Organic Nomenclature
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
I. Hydrocarbons
= a category of compounds that only contain C and H (no other atoms)
1) Alkanes
a type of hydrocarbon
= containing only C, H, and single bonds
(this means that there are hydrogens on every carbon, so it is FULLY SATURATED)
CnH2n+2
-ane
Methane
a type of Alkane
(Marvin)
CH4
Ethane
a type of Alkane
(Eats)
C2H6
Propane
a type of Alkane
(Peanut)
C3H8
Butane
a type of Alkane
(Butter)
C4H10
Pentane
a type of Alkane
C5H12
Hexane
a type of Alkane
C6H14
Heptane
a type of Alkane
C7H16
Octane
a type of Alkane
C8H18
Nonane
a type of Alkane
C9H20
Decane
a type of Alkane
C10H22
Cyclic Alkanes
= alkanes configured in a circle
Prefix: Cyclo-
ex.
Cyclopentane
Cyclohexane
2) Alkenes
a type of hydrocarbon
= at least one carbon-carbon double bond
Suffix: -ene
ex. Ethene/Ethylene
H2C=CH2
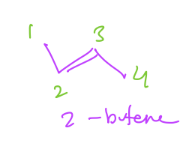
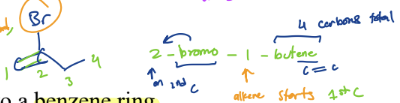
ex. 2-butene (double bond starts on second carbon)
(see pic)
3) Alkynes
a type of hydrocarbon
= at least one carbon-carbon triple bond
Suffix: -yne
ex. Ethyne/Acetylene
HC≡CH
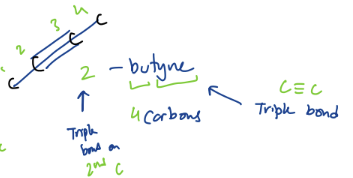
ex. 2-butyne
(see pic)
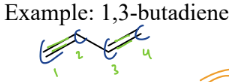
4) Dienes
a type of hydrocarbon
= contain 2 alkenes next to each other (conjugated, so alt. single double bonds)
Electrons are delocalized by resonance
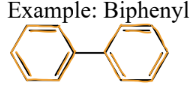
5) Arenes
a type of hydrocarbon
= contain at least one benzene ring
II. Halogen-Substituted Hydrocarbon Derivatives
= a category of compounds where at least one hydrogen atom is replaced by a halogen in hydrocarbon compounds
II. 1) Alkyl Halides
A Halogen-Substituted Hydrocarbon Derivative
= contain a halide connected to a saturated hydrocarbon

