of data. Provide data management for agencies, universities, companies, etc. Designed for multi-user environments with enhanced security needs. Focus on data ables with tools for queries, reporting, graphing, etc.
Flat file DBMS
Stores data as rows of information in files. Simple and robust. Inefficient for search and query.
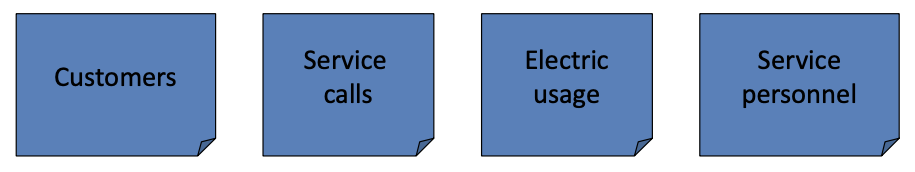
Hierarchial DBMS
Stores data in multiple tables. Tables have defined parent-child relationships. Pre-set hierarchy of table repationships designed for specific queries. Very efficient for specific quetries. Range of queries limited by structure.
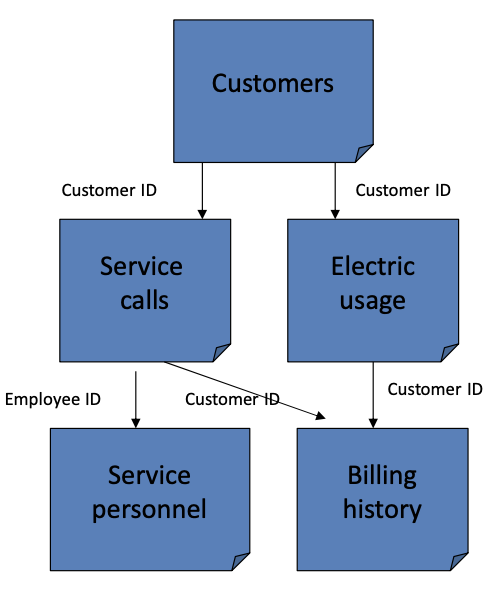
Relational DBMS
Stores data in multiple tables. Table relationships are defined as needed. Very flexible. Ideal for open-ended applications when queries not known beforehand. Most common type used in GIS applications.
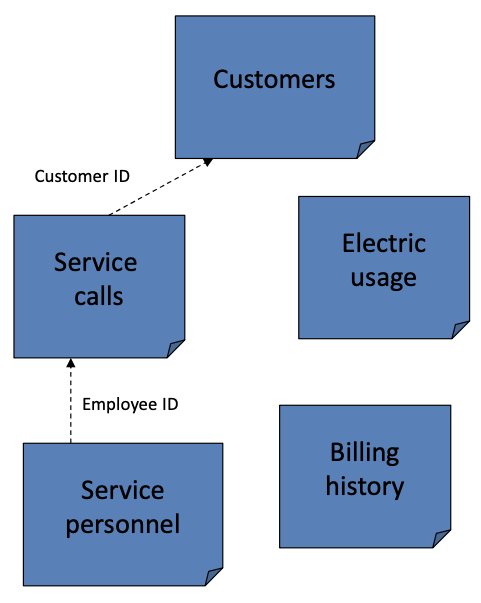
Joining tables
Allows two tables to be used as a singel table. Records are linked using a common field. The target table recieves additional information and the join table prvides the additional information.
Key
A common field is also known as a…
Target table
Recieves the additional information in a join.
Join table
Provides the additional information in a join.
Multiple joins
More than two tables may be joined to a target table.
One-to-one joins
One record in the join table matches one record in the target table.
Cardinality
How many join records match each target record.
Many-to-one join
One record in the join table matches many records in the target table. The join record is repeated as needed to fill out the target records.
One-to-many join
Many records in the join table match one record in the target table. Cannot be joined, and are instead related.
Relate
When tables remain seperate but are linked together so that a selection in one table can be used to select the linked records in the other table.
Rule of Joining
Each record in the target table must match one and only one record in the join table (one-to-one and many-to-one).
Many-to-many cardinality
Multiple records in one table match multiple records in another table. Can be related, but are not usually satisfactorily treated in GIS.
Summary statistics tool
Used to calculate statistics for one or more fields. Results are stored in a new table.
Case field
Can be used to group features first.
Fields
Specific types available and must be defined before use. Once defined, they cannot be changed.
No more than 13 characters
Use only letters and numbers
Must start with a letter
Field naming rules:
Short, long, float, double, text, date
ArcGIS field data types:
Short field type
Integers stored as 2-byte binary numbers
Range of values -32,000 to +32,000
Examples: 255 and 12001
Long field type
Integers stored as 10-byte binary numbers
Range of values -2.14 billion to +2.14 billion
Examples: 156000 and 457890
Float field type
Floating-point values with 8 significant digits in the mantissa
Examples: 1.289385e12 or 1.5647894e −02
Double field type
Double-precision floating-point values with 16 significant digits in the mantissa
Example: 1.12114118119141e13
Text field type
Alphanumeric strings
Examples: ‘Maple St"‘ and ‘John H. Smith’
Date field type
Date/time format for calendar dates and times
Examples: 07/12/2008 and 10/17/1963 13:24:06
Calculate Field tool
Used to enter an expression to calculate new values for a field in a table.