Saturated Hydrocarbons
= Hydrocarbons where every C has as many Hs on it as it can hold
All single bonds (NO double or triple bonds, so no pi bonds)
If fully saturated —> nonreactive
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons with pi bonds
Functional Group
= any group that is REACTIVE
= any group that is NOT fully saturated
ex. alkenes and alkynes
ex. groups with N and O
ex. all carbonyl derivatives
II. 2) Alkenyl Halides
A Halogen-Substituted Hydrocarbon Derivative
= contain a halide directly connected to an alkene
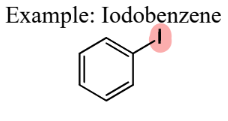
II. 3) Aryl Halides
A Halogen-Substituted Hydrocarbon Derivative
= contain a halide directly connected to a benzene ring
III. Oxygen-Containing Compounds
= a category of compounds that contain oxygen
III. 1) Alcohols
A type of Oxygen-Containing Compound
= contain an OH group
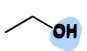
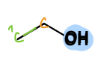
Primary Alcohol
a type of alcohol
= OH is bonded to carbon that is bonded to one other carbon
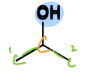
Secondary Alcohol
a type of alcohol
= OH is bonded to carbon that is bonded to two other carbons
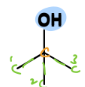
Tertiary Alcohol
a type of alcohol
= OH is bonded to carbon that is bonded to three other carbons
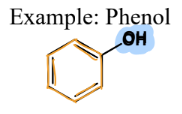
III. 2) Phenols
A type of Oxygen-Containing Compound
= contain an OH directly connected to a benzene ring
III. 3) Ethers
A type of Oxygen-Containing Compound
= contain an O bonded in between two carbons
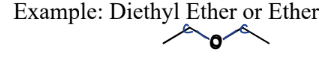
III. 4) Epoxides
A type of Oxygen-Containing Compound
= 3-membered ring ether
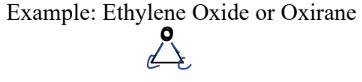
III. 5) Carbonyl
A type of Oxygen-Containing Compound
= any C=O bond
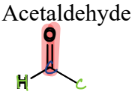
III. 5) a) Aldehydes
A type of Oxygen-Containing Compound
= contain a carbonyl connected to an H and a C
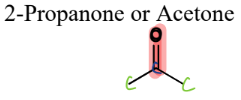
III. 5) b) Ketones
A type of Oxygen-Containing Compound
= contain a carbonyl connected to two Cs
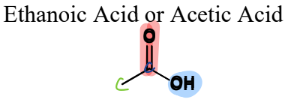
III. 5) c) Carboxylic Acids
A type of Oxygen-Containing Compound
= contain a carbonyl connected to an OH and a C
IV. Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
a category of Derivatives of Carboxylic Acids
can be distinguished from aldehydes and ketones by the presence of a group containing an electronegative heteroatom (usually oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur) bonded directly to the carbonyl carbon
Heteroatom
= any atom that is not carbon or hydrogen
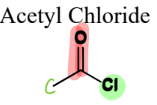
IV. 1) Acid Chlorides
a Carboxylic Acid Derivative
= contain a carbonyl connected to a chloride and a C
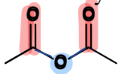
IV. 2) Anhydrides
a Carboxylic Acid Derivative
= contain TWO carbonyls connected by an Oxygen
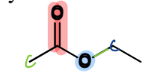
IV. 3) Esters
a Carboxylic Acid Derivative
= contain a carbonyl connected to O-C and a C
IV. 4) Amides
a Carboxylic Acid Derivative
= contain a carbonyl connected to a N and a C
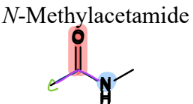
V. Nitrogen-Containing Compounds
= a category of compounds that contain nitrogen
V. 1) Amines
a Nitrogen-Containing Compound
= contain N connected to H or C (saturated)

Primary Amine
a type of Amine
= N bonded to ONE C

Secondary Amine
a type of Amine
= N bonded to TWO C
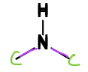
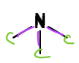
Tertiary Amine
a type of Amine
= N bonded to THREE C
V. 2) Nitriles
a Nitrogen-Containing Compound
= contain a C triple bonded to N
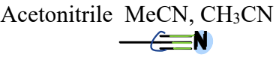
V. 3) Nitro Compounds
a Nitrogen-Containing Compound
= contain an NO2 group
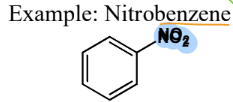
Methyl
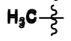
Ethyl
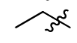
Propyl
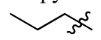
Isopropyl
1-Methylethyl
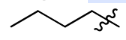
n-Butyl
Butyl
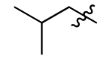
Isobutyl
2-Methylpropyl
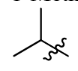
Secbutyl
1-Methylpropyl
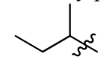
t-Butyl
1,1-Dimethylethyl
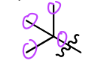
Neopentyl
2,2-Dimethylpropyl
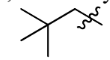
Vinyl
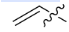
Allyl
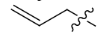
Acetyl
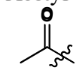
Phenyl
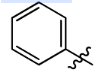
Benzyl